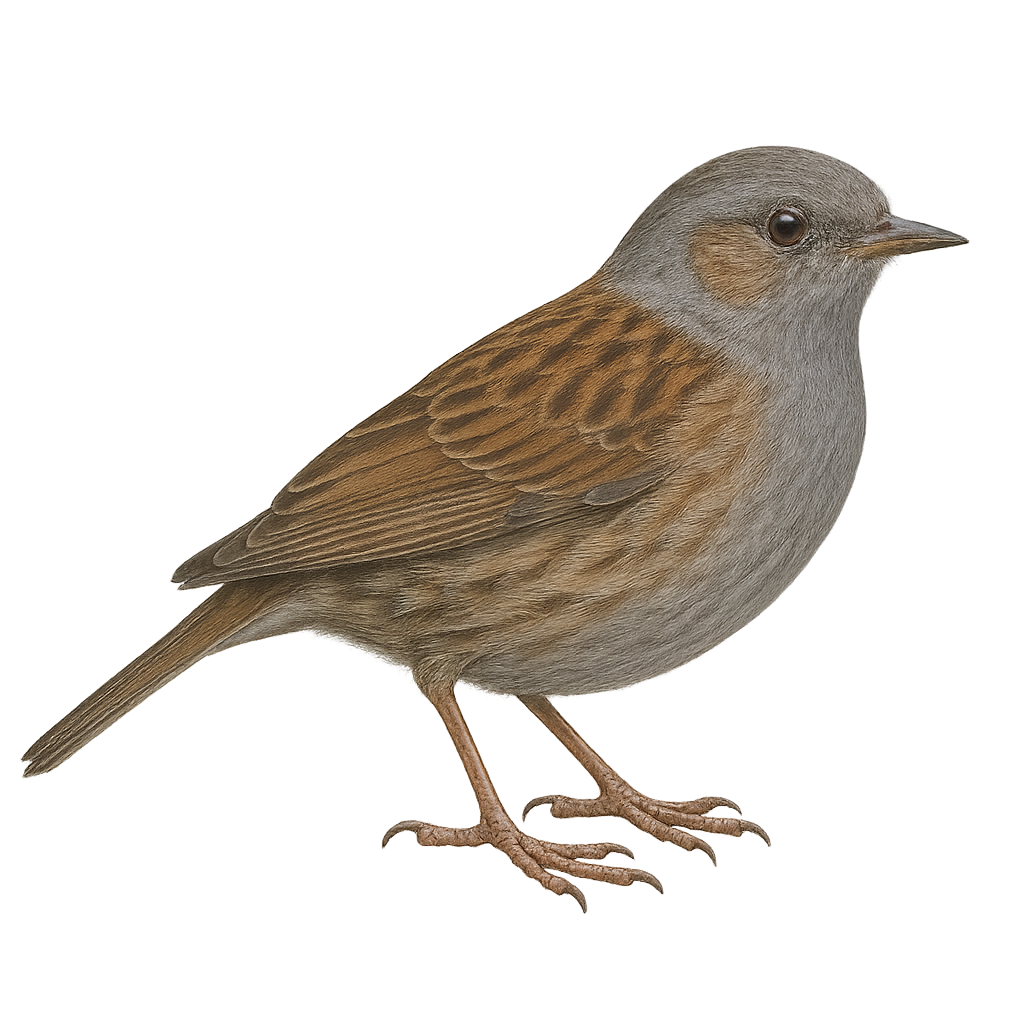
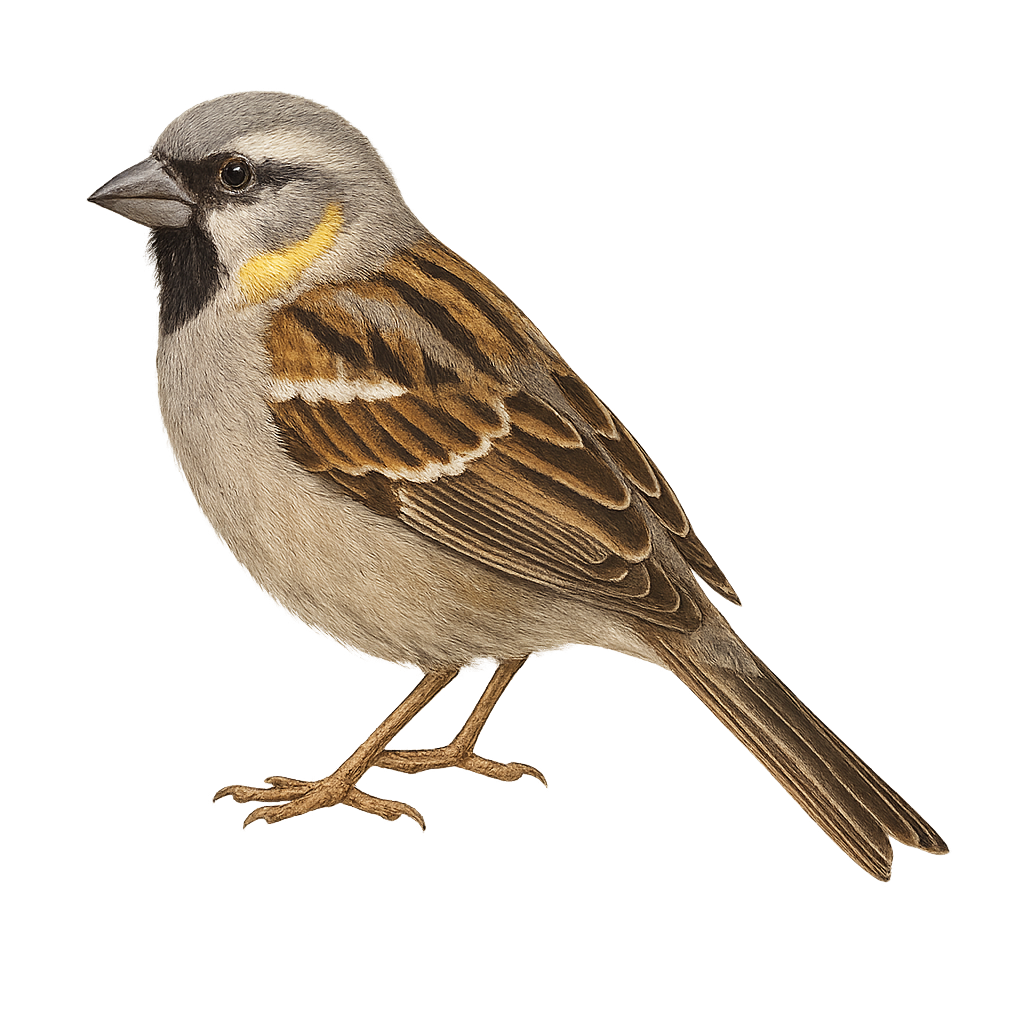
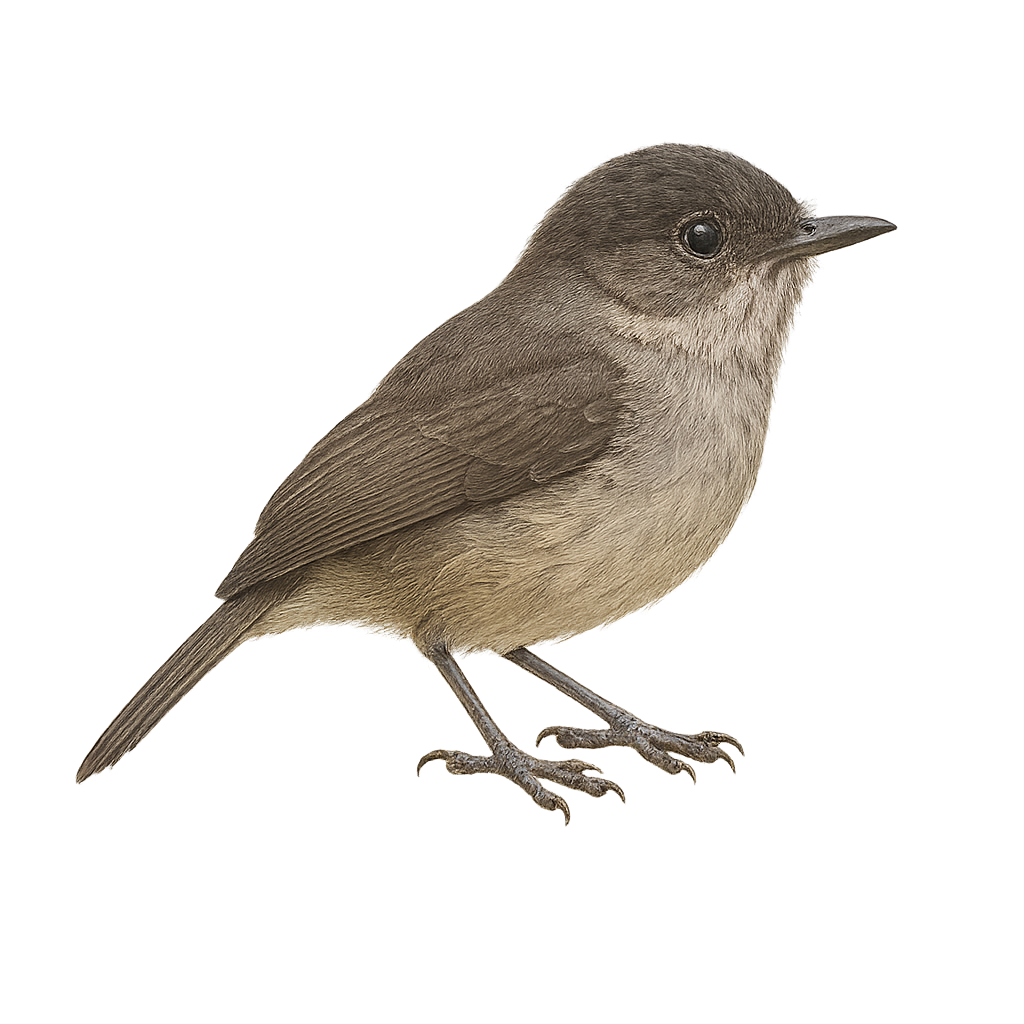
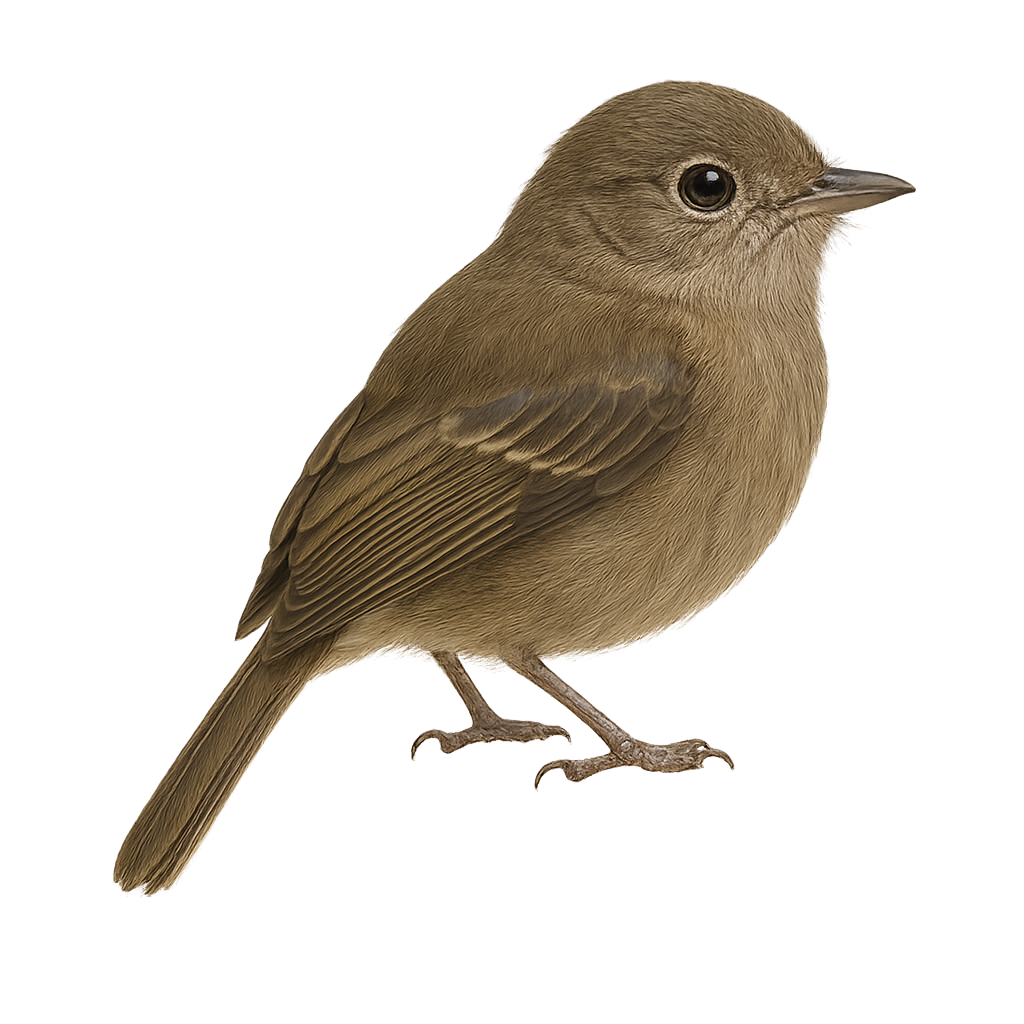
The dunnock is a small passerine, 12–14 cm long, with streaked brownish-grey plumage, an unobtrusive posture and a quick, darting flight. It inhabits hedgerows, woodland edges and gardens, feeding on seeds and insects searched for on the ground or in foliage. During the breeding season, the male sings from a low perch to attract the female and defend a compact territory.
