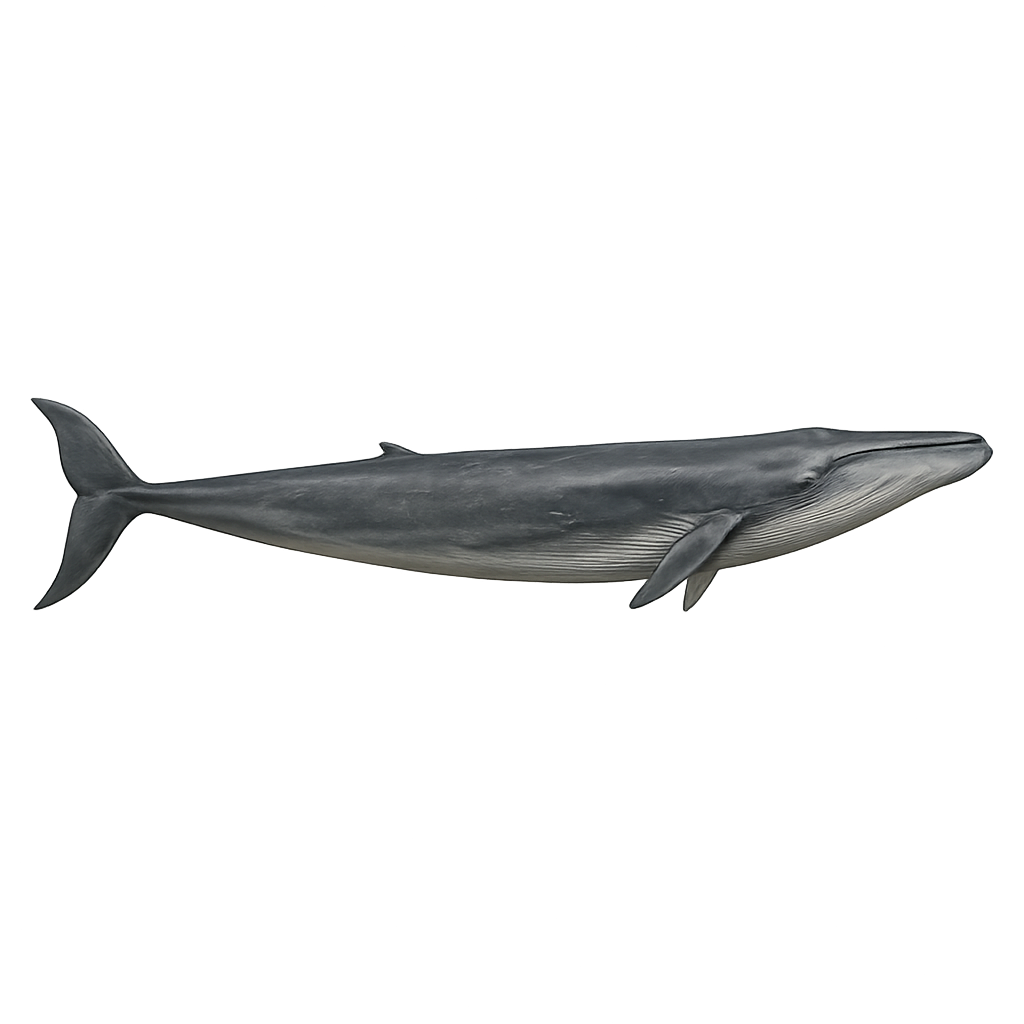
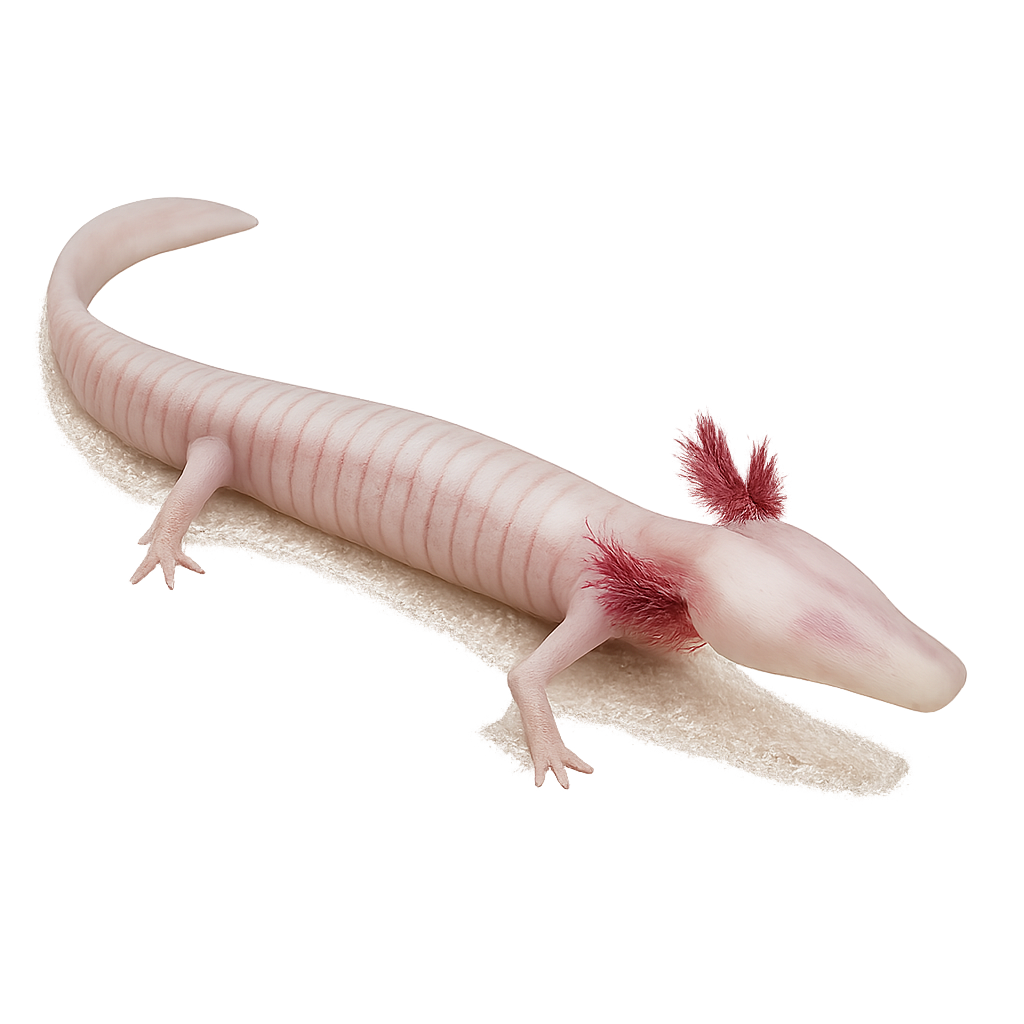
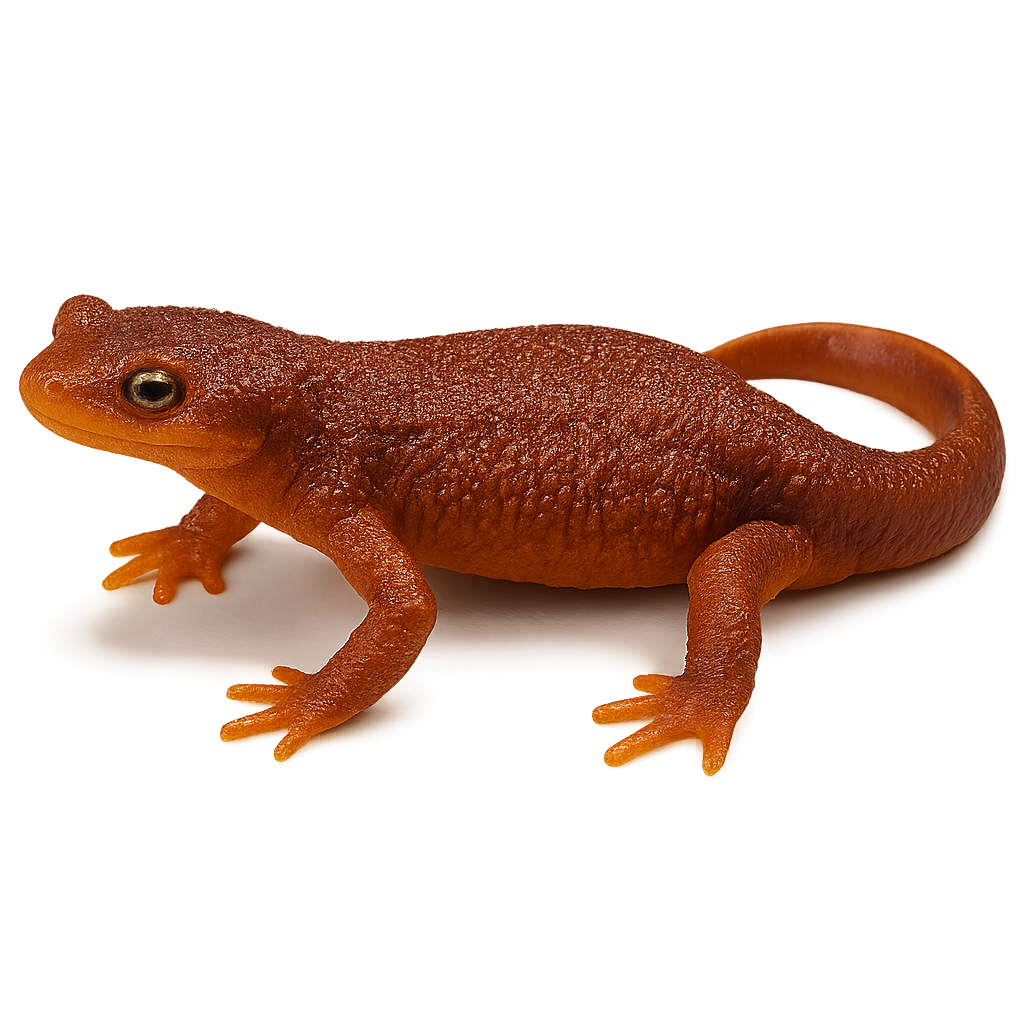
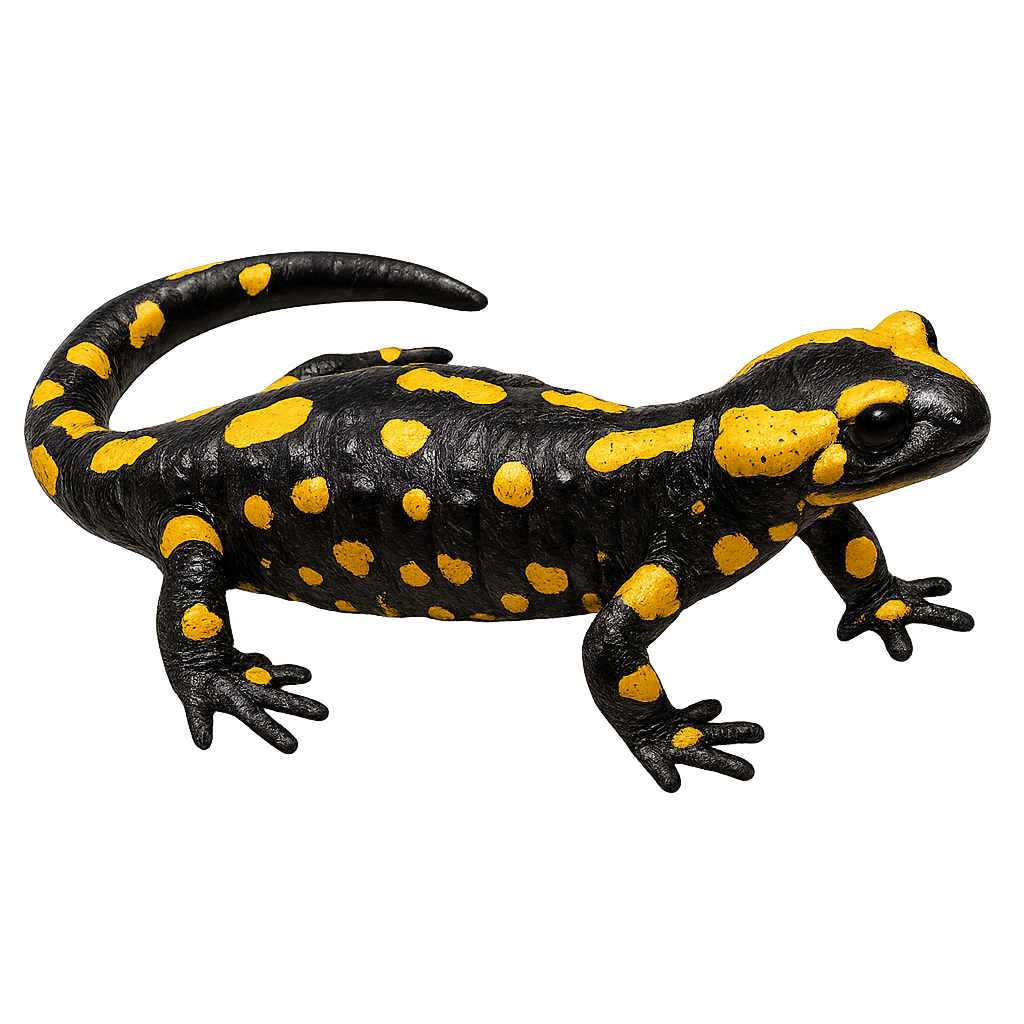
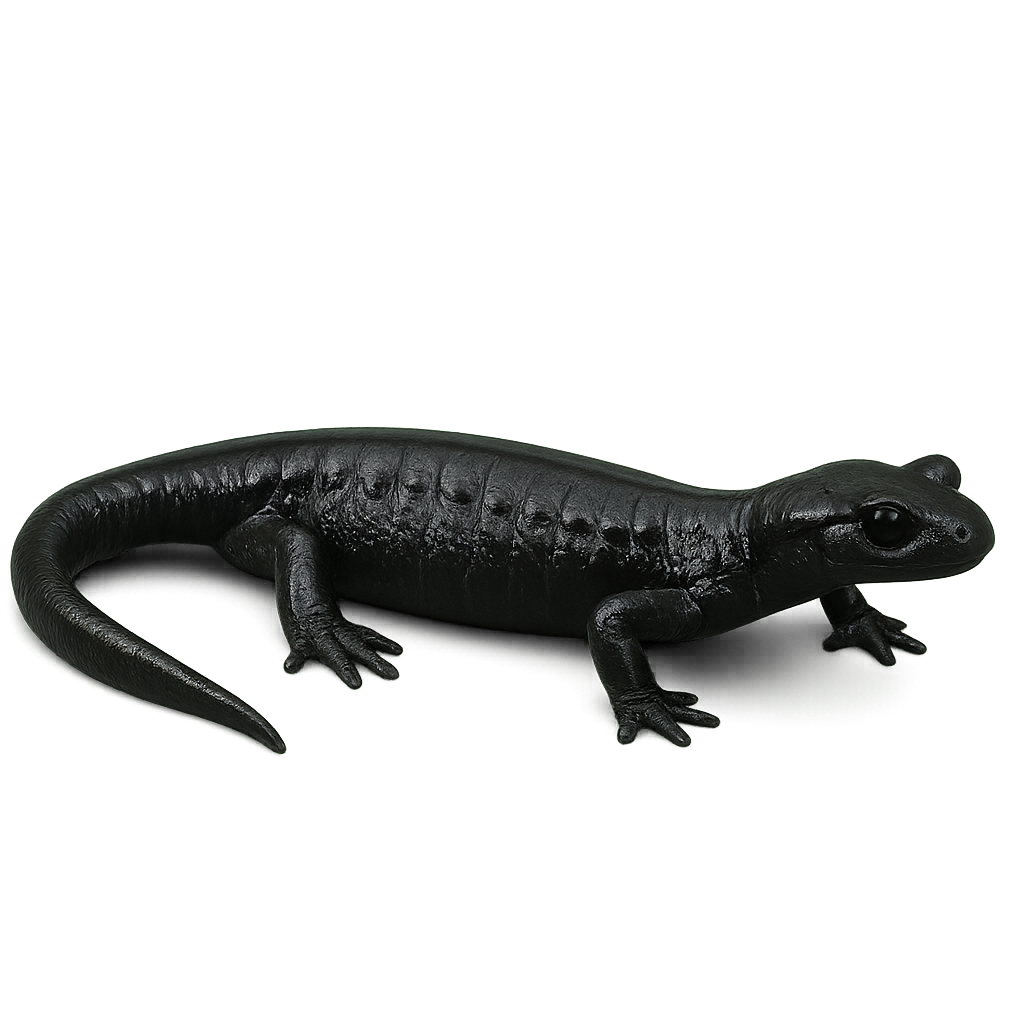
The Fin whale, also known as the Minke whale, is one of the largest whale species, reaching lengths of up to 18 meters and weighing 70 tons. It primarily feeds on krill and small fish, capturing them by filtering water. This migratory whale travels long distances between breeding and feeding areas and is found in all oceans worldwide. While the Fin whale is a protected species, it is still threatened by pollution, ship strikes, and illegal whaling.
The Long-tailed Rosefinch, Carpodacus sibiricus, is a small passerine bird belonging to the Fringillidae family. It is easily recognizable by its long tail and bright pink plumage in males, while females display more brownish hues. This rosefinch is primarily found in Asia, particularly in