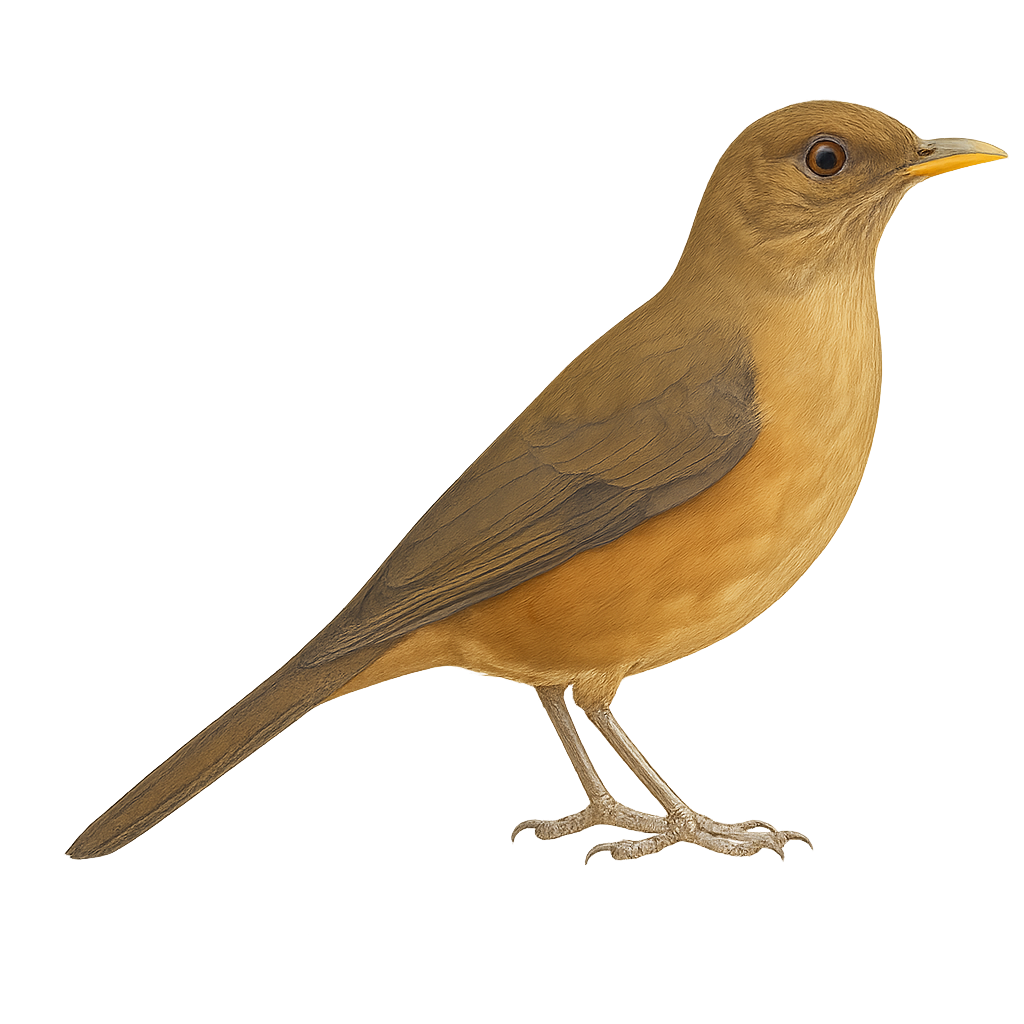
The Clay-colored Thrush, or Turdus grayi, is a medium-sized bird, measuring about 23 to 27 cm in length. Its plumage is primarily light brown, allowing it to blend into its natural surroundings. Known for its melodious song, it is often heard at dawn and dusk. This bird is widely distributed in Central America, from southern Mexico to northern Colombia. It prefers open habitats such as gardens, parks, and secondary forests. The Clay-colored Thrush is an omnivorous bird, feeding on fruits, insects, and small invertebrates. It is often seen foraging on the ground in search of food.
The coal tit is a small passerine, 10–12 cm long, with slate-grey plumage, a black cap, white bib, and subtly streaked flanks. It frequents coniferous and mixed woodlands across Europe, often at edges or low in the canopy, where it forages on branches and trunks for insects and spiders. Solitary or in small family groups, it may join communal roosts in winter. During the breeding season, pairs defend their nest site together, placing the nest in a tree cavity or an old tit nest.
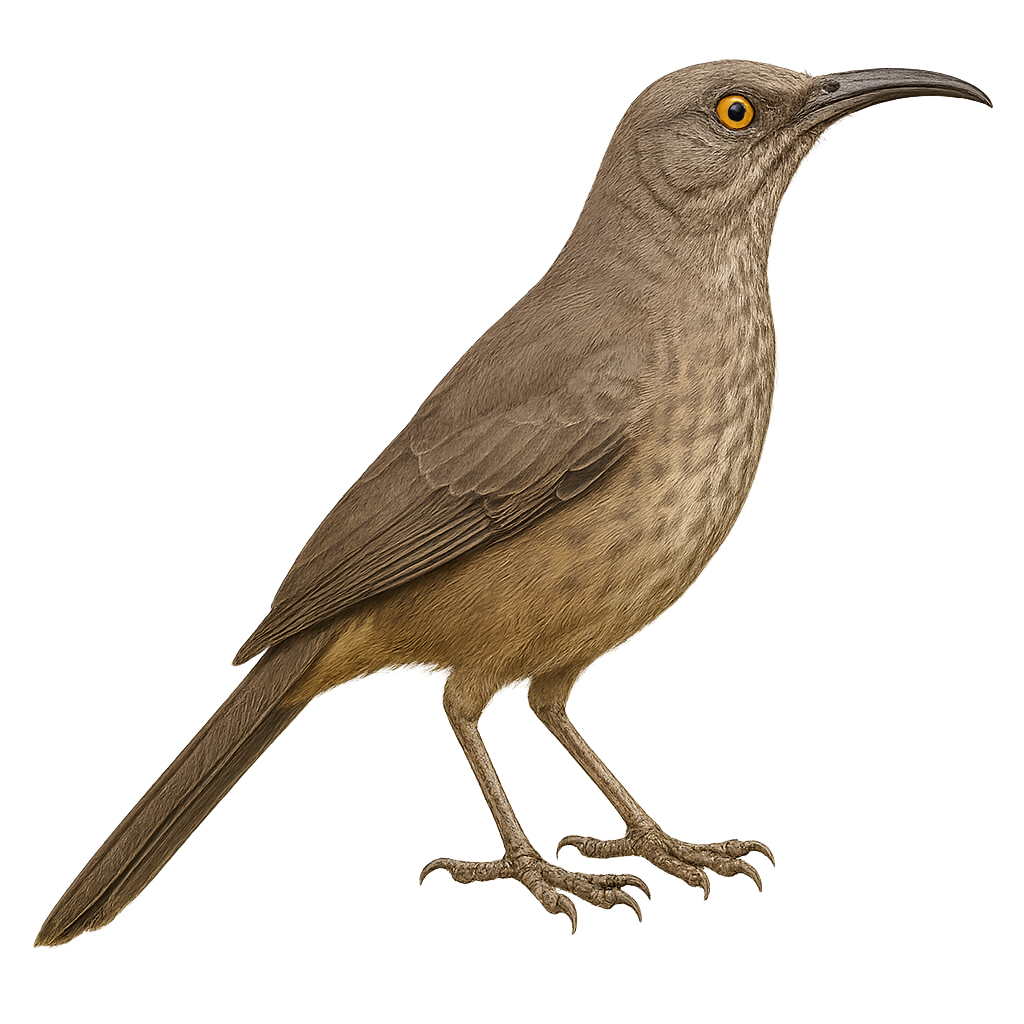
The Curve-billed Thrasher is a bird with gray-brown plumage and lighter spots on its belly. Its long, curved bill is distinctive, allowing it to probe the ground for food. Primarily insectivorous, it also eats fruits and seeds. Found in the arid and semi-arid regions of the southwestern United States and Mexico, it frequents thorny bushes and desert areas. Known for its varied and melodious song, it uses this to defend its territory and attract a mate. The Curve-billed Thrasher is a resilient bird, capable of adapting to harsh environments.
