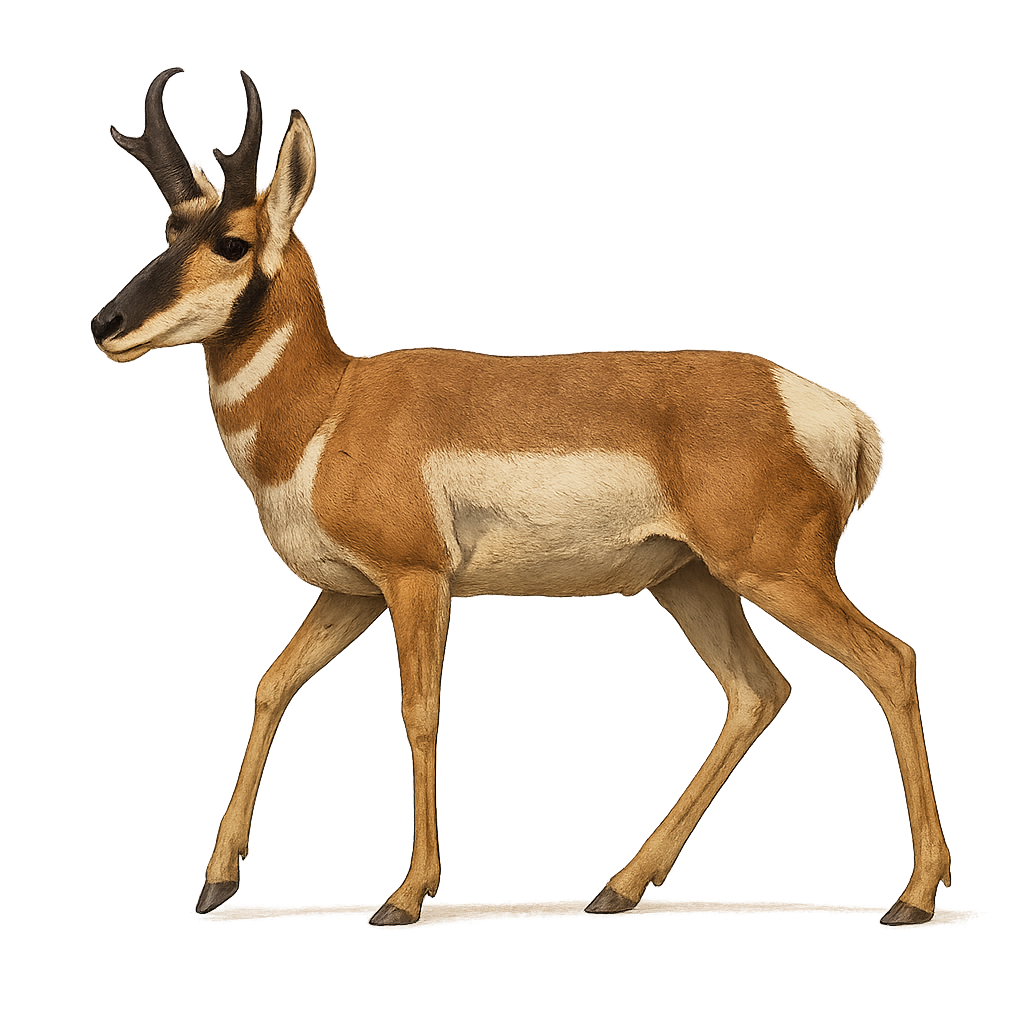
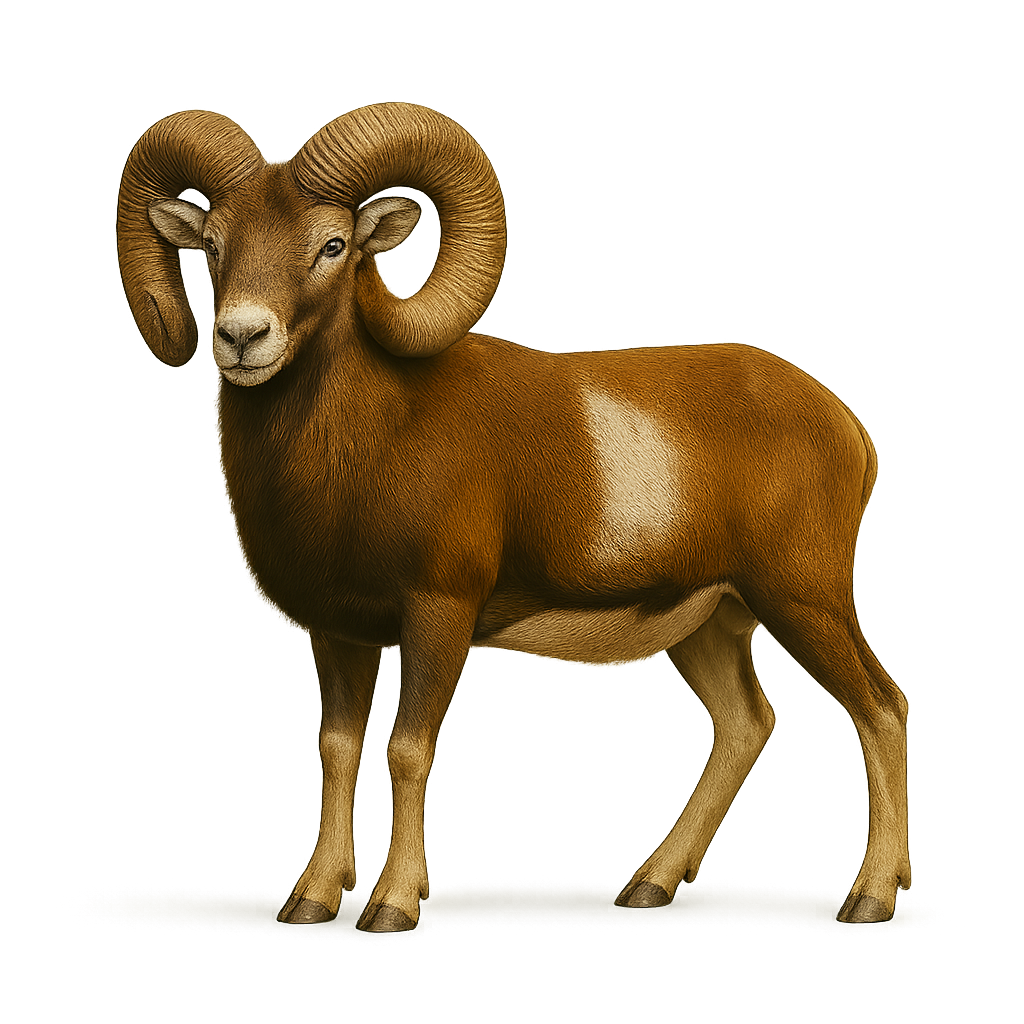
The pronghorn is an ungulate 1.2–1.5 m long and 35–65 kg, with light brown and white striped fur and curved horns. It inhabits grasslands and arid steppes of North America, feeding on herbaceous plants and leaves. During the rut, males loaf near females and perform high-speed intimidation runs.
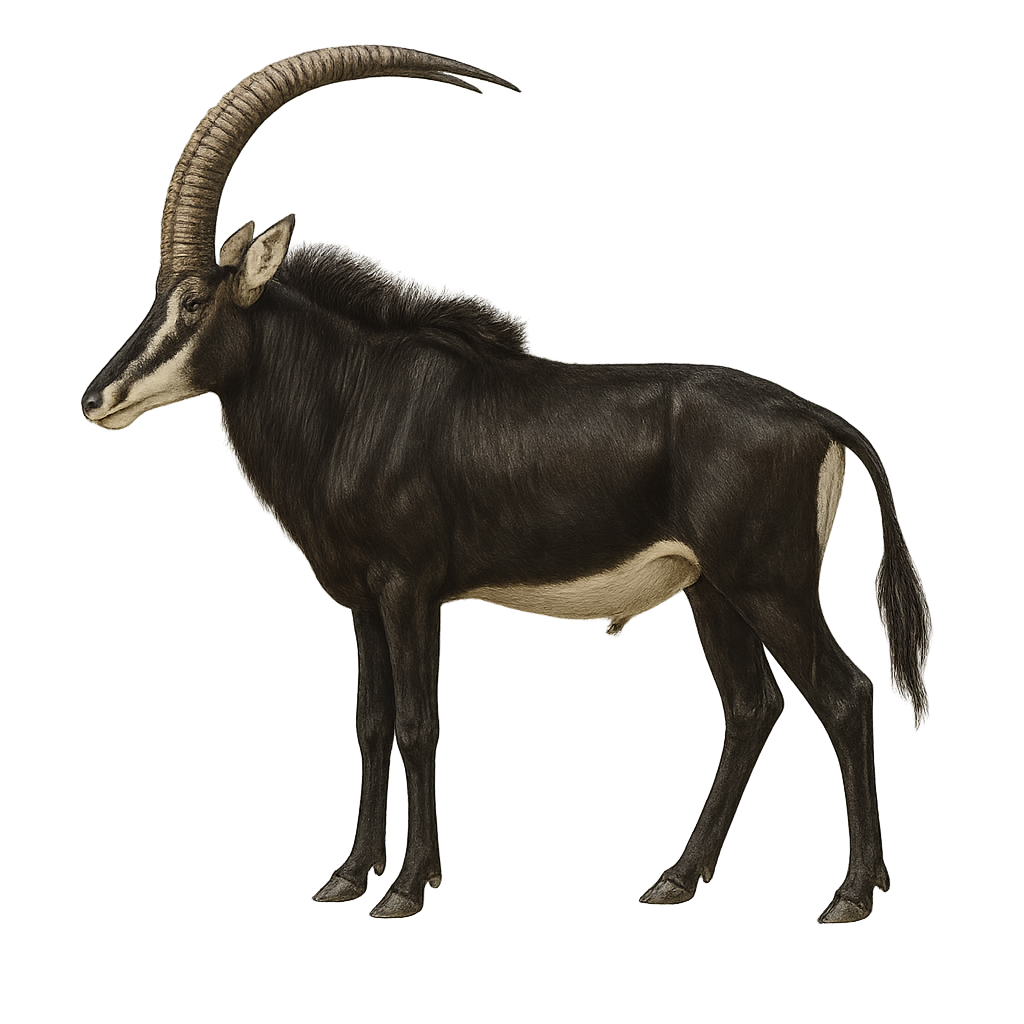
The sable antelope, or Hippotragus niger, is a majestic African herbivore, recognizable by its black coat in adult males and dark brown in females and juveniles. Both sexes have long, backward-curving horns. These animals live in herds, often led by a dominant female, and are primarily found in wooded savannas and open grasslands. Their diet mainly consists of grasses and foliage. Males are territorial and can be aggressive during the rutting season. The sable antelope is an iconic species of African wildlife, admired for its beauty and grace.
