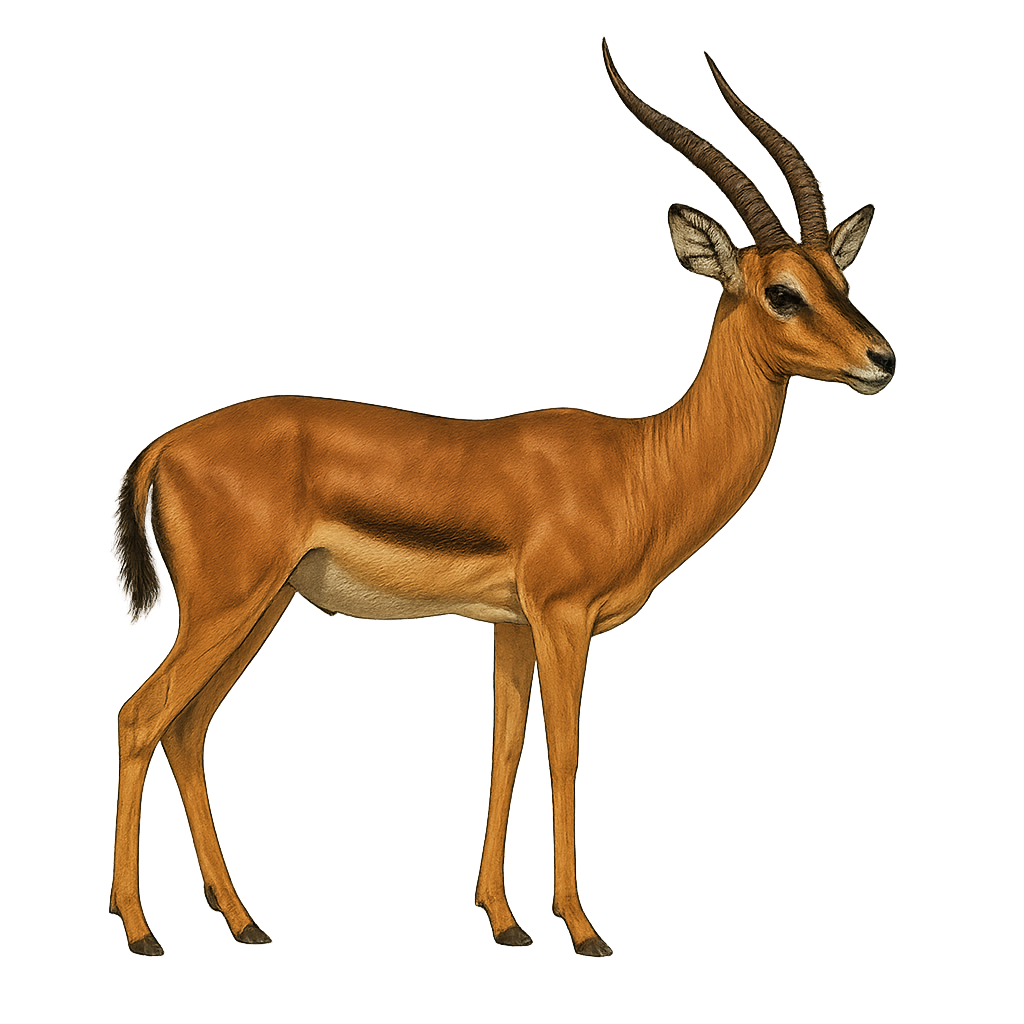
The goitered gazelle, or Gazella subgutturosa, is a species of gazelle known for its enlarged neck, particularly in males. It primarily inhabits the steppes and deserts of Central Asia and the Middle East. This gazelle is well adapted to arid environments and can survive with minimal water, feeding on drought-resistant plants. It is known for its speed and agility, which help it evade natural predators. Males have lyre-shaped horns, while females have smaller horns or none at all. The goitered gazelle is a vulnerable species due to hunting and habitat loss.
The Bright's Gazelle is an elegant, medium-sized antelope, recognizable for its slender proportions and long, thin legs. It stands about 75 cm at the withers and weighs between 30 and 40 kg. Its coat is generally light beige, with darker markings on the flanks and a distinctive black stripe running along its lateral line. Adult males have fine, curved horns, while females generally lack them. The Bright's Gazelle primarily inhabits the savannas and steppes of East Africa, particularly in Ethiopia and Kenya. It is herbivorous, feeding mainly on grasses, leaves, and plants. Like all gazelles, it is fast and agile, capable of running at speeds of up to 80 km/h to escape predators. Although the Bright's Gazelle is not currently endangered, it faces threats related to habitat loss, hunting, and competition with livestock for food resources.
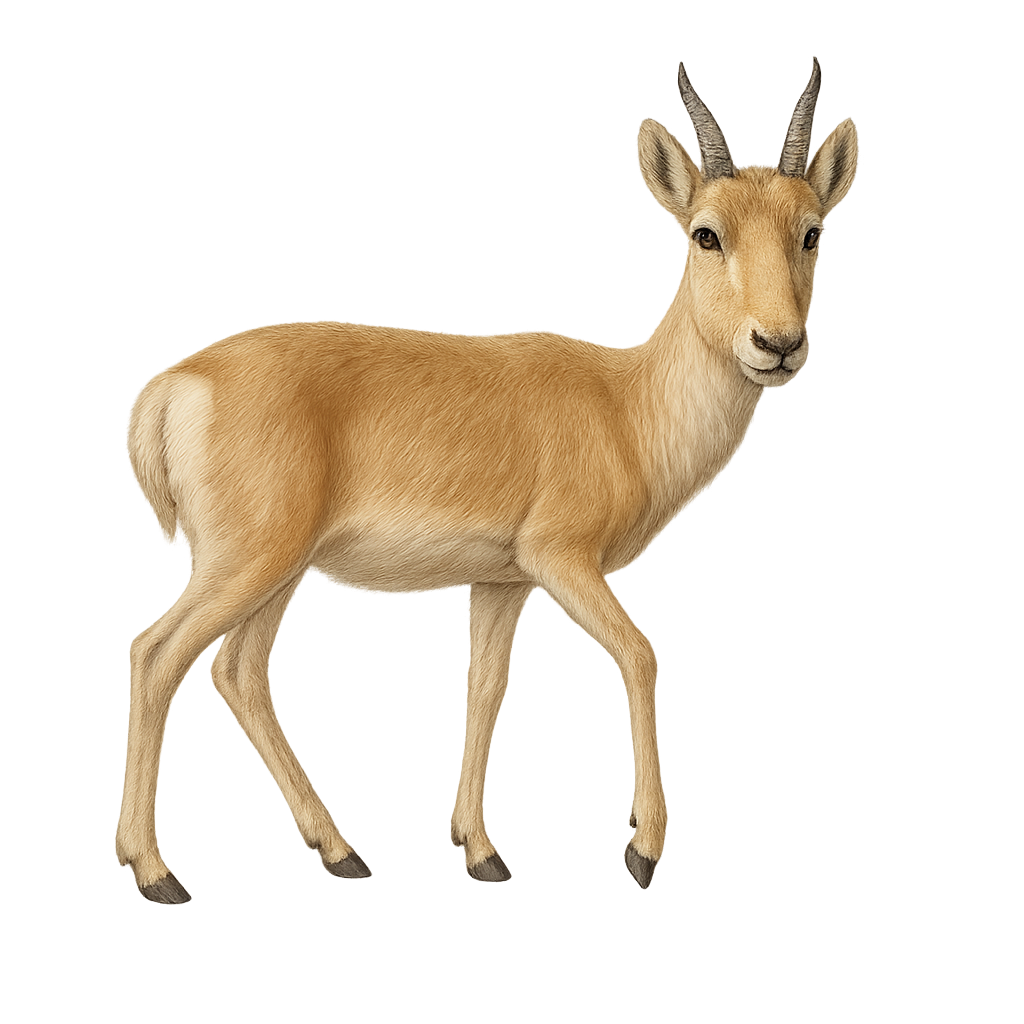
The Cuvier's gazelle is a species of gazelle native to North Africa, mainly found in Algeria, Tunisia, and Morocco. It is characterized by its medium size, lyre-shaped horns, and light brown coat with white markings on the belly and legs. Adapted to arid environments, it inhabits steppes, mountains, and semi-desert areas. It is herbivorous, feeding mainly on grasses and leaves. The Cuvier's gazelle is an endangered species, primarily due to excessive hunting and habitat loss. Conservation efforts are underway to protect this iconic species of North African wildlife.
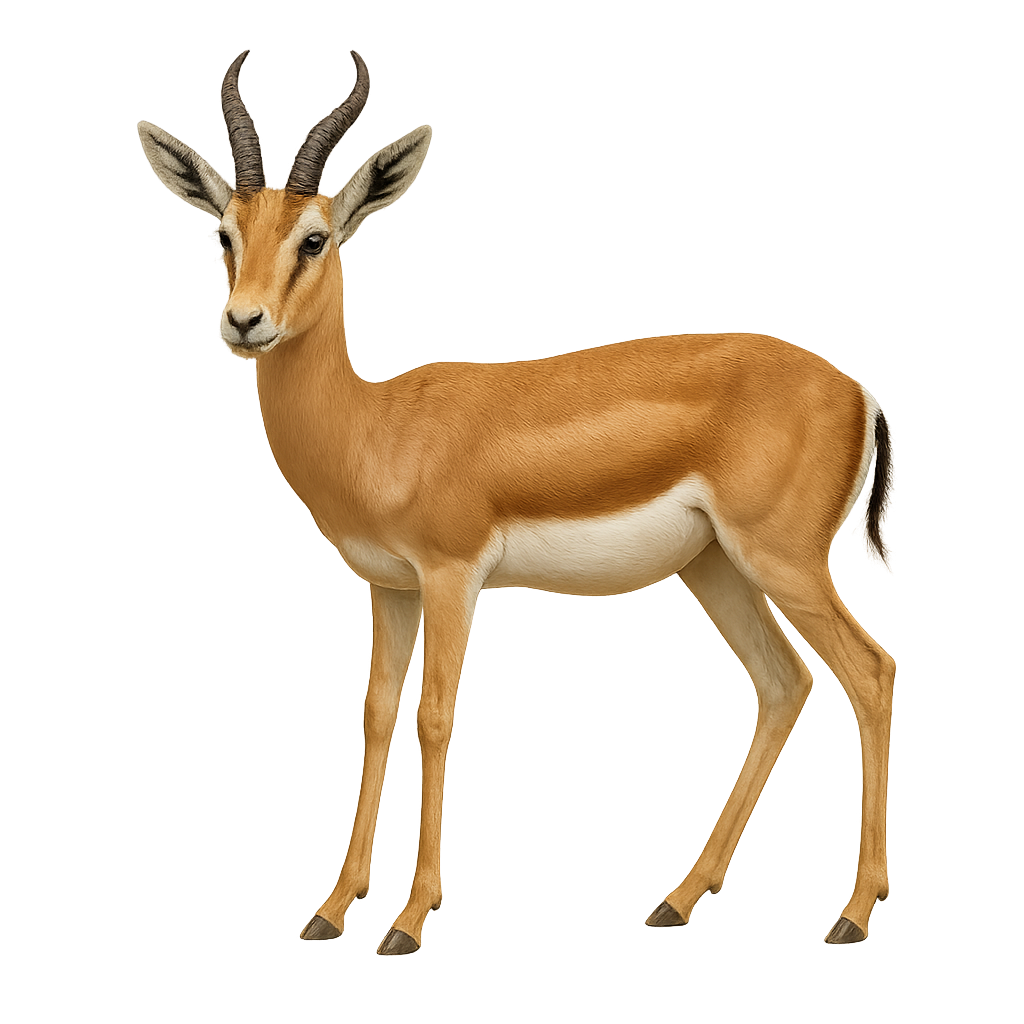
The Grant's Gazelle is an elegant, medium-sized antelope, easily recognizable by its long legs and generally sandy-colored coat with distinctive markings. It stands about 75 cm at the withers and weighs between 40 and 60 kg. The coat of the Grant's Gazelle is primarily beige with darker vertical stripes along the flanks and a black stripe running across its back. Adult males have long, slightly curved horns in the shape of a lyre, while females generally lack them. This gazelle primarily inhabits savannas, grasslands, and wooded areas in East Africa, particularly in Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda. Herbivorous, it primarily feeds on herbaceous plants, leaves, fruits, and bark. Very fast and agile, the Grant's Gazelle can reach speeds of up to 80 km/h, allowing it to escape many predators. Although the species is not endangered, it faces threats such as habitat loss, hunting, and competition with livestock for food resources.
