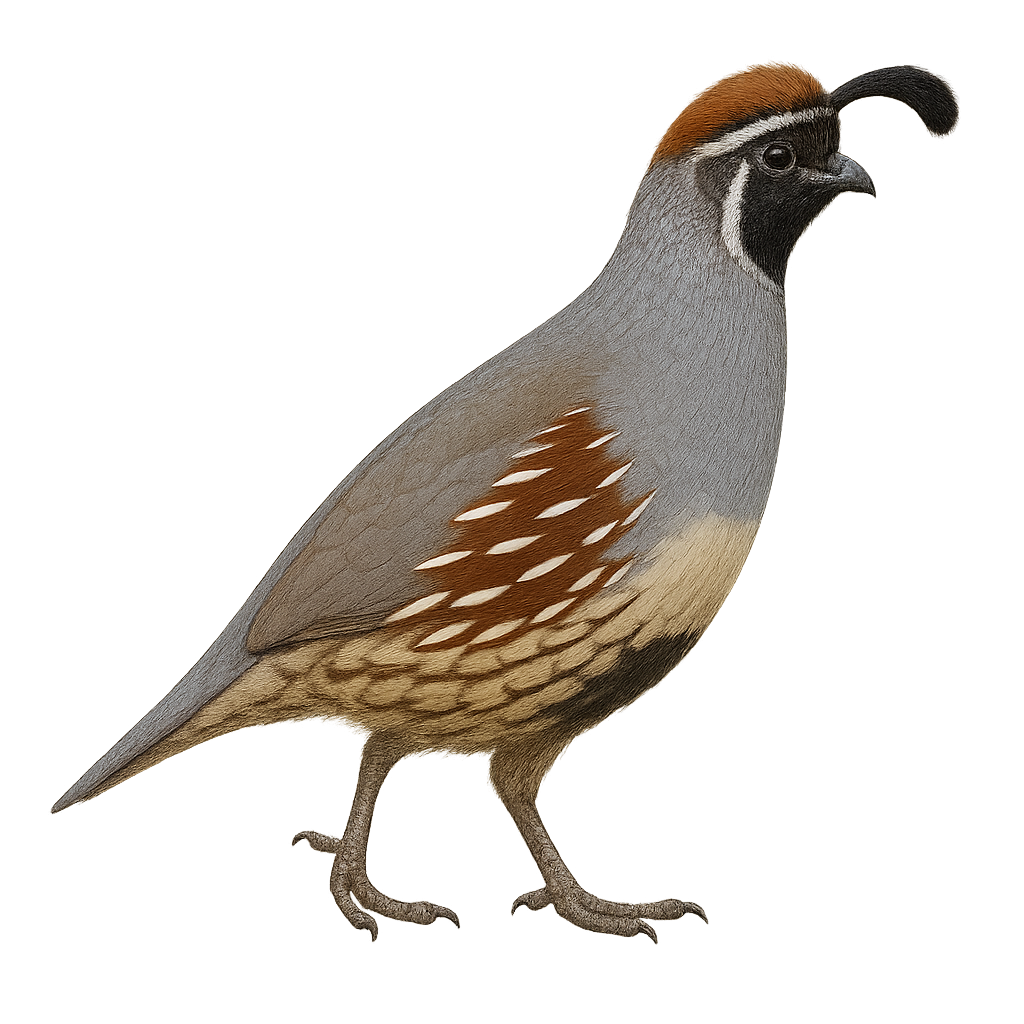
The Gambel's Quail, scientifically known as Callipepla gambelii, is a medium-sized ground-dwelling bird recognized for its distinctive comma-shaped topknot and bluish-gray plumage with black and white markings. It inhabits the arid regions of the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. This bird favors desert and semi-desert habitats, feeding primarily on seeds, leaves, and insects. Social by nature, Gambel's Quail often forms groups called "coveys". During the breeding season, males perform courtship displays to attract females. Although capable of flight, it prefers to run to evade predators.
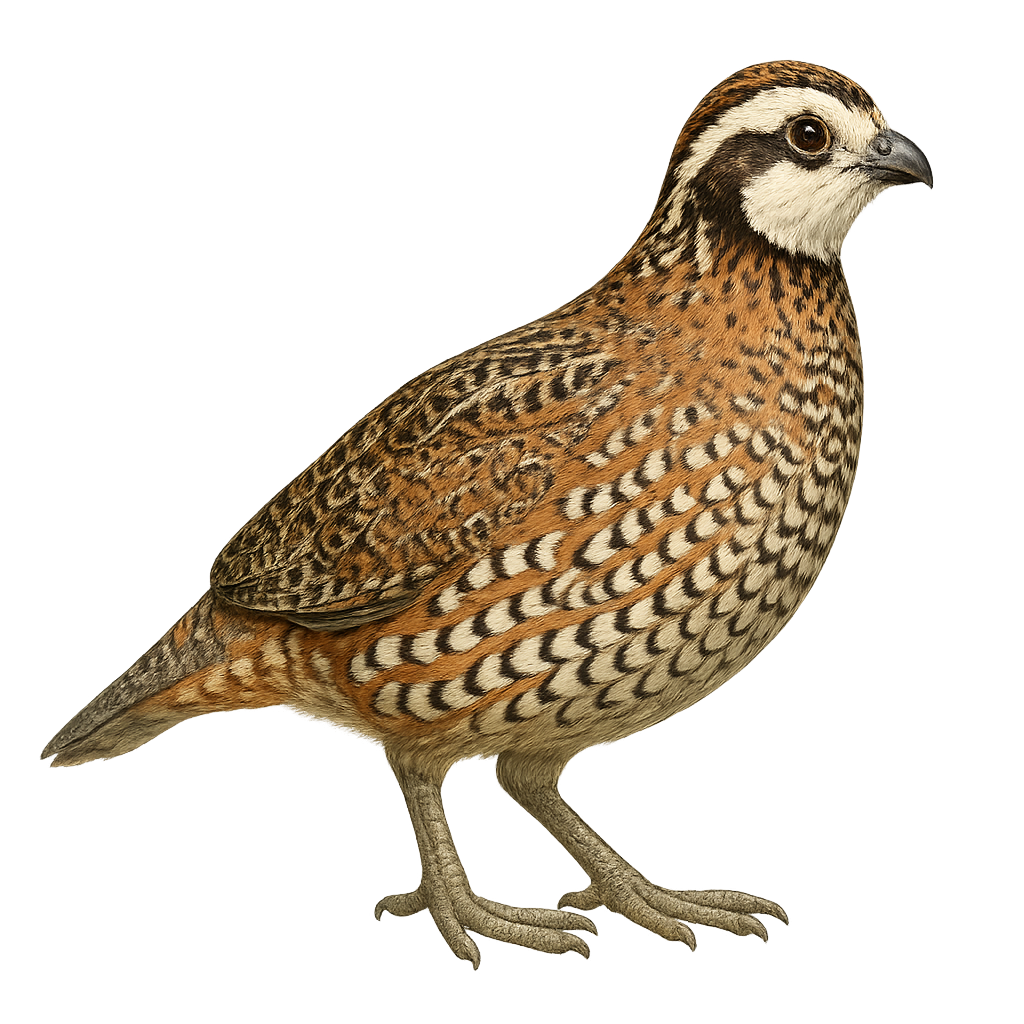
The Northern Bobwhite, or Colinus virginianus, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Odontophoridae family. It is easily recognizable by its brown speckled plumage and distinctive white-striped head. This bird is primarily terrestrial and prefers open habitats such as grasslands, agricultural fields, and sparse forests. It is known for its characteristic call, a clear and melodious "bob-white," often heard at dusk. The Northern Bobwhite is a social bird, living in groups called "coveys" outside the breeding season. Although widespread in North America, its populations have declined due to habitat loss and intensive agriculture.
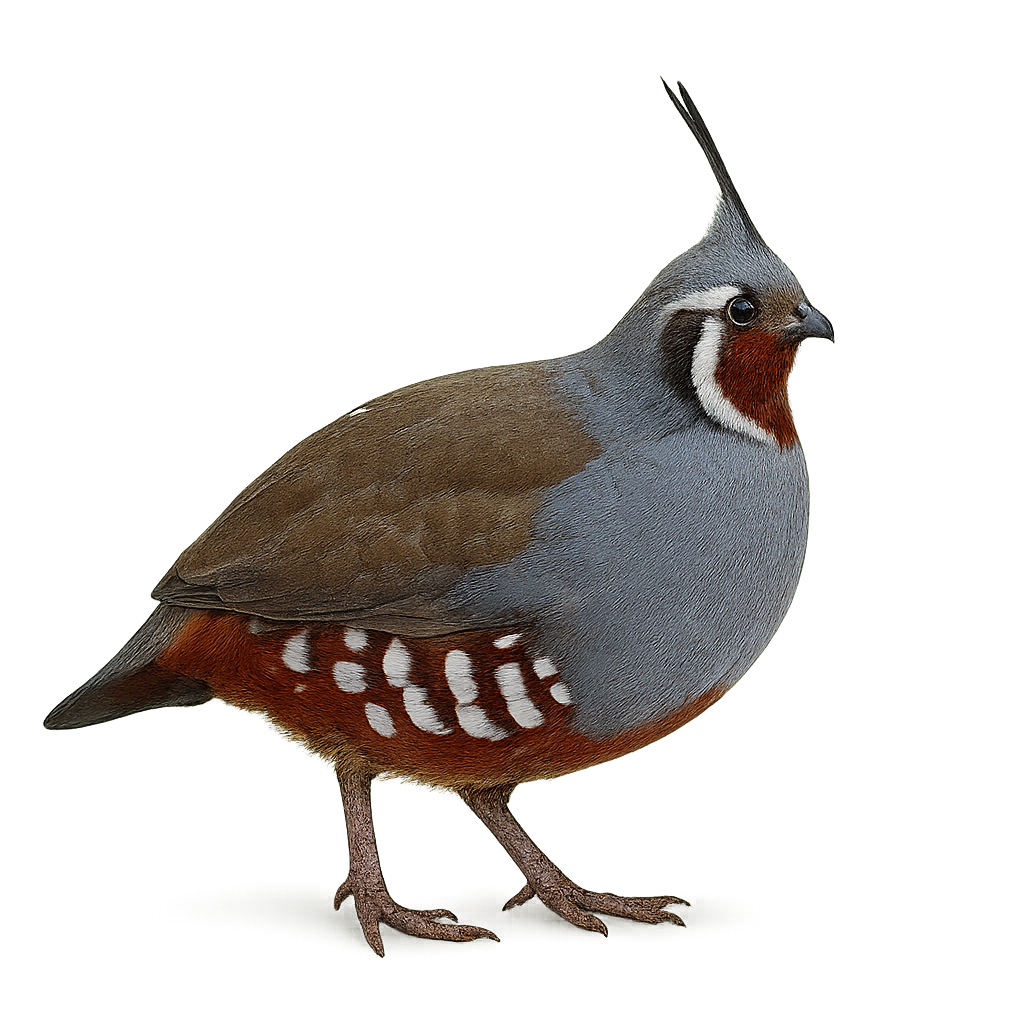
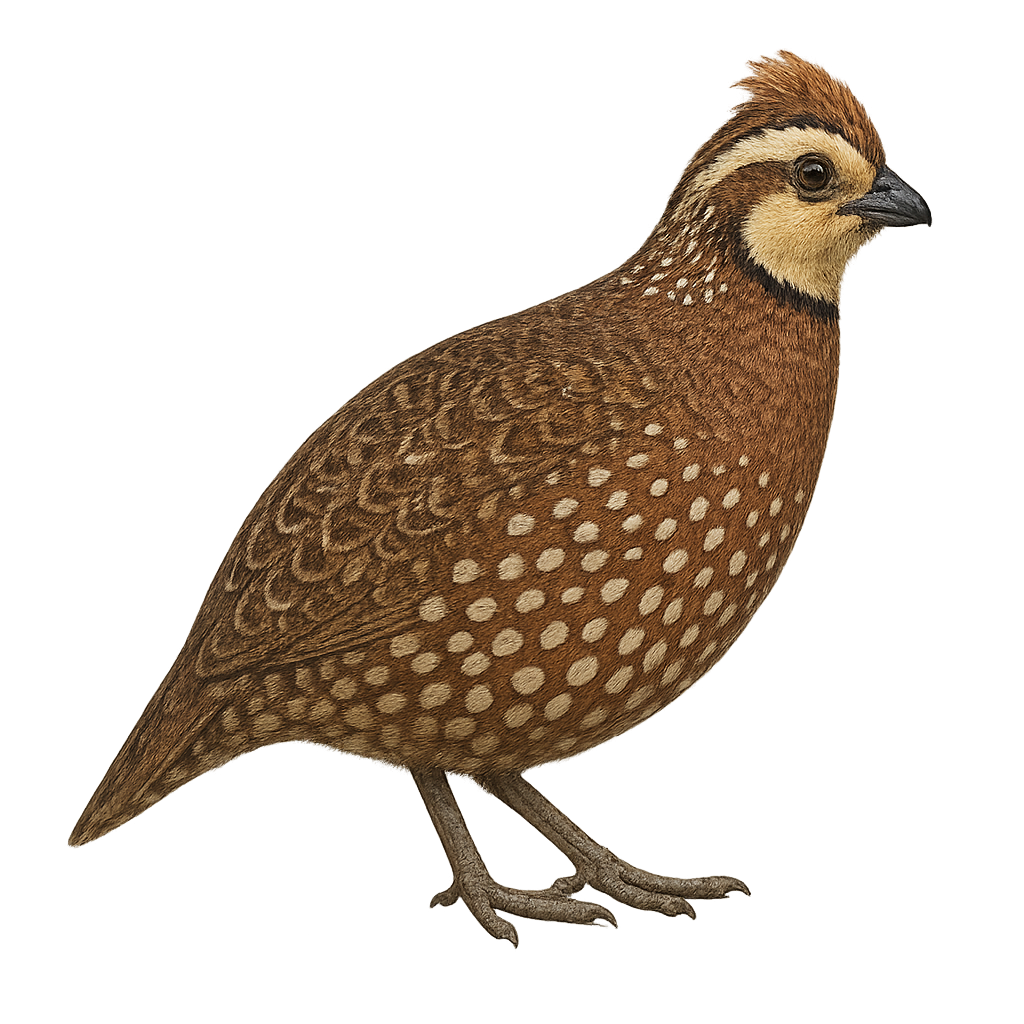
The Mountain Quail, or Oreortyx pictus, is a medium-sized ground-dwelling bird distinguished by its prominent crest and varied plumage of brown, gray, and white hues. It is primarily endemic to the mountainous regions of the western United States, where it inhabits coniferous forests and shrublands. This bird is particularly adapted to rugged terrains and primarily feeds on seeds, berries, and insects. Although capable of flight, it generally prefers to run to evade predators. The Mountain Quail is known for its elusive nature and shy behavior, making it difficult to observe in its natural habitat.
