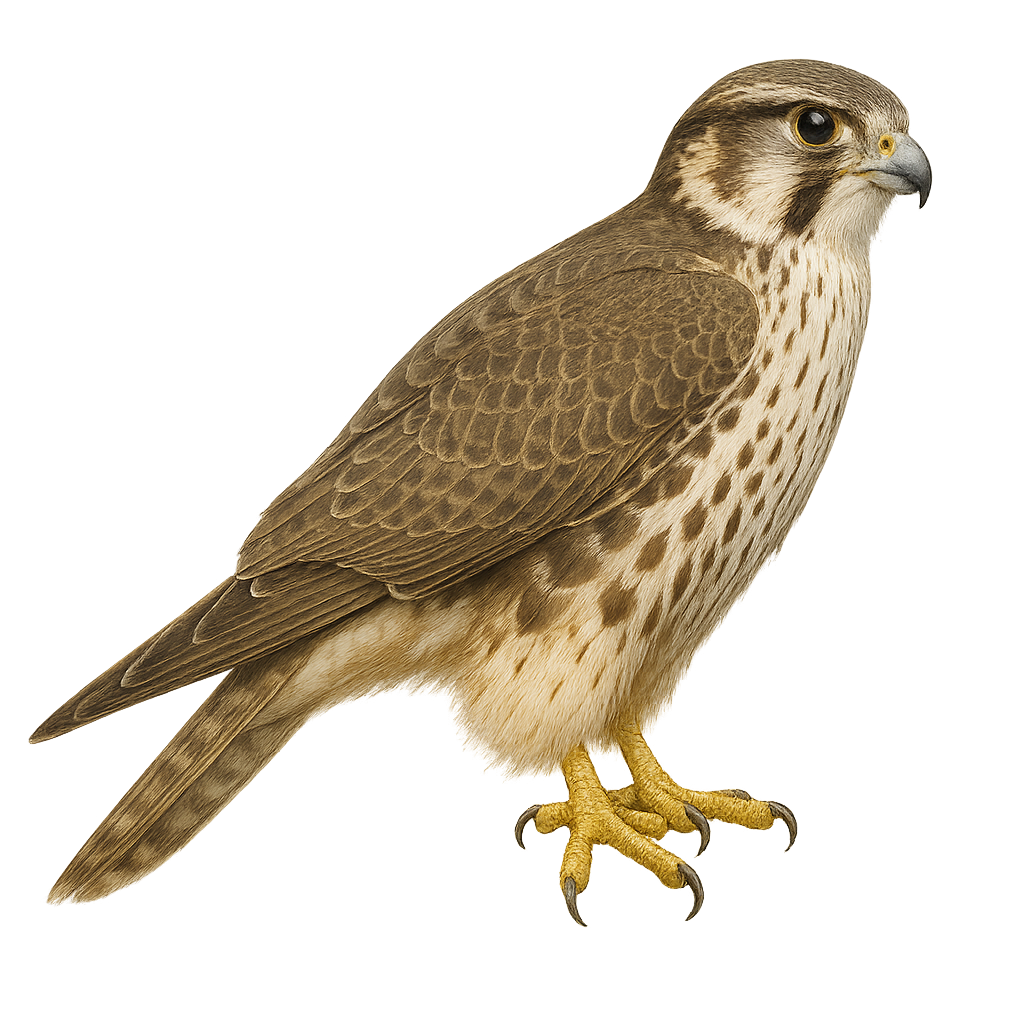
The Prairie Falcon, or Falco mexicanus, is a medium-sized raptor native to the arid and semi-arid regions of North America. This falcon is identifiable by its light brown plumage, long pointed wings, and narrow tail. It primarily feeds on small mammals and birds, hunting them with swift and agile flight. The Prairie Falcon is a solitary bird, except during the breeding season when it forms monogamous pairs. It often nests on cliffs or artificial structures, using cavities or ledges for its nest. Although its habitat is threatened by human expansion, it is currently classified as of least concern by the IUCN.
The Peregrine Falcon is a medium-sized raptor, known for its impressive speed and exceptional hunting abilities. It measures between 40 and 50 cm in length, with a wingspan of 100 to 120 cm, and weighs between 600 and 1,000 g. Its plumage is typically blue-gray on the back, with a lighter belly and black markings on the head and wings. The Peregrine Falcon is especially famous for its stooping hunting technique, where it can reach speeds exceeding 300 km/h, making it the fastest animal in the world. It primarily feeds on birds, which it catches in flight, but can also hunt small mammals. The Peregrine Falcon lives in a variety of habitats, including cliffs, urban buildings, and coastal areas. It is a widely distributed species, found on every continent except Antarctica. Although it was once threatened by hunting and pesticides, it has now made a recovery thanks to conservation efforts, including the release of young birds and habitat protection programs.
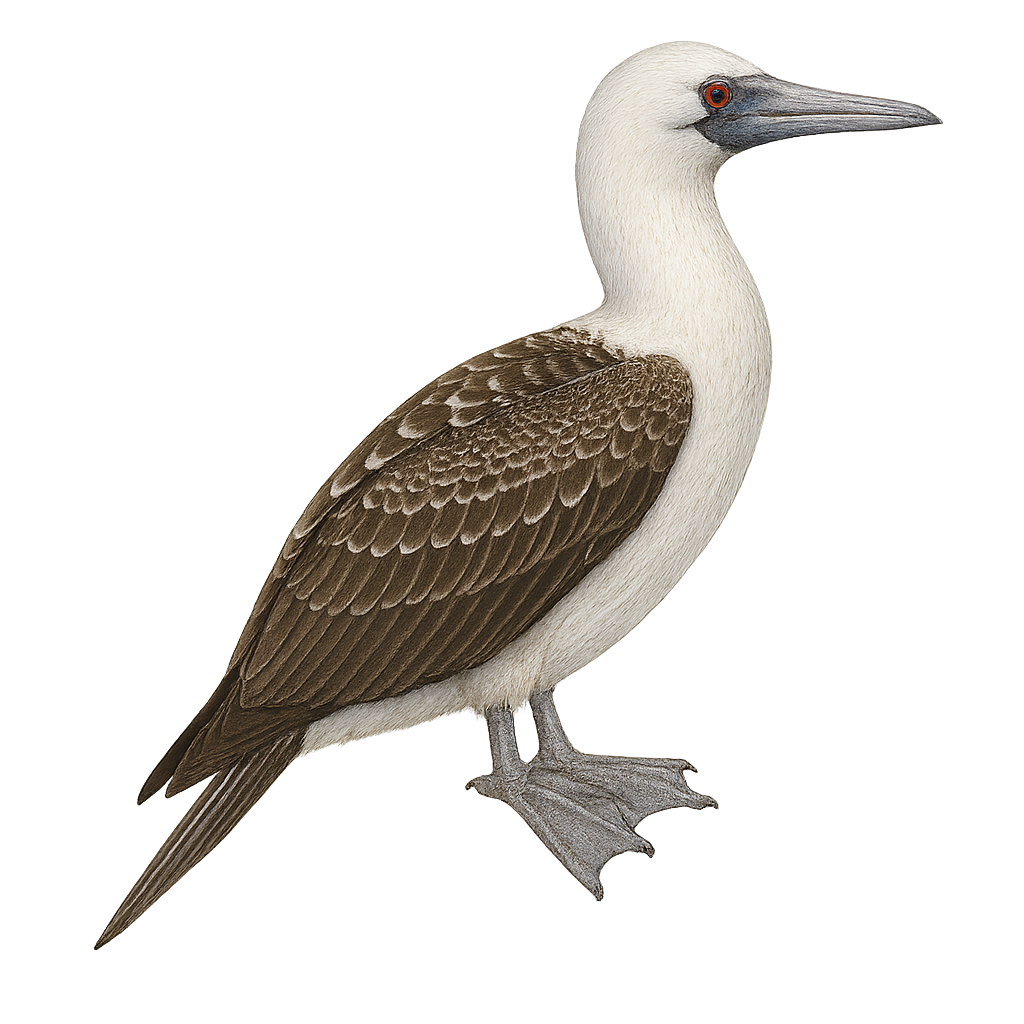
The Peruvian Booby, or Sula variegata, is a medium-sized seabird primarily found along the coasts of Peru and Chile. It is characterized by its striking black and white plumage, pale blue bill, and gray feet. This bird is an exceptional diver, capable of plunging to impressive depths to catch fish and cephalopods, its main food source. Peruvian Boobies nest in large colonies on islands and coastal cliffs, where they build rudimentary nests on the ground. Their breeding period is closely linked to food availability, influenced by the Humboldt Current. Although their population is currently stable, they remain vulnerable to environmental changes and overfishing.
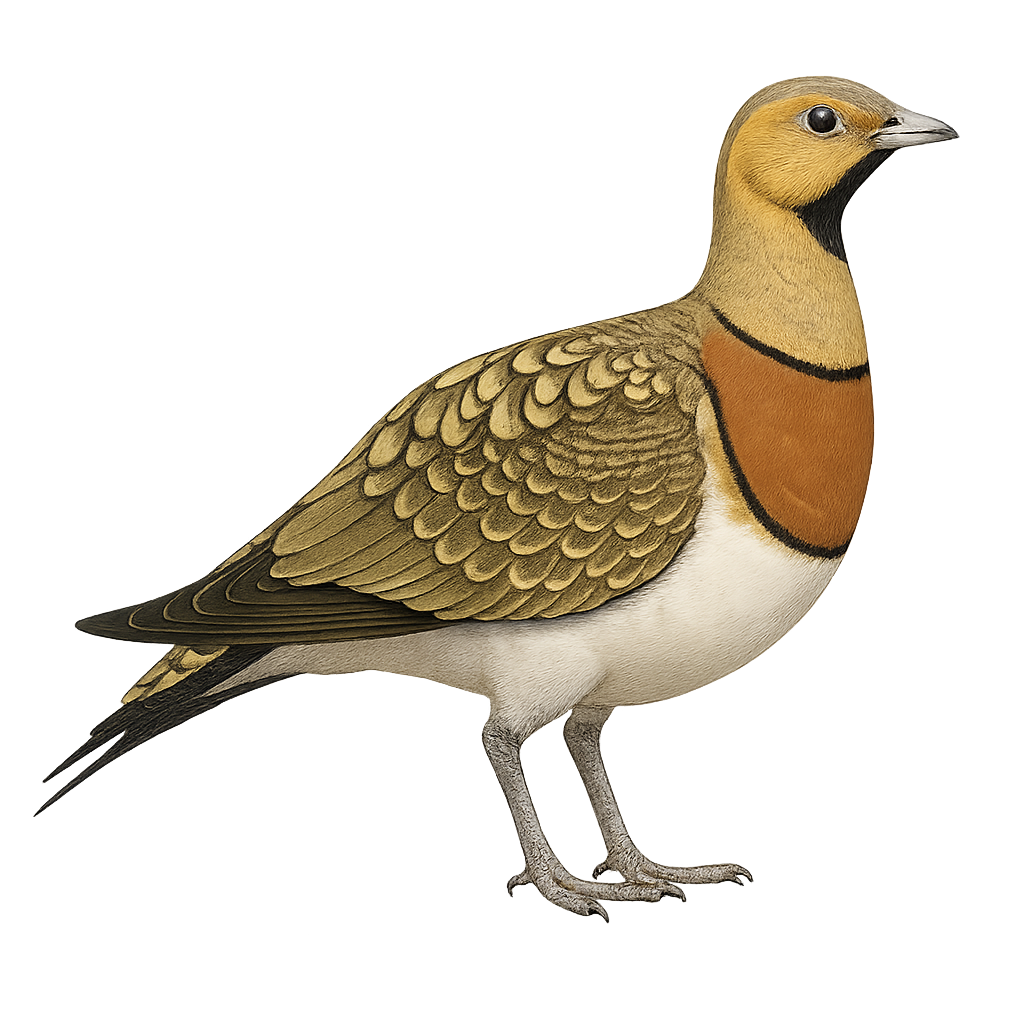
The Pin-tailed Sandgrouse, or Pterocles alchata, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Pteroclidae family. It is recognizable by its cryptic plumage, which allows it to blend into its desert environment. Males have more colorful plumage with distinctive patterns on the chest and wings, while females are duller. This bird is primarily granivorous, feeding on seeds found in arid and semi-arid areas. It is often seen in small groups, especially near water sources where it comes to drink. The Pin-tailed Sandgrouse is a partial migrant, moving according to resource availability. It is known for its fast, direct flights, often at low altitudes.