The Mongolian gazelle, or Procapra gutturosa, is a species of gazelle primarily inhabiting the vast steppes of Mongolia and parts of China. It is recognizable by its light brown coat, which helps it blend into its arid surroundings. Males are distinguished by their ringed horns and thicker necks, especially during the rutting season. These gazelles live in large herds, which provide protection against predators. They are extremely agile and can run at high speeds to escape danger. Their diet mainly consists of grasses and low-lying plants, adapted to the harsh climatic conditions of their habitat.
The Thomson's Gazelle is a small, elegant gazelle known for its speed and grace. It stands about 60 cm at the withers, with a body length of 90 cm, and weighs between 20 and 30 kg. Its coat is mainly beige, with distinct white markings on its belly and a black stripe running along each side of its body. The adult male has curved lyre-shaped horns, while females generally lack them. The Thomson's Gazelle primarily inhabits the savannas and grasslands of East Africa, particularly in Tanzania and Kenya. It is herbivorous, feeding mainly on grasses, young shoots, and leaves. Very fast, the Thomson's Gazelle can reach speeds of 80 to 90 km/h, allowing it to escape many predators. Although it is currently relatively common, the Thomson's Gazelle faces threats related to habitat loss and human activities, including hunting and competition with livestock.
The Dorcas gazelle is a small, graceful antelope well adapted to the arid environments of the Sahara and surrounding regions. It is distinguished by its light beige coat, which allows it to blend into the desert, and its elegantly curved horns. Standing about 55 to 65 cm at the shoulder and weighing between 15 and 20 kg, it is agile and fast, capable of running at high speeds to escape predators. Its diet mainly consists of leaves, flowers, and fruits, enabling it to survive in areas where water is scarce. The Dorcas gazelle is a symbol of grace and resilience in extreme conditions.
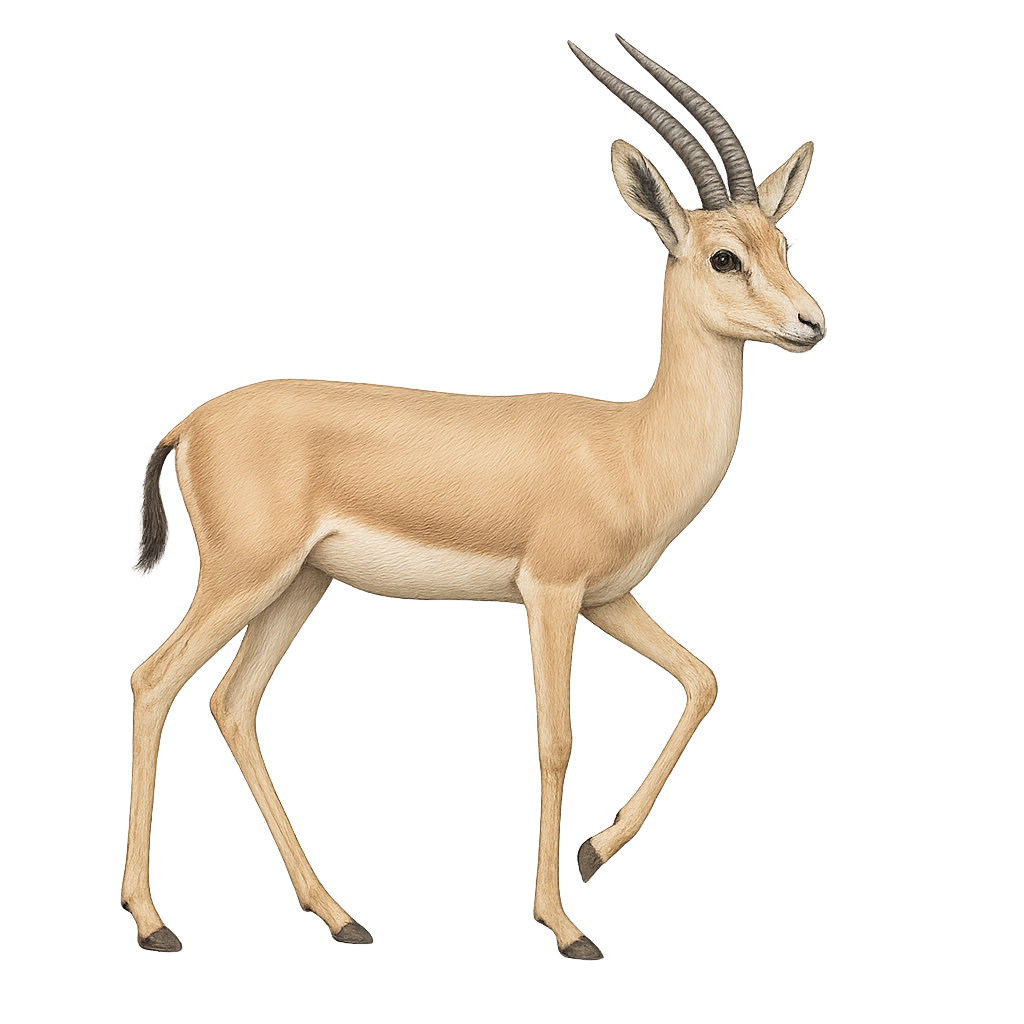
The slender-horned gazelle, or Gazella leptoceros, is a species of gazelle that primarily inhabits the desert regions of the Sahara. It is recognizable by its slender, elongated horns, which can reach up to 40 cm in length. Its coat is pale, almost white, allowing it to blend into the sandy dunes. This gazelle is well adapted to its arid environment, capable of surviving with very little water, feeding mainly on leaves, shoots, and fruits. Unfortunately, it is critically endangered due to excessive hunting and habitat degradation.
The Cyanocorax affinis, or White-throated Magpie-Jay, is a striking bird known for its vivid blue plumage and distinctive white face with a black crest. It is primarily found in Central America, particularly in Costa Rica and Panama. This social bird lives in family groups and is noted for its intelligence and ability to mimic sounds. It inhabits tropical dry and humid forests, forest edges, and cultivated areas. The White-throated Magpie-Jay is omnivorous, feeding on fruits, insects, and occasionally small vertebrates. Its curious behavior and adaptability to human-altered environments make it a fascinating species to observe. Although not currently threatened, deforestation could impact its populations in the long term.
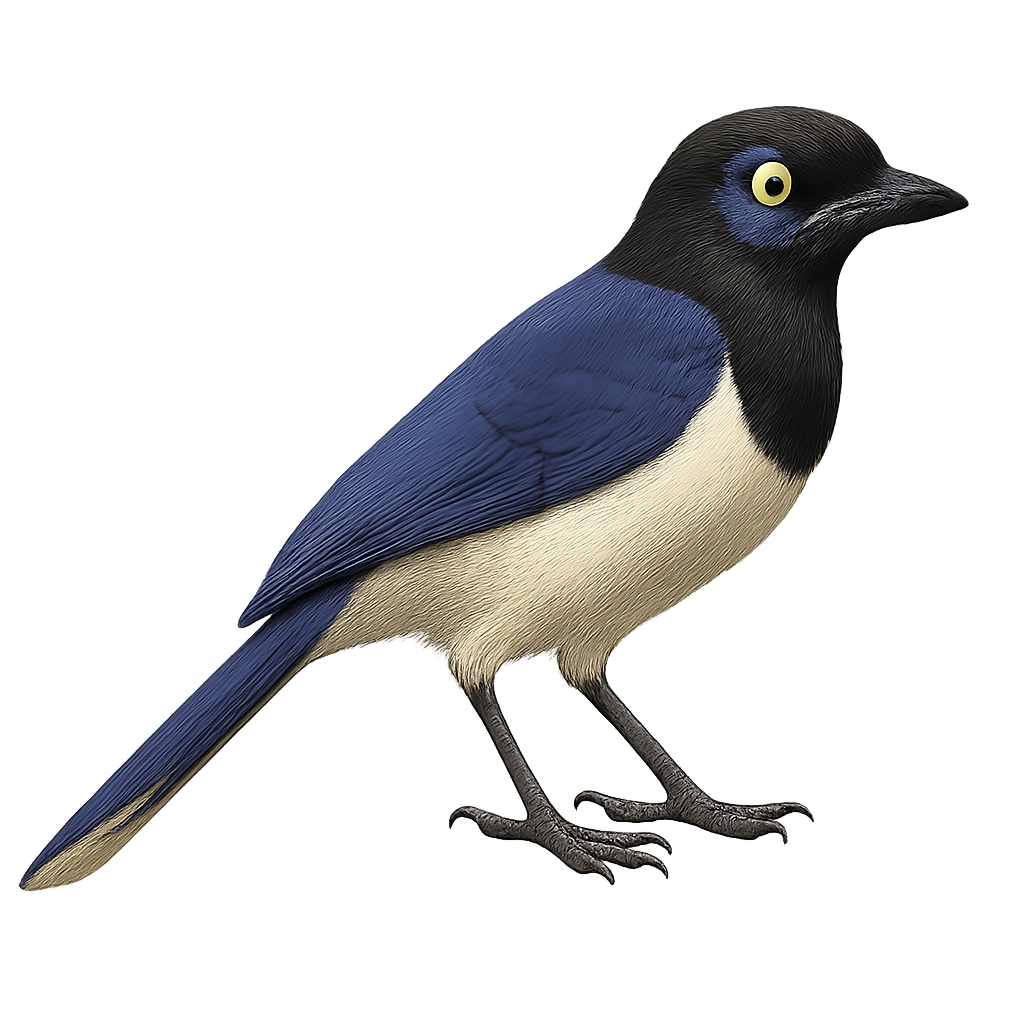
The White-throated Magpie-Jay, Cyanocorax formosus, is a striking bird with a long tail and vibrant blue plumage contrasting with a black face. It primarily inhabits dry tropical forests and wooded areas in Mexico and Central America. This sociable bird lives in family groups and feeds mainly on insects, fruits, and seeds. Its distinctive and varied call is often heard before it is seen. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it remains relatively common within its range. The White-throated Magpie-Jay is a fascinating example of the avian diversity of the Neotropical region.