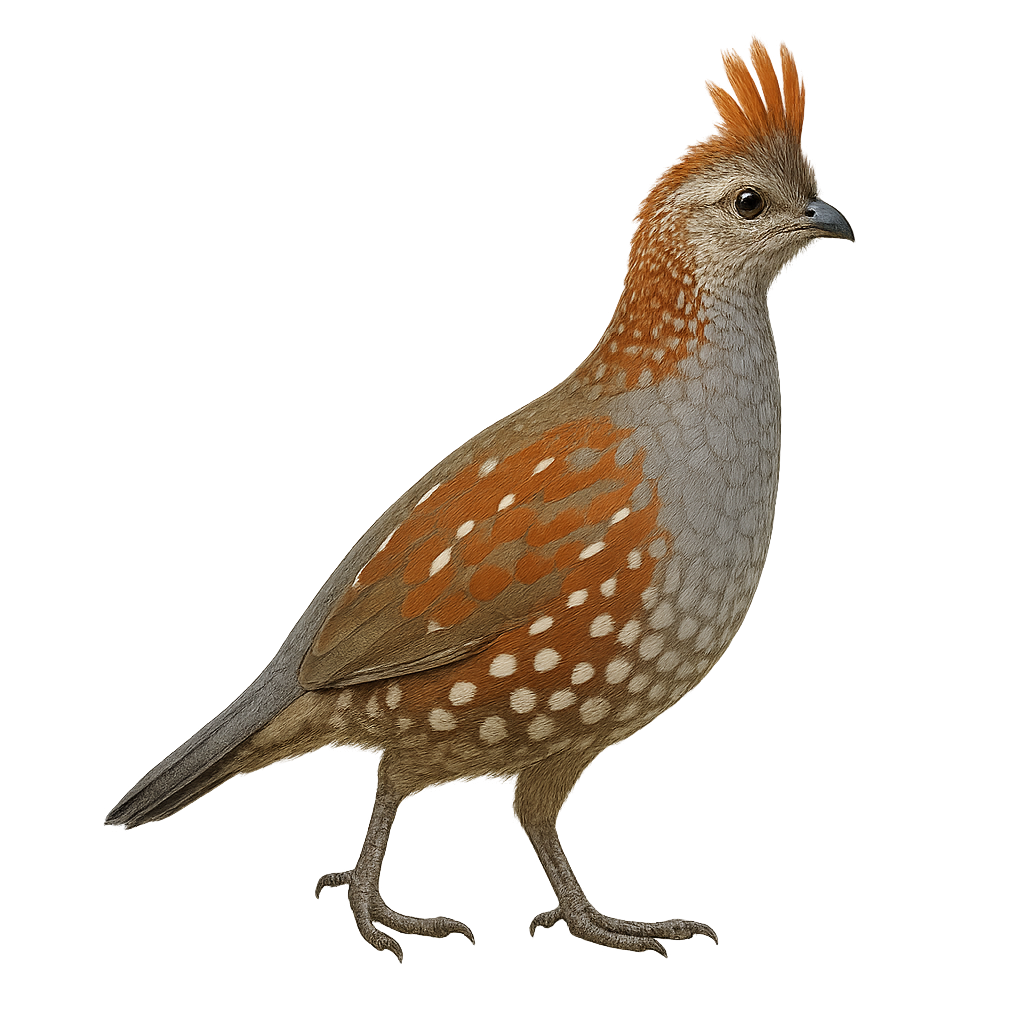
The Elegant Quail, or Callipepla douglasii, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Odontophoridae family. It is primarily found in the arid and semi-arid regions of northwestern Mexico. This bird is distinguished by its elegant plumage, with shades of gray, brown, and distinctive head patterns. Males sport a characteristic black crest, while females are more subdued. The Elegant Quail is a terrestrial bird that prefers running to flying when disturbed. It primarily feeds on seeds, insects, and small fruits. Its breeding season coincides with the rainy season, ensuring an abundance of food for the young.
The Crested Bobwhite, Colinus cristatus, is a bird from the Odontophoridae family, recognizable by its distinctive crest. It measures about 22 to 25 cm in length and weighs between 140 and 180 grams. Its plumage is mainly brown with white and black patterns on the head and neck. Males and females are similar, although males often have brighter colors. This bird is primarily terrestrial and prefers open habitats such as grasslands and savannas. It feeds mainly on seeds, insects, and small fruits. The Crested Bobwhite is known for its distinctive calls, often heard at dusk. It forms family groups and is generally monogamous.
The Red-faced Mousebird, or Urocolius indicus, is a fascinating bird from the Coliidae family, known for its distinctive red face and grey-brown plumage. It is primarily found in the arid and semi-arid regions of sub-Saharan Africa, where it moves in small groups. This bird measures about 34 cm in length, with a long tail that accounts for much of its total length. It feeds mainly on fruits, buds, and leaves, making it an important player in seed dispersal. The Red-faced Mousebird is a social bird, often seen sunbathing or grooming each other. Although it can fly, it often prefers to hop from branch to branch.
The Western Red Colobus, or Piliocolobus badius, is an arboreal primate found mainly in the forests of West Africa. Recognizable by its reddish fur and black face, it is a social animal living in groups of up to 80 individuals. These monkeys primarily feed on leaves, but also consume fruits and flowers. Their specialized diet makes them vulnerable to deforestation and habitat loss. The Western Red Colobus is also known for its complex vocalizations used for group communication. Unfortunately, this species is threatened by hunting and habitat destruction, leading to a significant population decline in recent decades.
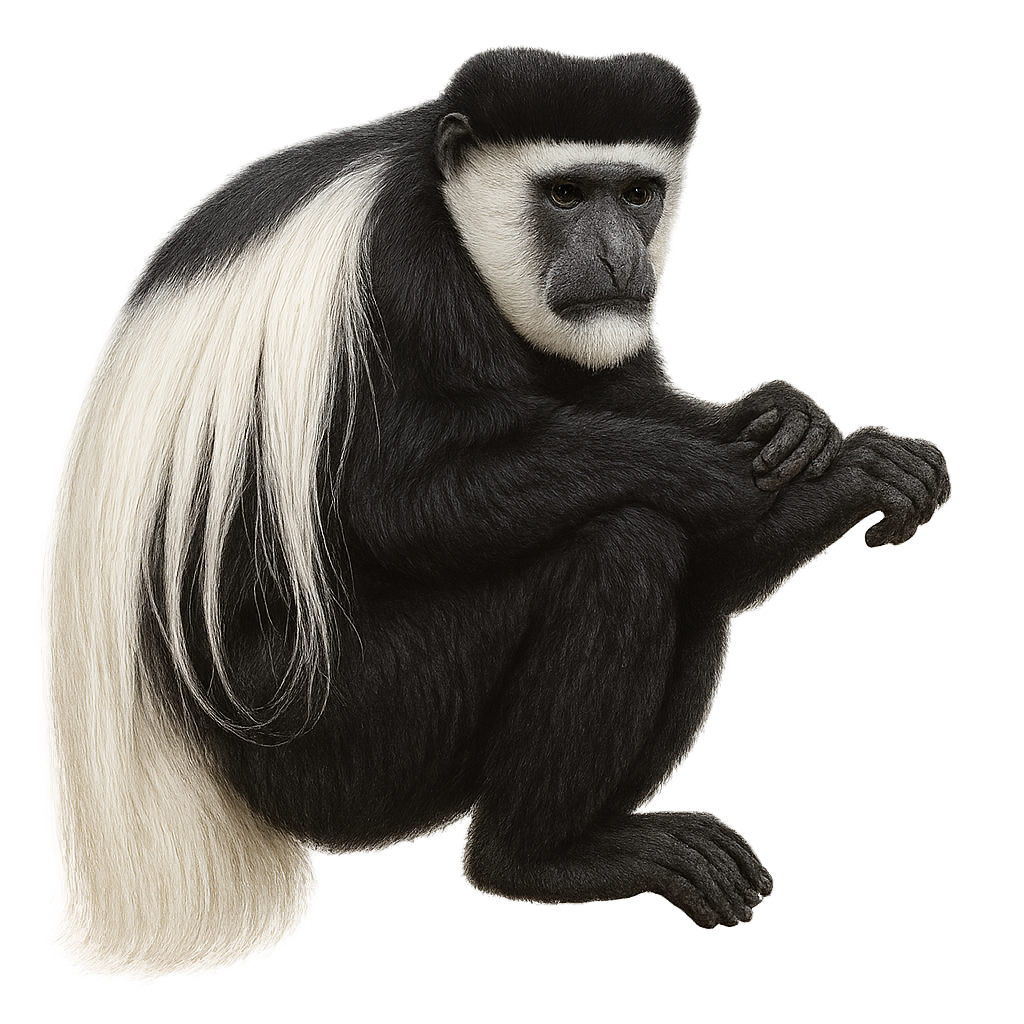
The Angolan colobus, or Colobus angolensis, is an arboreal primate known for its striking black and white fur. This monkey is particularly recognizable by the long white fringes adorning its shoulders and tail. It primarily inhabits the tropical forests of Central and East Africa, spending most of its time in the canopy. The Angolan colobus is a strict herbivore, feeding mainly on leaves, fruits, and flowers. It lives in social groups of up to 15 individuals, led by a dominant male. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it remains relatively widespread in some areas.
The Ursine Colobus, or Colobus vellerosus, is a medium-sized arboreal primate primarily found in West Africa. Its coat is predominantly black with distinctive white tufts around the face and shoulders, giving it an elegant appearance. It lives in social groups composed of several females and one or two dominant males. These monkeys are mainly folivorous, feeding on leaves, fruits, and flowers. They play a crucial role in seed dispersal, contributing to forest health. Although they are agile in trees, they rarely descend to the ground. Their habitat is threatened by deforestation and hunting, leading to a decline in their population.
