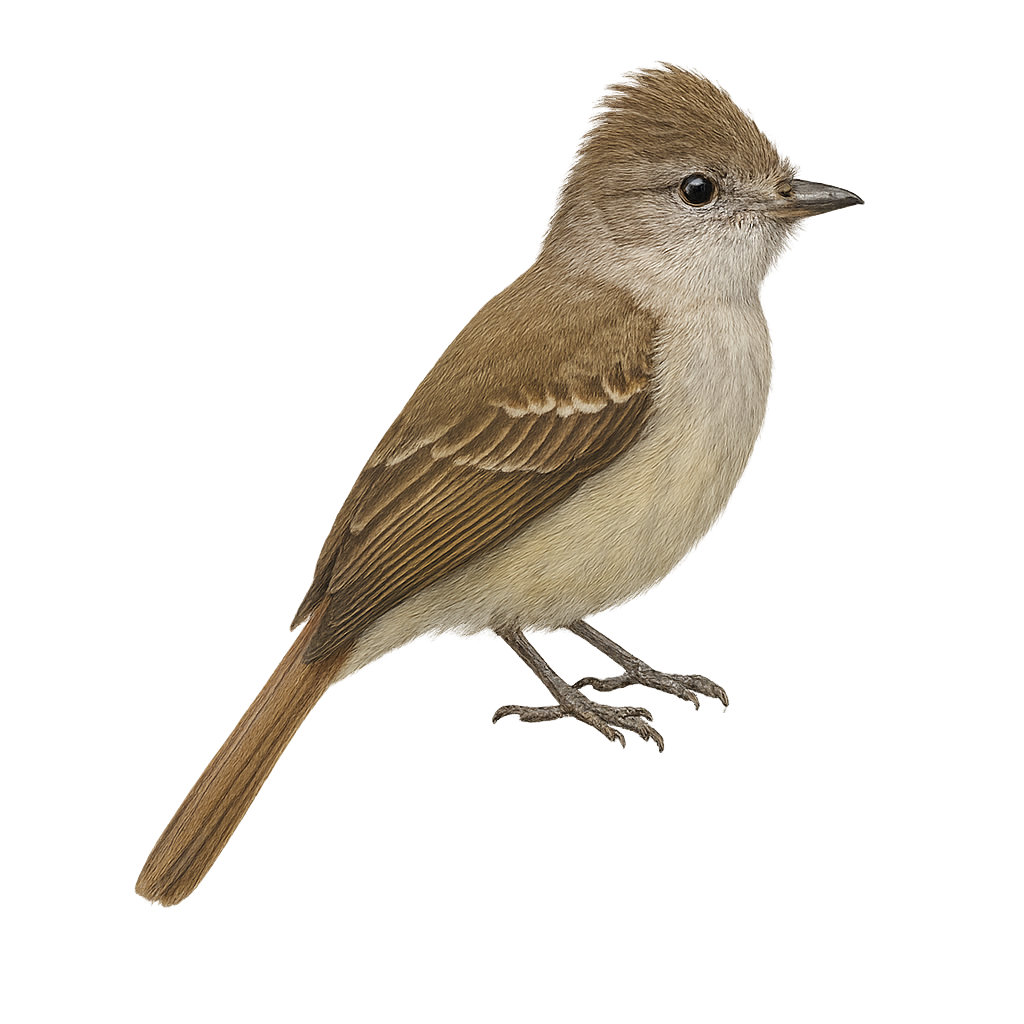
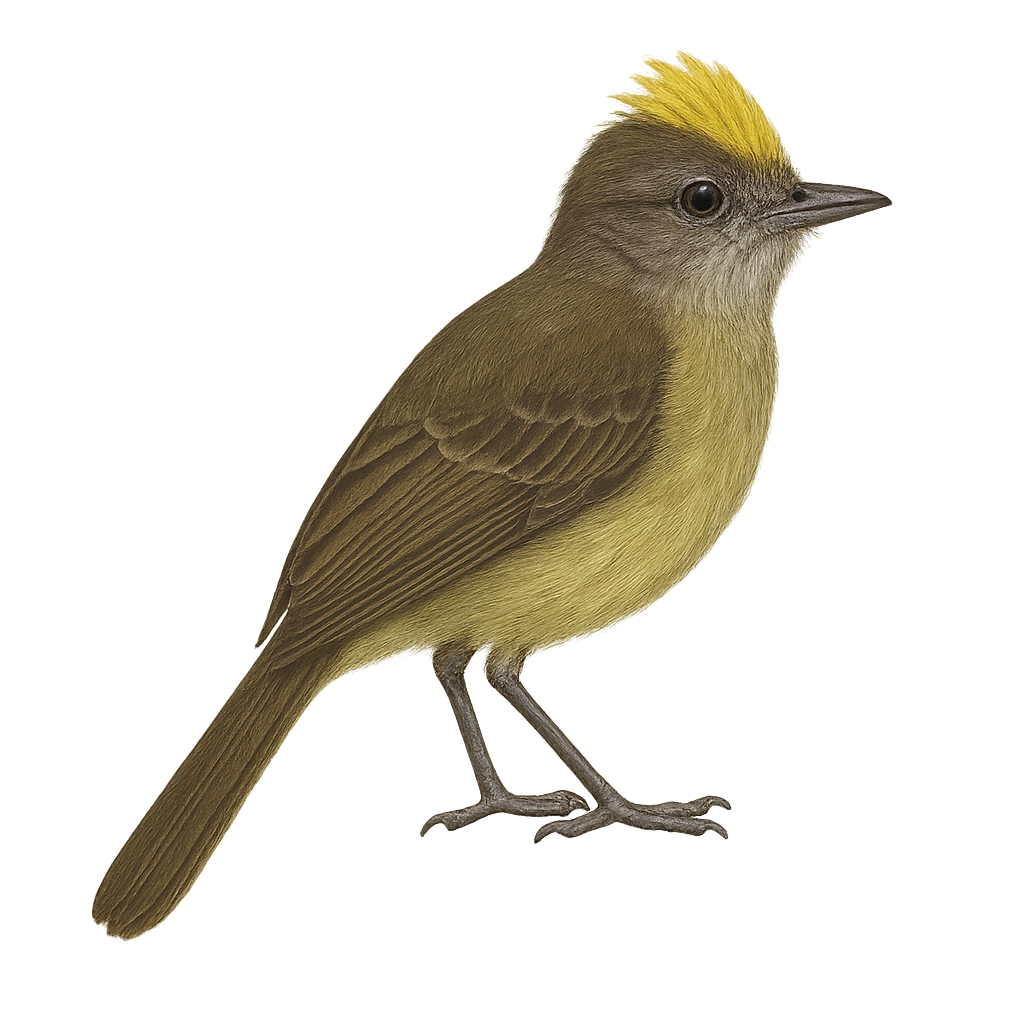
The Red Squirrel is a small tree-dwelling mammal, well-known for its reddish-brown fur and long ears, often tipped with tufts of hair. It typically measures between 20 and 25 cm in length, with a bushy tail that can reach up to 25 cm in length. This rodent is mainly found in deciduous and mixed forests across Europe and Asia, but it is also present in urban parks and gardens. The Red Squirrel is omnivorous, feeding mainly on nuts, seeds, mushrooms, and occasionally insects or bird eggs. Highly agile, it moves with ease between trees, using its tail as a stabilizer. It is a territorial animal that builds ball-shaped nests made of twigs, moss, and leaves, often placed in tree trunks or branches. While the species is still fairly widespread, it faces threats such as habitat loss, competition with the introduced Grey Squirrel, and collisions with vehicles.