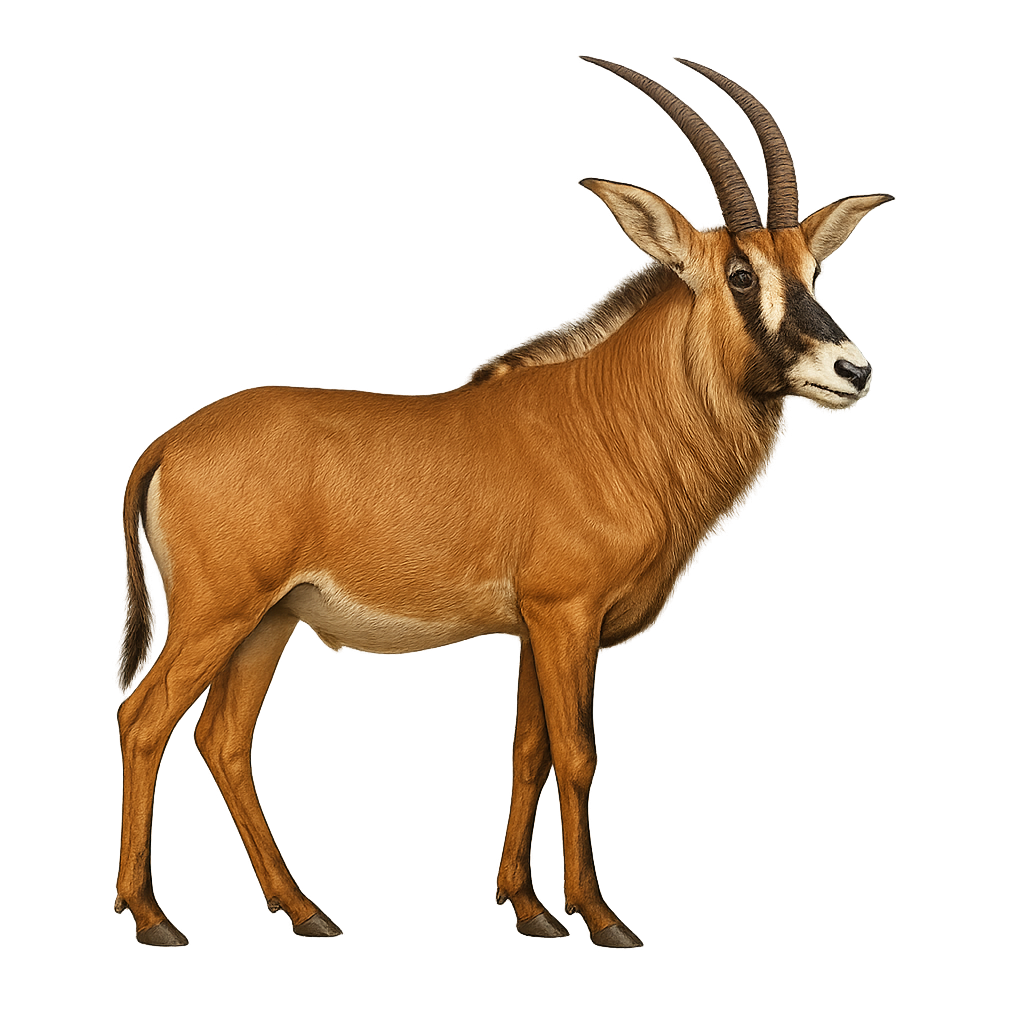
The roan antelope, Hippotragus equinus, is a large African herbivore known for its reddish-brown coat and long, ringed horns. It primarily inhabits the savannas and wooded grasslands of sub-Saharan Africa. Males are slightly larger than females, reaching up to 1.5 meters at the shoulder and weighing around 300 kg. Both sexes have horns that can grow up to a meter long. The roan antelope is a gregarious animal, living in small herds led by a dominant female. It is known for its wary nature and ability to vigorously defend its young from predators.
The four-horned antelope, or Tetracerus quadricornis, is a unique small ruminant, primarily due to its distinctive four horns. Native to the Indian subcontinent, this species prefers dry forests and scrublands where it can blend into the landscape to escape predators. It stands about 55 to 64 cm at the shoulder and weighs between 17 and 22 kg. Its coat ranges from light to dark brown, with a lighter belly. Males sport two pairs of horns, the longest reaching up to 12 cm. The four-horned antelope is a solitary animal, except during the breeding season. It is primarily herbivorous, feeding on leaves, fruits, and young shoots.
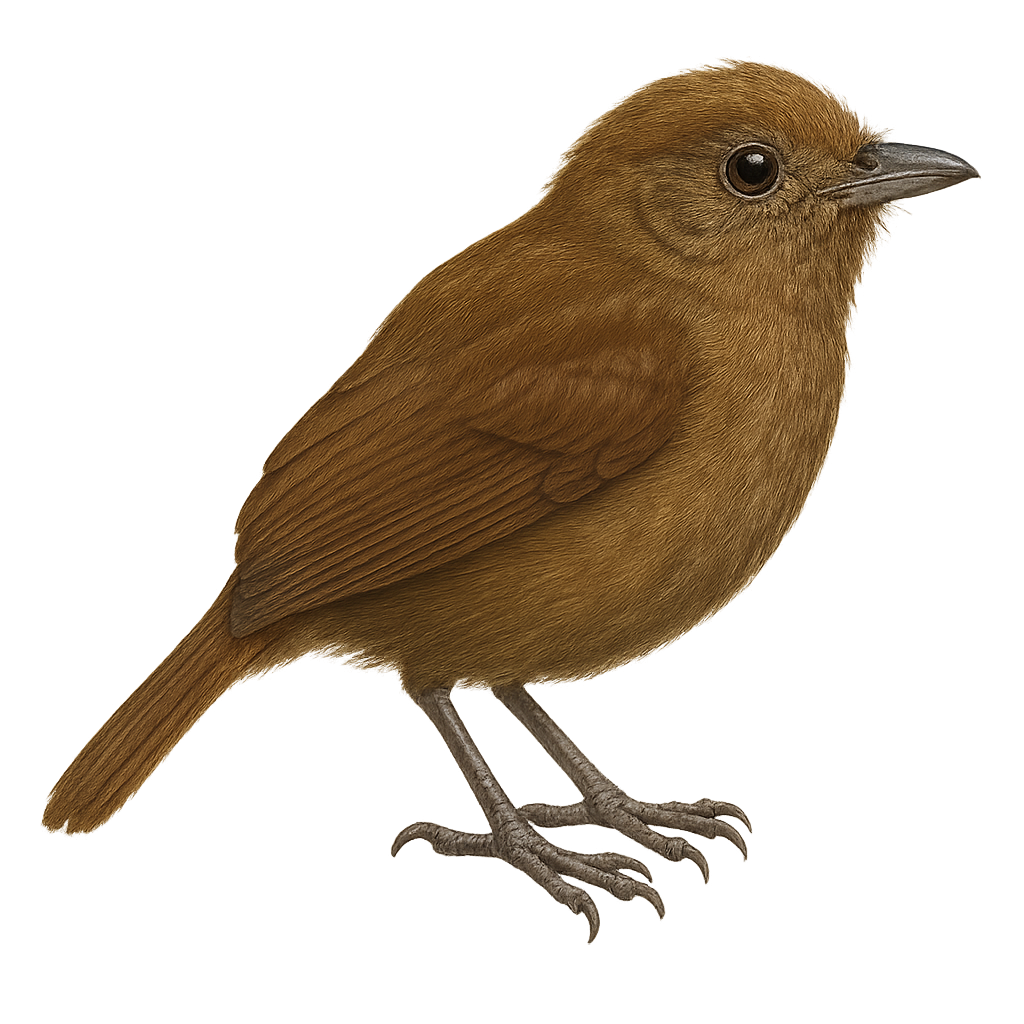
The Brown Schiffornis is a discreet and mysterious bird, often difficult to spot due to its reserved behavior. It primarily inhabits the humid tropical forests of Central America, notably in Guatemala and Honduras. This medium-sized bird has a uniform brown plumage that allows it to blend into its surroundings. Its melodious and enchanting song is often the first clue to its presence. It feeds mainly on insects and fruits, which it captures by moving slowly through the canopy. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, the Brown Schiffornis remains relatively common in protected areas.
The Bar-throated Apalis is a small passerine bird from the Cisticolidae family, predominantly found in the mountainous regions of southern Africa. It is characterized by its black throat, contrasting with a white belly and olive-grey back. Males and females look similar, although males may exhibit slightly brighter colors. This bird is often seen in pairs or small groups, actively moving through dense bushes and forests in search of insects. Its song is melodious and varied, often used to mark its territory. The Bar-throated Apalis is a resilient bird, capable of adapting to various habitats, though it prefers wooded areas and dense thickets.
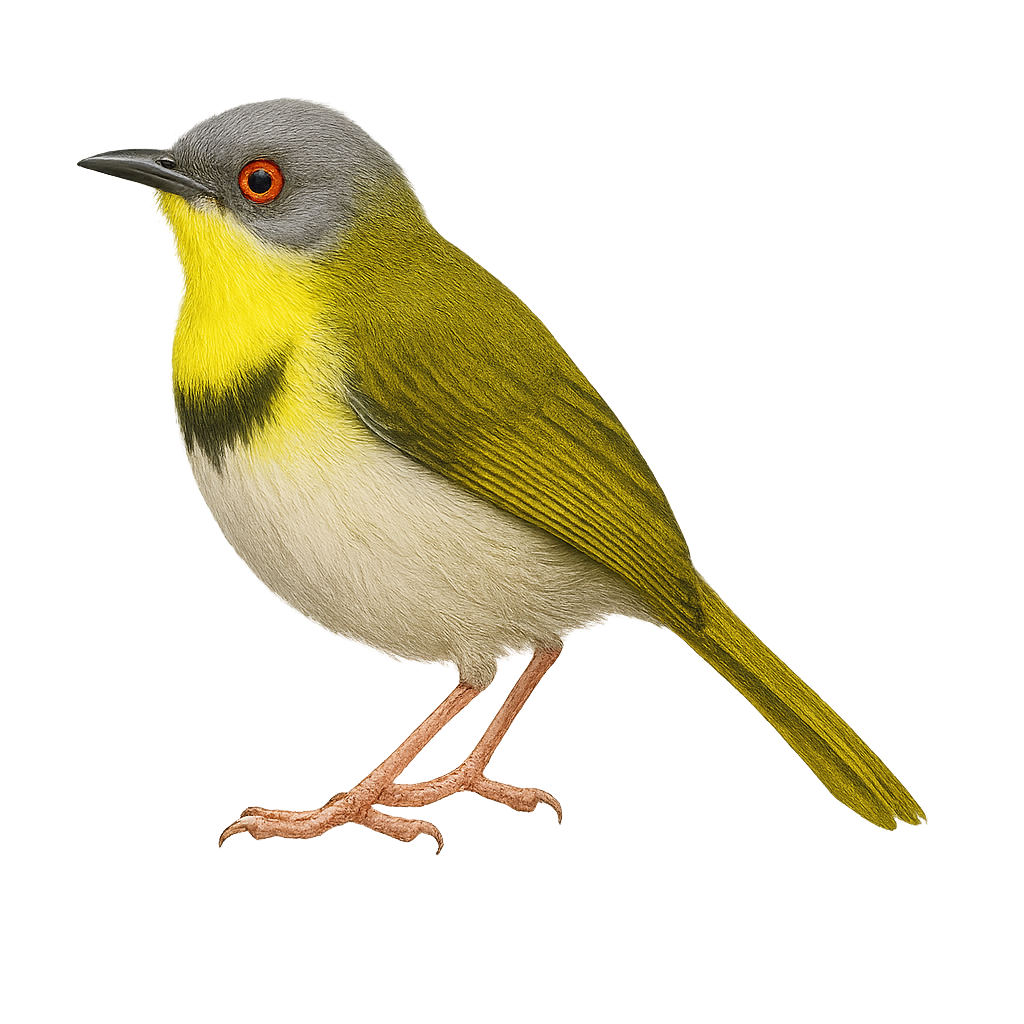
The Yellow-breasted Apalis is a small passerine bird belonging to the Cisticolidae family, primarily found in sub-Saharan Africa. It measures about 11 to 13 cm in length and is distinguished by its bright yellow throat, white belly, and olive-green back. Its natural habitat includes dry forests, savannas, and shrublands. This bird is often seen in pairs or small groups, feeding mainly on insects and small invertebrates. Its song is a melodious trill, often heard at dawn. Although widely distributed, it is sometimes threatened by deforestation and habitat loss.