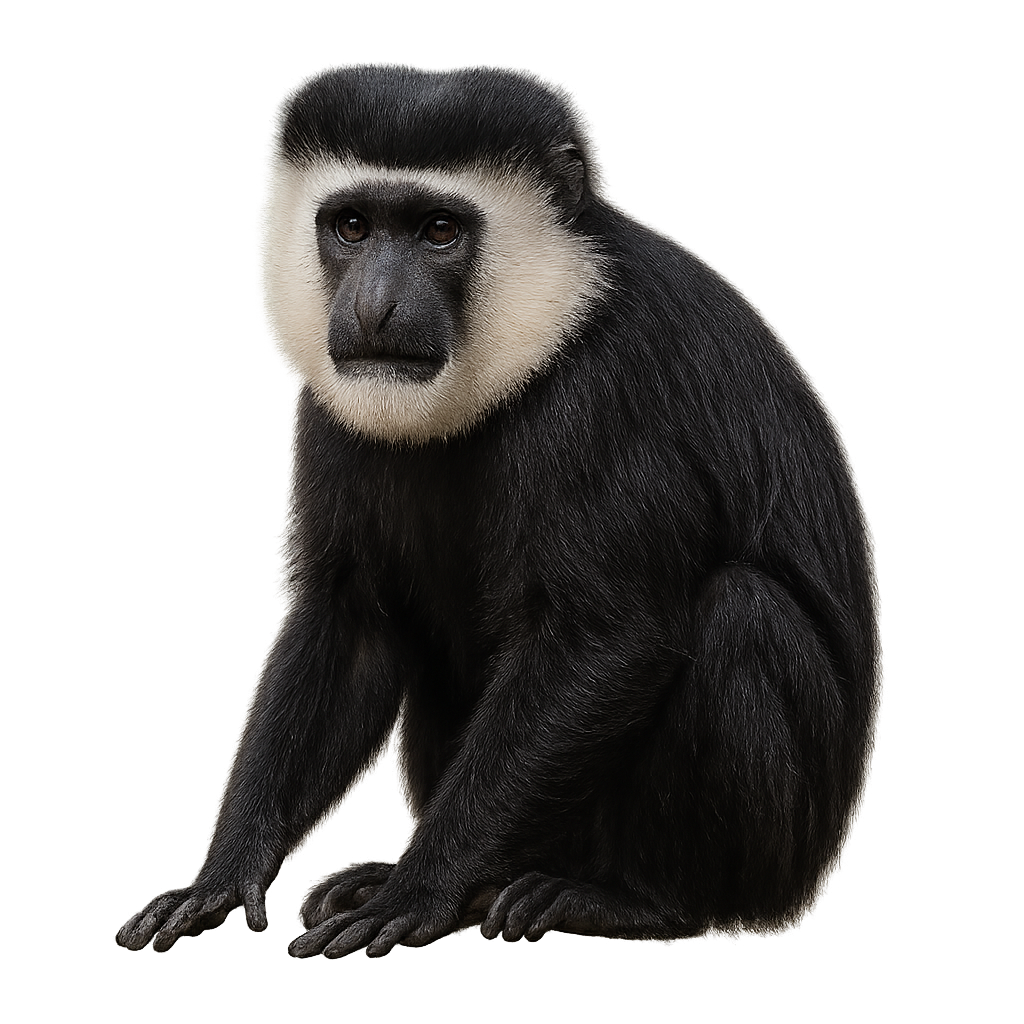
The Guereza Colobus is a large primate belonging to the family Cercopithecidae, easily recognized by its distinctive black and white fur. It has a white mane around its face, white limbs, and a long, bushy tail that helps it stabilize in the trees. Its black body is contrasted by tufts of white fur along the sides and back, making it one of the most elegant primates of the forest. It primarily lives in the tropical and subtropical forests of East Africa, spending most of its time in the trees.
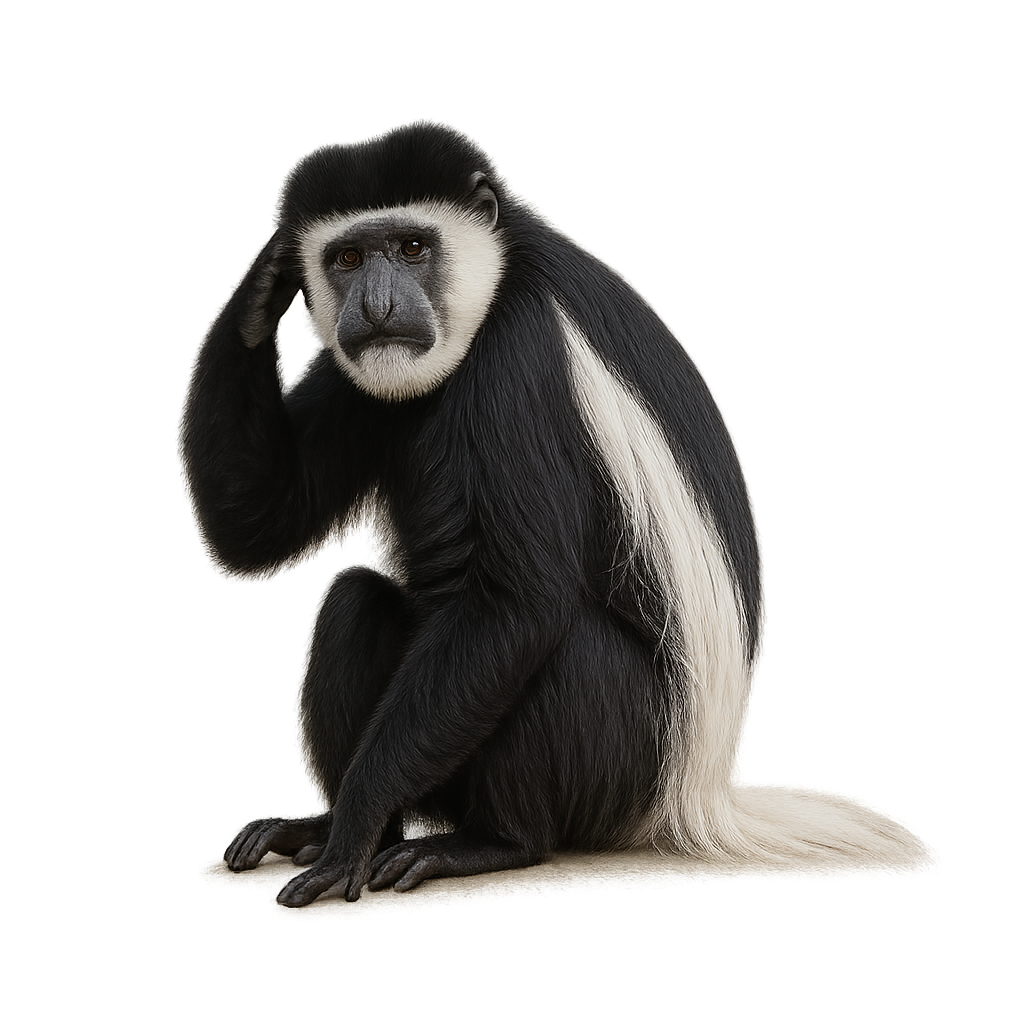
The Guereza Colobus is primarily herbivorous, feeding on leaves, fruits, seeds, and flowers. With its specialized stomach, it can digest tough, fibrous leaves that other animals cannot consume. It lives in social groups led by a dominant male and is generally very calm, moving gracefully and agilely through the forest canopy. Although its population remains stable in some protected areas, it faces threats due to deforestation and hunting, causing some populations to be classified as vulnerable.
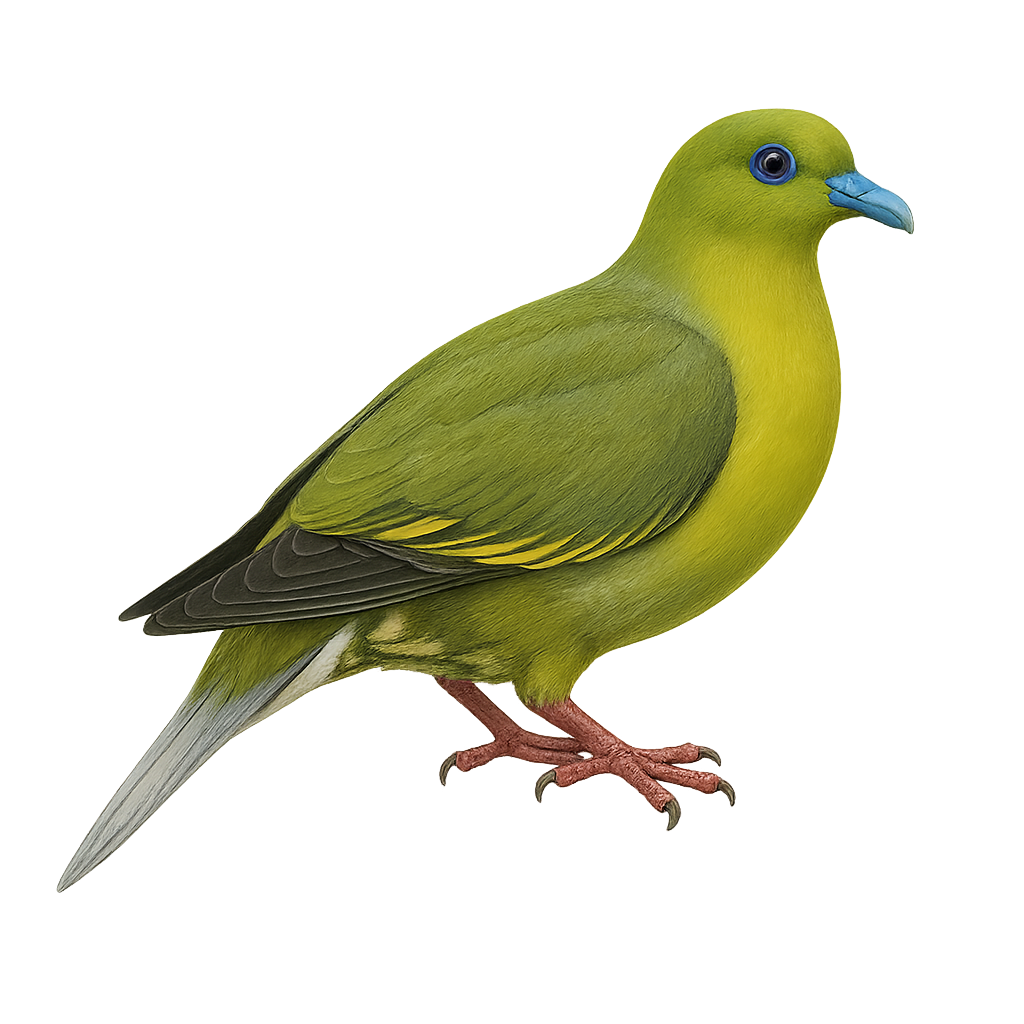
The Grey-cheeked Green Pigeon, Treron griseicauda, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Columbidae family. It is characterized by its vibrant green plumage, with a distinctive grey head and tail. This bird is primarily arboreal, inhabiting tropical and subtropical moist forests. It feeds mainly on fruits, playing a crucial role in seed dispersal. Its call is soft and melodious, often heard at dawn and dusk. Although generally discreet, it can be observed in small groups, especially near food sources. Its population is stable, but deforestation poses a potential threat to its natural habitat.
The Pin-tailed Green Pigeon, or Treron apicauda, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Columbidae family. It is characterized by its vibrant green plumage, pointed tail, and shades of yellow and grey on its wings. This bird is primarily arboreal and feeds on fruits, especially figs. It is found in the tropical and subtropical forests of Southeast Asia, including India, Bangladesh, Thailand, and Vietnam. Often seen in small flocks, it moves from tree to tree in search of food. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it is currently classified as "least concern" by the IUCN.