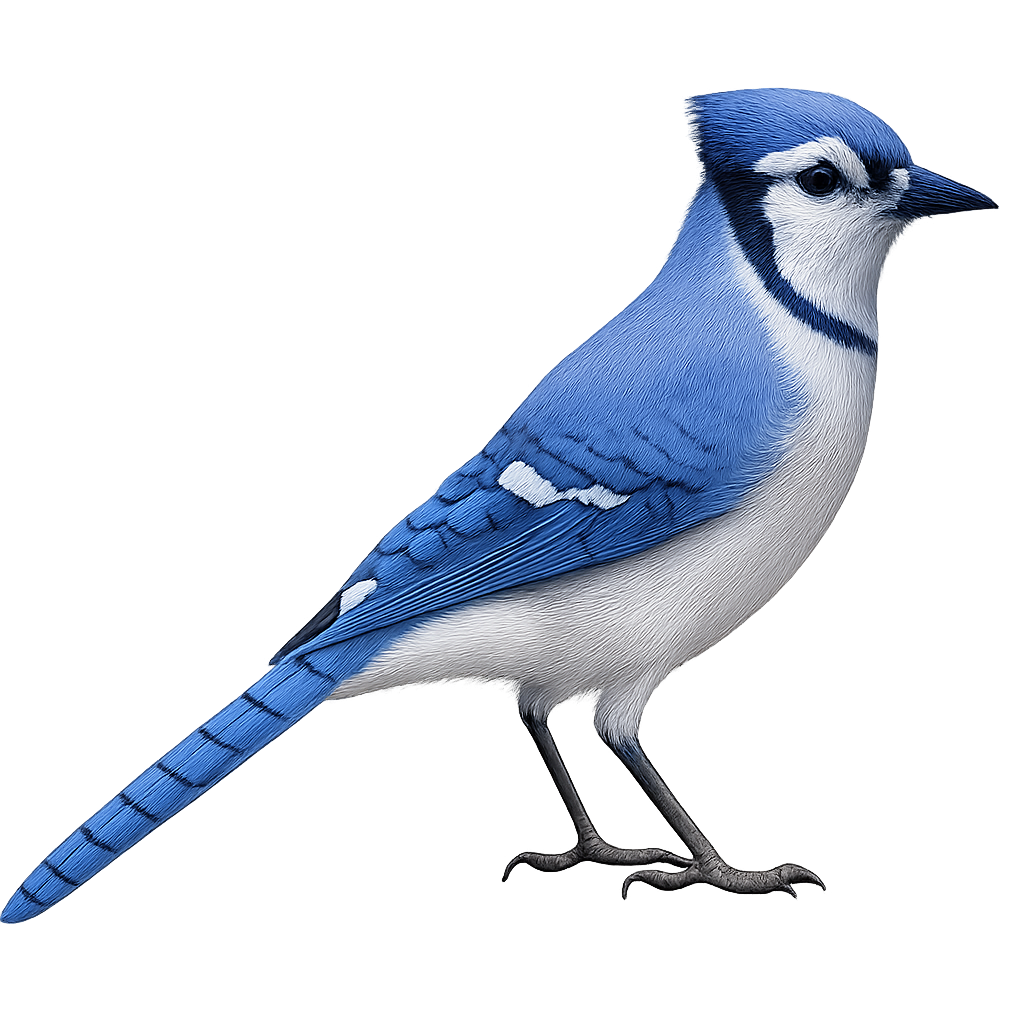
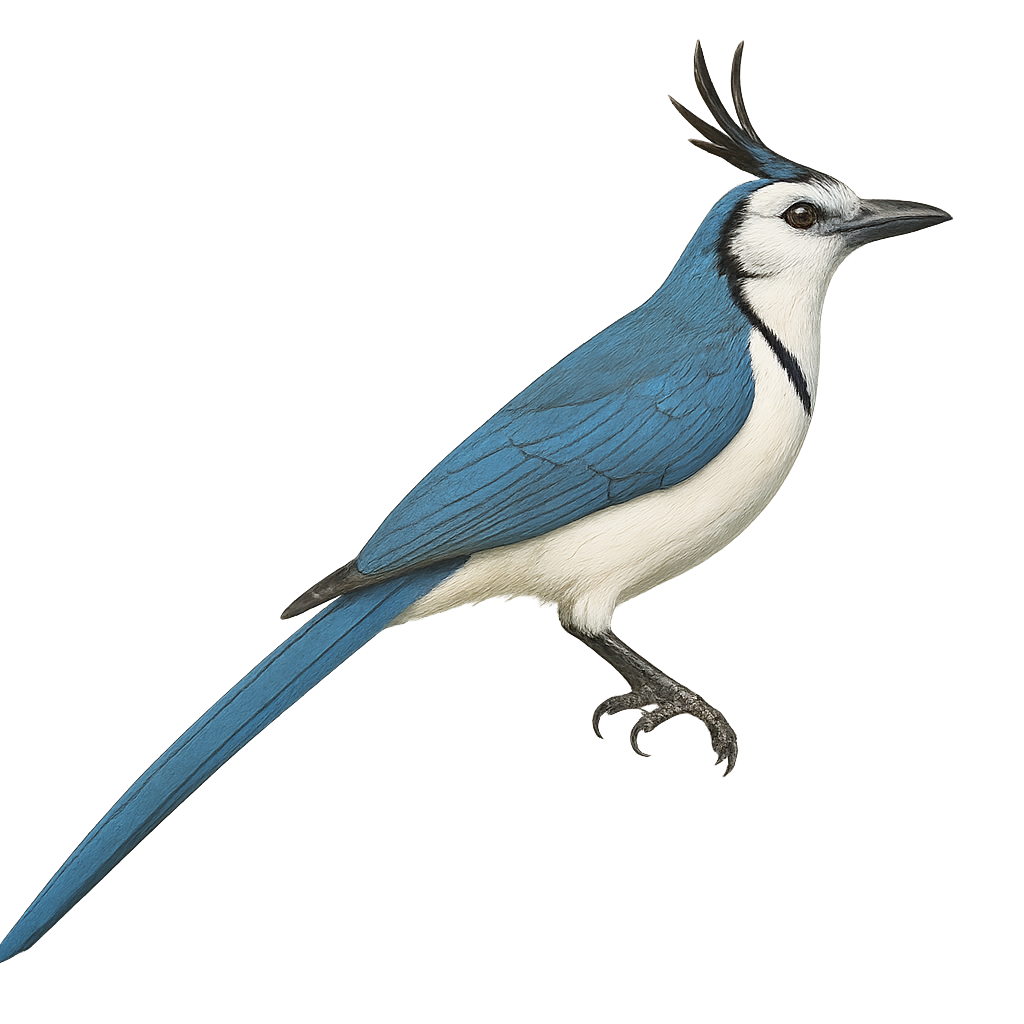
The Blue Jay, Cyanocitta cristata, is a striking bird with predominantly blue plumage accented with white and black. Easily recognizable by its distinctive crest and loud call, this bird is omnivorous, feeding on seeds, insects, and occasionally small vertebrates. It is commonly found in deciduous and mixed forests, as well as urban parks and gardens. Known for its intelligence, the Blue Jay can mimic sounds, including the calls of other birds. It plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding forest regeneration.
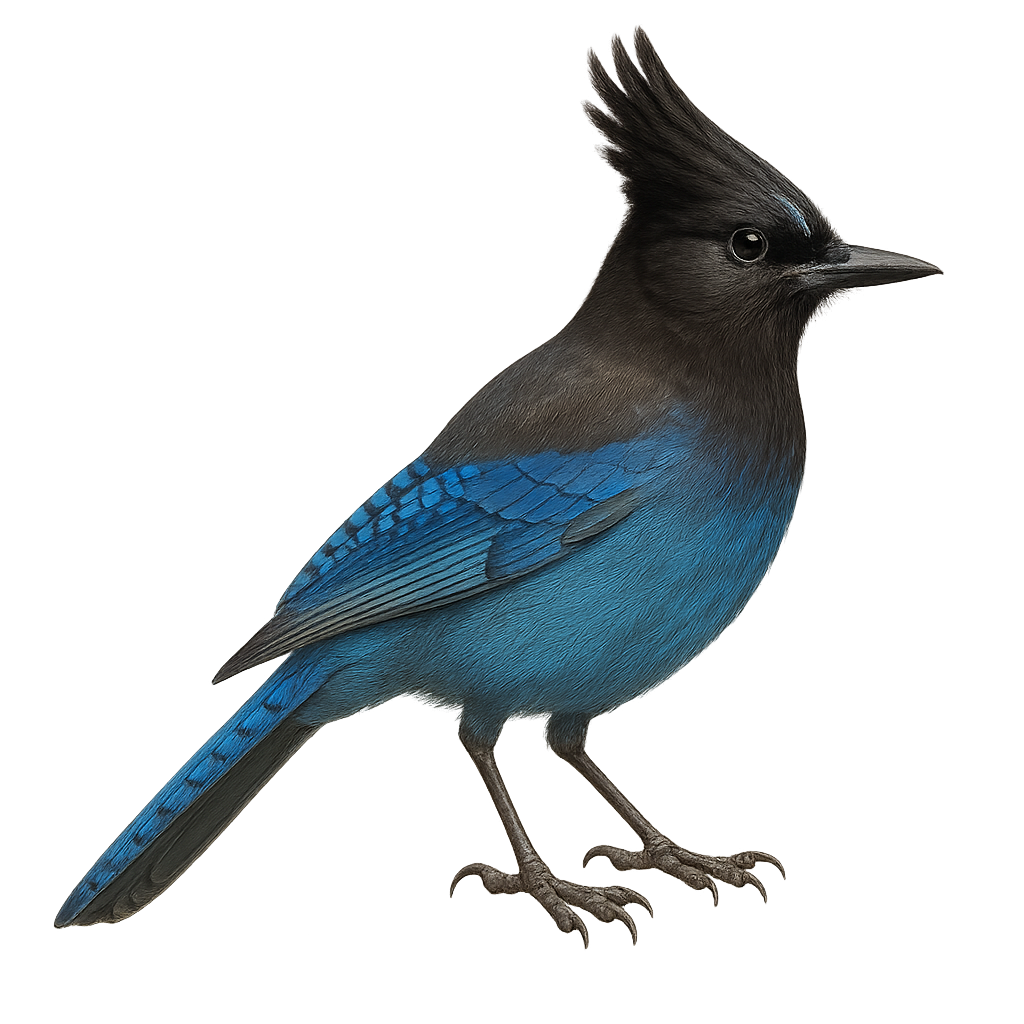
The Steller's Jay, with its striking blue plumage and distinctive black crest, is a fascinating bird of the coniferous forests of western North America. Measuring about 30 to 34 cm in length, it is distinguished by its black head and bright blue body. This bird is known for its bold and curious behavior, often seen foraging on the ground for food or skillfully flying between trees. Omnivorous, it feeds on seeds, fruits, insects, and even small animals. The Steller's Jay is also an excellent mimic, capable of reproducing the calls of other birds and even some human sounds.
The Japanese Jay is a medium-sized bird known for its colorful plumage and distinctive crest. It features a mix of colors from pinkish-brown to bright blue on the wings, with black and white markings. This bird is primarily arboreal, inhabiting deciduous and coniferous forests in Japan. It is known for its intelligence and ability to mimic sounds. Omnivorous, it feeds on acorns, insects, and small animals. The Japanese Jay plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding forest regeneration.