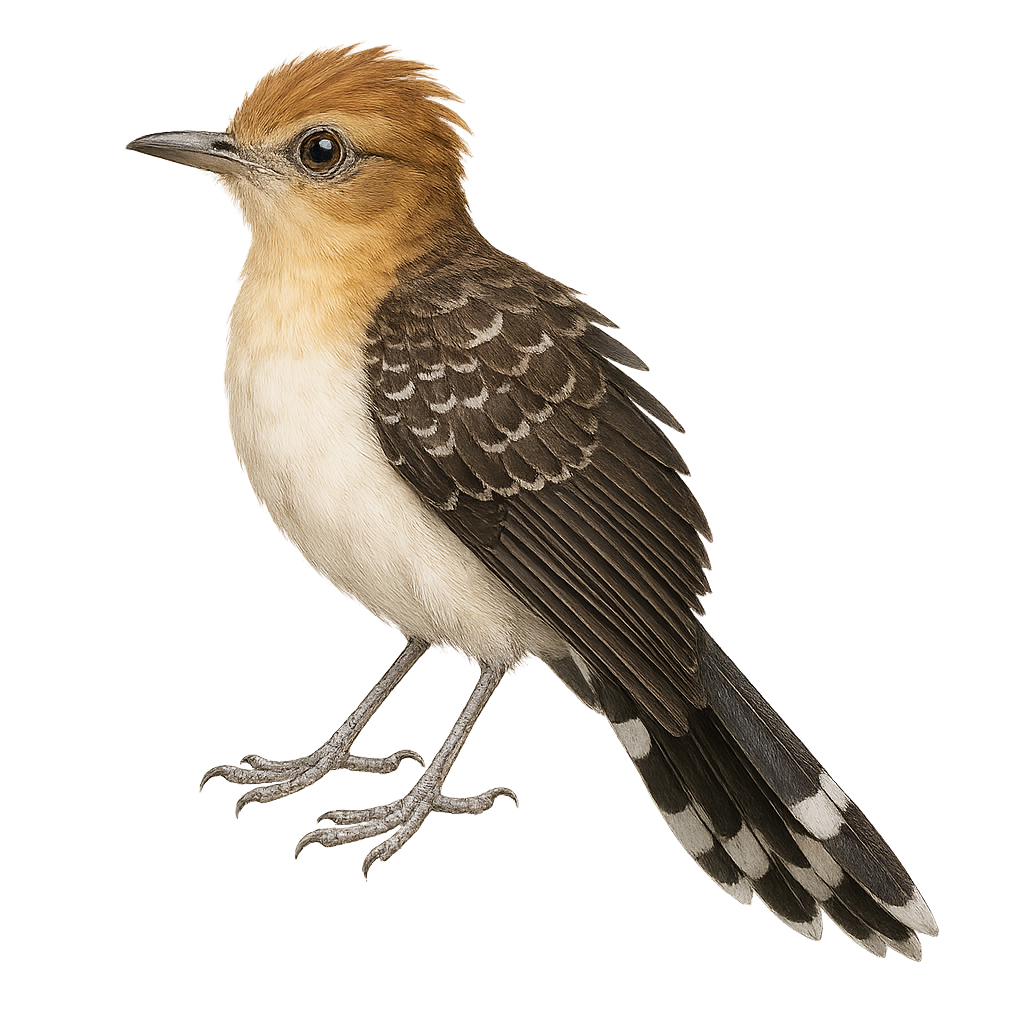
The Pavonine Cuckoo is a mysterious and fascinating bird belonging to the Cuculidae family. It is primarily found in the dense tropical forests of South America, notably in Brazil, Bolivia, and Paraguay. This bird is recognizable by its brown and black plumage, with distinctive patterns reminiscent of peacock feathers, hence its name. The Pavonine Cuckoo is a discreet bird, often heard rather than seen, thanks to its melodious and repetitive song. It is known for its brood parasitism behavior, laying its eggs in the nests of other bird species. Although its conservation status is currently assessed as "least concern," deforestation continues to threaten its natural habitat.
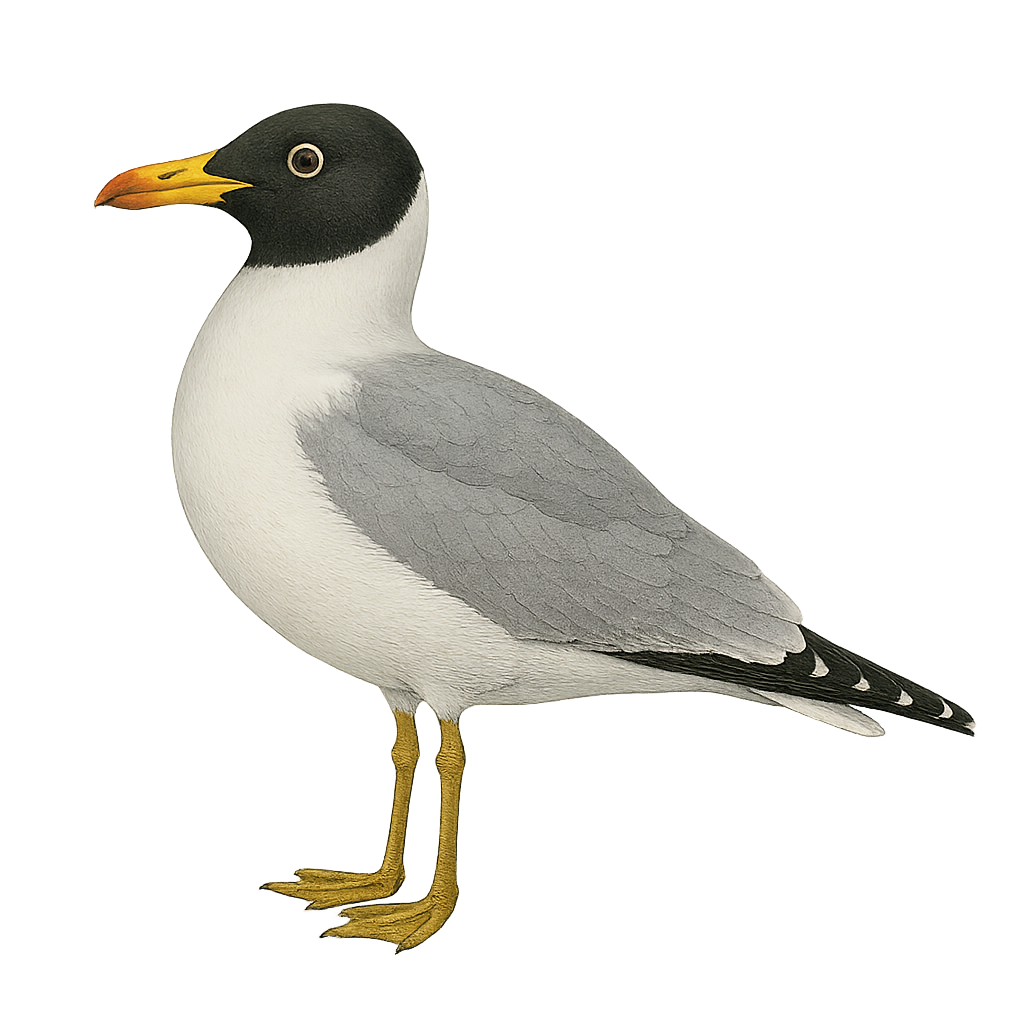
The Pallas's Gull is a large seabird, easily identifiable by its distinctive black head and bright yellow bill. It primarily inhabits the lakes and rivers of Central Asia but migrates to the southern coasts of Asia and the Middle East during winter. Its plumage is mostly white with grey wings and black wingtips. It feeds mainly on fish but also consumes crustaceans and small mammals. Its call is harsh and loud, often heard when defending its territory. The Pallas's Gull nests in colonies on islands or sandbanks, typically laying two to three eggs.
