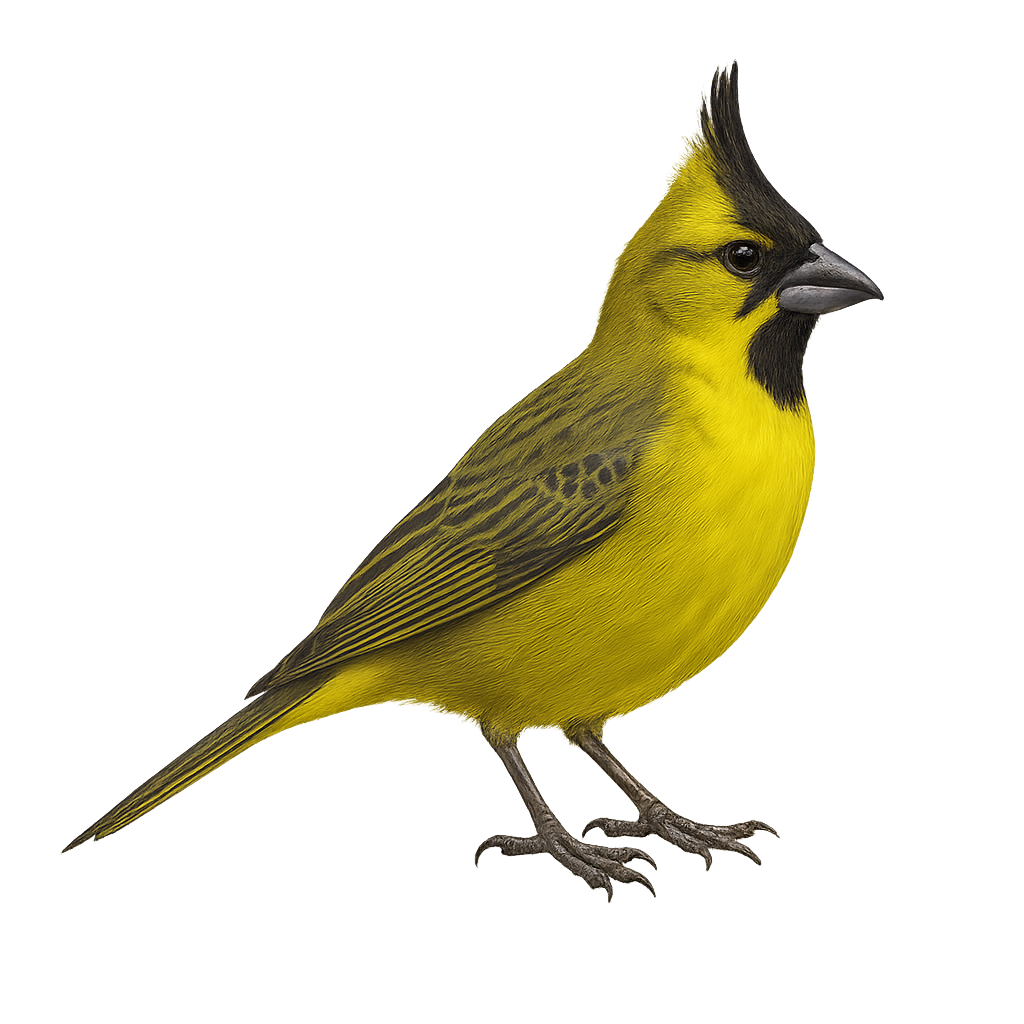
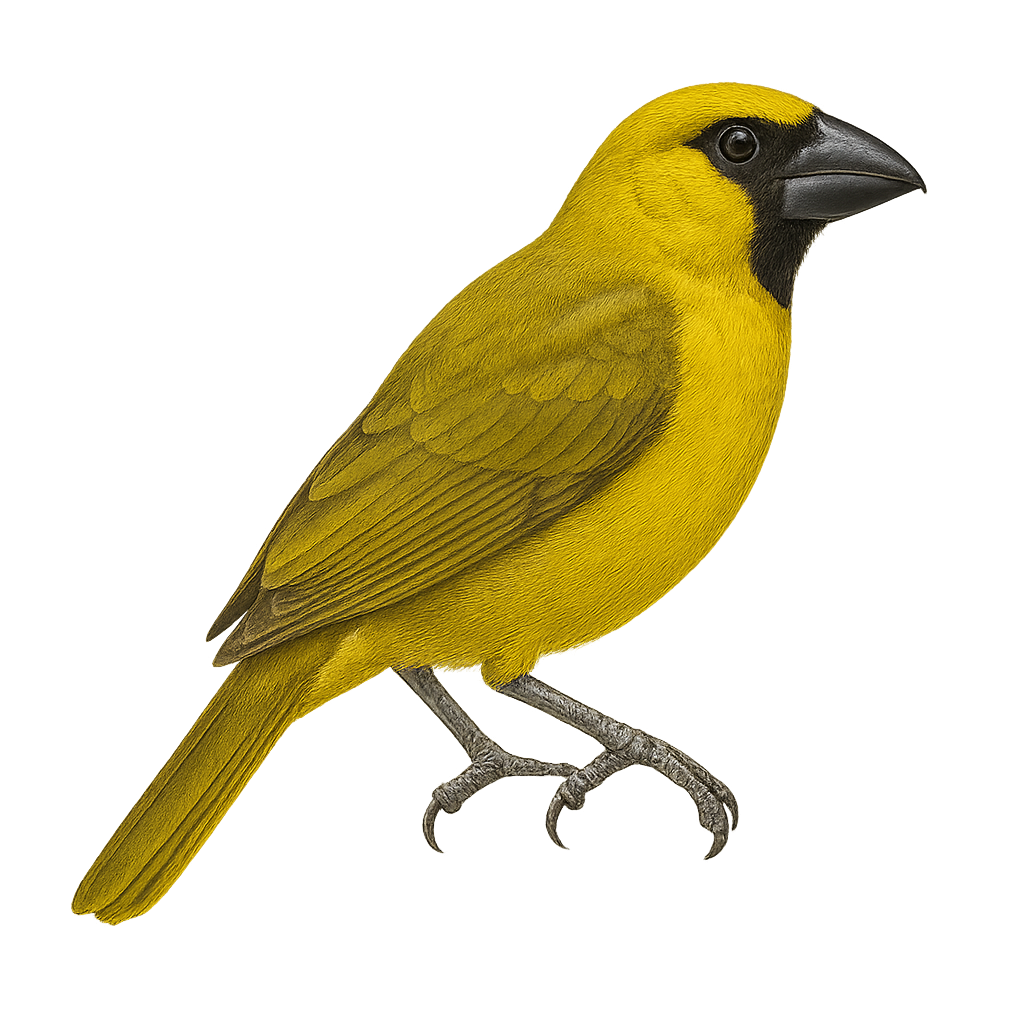
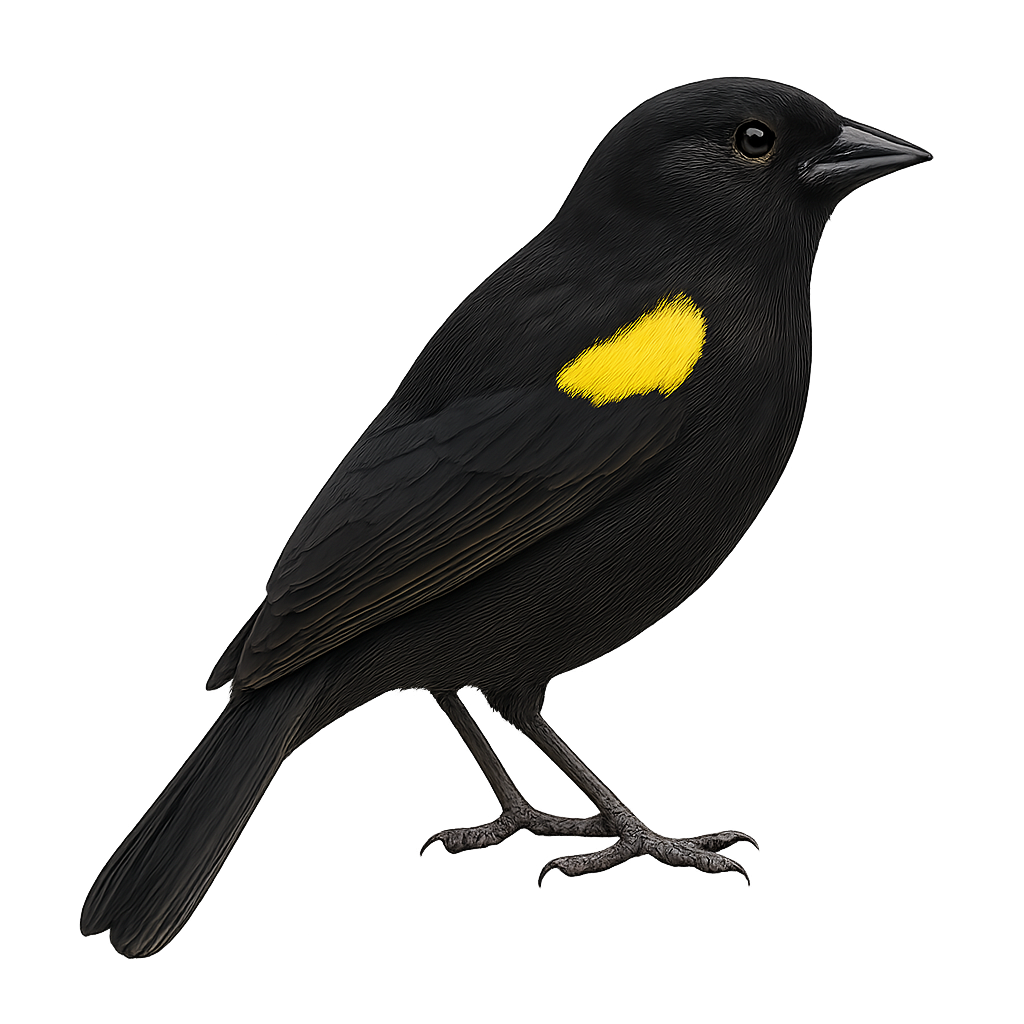
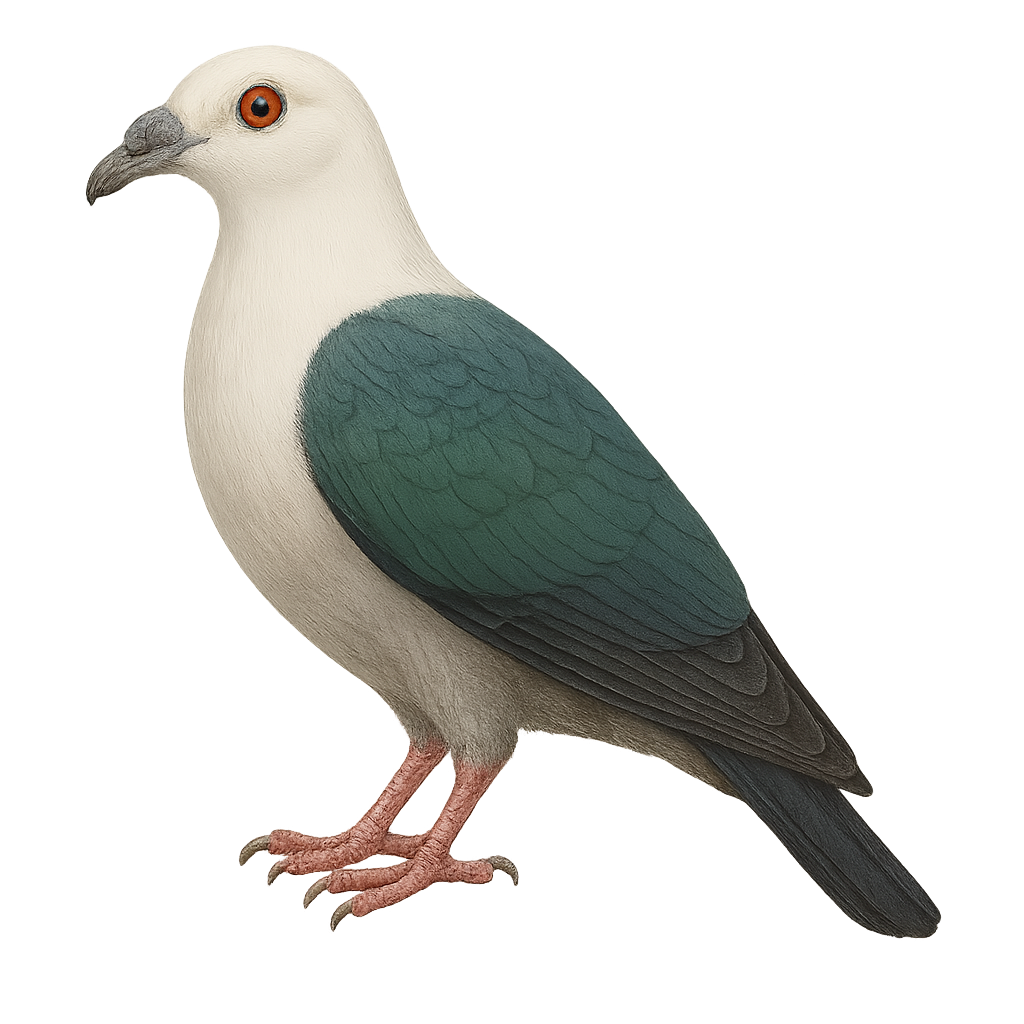
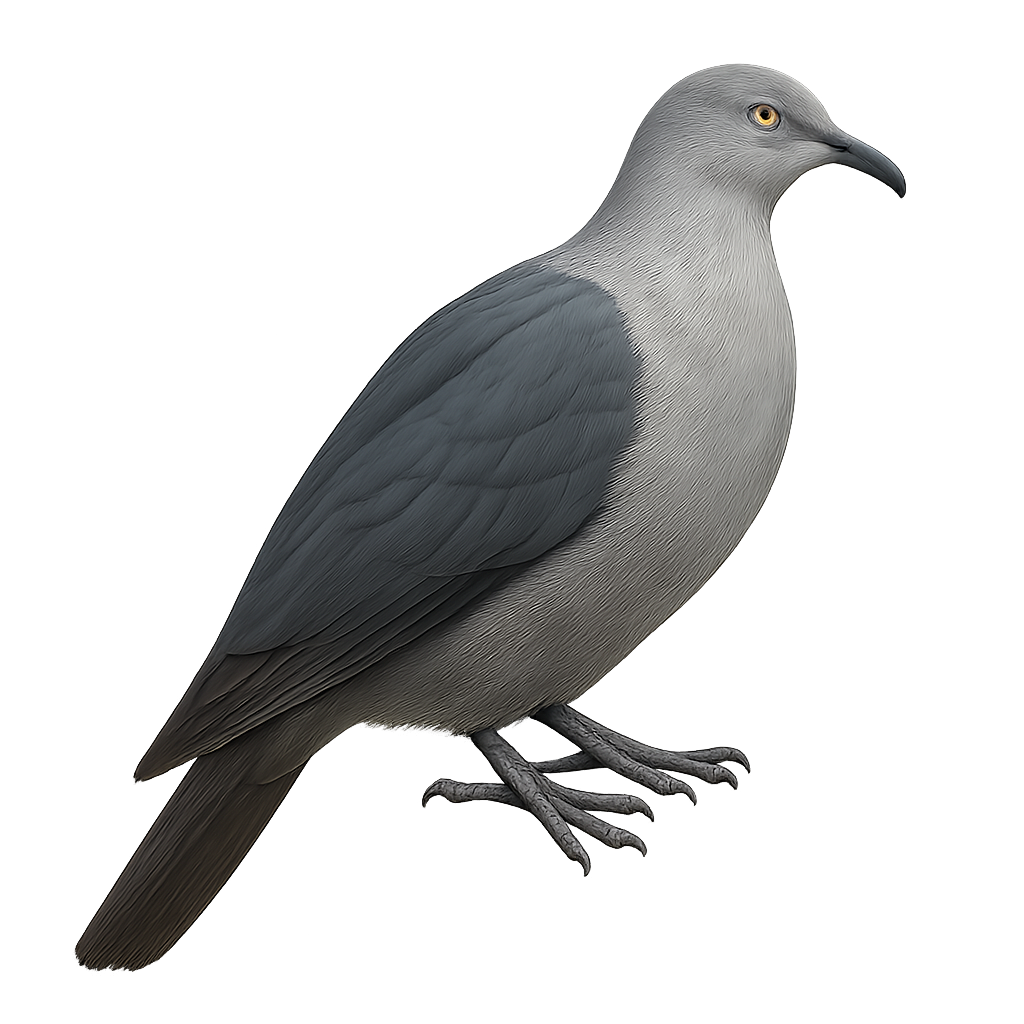
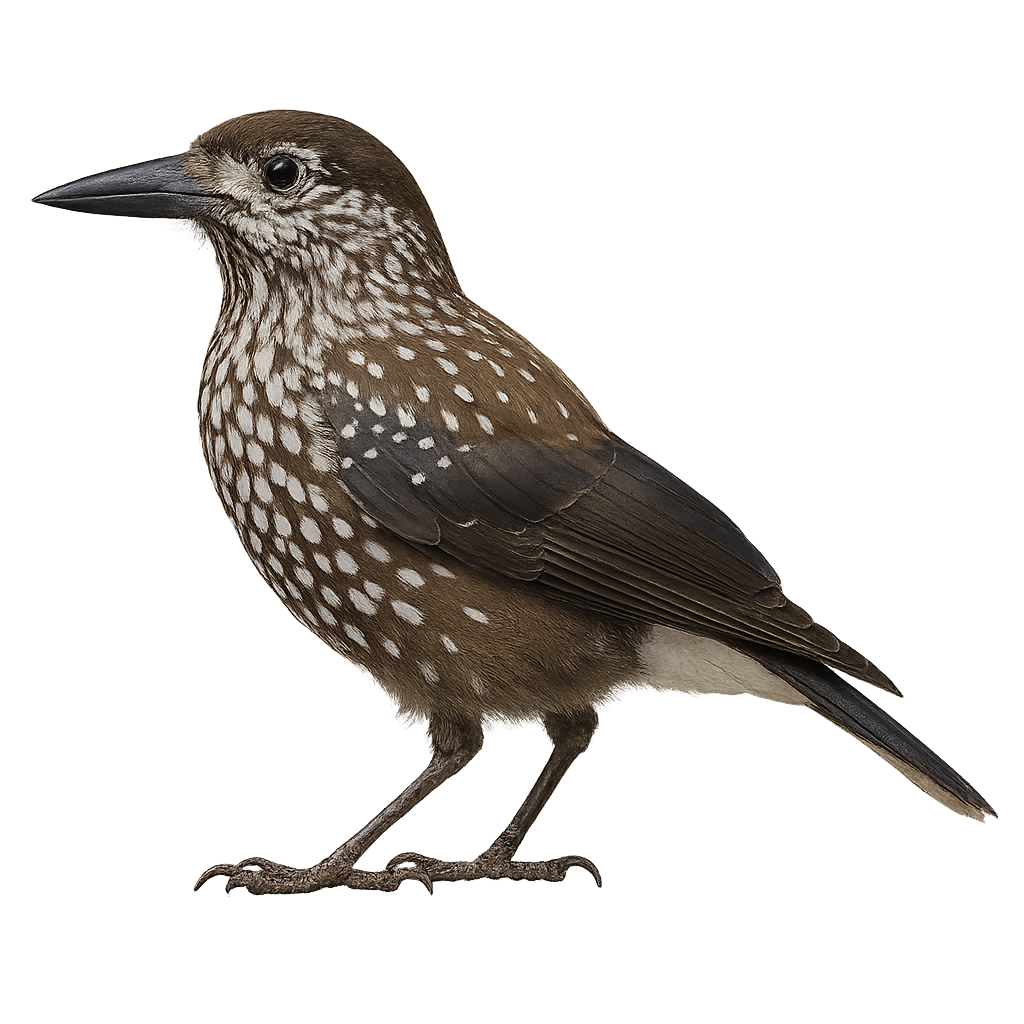
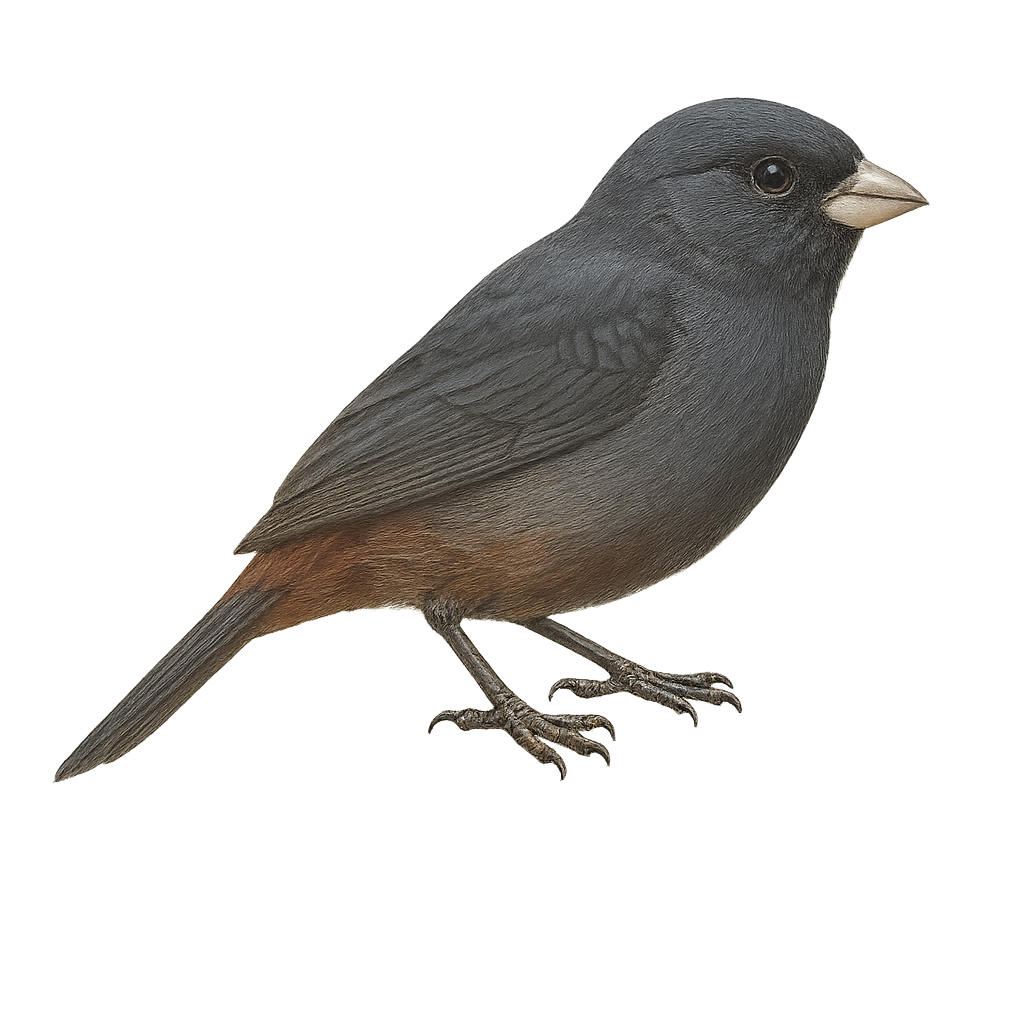
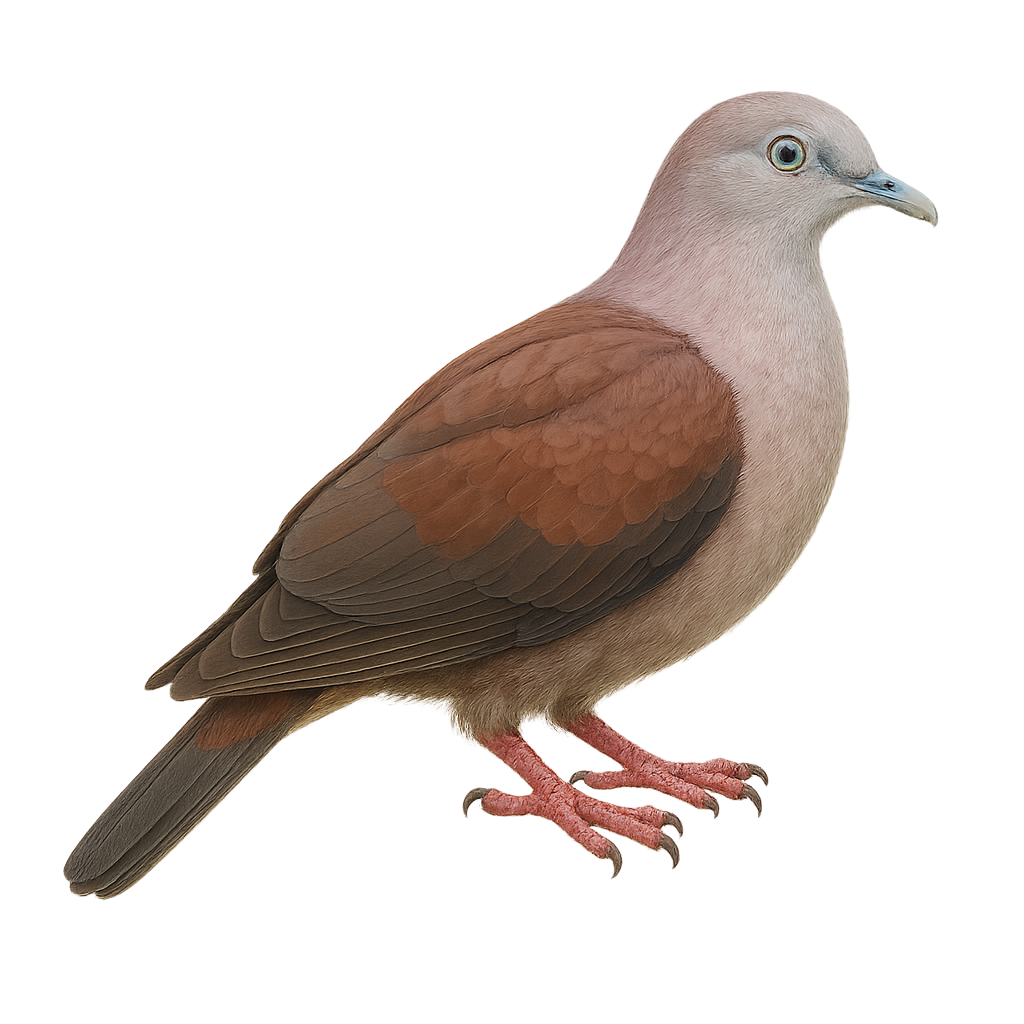
The Gubernatrix cristata, commonly known as the Yellow Cardinal, is a medium-sized songbird recognizable by its distinctive crest and bright yellow plumage. Native to South America, it primarily inhabits the wooded regions and open savannas of Argentina, Uruguay, and Brazil. Unfortunately, this species is endangered due to illegal capture for the pet trade and habitat loss. The Yellow Cardinal is a social bird, often observed in small groups. Its melodious and powerful song is a characteristic trait that attracts the attention of ornithologists and bird enthusiasts. Conservation efforts are underway to ensure its survival, including the protection of its natural habitat and captive breeding programs.