The Rufous-throated Apalis is a small passerine bird belonging to the Cisticolidae family. It is primarily found in the tropical and subtropical forests of Central and East Africa. This bird is distinguished by its reddish throat, which contrasts with its white belly and olive-grey back. The wings and tail are generally darker, providing a nice contrast with the rest of the plumage. The Rufous-throated Apalis is an active bird, often observed in small groups or pairs, moving quickly through foliage in search of insects and spiders. Its song is a soft, melodious trill, often heard before the bird is seen. Although not considered threatened, deforestation and habitat loss pose potential threats to its populations.
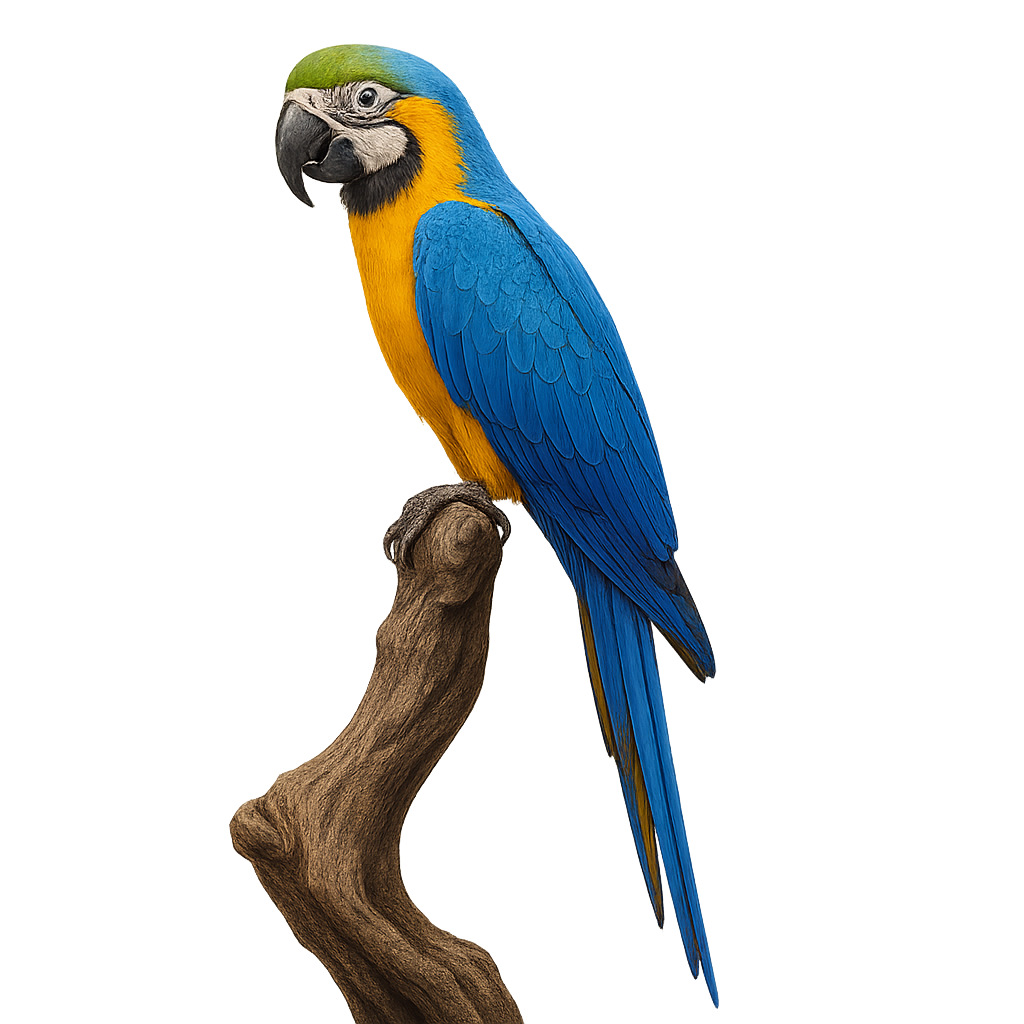
The Blue-and-yellow Macaw, or Ara ararauna, is a striking parrot native to the tropical forests of South America. Known for its vibrant blue plumage and bright yellow belly, this bird is a symbol of Amazonian biodiversity. Measuring about 86 cm in length, it has a strong beak suited for consuming nuts and fruits. Sociable and intelligent, the Blue-and-yellow Macaw lives in groups and communicates through a variety of calls. It plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding forest regeneration. Unfortunately, it is threatened by deforestation and illegal trade, although conservation efforts are underway to protect its natural habitat.
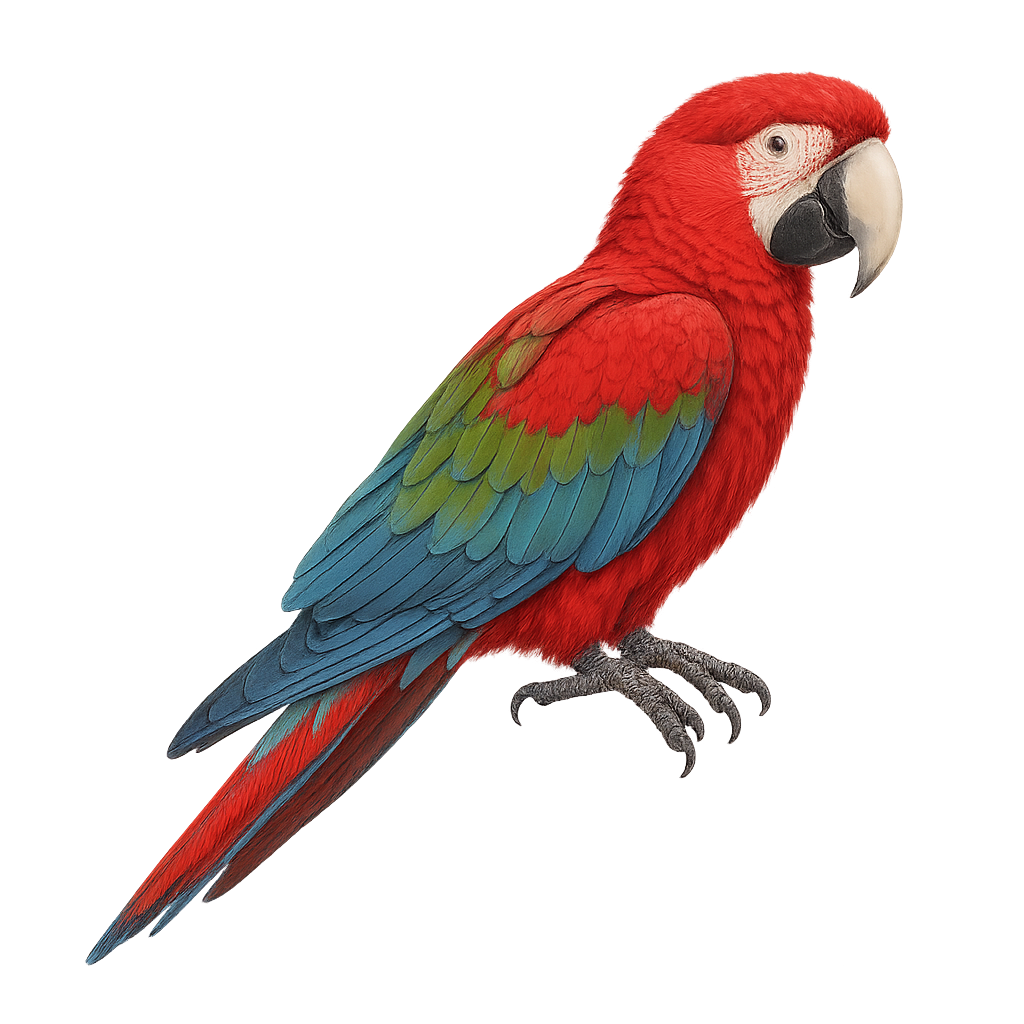
The Red-and-green Macaw, scientifically known as Ara chloropterus, is a large parrot species native to the tropical rainforests of South America. It is renowned for its striking red plumage, complemented by green and blue on its wings and tail. These macaws are highly intelligent and social, often seen in pairs or small family groups. They feed primarily on fruits, nuts, and seeds. With a length of about 90 to 95 cm and a wingspan that can be quite impressive, they are a sight to behold. In captivity, they can live up to 50 years, making them a long-term commitment for bird enthusiasts.
The Hyacinth Macaw, or Anodorhynchus hyacinthinus, is the largest parrot in the world, reaching up to one meter in length. Its striking cobalt blue plumage and powerful beak make it a remarkable bird. Native to the tropical regions of South America, particularly Brazil, it primarily inhabits rainforests and savannas. Although sociable, it is often seen in small groups or pairs. Its diet mainly consists of palm nuts, which it easily cracks with its strong beak. Unfortunately, the species is threatened by deforestation and illegal trade, leading to a significant decline in its population.