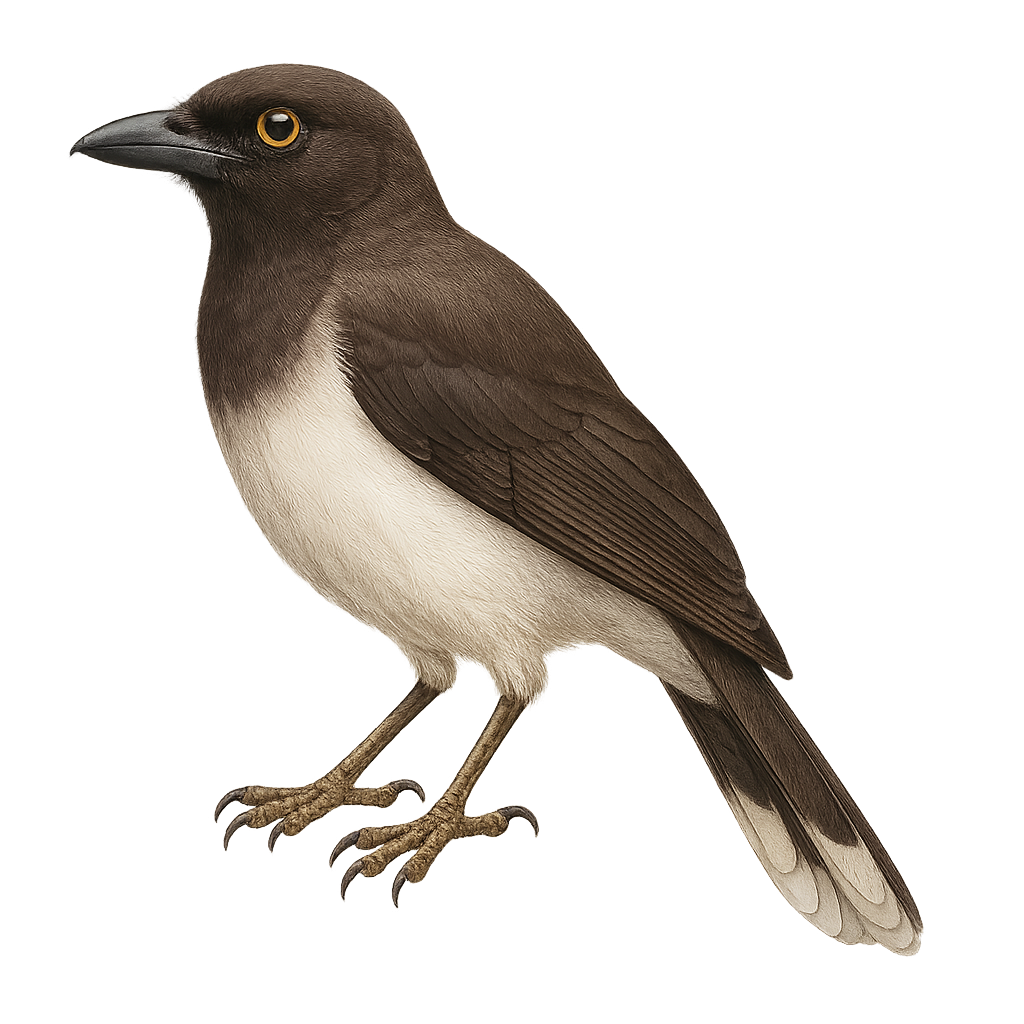
The Brown Jay, or Cyanocorax morio, is a bird from the Corvidae family, primarily found in Central America. It is characterized by its dark brown plumage, contrasting with lighter wings and tail. Its head features a black mask around the eyes and a strong beak. This sociable bird lives in family groups and is often seen in tropical forests, mangroves, and open woodlands. Opportunistic, it feeds on fruits, insects, and sometimes small vertebrates. Its call is loud and varied, used to communicate with its peers. The Brown Jay plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding forest regeneration.
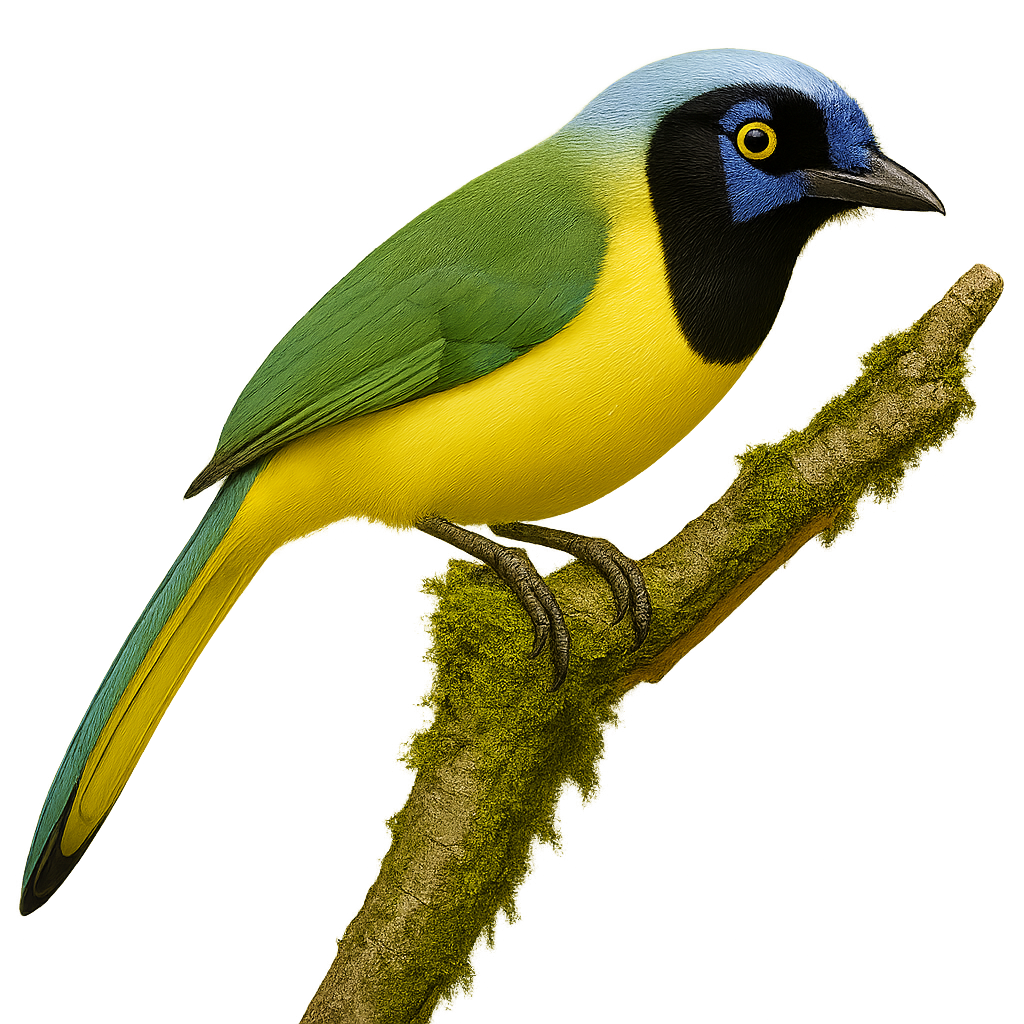
The Green Jay, or Cyanocorax yncas, is a striking bird with vibrant plumage, primarily green with shades of blue and yellow. It inhabits the tropical and subtropical forests of Central and South America. This sociable bird lives in groups and is known for its intelligence and tool-using abilities. It primarily feeds on insects, fruits, and seeds. The Green Jay is also an excellent mimic of sounds, allowing it to communicate effectively with its peers. Its presence is often marked by its distinctive calls and agile flight through the dense canopy.
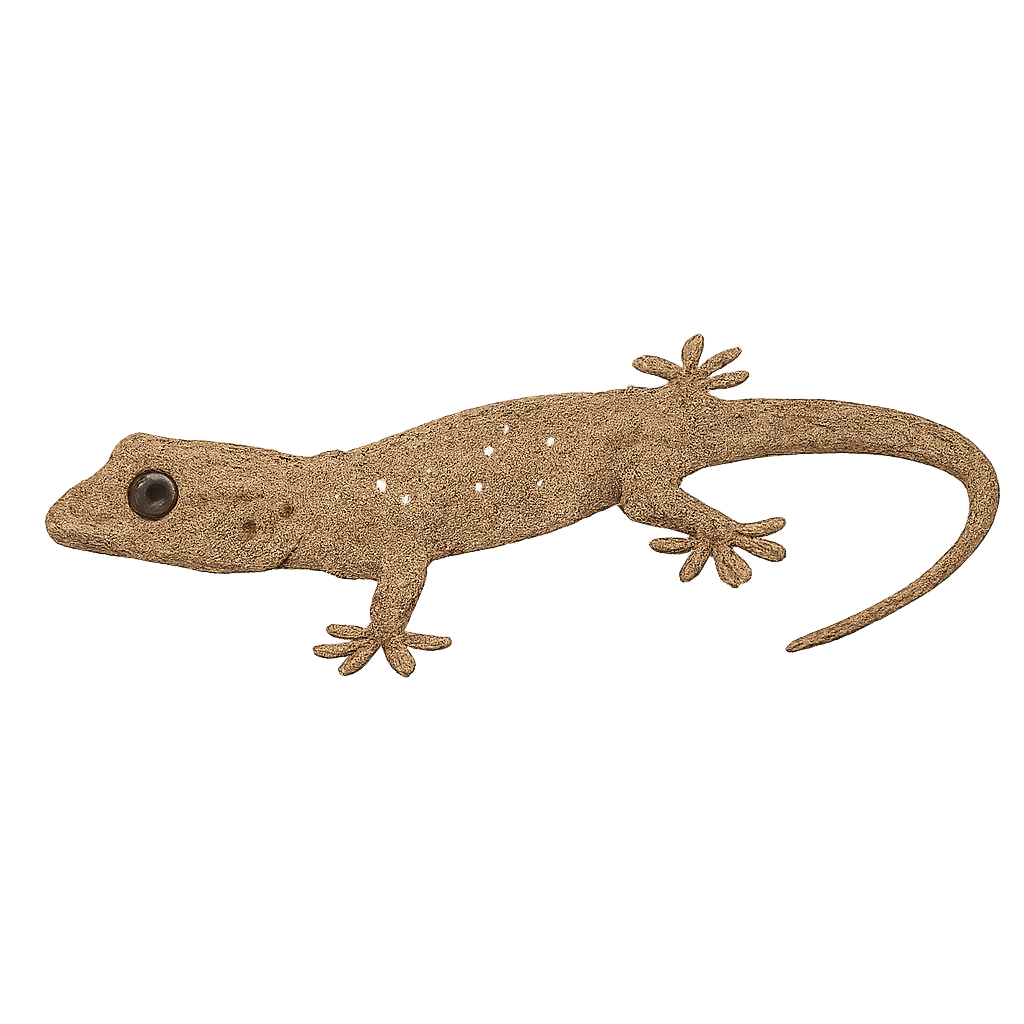
The Smith's green-eyed gecko (Gekko smithii) is a medium-sized nocturnal lizard (total length up to 35 cm, SVL 19 cm) with olive-green to brown mottled dorsal coloration and a pale throat bordered by dark mottling. Endemic to tropical and secondary forests of Southeast Asia (Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, Myanmar, Singapore), it occupies tree trunks and riparian vegetation where it forages for insects and arachnids. Reproduction occurs year-round, with females laying clutches of two eggs followed by an incubation period of 60–90 days. It uses crevices for shelter, produces harsh calls to communicate, and exhibits moderate wariness.