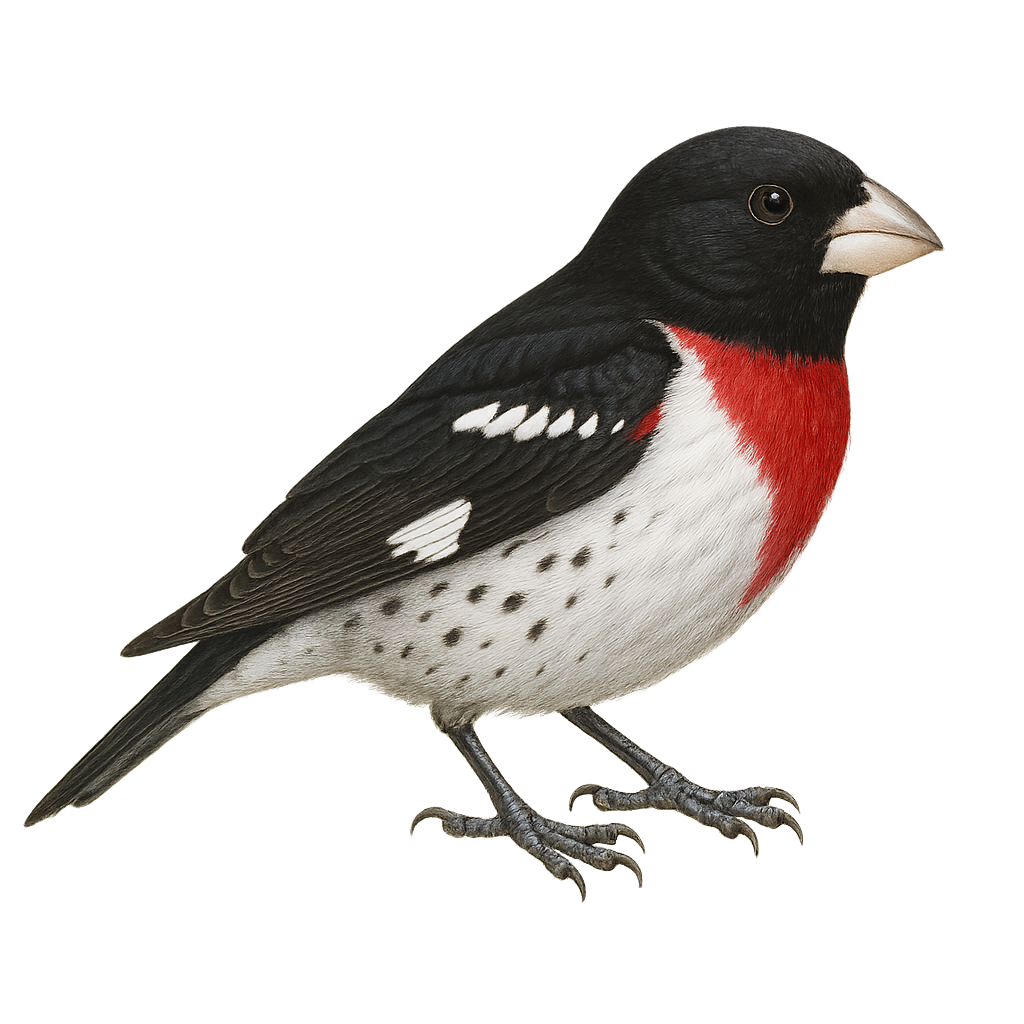
The Rose-breasted Grosbeak is a medium-sized songbird, easily identifiable by its vivid rose-colored breast contrasting with its black and white plumage. Males display brighter plumage than females, who are mostly brown with hints of yellow. This bird inhabits deciduous forests and woodland edges in North America, migrating to Central America for the winter. Its melodious song is often compared to that of a robin. It primarily feeds on seeds, fruits, and insects. The Rose-breasted Grosbeak is a sociable bird, often seen in small groups. Its breeding season extends from spring to summer, with nests built in trees or shrubs.
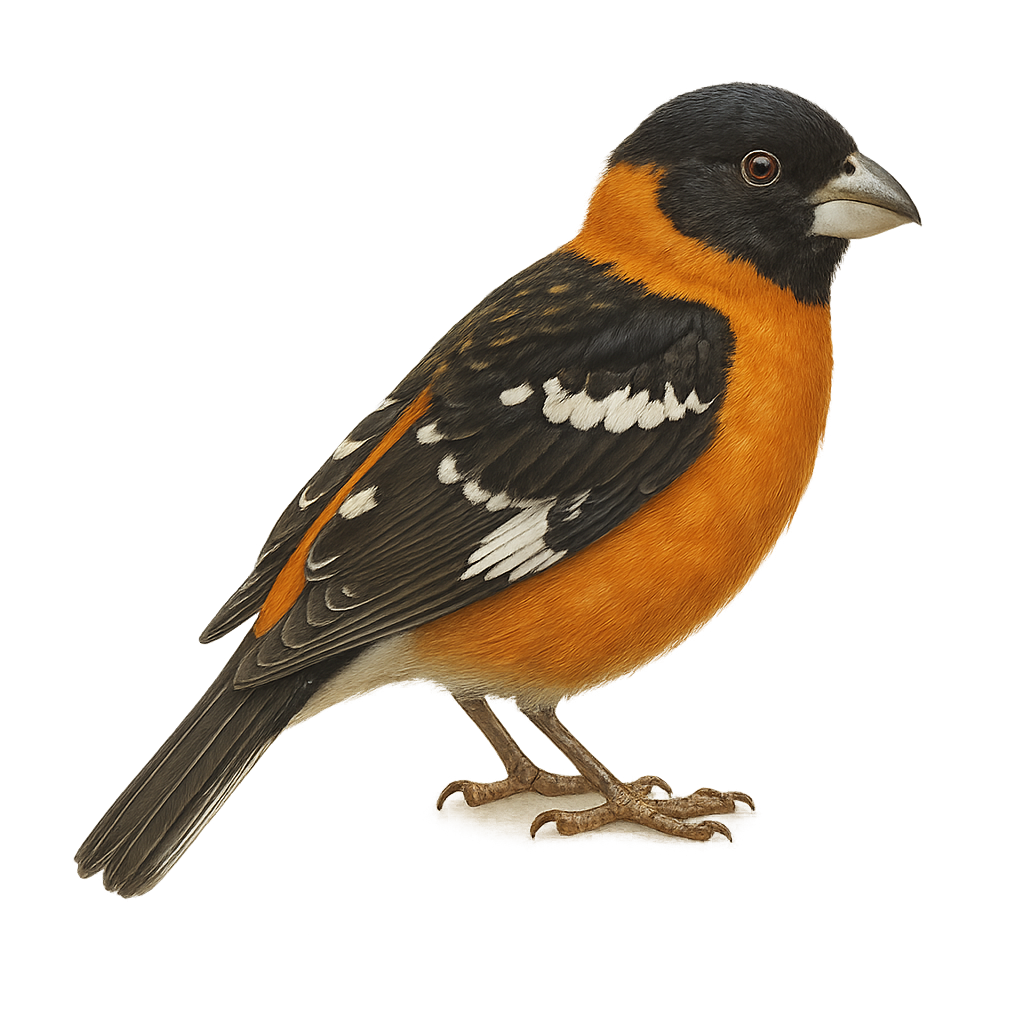
The Black-headed Grosbeak is a medium-sized songbird known for its striking black head and contrasting orange and white body. It primarily inhabits coniferous forests and open woodlands in North America. Its melodious song is often likened to that of a robin. This migratory bird feeds mainly on seeds, fruits, and insects, playing a crucial role in seed dispersal and insect population control. Its breeding season spans from spring to summer, during which it builds nests in trees or shrubs.
The Slate-colored Grosbeak is a medium-sized bird, identifiable by its predominantly slate-gray plumage and robust, thick beak, perfect for cracking seeds. It primarily inhabits the humid tropical forests of Central and South America, where it feeds on fruits, seeds, and insects. This bird is often seen in pairs or small groups, moving through the canopy in search of food. Although its song is melodious, it is often discreet and difficult to observe due to its suspicious behavior. Its presence is an indicator of the health of tropical forests, as it relies on these habitats for survival.
The Yellow-green Grosbeak, Caryothraustes canadensis, is a vibrant bird found primarily in the tropical rainforests of Central and South America. Its plumage is a bright green with yellowish hues on the belly, and it has a robust silver-colored beak, which gives it its name. This bird measures about 18 cm in length and feeds mainly on fruits, seeds, and insects. It is often seen in small groups, actively moving through the canopy in search of food. Although relatively common in its natural habitat, it remains discreet and can be difficult to spot due to its plumage blending into the dense foliage.
The Black-throated Saltator is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Thraupidae family. It is primarily found in the humid forests and wooded areas of South America, particularly in Brazil, Argentina, and Paraguay. This bird is characterized by its dark plumage, with a black throat contrasting with its lighter belly. The Black-throated Saltator is mainly granivorous, but it also feeds on insects and small fruits. It is often observed in pairs or small groups, actively moving through the canopy in search of food. Although not considered threatened, deforestation and habitat loss could impact its populations in the long term.
The Northern Cardinal, or Cardinalis cardinalis, is a striking bird found in North American gardens, easily recognized by the male's bright red plumage and the female's brownish-red hue. This medium-sized passerine, measuring about 21 to 23 cm in length, features a distinctive crest and a black mask around its beak. It is commonly seen in forests, gardens, and shrublands. Its melodious and varied song is a key aspect of its behavior, used to mark territory and attract mates. The Northern Cardinal is a non-migratory bird, known for its year-round territorial fidelity.