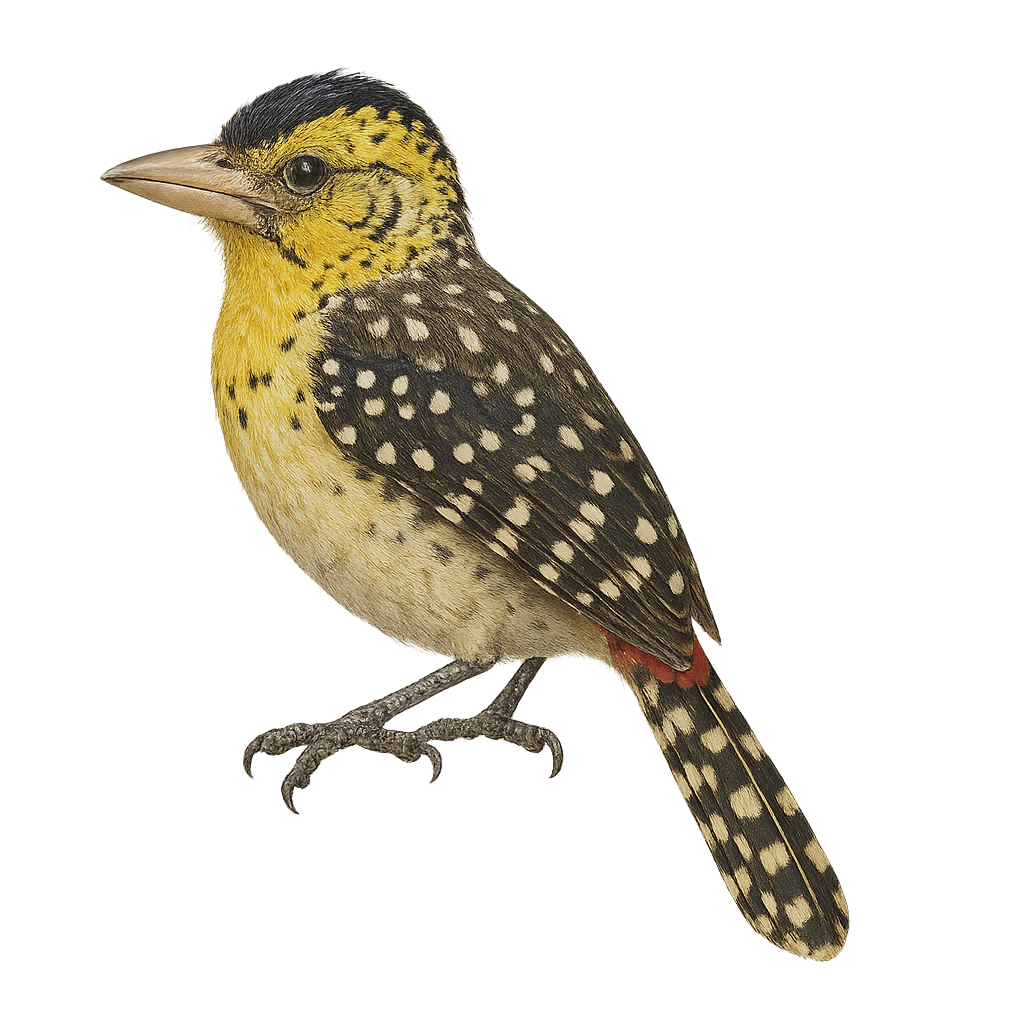
The D'Arnaud's Barbet is a colorful and fascinating bird native to the wooded regions and savannas of East Africa. This medium-sized bird, measuring about 20 cm in length, is easily recognizable by its bright plumage, featuring shades of yellow, black, and white, with distinctive red patches on its head and neck. It is often seen in small groups or pairs, feeding mainly on insects, fruits, and seeds. The D'Arnaud's Barbet is known for its melodious and repetitive song, which it uses to mark its territory. Although relatively common in its natural habitat, it is essential to preserve its ecosystems to ensure its long-term survival.
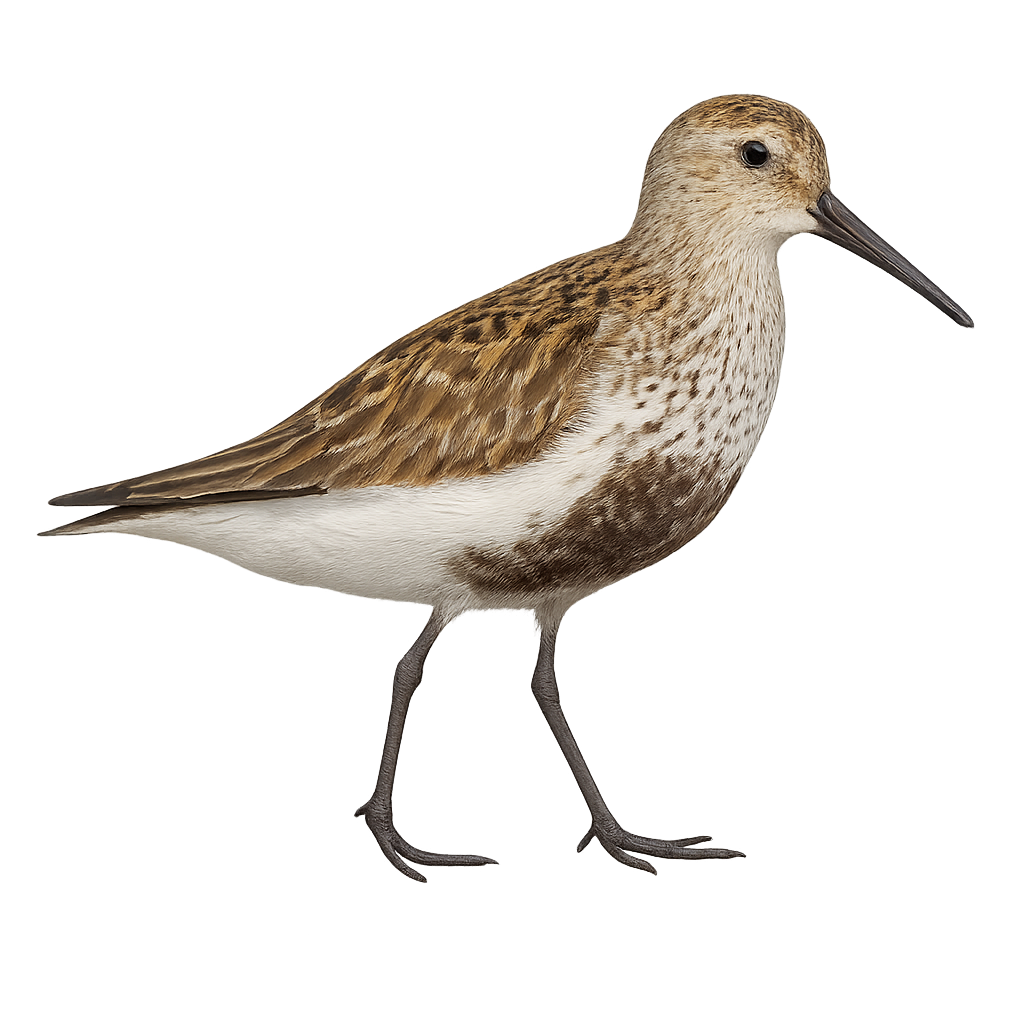
The Dunlin is a small, graceful wader, easily recognizable by its plumage that changes with the seasons, transitioning from gray-brown in winter to more contrasting black and white tones during breeding. This small bird primarily inhabits coastal areas of Europe, Asia, and North America, where it feeds on marine invertebrates, primarily worms and mollusks, which it finds by probing the sand and mud. The Dunlin exhibits social behavior and is often seen in groups, especially during migration.
This migratory wader covers long distances, leaving the cold regions of winter to reach more temperate or tropical areas for feeding and breeding. While relatively common, it can be affected by the disturbance of its coastal habitats.