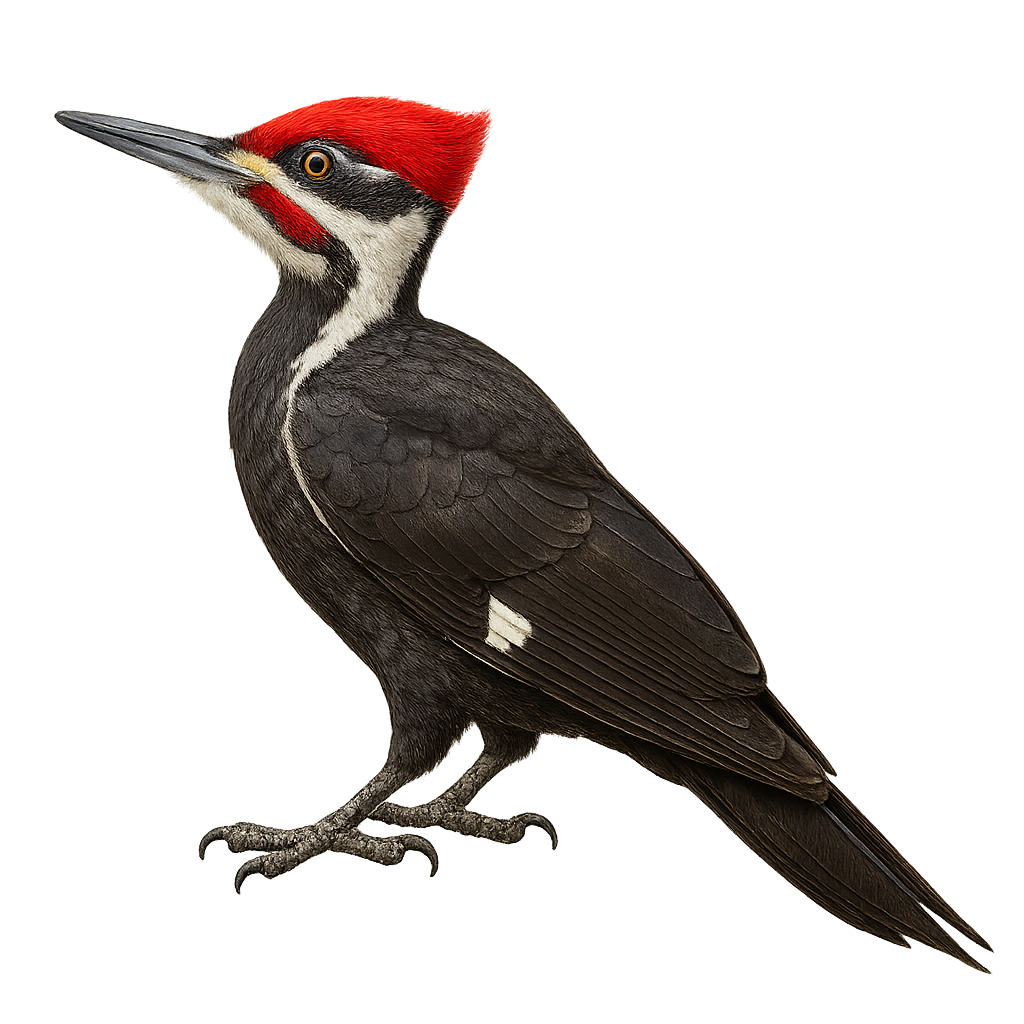
The Pileated Woodpecker is a striking bird, notable for its size and distinctive plumage. It is one of the largest woodpeckers in North America, measuring between 40 and 49 cm in length with a wingspan of up to 75 cm. Its plumage is predominantly black with a bright red crest on its head, more pronounced in males. The wings have white patches visible in flight. This forest bird is often found in coniferous and deciduous forests. Known for its powerful drumming on tree trunks, it uses this to communicate and mark its territory. It primarily feeds on ants and insect larvae, which it extracts from dead wood with its long bill.
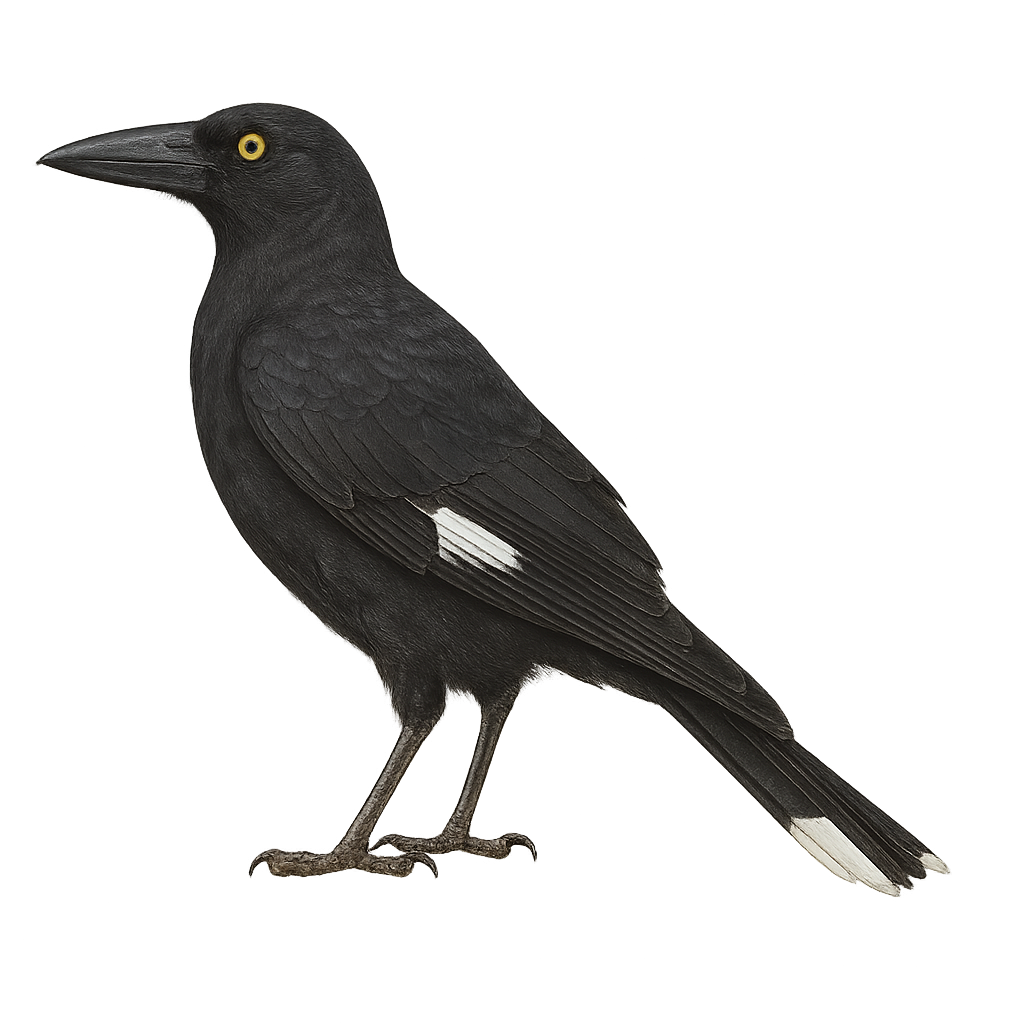
The Pied Currawong, scientifically known as Strepera graculina, is a bird native to Australia, easily identified by its glossy black plumage and striking yellow eyes. It measures about 48 to 50 cm in length and has a strong, slightly hooked beak. This bird is often found in rainforests, open woodlands, and occasionally in urban parks. It is renowned for its melodious and varied song, which can include whistles, calls, and mimicry of other birds. As an opportunistic feeder, it primarily consumes fruits, insects, and small animals. The Pied Currawong is a social bird, often seen in small groups or pairs, especially during the breeding season.
The Pied-billed Grebe, scientifically known as Podilymbus podiceps, is a small water bird easily identified by its thick, black-banded bill. It inhabits ponds, lakes, and marshes across North and South America. Adapted to aquatic life, its legs are positioned towards the rear of its body, making it clumsy on land but highly agile in water. It primarily feeds on fish, aquatic insects, and crustaceans. During the breeding season, it constructs a floating nest from aquatic vegetation. Adults are often solitary or found in small groups, and their brownish plumage helps them blend into their surroundings.
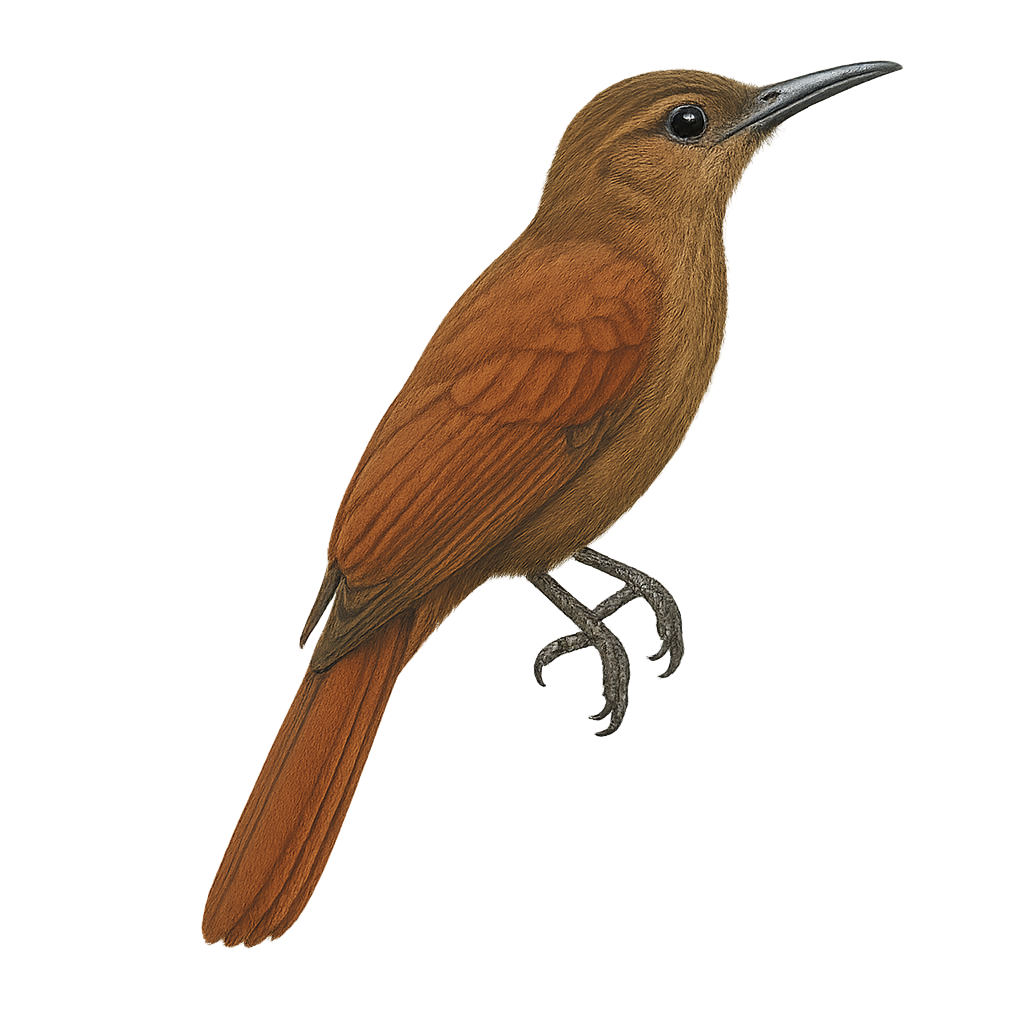
The Plain-brown Woodcreeper, scientifically known as Dendrocincla fuliginosa, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Furnariidae family. It is primarily found in the humid tropical forests of Central and South America, where it is recognized by its uniform brown plumage and slender silhouette. This bird is often seen climbing tree trunks, using its slightly curved beak to search for insects and other small invertebrates hidden under the bark. Although discreet, its melodious song can be heard through the dense canopy. The Plain-brown Woodcreeper plays an essential role in the forest ecosystem by helping control populations of harmful insects.