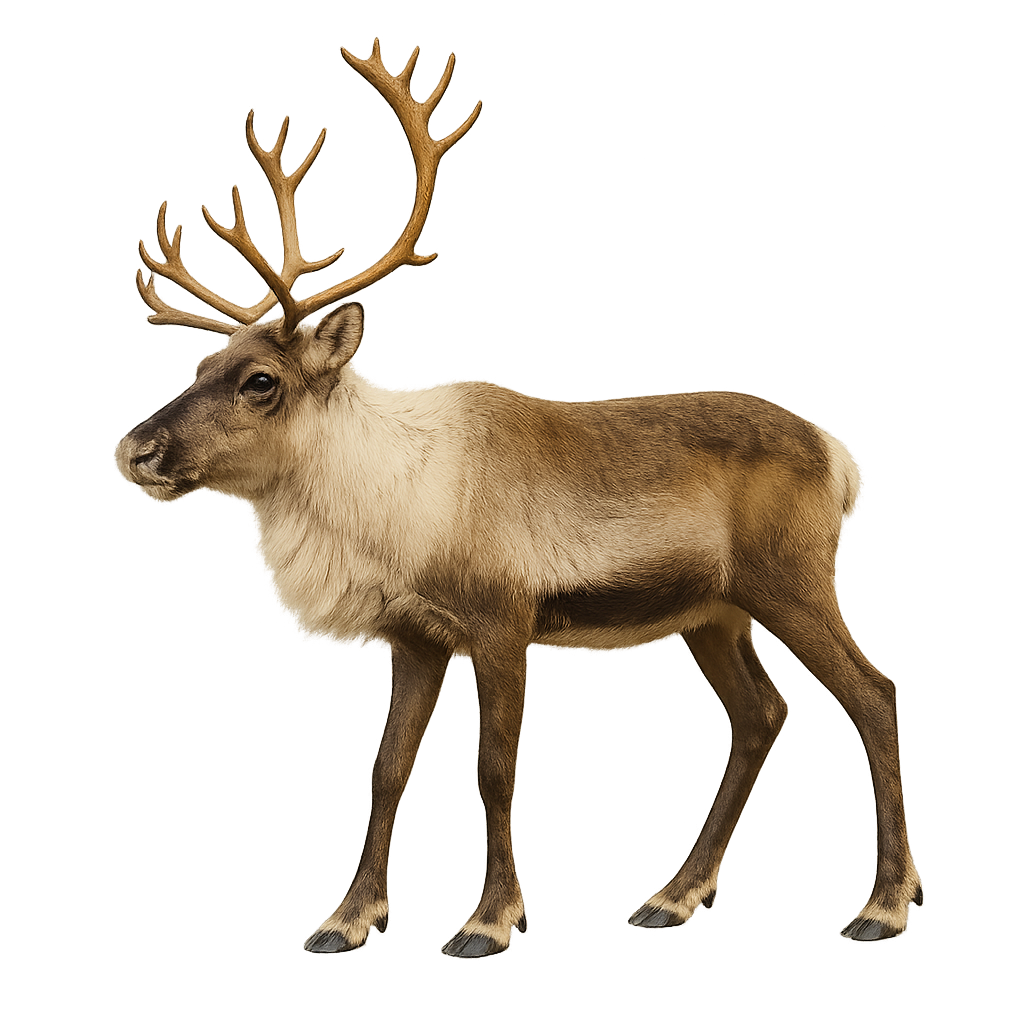
The Caribou, or Reindeer in Europe, is a large cervid adapted to cold and northern environments. It is easily recognizable by its distinctive antlers, which are present in both males and females, a unique trait among cervids. Its thick, woolly coat, typically brown with lighter shades on the belly and neck, allows it to survive in the harshest climates. Caribou populations are found primarily in arctic and subarctic regions, including Iceland, where they were introduced and have thrived in the mountainous and tundra landscapes.
The Caribou is a migratory species, undertaking long seasonal migrations to find food resources. It primarily feeds on lichens, grasses, and tundra plants, which it digs out from under the snow during the winter. The Caribou plays a crucial role in its ecosystem by affecting vegetation and serving as prey for large carnivores such as wolves. However, it is threatened by climate change and habitat loss.
The Collared Forest Falcon, or Micrastur semitorquatus, is a medium-sized raptor primarily found in the dense tropical forests of Central and South America. It is distinguished by its dark plumage, often black or dark gray, with a distinctive white collar around its neck. This agile and discreet predator feeds mainly on small mammals, birds, and reptiles. Known for its ability to hunt in cluttered forest environments, it uses silent flight and great agility. Although not extensively studied, it plays a crucial role in the ecological balance of its natural habitat.
The Yellow-winged Blackbird, Agelaius thilius, is a medium-sized bird easily recognizable by its distinctive yellow shoulders. It primarily inhabits wetlands, marshes, and open grasslands in South America. Its glossy black plumage contrasts with its bright yellow shoulders, making it particularly visible in its natural habitat. Males are generally more colorful than females, who have duller plumage. This bird is often seen in flocks, especially outside the breeding season. Its song is melodious and varied, used to mark its territory and attract females. Although quite common, it is important to preserve its habitats to ensure its survival.
The Red-bellied Grackle, or Hypopyrrhus pyrohypogaster, is an endemic bird of Colombia, primarily found in the humid forests of the Andes. This medium-sized passerine is notable for its glossy black plumage contrasted by a bright red belly. It typically lives in small groups and feeds mainly on fruits, insects, and small invertebrates. Deforestation and habitat fragmentation are the main threats to this species, classifying it as vulnerable according to the IUCN. Conservation efforts focus on habitat protection and raising awareness among local communities about the importance of preserving this unique species.
The Ducula rubricera, or Red-knobbed Imperial Pigeon, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Columbidae family. It is primarily found in the tropical rainforests of New Guinea and surrounding islands. This pigeon is notable for its bright red head, contrasting with its grey and white plumage. It mainly feeds on fruits, playing a crucial role in seed dispersal. Although its habitat is relatively stable, deforestation poses a potential threat. Its behavior is generally suspicious, but it can become accustomed to human presence in protected areas. Its breeding period varies depending on the availability of food resources.
The Mountain Imperial Pigeon, scientifically known as Ducula badia, is a large bird belonging to the Columbidae family. It is characterized by its predominantly grey plumage with metallic green hues on its wings and back. Its head is lighter, often a pale grey, contrasting with its reddish eyes. This bird is primarily arboreal, inhabiting the tropical and subtropical forests of Southeast Asia. It mainly feeds on fruits, thus contributing to seed dispersal in its habitat. The Mountain Imperial Pigeon is a discreet bird, often identified by its soft and melodious call. It plays a crucial role in the forest ecosystem, helping to maintain biodiversity.
The Pied Imperial Pigeon, Ducula bicolor, is a large pigeon species known for its striking white plumage contrasted by black wings and tail. It is primarily found in the tropical forests and mangroves of Southeast Asia, including Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines. This pigeon is an excellent flyer, capable of covering long distances to feed on fruits, its main food source. It plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding forest regeneration. Although generally solitary, it can be seen in small groups during the breeding season. Its ability to adapt to various habitats, including urban areas, demonstrates its resilience. However, deforestation and hunting pose threats to some local populations.
The Spice Imperial Pigeon, or Ducula myristicivora, is a large pigeon species endemic to the Maluku Islands in Indonesia. It is distinguished by its elegant plumage, primarily gray with metallic green hues on the wings and back. Its robust beak is adapted to its diet, which mainly consists of fruits, especially nutmeg, from which it derives its scientific name. It plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, contributing to the regeneration of tropical forests. This pigeon prefers dense forests and wooded areas, where it can move with agility thanks to its powerful wings. Although its conservation status is concerning due to deforestation, it remains relatively common in its natural habitat.
The Marquesan Imperial Pigeon, or Ducula galeata, is a large pigeon species endemic to the Marquesas Islands in French Polynesia. It is distinguished by its ash-gray plumage and slightly darker head. This bird primarily inhabits the humid forests and wooded areas of the islands, feeding on fruits and seeds. Unfortunately, it is critically endangered due to deforestation, hunting, and the introduction of invasive species. Conservation efforts are vital for its survival. The Marquesan Imperial Pigeon symbolizes the unique biodiversity of the Marquesas and the importance of preserving these fragile ecosystems.
The Sumba Imperial Pigeon, Ducula lacernulata, is a medium-sized bird endemic to the island of Sumba in Indonesia. It is recognized for its elegant plumage, predominantly grey with iridescent hues on the neck and wings. Its head is lighter, contrasting with its bright red eyes. It primarily inhabits the island's tropical rainforests and wooded areas. Although its habitat is limited, it adapts well to secondary forests. This pigeon mainly feeds on fruits, playing a crucial role in seed dispersal. Unfortunately, deforestation and hunting have reduced its populations, classifying it as vulnerable by the IUCN. Preserving its habitat is vital for its survival.