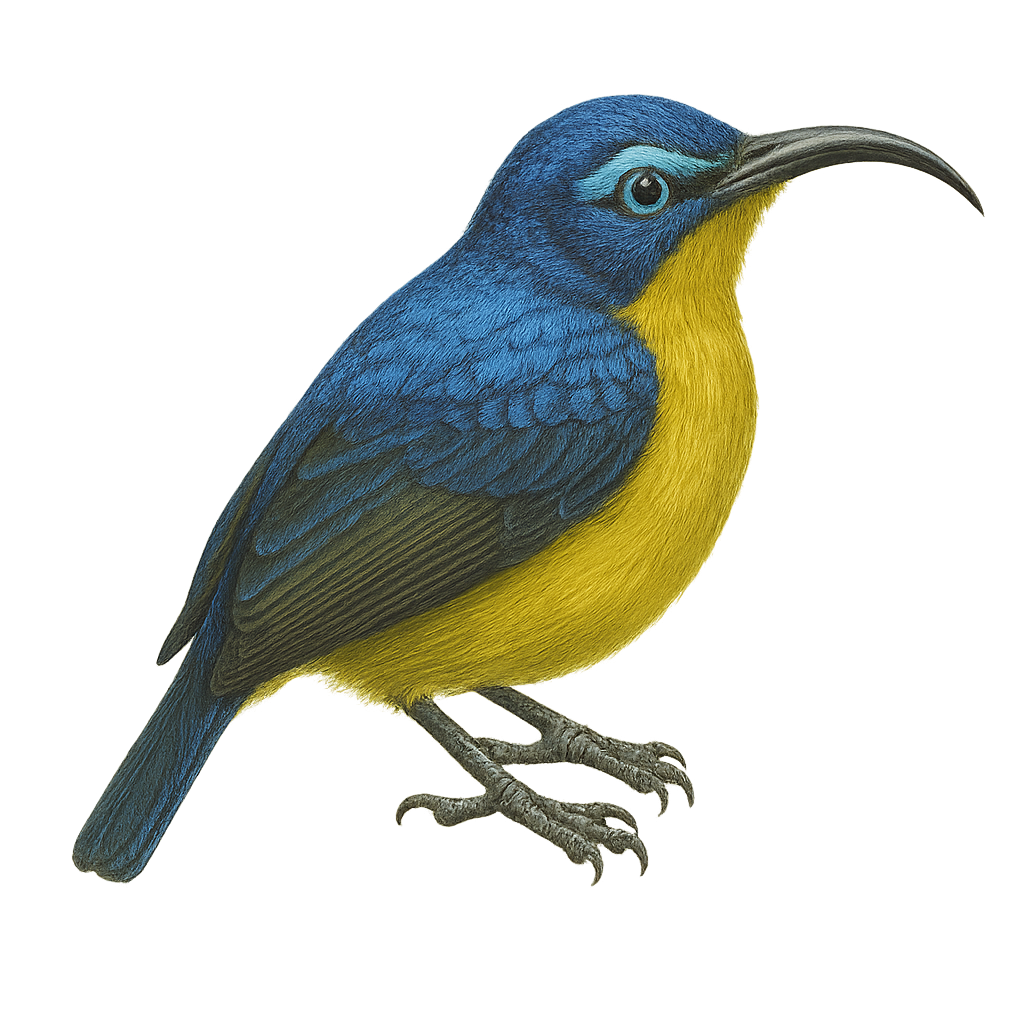
The Crimson Myzomela, scientifically known as Myzomela rubratra, is a small, vibrant bird with predominantly red plumage and black accents on its wings and tail. It is native to several Pacific islands, including New Caledonia and the Solomon Islands. This nectarivore primarily feeds on flower nectar, but also consumes insects and fruits. Its slender, curved beak is perfectly adapted for nectar extraction. The Crimson Myzomela is often found in tropical rainforests, mangroves, and gardens. Known for its melodious song and active nature, it is frequently seen flitting from flower to flower. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it is currently listed as of least concern by the IUCN.
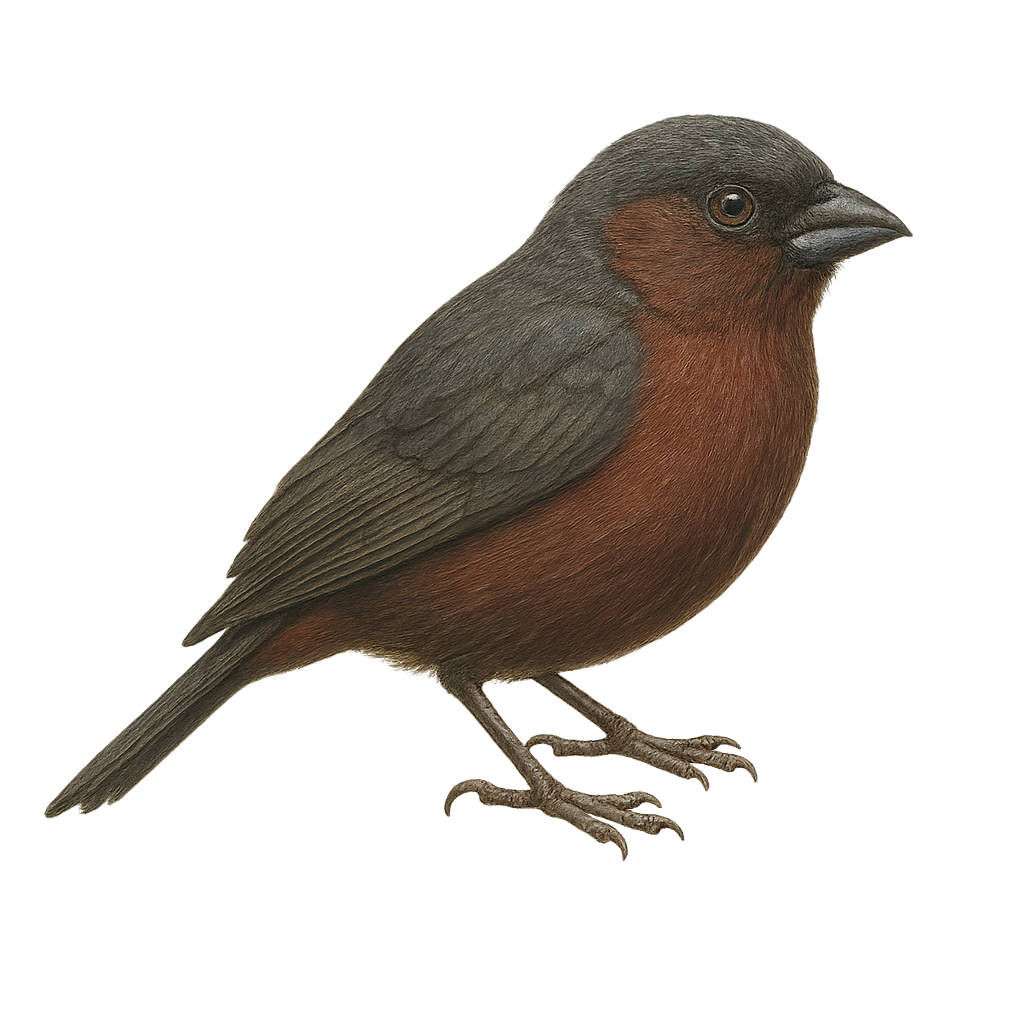
The Chestnut-breasted Nigrita is a small African bird belonging to the Estrildidae family. It is characterized by its chestnut-brown breast and black body, giving it an elegant and distinctive appearance. This bird is primarily found in the tropical rainforests and wooded savannas of Central and West Africa. Often seen in small groups, it feeds on seeds and insects. The Chestnut-breasted Nigrita is known for its melodious song and complex social behaviors. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it is currently listed as a species of least concern by the IUCN.
The Colombian Chachalaca is a medium-sized bird, measuring about 50 to 60 cm in length. It features an olive-brown plumage with lighter shades on the belly and a long, rounded tail. This bird is often seen in small groups in the tropical and subtropical forests of Colombia, where it primarily feeds on fruits, leaves, and flowers. Although its flight is somewhat clumsy, it can move swiftly through dense vegetation. The Colombian Chachalaca plays an important role in seed dispersal, thus aiding forest regeneration. It is also known for its loud vocalizations, often heard at dawn and dusk.
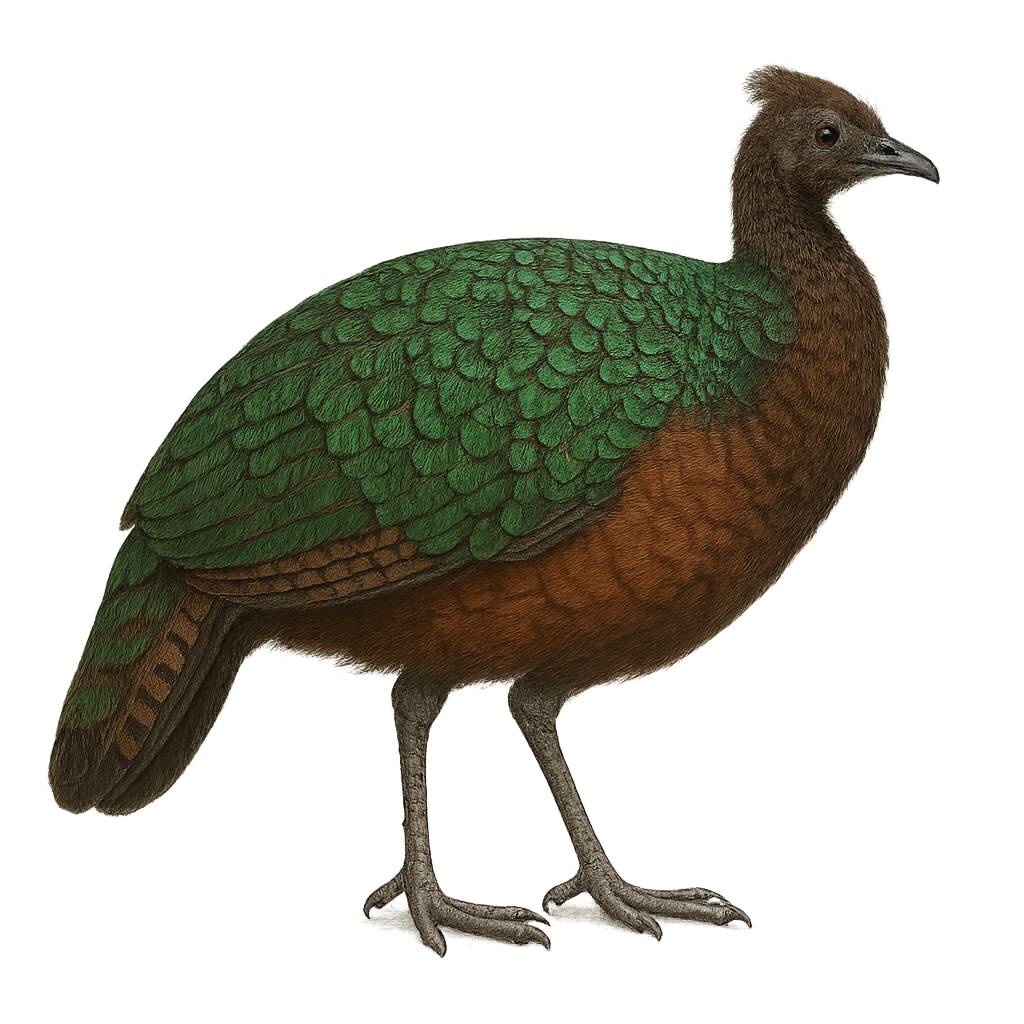
The Congo Peafowl, or Afropavo congensis, is a rare and fascinating bird species endemic to the tropical forests of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. This magnificent bird is distinguished by its iridescent plumage with metallic hues of blue, green, and bronze. Unlike its Asian cousin, the Indian Peafowl, the Congo Peafowl is smaller and less flamboyant but equally captivating. Males display a distinctive crest and a relatively short tail, while females have duller plumage, aiding their camouflage in dense vegetation. These birds are primarily terrestrial, feeding on seeds, fruits, and small invertebrates. Their discreet behavior and restricted habitat make them difficult to observe, but their conservation is crucial for the region's biodiversity.