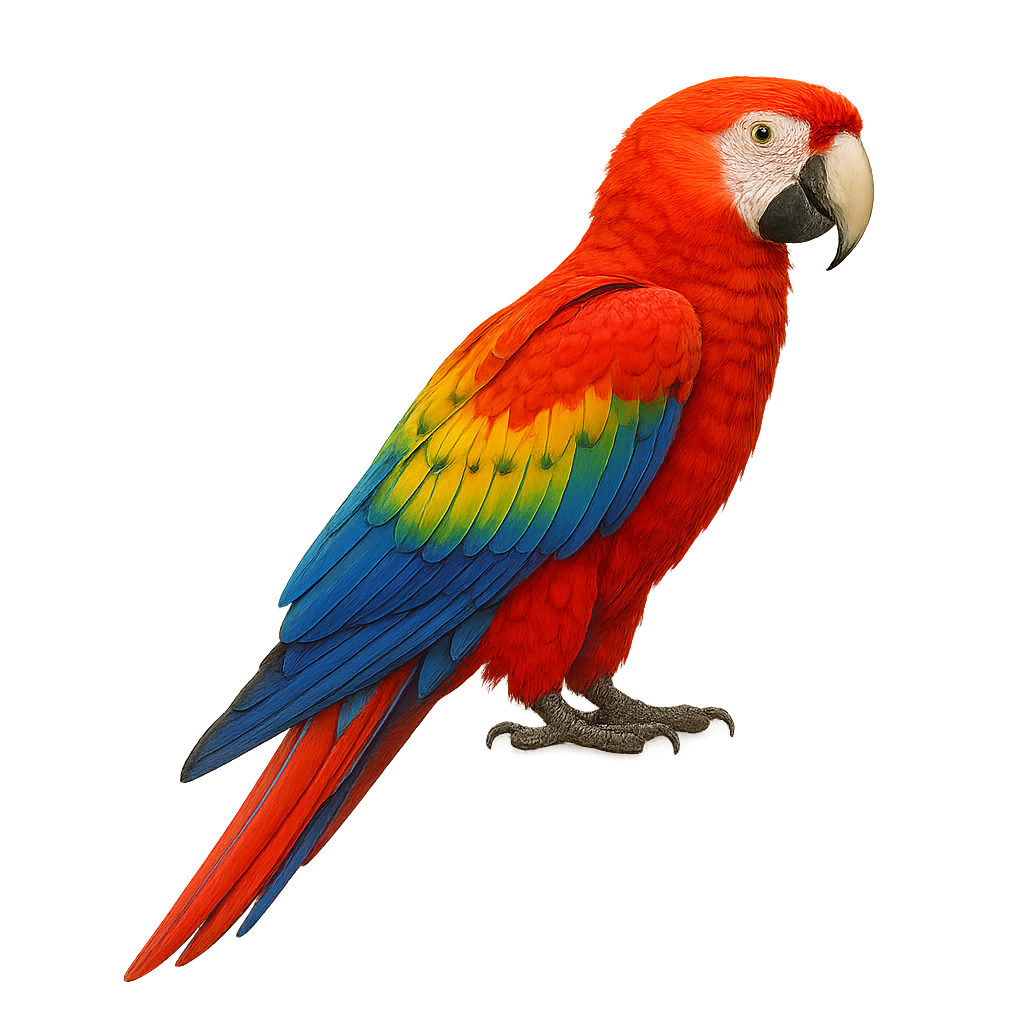
The Scarlet Macaw is one of the most iconic and colorful parrots, easily recognized by its vibrant red, blue, and yellow plumage. This large parrot primarily inhabits the humid tropical forests of Central and South America, where it feeds on fruits, nuts, and seeds. The Scarlet Macaw is a social bird, living in groups and possessing a highly developed vocal behavior. Its powerful call is often heard throughout the forest canopy. It is also known for its ability to fly long distances, gliding with grace and agility.
Unfortunately, the Scarlet Macaw is threatened in certain regions due to habitat loss and illegal wildlife trade. Conservation efforts are underway to protect this majestic species.
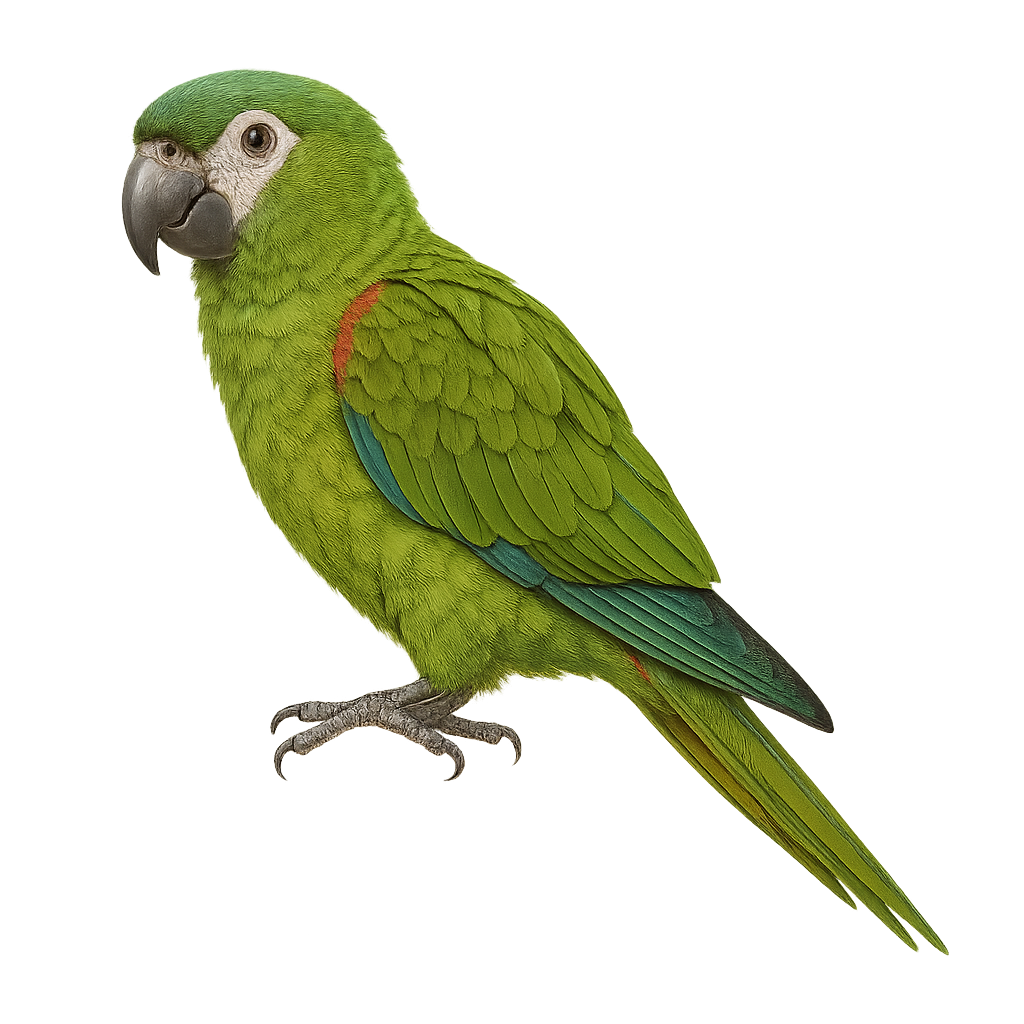
The Red-shouldered Macaw, or Diopsittaca nobilis, is a small, colorful parrot native to South America. It is distinguished by its bright green plumage, red shoulders, and black beak. Measuring about 30 cm in length, it is one of the smallest macaws. Its natural habitat includes tropical forests, savannas, and wooded areas. The Red-shouldered Macaw is known for its intelligence and ability to mimic sounds. It lives in social groups and primarily feeds on seeds, fruits, and nuts. Although often kept as a pet, it requires special attention and a stimulating environment to thrive.