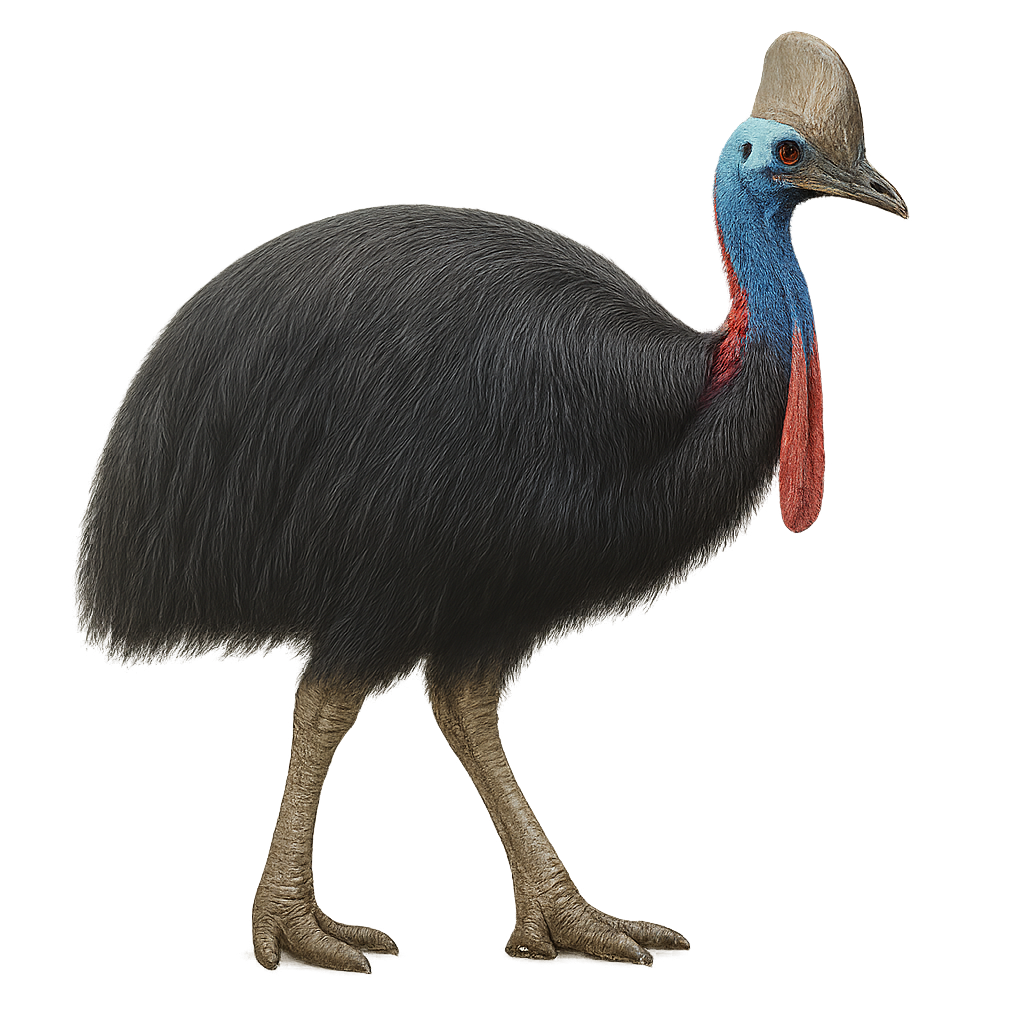
The Southern Cassowary, Casuarius casuarius, is a large and fascinating bird native to the tropical forests of New Guinea, Australia, and surrounding islands. It is distinguished by its glossy black plumage, striking blue head, and unique horned casque. This casque, which can reach 18 cm in height, is used to navigate through dense vegetation. Cassowaries are solitary and territorial birds, known for their shy behavior. They primarily feed on fallen fruits but can also consume small animals and fungi. Their ecological role is crucial as they disperse seeds of many plant species. Although capable of running at high speeds and swimming, they are threatened by habitat loss and vehicle collisions.
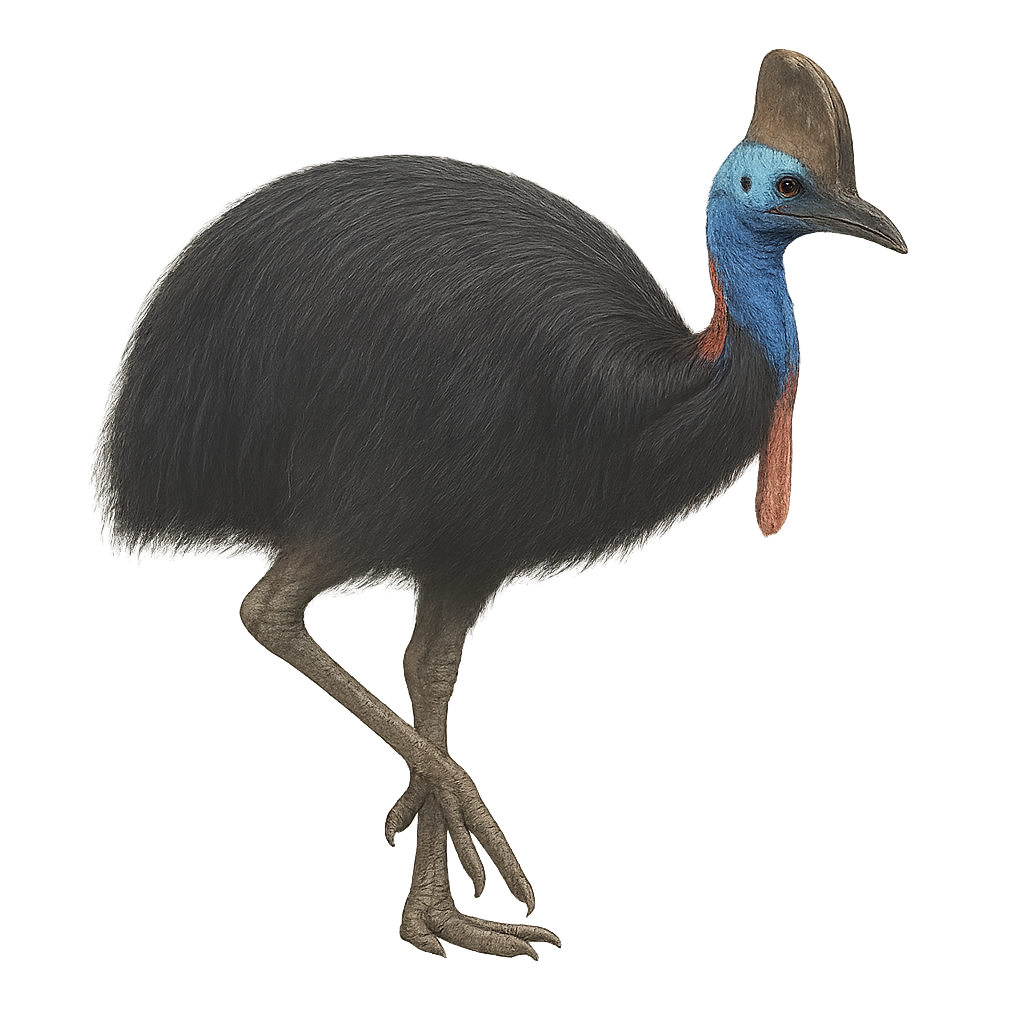
The Dwarf Cassowary, also known as Bennett's Cassowary, is a large and majestic bird native to the tropical forests of New Guinea and surrounding islands. It stands out with its impressive height, reaching up to 1.5 meters, and its glossy black plumage. Its head is adorned with a bony crest, known as a casque, giving it a prehistoric appearance. This solitary bird is primarily frugivorous, feeding on fallen fruits, but it can also consume small animals and insects. The Dwarf Cassowary is an excellent runner, capable of moving swiftly through dense forest vegetation. Although generally discreet, it can become aggressive if it feels threatened.
The Spotted Nutcracker is a medium-sized bird, easily recognizable by its spotted black and white plumage, which helps it blend perfectly into the coniferous forests where it lives. This passerine is primarily found in the mountainous regions of Europe and Asia, where it mainly feeds on pine seeds and other fruits, which it hides in tree crevices to consume later, a behavior that makes it an excellent food gatherer. The Spotted Nutcracker is also a migratory bird, although it may sometimes remain in colder areas during the winter.
This crow is known for its great intelligence and curious behavior, and it plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by dispersing tree seeds, thus promoting forest regeneration. While the population of this bird is generally stable, it may be threatened by the destruction of forest habitats, particularly in areas where coniferous forests are reduced by logging.
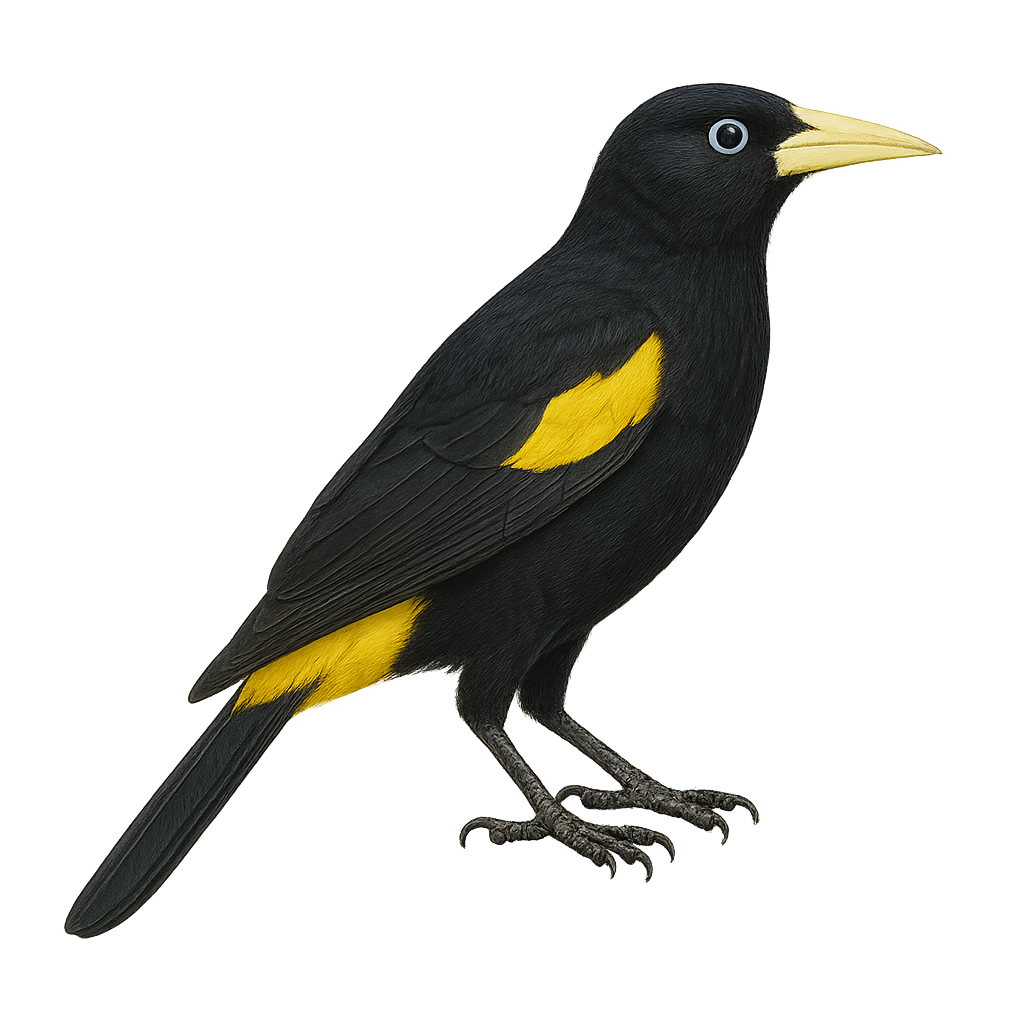
The Mountain Cacique, or Cacicus chrysonotus, is a striking bird with its black plumage contrasted by a bright yellow back. It primarily inhabits the humid forests of the Andes, often seen in noisy flocks. Known for its melodious and complex song, it uses this to communicate with its peers. It feeds mainly on insects and fruits found in the tree canopy. The Mountain Cacique builds hanging bag-shaped nests, often in colonies, providing protection against predators. Although relatively common in its habitat, deforestation poses a potential threat to its populations.