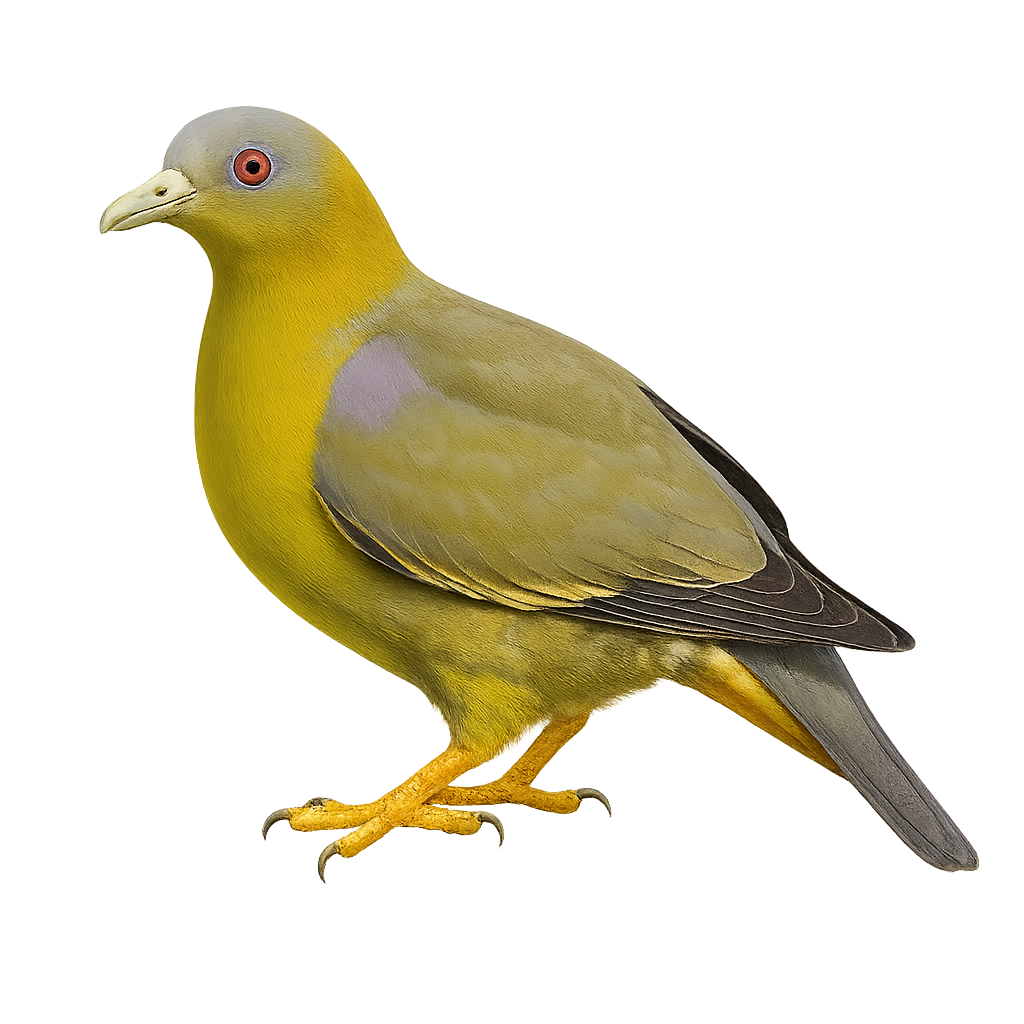
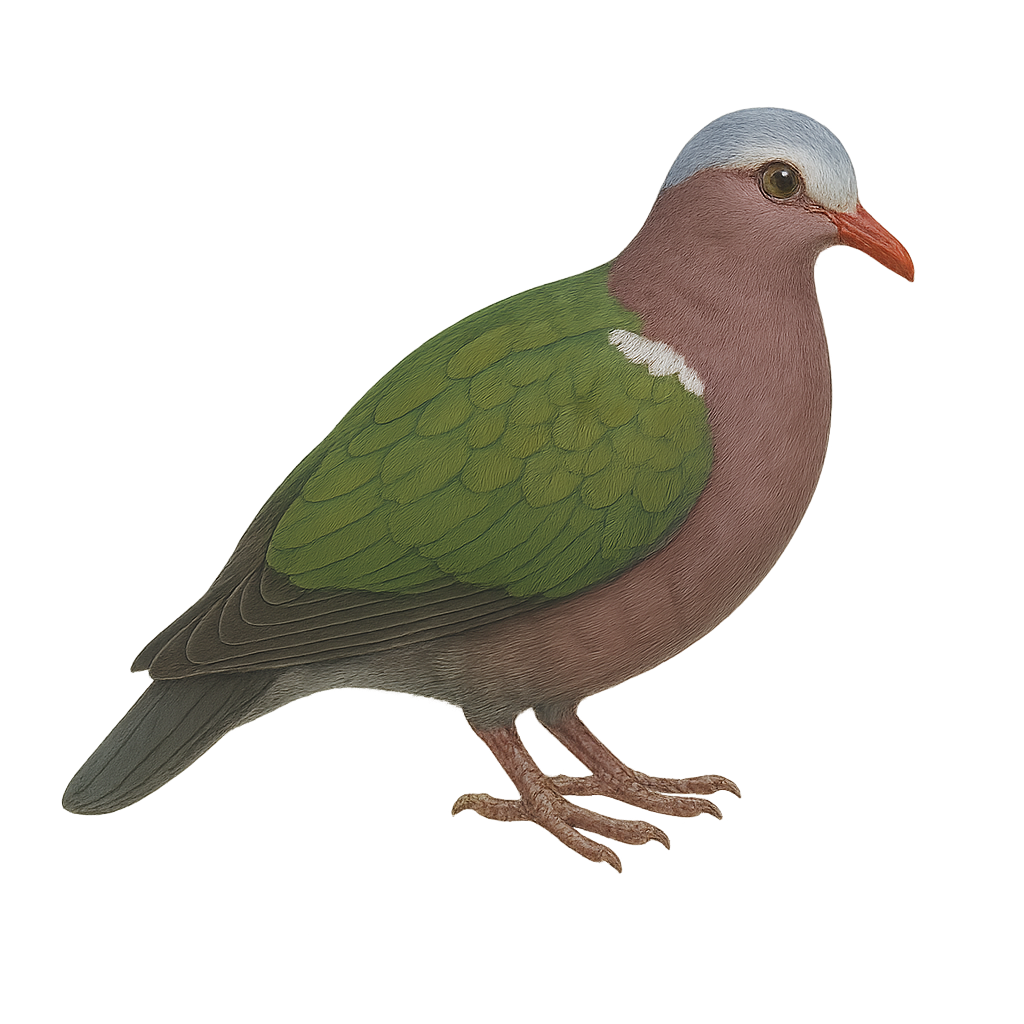
The Yellow-footed Green Pigeon, or Treron phoenicopterus, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Columbidae family. It is easily recognizable by its bright green plumage, yellow legs, and barred grey tail. This bird is primarily arboreal and feeds on fruits, especially figs. It is found in tropical and subtropical forests, mangroves, and open wooded areas of South Asia. Often seen in groups, it perches in trees or flies from one tree to another. The Yellow-footed Green Pigeon plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding forest regeneration. Although generally discreet, its soft and melodious call can be heard from a distance.
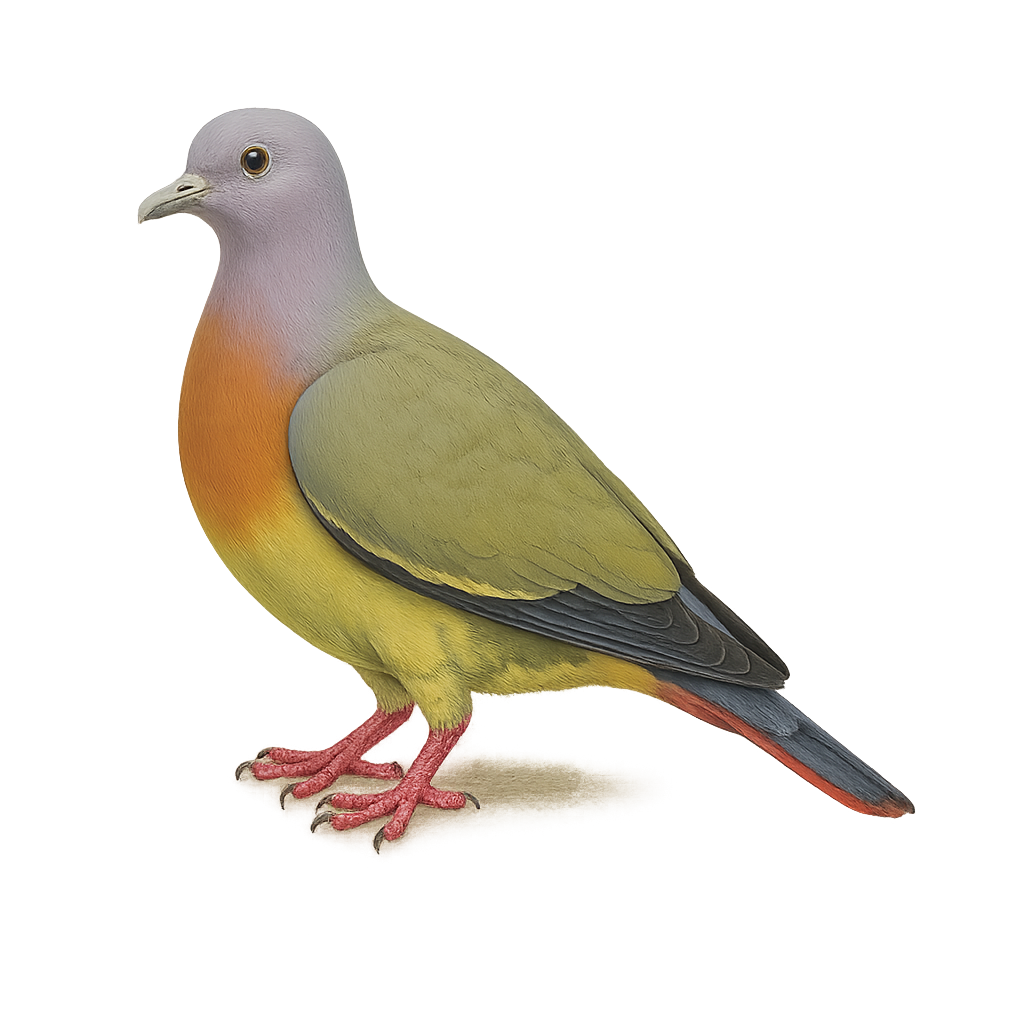
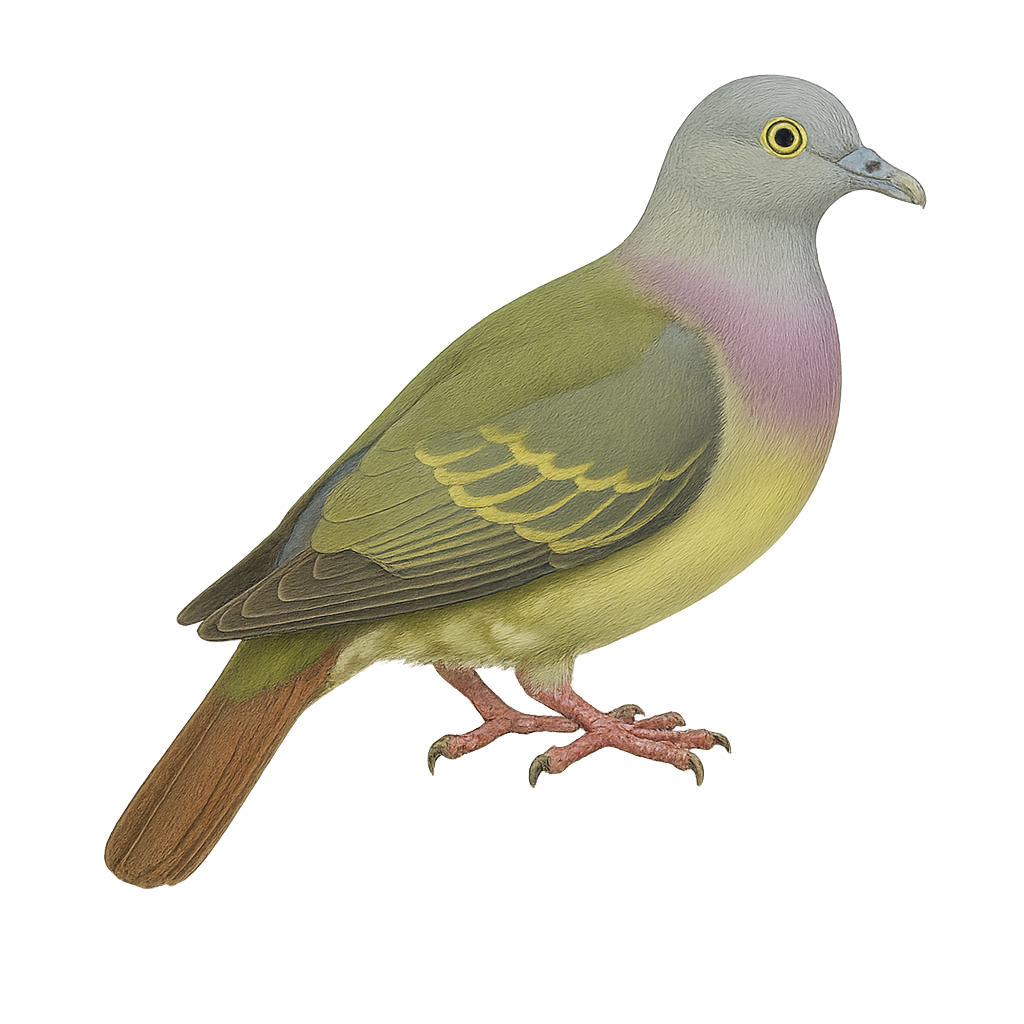
The Pink-necked Green Pigeon, scientifically known as Treron vernans, is a vibrant and fascinating bird native to Southeast Asia. This pigeon is notable for its colorful plumage, with males displaying a distinctive pink chest and shades of green and yellow across the body. Females are more subdued in color, predominantly green. These birds favor forested habitats and urban areas with dense vegetation. They primarily feed on fruits and play a crucial role in seed dispersal. Their flight is swift and direct, often in small flocks. Although generally not very shy, they can be cautious when threatened.