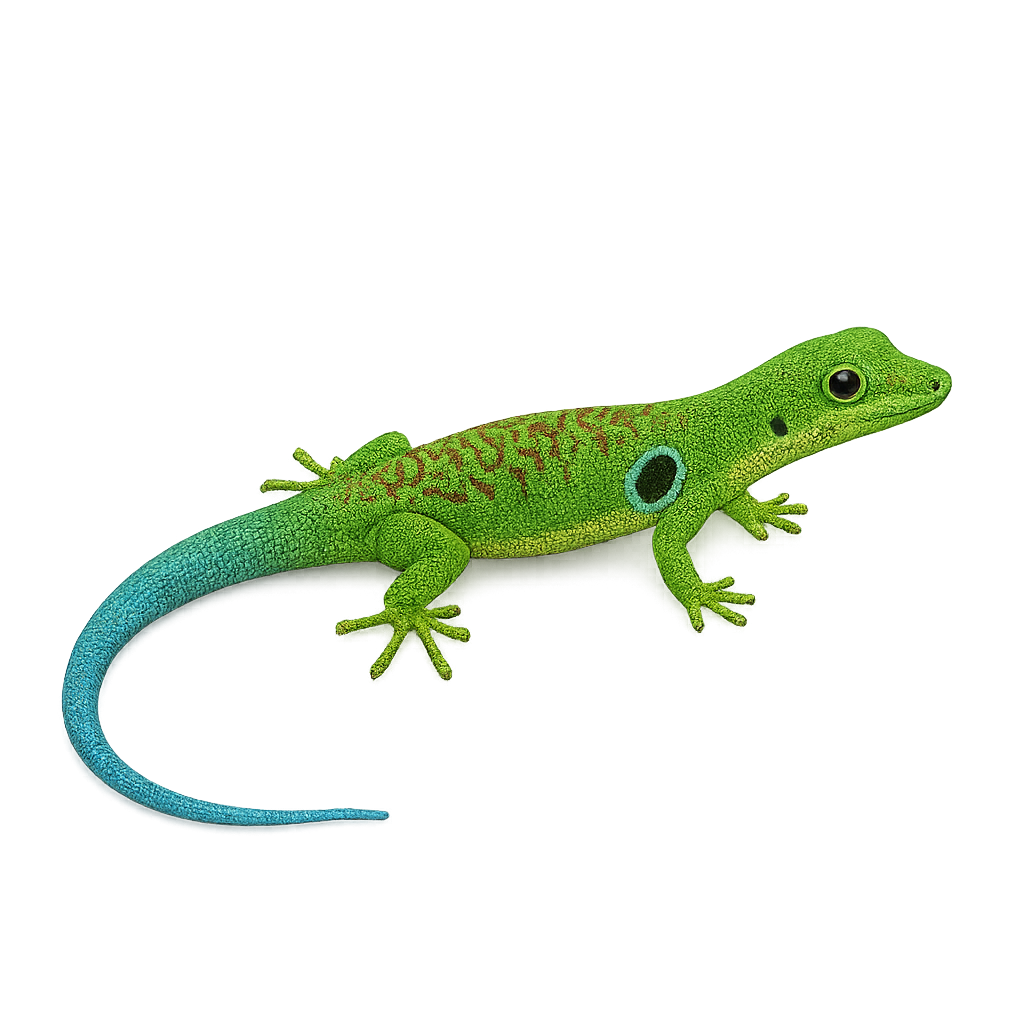
The Phelsuma quadriocellata, or four-spotted day gecko, is a small, colorful lizard native to Madagascar. It is known for its bright green skin adorned with blue and red spots, and its distinctive four black spots on the back. This diurnal gecko is often found in humid tropical forests, feeding mainly on insects and nectar. It is appreciated for its adaptability to various environments, including gardens and human dwellings. Although generally suspicious, it can become tolerant of humans over time. Its reproduction is oviparous, with a gestation period of about 40 to 45 days.
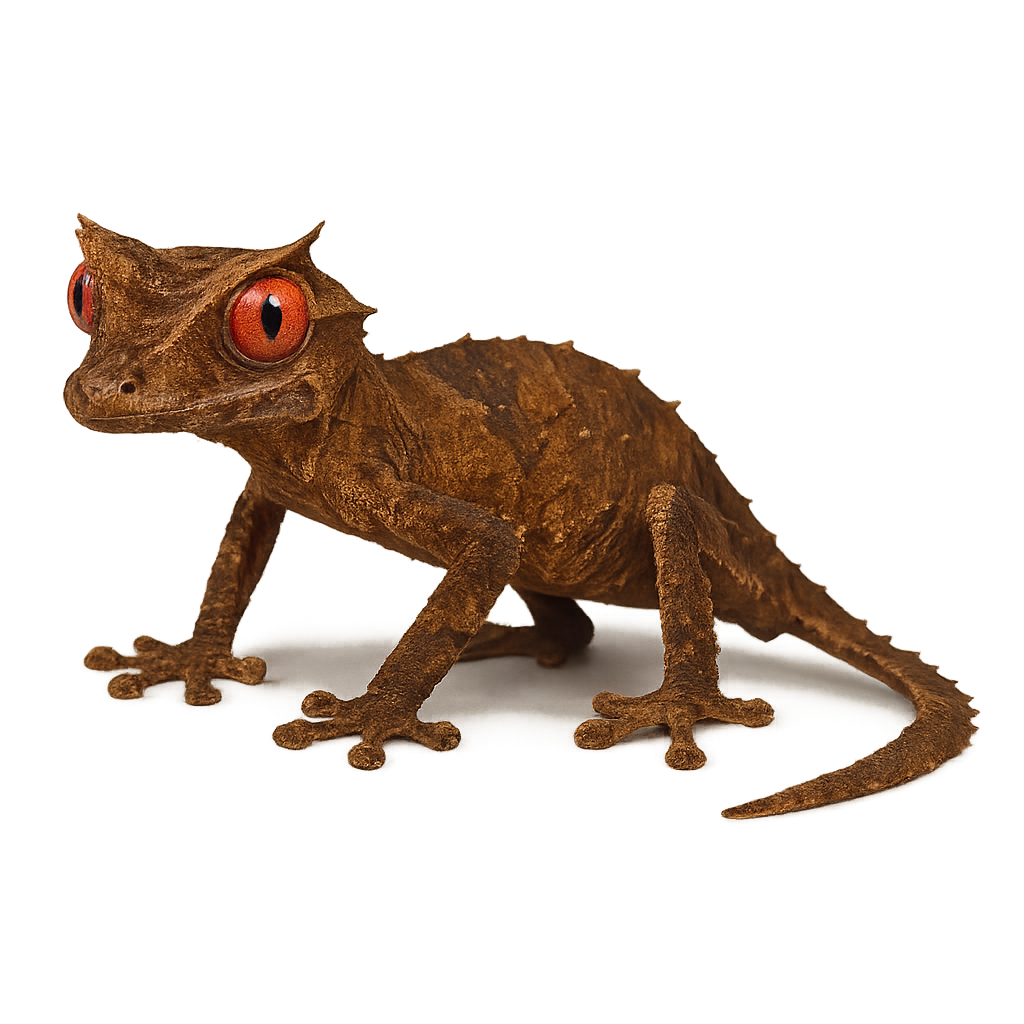
The Sikora's Leaf-tailed Gecko, Uroplatus sikorae, is a master of disguise, blending seamlessly into its surroundings with skin that mimics tree bark. Native to Madagascar, it primarily inhabits humid tropical forests. This nocturnal reptile is known for its ability to remain motionless for extended periods, making it difficult to spot. Its leaf-shaped tail is not only a tool for camouflage but also a means of communication with its peers. Measuring between 15 and 20 cm, it primarily feeds on insects. Although its appearance is striking, it is harmless to humans.
The Uroplatus ebenaui is a fascinating gecko endemic to Madagascar, renowned for its exceptional ability to blend into its surroundings. Its brown coloration and flattened shape allow it to resemble a dead leaf, providing perfect camouflage against predators. Measuring about 10 cm in length, it has a leaf-shaped tail that enhances its mimicry. This nocturnal gecko is primarily arboreal, inhabiting humid tropical forests. It feeds on insects and other small invertebrates. Its reproduction is oviparous, with eggs laid in the forest litter. Although discreet, it plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by regulating insect populations.
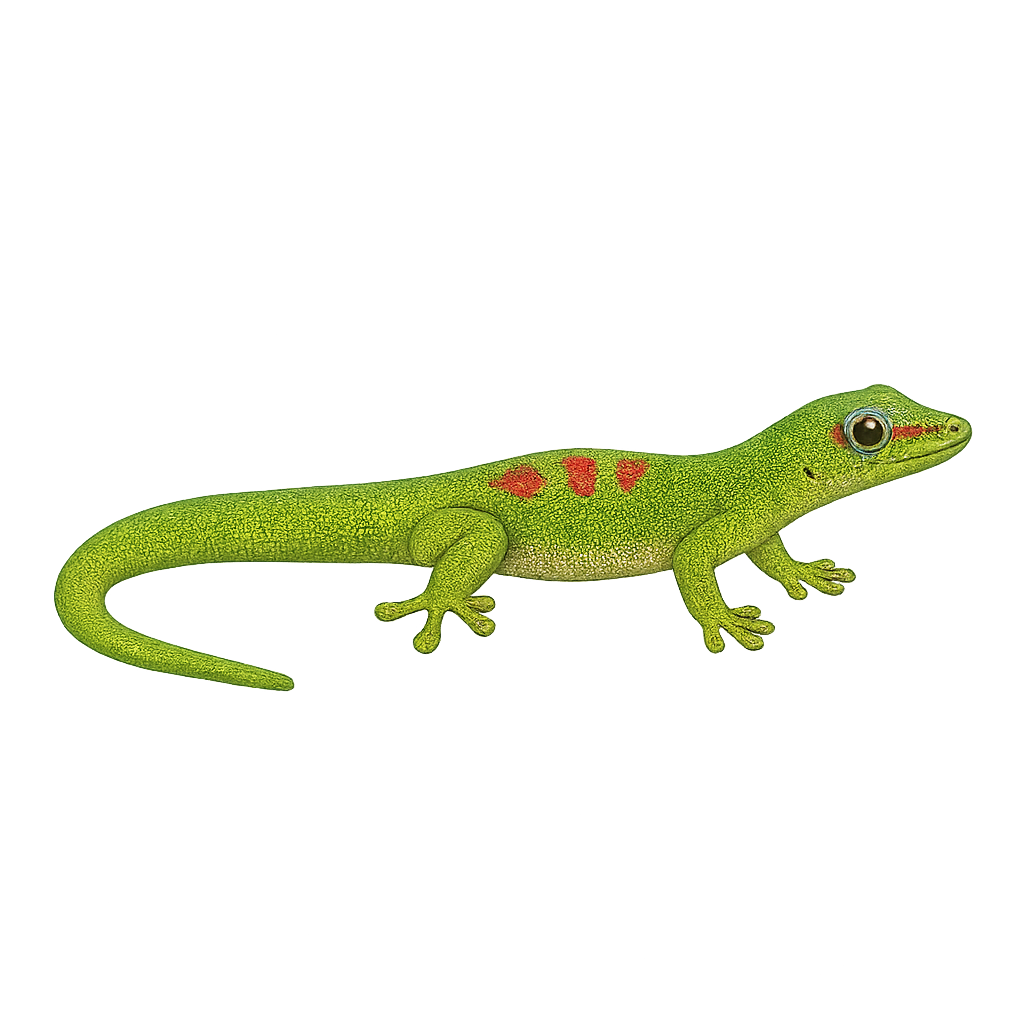
The Phelsuma laticauda, commonly known as the gold dust day gecko, is a small, brightly colored lizard native to Madagascar and nearby islands. It is easily recognizable by its vibrant green color, often adorned with golden or red spots on its back. Its size typically ranges from 10 to 15 cm, including the tail. This gecko is diurnal, meaning it is active during the day, and is often seen on tree trunks or the walls of human dwellings. It primarily feeds on insects but also enjoys nectar and fruits. Its ability to adapt to various environments, including urban areas, makes it a fascinating example of animal adaptation.