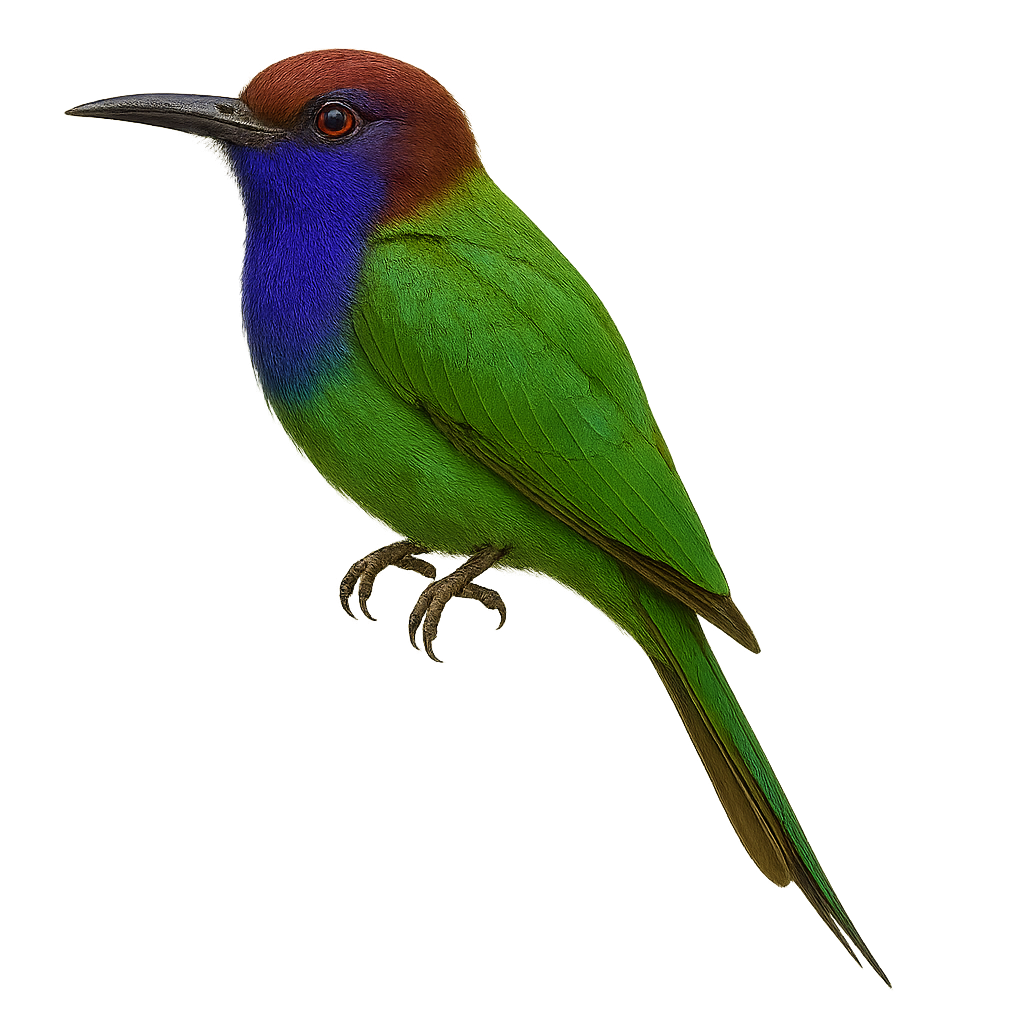
The Purple-bearded Bee-eater is a colorful and fascinating bird endemic to the forests of Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is distinguished by its purple beard and bright green plumage, which allow it to blend into the dense canopy. This bird measures about 25 cm in length and primarily feeds on insects, especially bees and wasps, which it catches in flight with its slender, elongated beak. The Purple-bearded Bee-eater is a sociable bird, often seen in small groups. It prefers humid forest habitats and wooded areas at mid-altitude. Although its conservation status is concerning due to deforestation, it remains relatively common in some protected areas.
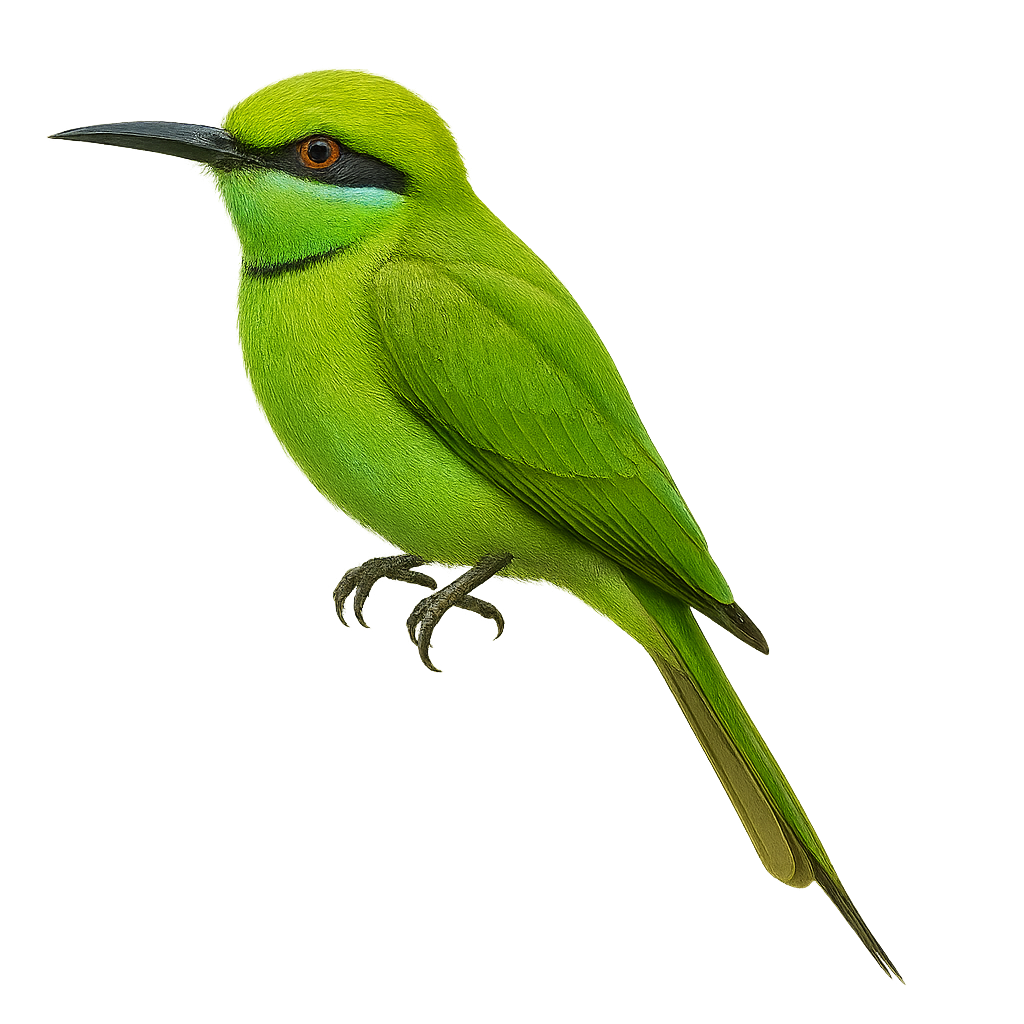
The Persian Green Bee-eater, Merops viridissimus, is a colorful and graceful bird, primarily green with shades of blue and yellow. Known for its long central tail feathers and curved beak, it is adept at catching insects mid-flight. This bee-eater inhabits mainly arid and semi-arid regions, favoring open areas with sparse trees. Often seen in small groups, it perches on exposed branches. Its flight is agile and swift, allowing it to catch prey in mid-air. The Persian Green Bee-eater is also noted for its melodious calls, often heard during its flights.
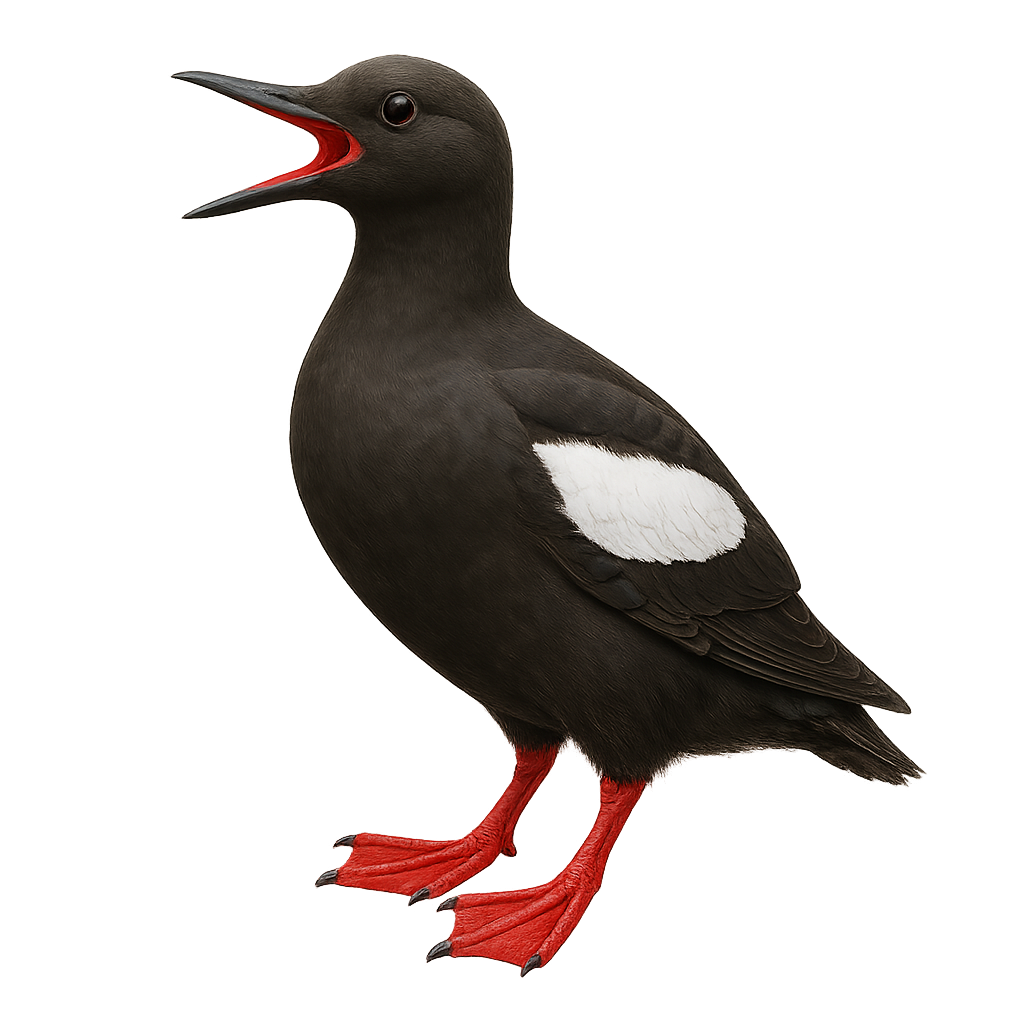
The Pigeon Guillemot, Cepphus columba, is a medium-sized seabird belonging to the Alcidae family. It is primarily black with distinctive white wing patches and red legs. Its slender, pointed bill is adapted for catching small fish and marine invertebrates. Found mainly along the rocky coasts of the North Pacific, from Alaska to California, it is known for its impressive diving abilities, reaching significant depths to hunt its prey. During the breeding season, it nests in rocky crevices, often in scattered colonies. The Pigeon Guillemot is a resilient bird, well-adapted to its marine environment, but remains sensitive to human disturbances and environmental changes.