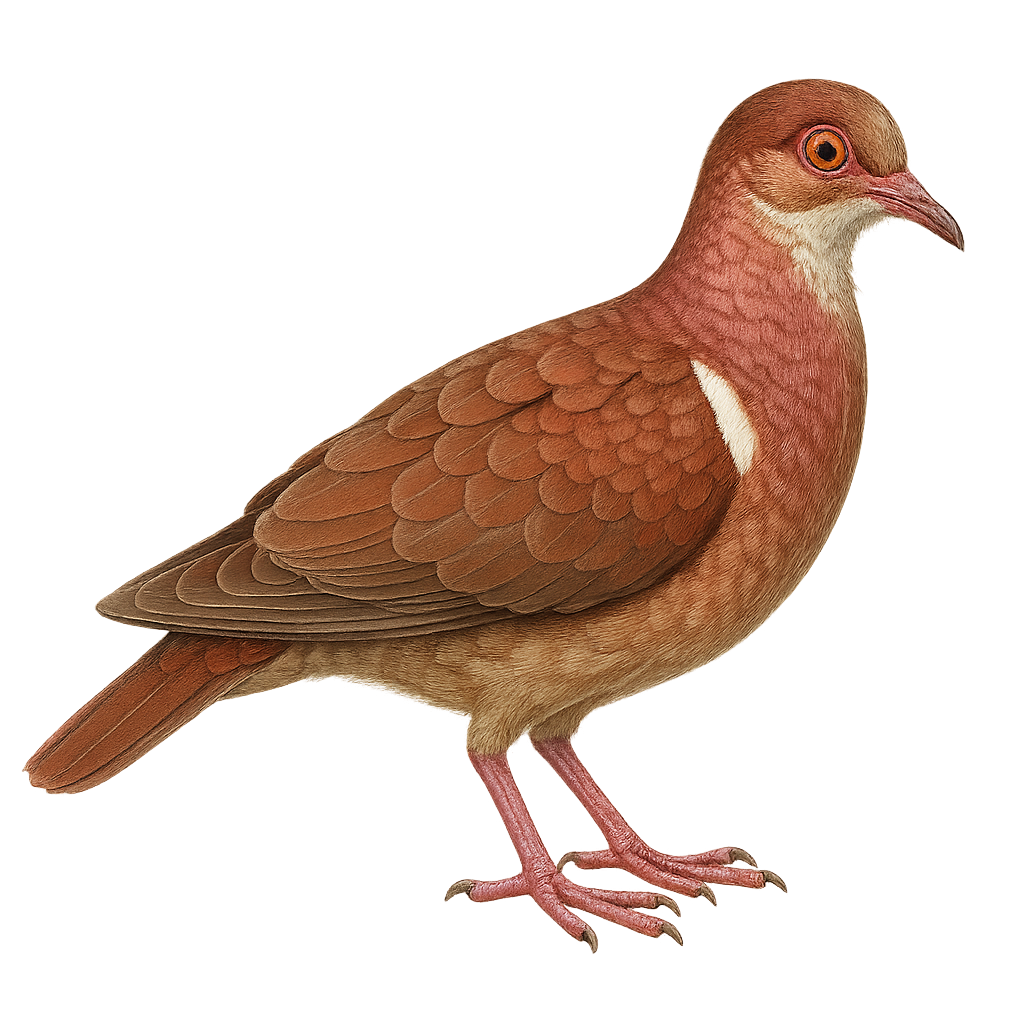
The Ruddy Quail-Dove, or Geotrygon montana, is a discreet, ground-dwelling bird found mainly in the tropical rainforests of Central and South America. It is recognizable by its reddish-brown plumage, distinctive black tail, and iridescent neck sheen. Measuring about 22 to 26 cm in length, it primarily feeds on seeds and fallen fruits. This bird is often solitary or in small groups and prefers walking to flying. Its soft, repetitive call is often heard at dawn and dusk. Although relatively common, its discreet nature makes it difficult to spot in its natural habitat.
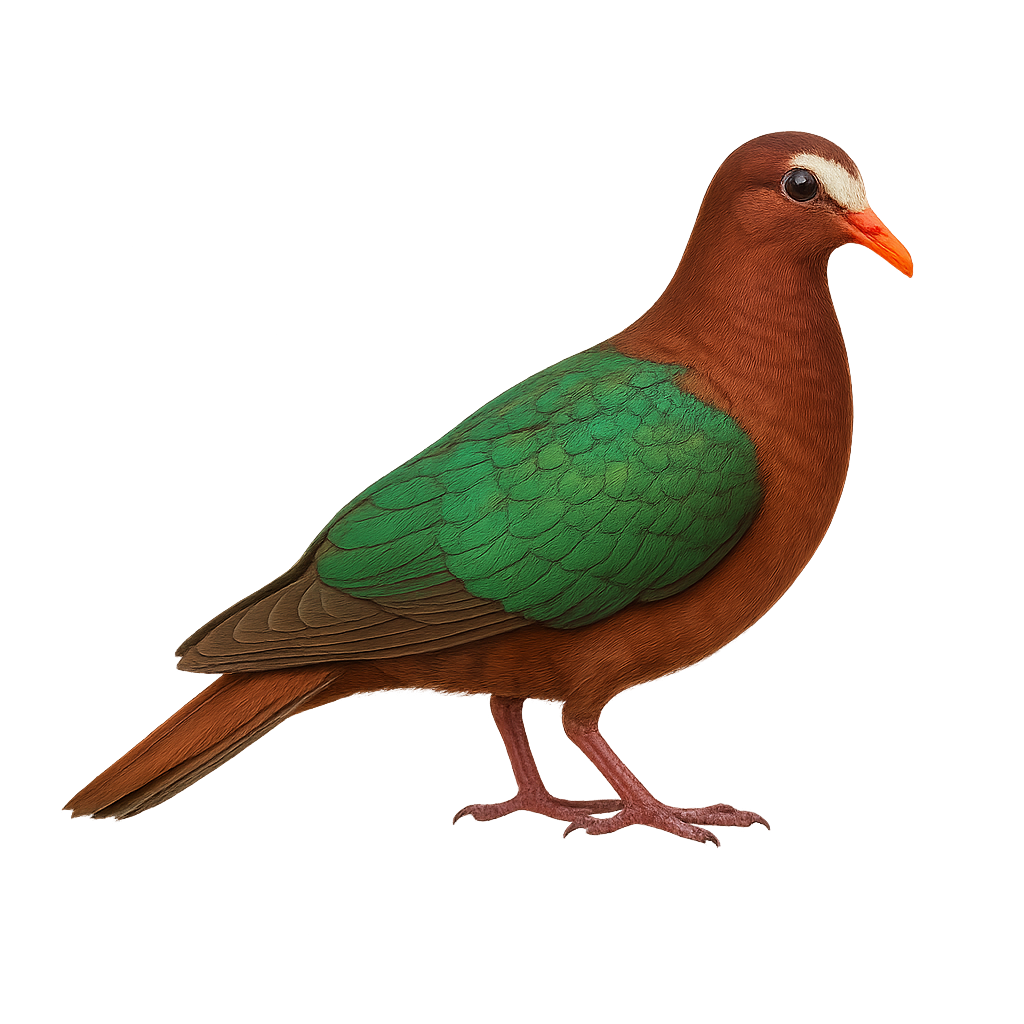
The Stephens's Emerald Dove, or Chalcophaps stephani, is a medium-sized pigeon known for its striking plumage with shades of emerald green. It primarily inhabits the tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia and Australia. Its bright red beak and pink legs contrast with its green and brown body, creating a stunning visual display. Often seen alone or in small groups, it feeds on seeds and fallen fruits. Although its flight is fast and direct, it prefers to walk on the forest floor in search of food. This species is generally discreet, blending into its environment with its camouflaged plumage.
The Emerald Dove, or Chalcophaps indica, is a strikingly colorful bird known for its shimmering emerald-green plumage. It inhabits the tropical and subtropical forests of Southeast Asia, Australia, and the Pacific islands. This medium-sized bird, measuring about 23 to 28 cm in length, has a stout body with a greyish head and neck, contrasting with its green wings and brown back. The bill is bright red, as are the legs. The Emerald Dove is often seen alone or in pairs, foraging for seeds, fruits, and insects on the ground. Its flight is fast and direct, often accompanied by a distinctive wing-beating sound.
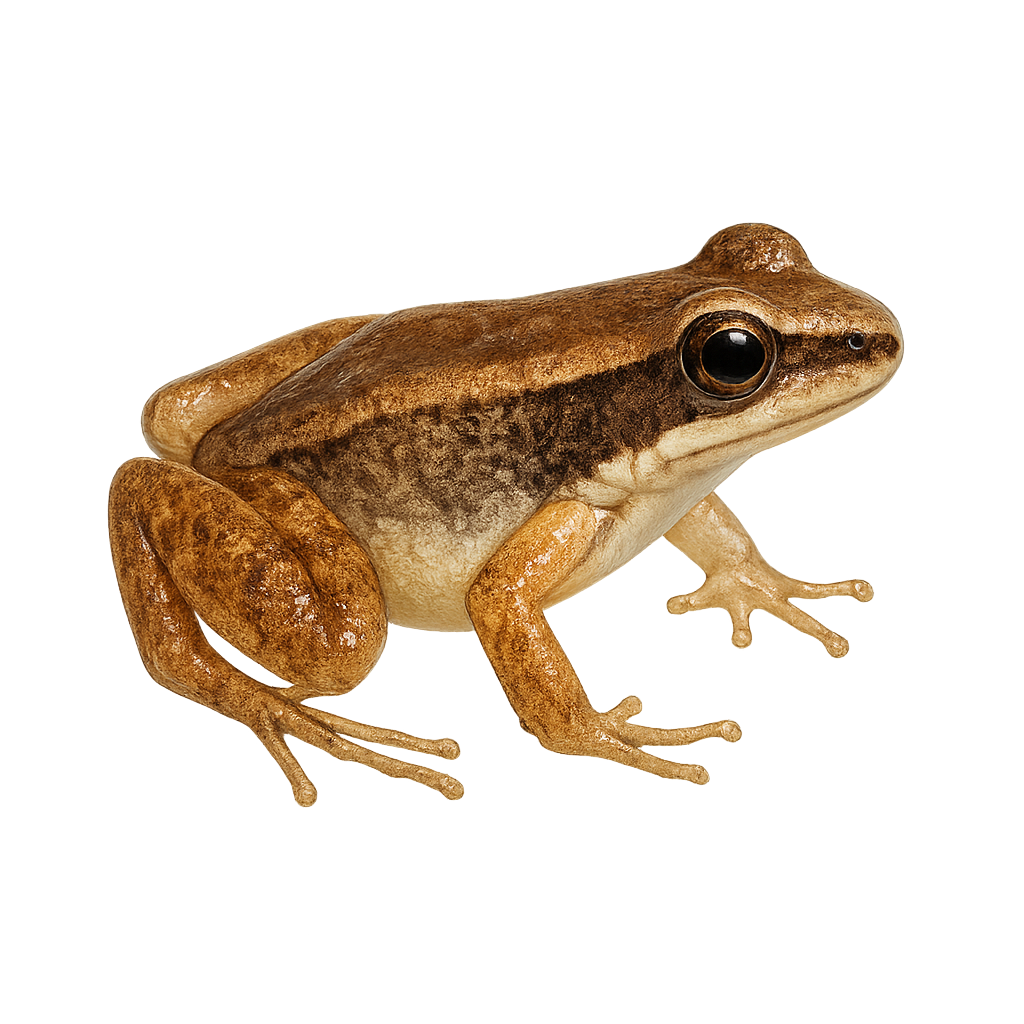
The Palm rocket frog is a small, colorful frog native to the humid tropical forests of South America, particularly in Colombia and Ecuador. It is characterized by its smooth skin and vibrant color patterns, ranging from brown to green with black spots. This species is primarily terrestrial, although it is often found near water bodies where it breeds. Males are known for their distinctive calls, which play a crucial role in attracting females. The Palmate Rocket Frog is diurnal, meaning it is active during the day. It primarily feeds on small insects and other invertebrates. Although its population is stable, it is threatened by deforestation and habitat loss.