The Crinkle-collared Manucode is a fascinating bird endemic to the tropical forests of New Guinea. It is distinguished by its iridescent black plumage with metallic sheen and a frizzled feather collar around its neck. This medium-sized bird, measuring about 42 cm, is known for its complex and melodious vocalizations. It primarily inhabits the dense forest canopy, feeding on fruits and insects. The Crinkle-collared Manucode is monogamous and forms stable pairs. Its breeding period is not well documented, but it is known to build a cup-shaped nest in trees. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it is currently classified as Least Concern by the IUCN.
The Connecticut Warbler, or Oporornis agilis, is a migratory bird belonging to the Parulidae family. It is characterized by its subtle plumage, with an olive back and bright yellow belly. Its head is gray with a distinctive white eye-ring. This bird primarily inhabits the boreal forests of Canada and the northern United States during the breeding season, migrating to South America for the winter. Often elusive, it prefers dense habitats, making it challenging to spot. The Connecticut Warbler feeds mainly on insects and larvae, foraging in leaf litter. Its population is stable, but it faces threats from habitat loss due to deforestation.
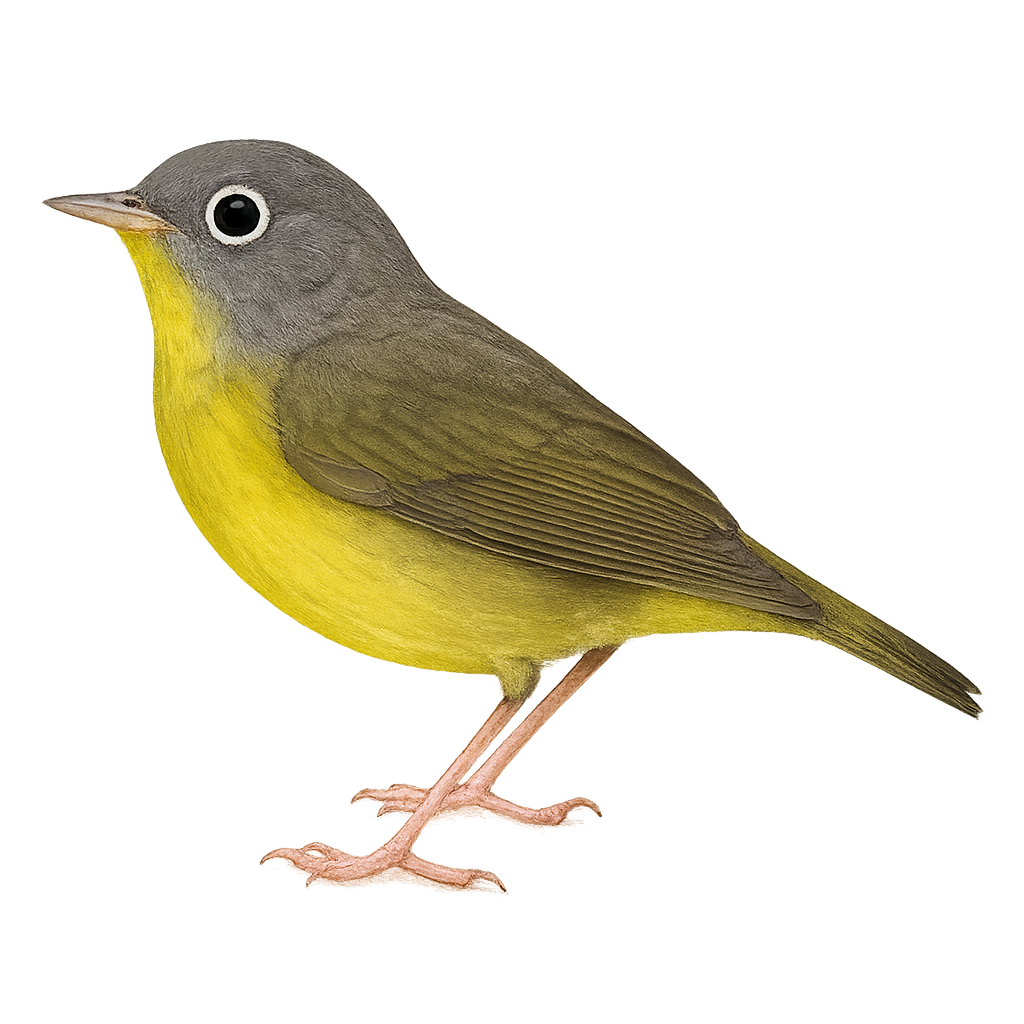
The Canada Warbler is a small songbird known for its vibrant plumage and presence in North American forests. It features a bright yellow breast, contrasting with a gray head adorned with a distinctive black necklace. This migratory bird travels long distances between its breeding grounds in Canada and its wintering areas in South America. The Canada Warbler prefers moist forest habitats, often near watercourses, where it primarily feeds on insects. Although its song is melodious and easily recognizable, it can be challenging to spot due to its discreet behavior and preference for dense, shaded areas.
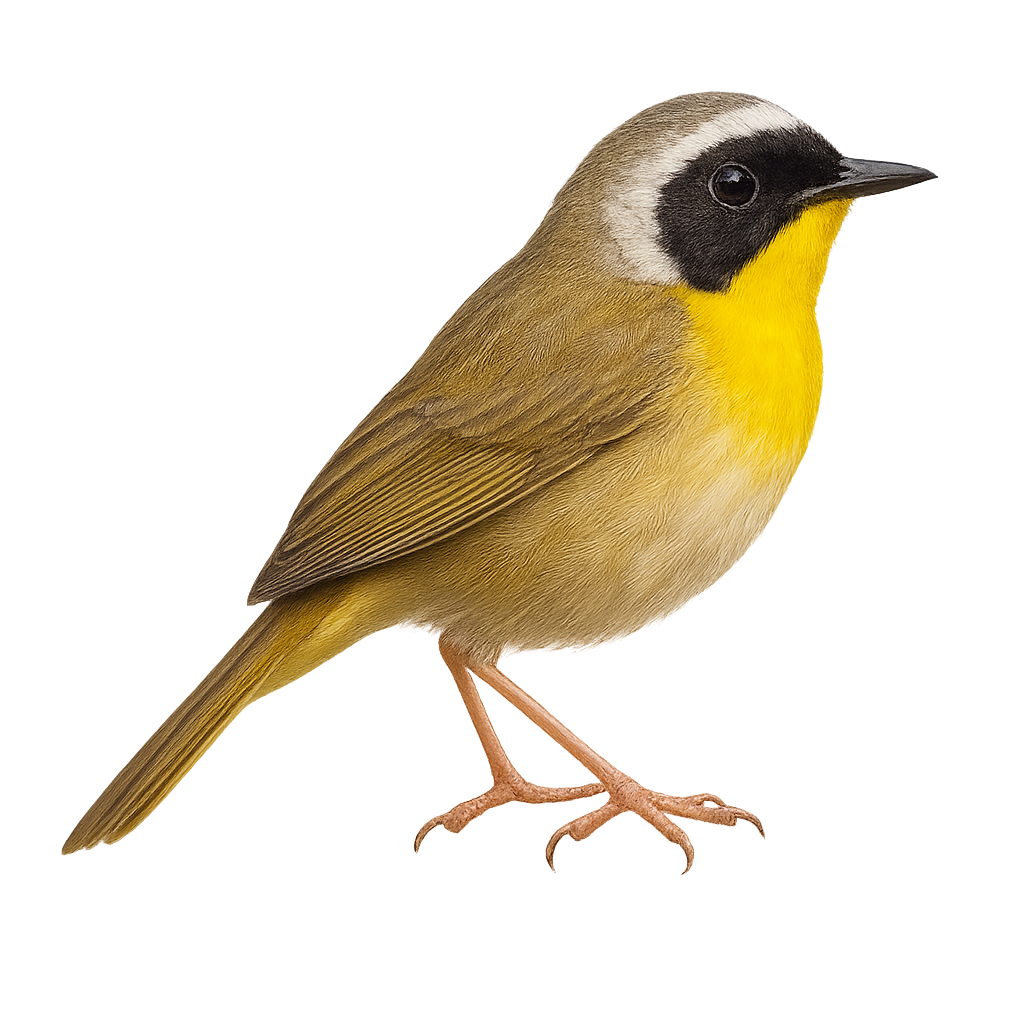
The Common Yellowthroat, Geothlypis trichas, is a small songbird in the Parulidae family. It is easily recognized by its distinctive black mask that contrasts with its bright yellow throat. Males sport this black mask, while females and juveniles have duller colors. It primarily inhabits marshes, wet meadows, and shrubby areas across North America. Its song is a distinctive "wichity-wichity-wichity." The Common Yellowthroat is a migratory bird, wintering in Central America and the southern United States. It feeds mainly on insects and spiders, which it captures by foraging in dense vegetation.