Siberia, which is reflected in its scientific name. It inhabits coniferous forests, taigas, and shrublands. Its diet mainly consists of seeds, supplemented by insects during the breeding season. The Long-tailed Rosefinch is a partial migratory bird, moving southward in winter to avoid harsh climatic conditions.
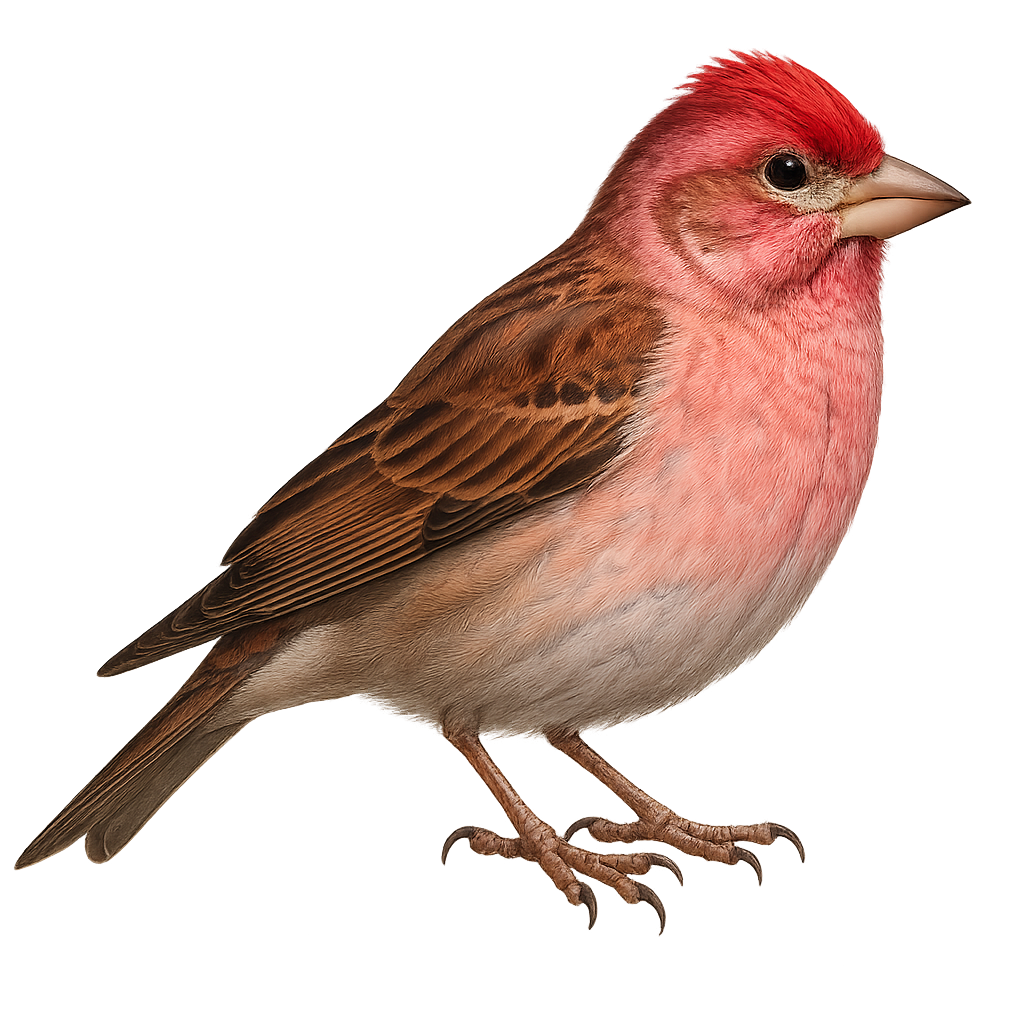
The Common Rosefinch, Carpodacus erythrinus, is a small passerine bird known for its striking plumage. Males display a bright red color on the head, chest, and rump, contrasting with the brown wings and back. Females are more subdued, with brownish tones and streaks on the belly. This bird measures about 13 to 15 cm in length with a wingspan of 22 to 26 cm. It is primarily found in deciduous forests, shrublands, and wet meadows across Europe and Asia. A migratory species, it winters in India and Southeast Asia. Its melodious and varied song is often heard in spring and summer, the breeding season.