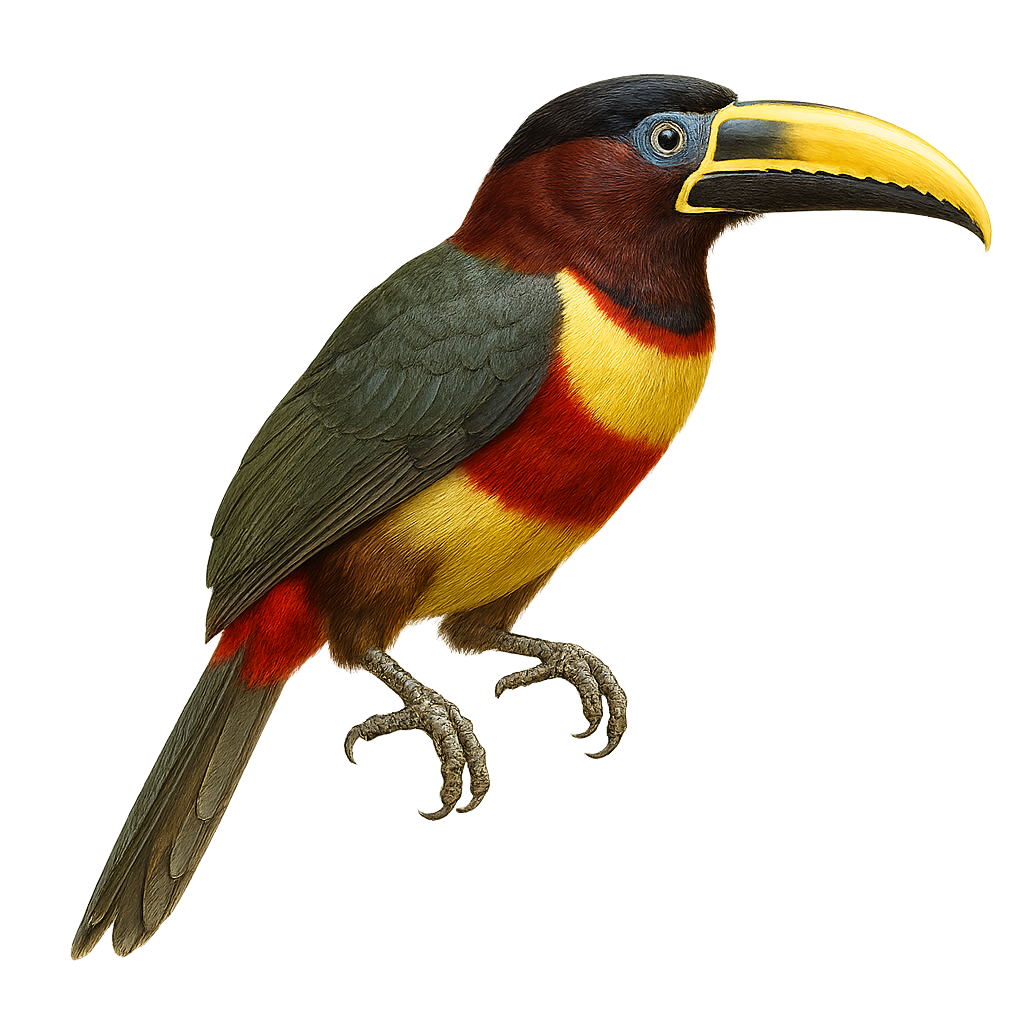
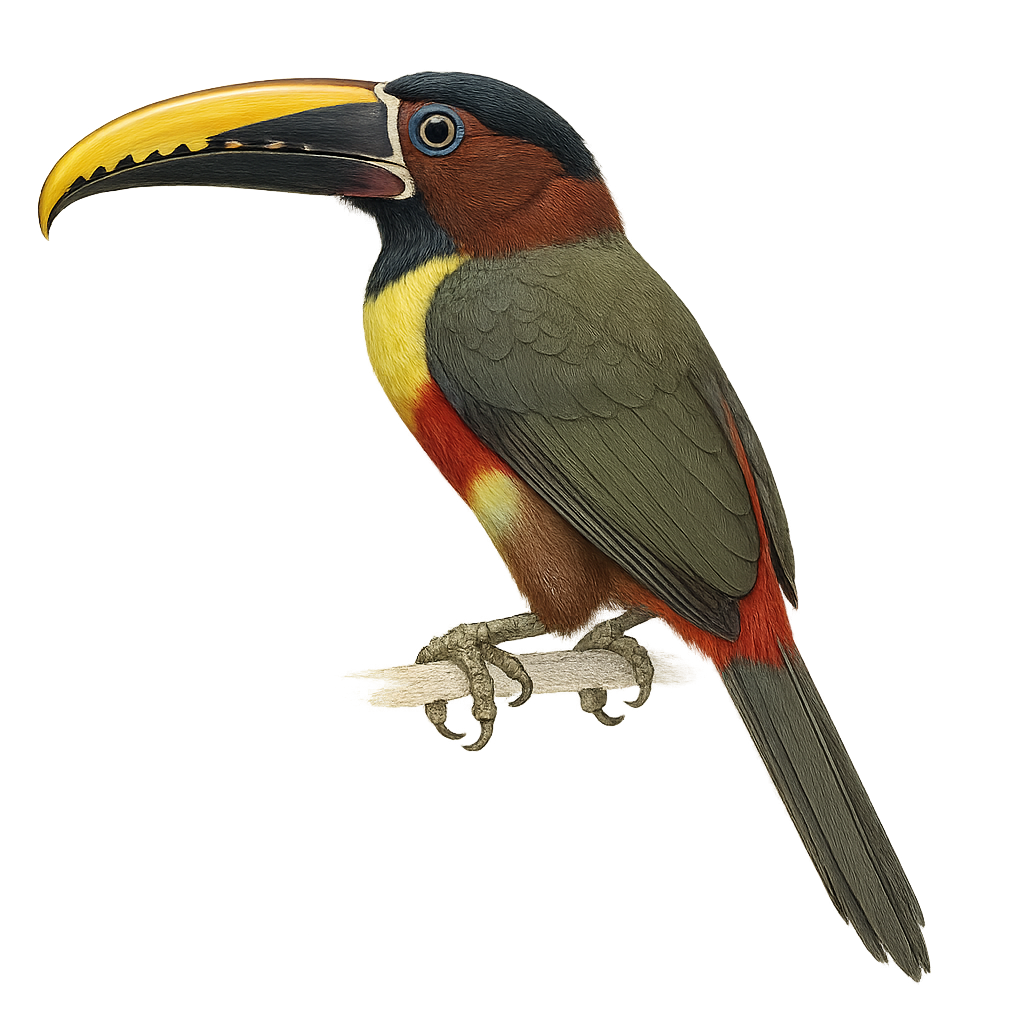
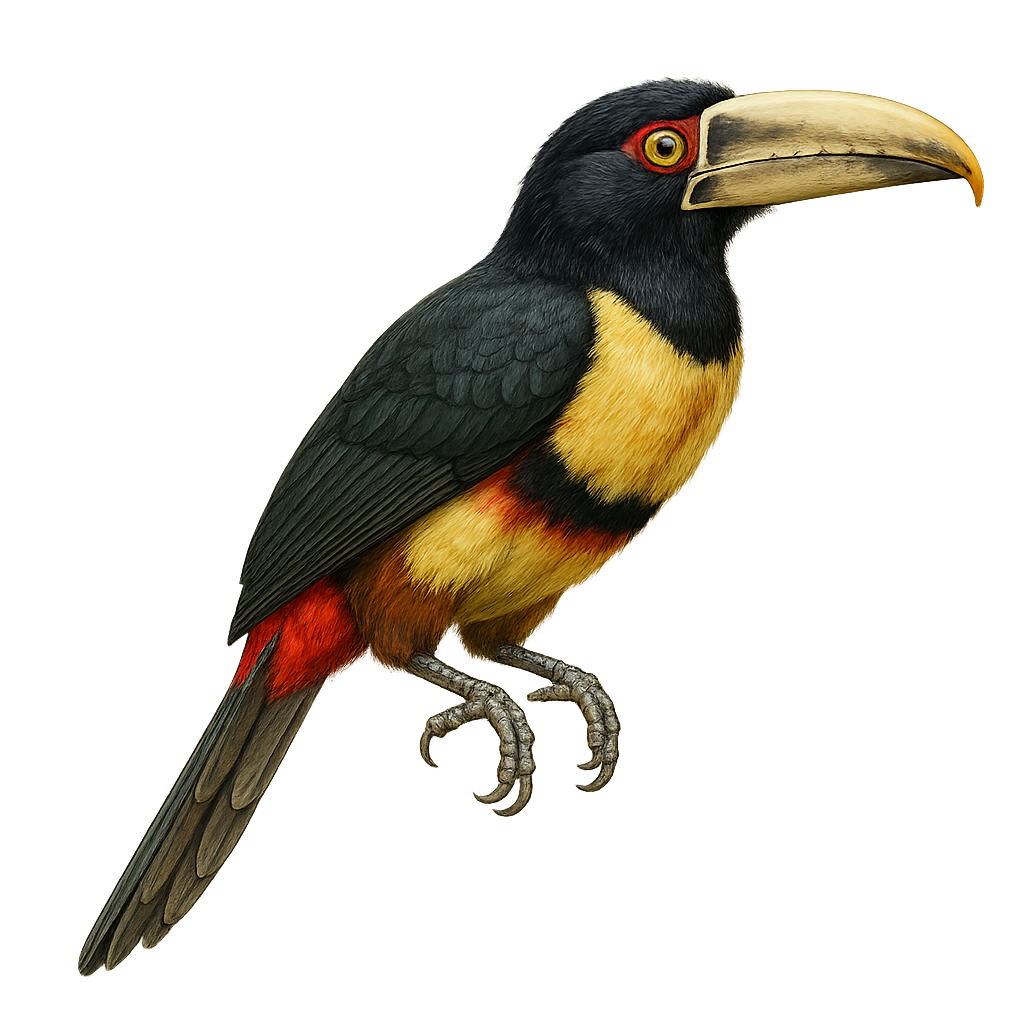
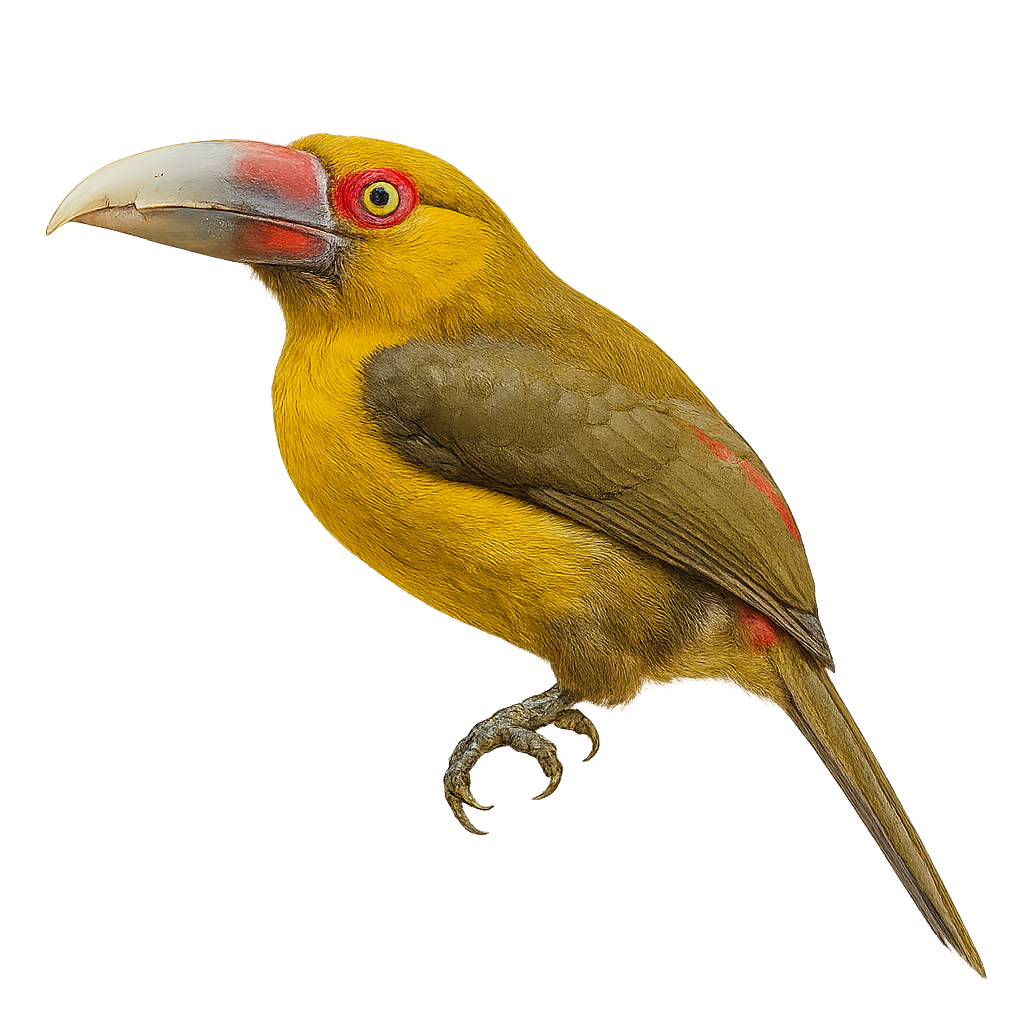
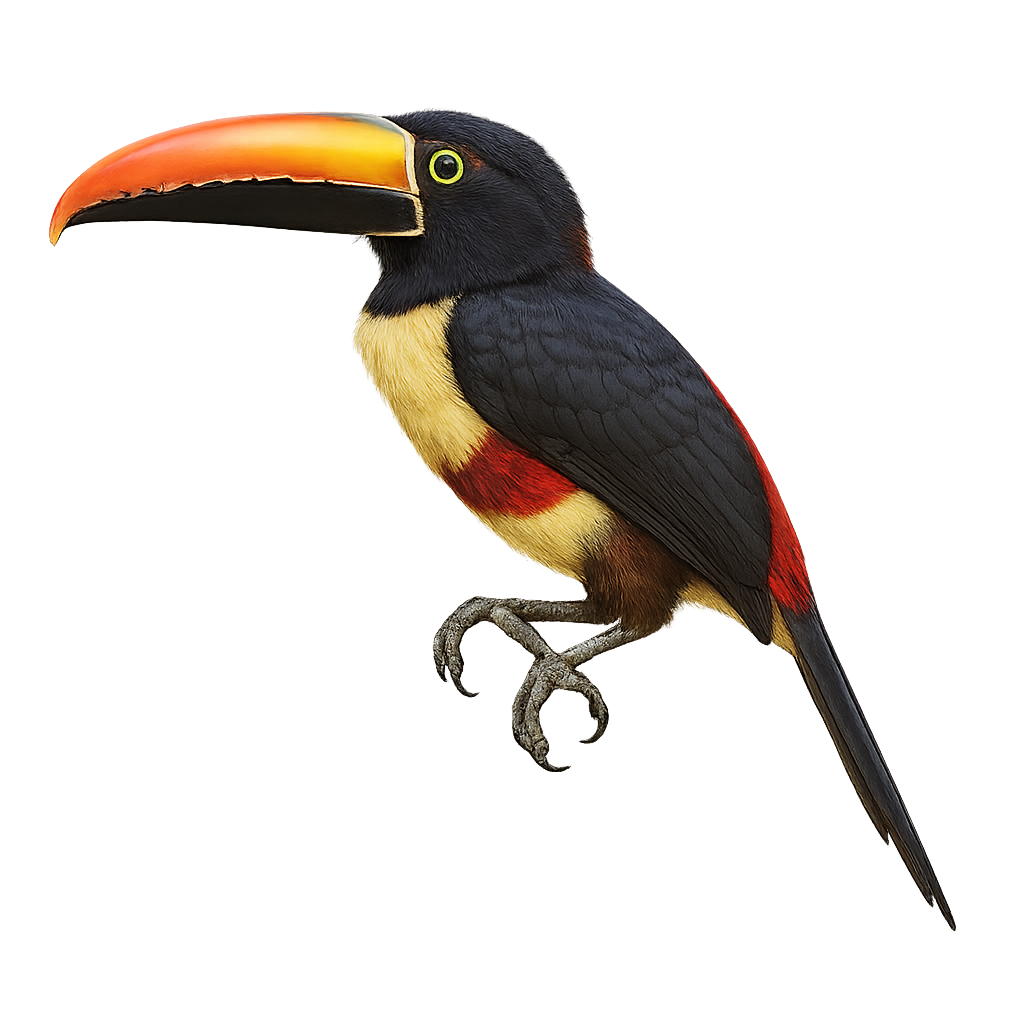
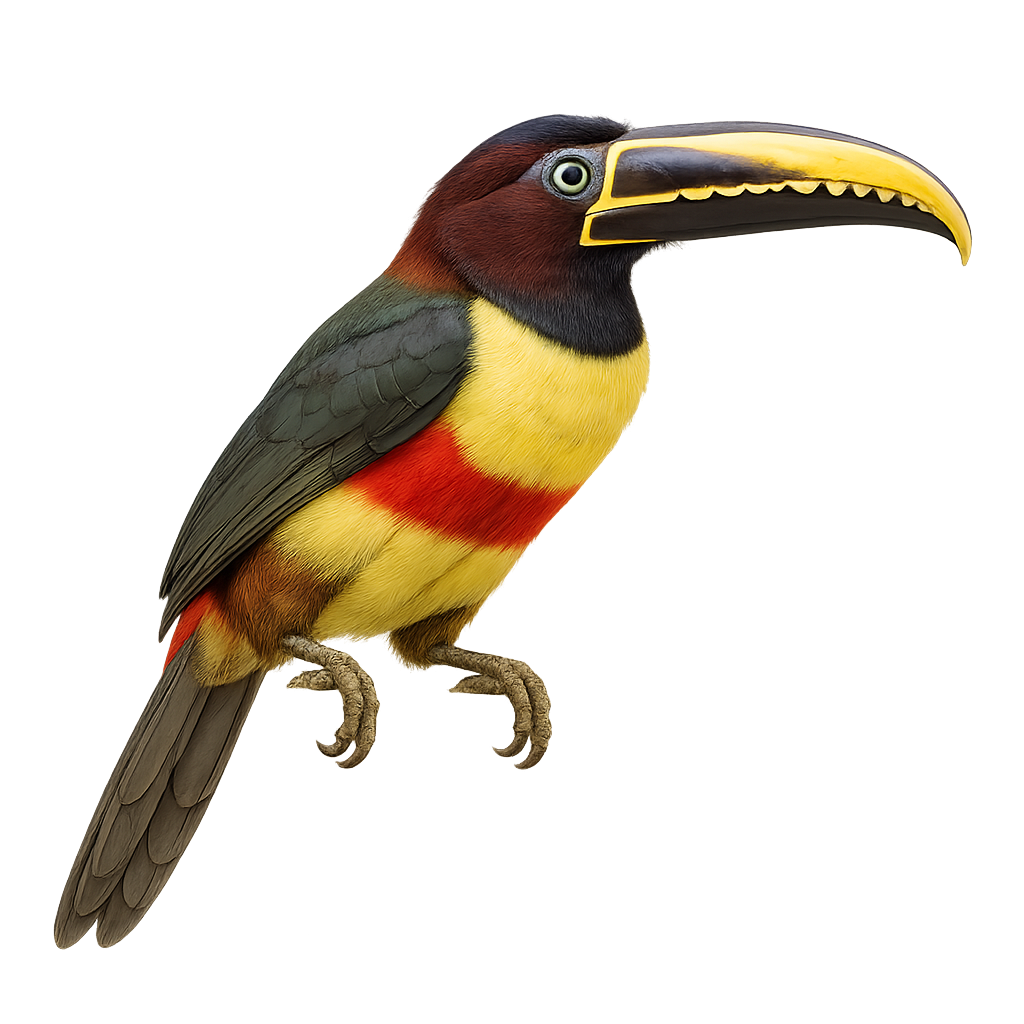
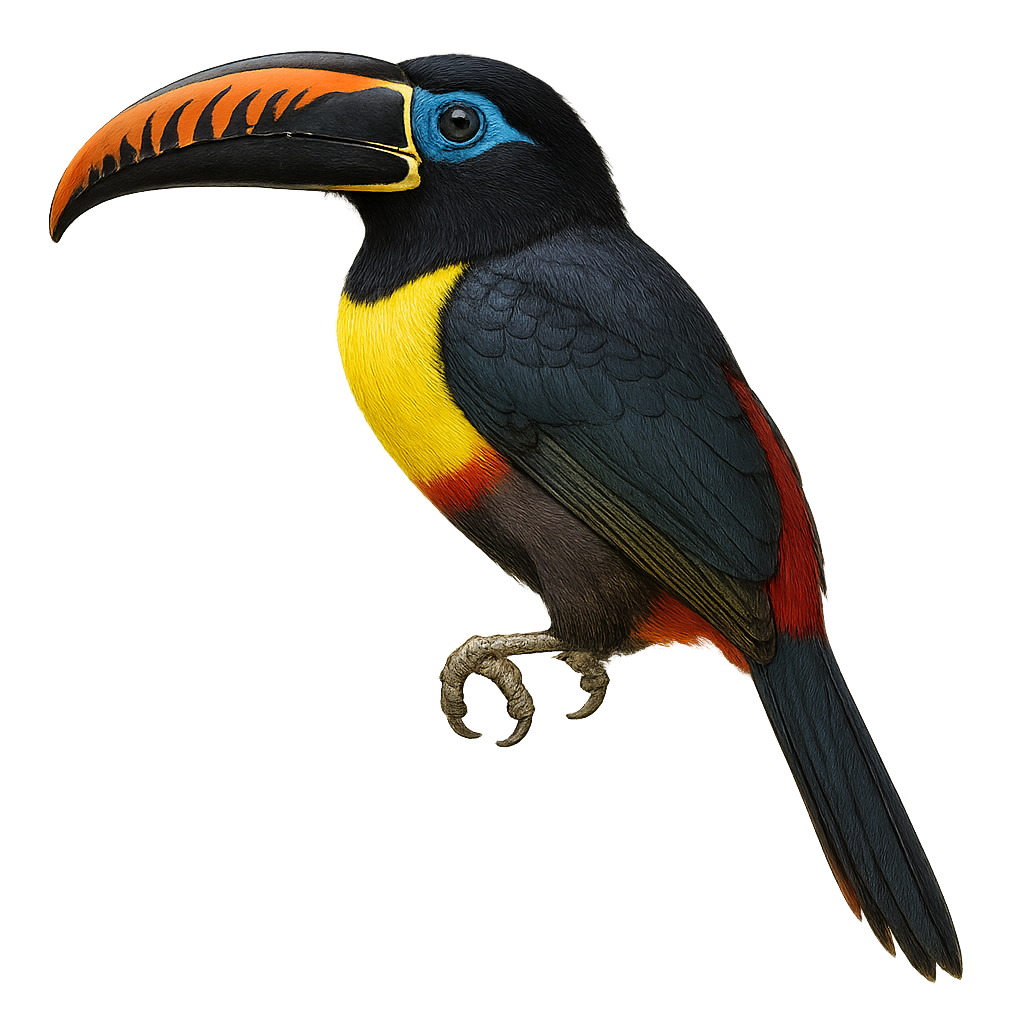
The Red-necked Aracari, or Pteroglossus bitorquatus, is a colorful bird from the Ramphastidae family, native to the tropical rainforests of South America, particularly Brazil. It is distinguished by its vibrant plumage, with a black head, bright red neck, and olive-green body. Its long, curved bill, typical of toucans, features colorful patterns. This bird measures about 35 to 40 cm in length and weighs between 150 and 200 grams. It lives in small groups and primarily feeds on fruits, but also insects and small vertebrates. The Red-necked Aracari plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, thus contributing to forest regeneration.