The American Barn Owl, or Tyto furcata pratincola, is a medium-sized nocturnal raptor, easily identified by its heart-shaped facial disc and pale plumage. It is widespread across the Americas and inhabits farmland, open grasslands, wetlands, and man-made structures like barns and silos. Its flight is completely silent, making it an efficient hunter of small mammals, especially rodents. Its sharp, screeching call contrasts with its ghostly appearance. The population is generally stable but may be affected by the loss of nesting sites and pesticide use. No black or melanistic form is known in this subspecies.
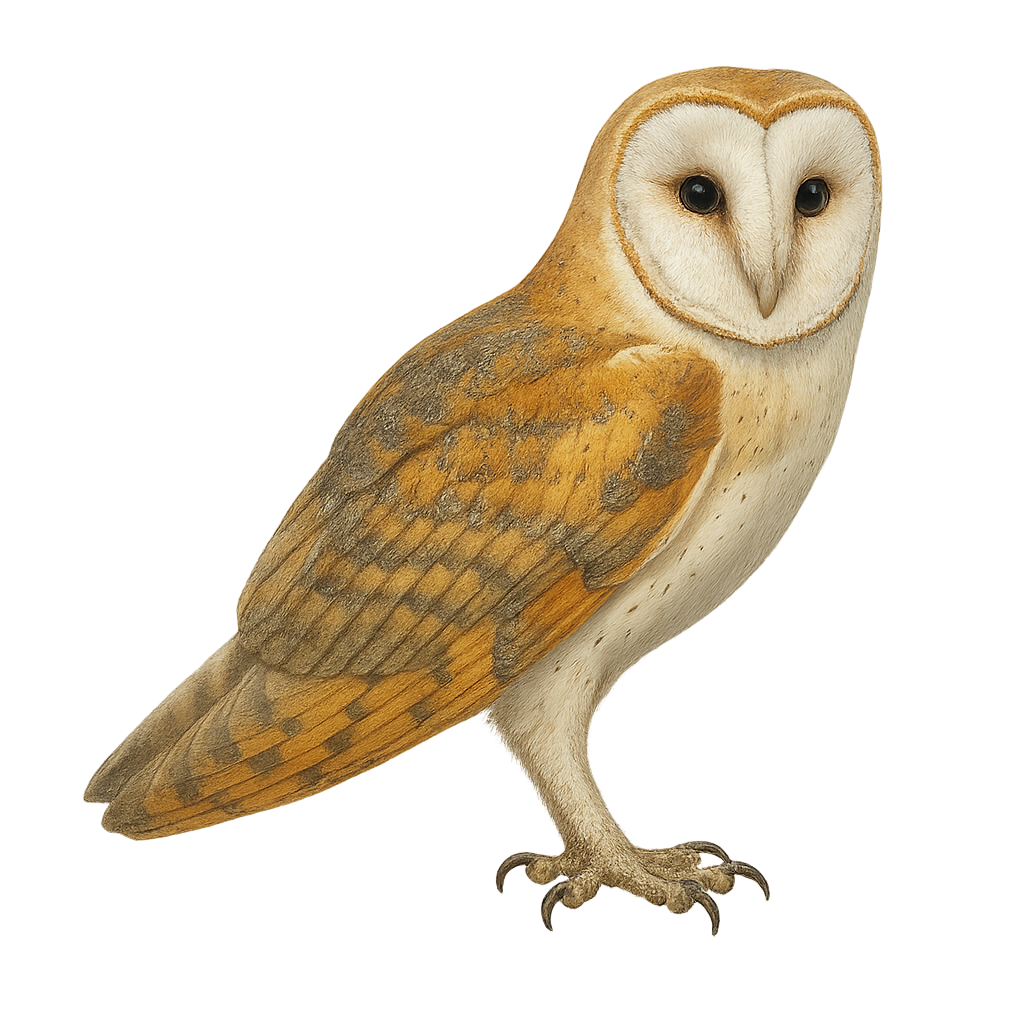
The Barn Owl is a nocturnal bird of prey, easily recognizable by its heart-shaped face and large white wings. It typically measures between 33 and 40 cm in length, with a wingspan of 80 to 95 cm. Its plumage is mainly white with beige and brownish hues on its back, while its face, with its distinct shape, is a bright white, making it immediately identifiable. The Barn Owl primarily inhabits agricultural areas, open meadows, clear forests, and abandoned buildings or churches, where it finds places to nest. It primarily feeds on small mammals, such as mice and voles, but may also hunt birds or insects. Its hunting method is very silent, due to the unique structure of its feathers, which reduce flight noise. It is a solitary bird that usually hunts at night. While the Barn Owl is not currently endangered, it faces threats such as habitat loss, secondary poisoning from consuming contaminated prey, and collisions with vehicles.