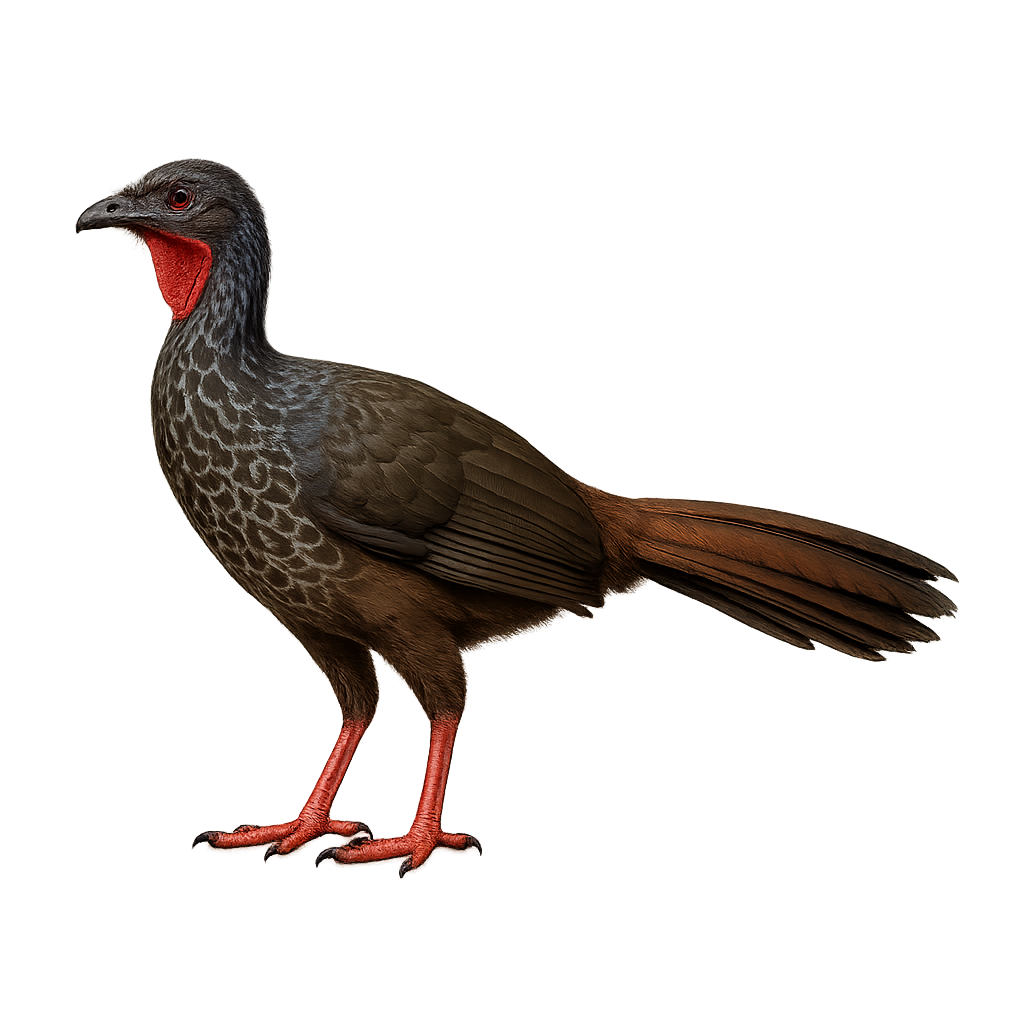
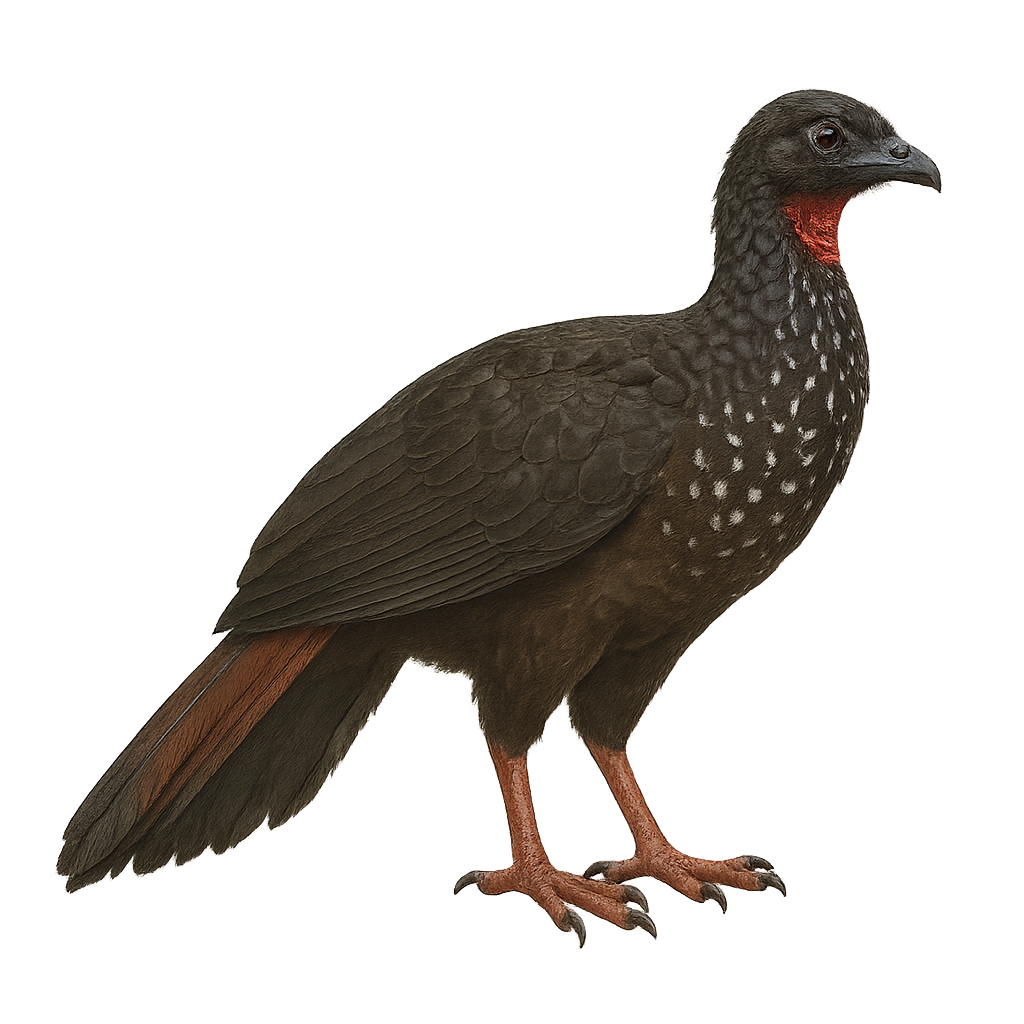
The Cauca Guan is a rare and endemic bird of Colombia, primarily found in the humid forests of the Western Andes. This medium-sized bird, measuring about 85 cm, is distinguished by its dark brown plumage and reddish throat. It lives in small groups and feeds mainly on fruits, leaves, and flowers. Unfortunately, it is threatened by deforestation and hunting, leading to a significant decline in its population. Conservation efforts are crucial for its survival. Its call is a deep, resonant sound, often heard at dawn and dusk.
The Crested Guan is a large forest bird, measuring between 76 and 91 cm in length and weighing up to 2.4 kg. It has dark olive-brown plumage with white spots on the neck and chest, a rufous rump and belly, and a bushy crest on its head. Its throat features a large red wattle, and the skin around the eye is bluish-gray. Social in nature, it lives in pairs or family groups of 6 to 12 individuals, feeding on fruits and young leaves in the trees. It builds its nest in trees, where the female lays two or three white eggs. Although classified as Near Threatened by the IUCN, it is vulnerable to habitat loss and hunting.
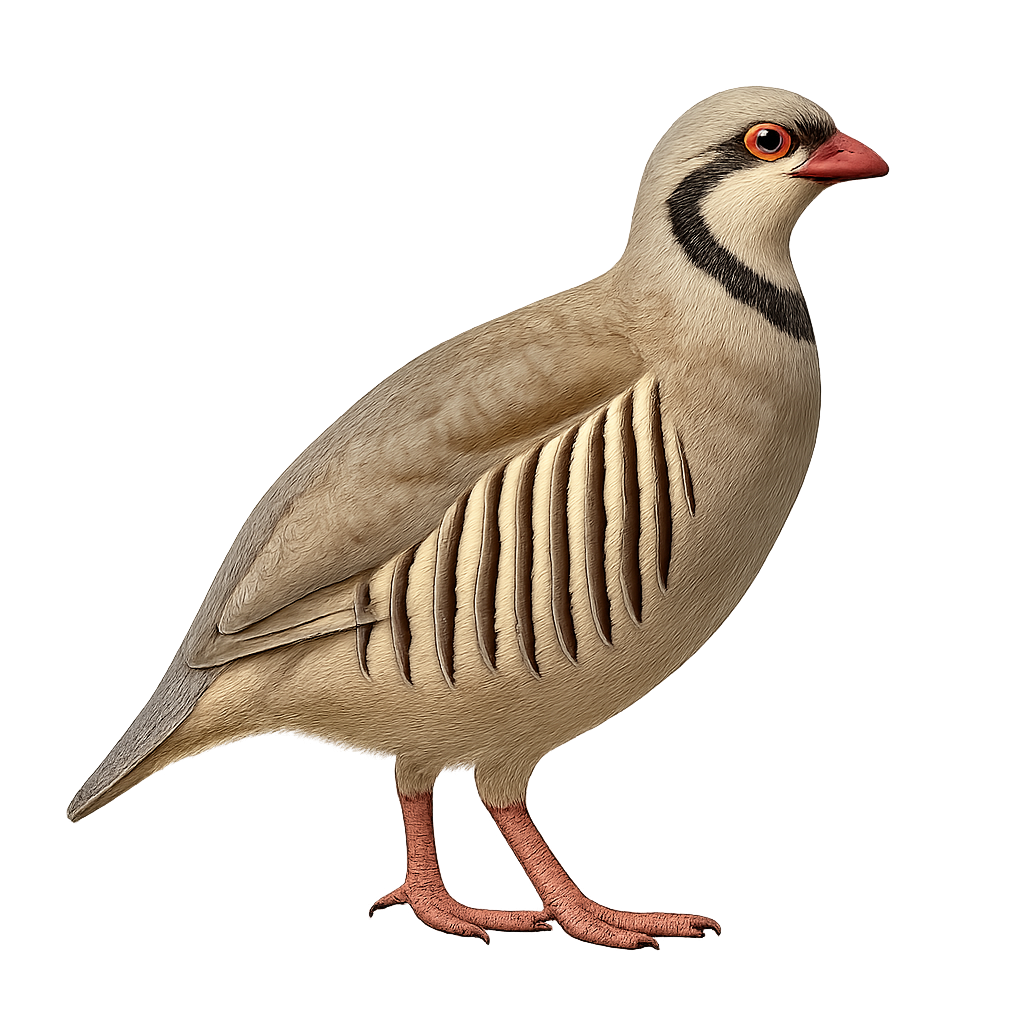
The chukar partridge is a medium-sized bird (30–35 cm), with grey-brown plumage barred with black and white, featuring a glossy black cap and eye-stripe. Native to arid regions of Asia and introduced in North America, it inhabits rocky slopes, scrublands and fallow fields, feeding on seeds, leaves, and insects. During the breeding season (March 1 to July 31), the male performs formal courtship displays and defends his territory with calls and rapid chases.