The Purple Honeycreeper is a small tropical bird with vibrant plumage, primarily blue with shades of violet, and black wings. Males have a curved black bill, while females display a more subdued green plumage. This bird inhabits the humid forests of Central and South America, feeding mainly on nectar, fruits, and insects. Its behavior is generally active and sociable, often seen in small groups. It plays a crucial role in the pollination of tropical plants. Although not currently threatened, deforestation poses a potential risk to its natural habitat.
The Purple Heron, or Ardea coromanda, is a large, slender wading bird distinguished by its rich reddish-brown plumage and long neck. It inhabits rice fields, swamps, wooded wetlands, and lake edges across East and Southeast Asia. This heron is partially migratory, with seasonal movements depending on climate conditions. Typically solitary, it hunts slowly in shallow waters, feeding mainly on fish, amphibians, and aquatic invertebrates. The population is considered stable overall, although local declines may occur due to wetland loss.
The Purple Heron is a large wading bird, easily recognizable by its colorful plumage, ranging from purple to reddish, with shades of brown and blue. It measures about 80 to 100 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.3 to 1.5 meters, and weighs between 600 and 1,200 g. Its beak is long, thin, and pointed, with a yellowish-green color, while its legs are long and gray. During the breeding season, the Purple Heron sports decorative plumes on its head and neck. It primarily inhabits wetlands, marshes, rivers, and lakes across Europe, Africa, and Asia, where it feeds on fish, crustaceans, small mammals, and occasionally insects. It primarily hunts at night or during twilight, using its great agility to capture prey in the water. Although the species is not immediately endangered, it is vulnerable to habitat loss, water pollution, and human disturbance.
The Purple Martin, or Progne subis, is a migratory bird belonging to the Hirundinidae family. It is recognizable by its glossy blue-black plumage in males, while females have duller tones with a grayish belly. This bird is the largest swallow in North America and is noted for its agile and graceful flight. It often nests in colonies in man-made birdhouses, making it dependent on humans for reproduction. Its diet consists mainly of insects caught in flight. As a migratory species, it winters in South America and returns to North America for the breeding season.
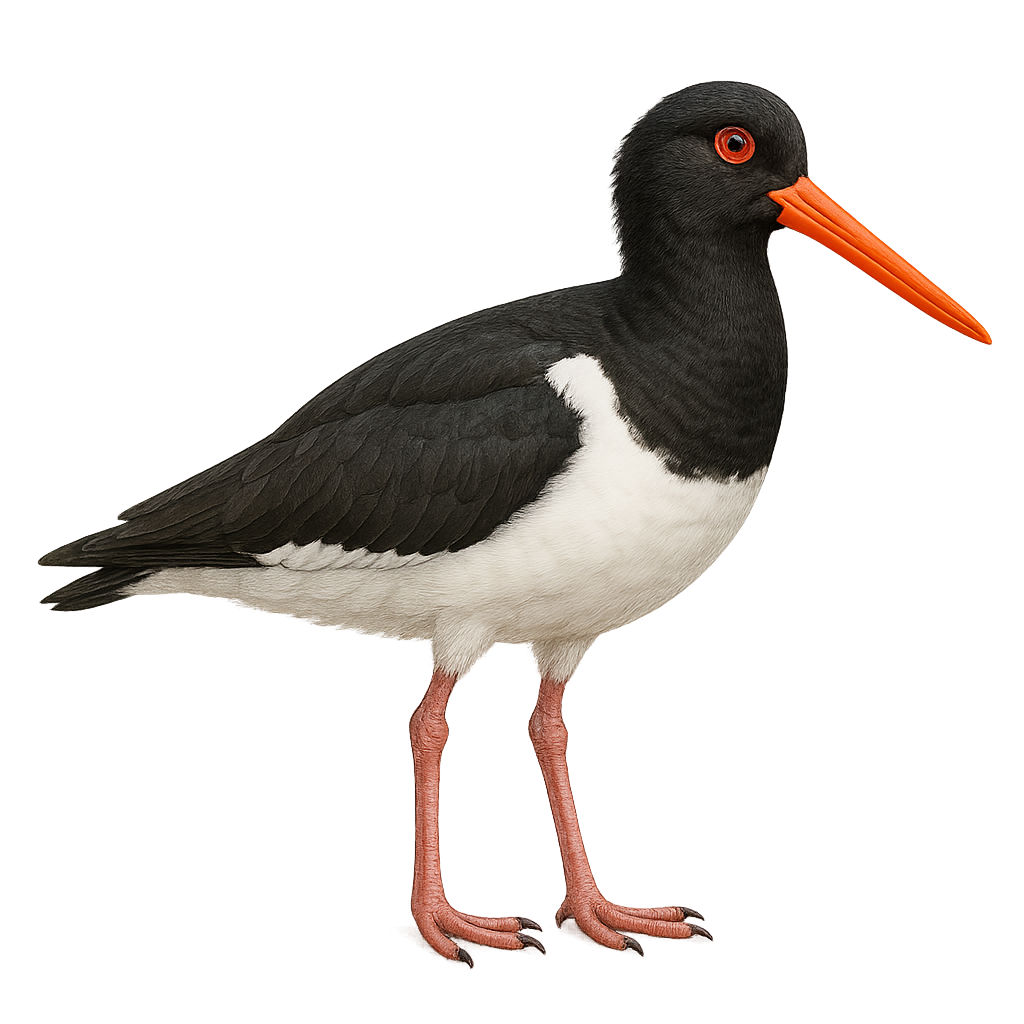
The Pied Oystercatcher is a medium-sized coastal bird, easily identifiable by its distinctive black and white plumage and long, bright red bill. It primarily inhabits the sandy and rocky shores of Australia, where it feeds mainly on mollusks, crustaceans, and other marine invertebrates. Its powerful bill allows it to skillfully open the shells of its prey. This bird is often seen in small groups, although it can also be solitary. It is known for its piercing calls and territorial behavior, especially during the breeding season. Pied Oystercatchers are monogamous and form lasting pairs. Their nest is usually a simple scrape in the sand or pebbles, where they lay two to three eggs.
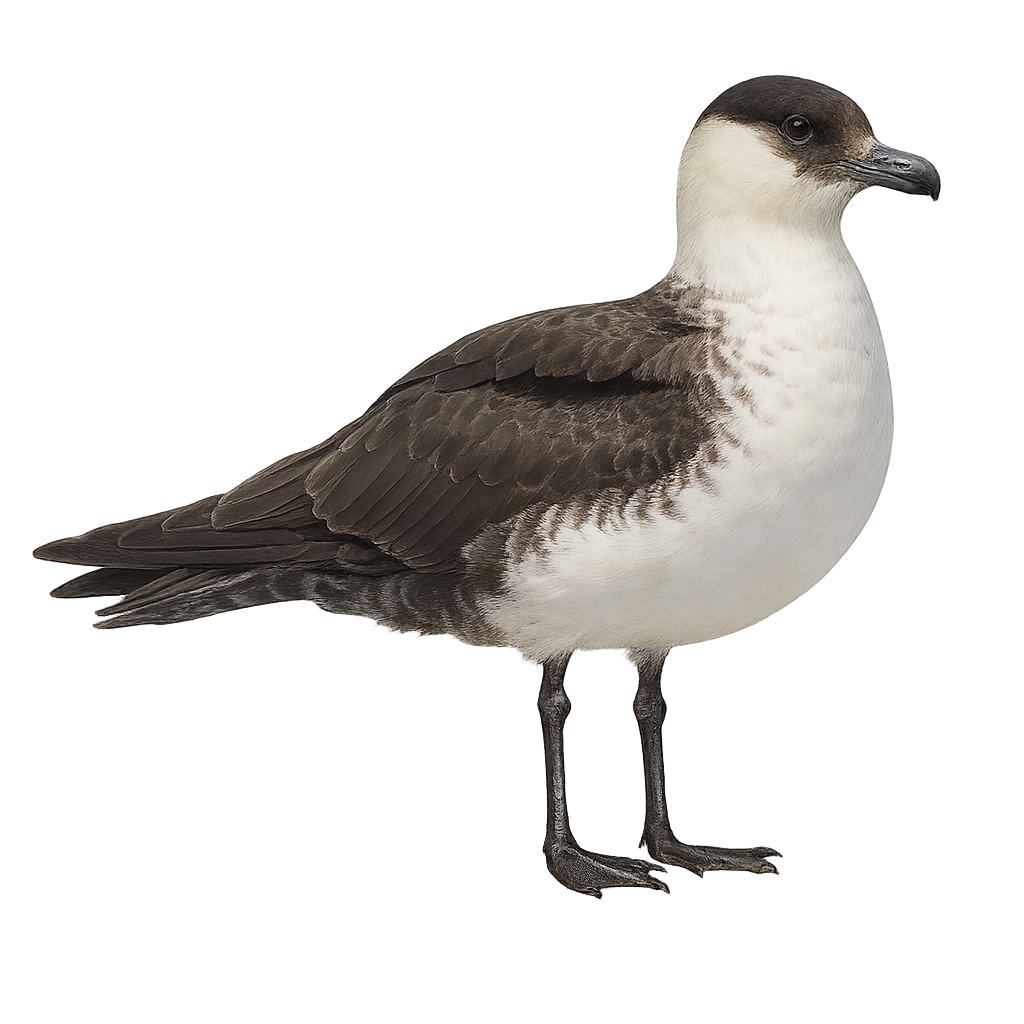
The Parasitic Jaeger, or Stercorarius parasiticus, is a medium-sized seabird, easily recognizable by its pointed wings and dark plumage. It measures about 45 to 50 cm in length, with a wingspan of 110 to 125 cm, and weighs between 300 and 450 g. Its plumage is typically dark brown or gray on the back, with a lighter belly. Adults have a distinctive feature: a forked tail with extended feathers, especially in males. The Parasitic Jaeger is a migratory bird that primarily inhabits the Arctic and subarctic regions but moves to more temperate zones during the winter. This bird is particularly known for its parasitic behavior, in which it chases other seabirds to force them to drop their catch, allowing the Jaeger to steal their food. The Parasitic Jaeger is also an excellent flyer, capable of traveling long distances. While the species is not endangered, it is sensitive to human disturbances and climate changes that affect its coastal habitat.