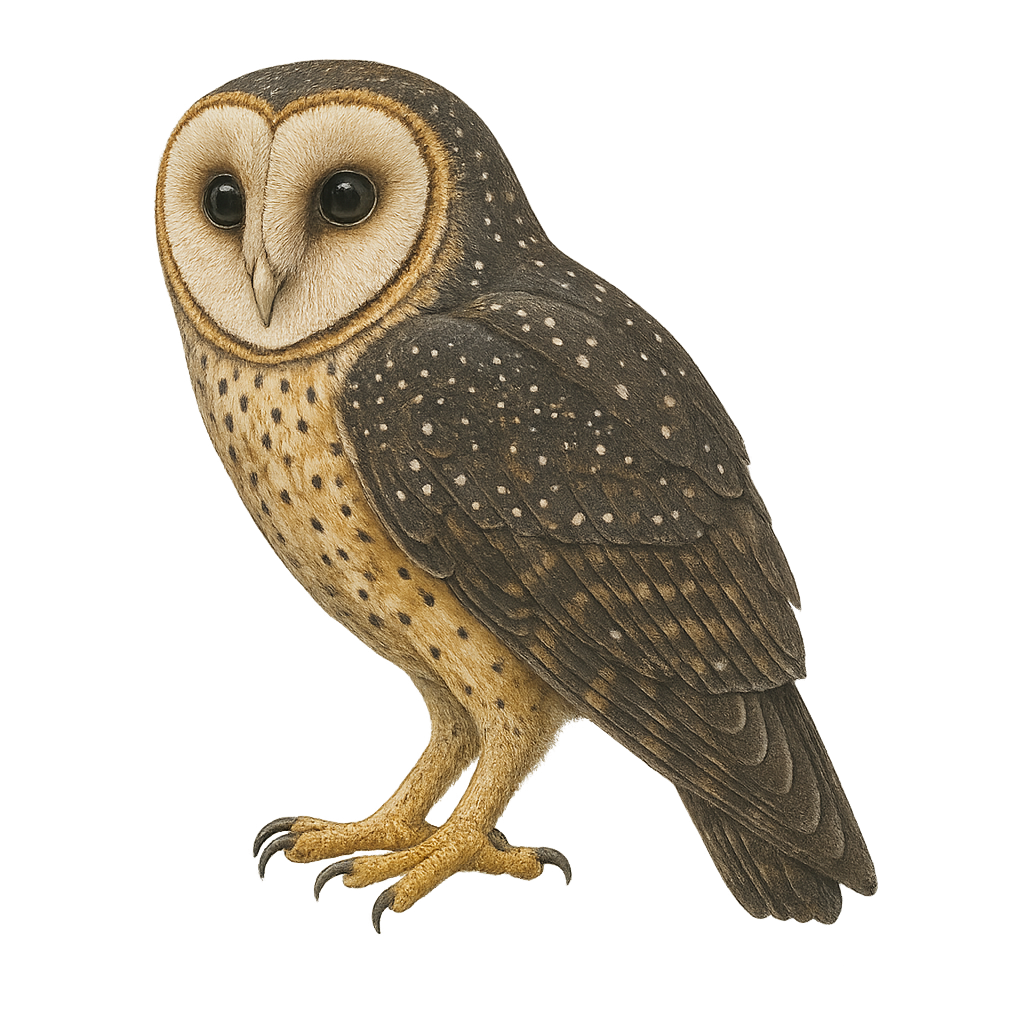
The Masked Owl, or Tyto novaehollandiae, is a medium-sized nocturnal bird of prey native to Australia and some surrounding islands. It is characterized by its heart-shaped facial disc, often white or cream, bordered by a dark edge. Its plumage is generally brown with white spots, allowing it to blend effectively into its natural habitat. It primarily inhabits forests, open woodlands, and agricultural areas but can also be found in urban zones. A nocturnal hunter, it feeds mainly on small mammals, birds, and insects. Although its conservation status is concerning in some areas, it remains relatively widespread.