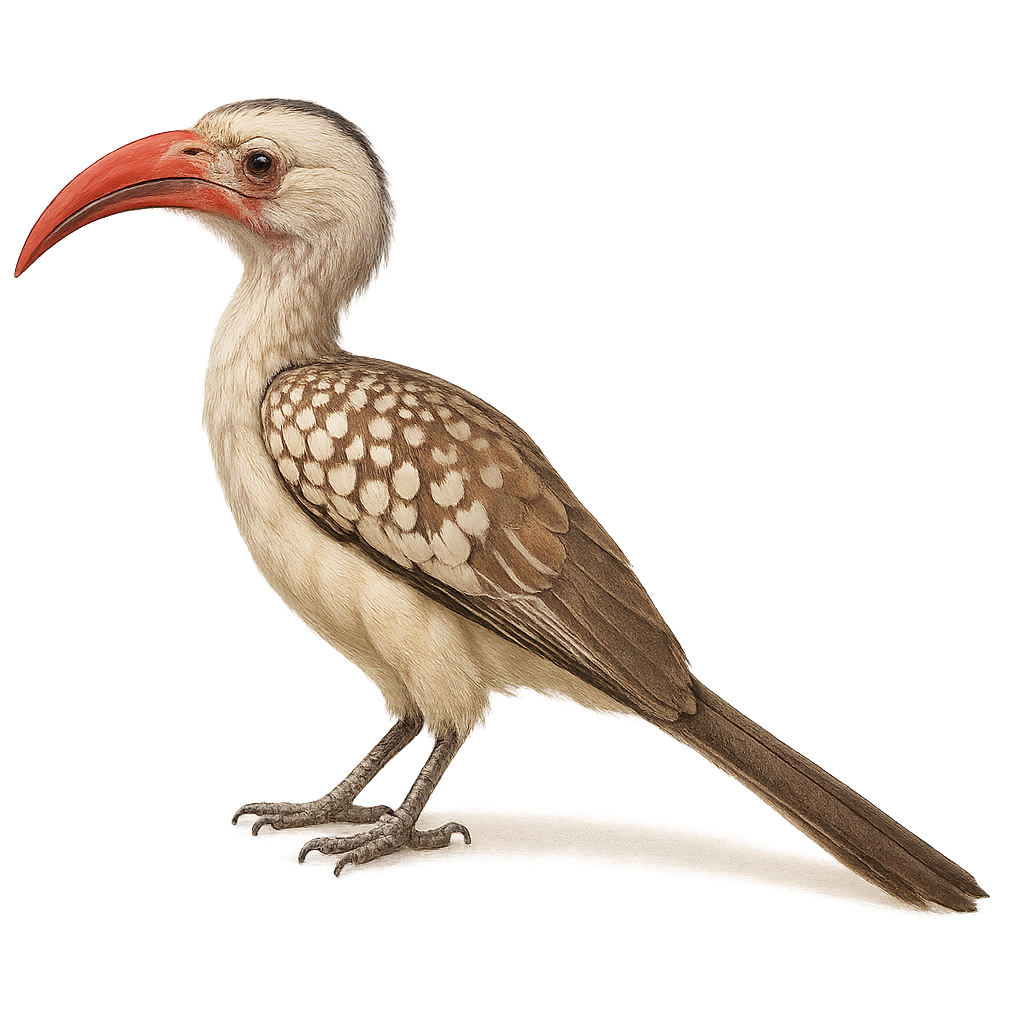
The Damara Red-billed Hornbill is a fascinating bird, easily recognizable by its large bill and contrasting coloration. It sports primarily black and white plumage, with shades of gray on the wings. This bird is endemic to the arid regions of southwestern Africa, particularly in Namibia and Angola. It is often seen in small groups, exploring savannas and wooded areas in search of food. Its diet is varied, including insects, fruits, and occasionally small vertebrates. The Damara Red-billed Hornbill is also known for its complex social behaviors, especially during the breeding season when pairs are particularly attentive to each other.
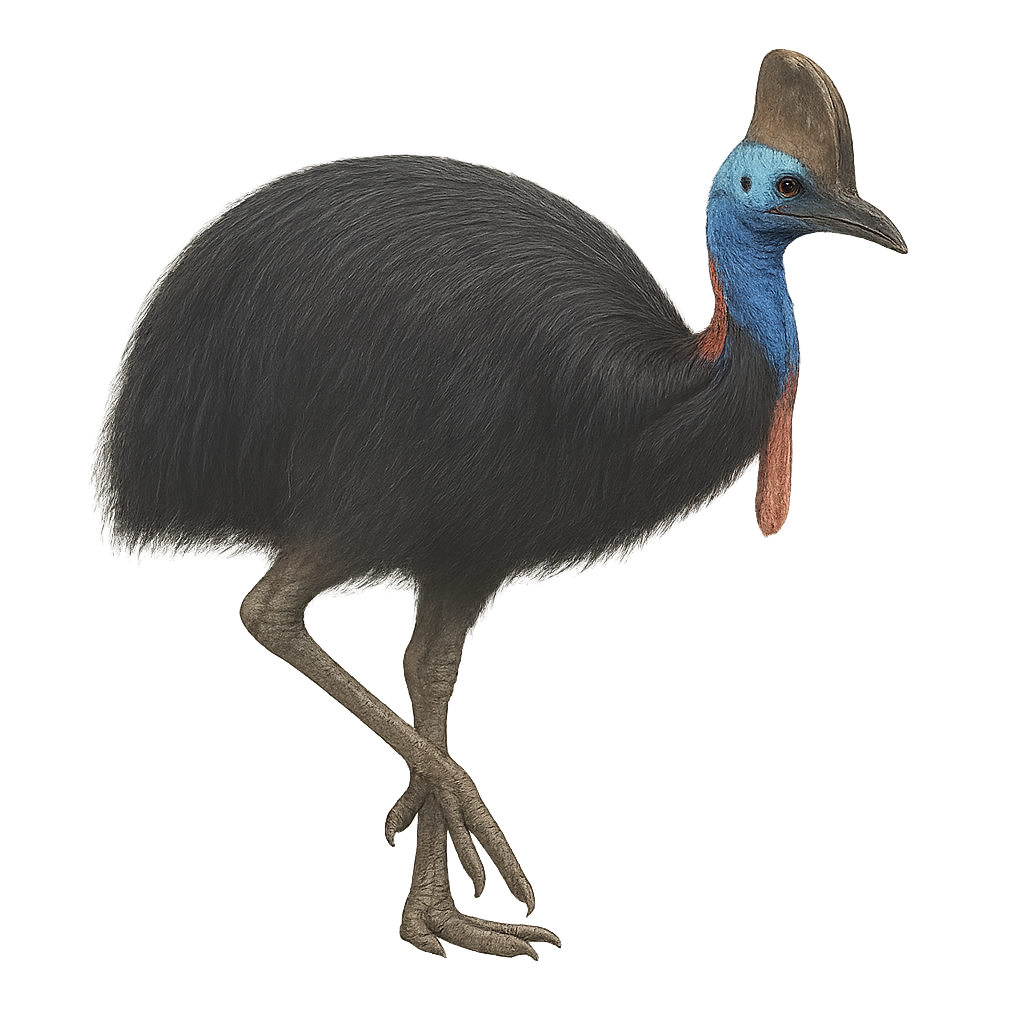
The Dwarf Cassowary, also known as Bennett's Cassowary, is a large and majestic bird native to the tropical forests of New Guinea and surrounding islands. It stands out with its impressive height, reaching up to 1.5 meters, and its glossy black plumage. Its head is adorned with a bony crest, known as a casque, giving it a prehistoric appearance. This solitary bird is primarily frugivorous, feeding on fallen fruits, but it can also consume small animals and insects. The Dwarf Cassowary is an excellent runner, capable of moving swiftly through dense forest vegetation. Although generally discreet, it can become aggressive if it feels threatened.
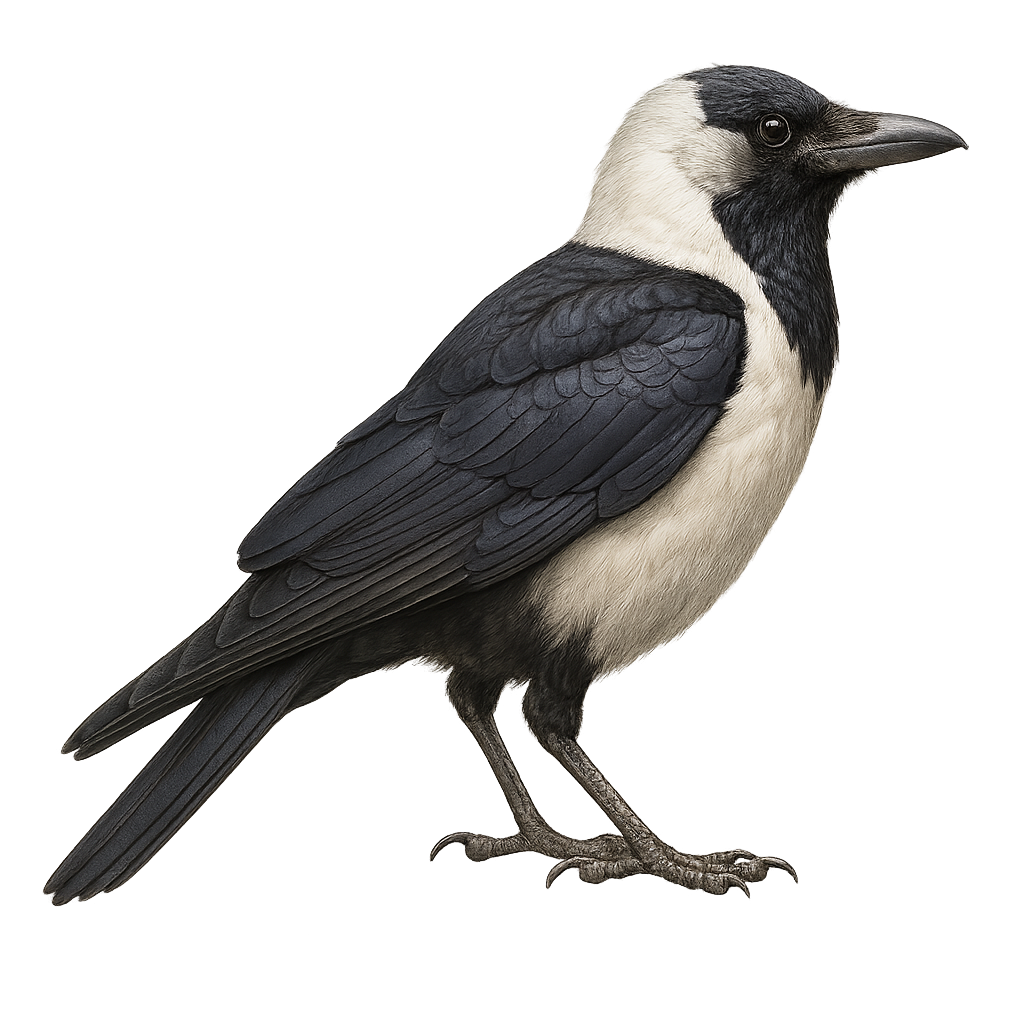
The Daurian Jackdaw, Coloeus dauuricus, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Corvidae family. It is characterized by its black and gray plumage, with a black cap and white cheeks. This bird is mainly found in East Asia, particularly in China, Mongolia, and Russia. It inhabits open areas, sparse forests, and agricultural lands. The Daurian Jackdaw is a sociable bird, often seen in groups. It primarily feeds on insects, seeds, and small fruits. Its behavior is generally tolerant towards humans, making it relatively easy to observe. The breeding season extends from spring to summer, with nests built in tree cavities or buildings.