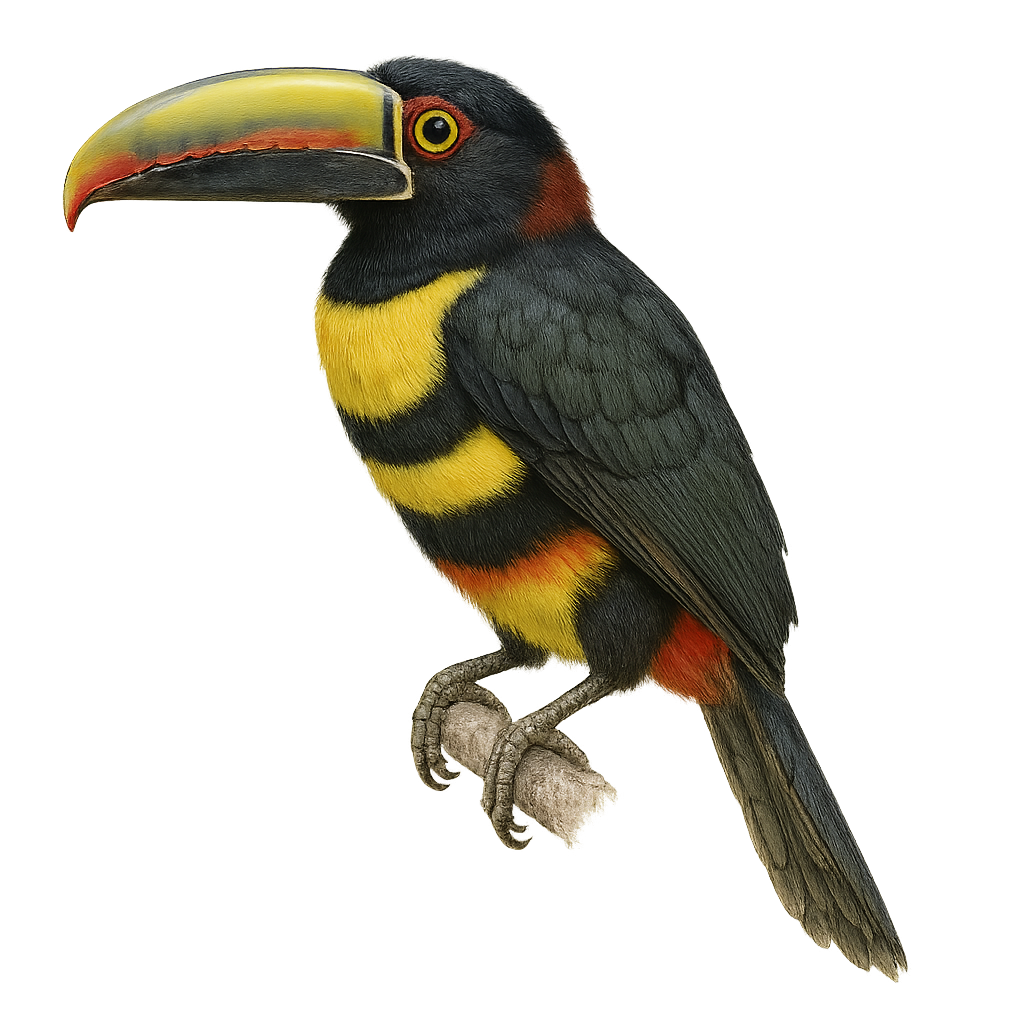
The Chestnut-eared Aracari is a colorful bird from the Ramphastidae family, known for its vibrant plumage and distinctive bill. It features bright colors with shades of green, yellow, and red, along with its characteristic chestnut-colored ear patches. This bird measures about 34 to 45 cm in length. It primarily inhabits the tropical rainforests of South America, notably in Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay, and Argentina. The Chestnut-eared Aracari is a social bird, often seen in small groups. It mainly feeds on fruits, but also consumes insects and small vertebrates. Its presence is an indicator of the health of tropical forests, as it plays a crucial role in seed dispersal.
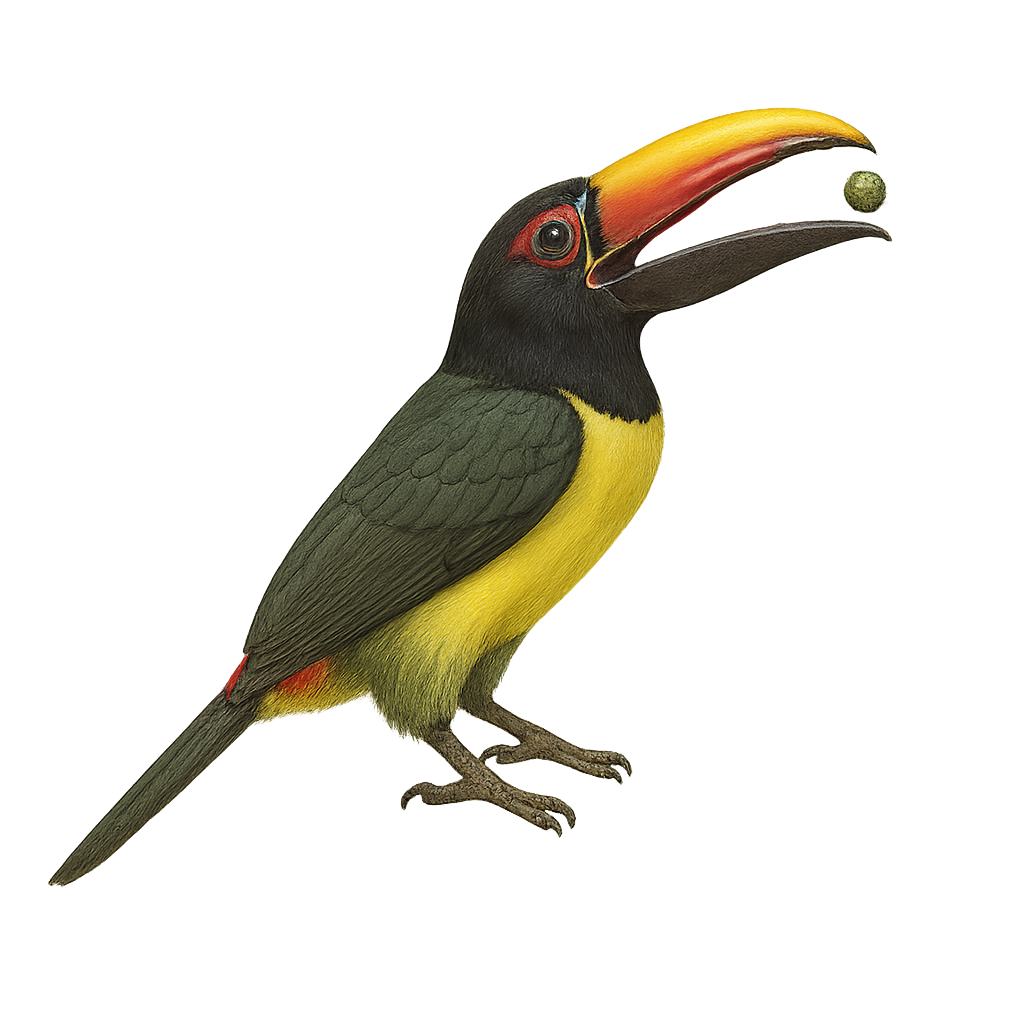
The Azara's Tanager is a colorful bird belonging to the toucan family. It is distinguished by its vibrant plumage, mainly black with touches of red, yellow, and green. Its long, curved beak is typical of toucans and features distinctive patterns. This bird measures about 30 to 40 cm in length. It primarily inhabits the tropical rainforests of South America, notably in Brazil, Bolivia, and Paraguay. The Azara's Tanager is a social bird, often seen in small groups. It mainly feeds on fruits but also consumes insects and small vertebrates. Although not considered threatened, deforestation poses a potential threat to its natural habitat.
The Baillon's Aracari is a colorful bird belonging to the Ramphastidae family. It is distinguished by its vibrant plumage, mixing shades of green, red, and yellow, and its large, multicolored beak. This bird measures about 35 cm in length and weighs between 150 and 200 grams. It primarily inhabits the humid tropical forests of South America, where it feeds on fruits, insects, and sometimes small vertebrates. Sociable, it often lives in small groups and is quite tolerant of human presence. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it is currently classified as least concern by the IUCN.
The Curl-crested Aracari is a captivating bird belonging to the Ramphastidae family. It is distinguished by its vibrant plumage and a unique curly crest on its head, giving it a distinctive appearance. Its long, colorful bill, typical of toucans, plays a crucial role in its diet, which mainly consists of fruits, but also includes insects and small vertebrates. This bird primarily inhabits the tropical rainforests of South America, particularly in Brazil. It is often seen in small groups, moving agilely among the trees. Although its conservation status is concerning due to deforestation, it remains a vibrant symbol of Amazonian biodiversity.
The Fiery-billed Aracari is a colorful and fascinating bird, endemic to the humid tropical forests of Costa Rica and western Panama. It is distinguished by its large, colorful bill, primarily orange-red with a black base. Its plumage is a vibrant mix of green, yellow, and red, making it easily recognizable. This bird measures about 40 cm in length and weighs between 200 and 250 grams. It typically lives in small groups and primarily feeds on fruits, but it can also consume insects and small vertebrates. The Fiery-billed Aracari plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, thus contributing to forest regeneration.
The Collared Aracari is a colorful bird from the toucan family, recognizable by its long, curved beak adorned with distinctive patterns. It features primarily black plumage with a red chest band and a bright yellow belly. This bird measures about 40 to 45 cm in length and weighs between 190 and 275 grams. It inhabits the tropical rainforests of Central and South America, feeding on fruits, insects, and occasionally small vertebrates. Sociable by nature, it often moves in small family groups. Although relatively common, deforestation poses a threat to its natural habitat.
The Lettered Aracari, or Pteroglossus inscriptus, is a vibrant bird from the toucan family, primarily inhabiting the tropical forests of South America. It is recognized for its striking plumage, which combines shades of green, yellow, and red, and its large, intricately patterned bill. This bird measures about 30 to 35 cm in length and weighs between 130 and 160 grams. Often seen in small groups, it feeds mainly on fruits, but also on insects and small vertebrates. The Lettered Aracari plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding forest regeneration. Although relatively common, its natural habitat is threatened by deforestation.
The Many-banded Aracari, a captivating bird from the Ramphastidae family, is known for its colorful plumage and large bill. Native to the humid tropical forests of South America, particularly the Amazon, it is often seen in small groups. Its plumage features a vibrant mix of colors, with distinct bands on its body and bill. This bird is primarily frugivorous but can also consume insects and small vertebrates. It plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding forest regeneration. Although relatively tolerant of human presence, respecting its natural habitat is vital for its survival.
The Green Aracari, Pteroglossus viridis, is a colorful bird from the Ramphastidae family. It is distinguished by its bright green plumage, large bill, and red and yellow markings on its head and neck. This bird measures about 30 to 35 cm in length and weighs between 110 and 160 grams. It primarily inhabits the tropical rainforests of South America, particularly in Venezuela, Guyana, and northern Brazil. Arboreal, it mainly feeds on fruits but also consumes insects and small vertebrates. Sociable, it often lives in small family groups. Its call is a series of high-pitched, repetitive cries. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, the species is currently classified as "Least Concern" by the IUCN.