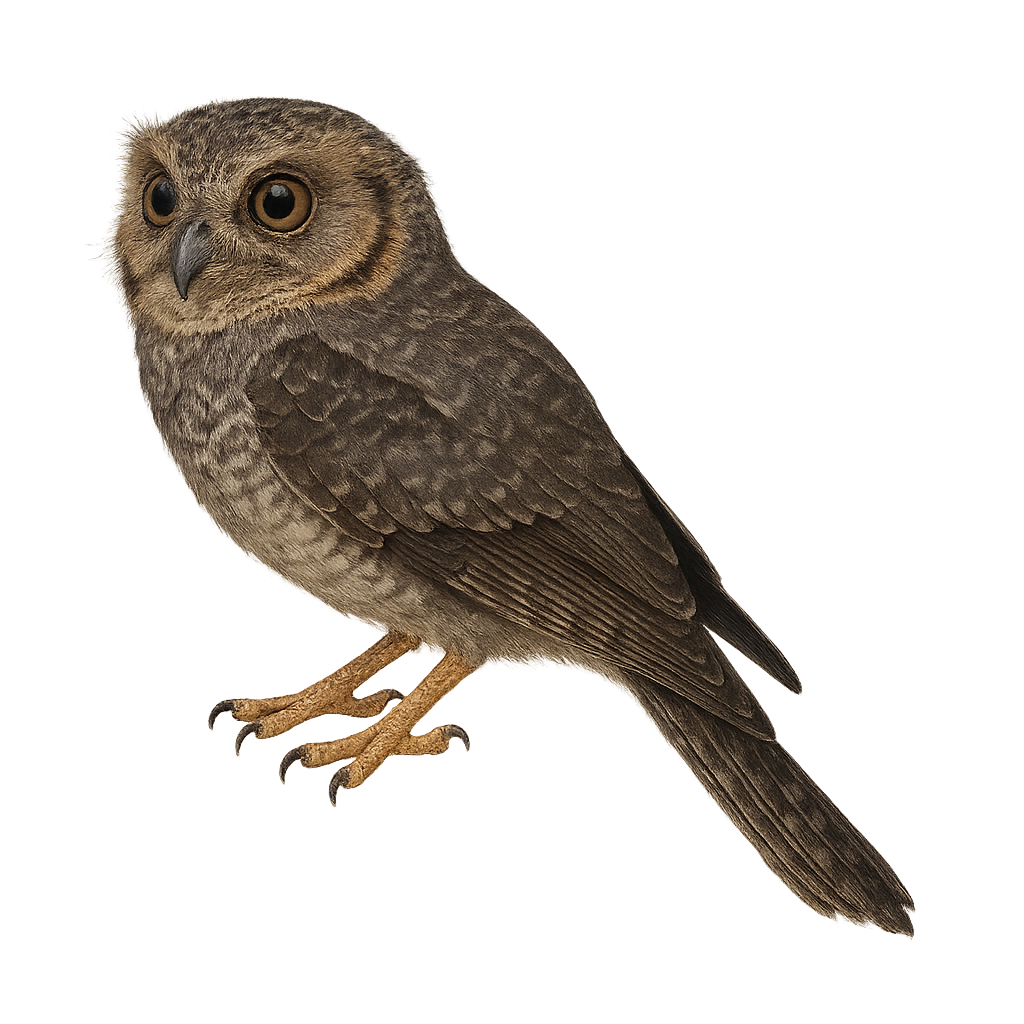
The Australian Owlet-nightjar is a small, nocturnal bird belonging to the Aegothelidae family. It is identifiable by its grey-brown plumage, distinctive white eyebrows, and large eyes adapted for night vision. This bird is primarily endemic to Australia, inhabiting various forest types, including eucalyptus forests and open woodlands. It feeds mainly on insects, which it catches in flight or by foraging through foliage. The Australian Owlet-nightjar is known for its melodious song and varied calls, often heard at dusk and dawn. Although discreet, it is sometimes observed perched at the entrance of tree cavities, where it nests and rests during the day.
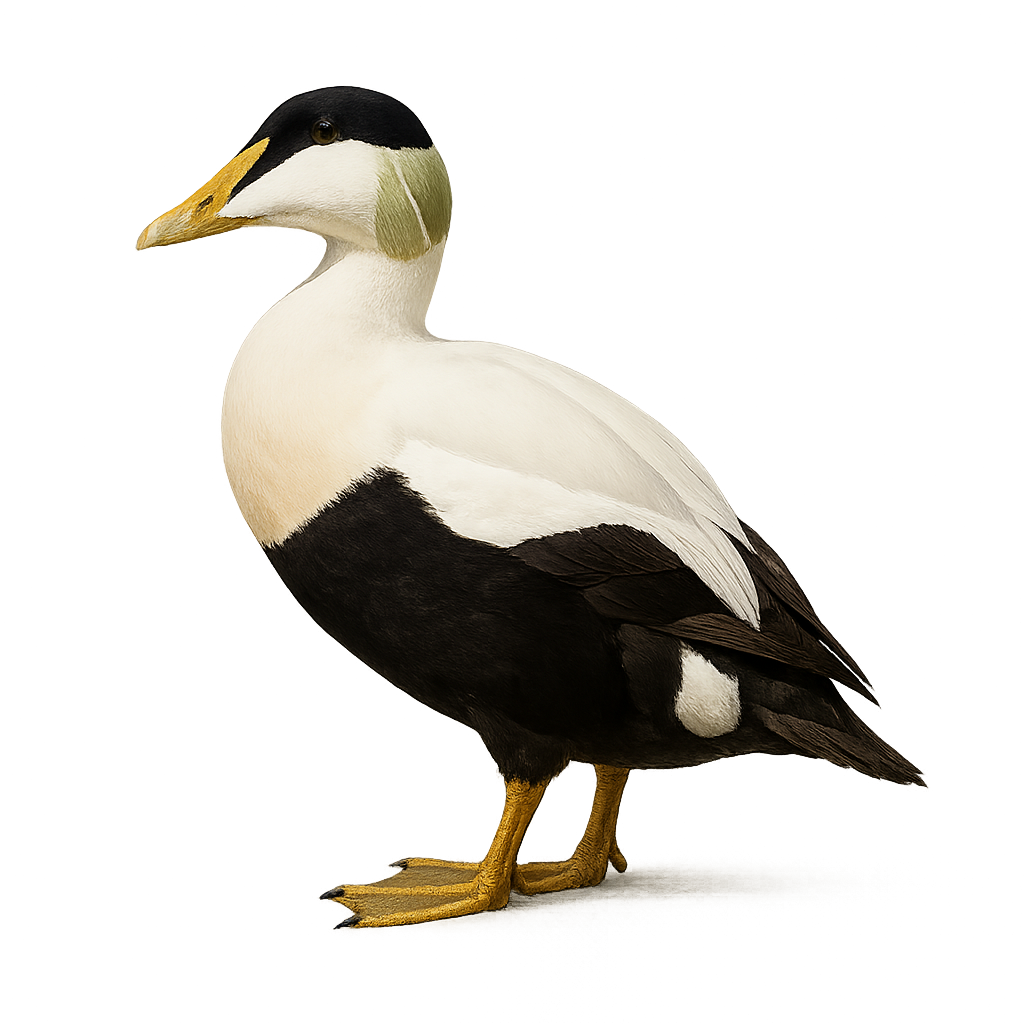
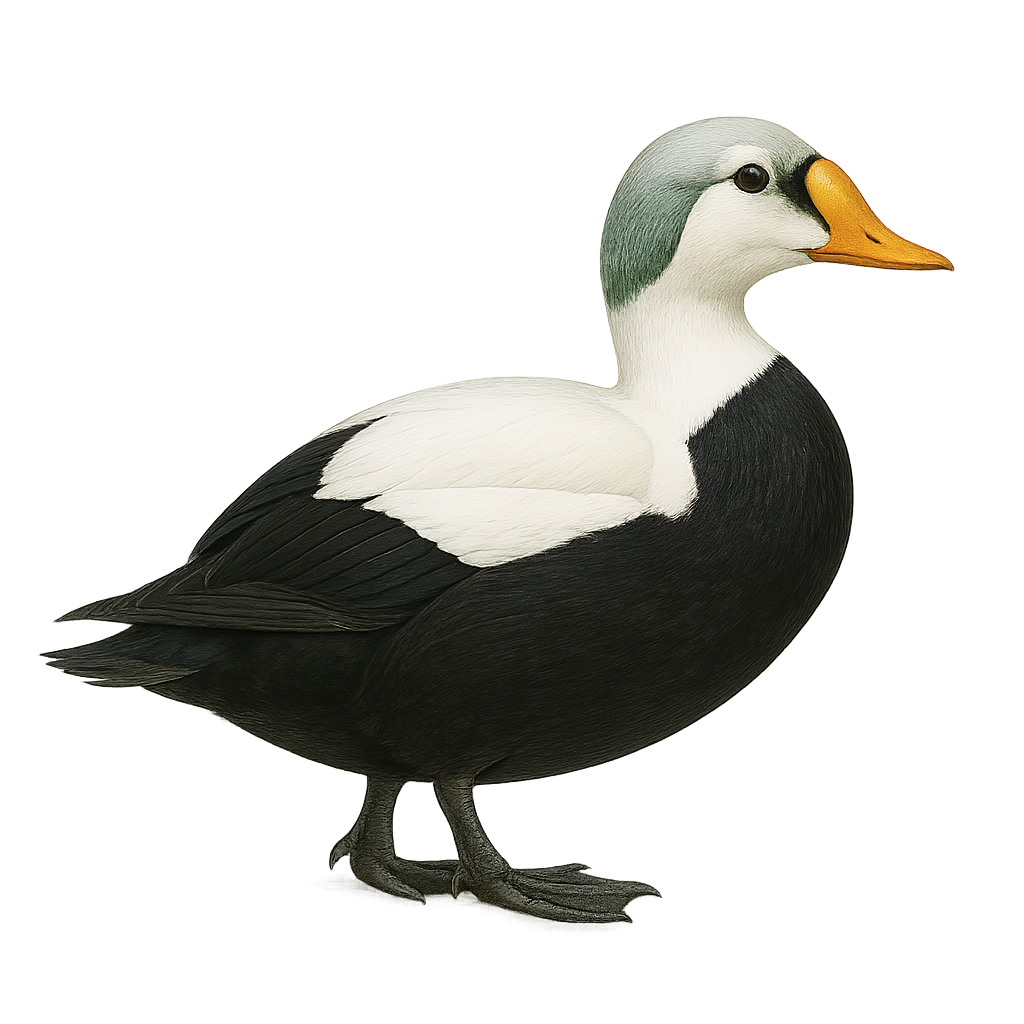
The Eider Duck is a large sea duck, easily recognized by its distinctive plumage. The adult male has a white body with a black head and neck, while the female is more muted with a brown speckled plumage. The Eider measures about 55 to 70 cm in length, with a wingspan of 100 to 125 cm, and weighs between 1.5 and 2.5 kg. It is primarily found in coastal regions of the North Atlantic, notably in Northern Europe, Canada, and Alaska. This duck primarily feeds on mollusks, crustaceans, and small fish, which it finds by diving underwater. It is also known for its social behavior, often living in large colonies during the breeding season. The Eider Duck is particularly famous for its down, a soft and insulating material harvested from the female's nests after laying, used to make luxury duvets and pillows. While the species is not immediately endangered, it is threatened by marine pollution, habitat loss due to coastal urbanization, and hunting.
The Spectacled Eider (Somateria fischeri) is a striking sea duck found in Arctic regions, especially along the coasts of Alaska and eastern Siberia. This medium-sized duck is named for the distinctive black "spectacle" markings around the male's eyes, set against a pale cream head, with a greenish nape and bright orange bill. The female is more subdued in appearance, with a uniform brown plumage that blends well into coastal surroundings. Spectacled Eiders are typically seen in small groups, diving in shallow waters for mollusks, crustaceans, and sea urchins. Though rare and considered vulnerable, this unique bird captivates those lucky enough to spot it in the wild.