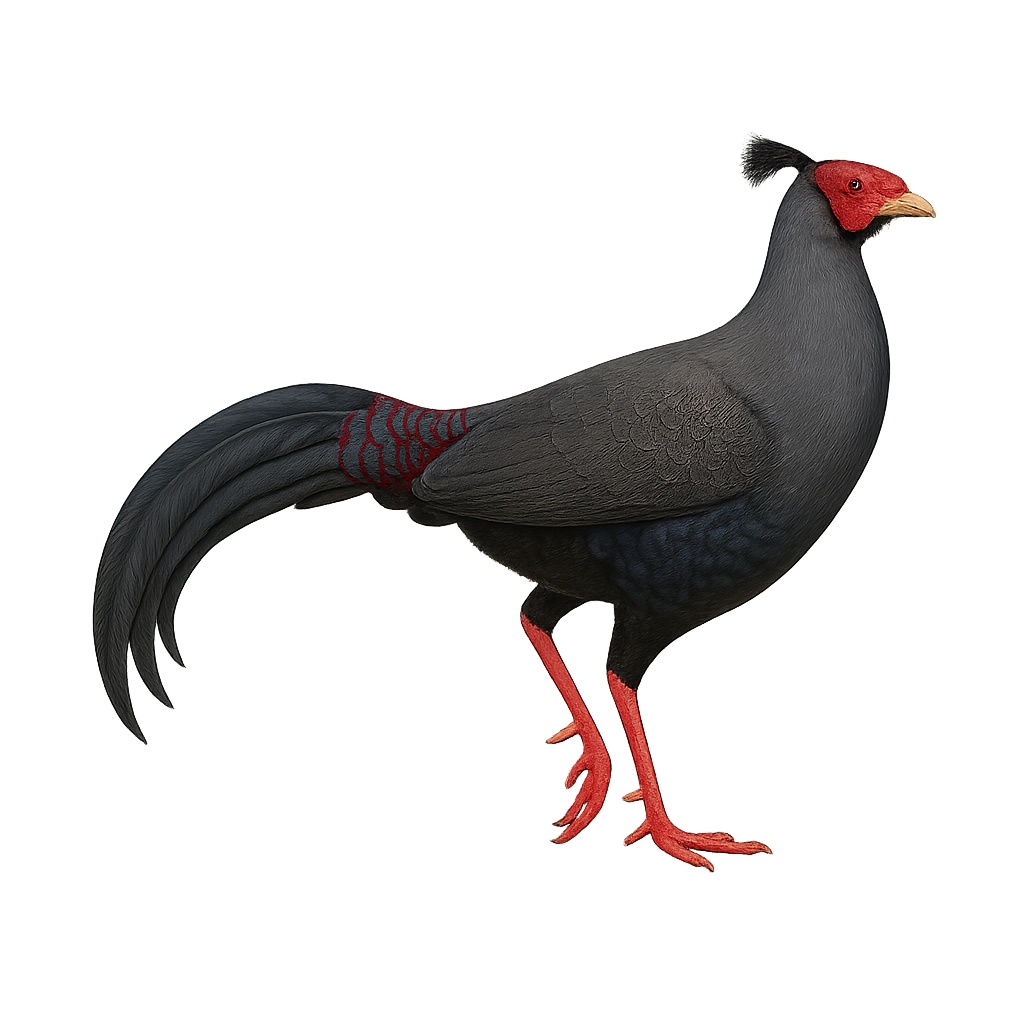
The Diard's Fireback, or Lophura diardi, is an elegant and colorful bird native to the tropical forests of Southeast Asia. Males display a striking metallic blue plumage with iridescent hues, while females are more subdued with brownish tones. This pheasant is known for its long tail and distinctive crest. It primarily inhabits dense forests and wooded areas, feeding on seeds, fruits, and insects. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it remains relatively common in some regions. The Diard's Fireback is a symbol of beauty and grace in its natural environment.
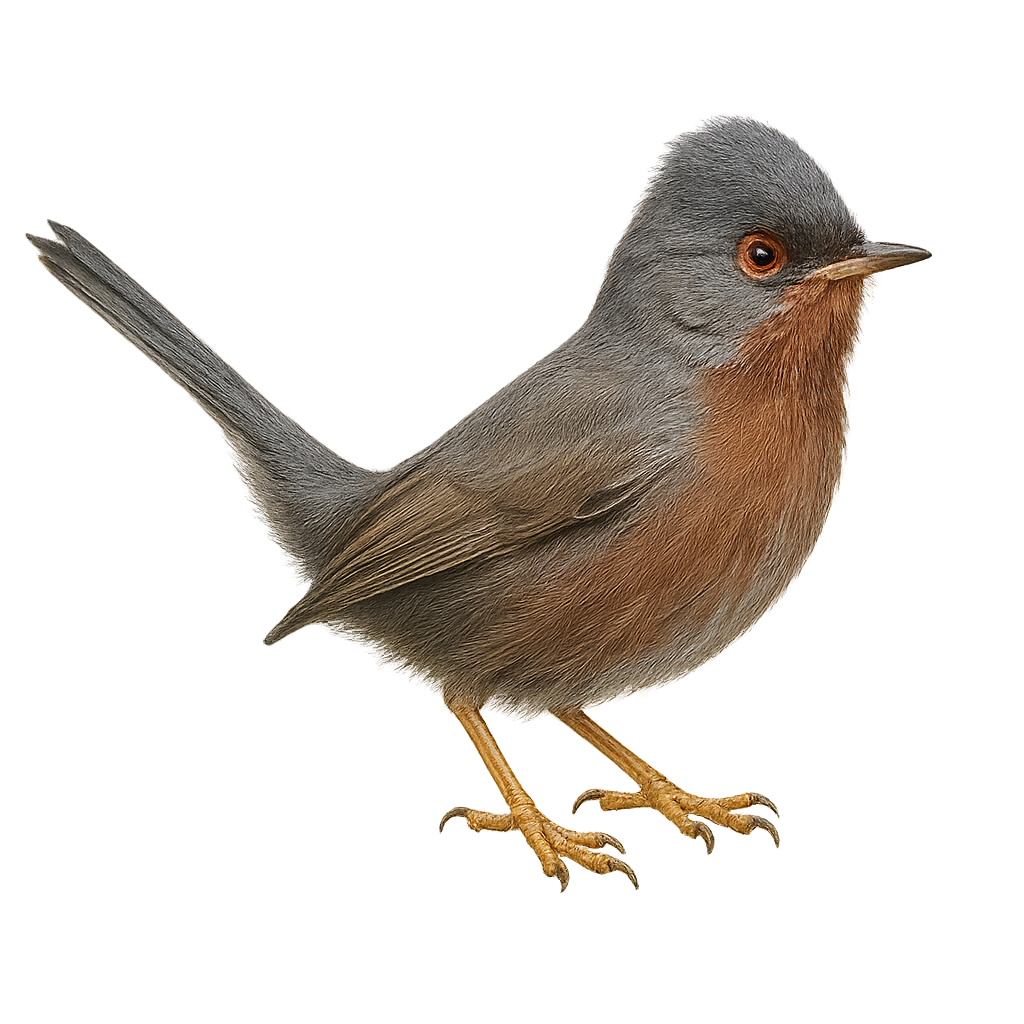
The Dartford Warbler, Sylvia undata, is a small passerine bird with slate-grey plumage and a reddish throat. It is mainly found in Mediterranean regions, frequenting scrublands and heathlands. This bird is sedentary, although some populations may undertake short altitudinal migrations. The Dartford Warbler is known for its melodious and complex song, often delivered from a high perch. It primarily feeds on insects but can also consume berries. The breeding season extends from spring to summer, with nests built low in dense vegetation. Although its conservation status is concerning due to habitat loss, it remains relatively common within its range.
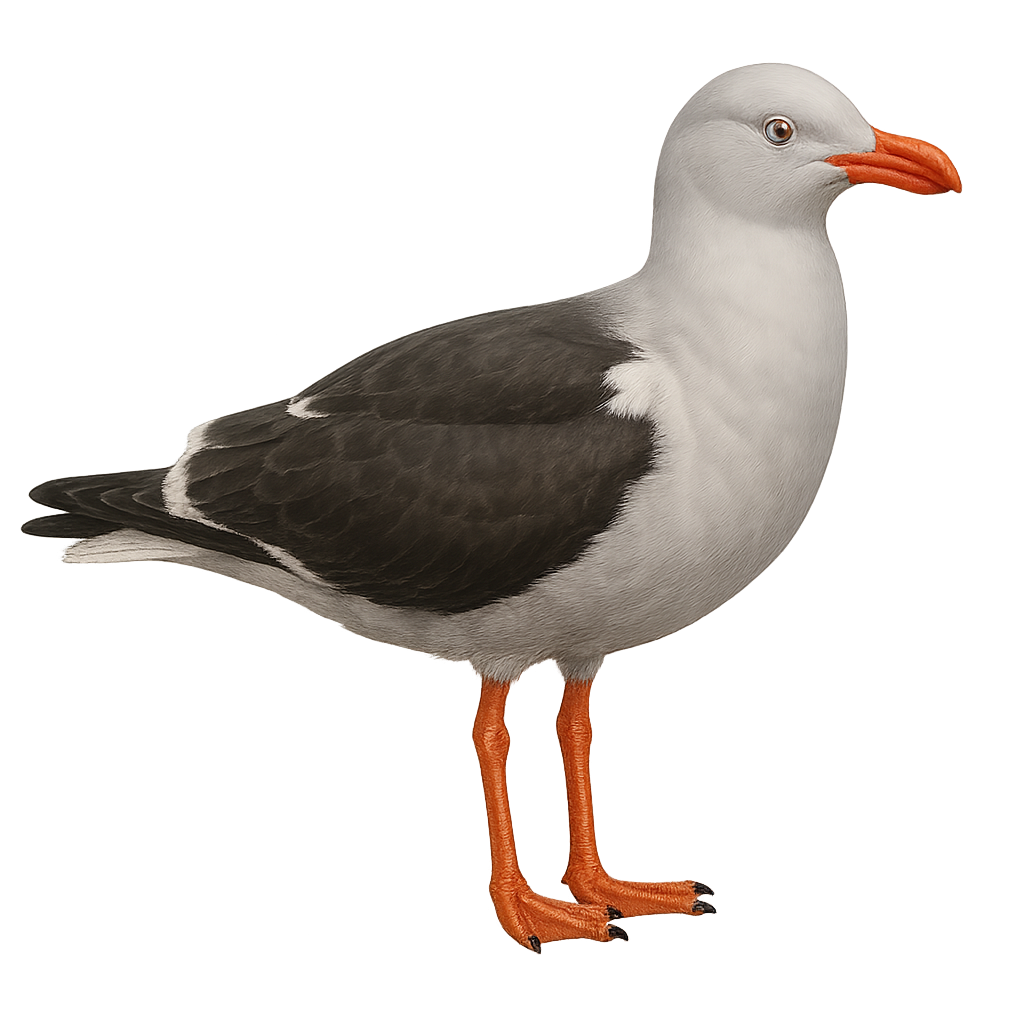
The Dolphin Gull, scientifically known as Leucophaeus scoresbii, is a medium-sized gull species primarily found along the coastal regions of South America, particularly in Patagonia and the Falkland Islands. It features a predominantly grey plumage with darker shades on the wings and back, while its head is white. This gull is notable for its bright red bill and pinkish legs. Often seen in small groups, it feeds on fish, crustaceans, and marine debris. Known for its opportunistic behavior, it frequently approaches inhabited areas in search of food.