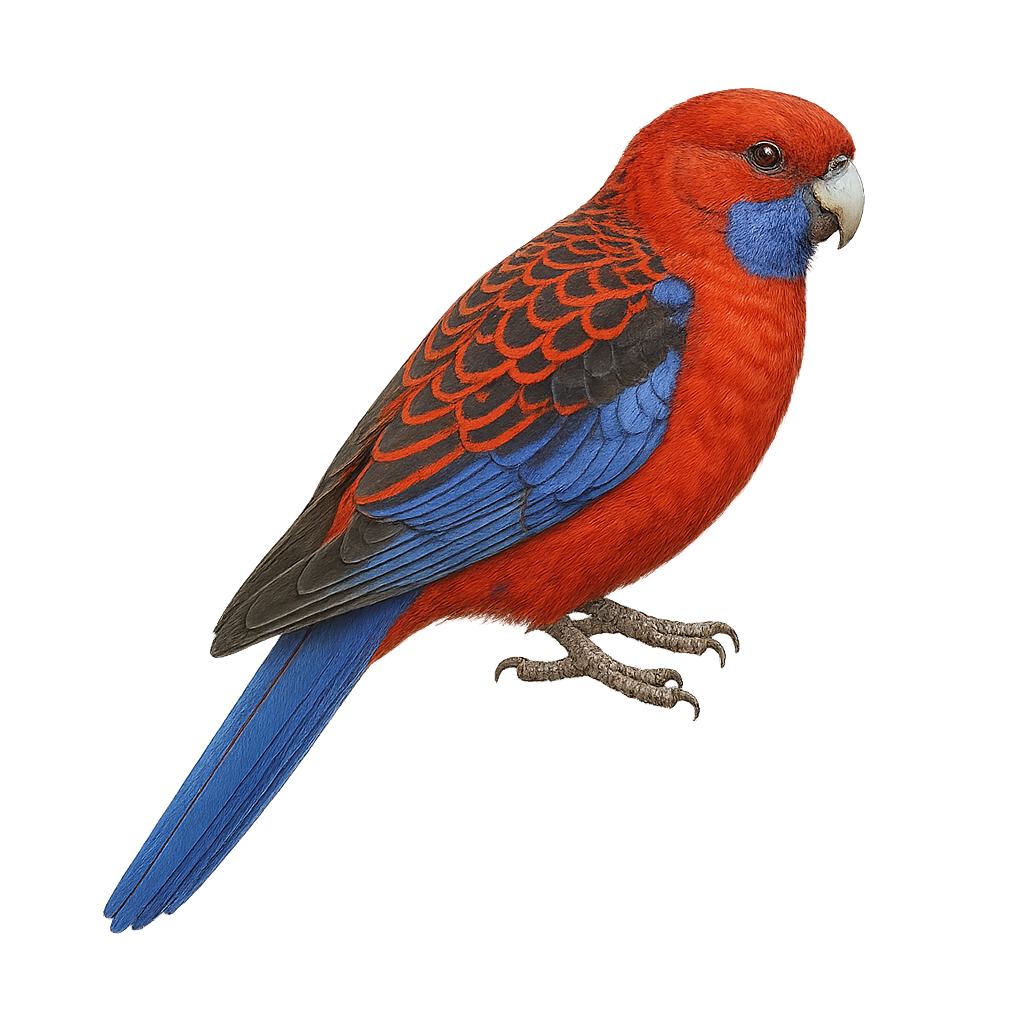
The Crimson Rosella, or Platycercus elegans, is a vibrant bird native to Australia. It is easily identified by its bright red plumage, contrasted with blue feathers on its wings and tail. Juveniles have a duller, often greenish plumage that transitions to the vivid colors of adults. It primarily inhabits wet forests, woodlands, and urban gardens. Sociable by nature, it often moves in small groups. Its diet is varied, including seeds, fruits, flowers, and insects. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it remains relatively common. Its adaptability to human-modified environments aids its survival.
The Common Sunbird-Asity, or Neodrepanis coruscans, is a small bird endemic to Madagascar, known for its vibrant plumage and fascinating behaviors. It primarily inhabits the island's humid tropical forests, where it feeds mainly on nectar, but also on insects and spiders. This small bird features bright yellow plumage with metallic sheens, making it easily identifiable. Males, in particular, display more vivid colors during the breeding season to attract females. Though discreet, the Common Sunbird-Asity plays a crucial role in pollinating local plants. Its population is stable, but deforestation poses a potential threat to its natural habitat.
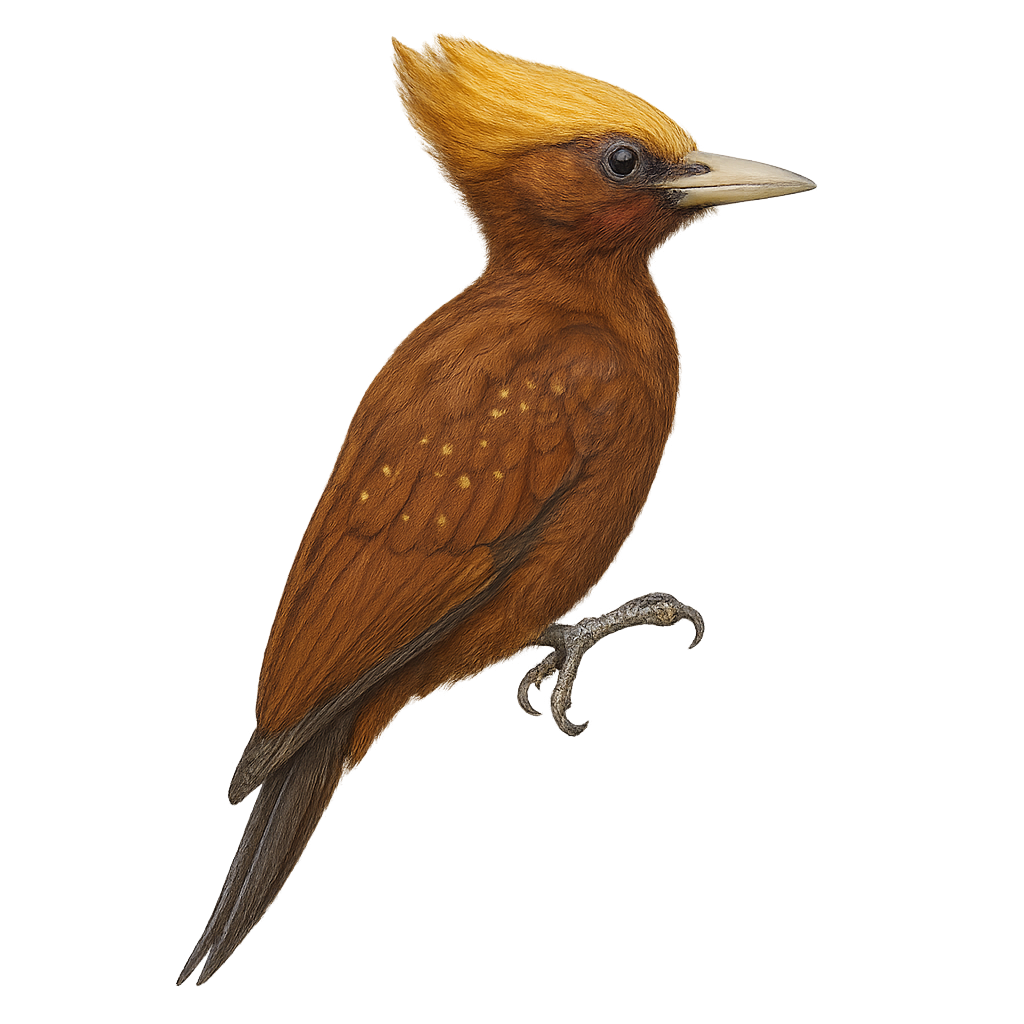
The Chestnut Woodpecker, or Celeus elegans, is a captivating bird native to the tropical forests of South America. It is characterized by its striking reddish-brown plumage and distinctive crest. Its medium size and sturdy beak allow it to bore into wood to find its food, mainly consisting of insects and larvae. Often seen in pairs or small groups, it moves nimbly through the dense canopy. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, the Chestnut Woodpecker remains relatively common in some areas. Its call is a mix of sharp cries and drumming on tree trunks, making it easily noticeable to keen observers.