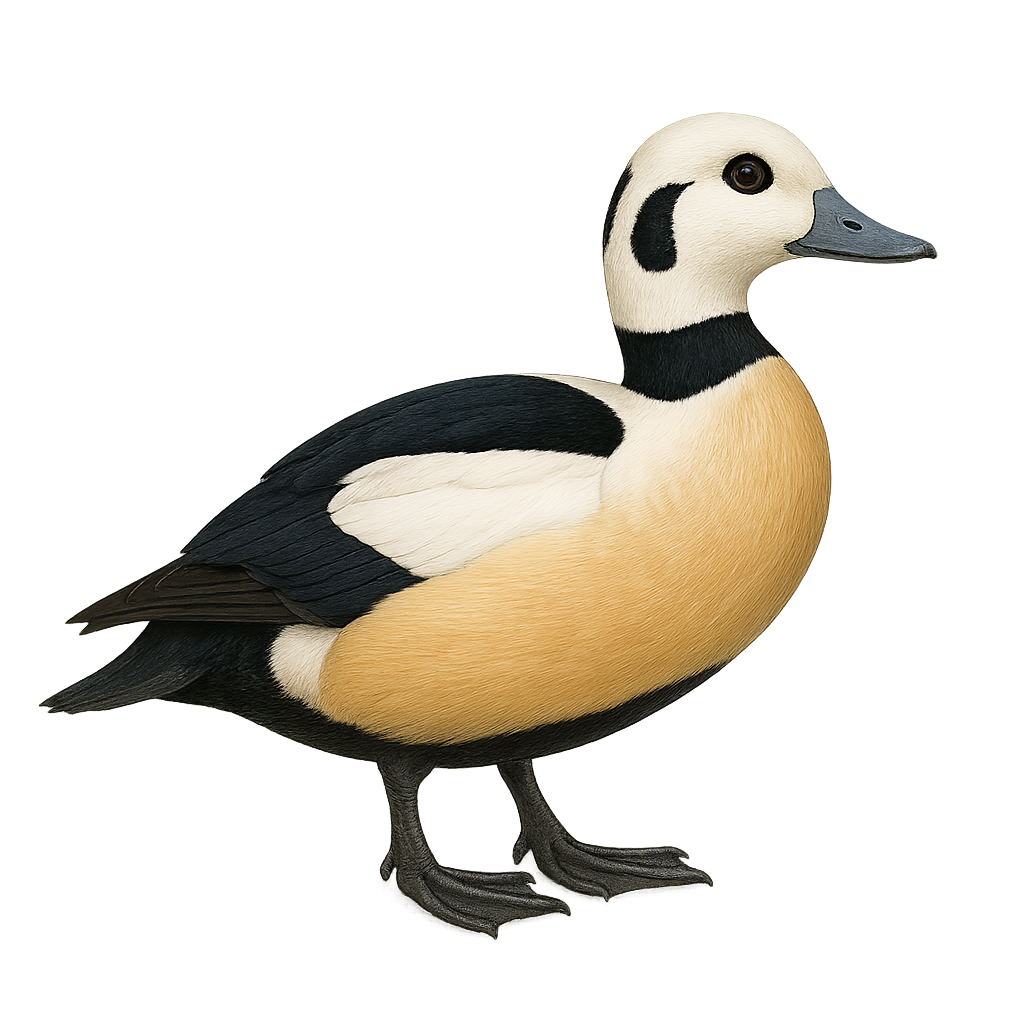
The King Eider, Somateria spectabilis, is a striking sea duck known for its distinctive plumage and lifestyle. The male boasts a colorful head with shades of blue, green, and orange, while the female has a more subdued brown plumage, ideal for nesting. These birds breed in Arctic and subarctic regions, often on remote coasts and islands. They primarily feed on mollusks and crustaceans, diving to capture them in cold waters. In winter, they migrate to more temperate areas, forming large flocks on coastal waters. Their social behavior is fascinating, with elaborate courtship displays and distinctive vocalizations.
The Steller's Eider is a distinctive sea duck known for its striking plumage and migratory habits. Males display a striking breeding plumage with a white head, black eye patches, and a brown and black body. Females are more subdued, primarily brown, allowing them to blend into their natural habitat. These birds breed in the Arctic regions of Russia and Alaska, often nesting near lakes and rivers. In winter, they migrate to more temperate coasts, where they primarily feed on mollusks and crustaceans. The Steller's Eider is a vulnerable species, threatened by habitat loss and climate change.
The Moose is a large deer found primarily in North America, particularly in coniferous forests and wetlands. It can reach up to 2 meters in height at the withers and weigh between 350 and 600 kg. Males are distinguished by their large antler racks, which can reach a span of 1.8 meters. Their coat is typically dark brown to black, with a lighter belly and a small mane of hair under the neck. The Moose is a herbivore, feeding mainly on leaves, branches, bark, fruits, and aquatic plants. It is an excellent swimmer and spends a great deal of its time feeding in lakes and rivers. While its population remains stable, it is threatened by habitat loss and hunting.
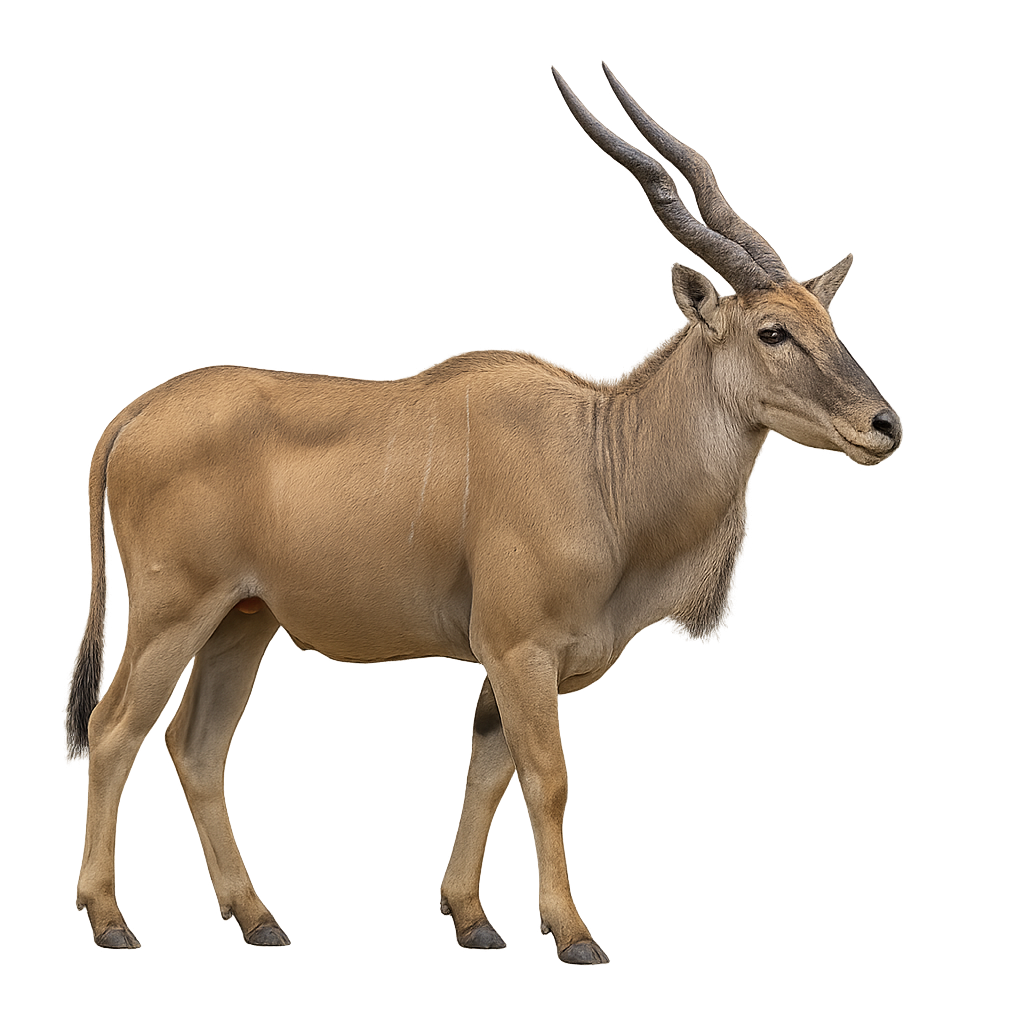
The Common Eland is a large herbivorous ungulate, belonging to the bovidae family, and one of the largest species of antelope. It can stand up to 1.5 meters tall at the withers and weigh between 400 and 900 kg, with males generally being larger than females. Its coat is usually light brown or gray, with lighter vertical stripes on the flanks. The Common Eland has large, spiral horns that can reach up to 80 cm in males. It primarily inhabits savannas and grasslands in sub-Saharan Africa, where it feeds mainly on grasses, leaves, and bushes. It is a social animal, living in large groups, especially during the breeding season. While the Common Eland is currently listed as of least concern, it faces threats such as habitat loss, hunting, and competition with livestock for food resources.