The Cassin's Finch is a medium-sized songbird belonging to the Fringillidae family. It is primarily found in the coniferous forests of western North America, especially in the Rocky Mountains. Males display a rosy hue on their head, chest, and rump, while females and juveniles are duller with brownish patterns. This finch primarily feeds on seeds, buds, and small fruits. It is often seen in small flocks, especially outside the breeding season. Its melodious and varied song is a distinctive feature of its behavior, used to attract mates and mark territory.
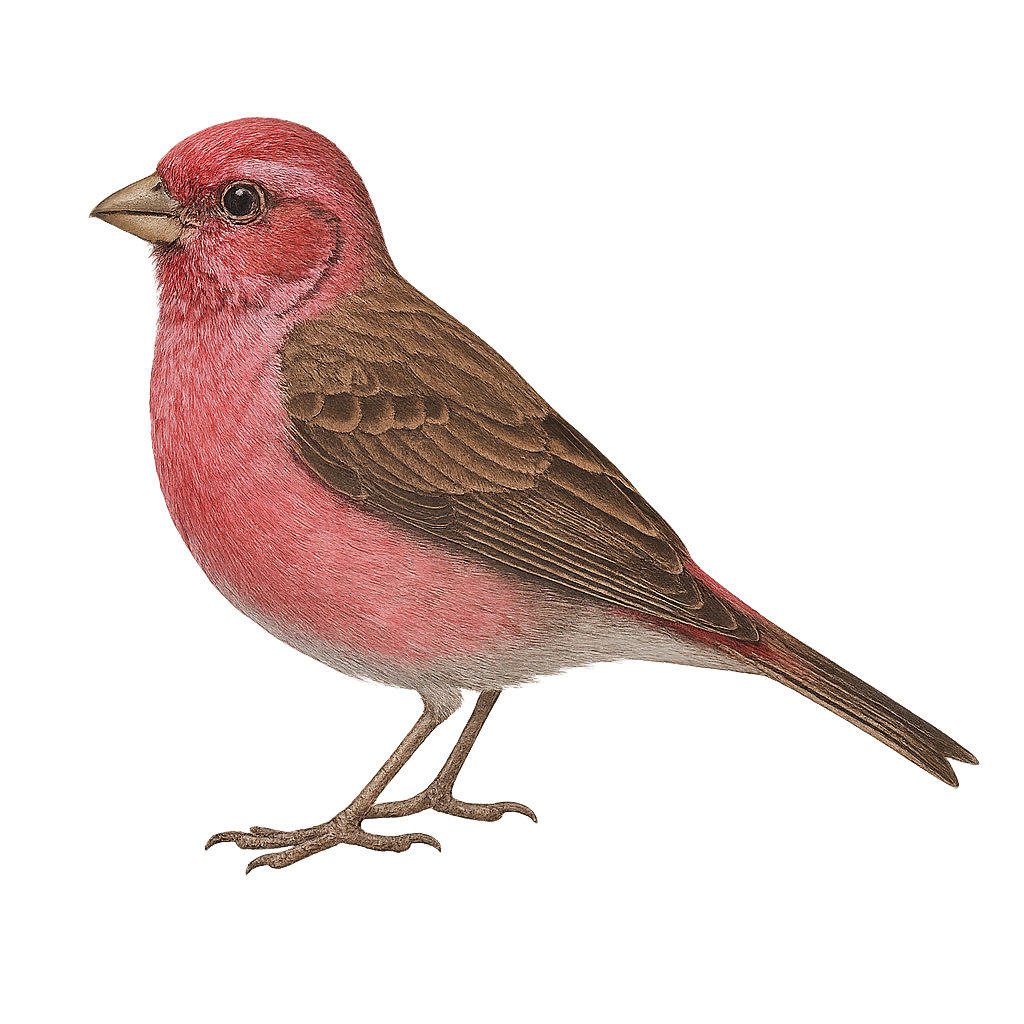
The Walton's Finch, scientifically known as Carpodacus waltoni, is a member of the Fringillidae family. It is primarily found in the mountainous regions of the Himalayas, especially in Tibet and parts of China. This small passerine bird is notable for its striking plumage, with shades of pink and red on its chest and head, contrasting with a paler belly. Males display brighter colors than females, which are generally duller. The Walton's Finch is often seen in small groups, feeding on seeds and berries. It prefers open habitats such as alpine meadows and shrublands, where it can easily find food.
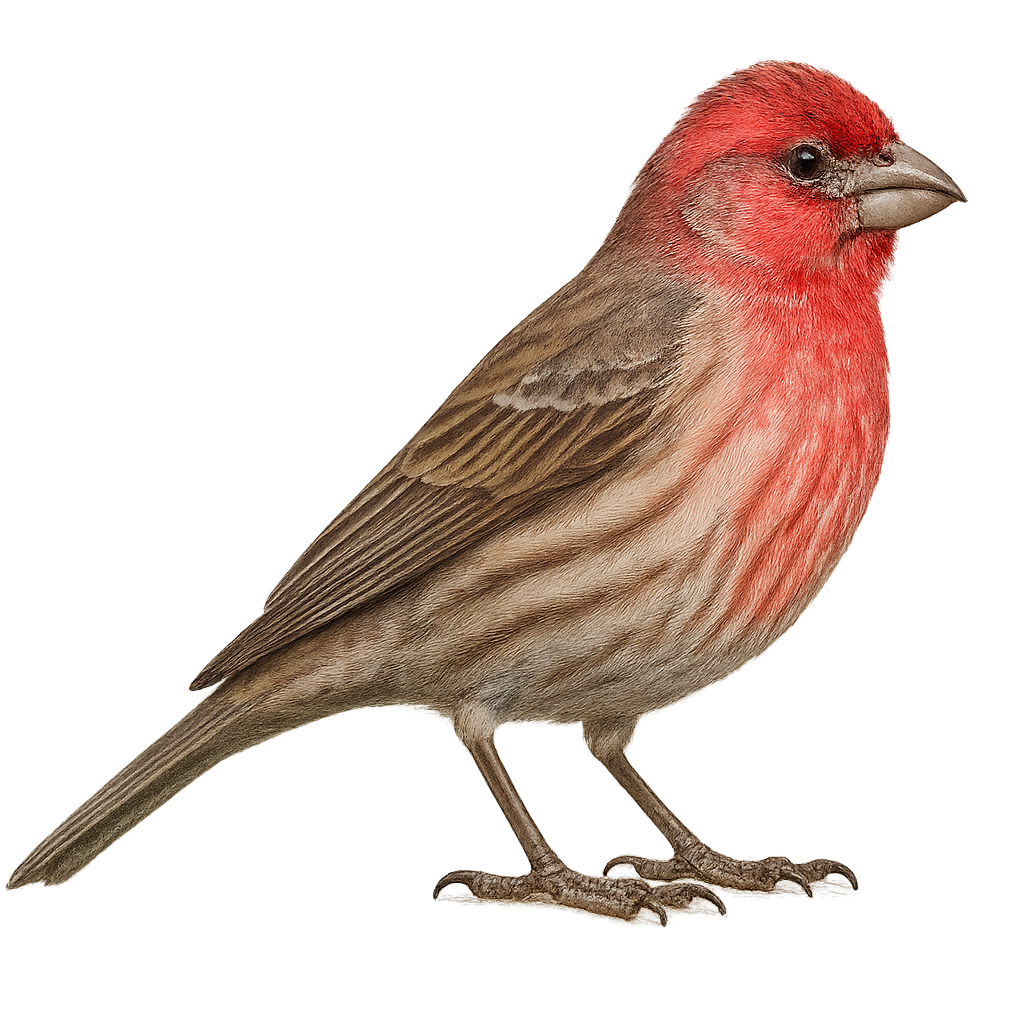
The House Finch, or Haemorhous mexicanus, is a small songbird native to North America. It is easily recognizable by its bright red plumage on the head, chest, and rump in males, while females display more subdued shades of brown and gray. These birds measure about 12 to 15 cm in length and have a wingspan of 20 to 25 cm. They are often seen in flocks, feeding on seeds, fruits, and occasionally insects. The House Finch is highly adaptable and can be found in various habitats, including urban areas, gardens, and open forests. It is known for its melodious song and ability to thrive in human-altered environments.
The Pallas's Rosefinch, scientifically known as Carpodacus roseus, is a small bird with striking plumage, predominantly bright pink in males and duller in females. It belongs to the Fringillidae family and is mainly found in the coniferous forests and shrublands of Northeast Asia. Its conical beak is well-suited for its granivorous diet, although it also consumes insects during summer. The Pallas's Rosefinch is a migratory bird, moving southward in winter. It is admired for its melodious song and vibrant colors, making it a favorite subject for birdwatchers and photographers. Although its conservation status is currently of least concern, habitat destruction could pose future threats.