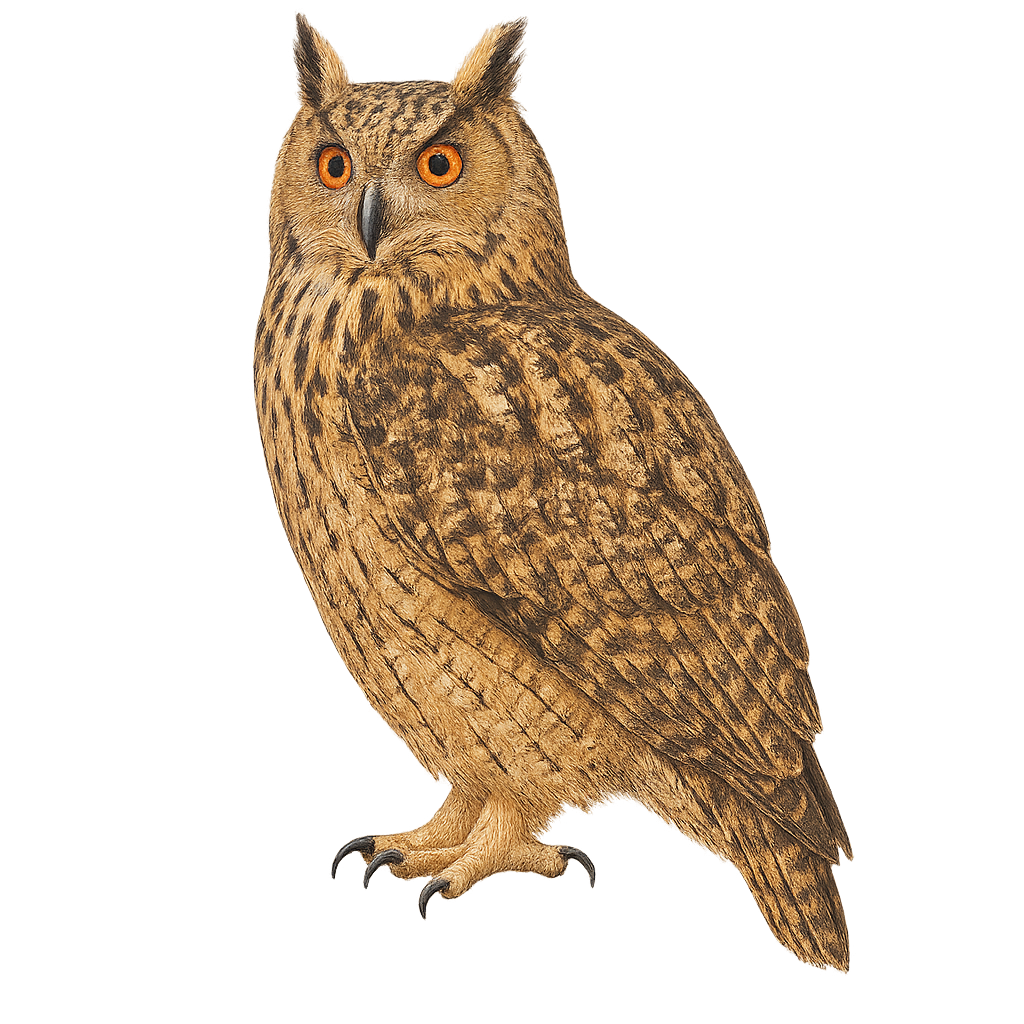
The Bubo ascalaphus, or Desert Owl, is an impressive nocturnal bird of prey, primarily found in the arid regions of North Africa and the Middle East. This owl is distinguished by its sandy plumage, which allows it to blend seamlessly into its desert environment. It has large yellow eyes and prominent ear tufts. An efficient predator, it primarily feeds on small mammals, birds, and insects. Its call is a deep, resonant hoot, often heard at dusk. The Desert Owl is a solitary bird, except during the breeding season when it forms monogamous pairs. Its ability to survive in extreme conditions makes it a fascinating example of animal adaptation.
The Double-banded Plover, Anarhynchus bicinctus, is a medium-sized bird known for its distinctive two black bands on the chest, contrasting with its grey-brown back and white belly. It is primarily found in New Zealand, frequenting sandy beaches, estuaries, and coastal wetlands. This bird is known for its ground-nesting behavior, often in open areas where it can easily watch for predators. Although generally discreet, it can become territorial during the breeding season. Its diet mainly consists of insects, small crustaceans, and worms, which it captures by quickly pecking at the ground.
The Dusky Antbird, or Cercomacroides tyrannina, is a small bird from the Thamnophilidae family, primarily found in the humid tropical forests of Central and South America. It is characterized by its dark gray, almost black plumage, and piercing red eyes. Males and females exhibit sexual dimorphism, with females having browner hues. This bird is often seen in pairs or small groups, moving through the undergrowth in search of insects. Although discreet, its distinctive call, a high-pitched whistle, often reveals its presence. The Dusky Antbird plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by regulating insect populations.
The Double-toothed Kite, or Harpagus bidentatus, is a medium-sized raptor found mainly in the tropical forests of Central and South America. It is easily recognizable by its grayish plumage and short, rounded wings, which allow it to maneuver skillfully through dense forest canopies. This bird of prey primarily feeds on reptiles, insects, and occasionally small mammals. Its name comes from the two prominent teeth on its beak, which help it grasp and tear its prey. The Double-toothed Kite is often observed following groups of capuchin monkeys, taking advantage of the commotion they cause to catch frightened prey.
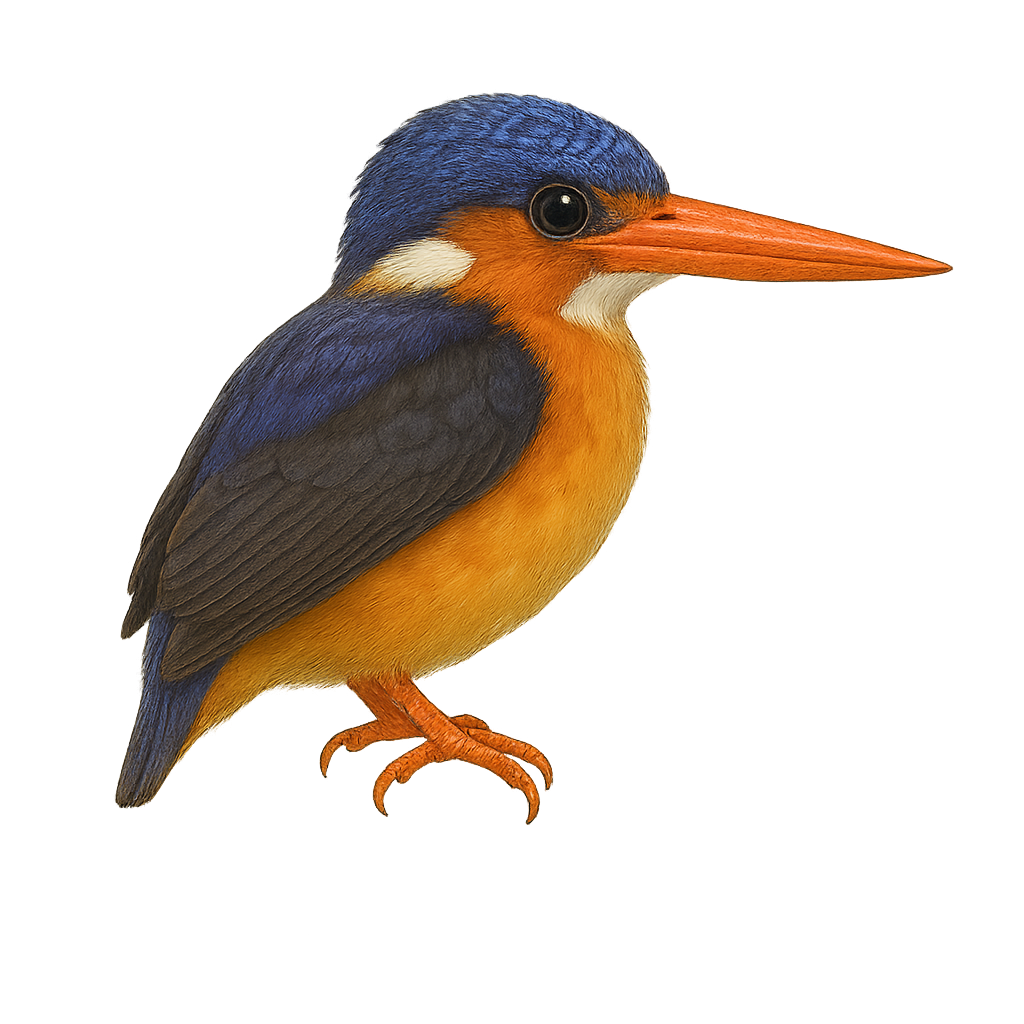
The Dimorphic Dwarf Kingfisher, or Ceyx margarethae, is a small, brightly colored bird endemic to the island of Sulawesi in Indonesia. This kingfisher is distinguished by its vibrant plumage, featuring shades of blue, orange, and white. It primarily inhabits tropical rainforests and wooded areas near water bodies. Although discreet, it is often spotted due to its sharp and distinctive call. This kingfisher feeds mainly on small fish and insects, which it catches by swiftly diving into the water from a perch. Its small size and discreet behavior make it difficult to observe, but it is a true gem for birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts.