The Giant Eland, or Tragelaphus derbianus, is a large, robust, and majestic antelope, easily recognizable by its spiral-shaped horns, present only in males. It measures between 1.4 and 1.7 meters at the shoulder and can reach a length of 2.5 to 3 meters, including its tail. Its weight ranges between 600 and 1,000 kg, making it one of the largest antelopes. Its coat is generally light brown to gray, with white markings on the belly and throat. The Giant Eland primarily inhabits open savannas, light forests, and mountainous regions in Central and West Africa, mainly in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Cameroon, Gabon, and Angola. Herbivorous, the Giant Eland primarily feeds on grasses, leaves, and fruits, and it is capable of consuming a wide variety of vegetation, allowing it to adapt to different environments. It is a social animal that lives in family groups or small herds. While the species is classified as of least concern, it is threatened by habitat loss and hunting.
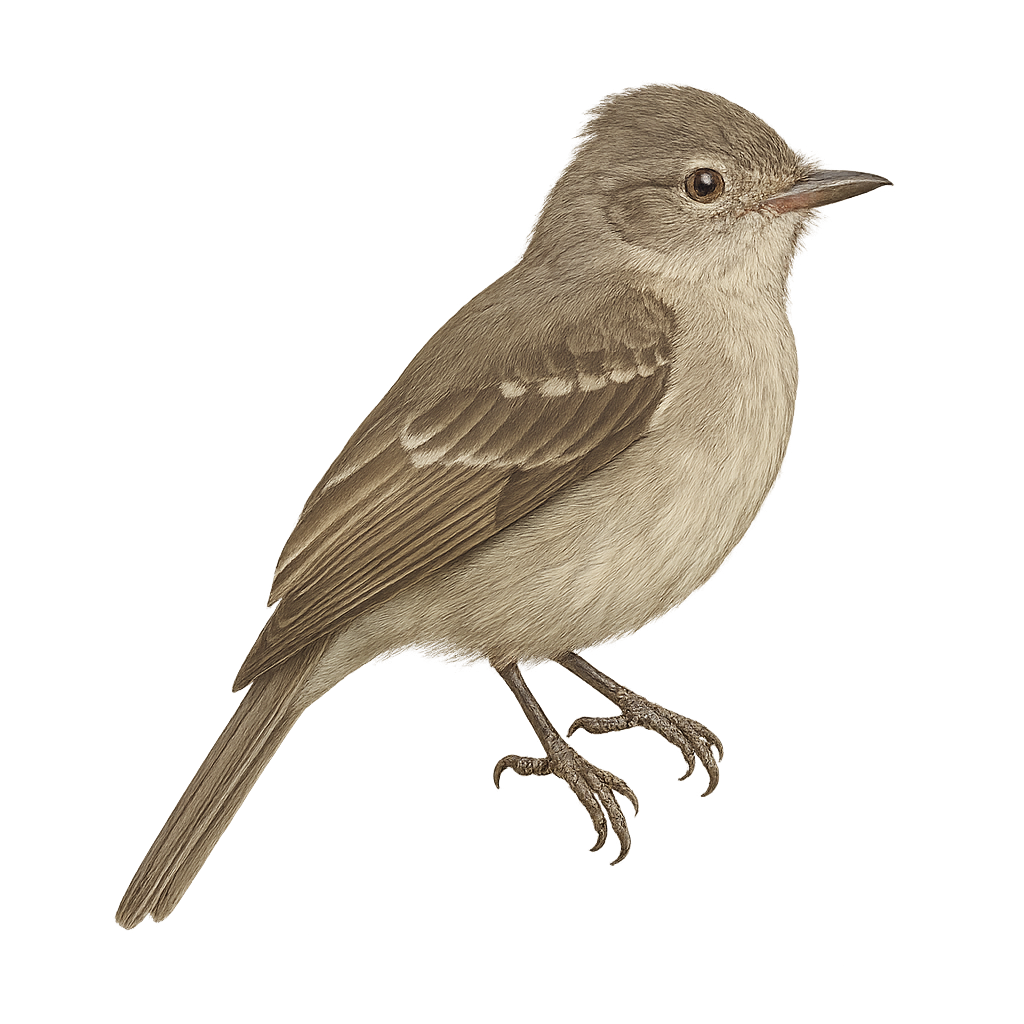
The Small-billed Elaenia is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in South America, especially in wooded areas and savannas. This bird is characterized by its olive-gray plumage on the back and lighter underparts, as well as its relatively short bill, which gives it its name. Small-billed Elaenias are often seen feeding on insects and fruits, which they catch in flight or on branches. Their song is a key element of their communication, often described as a soft and melodious whistle. Although generally discreet, they can be observed in small groups or pairs.