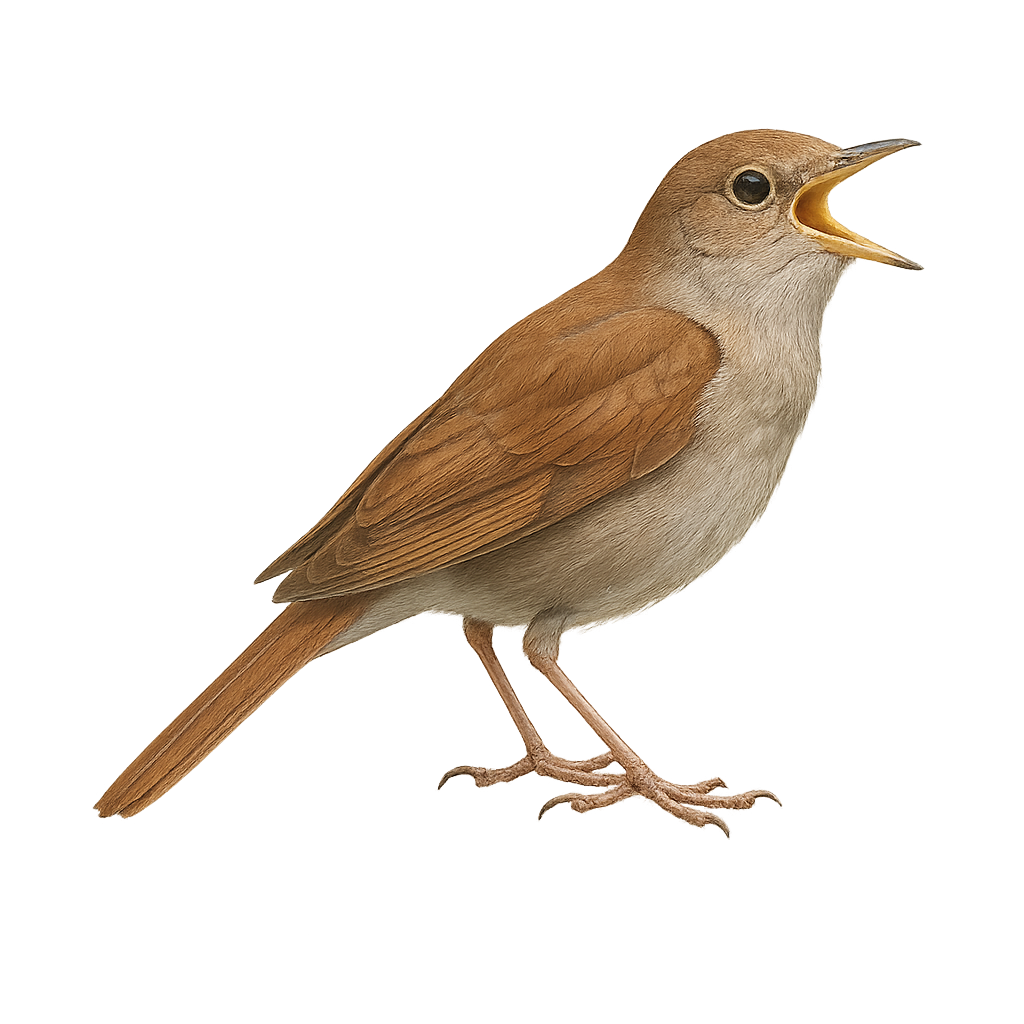
The nightingale is a small passerine bird known for its melodious and powerful song, found primarily in woodlands, thickets, and gardens across Europe and Asia. It is easily recognized by its brown-russet plumage and light belly, as well as its relatively short beak. The nightingale is especially famous for its song, which is particularly vibrant and long, especially during the breeding season. It prefers dense and well-hidden habitats to feed on insects and worms.
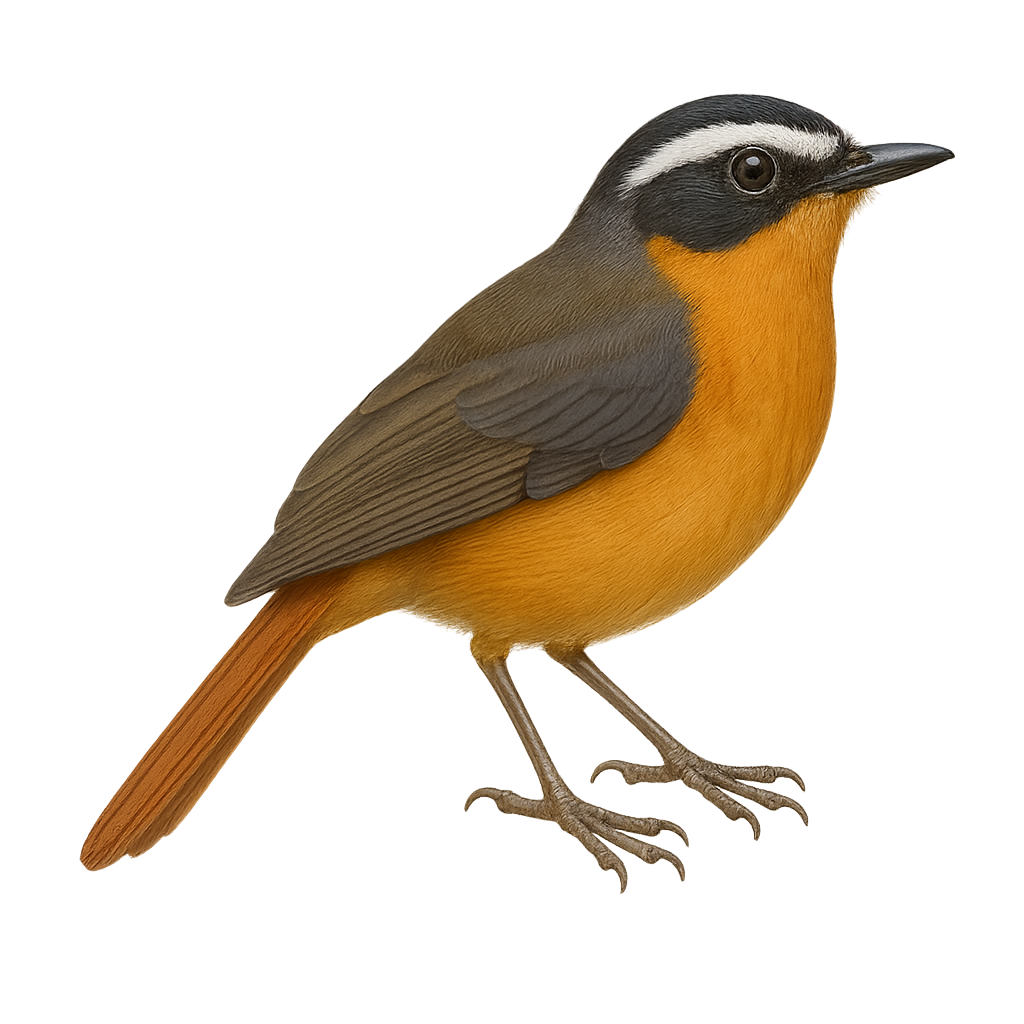
The Grey-winged Robin-chat, or Sheppardia polioptera, is a discreet and charming bird found mainly in the humid forests of Central and East Africa. This small passerine, about 15 cm long, is distinguished by its olive-brown plumage and characteristic grey wings. It is often seen in dense undergrowth, where it feeds on insects and small invertebrates. Its melodious and varied song is a delight for birdwatchers. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, the species is currently classified as of least concern by the IUCN. The Grey-winged Robin-chat is a shy bird, difficult to observe, but its presence is an indicator of the health of forest ecosystems.
The Eurasian robin is a small bird from the Muscicapidae family, easily recognized by its bright red breast. It is widely distributed across Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa. This bird is mostly active during the day, feeding mainly on insects, worms, and berries. Although very territorial, it is admired by photographers for its curious nature and active behavior.
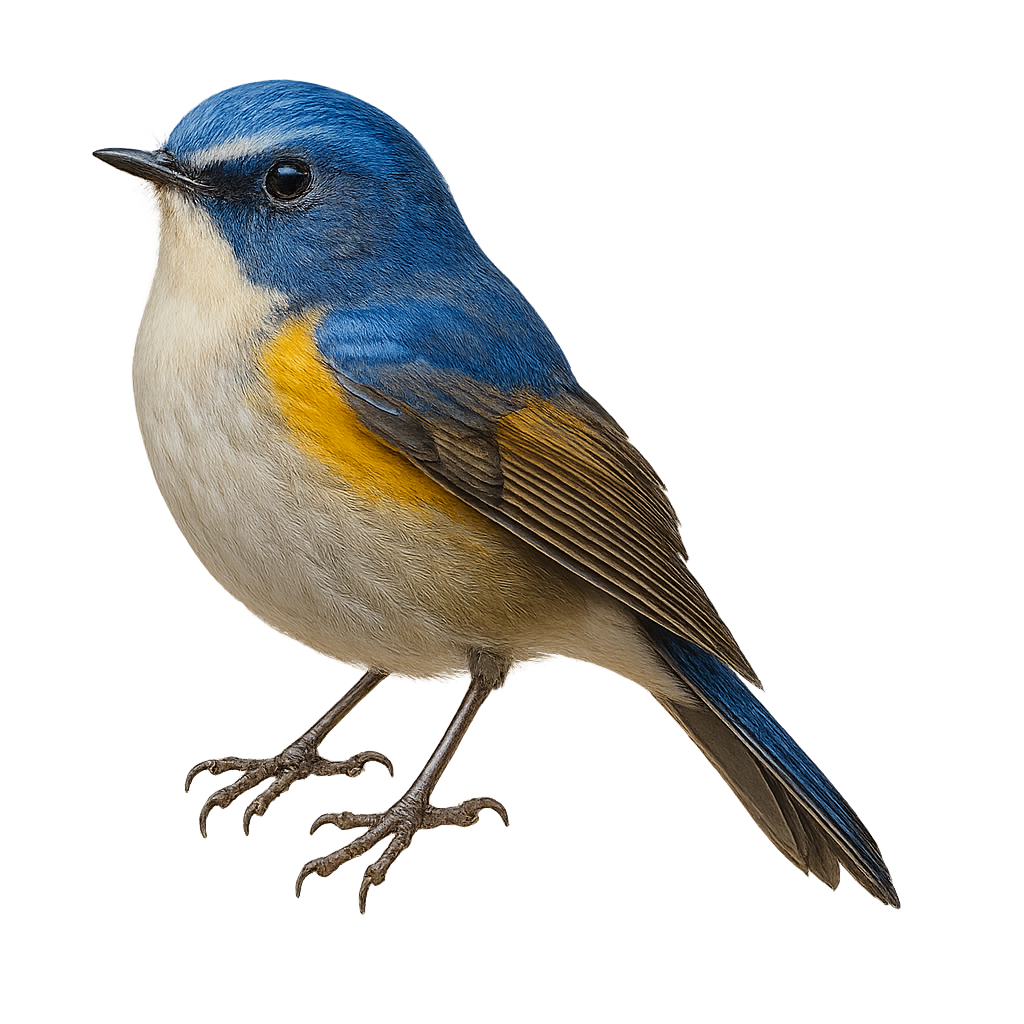
The Tarsiger cyanurus, commonly known as the Red-flanked Bluetail, is a small passerine bird from the Muscicapidae family. It is distinguished by its vibrant plumage, with rufous flanks and a blue tail in males, while females have more subdued tones. This migratory bird primarily inhabits coniferous forests and dense undergrowth in Eurasia. It is often seen hopping on the ground searching for insects and berries. Although discreet, its melodious song indicates its presence. Its population is stable, but it is sensitive to environmental changes, especially deforestation.