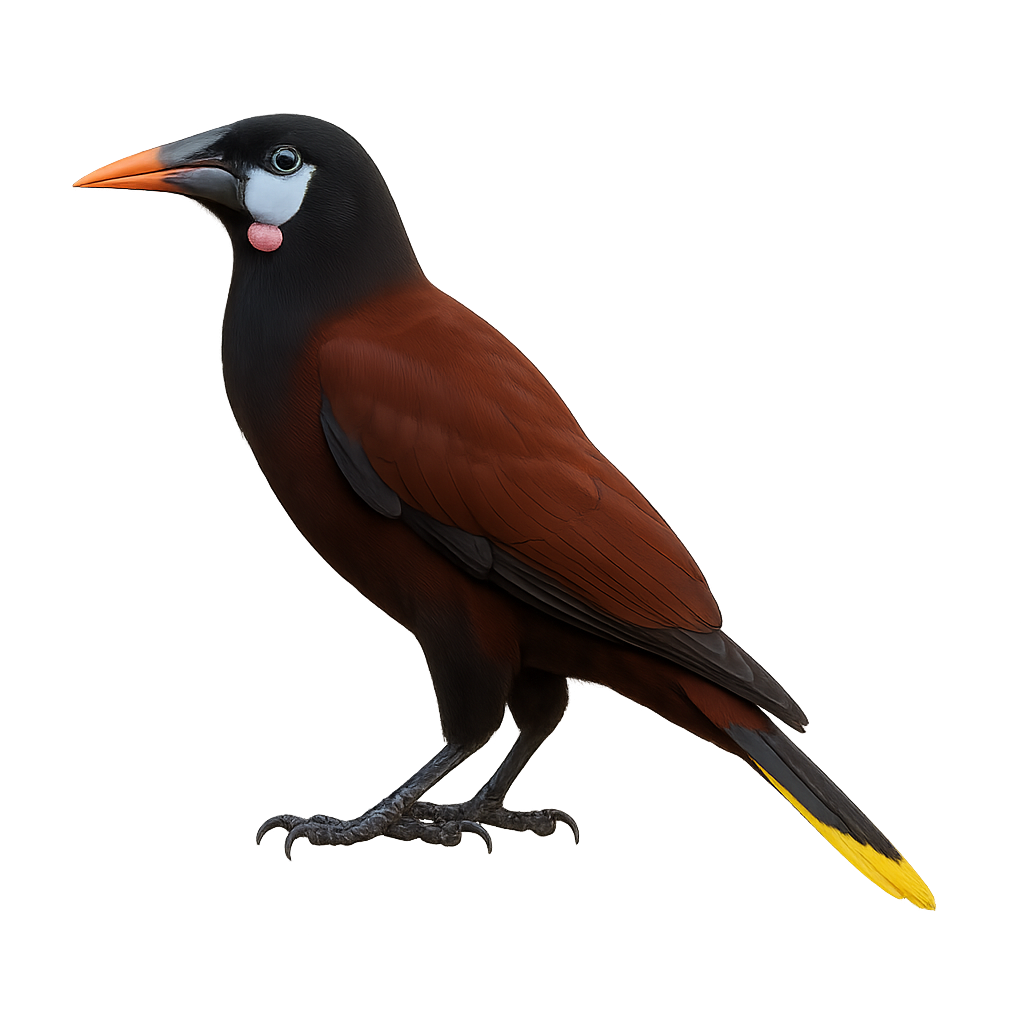
The Montezuma Oropendola is an exotic and colorful bird, easily recognizable by its vibrant plumage, which blends shades of black, yellow, and red. This large bird belongs to the Icteridae family and primarily inhabits the tropical forests and wooded areas of Mexico and Central America. It is especially famous for its long tail feathers, giving it a striking and elegant silhouette.
The Montezuma Oropendola is a social bird that lives in groups, often consisting of several individuals. It feeds primarily on fruits, seeds, and small insects, which it finds in trees and climbing plants. It is also known for its suspended nests, which it constructs with great skill in the trees. While its population remains generally stable, it may be threatened by deforestation and habitat loss.
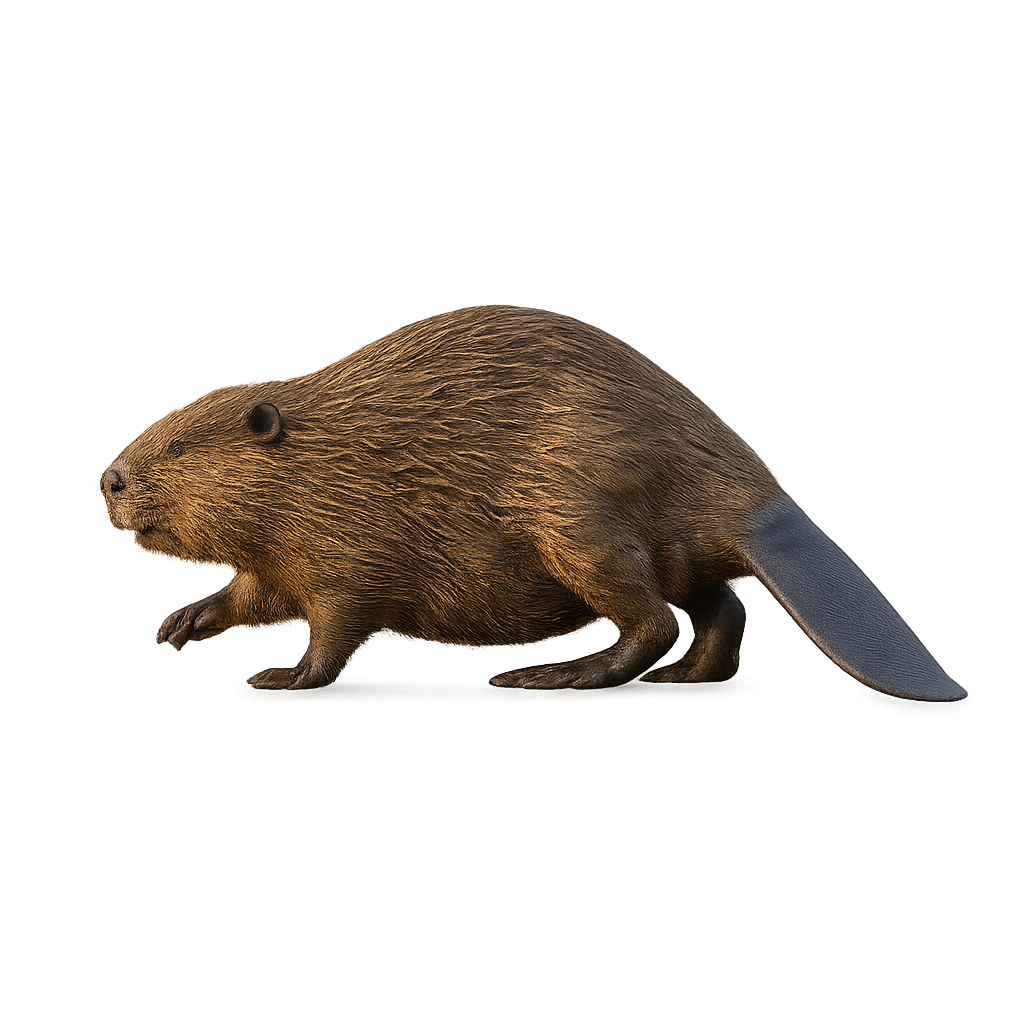
The European Beaver is a large, semi-aquatic rodent renowned for its exceptional ability to alter its environment. This rodent is easily identifiable by its brown fur, large orange incisors, and flat, scaly tail. It primarily inhabits rivers, lakes, and wetlands, where it builds dams to create ponds and wetlands that serve as refuges. The European Beaver is an excellent swimmer, capable of staying underwater for several minutes to move or escape danger.
It feeds mainly on bark, roots, and young tree shoots. In addition to its ability to modify waterways, the European Beaver plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by promoting the regeneration of wetland areas, which benefits many other animal species. Although its population was historically threatened by hunting and habitat loss, conservation efforts have stabilized its numbers, and the species is now protected in many regions.
The American Beaver is a large, semi-aquatic rodent famous for its construction skills and its ability to modify its environment. It is easily recognizable by its wide head, large orange incisors, and its flat, scaly tail. The American Beaver primarily lives in rivers, lakes, and wetlands, where it builds dams and lodges using branches, tree trunks, and mud to create safe, stable habitats.
This rodent is an excellent swimmer and spends much of its life in the water, where it feeds mainly on bark, roots, and young tree shoots. The American Beaver plays a crucial role in its ecosystem by altering waterways, creating ponds and wetlands that are beneficial to many other species. However, it is sometimes threatened by habitat loss due to urbanization and water management.