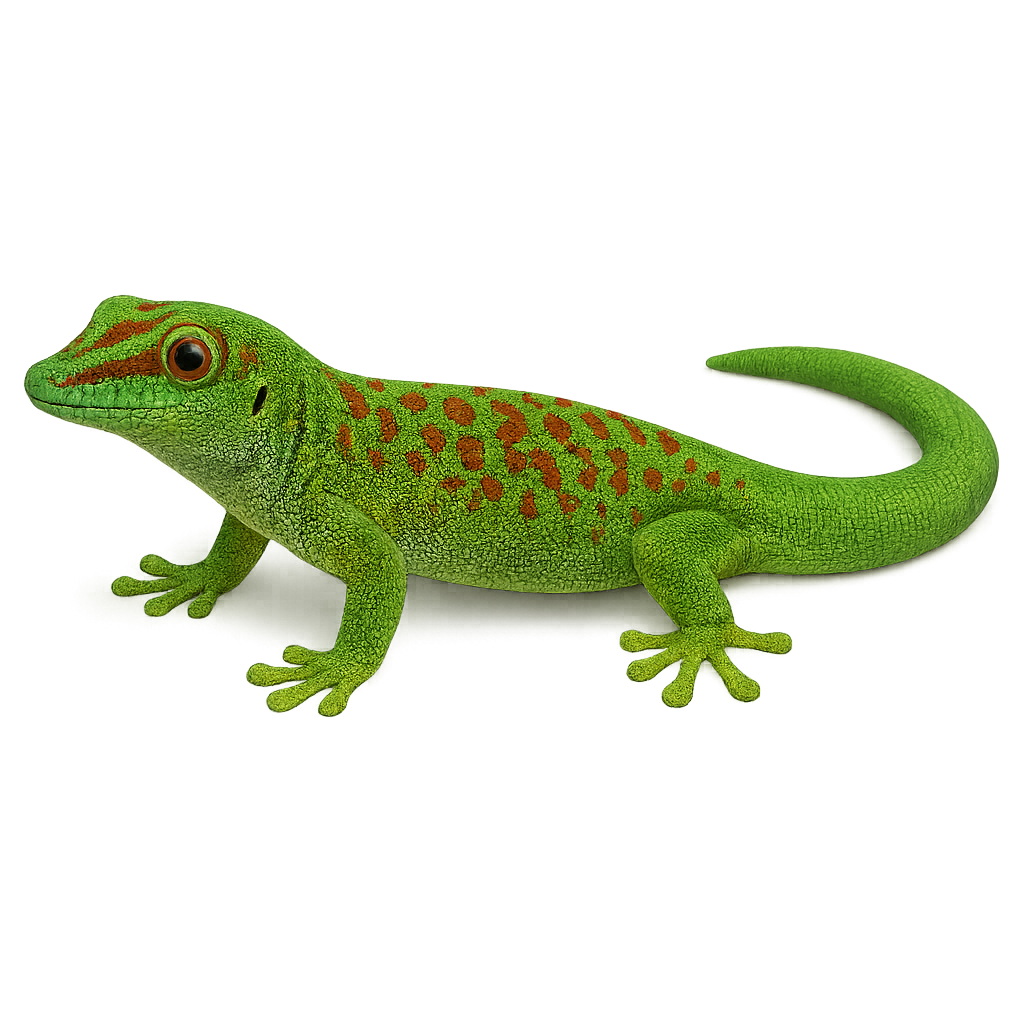
The Phelsuma madagascariensis, or Madagascar day gecko, is a colorful and fascinating lizard native to Madagascar. It is renowned for its bright colors, often green with red and blue spots, which help it blend into its natural environment. Typically measuring between 20 and 25 cm, this gecko is diurnal, meaning it is active during the day. It primarily inhabits humid tropical forests but can also be found in gardens and plantations. Although mainly insectivorous, it also feeds on nectar and fruits. Its ability to climb smooth surfaces thanks to its adhesive pads makes it an excellent climber.
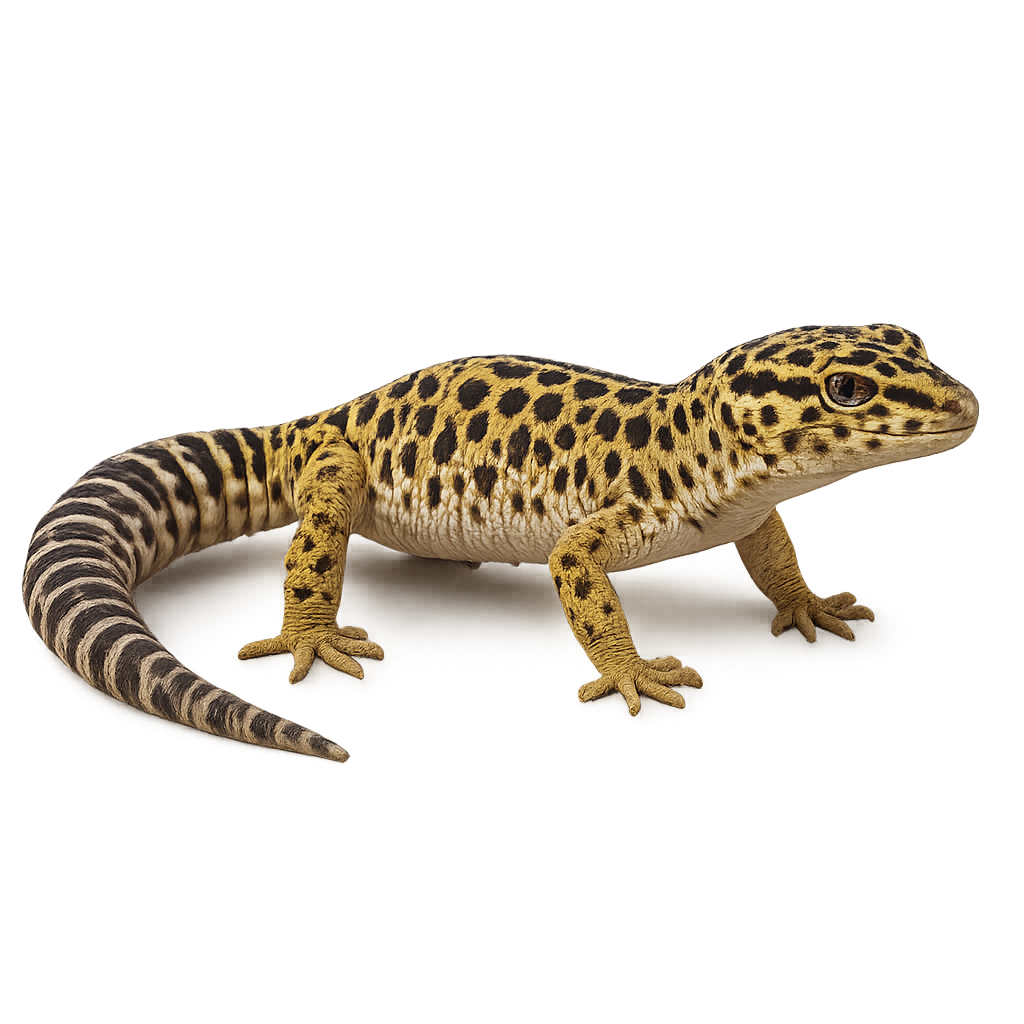
The Leopard gecko is a terrestrial species native to the desert and semi-desert regions of Asia, particularly Pakistan, India, and Nepal. This gecko is easily recognized by its dark spots on a pale yellow background, giving it a unique appearance. Unlike other geckos, it has movable eyelids, allowing it to blink, unlike other species that have fixed eyelids. The Leopard gecko is a nocturnal predator, primarily feeding on insects and small invertebrates. It is popular in the reptile trade due to its calm temperament and ease of care.
The Satanic Leaf-Tailed Gecko, Uroplatus phantasticus, is a master of camouflage native to Madagascar. Its ability to blend into its surroundings is remarkable, thanks to its skin that mimics the appearance of dead leaves. This small reptile, measuring about 10 cm, has a leaf-shaped tail that allows it to effectively hide from predators. Primarily active at night, it feeds on insects and other small invertebrates. Its coloration ranges from brown to gray, with occasional reddish hues, enabling it to blend into leaf litter. Although fascinating, it is vulnerable to deforestation and habitat loss.