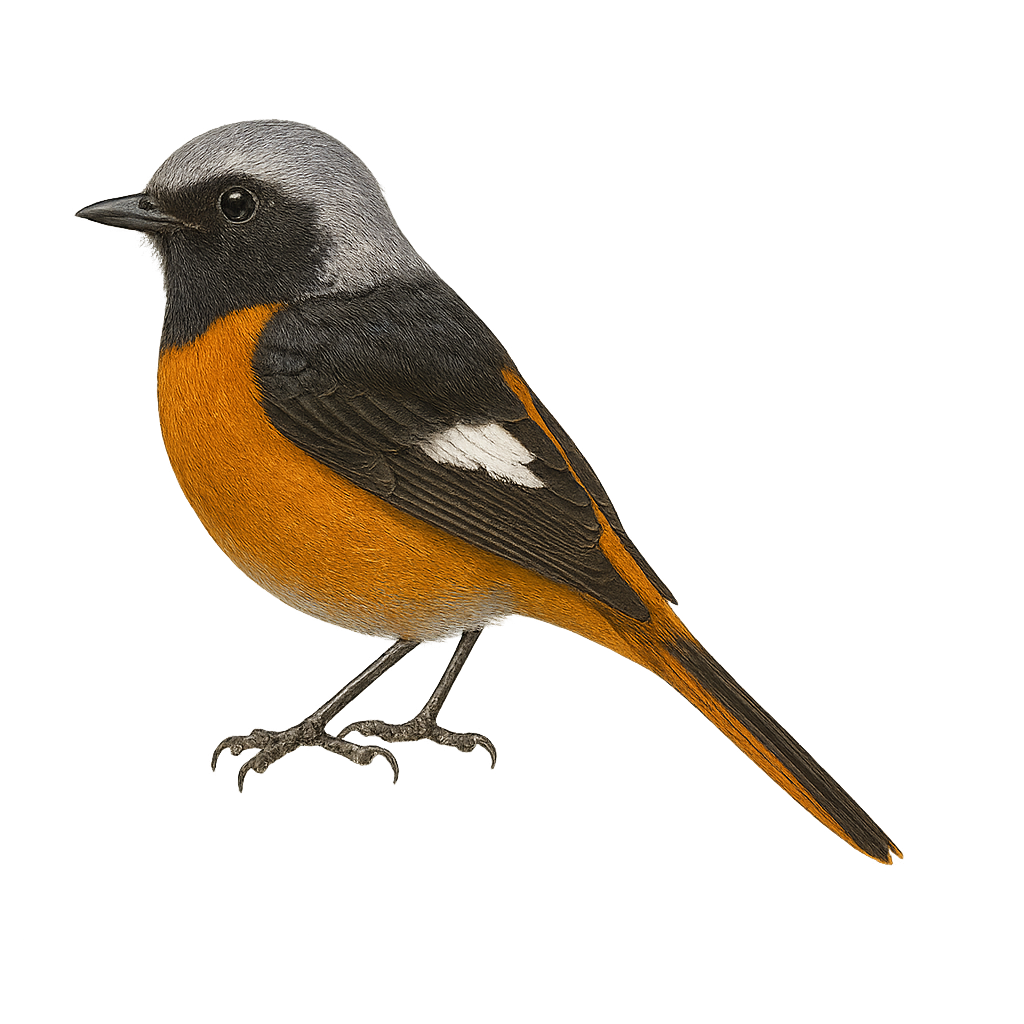
The common redstart is a small passerine of 12–14 cm with bluish-grey upperparts and bright orange underparts, featuring a white forehead and black facial mask. It inhabits mixed woodlands, edges, parks and gardens, feeding mainly on insects caught on the wing and on the ground. During breeding, males sing from low perches to attract females and defend territories.
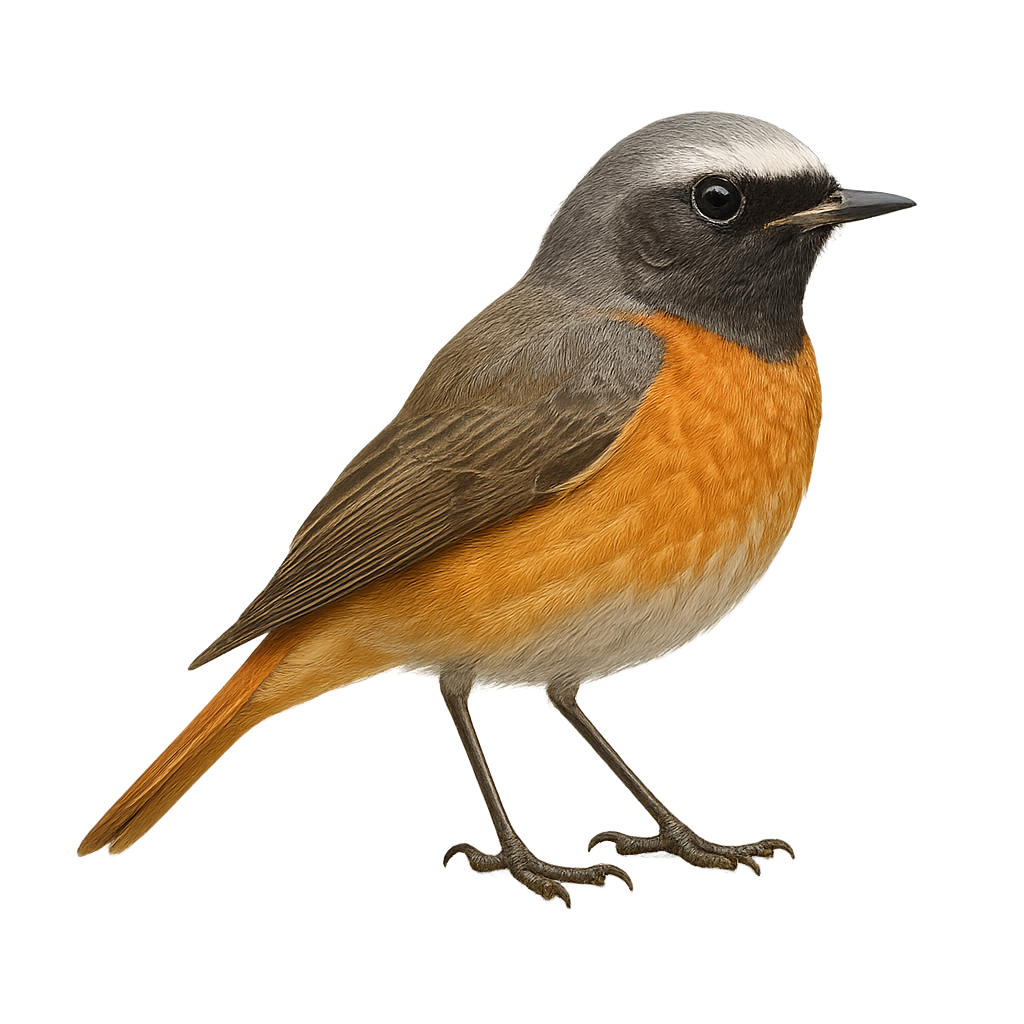
The Daurian Redstart, or Phoenicurus auroreus, is a small passerine bird belonging to the Muscicapidae family. It is easily identifiable by its distinctive plumage: the male sports a black head with a white forehead patch, a gray back, and a bright orange chest, while the female displays more subdued shades of brown and orange. This small bird is often seen in forests, parks, and gardens across East Asia, particularly in China, Korea, and Japan. Known for its melodious song, it adapts well to various habitats, including urban areas. As a partial migrant, it moves southward during winter months to escape cold temperatures.
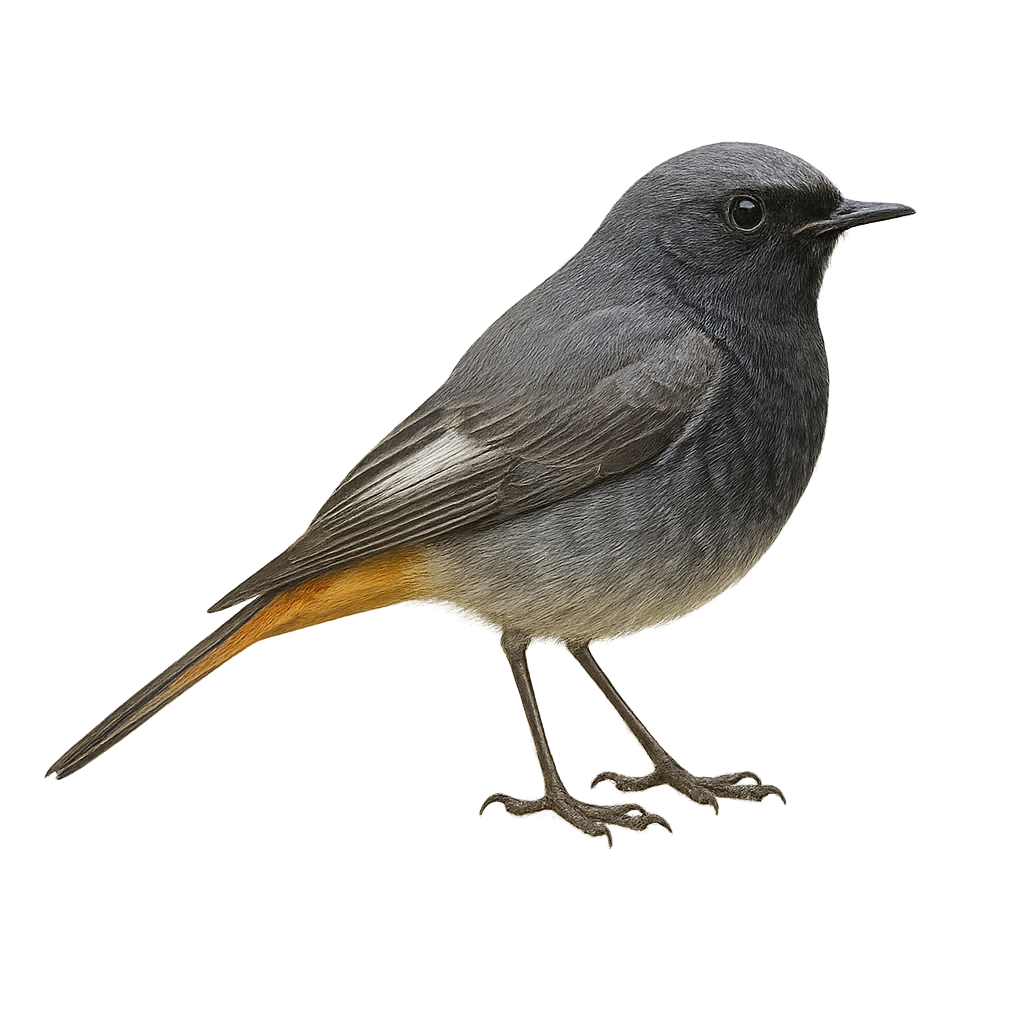
The black redstart is a small passerine bird found primarily in urban areas, gardens, rocky habitats, and steep slopes across Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. It is distinguished by its dark gray plumage, light belly, and orange-red tail. This small bird is especially known for its lively behavior and ability to adapt to human environments. It primarily feeds on insects and berries, which it finds in urban spaces or wooded areas.