The Pomarine Jaeger is a medium-sized seabird known for its long, pointed wings and spatula-shaped tail. It has a dark brown plumage with lighter underparts and distinctive white wing markings. This agile predator is often seen chasing other birds to steal their food. It breeds mainly in Arctic regions and migrates to southern oceans in winter. Its preferred habitat includes coastal areas and open seas. The Pomarine Jaeger is an opportunistic bird, capable of adapting to various marine environments to survive.
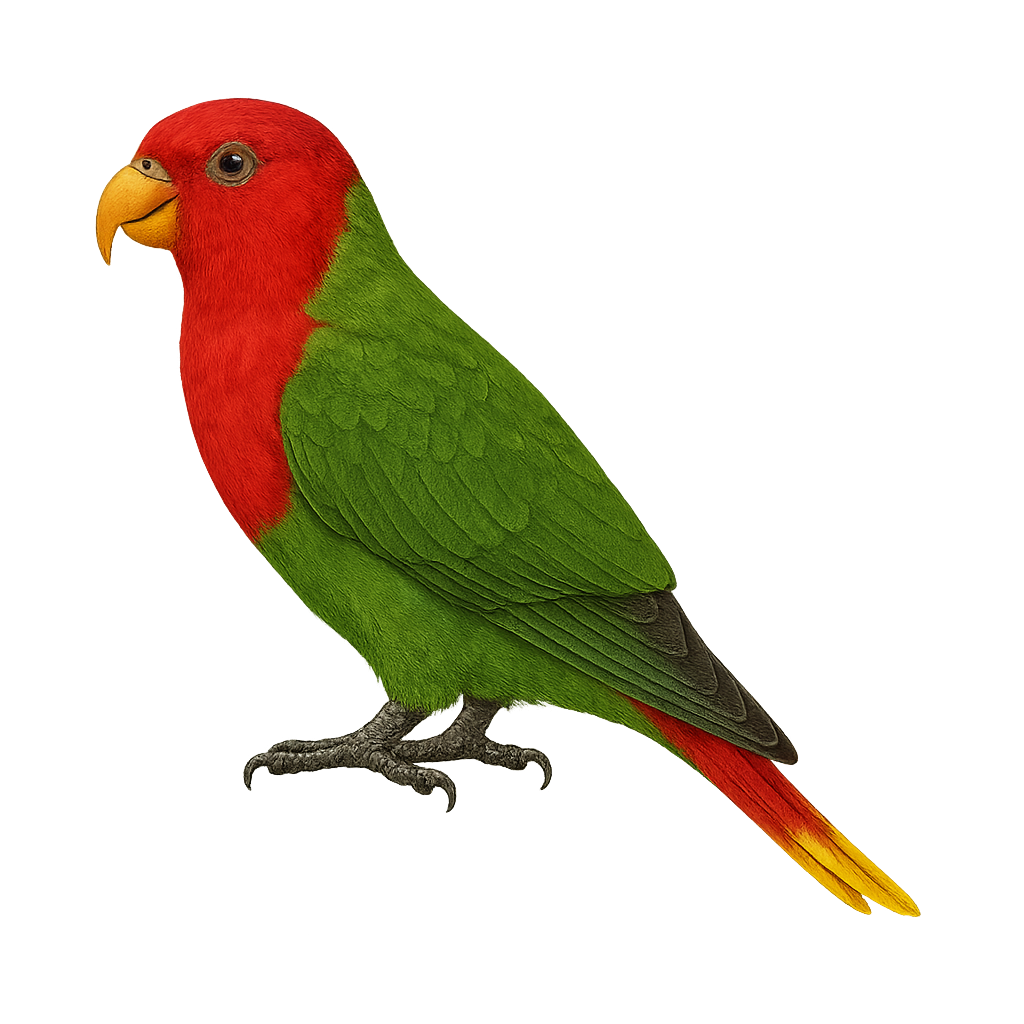
The Papuan Lorikeet, Charmosyna pulchella, is a small, colorful parrot native to New Guinea. This stunning bird features a vibrant plumage with shades of green, red, and blue, making it easily recognizable. It measures about 18 cm in length and is characterized by its tapered tail and pointed wings. The Papuan Lorikeet is a sociable bird, often seen in small groups, feeding primarily on nectar, pollen, and fruits. It inhabits tropical rainforests, forest edges, and occasionally gardens. Although relatively common in its natural habitat, preserving its environment is crucial for its long-term survival.
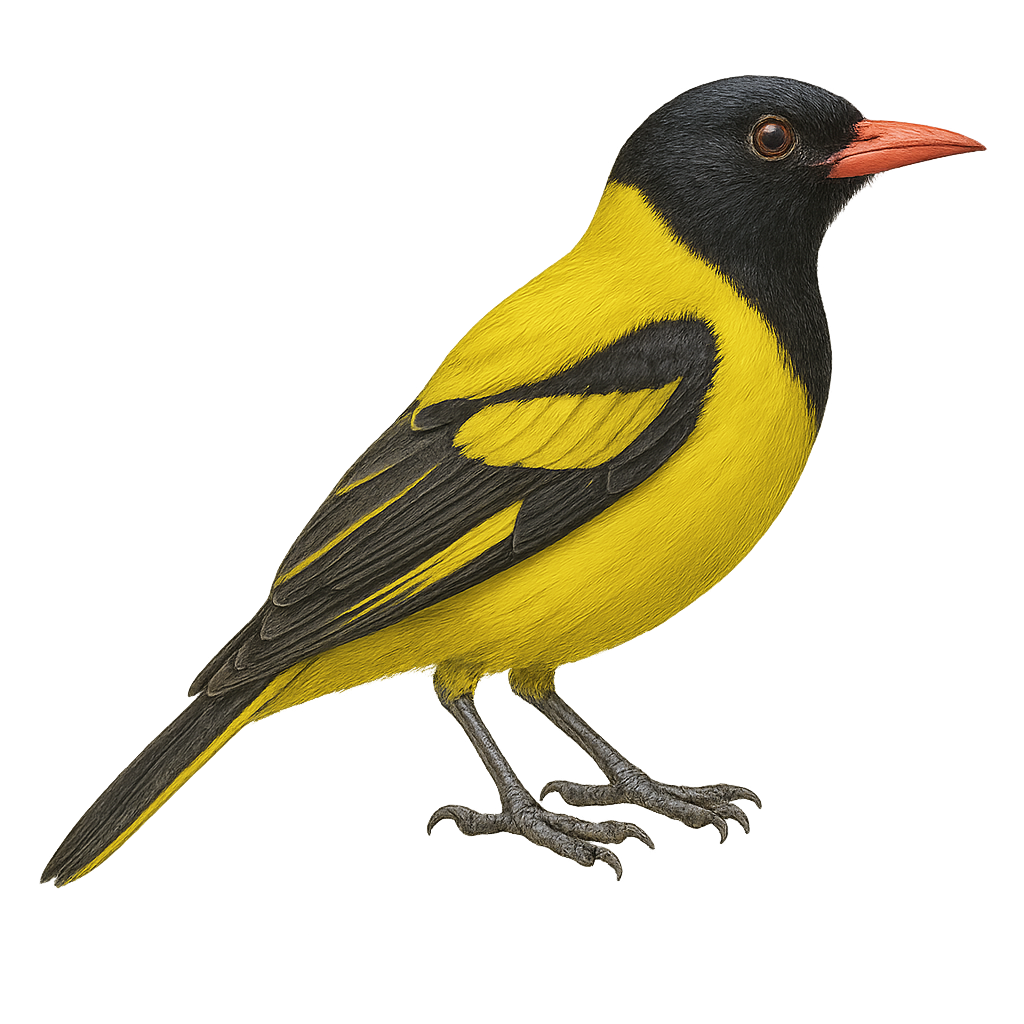
The Percival's Oriole is a fascinating bird primarily inhabiting the tropical and subtropical forests of East Africa. Recognizable by its striking plumage, it features a vibrant mix of colors, including shades of yellow, black, and sometimes green. This oriole is a medium-sized bird, measuring about 20 to 25 cm in length. It is known for its melodious and complex song, often heard at dawn. The Percival's Oriole is a sociable bird, often seen in small groups or pairs. It mainly feeds on insects, fruits, and nectar, playing a crucial role in the pollination of many plants. Although relatively common in its natural habitat, deforestation and habitat loss pose potential threats to its population.