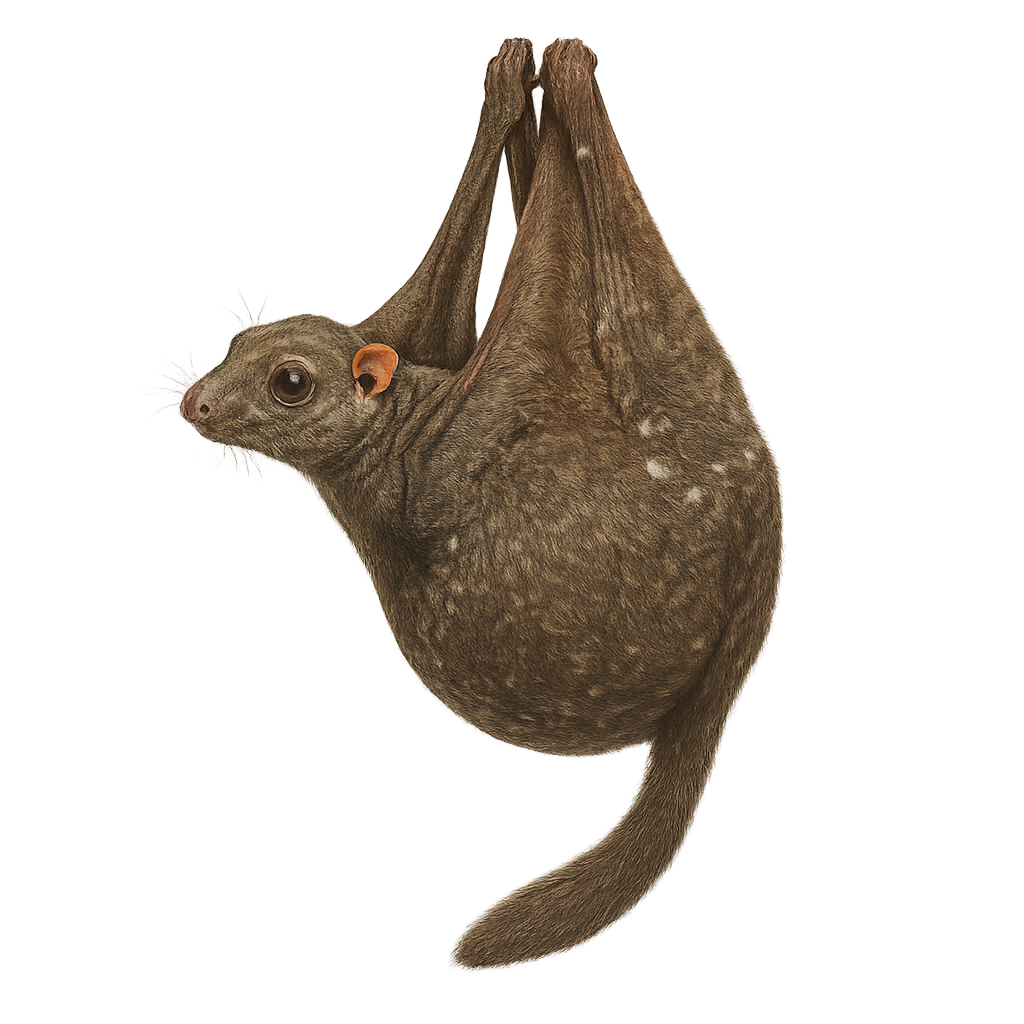
The Colugo, also known as the flying lemur, is a small tree-dwelling mammal native to Southeast Asia. While not a true lemur, it is often called so due to its gliding abilities, which it performs using a thin membrane of skin that connects its limbs to its body. This gliding allows it to move efficiently from tree to tree in search of food, primarily consisting of leaves, fruits, and flowers. The Colugo is a nocturnal and rather discreet animal, using its dense fur and camouflage to blend into the forest environment.
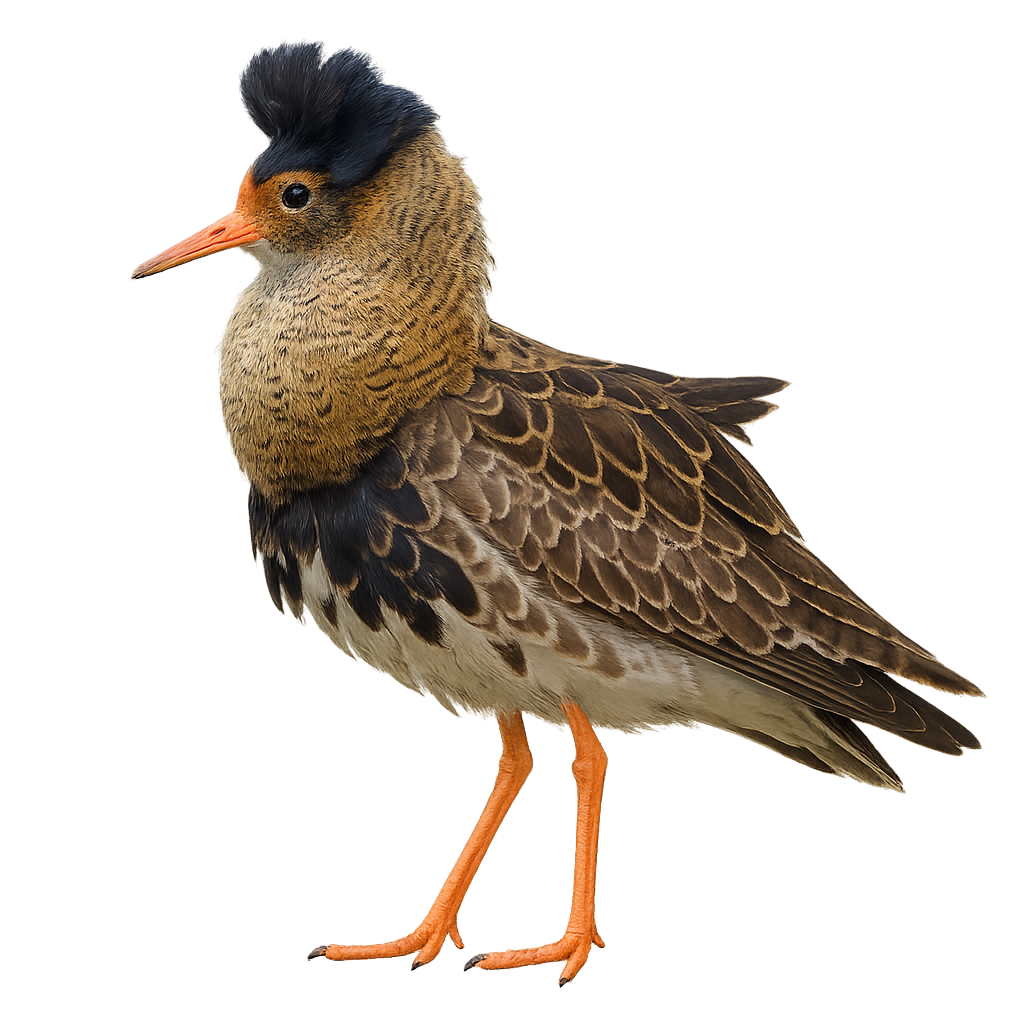
The Ruff is a medium-sized wader bird, easily recognizable by its colorful plumage and relatively large size for a bird in its family. The male is particularly distinctive during the breeding season, with vibrant plumage ranging from brown and white to red and orange, and a large ruff that surrounds its head. Outside the breeding season, the male loses its bright colors and presents a more subdued plumage similar to the female.
This wader inhabits wetlands, marshes, and riverbanks across Europe and Asia. During the breeding season, males engage in spectacular courtship displays to attract females, including throat inflations and dances. The Ruff primarily feeds on small invertebrates and aquatic plants. It migrates south for the winter. While its population remains relatively stable, it is threatened by habitat loss due to the draining of wetlands and pollution.
The Common rocket frog, scientifically known as Colostethus inguinalis, is a small amphibian species distinguished by its vibrant coloration. It features a bright yellow belly contrasting with a brownish back, often speckled with dark spots. This frog is primarily terrestrial and inhabits the humid tropical forests of Central and South America. It is often observed near water bodies where it breeds. Its distinctive call is an essential means of communication, especially during the breeding season. Although discreet, it plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by regulating insect populations.
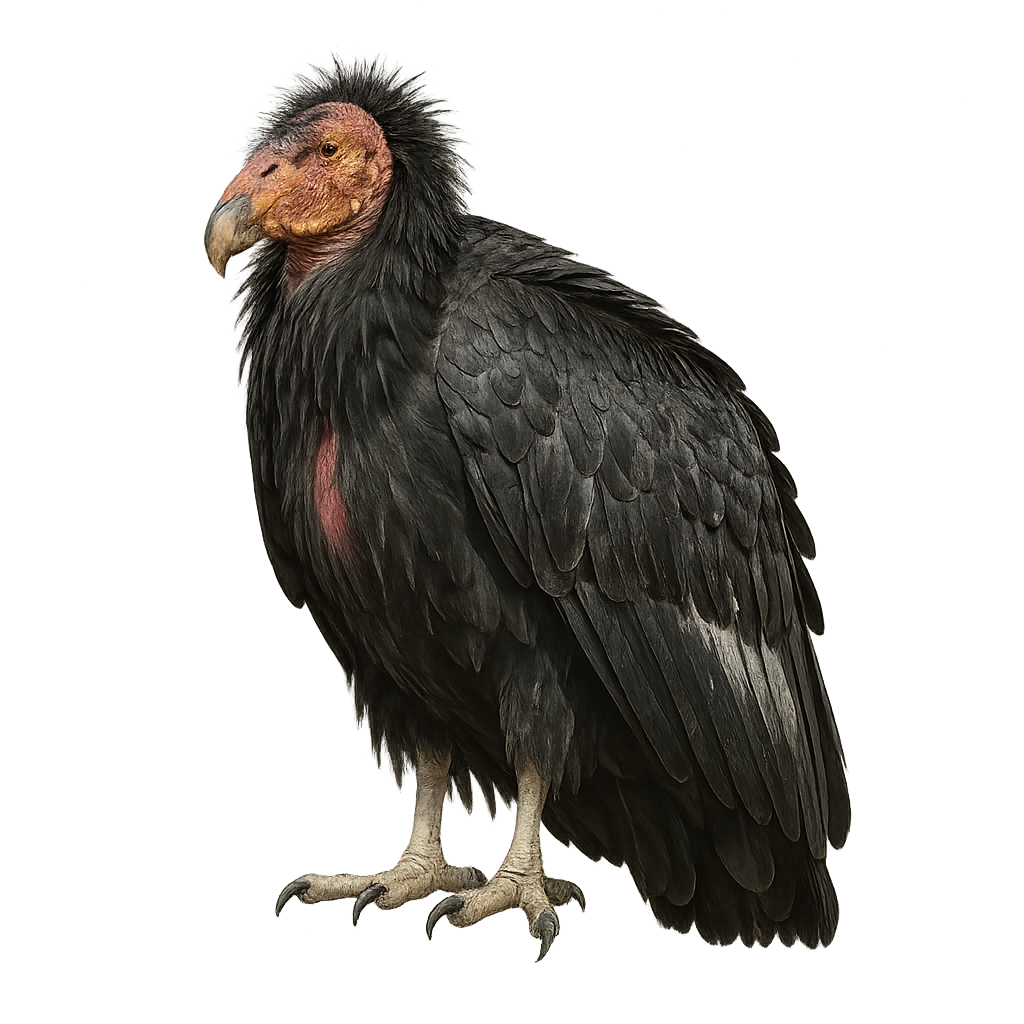
The California condor is a large terrestrial vulture in the family Cathartidae, with a wingspan of 2.7–3.2 m, black plumage and a bare head and neck. It inhabits coastal cliffs and arid canyons, feeding mainly on carrion of large mammals. Pairs nest on cliff ledges, laying one egg every other year.
The Andean condor is one of the largest flying birds in the world, known for its impressive wingspan reaching up to 3.3 meters. It primarily inhabits the Andean mountains, where it feeds on animal carcasses. Its majestic flight and habit of soaring at high altitudes make it a fascinating subject for photographers. Although protected, the Andean condor is threatened by habitat loss and poisoning from consuming contaminated carcasses.