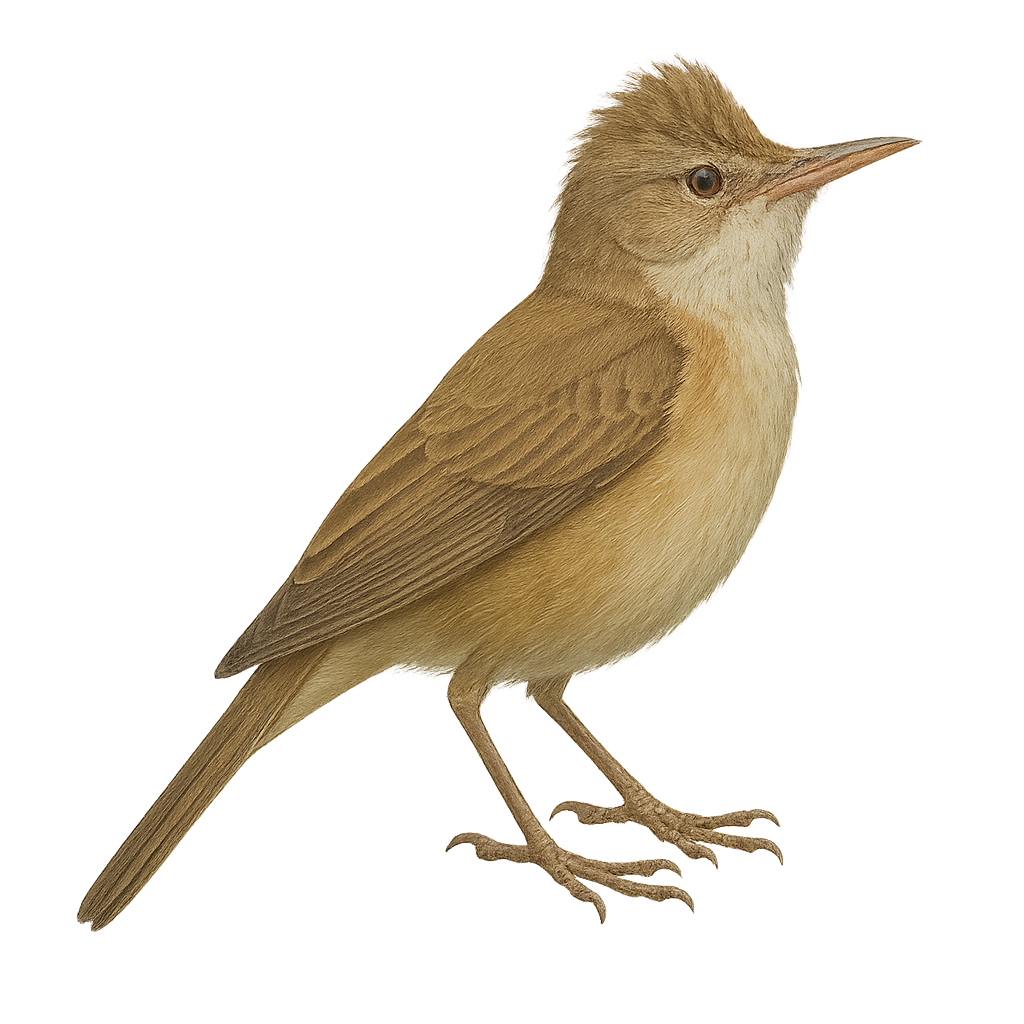
The Oriental Reed Warbler, Acrocephalus orientalis, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Acrocephalidae family. It is primarily found in Asia, particularly in eastern Russia, China, and Japan. This migratory bird is known for its long journeys to Southeast Asia during the winter. Its plumage is generally olive-brown on the top and lighter underneath, allowing it to blend into the reeds and marshes it frequents. The Oriental Reed Warbler feeds mainly on insects and small invertebrates, which it captures in dense foliage. Its song is melodious and varied, often heard in spring and summer.
Cetti's warbler is a small passerine, 11–13 cm long, with dull brown-olive plumage and pink legs. Secretive species of riverside scrub and reedbeds, feeding mainly on insects and spiders. During breeding the male sings loudly from an exposed perch to mark its territory.
The Rodrigues Warbler, or Acrocephalus brevipennis, is a small passerine bird endemic to Rodrigues Island in the Indian Ocean. This bird is primarily recognized for its olive-brown plumage and melodious song. It inhabits the wooded areas and marshes of the island, where it feeds mainly on insects. The Rodrigues Warbler is critically endangered, mainly due to deforestation and habitat loss. Conservation efforts are underway to protect this unique species, including habitat restoration and captive breeding programs.
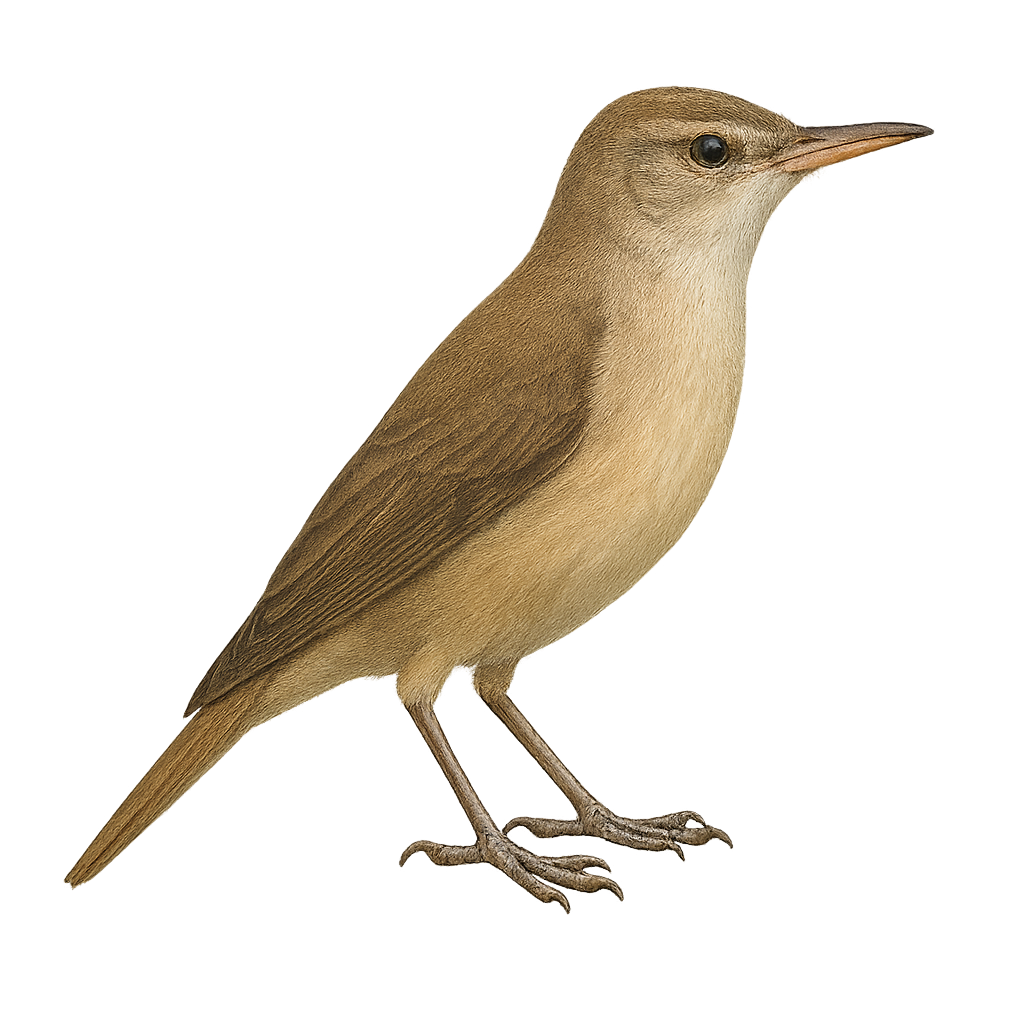
The common reed warbler is a medium-sized warbler, about 13 cm long, with plain brown upperparts and buff underparts. It is secretive in reedbeds, feeding chiefly on insects and spiders gleaned from stems. During breeding, the male sings from a low perch to defend its territory and court the female.
The great reed warbler is an insectivorous passerine and the largest of the European reed warblers, measuring 18.5–20 cm in length with a 24–27 cm wingspan and weighing 25–38 g. It has unstreaked brown upperparts, buffish-white underparts and a pale supercilium. It inhabits dense reed beds, marshes and waterside vegetation, feeding mainly on insects, spiders and small amphibians.