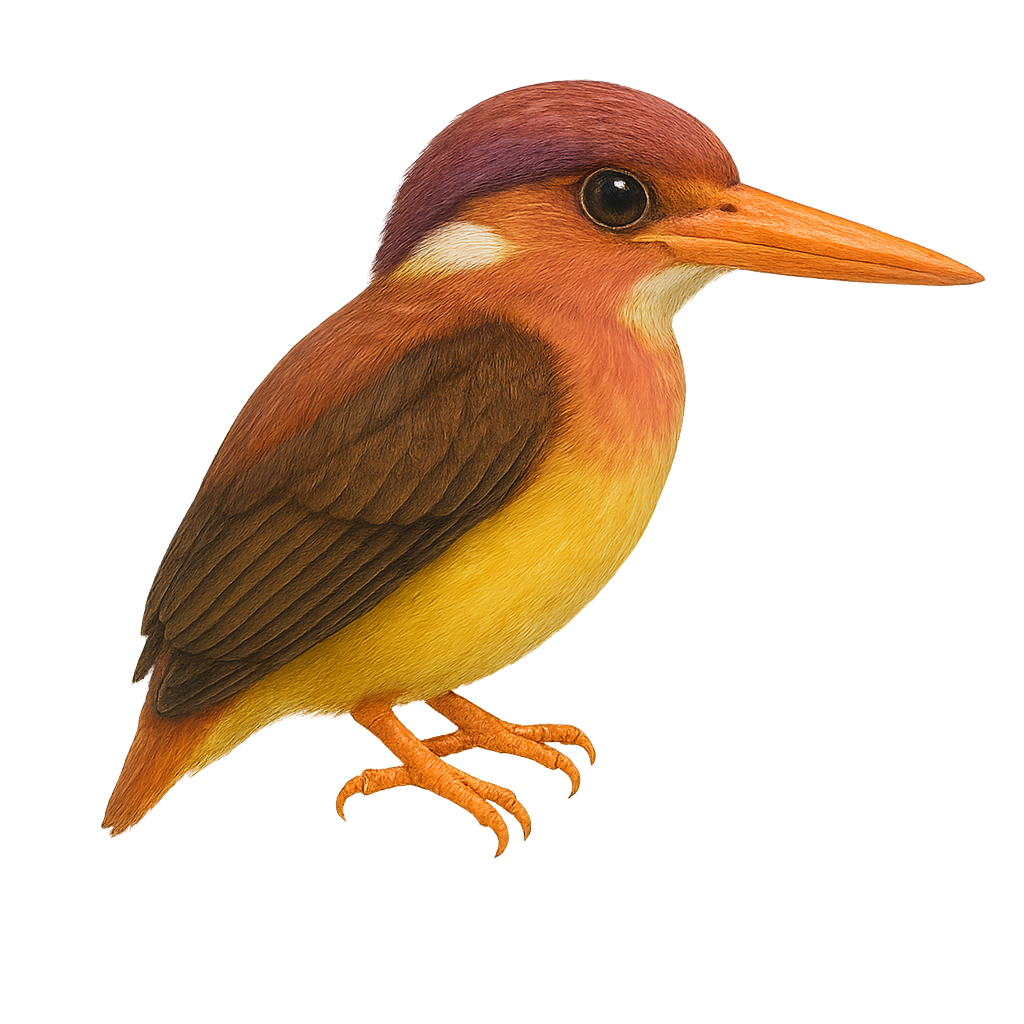
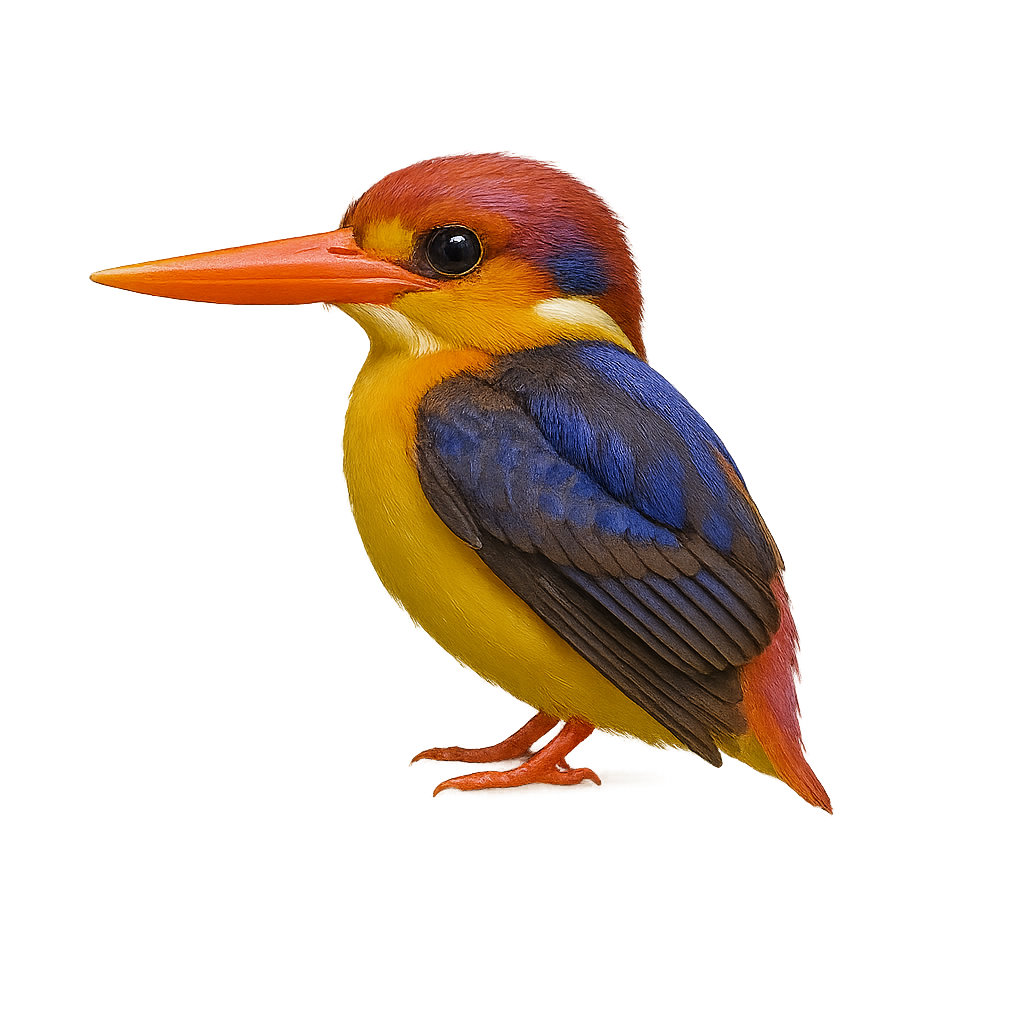
The Philippine Dwarf Kingfisher, or Ceyx melanurus, is a small bird, measuring about 13 cm in length. It is primarily found in the humid tropical forests of the Philippines. Its vivid coloration, with a black back contrasting with bright blue wings and an orange belly, makes it a striking sight. This kingfisher feeds mainly on small fish and insects, which it captures by quickly diving from a low branch. It is often seen near rivers and streams, where it builds its nest in tunnels dug into the banks. Although its population is stable, deforestation poses a potential threat to its natural habitat.
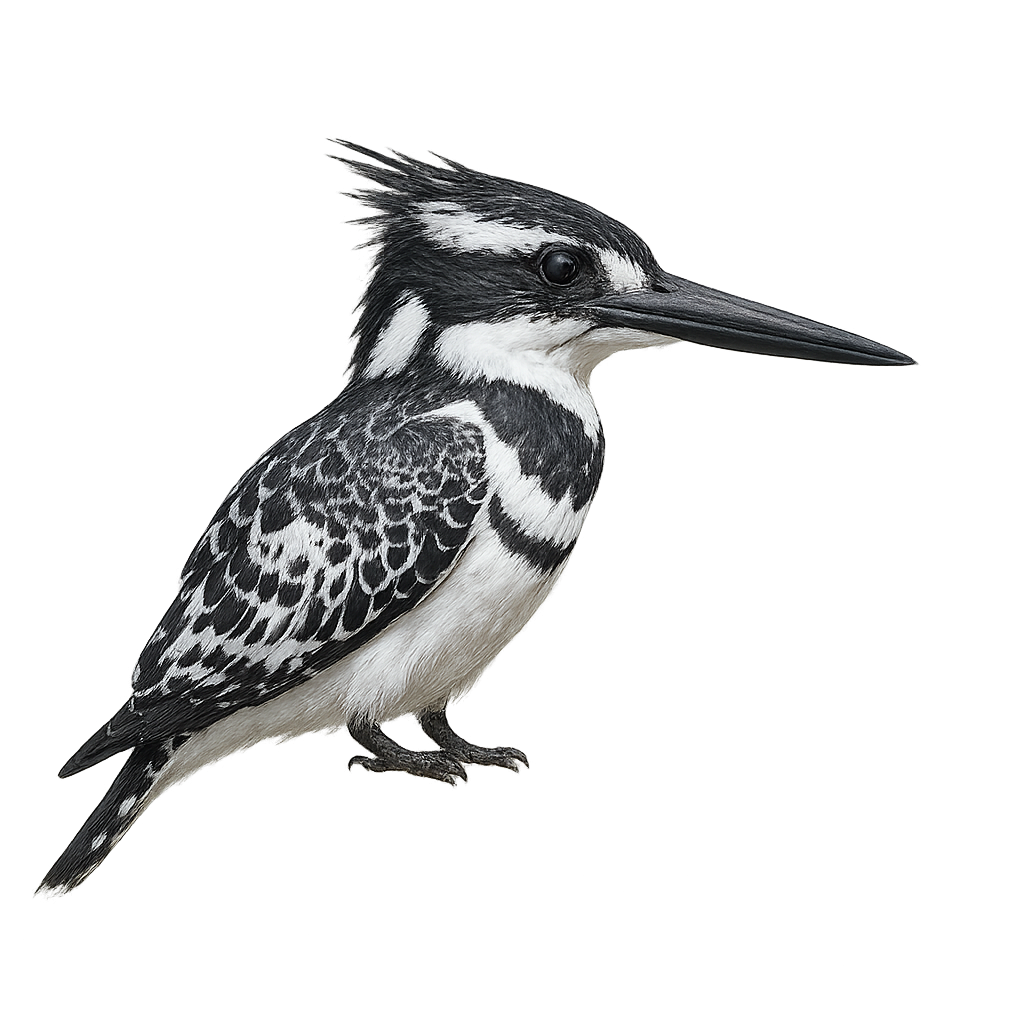
The Pied Kingfisher is a medium-sized aquatic bird, measuring about 25 cm in length and weighing between 80 and 120 g. It is easily recognized by its distinctive black and white plumage, with a black head, white back, and wings that are also black and white. Its belly is generally white, and it has a long, straight, pointed bill, perfectly suited for catching fish and aquatic insects. This kingfisher primarily inhabits coastal areas, rivers, lakes, and marshes in sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, and southern Asia. It primarily feeds on small fish, but can also catch insects, crustaceans, and small frogs. The Pied Kingfisher is an excellent diver, often seen diving into the water at high speed from a perch to catch its prey. While often observed alone or in small groups, it can sometimes be seen in pairs during the breeding season. While it is widely distributed, it can be threatened by water pollution and habitat loss.
The Purple Kingfisher is a small aquatic bird distinguished by its vibrant plumage and bright colors. It measures about 16 to 17 cm in length and weighs between 30 and 40 g. Its plumage is an intense blue with purple hues and bright orange tones on the belly. This kingfisher has a long, straight, pointed bill, perfectly suited for catching fish and aquatic insects. It primarily inhabits the humid regions and tropical forests of Southeast Asia, especially in areas along rivers and marshes. The Purple Kingfisher often hunts by perching on branches or rocks near the water, diving quickly to catch its prey. While generally solitary, it sometimes forms pairs during the breeding season. Although the species is relatively widespread, it faces threats such as deforestation and pollution of waterways.