The Pileated Finch, or Coryphospingus pileatus, is a small bird with distinctive plumage, primarily bright red on the head and body, with shades of gray on the wings and tail. It is often observed in wooded regions and savannas of South America, notably in Brazil, Bolivia, and Paraguay. This passerine is known for its melodious song and its ability to adapt to various habitats, although it prefers open areas with bushes and sparse trees. It primarily feeds on seeds and insects, which it finds by foraging on the ground or exploring low vegetation. The Pileated Finch is a sociable bird, often seen in small groups or pairs, especially during the breeding season.
The Red-crested Finch, or Coryphospingus cucullatus, is a small, colorful bird primarily found in South America. It is easily recognizable by its bright red plumage on the head and upper body, contrasting with darker shades on the wings and tail. This bird prefers open habitats such as savannas, shrublands, and forest edges. It is often seen in small groups, feeding on seeds and insects. The Red-crested Finch is a diurnal bird, active mainly during the day. It is known for its melodious song and its ability to adapt to various environments, making it a relatively common species within its range.
The Bare-throated Bellbird, or Procnias averano, is a captivating bird belonging to the Cotingidae family. This passerine is renowned for its powerful and distinctive call, often likened to a resounding bell. The male boasts a striking white plumage with a vividly colored bare throat, while the female displays more subdued hues. This bird is primarily found in the tropical forests of South America, where it feeds on fruits and small insects. Its ability to produce loud sounds allows it to communicate effectively through the dense canopy. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it remains relatively common in certain areas.
The White Bellbird, or Procnias albus, is a fascinating bird from the Cotingidae family, known for its piercing and distinctive call. It is primarily found in the tropical rainforests of South America, particularly in Brazil, Venezuela, and Guyana. The male is notable for its striking white plumage and fleshy wattle on its beak, used to attract females during mating season. The female, on the other hand, has a more subdued olive-green plumage, allowing her to blend into the foliage. This bird is mainly frugivorous, feeding on fruits and berries, but may also consume insects occasionally.
The Argali is the largest wild sheep in the world, known for its imposing size and majestic spiral horns. It primarily inhabits the mountains of Central Asia, where it frequents the arid and semi-arid regions of steppes and high plateaus. This large ungulate is perfectly adapted to mountainous environments, moving nimbly on steep terrain at high altitudes. The Argali is a herbivore, feeding on grasses and woody plants.
The Argali is also a symbol of strength and resilience, but it is threatened by habitat loss and overhunting. Conservation efforts are underway to protect this iconic species and preserve its natural habitat.
The Great Argus, or Argusianus argus, is a remarkable bird from the Phasianidae family, renowned for its spectacular plumage and fascinating courtship displays. Native to the tropical forests of Southeast Asia, this bird is distinguished by its long, ocellated feathers adorning its wings and tail. The male, larger than the female, uses these feathers to attract mates during elaborate courtship rituals. Primarily terrestrial, it prefers dense habitats where it can blend in. Although the Great Argus is a shy bird, it is sometimes seen in clearings searching for food, mainly fruits, insects, and small invertebrates. Its population is threatened by deforestation and hunting, leading to its classification as near threatened by the IUCN.
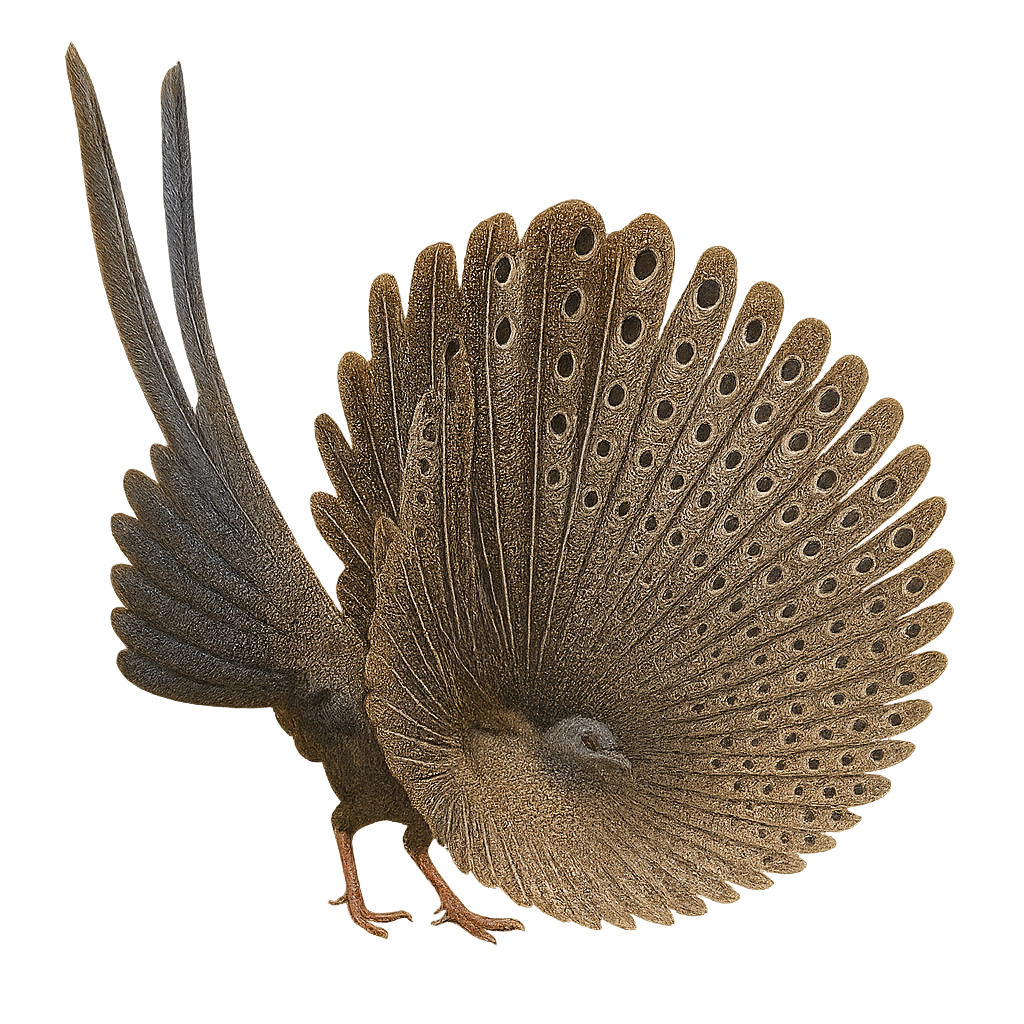
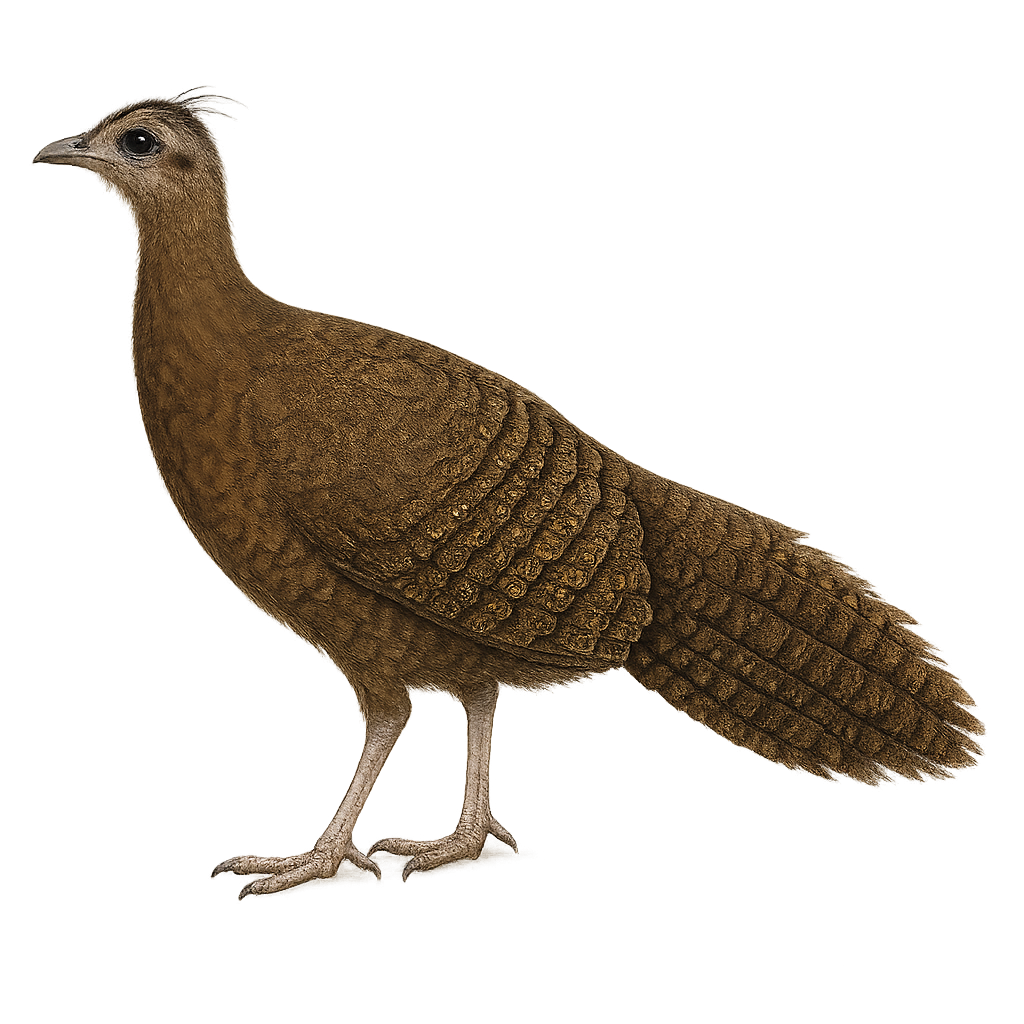
The Crested Argus, or Rheinardia ocellata, is a fascinating bird belonging to the Phasianidae family. This large pheasant is primarily known for its spectacular plumage and long tail feathers adorned with eye-like patterns reminiscent of a peacock. Males, larger than females, can reach up to 2 meters in length, including the tail. They sport a brown plumage with intricate patterns, while females are more discreet with brown and gray hues. The Crested Argus inhabits the dense tropical forests of Southeast Asia, particularly in Vietnam, Thailand, and Malaysia. This bird is mainly terrestrial, feeding on seeds, fruits, and insects. Unfortunately, it is threatened by deforestation and hunting, leading to a decline in its populations.