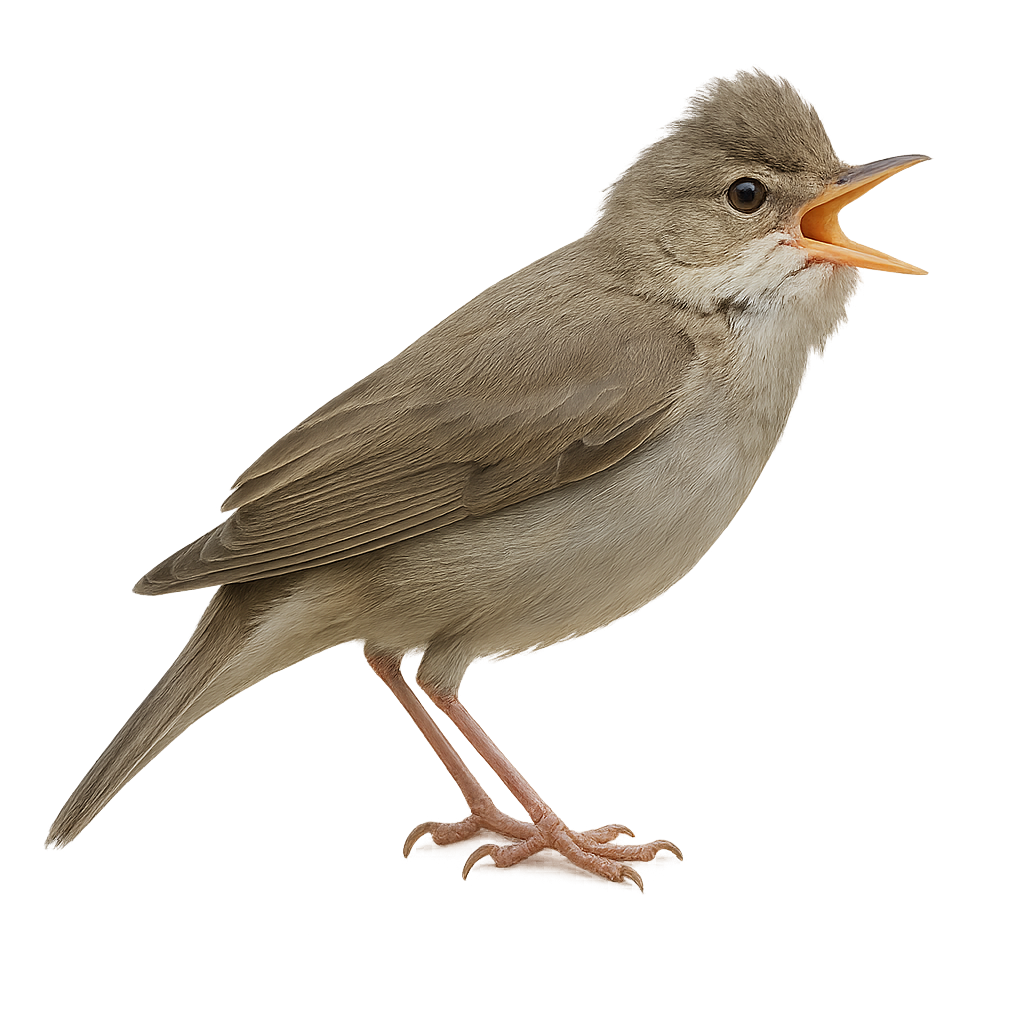
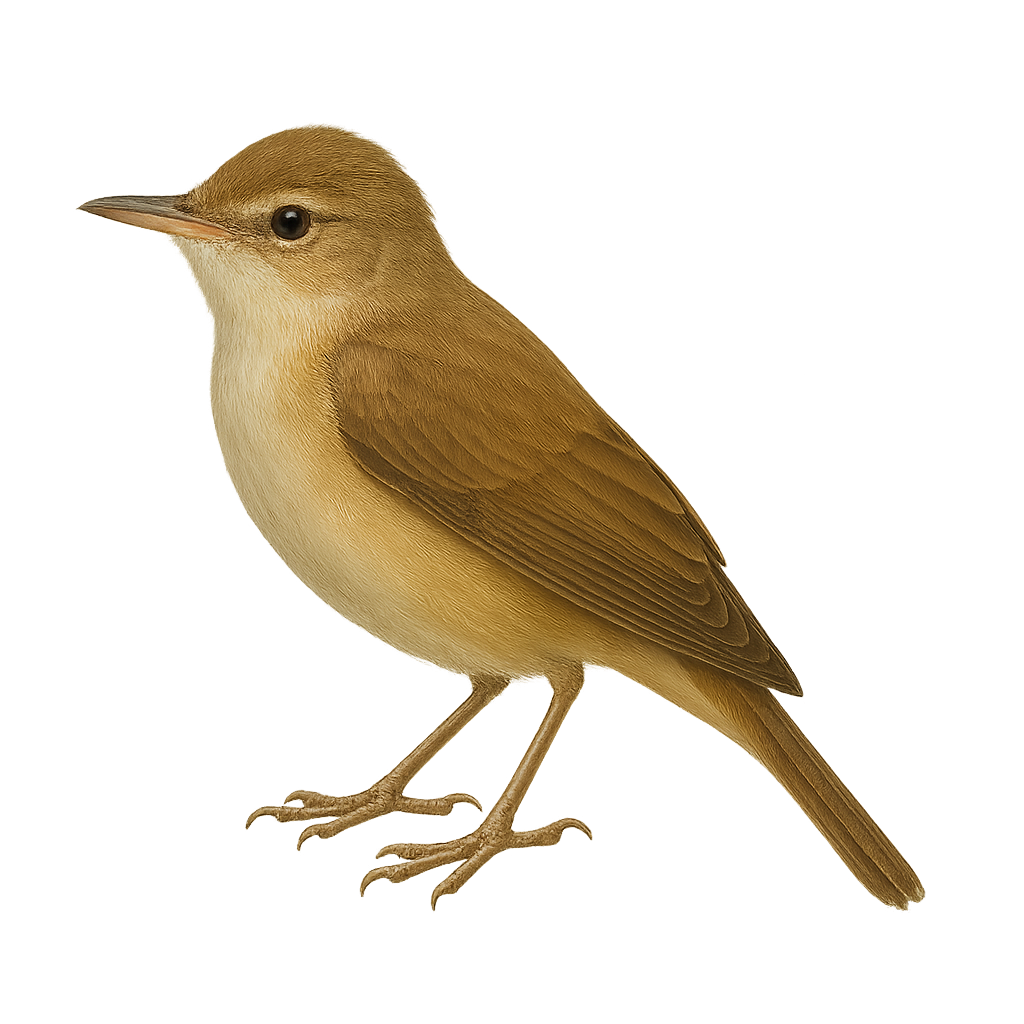
The Eurasian reed warbler is a small migratory passerine, 11–13 cm long, with olive-brown plumage and a repetitive, hiss-like song. It inhabits reed beds and freshwater marshes, feeding on insects and larvae. During the breeding season, the male sings from an exposed perch and the pair builds a vase-shaped woven nest within dense reed vegetation.
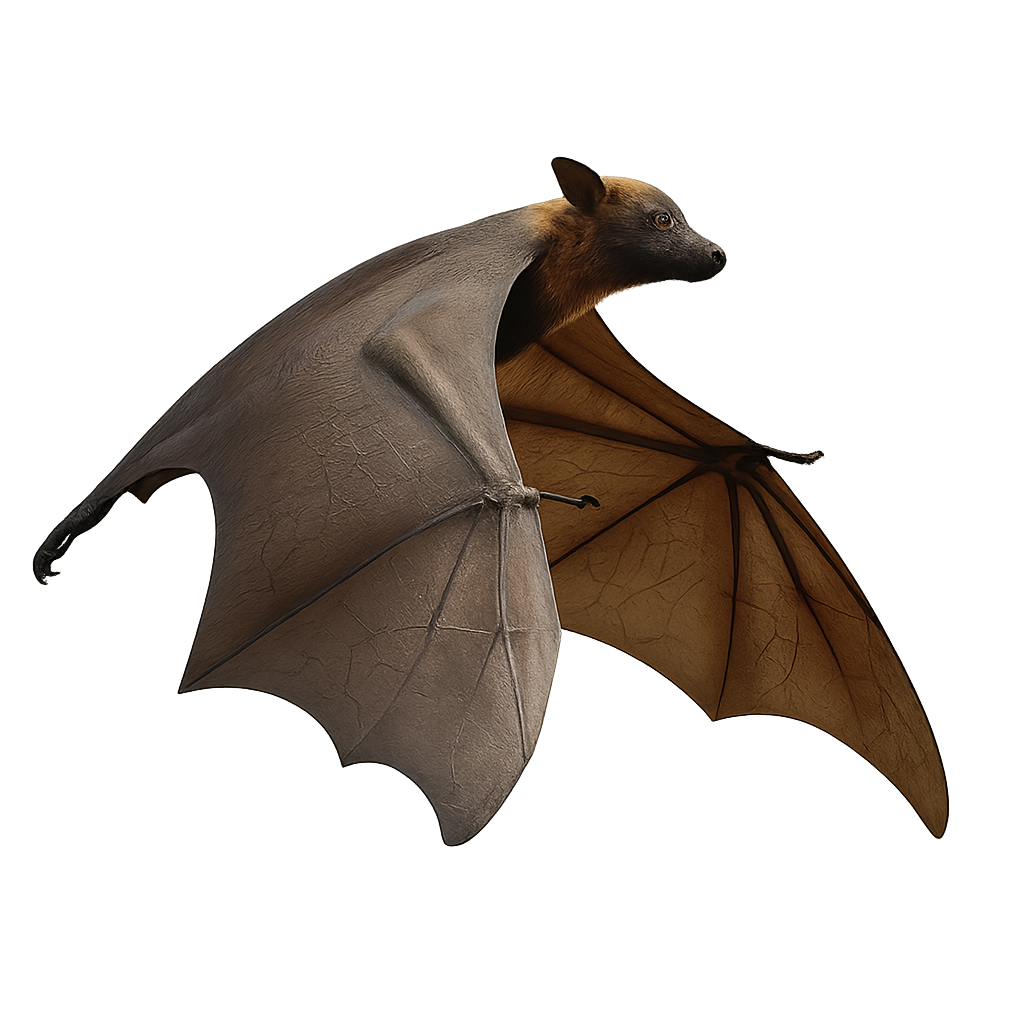
The large flying fox is a large frugivorous bat with a wingspan up to 1.5 m and weight up to 1 kg. Its grey-brown fur, accented by a pale yellow collar, covers its elongated body and long muzzle. Endemic to Southeast Asia (Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines, Thailand), it roosts in colonies in forests and coastal mangroves, feeding on fruits, nectar, and flowers. During the breeding season, males defend a small harem and mate between November and January, with a single pup born in March-April.
The African straw-coloured fruit bat is a fruit-eating bat species native to sub-Saharan Africa. This bat is easily recognizable by its golden or straw-colored fur, which helps it blend into the foliage during the day. The African straw-coloured fruit bats primarily feed on fruits, nectar, and pollen, playing a crucial role in pollinating plants. They form large colonies and are often seen in flight at dusk as they head out to search for food. These bats can also travel long distances, making them adaptable to a wide range of habitats.