The Paramo Seedeater is a small seed-eating bird found primarily in the mountainous regions of South America. It is characterized by its uniformly brown-grey plumage, which allows it to blend into its environment. Its modest size and conical beak are well-suited to its diet of seeds. It frequents high-altitude grasslands and open shrublands, often seen in small flocks. Although discreet, its melodious song is a clear indicator of its presence. The species is well adapted to the harsh climatic conditions of the paramos, unique ecosystems located above the tree line.
The Andean Pipit, or Catamenia analis, is a small passerine bird found mainly in the mountainous regions of South America. It is recognizable by its brownish-grey plumage with dark streaks on the back and a lighter chest. This bird is well adapted to high altitudes, often seen between 1000 m and 4000 m. It primarily feeds on seeds and insects, which it finds by foraging on the ground. The Andean Pipit is a relatively discreet bird, but its melodious song can be heard during the breeding season. It builds its nest on the ground, hidden among grasses and shrubs.
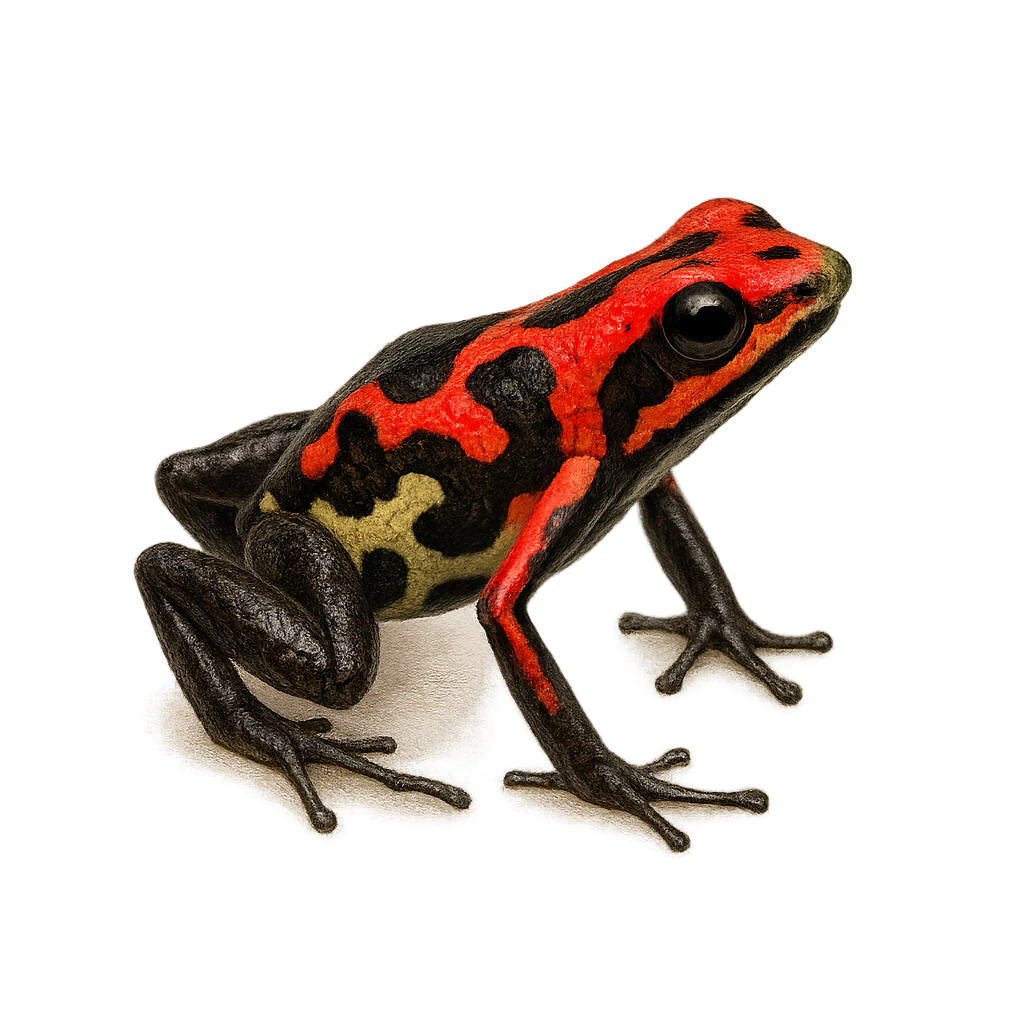
The Cauca poison frog is a small, brightly colored frog native to the humid rainforests of Colombia. Its skin features vivid and contrasting patterns, often red and black, serving as a warning to potential predators of its toxicity. This diurnal species primarily feeds on small insects and other arthropods, playing a crucial role in the ecosystem by regulating insect populations. Harlequin Poison Frogs are known for their territorial behavior, with males vigorously defending their space against intruders. Their reproduction involves parental care, with males carrying tadpoles on their backs to suitable water points. Unfortunately, this species is threatened by deforestation and habitat loss.
The Cauca poison frog is a small frog from the Dendrobatidae family, native to the humid tropical forests of South America. It is characterized by its smooth skin and bright colors, often a mix of green and brown, which allow it to blend effectively into its natural environment. This species is generally active during the day and primarily feeds on small insects. It is known for its territorial behavior, with males vigorously defending their space against intruders. Reproduction mainly occurs during the rainy season when conditions are optimal for tadpole development.
The Sunbittern is a medium-sized bird, about 43 cm long, known for its striking wing patterns that resemble eyespots. When threatened, it fans out its wings like a butterfly or stylized sun to startle predators. It has a long beak, slender neck, and thin legs adapted to walking along rivers and streams. Found in Central and South America, it inhabits shaded riverbanks and humid forests at moderate elevations. Solitary and elusive, it feeds on small fish, aquatic insects, and invertebrates. While not currently endangered, it is vulnerable to habitat loss and water pollution.
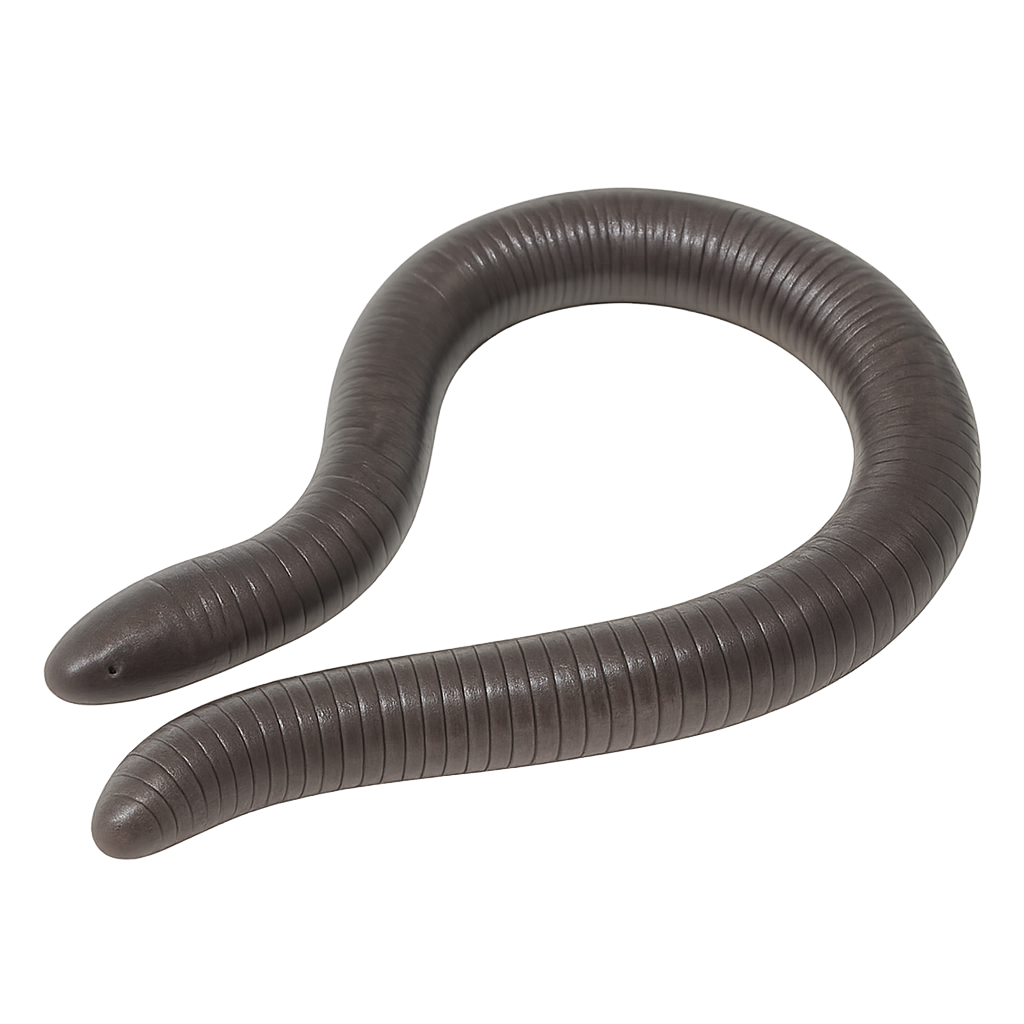
The Dermophis mexicanus, or Mexican burrowing caecilian, is a burrowing amphibian characterized by its elongated, limbless body, resembling an earthworm. Its smooth, segmented skin allows it to move easily underground. Primarily nocturnal, this species feeds on small invertebrates found in the soil. It has keen senses to detect prey in the dark. Mexican caecilians inhabit moist environments, often near rivers or in tropical forests. They are ovoviviparous, meaning the young develop in eggs inside the mother's body until hatching. Though discreet, they play a crucial role in the ecosystem by regulating invertebrate populations.