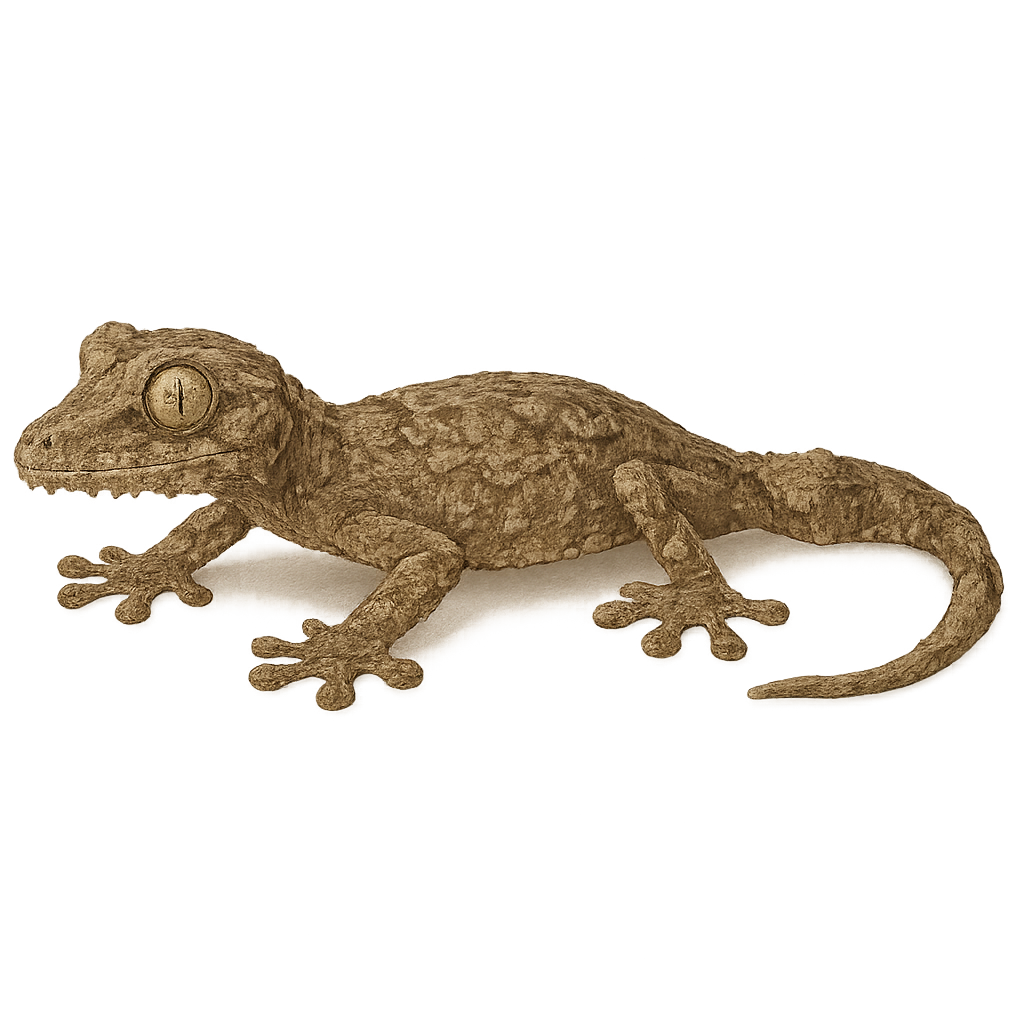
The Tokay gecko is a large lizard native to the tropical forests of Southeast Asia. This gecko is particularly known for its vibrant colors, with a gray or bluish body speckled with orange or red spots, making it easily recognizable. The Tokay gecko is nocturnal and arboreal, living in forested habitats, often near human dwellings. It is also famous for its distinctive call, resembling its name, tokay," which it uses to defend its territory or attract a mate. This gecko is a carnivorous predator, feeding mainly on insects and small vertebrates."
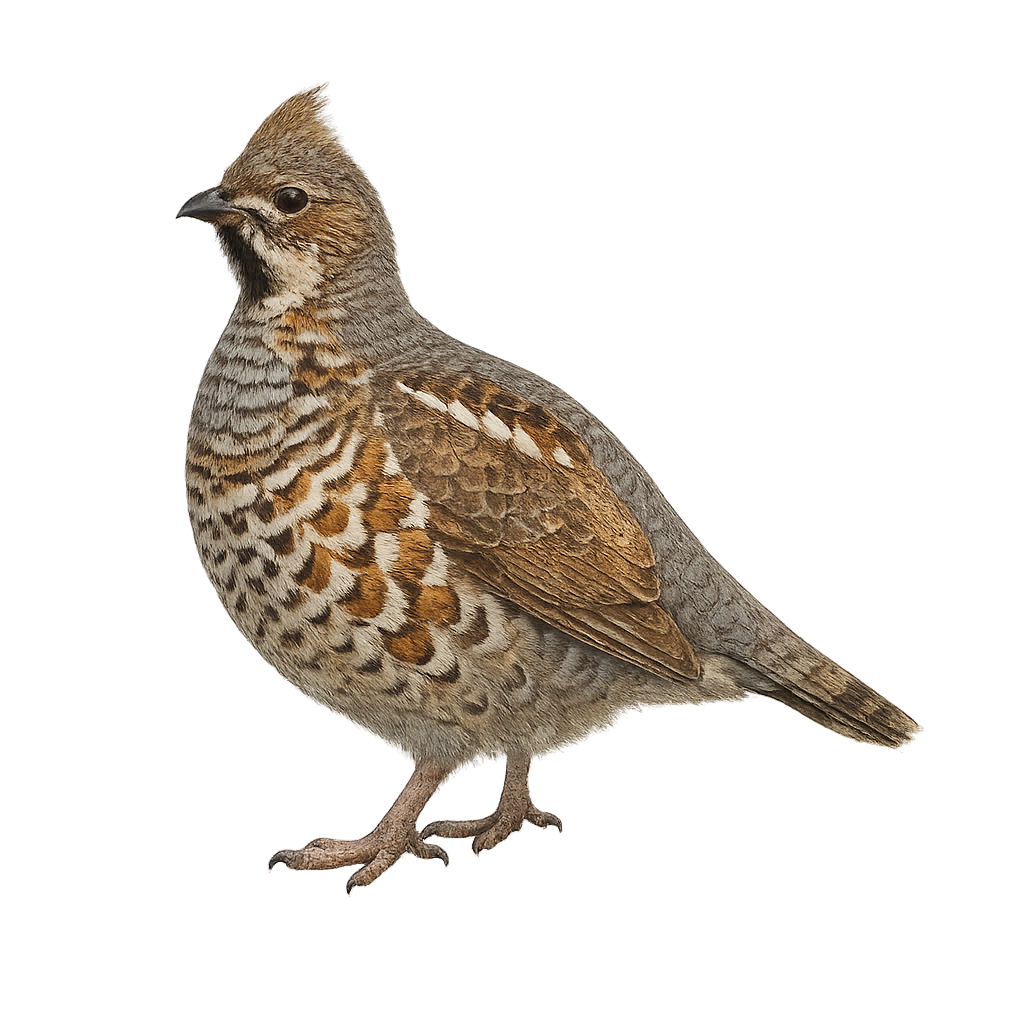
The Hazel Grouse is a small, terrestrial bird belonging to the pheasant family, easily recognizable by its subtly colored plumage and robust build. It measures about 40 to 45 cm in length and weighs between 500 and 700 g. Its plumage is primarily brown and gray, with patterns of spots and bars that allow it to blend effectively into the dense vegetation of forests. The Hazel Grouse primarily inhabits dense deciduous and mixed forests, where it feeds on seeds, berries, young shoots, and insects. Although it is rather discreet and difficult to spot, it is often heard through its soft, deep call. The Hazel Grouse is a fairly sedentary bird, but it may migrate short distances depending on weather conditions. It is also an emblematic bird of wooded areas and forest landscapes. While it is not endangered, the Hazel Grouse may be threatened by the loss of its forest habitat and the degradation of its breeding sites.
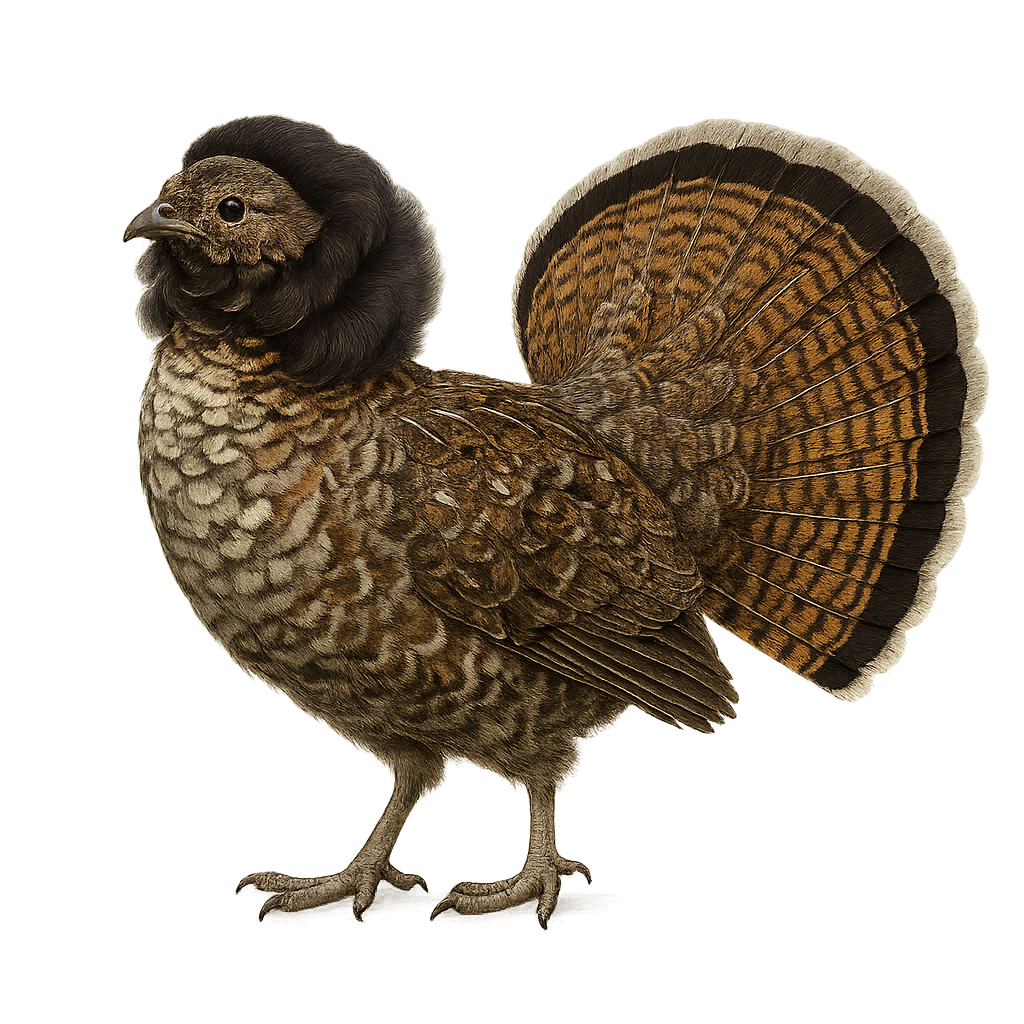
The Ruffed Grouse, Bonasa umbellus, is a medium-sized forest bird native to North America. It is easily identified by its mottled brown plumage, which provides excellent camouflage in its woodland habitat. Males are famous for their drumming display, a sound created by rapidly beating their wings, which echoes through the woods during the breeding season. This bird prefers mixed forests and dense wooded areas where it feeds on buds, leaves, and insects. Although generally solitary, the Ruffed Grouse can be seen in small groups outside the breeding season. Its ability to remain still and blend into its surroundings makes it a challenging subject for birdwatchers.