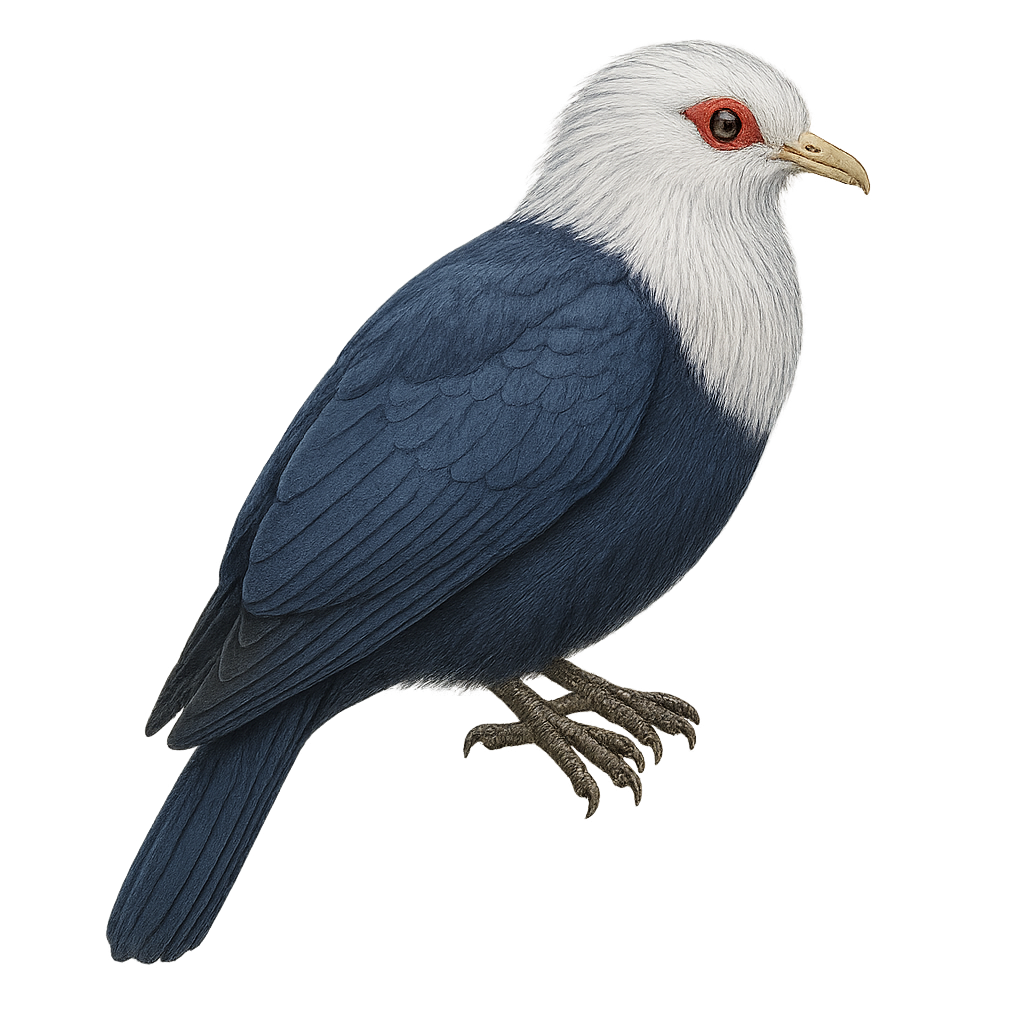
The Comoro Blue Pigeon, or Alectroenas sganzini, is an endemic bird of the Comoros, known for its striking blue plumage and distinctive red head. Measuring about 30 cm in length, it is characterized by its robust body and rounded wings. This bird prefers dense forests and wooded areas, where it primarily feeds on fruits, seeds, and small invertebrates. Although its habitat is limited, it adapts well to environmental changes. However, deforestation and hunting pose potential threats to its survival. Its suspicious nature makes it difficult to observe, but it is often heard due to its soft and melodious song.
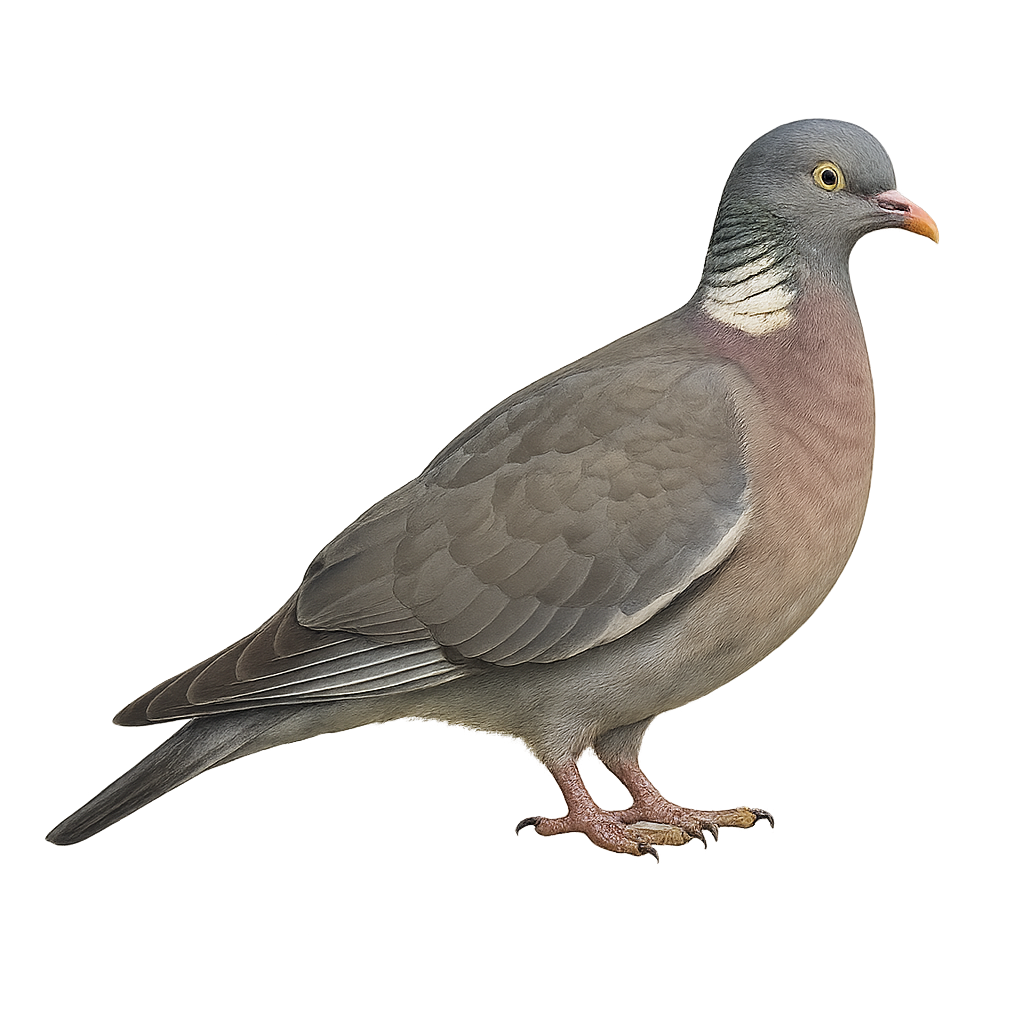
The Common Wood Pigeon, or Columba palumbus, is one of the largest pigeons in Europe, easily identifiable by its large size and distinctive white markings on its neck and wings. It has a grey-blue plumage with a pinkish breast and greenish neck sheen. Often seen in parks, gardens, and forests, it feeds mainly on seeds, fruits, and young shoots. Its flight is strong and direct, often accompanied by loud wing beats. The Wood Pigeon is also known for its soft, soothing cooing, which often echoes through woods and countryside.
The chaffinch is a small songbird found primarily in Europe and Western Asia. It is easily recognizable by its colorful plumage, with a brown back, pink breast, and beige belly. This passerine bird feeds on seeds, berries, and insects, and is commonly seen in forests, gardens, and parks. The chaffinch is also known for its melodious song, which varies depending on the region and season.