The saiga is an antelope from the Central Asian steppes, recognizable by its prominent, trunk-like nose that filters dust and warms inhaled air. Adapted to arid environments, it migrates in large herds in search of pastures. Its population, once declining, shows signs of recovery due to conservation efforts.
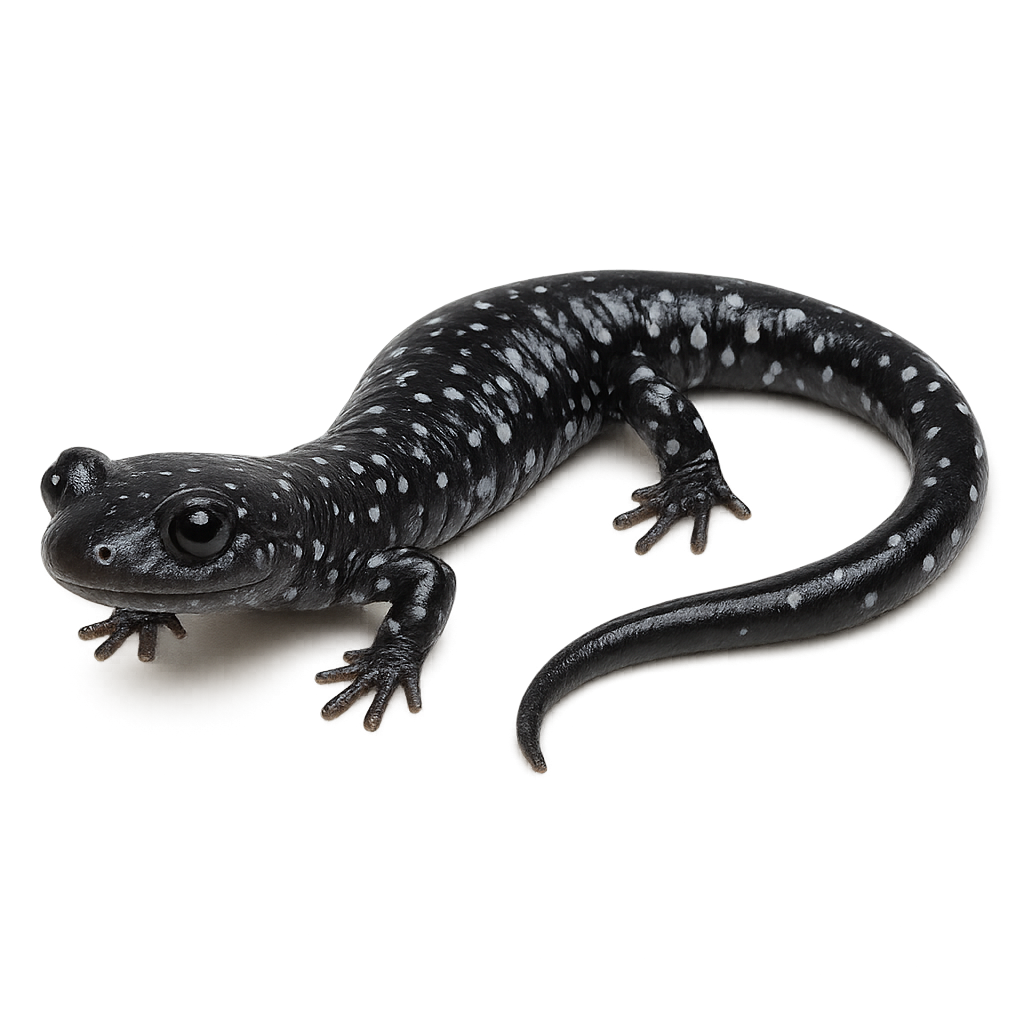
Plethodon albagula, commonly known as the Western Slimy Salamander, is an amphibian species in the Plethodontidae family. It is primarily found in the wooded regions of central United States, particularly in moist and shaded areas. This salamander is characterized by its smooth and moist skin, often black with white or grayish spots on its back. It typically measures between 10 and 15 cm in length. Nocturnal, it primarily feeds on insects and other small invertebrates. Unlike many other salamander species, it lacks lungs and breathes through its skin. Its reproduction is terrestrial, and it lays its eggs in moist places, where the larvae develop without an aquatic phase.
The Proteus anguinus, commonly known as the olm, is a fascinating amphibian inhabiting the karst caves of the Dinaric region in Europe. This curious animal is adapted to underground life, with depigmented skin and atrophied eyes, rendering its vision almost nonexistent. It typically measures between 20 and 30 centimeters in length and has an elongated, eel-like body with reduced limbs. Its respiration is ensured by feathery external gills, allowing it to live in oxygen-poor underground waters. The Proteus anguinus primarily feeds on small aquatic invertebrates. Its exceptional longevity, reaching up to 100 years, and its ability to survive without food for several years make it a captivating subject of study for scientists.
The California Newt, Taricha torosa, is a fascinating amphibian native to the west coast of the United States. It is distinguished by its rough skin and bright coloration, ranging from dark brown on the back to bright orange on the belly. This coloration serves as a warning to potential predators, as it secretes a powerful toxin called tetrodotoxin. Typically measuring between 12 and 20 cm, it primarily inhabits moist forests, grasslands, and riparian zones. During the breeding season, it migrates to ponds and streams to lay its eggs. Although primarily terrestrial, it returns to water to breed. Its ability to regenerate body parts makes it an interesting subject of study for scientists.
The Corsican Salamander, or Salamandra corsica, is an amphibian endemic to the island of Corsica. It is characterized by its black skin adorned with irregular yellow spots, a pattern that varies among individuals. This salamander prefers humid and shaded habitats, such as oak and pine forests, as well as rocky areas near watercourses. It is primarily nocturnal, hiding under stones or in crevices during the day. Its reproduction is viviparous, with females giving birth to aquatic larvae. Although its population is stable, it is sensitive to environmental changes and water pollution.
The Lanza's Alpine Salamander, or Salamandra lanzai, is a rare and fascinating species of salamander endemic to the Cottian Alps, straddling France and Italy. It is characterized by its glossy black skin, often dotted with small yellow spots. Adapted to alpine environments, it primarily inhabits rocky and humid areas at altitudes ranging from 1200 to 2800 meters. This salamander is viviparous, meaning it gives birth to fully formed young after a gestation period that can last several months. Due to its restricted habitat and sensitivity to environmental changes, it is classified as vulnerable by the IUCN. Its behavior is rather suspicious, and it is mainly nocturnal.
The Eastern hellbender is one of the largest salamander species in the world, growing up to 75 cm in length. It primarily inhabits clear rivers and streams in the United States, where it hides among rocks and feeds on small aquatic invertebrates. This amphibian is particularly sensitive to water pollution and habitat loss. Due to these threats, the Eastern hellbender is classified as a vulnerable species.
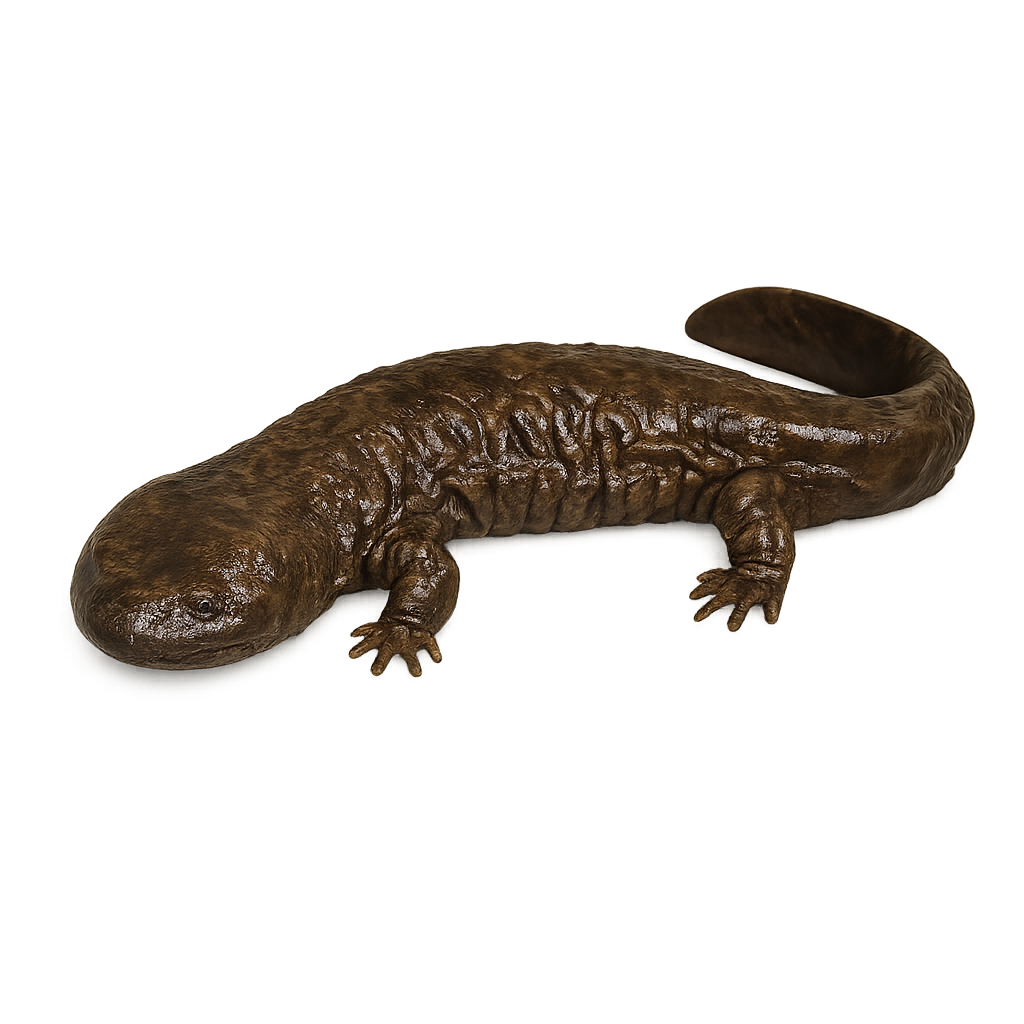
The Chinese giant salamander, Andrias davidianus, is the largest amphibian in the world, reaching up to 1.8 meters in length. It primarily inhabits mountain rivers and lakes in China. Its skin is rough and dark brown, allowing it to blend into its aquatic surroundings. It is mainly nocturnal and feeds on fish, crustaceans, and insects. Unfortunately, this species is critically endangered due to habitat loss and water pollution. The Chinese giant salamander is also threatened by illegal hunting for its meat, considered a delicacy.