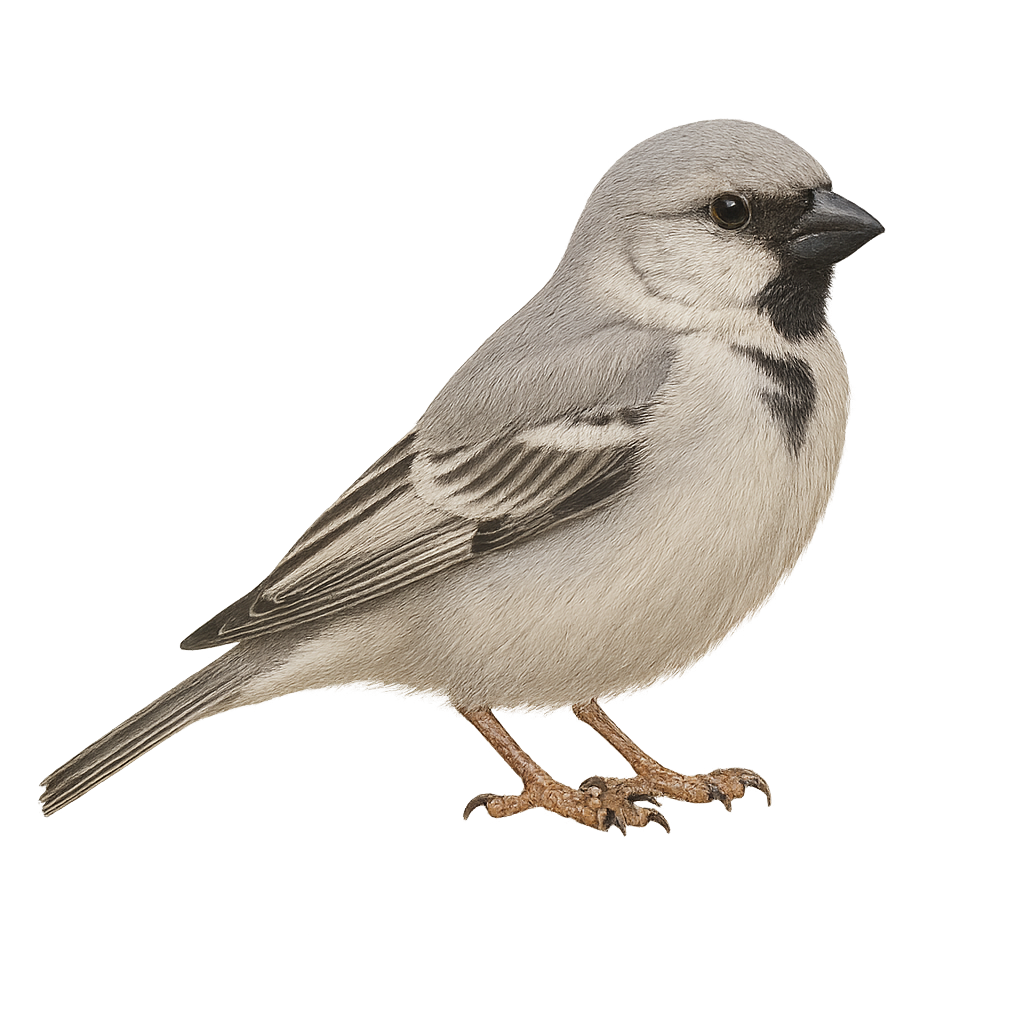
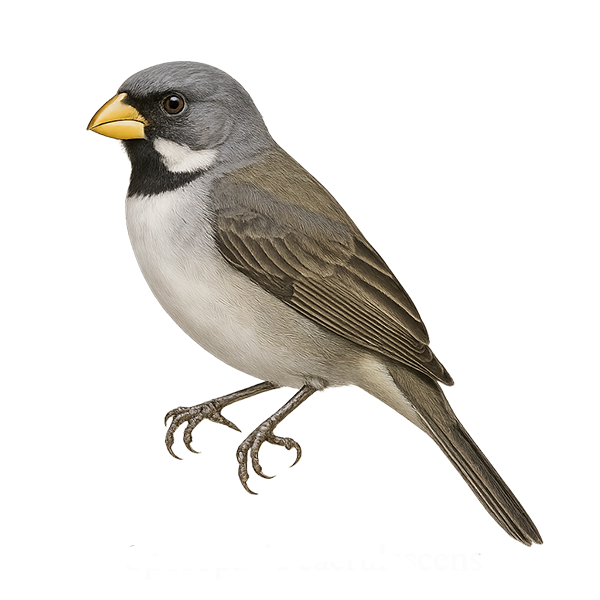
The Dead Sea Sparrow, or Passer moabiticus, is a small passerine bird belonging to the Passeridae family. It is primarily found in the arid and semi-arid regions of the Middle East, especially around the Dead Sea, which gives it its English name. This sparrow is characterized by its gray and brown plumage, with lighter shades on the belly. Males have a gray cap and a black throat, while females are duller. They often live in colonies and are known for their melodious song. Their diet mainly consists of seeds and insects. Although relatively common in their range, their habitat is threatened by environmental degradation.
The Desert Sparrow, Passer simplex, is a small, sturdy bird primarily inhabiting the arid regions of the Sahara and the Arabian Peninsula. Its plumage is generally pale, with shades of beige and gray, allowing it to blend into its desert surroundings. Males have a gray cap and a black throat, while females are more uniform and discreet. Adapted to life in extreme conditions, this sparrow feeds mainly on seeds and insects found in the sparse vegetation of oases. It is often seen in small groups, foraging or resting in the shade to escape the intense heat.
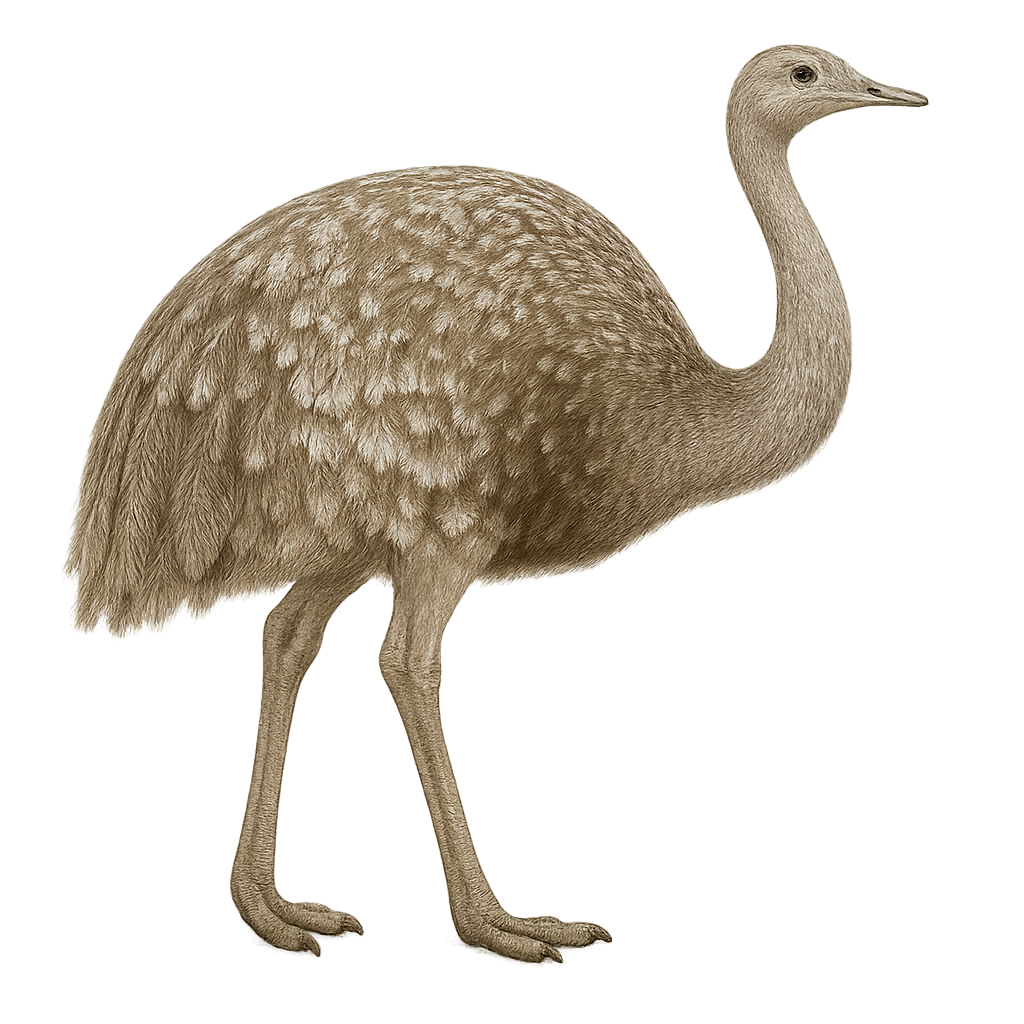
The Pterocnemia pennata, commonly known as Darwin's rhea, is a large, flightless bird native to the arid and semi-arid regions of South America. It is characterized by its grey-brown plumage and long legs adapted for fast running. Often mistaken for an ostrich, it is smaller in size. Darwin's rheas live in groups and primarily feed on plants, seeds, and insects. They are known for their complex social behavior, especially during the breeding season when males build nests and incubate eggs. Although they can cover large distances, their habitat is threatened by agricultural expansion and hunting.
The Dark Newtonia, or Newtonia amphichroa, is an endemic bird of Madagascar, belonging to the Vangidae family. This modest-sized bird is primarily recognizable by its dark throat, contrasting with its brownish plumage. It mainly inhabits the island's humid forests, where it feeds on insects and other small invertebrates. The Dark Newtonia is a discreet bird, often difficult to observe due to its suspicious behavior and dense habitat. Although its conservation status is not alarming, deforestation poses a potential threat to its populations. Its reproductive biology remains poorly documented but is assumed to be similar to other Newtonia species.