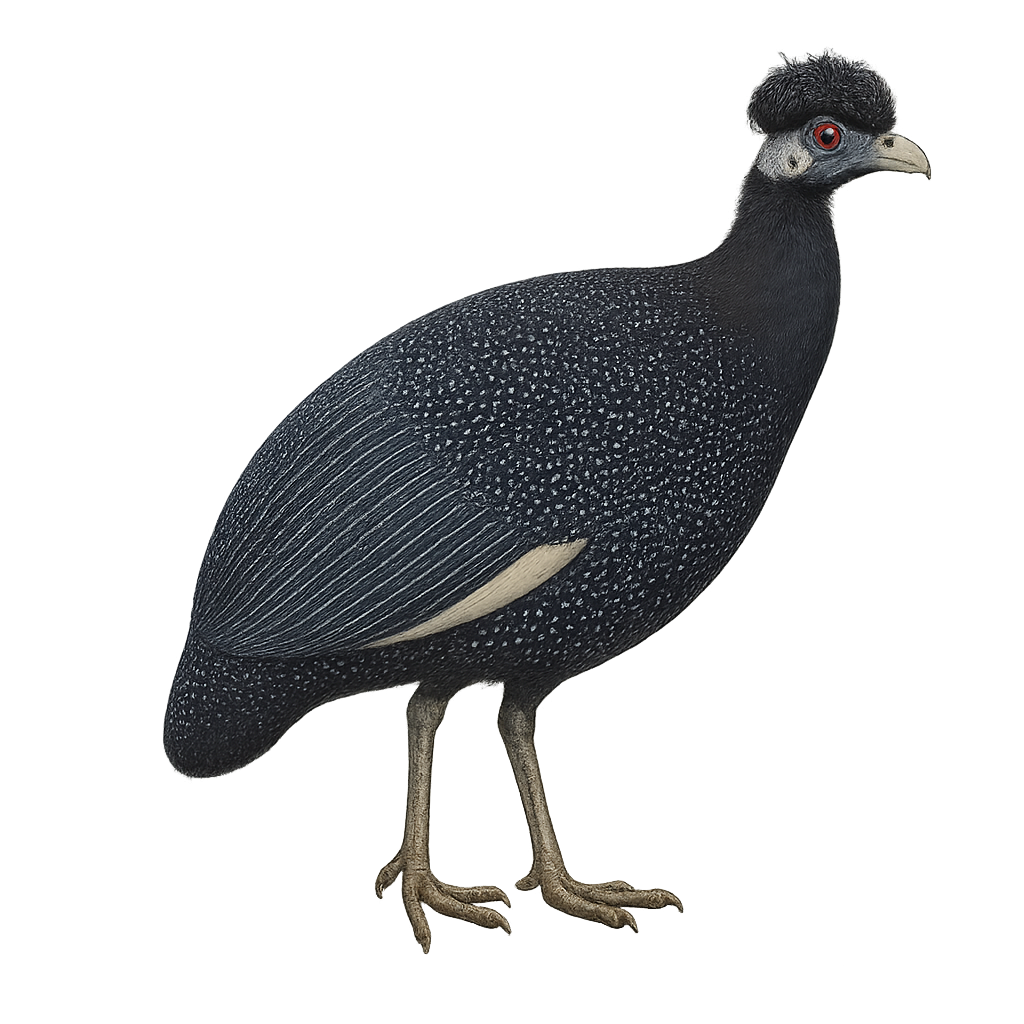
The Crested Guineafowl, or Guttera edouardi, is a medium-sized terrestrial bird known for its distinctive crest and black plumage dotted with white spots. It primarily inhabits the humid tropical forests of East Africa, moving in small groups in search of food. Its diet is varied, including seeds, insects, and small invertebrates. Although generally discreet, it can be noisy when disturbed. The Crested Guineafowl plays an important role in the ecosystem by helping control insect populations and dispersing seeds. Its ability to adapt to different habitats allows it to survive in changing environments, although deforestation poses a threat to some of its populations.
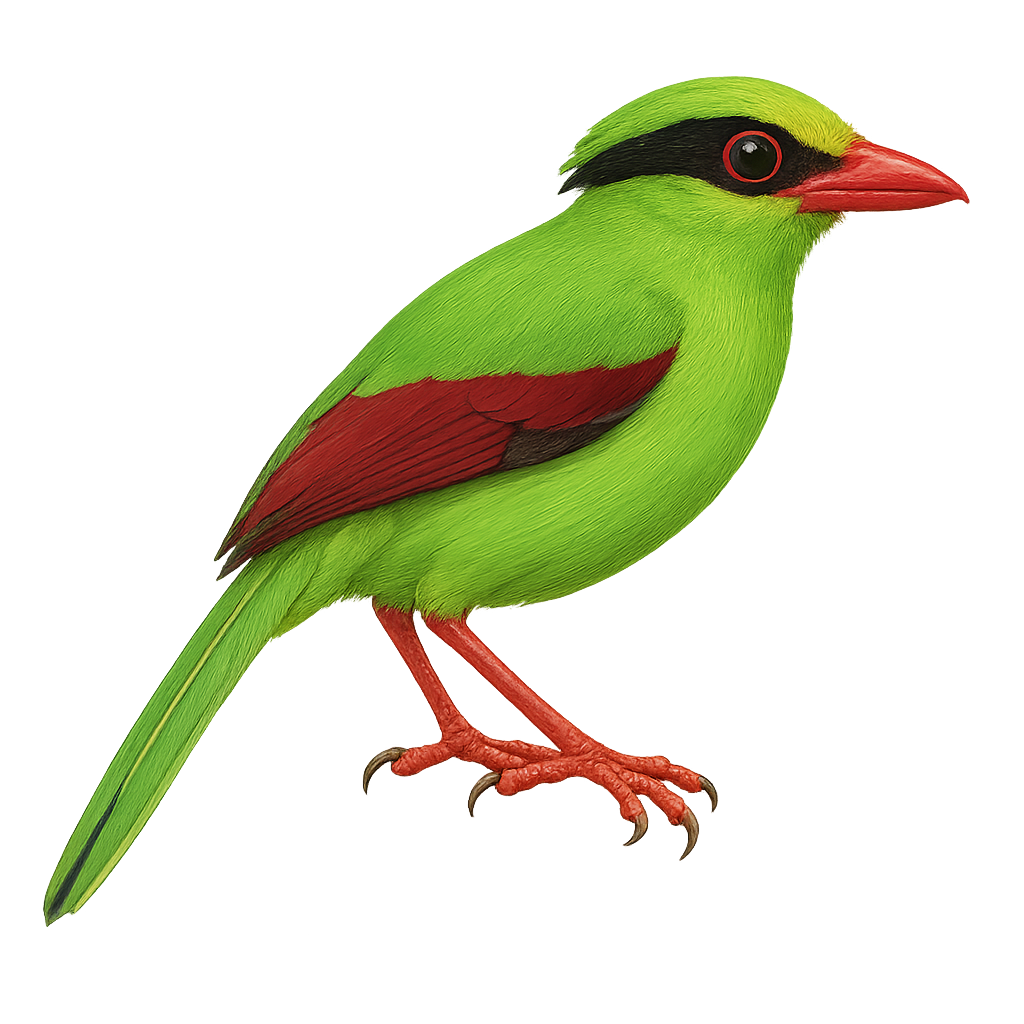
The Common Green Magpie, scientifically known as Cissa chinensis, is a striking bird with predominantly green plumage accented by shades of blue and yellow. Its head features distinctive black feathers, and its beak is a vivid red. This bird primarily inhabits the dense tropical forests of Southeast Asia, where it feeds on insects, small reptiles, and fruits. Known for its discreet behavior, it blends seamlessly into the dense foliage. The Common Green Magpie is a social bird, often seen in small groups. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it remains relatively common in some areas.
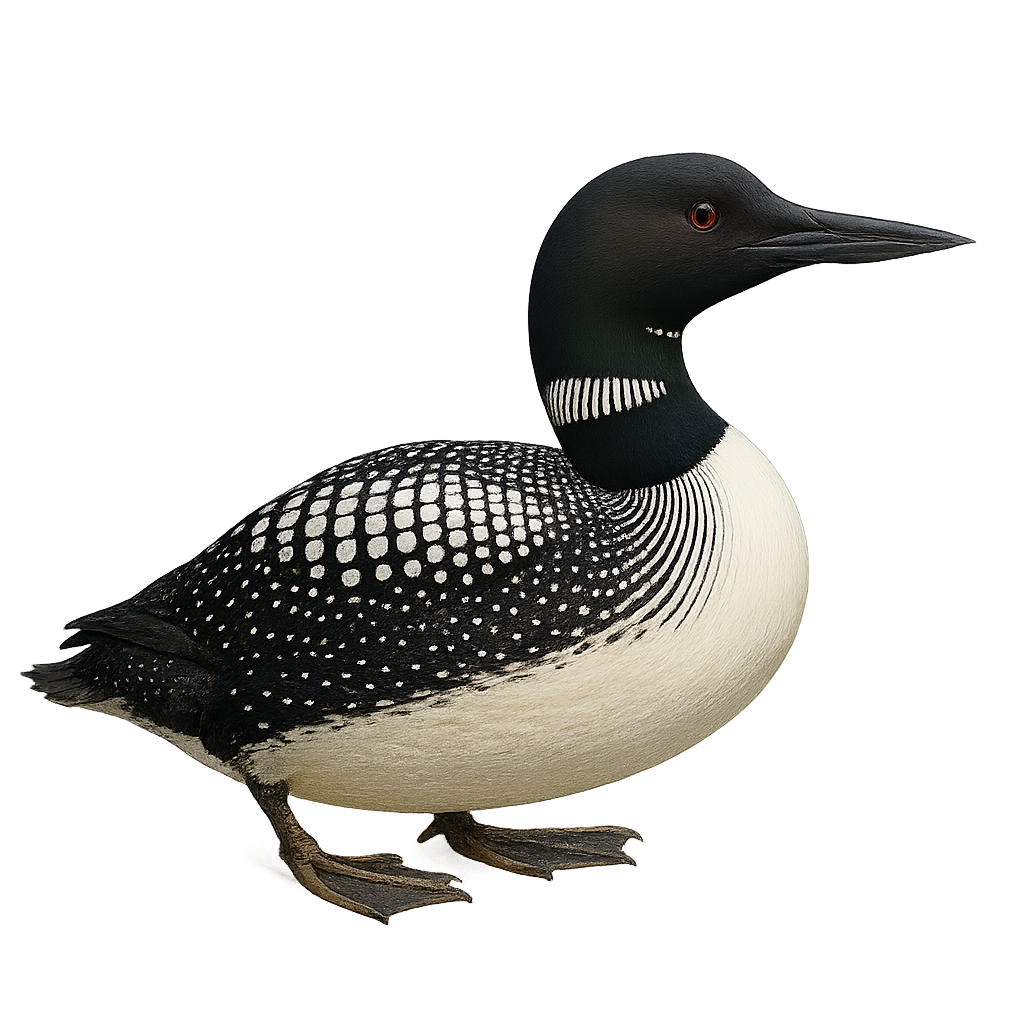
The Common Loon is a seabird primarily found in the cold waters of the North Atlantic, particularly in North America and Northern Europe. It measures about 60 to 70 cm in length, with a wingspan of 100 to 120 cm, and weighs between 1.5 and 2.5 kg. Its plumage is mainly black and white, with a dark back, white breast, and black head, giving it a distinctive appearance. The Common Loon is an exceptional diver, primarily feeding on fish and crustaceans, which it catches by diving deeply underwater. It is also known for its long migrations, moving to warmer areas during the winter. Although its population remains relatively stable, this species can be threatened by pollution, human disturbances, and habitat loss.