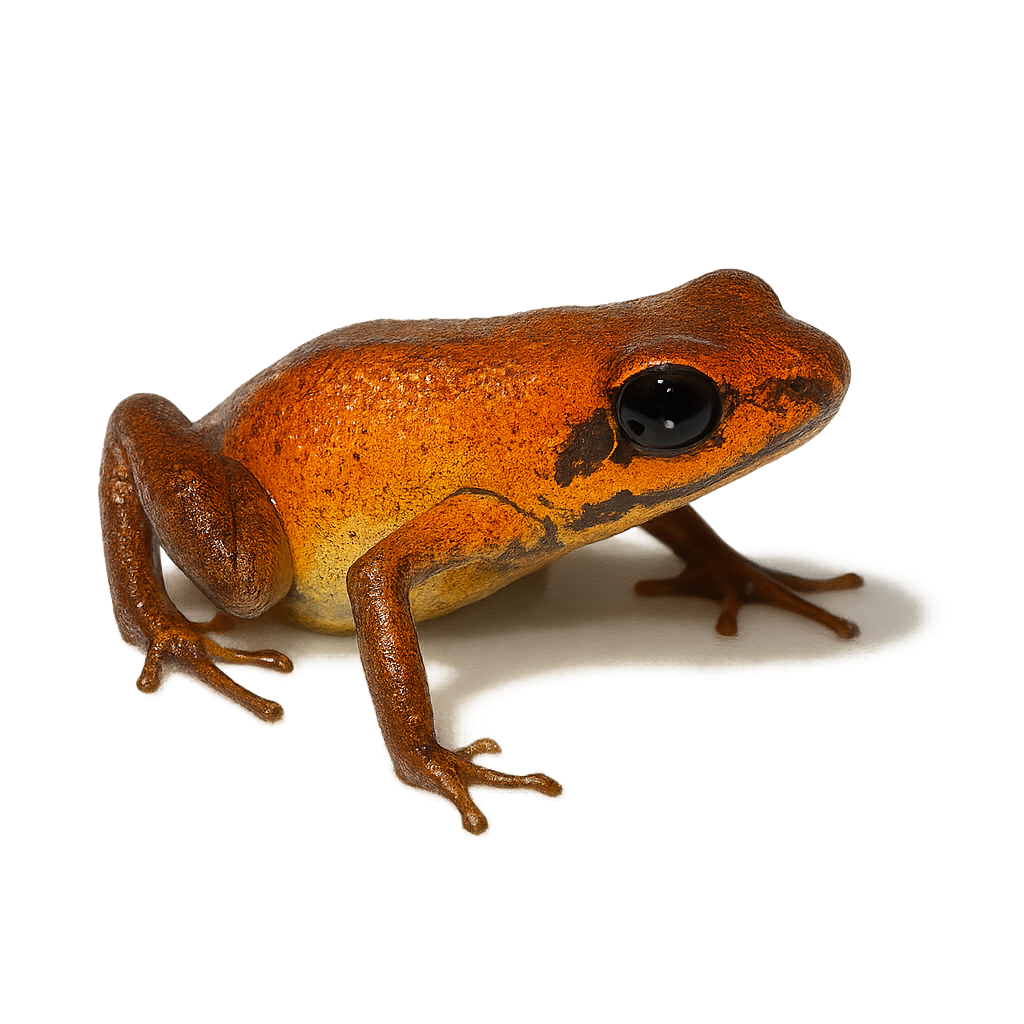
The Geminis’ dart frog, Andinobates geminisae, is a small, brightly colored frog native to the humid rainforests of Panama. Recently discovered, it is distinguished by its vivid orange color and small size, measuring about 1.5 cm. This species primarily inhabits leaf litter and moist forest areas, feeding on small invertebrates. Like other poison frogs, it is known for its toxic skin, a defense against predators. Reproduction involves laying eggs in moist spots, with notable parental care where adults transport tadpoles to water bodies. This species is currently classified as vulnerable due to habitat loss and collection for the pet trade.
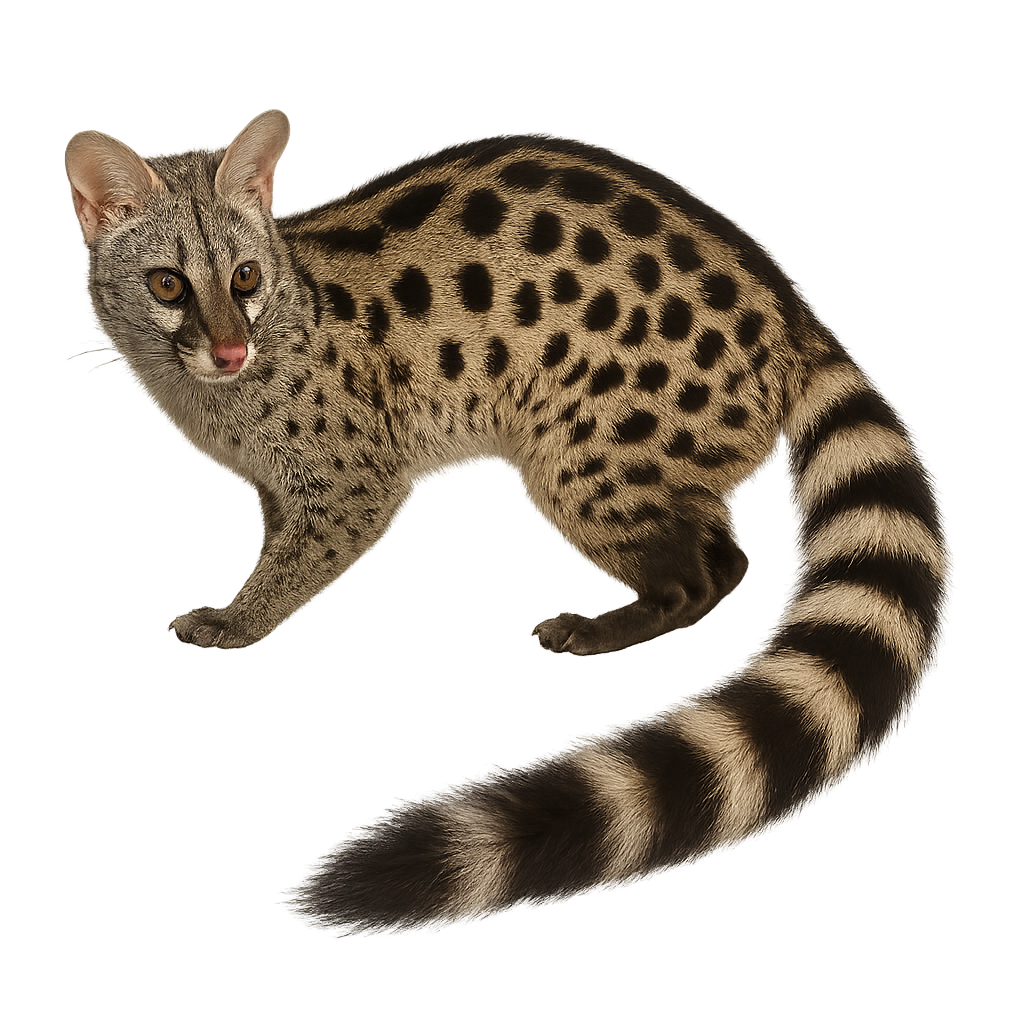
The Common Genet is a small, agile, and elegant carnivore, easily recognizable by its long and slender body, as well as its characteristic spots. It measures between 45 and 60 cm in length, with a tail measuring 40 to 50 cm, and typically weighs between 1.5 and 2.5 kg. Its coat is usually light gray or brown, speckled with dark spots that form a distinctive pattern on its back and flanks. The Common Genet has a bushy tail and a body shape that allows it to easily climb trees and slip into narrow spaces. It primarily inhabits forests, woodlands, and wooded areas in North and South Africa, as well as the Iberian Peninsula. This carnivore is omnivorous, feeding mainly on small mammals, birds, insects, fruits, and berries. The Common Genet is also an excellent climber, often seen moving through trees in search of food or to escape danger. While the Genet is not currently threatened, it faces threats related to habitat loss and human persecution.
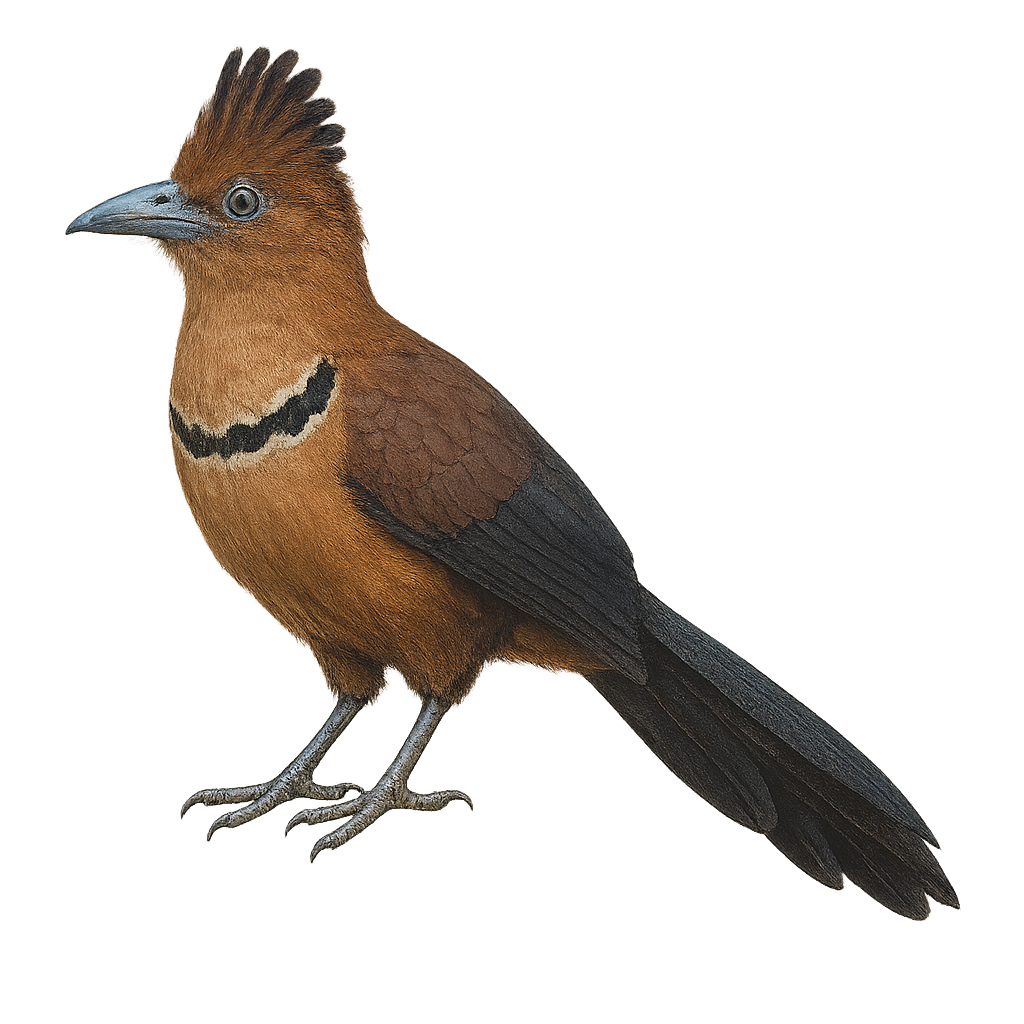
The Rufous-vented Ground Cuckoo, Neomorphus geoffroyi, is a rare and intriguing bird found in the tropical forests of Central and South America. It is recognizable by its rufous-brown plumage and distinctive long tail. This terrestrial bird prefers dense undergrowth where it moves stealthily in search of prey such as insects and small vertebrates. Although primarily ground-dwelling, it can fly short distances to escape predators. The Rufous-vented Ground Cuckoo is often heard before it is seen, thanks to its powerful and resonant calls. Its ability to blend into its environment makes it difficult to observe, adding to its mystery and appeal for birdwatchers.
The Pavonine Cuckoo is a mysterious and fascinating bird belonging to the Cuculidae family. It is primarily found in the dense tropical forests of South America, notably in Brazil, Bolivia, and Paraguay. This bird is recognizable by its brown and black plumage, with distinctive patterns reminiscent of peacock feathers, hence its name. The Pavonine Cuckoo is a discreet bird, often heard rather than seen, thanks to its melodious and repetitive song. It is known for its brood parasitism behavior, laying its eggs in the nests of other bird species. Although its conservation status is currently assessed as "least concern," deforestation continues to threaten its natural habitat.