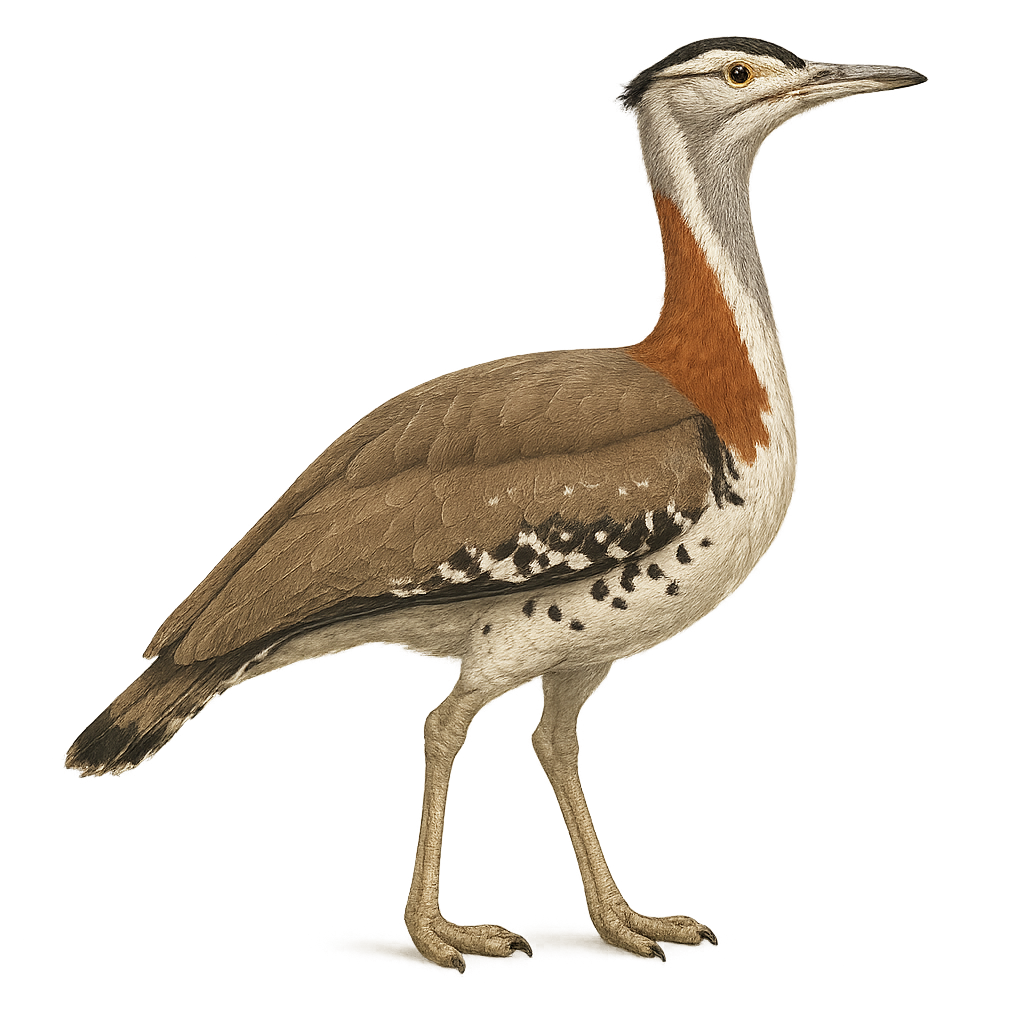
The Denham's Bustard, or Neotis denhami, is a large terrestrial bird found mainly in sub-Saharan Africa. It is recognizable by its brown and white plumage, with distinctive patterns on the wings and back. Males are generally larger than females and sport a black crest on their heads. This bird prefers open savannas and grasslands, where it primarily feeds on insects, small vertebrates, and seeds. Although generally solitary, it can be observed in small groups during the breeding season. The species is threatened by habitat loss and hunting, leading to population declines in some areas.
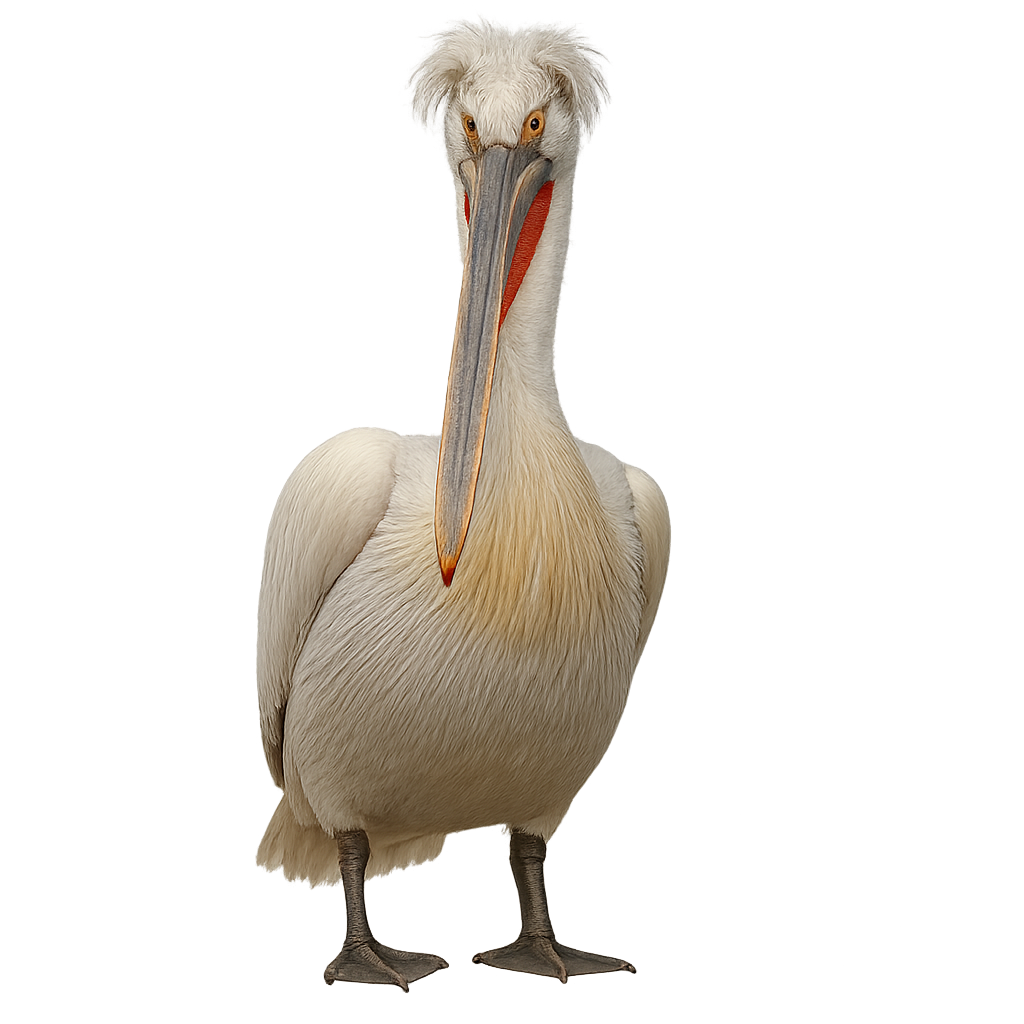
The Dalmatian Pelican is a large aquatic bird primarily found in Eastern Europe, the Middle East, and parts of Asia. It measures about 1.5 to 1.8 meters in length, with a wingspan of 2.3 to 2.5 meters, and weighs between 7 and 15 kg. What distinguishes the Dalmatian Pelican is its white plumage, sometimes tinged with yellow or pink, as well as its distinctive crest and long curved bill. It also has a pouch under its bill that allows it to capture fish. The Dalmatian Pelican primarily feeds on fish, which it catches by diving into the water or filtering with its bill. It is typically found near lakes, rivers, and wetlands. While the population of the Dalmatian Pelican is stable in some regions, it is still threatened by habitat loss, water pollution, and human disturbance.
The Duida Flowerpiercer is a small bird endemic to the mountainous regions of Venezuela, particularly around Mount Duida. It is characterized by its slender, curved bill, perfect for piercing flowers to access nectar, although its diet also includes insects. Its plumage is primarily blue-gray with darker shades on the wings and tail. This bird is often seen darting between shrubs and trees in search of food. It is known for its melodious song and distinctive calls that echo through the cloud forests.
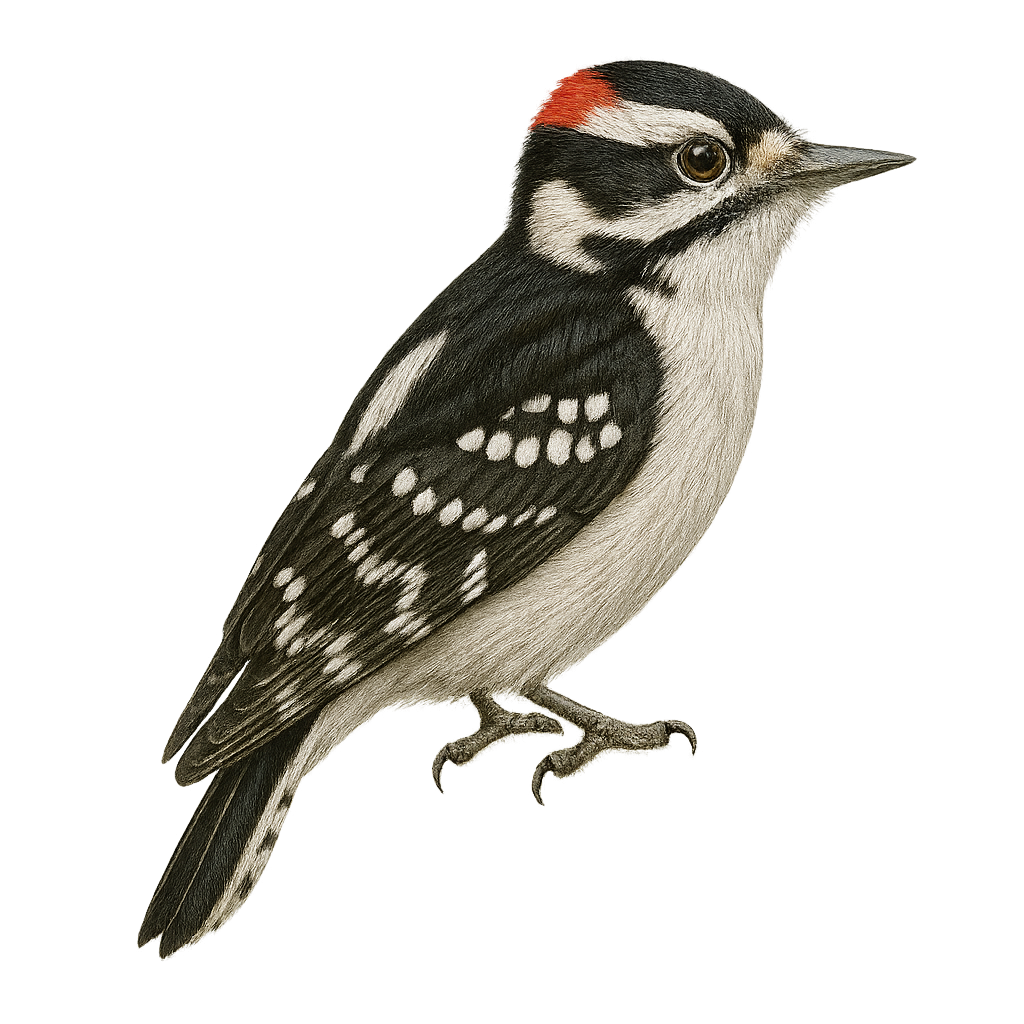
The Downy Woodpecker, Dryobates pubescens, is a small woodpecker native to North America. It is easily identified by its black and white plumage and small size, measuring about 14 to 17 cm in length. The male has a small red patch on the back of its head, which is absent in females. This woodpecker is often found in deciduous and mixed forests but also adapts to urban parks and gardens. It primarily feeds on insects, which it extracts by drumming on tree bark, but it also consumes seeds and berries. Its rapid and repeated drumming serves as a means of communication and territorial marking.