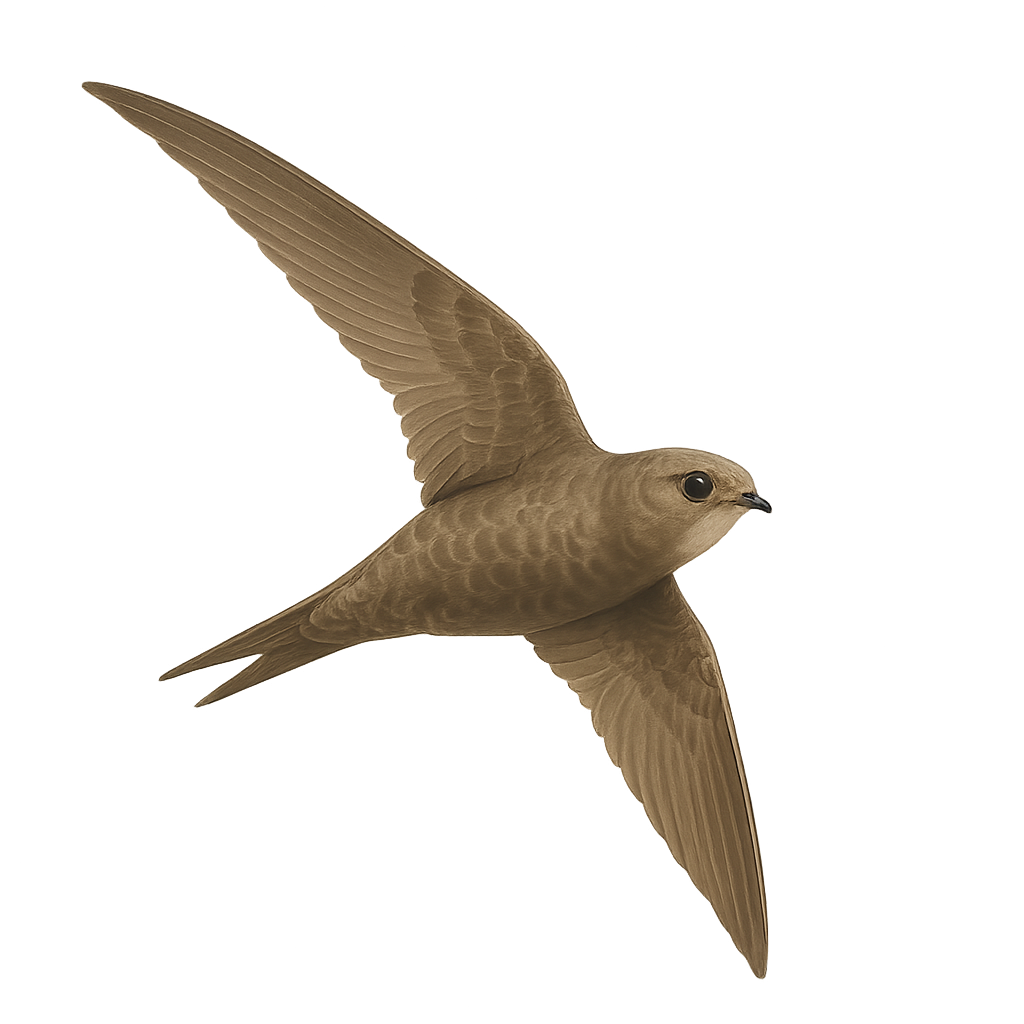
The Pale Swift is a migratory bird species that is mainly found in southern Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa. This small bird is easily recognizable by its grayish color and sleek body, perfectly adapted for speed and maneuverability in flight. It spends most of its life in flight, only landing to breed. It feeds primarily on insects that it catches while flying, often at high speed. The Pale Swift is an open-sky bird, frequently seen at high altitudes near mountains or soaring over urban areas in search of food.
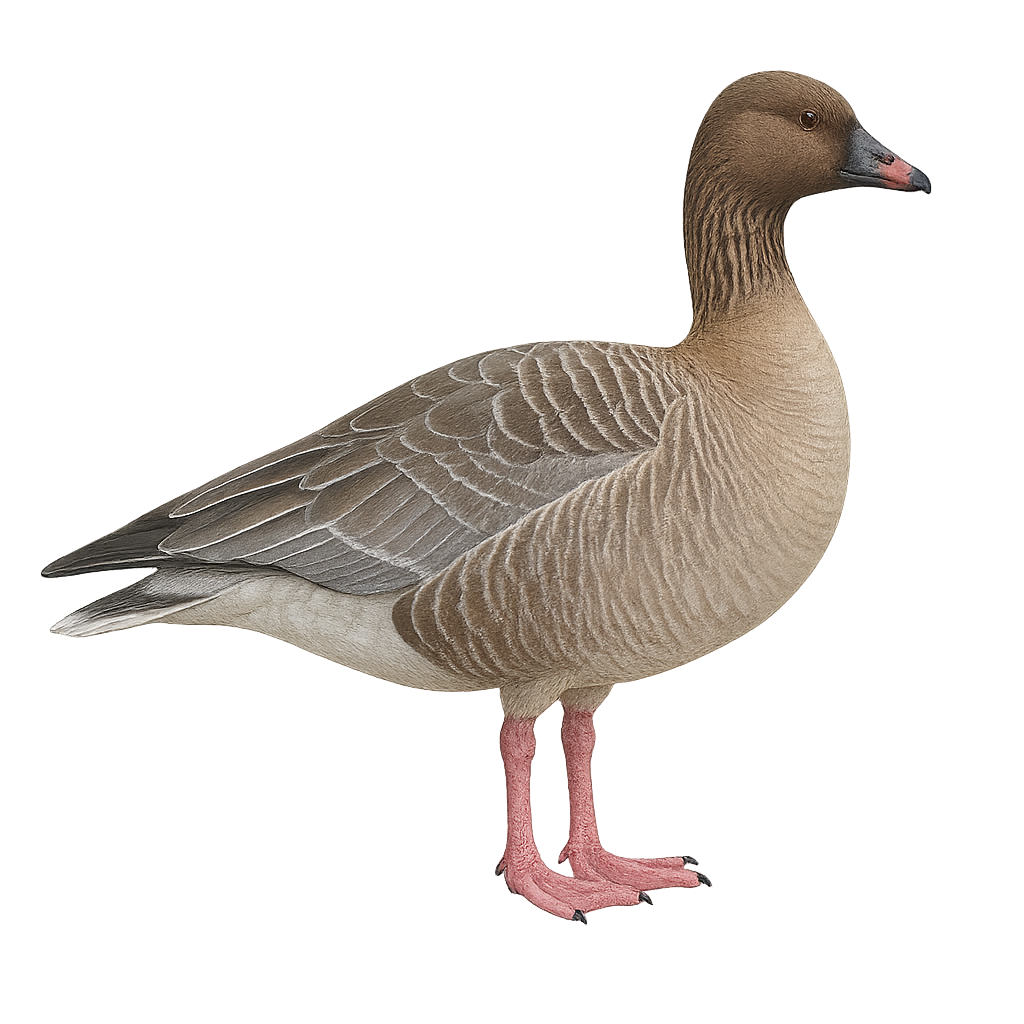
The Pink-footed Goose, Anser brachyrhynchus, is a medium-sized waterfowl species belonging to the Anatidae family. It is characterized by its short pink bill, pink legs, and grey-brown plumage. This goose breeds mainly in Iceland, Greenland, and Norway, migrating to the UK and the Netherlands for winter. It prefers wetlands, marshes, and grasslands for feeding, primarily on aquatic plants and grasses. In flight, it forms V-shaped groups, typical of geese. Although its conservation status is currently of "least concern," it is sensitive to climate change and habitat loss.
The Plumbeous Euphonia is a small, colorful bird native to the tropical forests of Central and South America. It is characterized by its blue-gray back and bright yellow belly. Males have a dark blue cap, while females display duller tones. This bird measures about 10 cm in length and weighs between 10 and 15 grams. Often seen in pairs or small groups, it primarily feeds on fruits and berries. Its song is melodious, consisting of soft, repetitive notes. The Plumbeous Euphonia plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding forest regeneration.
The Plain Chachalaca, or Ortalis vetula, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Cracidae family. It is primarily found in dry forests and wooded areas of Mexico and Central America. This bird is recognizable by its olive-brown plumage, long tail, and distinctive call, often described as a "cha-cha-lac". Chachalacas live in family groups and are known for their noisy and social behavior. They primarily feed on fruits, leaves, and flowers. Although their habitat is threatened by deforestation, they are still widespread and not considered endangered.
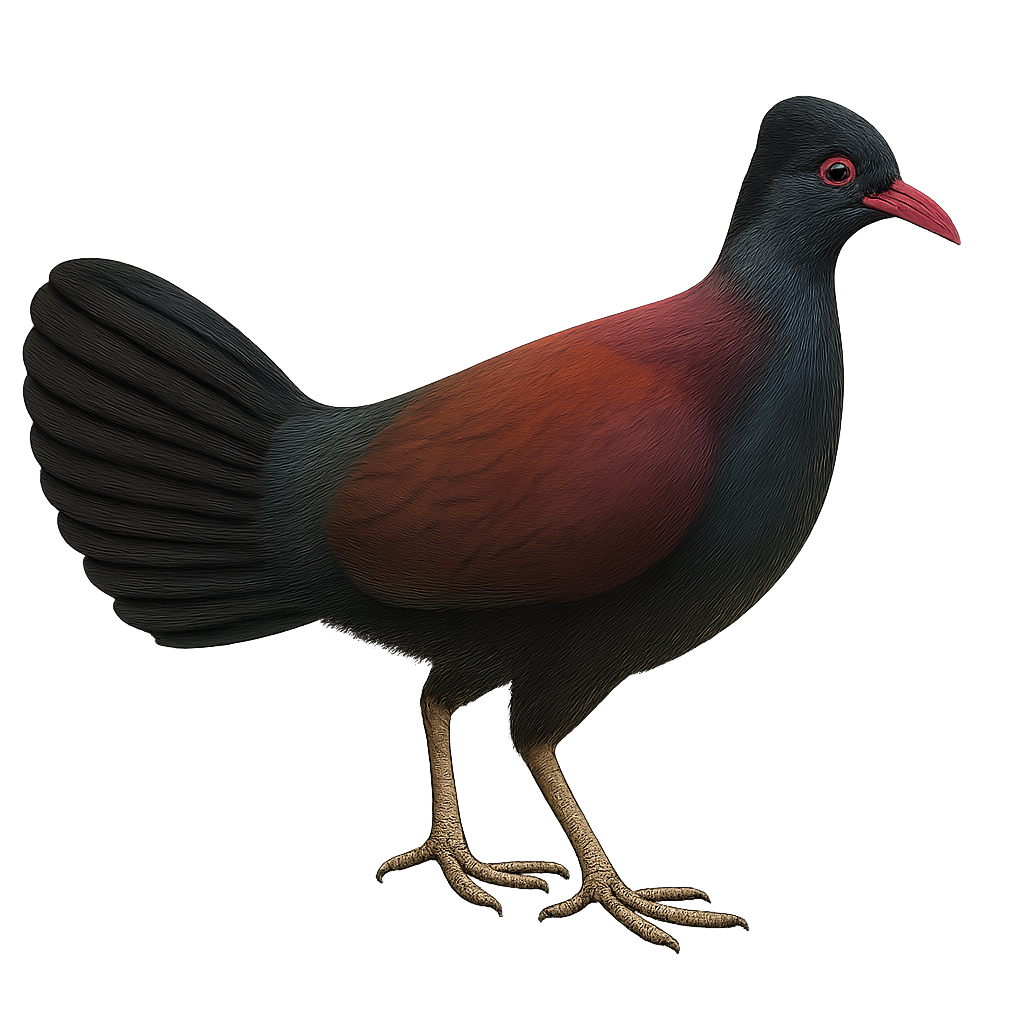
The Pheasant Pigeon, or Otidiphaps nobilis, is a fascinating bird native to the tropical forests of New Guinea. It is distinguished by its metallic green plumage and a head adorned with a white crest. Measuring about 40 cm in length, it has a robust body and strong legs, adapted to its terrestrial lifestyle. Although primarily ground-dwelling, it can fly short distances. Its diet mainly consists of fruits, seeds, and insects. The Pheasant Pigeon is a discreet bird, often difficult to observe due to its suspicious behavior. It plays an important role in seed dispersal, thus contributing to the regeneration of its forest habitat.