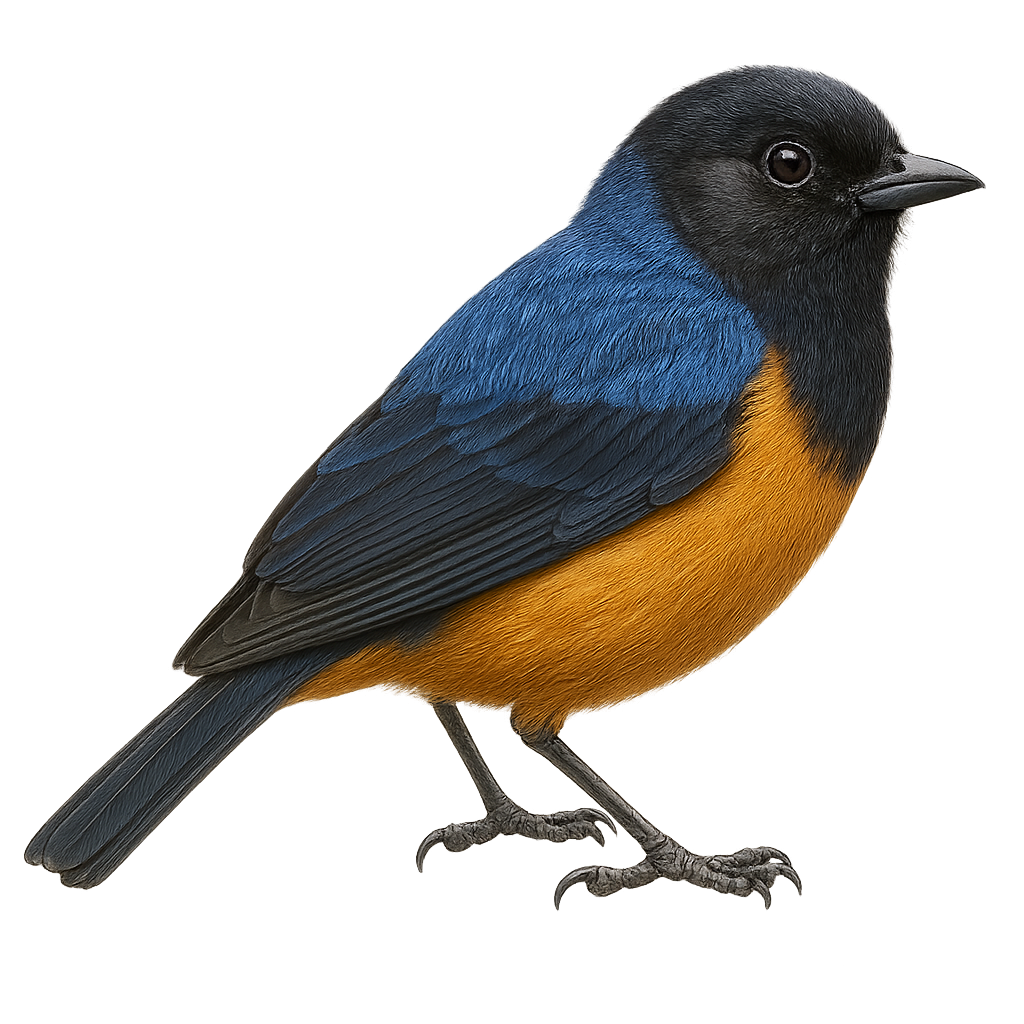
The Blue-backed Conebill is a small bird native to the Andes, easily identified by its bright blue back and distinctive rufous belly. It measures about 12 cm in length and weighs between 10 and 15 grams. Its conical bill is well-suited for its diet, which mainly consists of insects and nectar. This bird is commonly found in humid forests and shrublands at high altitudes. Known for its melodious song and social behavior, it is often seen in small flocks. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it is currently listed as Least Concern by the IUCN.
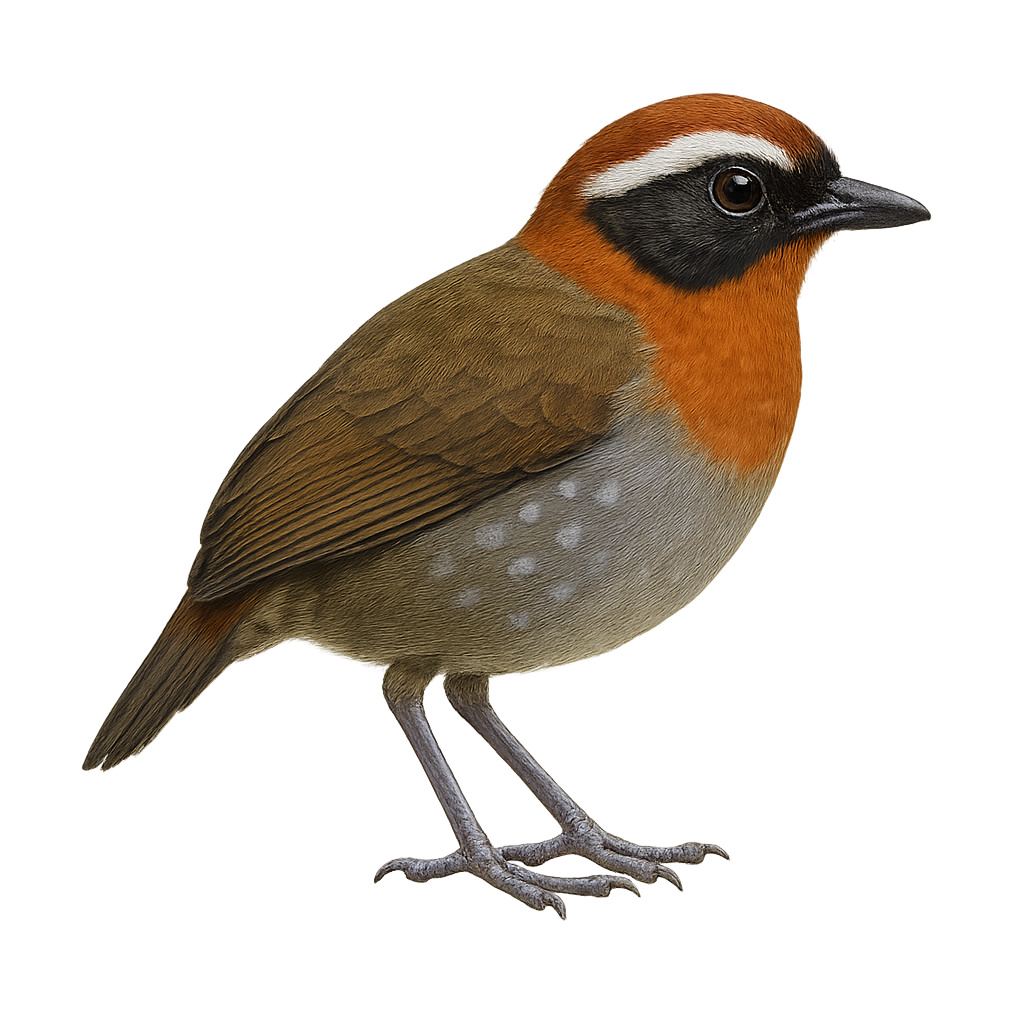
The Black-cheeked Gnateater is a small bird in the Conopophagidae family, primarily found in the humid tropical forests of South America. It is recognizable by its brown and black plumage, with distinctive markings around the eyes that resemble ears, hence its name. This discreet bird prefers dense undergrowth where it primarily feeds on insects. Its modest size and discreet behavior make it difficult to observe. It is often heard before being seen, thanks to its characteristic song. Although not currently threatened, deforestation poses a potential threat to its natural habitat.
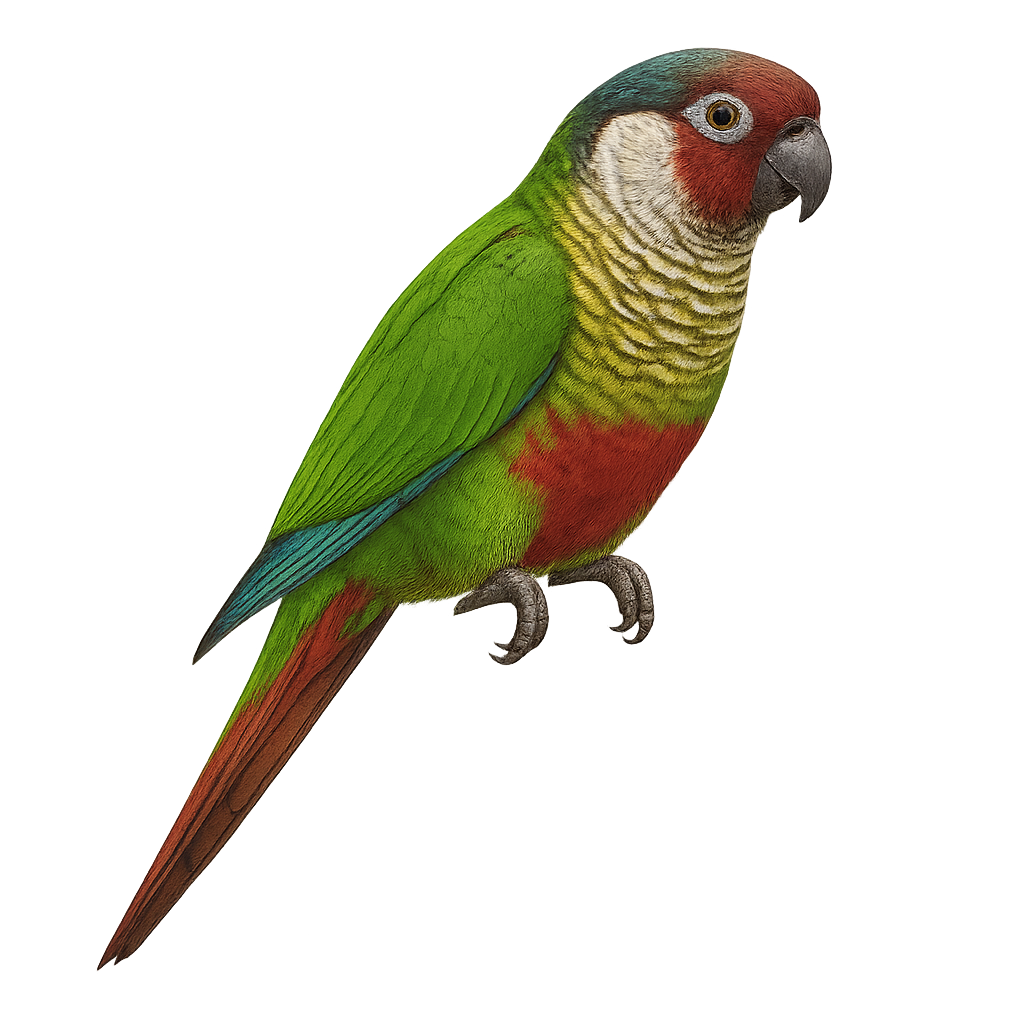
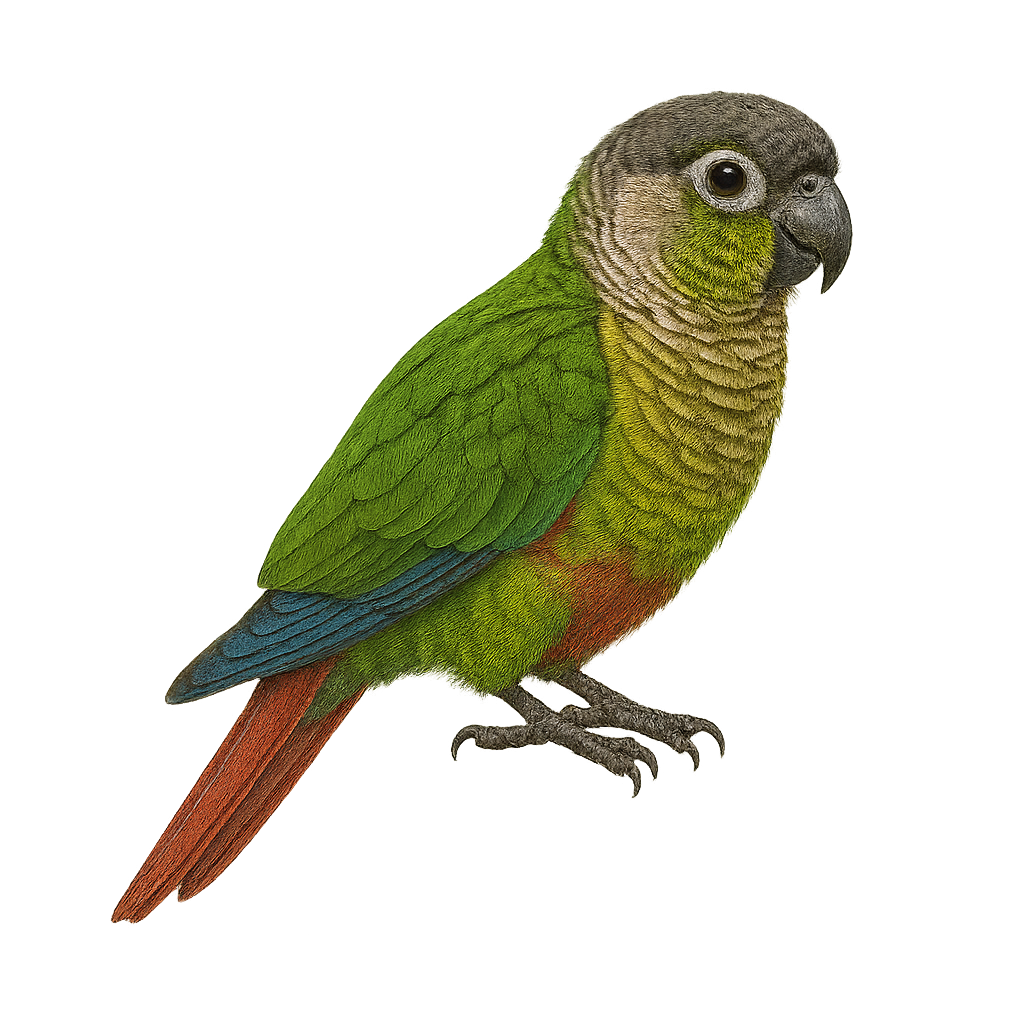
The White-eared Parakeet, or Pyrrhura leucotis, is a small, colorful parrot native to the forests of southeastern Brazil. It is distinguished by its bright green feathers, characteristic white ear patches, and reddish tail. Measuring about 22 cm in length, it is known for its social behavior and ability to form noisy flocks. It primarily feeds on fruits, seeds, and flowers. Although its natural habitat is threatened by deforestation, it adapts well to human-modified environments. This species is often seen in captivity due to its sociable nature and attractive plumage.