The Diademed Sandpiper-Plover, or Phegornis mitchellii, is a rare and fascinating bird of the Andes, known for its subtle beauty and unique habitat. This small bird, measuring about 16 cm in length, features a grey-brown plumage with a distinctive white band on the forehead and a rufous chest. It primarily inhabits high-altitude wetlands, often above 3000 meters, where it feeds on insects and small invertebrates. Its behavior is generally suspicious, making it difficult to observe. The breeding season is closely linked to the rainy seasons, as food resources become more abundant. Although its conservation status is concerning, efforts are underway to protect its fragile habitat.
The Eurasian Dotterel is a migratory bird primarily found in tundra areas and alpine meadows of Europe, Central Asia, and northern China. It measures about 25 cm in length, with a wingspan of 55 to 60 cm, and weighs between 100 and 150 g. Its plumage is primarily brown, with lighter underparts and white spots on the wings. It has a brown head with distinctive black patterns around the eyes and on the throat. During the breeding season, males display brighter plumage. The Eurasian Dotterel primarily feeds on small insects, worms, and seeds found on bare soils or in grassy areas. While its population remains relatively stable, this species can be threatened by habitat loss, particularly due to climate change and disturbances at its breeding sites.
The Dwarf Fruit Dove, or Ptilinopus nainus, is a small, colorful bird belonging to the Columbidae family. It is primarily found in the lowland tropical rainforests of New Guinea and some surrounding islands. This fruit dove is recognizable by its bright green plumage, often speckled with yellow and red hues, allowing it to blend effectively among the foliage. It primarily feeds on fruits, playing a crucial role in seed dispersal. Although discreet, the Dwarf Fruit Dove is a sociable bird, often seen in small groups. Its small size and shy behavior make it a challenge for birdwatchers to spot.
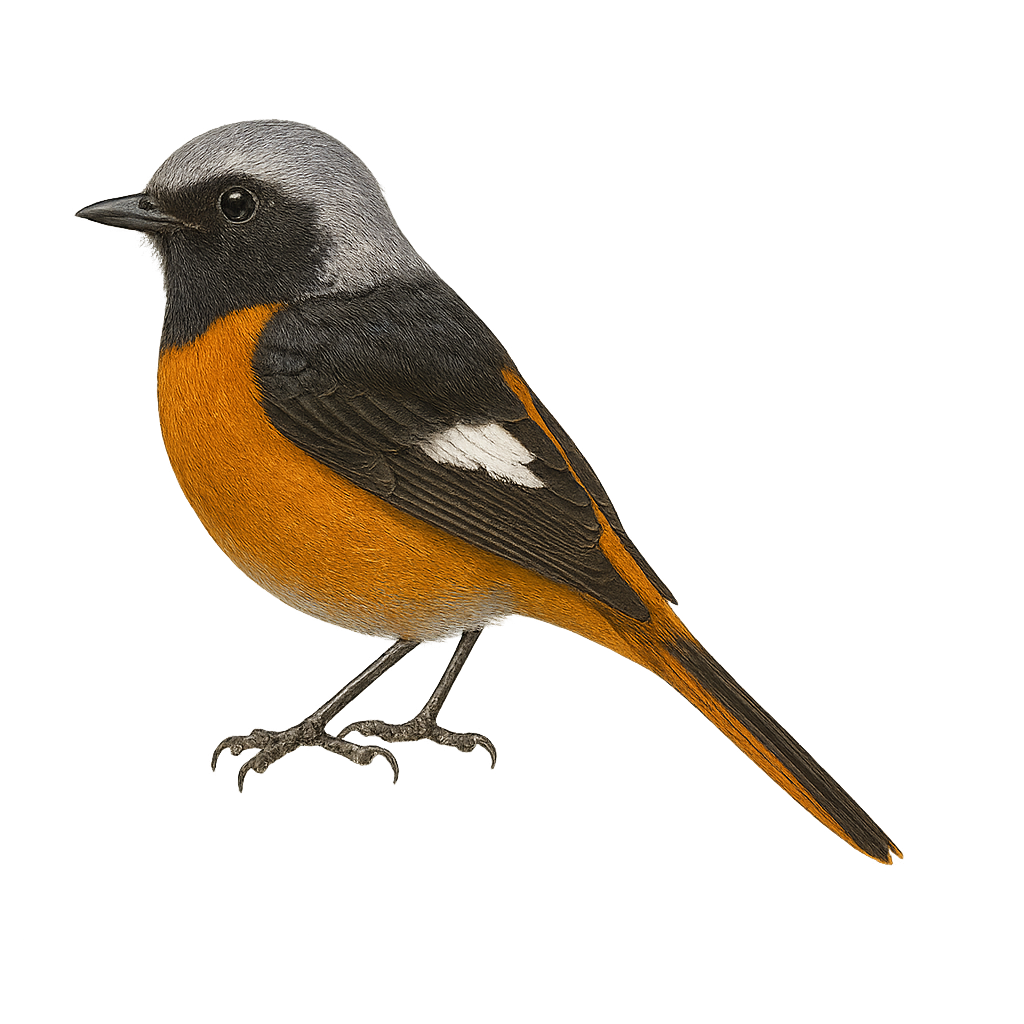
The Daurian Redstart, or Phoenicurus auroreus, is a small passerine bird belonging to the Muscicapidae family. It is easily identifiable by its distinctive plumage: the male sports a black head with a white forehead patch, a gray back, and a bright orange chest, while the female displays more subdued shades of brown and orange. This small bird is often seen in forests, parks, and gardens across East Asia, particularly in China, Korea, and Japan. Known for its melodious song, it adapts well to various habitats, including urban areas. As a partial migrant, it moves southward during winter months to escape cold temperatures.
The Double-collared Seedeater is a small passerine bird belonging to the Thraupidae family. It is primarily found in South America, particularly in Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay, and Uruguay. Its plumage is generally gray with lighter shades on the belly and a darker cap. Males and females exhibit sexual dimorphism, with males often displaying brighter colors. This bird inhabits various environments, from open forests to agricultural areas and urban gardens. It primarily feeds on seeds but can also consume insects. The Double-collared Seedeater is known for its melodious song and its ability to adapt to different environments.
The Dusky-cheeked Puffbird, or Malacoptila fusca, is a discreet bird found in the tropical forests of South America. It is characterized by its dark brown plumage, with lighter shades on the belly and a slightly darker head. This bird measures about 18 to 20 cm in length and has a robust beak, well-suited for its diet mainly consisting of insects and small fruits. It is often seen alone or in pairs, perched motionless on a low branch, watching for prey. Its song is soft and melodious, often heard at dawn or dusk. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it remains relatively common in some areas.
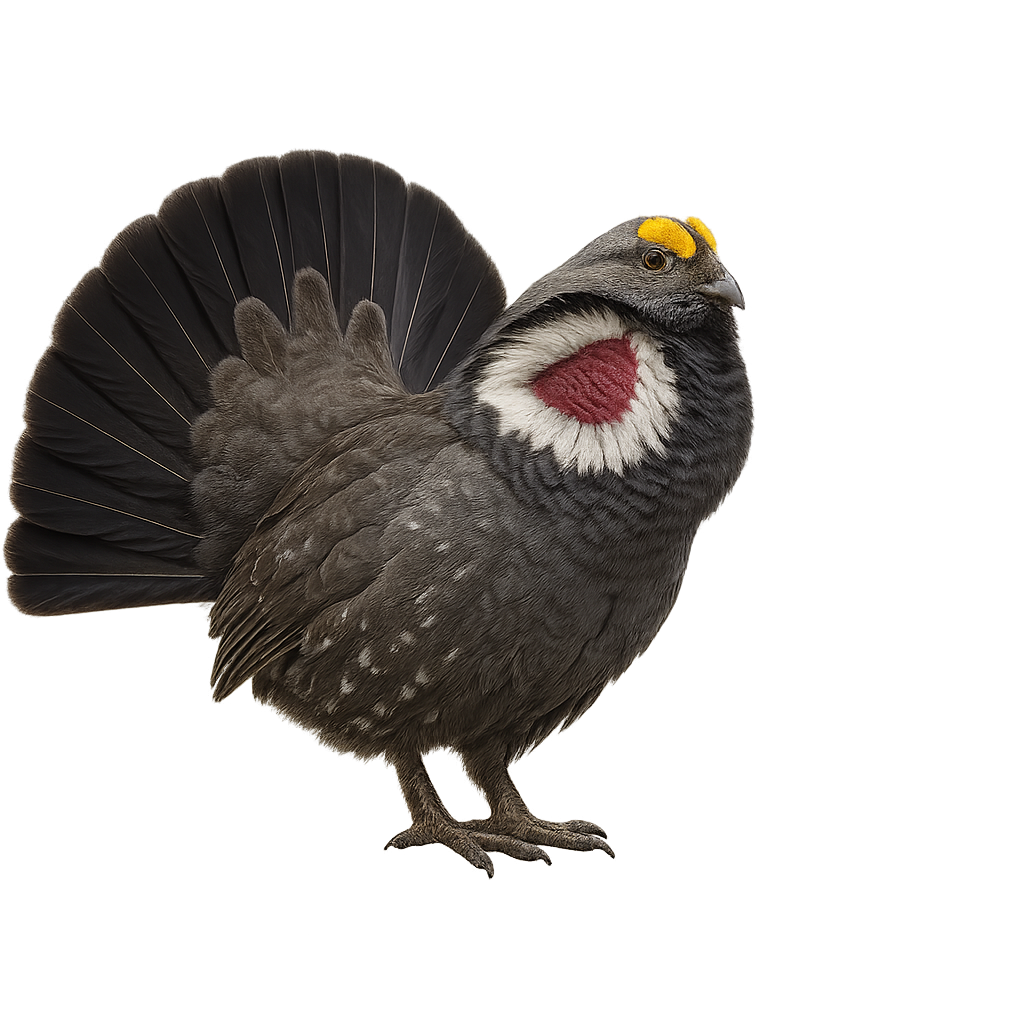
The Dusky Grouse, or Dendragapus obscurus, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Phasianidae family, primarily found in the mountainous regions of western North America. This bird is characterized by its dark gray, almost black plumage, and white markings on its wings. Males display a fan-shaped tail and a yellow vocal sac that inflates during the breeding season to attract females. The Dusky Grouse prefers forested habitats, particularly coniferous forests and shrublands. It mainly feeds on leaves, buds, and insects. Although generally discreet, it can be observed during its spectacular courtship displays.
The Drab-breasted Pygmy-Tyrant is a small passerine bird from the Tyrannidae family, primarily found in the humid forests and forest edges of South America. It is characterized by its dull plumage, with shades of brown and gray, and its small size, measuring about 9 to 10 cm in length. This bird is often difficult to spot due to its discreet and elusive behavior. It feeds mainly on insects, which it catches in flight or on leaves. The Drab-breasted Pygmy-Tyrant is a sedentary bird, not very migratory, preferring dense habitats where it can easily hide. Its population is stable, although deforestation may pose a potential threat to its natural habitat.