The Chestnut-crowned Babbler is a sociable and gregarious bird, primarily found in Australia. It is characterized by its chestnut-colored head contrasting with its brown body and darker wings. Measuring about 22 cm, it is often seen in noisy groups, moving around in search of food. It mainly feeds on insects, small invertebrates, and occasionally seeds. This bird is known for its elaborate nests, often built in colonies. It prefers arid and semi-arid habitats, such as open woodlands, scrublands, and sparse forests. Although its conservation status is currently of "least concern," habitat degradation could pose a future threat.
The chiffchaff is a small migratory passerine bird found primarily in clear woods, hedgerows, and gardens across Europe and Asia. It is easily recognized by its greenish plumage and pale belly. This small bird primarily feeds on insects, which it catches by rummaging through vegetation. During the breeding season, it is very active and emits a distinctive song, a series of repetitive notes characteristic of this species.
The Chinspot Batis is a small passerine bird belonging to the Platysteiridae family. It is primarily found in wooded areas and savannas of sub-Saharan Africa. This bird is characterized by its black back contrasting with its white belly and grey flanks. Males display a black breast band, while females have a browner band. They are often seen in pairs or small groups, feeding on insects caught in flight or on foliage. Their song is a soft whistle, often repeated. Although their habitat is relatively stable, they can be affected by deforestation.
The Cape Batis is a small passerine bird native to southern Africa. It is noted for its colorful plumage, featuring a black head, white belly, and a bright orange breast band. Males and females exhibit sexual dimorphism, with females having slightly duller colors. This bird is often found in forests, thickets, and gardens, where it primarily feeds on insects. Known for its melodious songs and territorial behavior, the Cape Batis is a sedentary bird, although it may undertake minor altitudinal migrations depending on the season. Its population is stable, and it is not currently threatened.
The Chinspot Batis is a small passerine bird found mainly in sub-Saharan Africa. It is easily recognizable by its distinctive plumage, featuring a black band across the chest and a contrasting white chin. Males and females show subtle differences in coloration, with males generally having brighter colors. These birds are often seen in pairs or small groups, actively moving through bushes and trees in search of insects. They are known for their melodious and repetitive song, which plays a crucial role in territory defense and mate attraction.
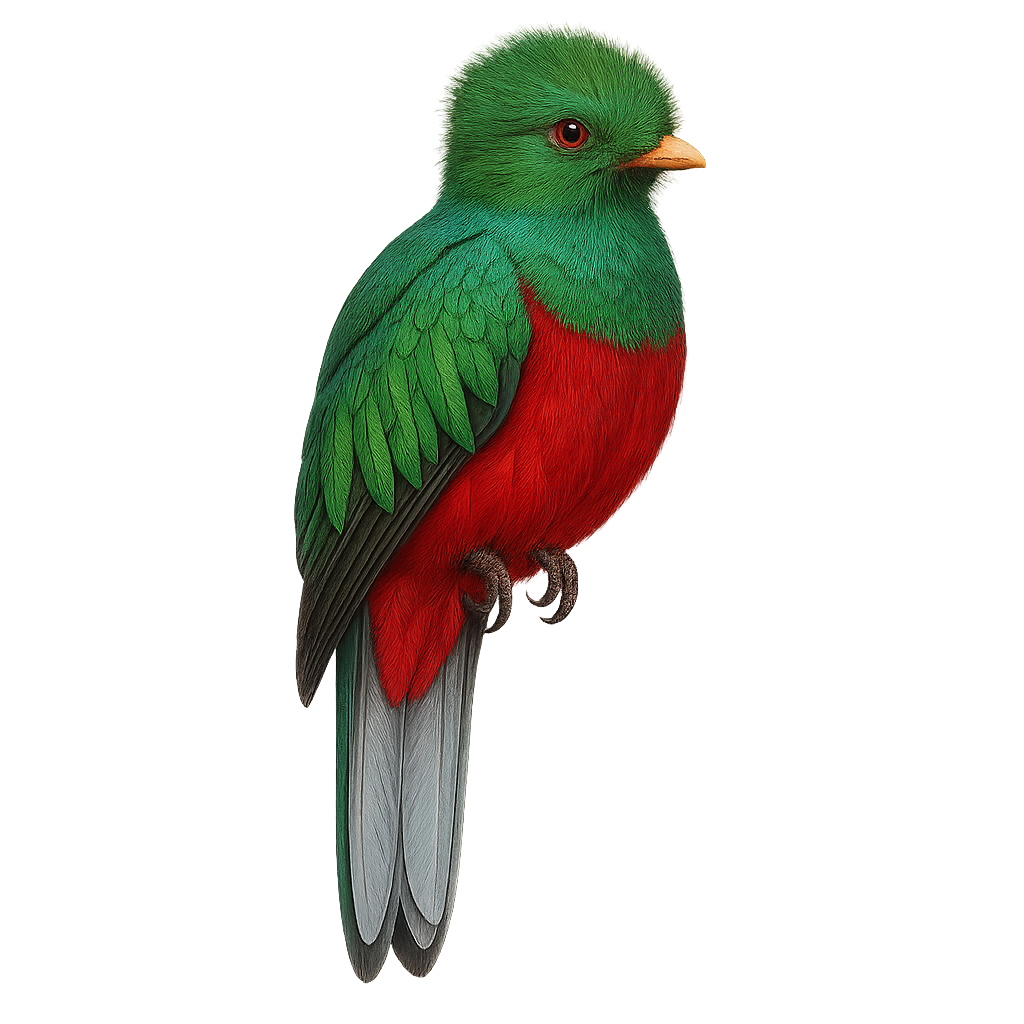
The Crested Quetzal, or Pharomachrus antisianus, is a striking bird found in the humid forests of the Andes. It is known for its vibrant plumage, with shades of emerald green and bright red, and the characteristic long tail of the males. This quetzal is a symbol of beauty and freedom in many South American cultures. It primarily feeds on fruits, but also consumes insects and small vertebrates. Its presence often indicates the health of its forest habitat. Although its conservation status is not alarming, deforestation poses a potential threat to its populations.
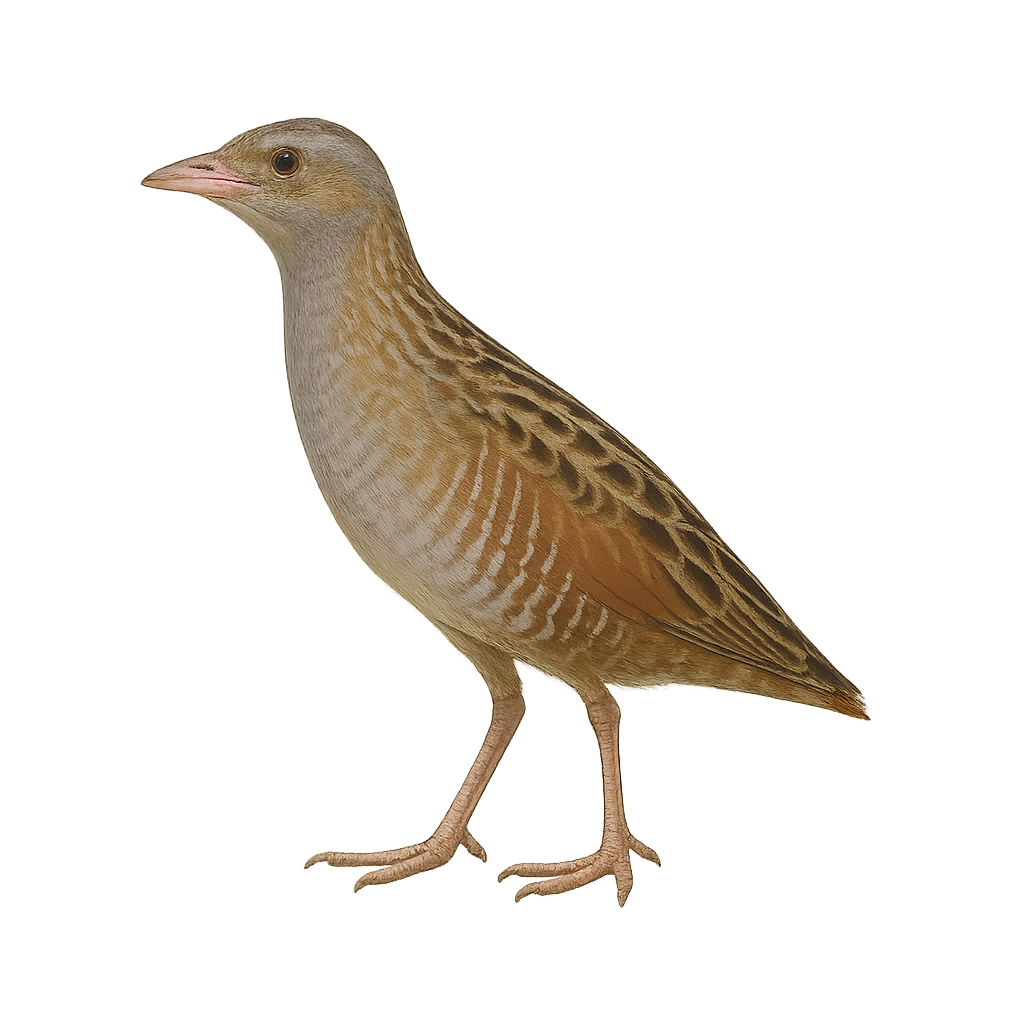
The corn crake is a rail in the family Rallidae, measuring 23–28 cm with cryptically streaked brown plumage and grey legs. It inhabits damp grasslands and tall vegetation, feeding mainly on insects, earthworms and molluscs taken from the ground. During breeding, the male emits a loud, repeated “crek-crek” call both night and day to attract females and defend territory.