The Green-cheeked Parakeet, or Pyrrhura molinae, is a small parrot native to South America, particularly the tropical forests of Brazil, Bolivia, and Argentina. It is recognizable by its bright green plumage, green cheeks, and reddish tail. Measuring about 26 cm in length, it is appreciated for its curious and sociable personality. It lives in groups and primarily feeds on fruits, seeds, and flowers. In captivity, it is often chosen as a pet due to its playful and affectionate nature. Although it can be noisy, it is generally less vocal than other parrots.
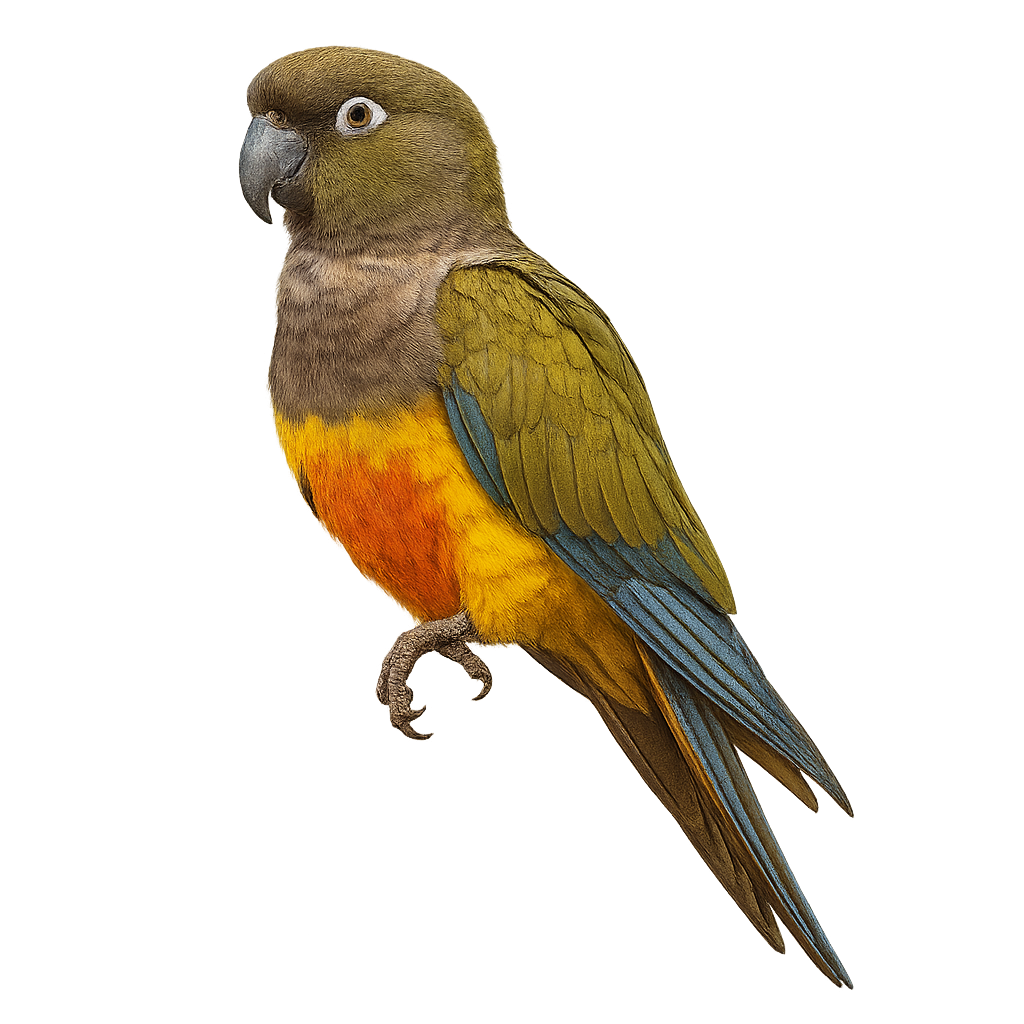
The Burrowing Parrot, Cyanoliseus patagonus, is a medium-sized parrot native to the arid regions of Argentina and Chile. It is distinguished by its predominantly olive-green plumage, with shades of yellow and blue on the wings and head. Its belly features a characteristic reddish hue. These birds live in colonies and are known for digging burrows in cliffs for nesting. Their diet mainly consists of seeds, fruits, and flowers. Although they are sociable among themselves, they can be wary of humans. Their population is stable, but some subpopulations are threatened by habitat loss and illegal capture.
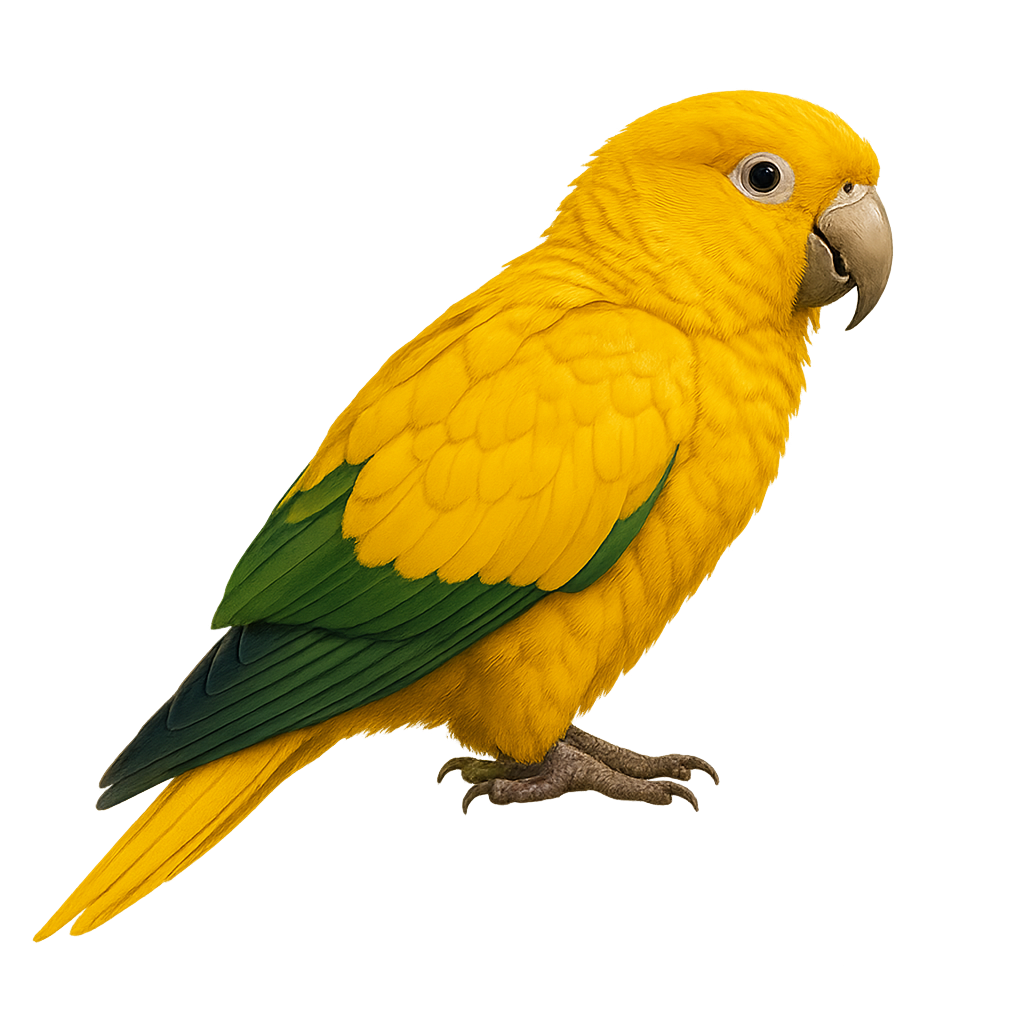
The Golden Parakeet, or Guaruba guarouba, is a medium-sized bird known for its bright yellow plumage and green wings. Native to the Amazon rainforest in Brazil, it is often seen in noisy flocks. This species is threatened by deforestation and illegal trade. It primarily feeds on fruits, seeds, and flowers. Its social behavior is characterized by strong interaction within groups, and it is known for its curious and playful nature. The Golden Parakeet is a symbol of Amazonian biodiversity and the importance of conserving natural habitats.
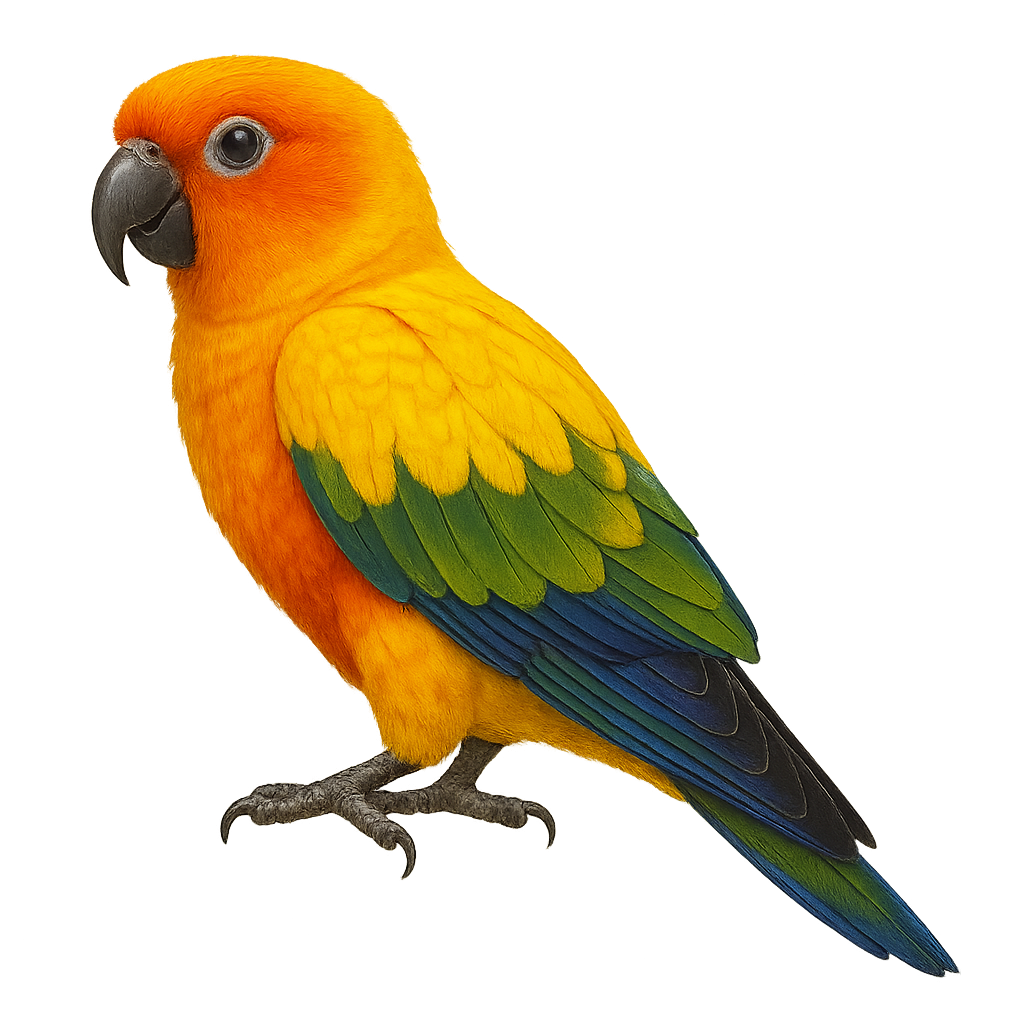
The Sun Conure, or Aratinga solstitialis, is a medium-sized parrot renowned for its vibrant plumage. Native to South America, primarily northeastern Brazil, it displays bright colors ranging from golden yellow to orange, with green touches on its wings and back. This parrot is highly social, living in groups in tropical forests, savannas, and wooded areas. Known for its loud call and ability to mimic sounds, the Sun Conure faces threats from deforestation and the illegal pet trade. It is listed as an endangered species by the IUCN.