The White-crested Elaenia is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is recognizable by its distinctive white crest on the head, contrasting with its gray-green plumage. This bird is widely distributed in South America, inhabiting various environments from tropical forests to shrublands. Known for its melodious voice and varied songs, the elaenia primarily feeds on insects and fruits, which it captures in flight or by foraging through foliage. It is often observed in small groups or pairs, especially during the breeding season. Its adaptability to different environments makes it a resilient species, although some populations may be affected by deforestation.
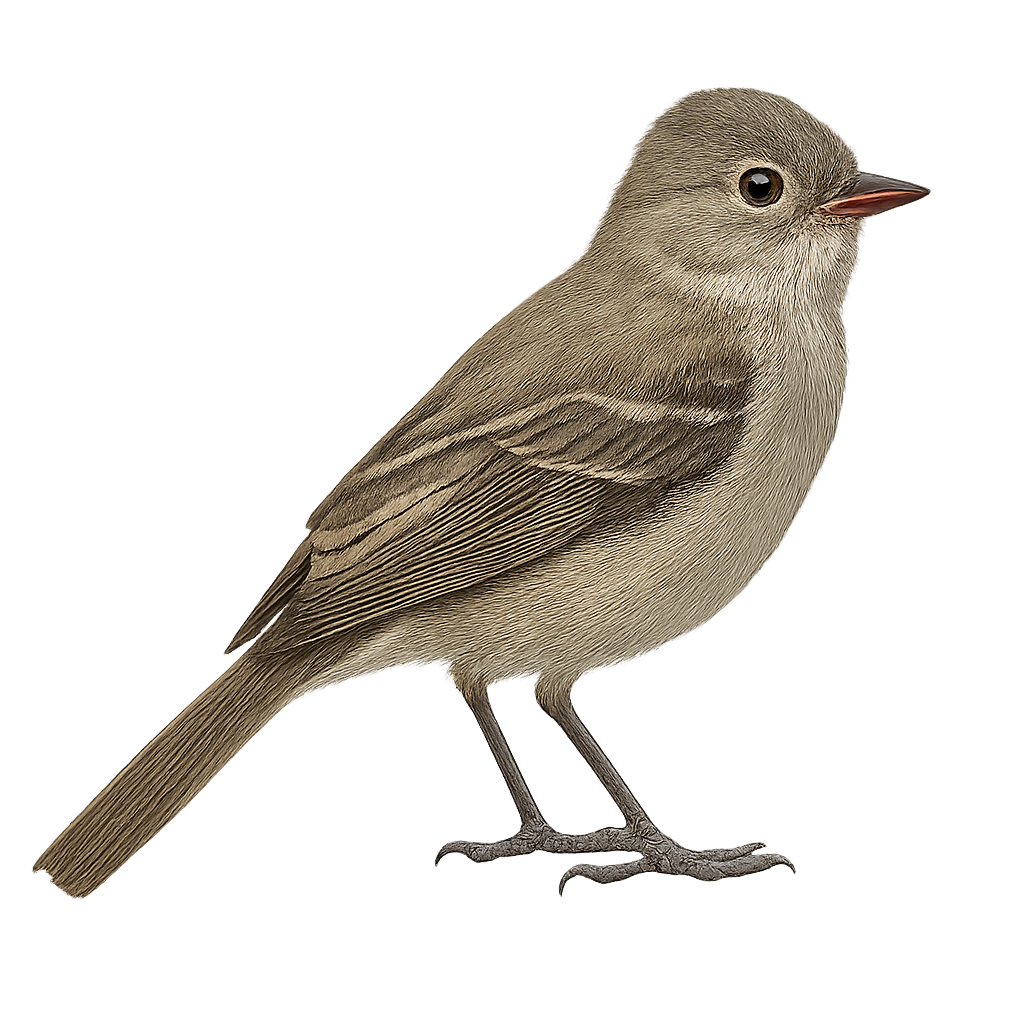
The Grey-capped Flycatcher is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in the tropical and subtropical forests of Central and South America. This bird is characterized by its grey head, white belly, and greenish wings. It is often seen catching insects in flight, thanks to its agile and swift movements. Although discreet, its melodious song can be heard throughout the canopy. The Grey-capped Flycatcher plays an important role in the ecosystem by regulating insect populations and participating in the pollination of certain plants.
The Yellow-bellied Elaenia is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. This bird is easily recognizable by its bright yellow belly contrasting with its dull olive back. It has a subtle crest and slightly white-striped wings. It is primarily found in tropical and subtropical forests but also adapts to open woodlands and savannas. Its song is distinctive, often described as a melodious whistle. The elaenia is a diurnal bird, active mainly in the morning and late afternoon. It feeds primarily on insects and fruits, which it captures in flight or by foraging through foliage.
The Pelzeln's Elaenia is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in the tropical and subtropical humid forests of South America, particularly in Brazil, Colombia, and Venezuela. This bird is characterized by its olive-green plumage on the back and lighter underparts, with a subtle crest on its head. It is often seen feeding on insects and fruits in the canopy. Although its song is discreet, it plays an important role in communication between individuals. The Pelzeln's Elaenia is not very shy, making it easier for birdwatchers to observe.
The Highland Elaenia is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in the mountainous regions of South America, particularly in Colombia, Venezuela, and Ecuador. Its plumage is generally dull, with shades of gray and brown, allowing it to blend into its natural environment. This bird is often identified by its distinctive song, a melodious whistle that echoes through cloud forests and wooded areas. Although discreet, the Highland Elaenia plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by aiding in seed dispersal and insect population control.
The Greenish Elaenia, Myiopagis gaimardii, is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in the tropical rainforests of Central and South America, where it is distinguished by its olive-green plumage and lighter belly. This bird is often observed alone or in small groups, feeding mainly on insects caught in flight. Its ability to blend into dense foliage sometimes makes it difficult to spot. Although not currently threatened, deforestation poses a potential risk to its natural habitat. The Greenish Elaenia is also known for its distinctive song, which plays a crucial role in communication between individuals, especially during the breeding season.
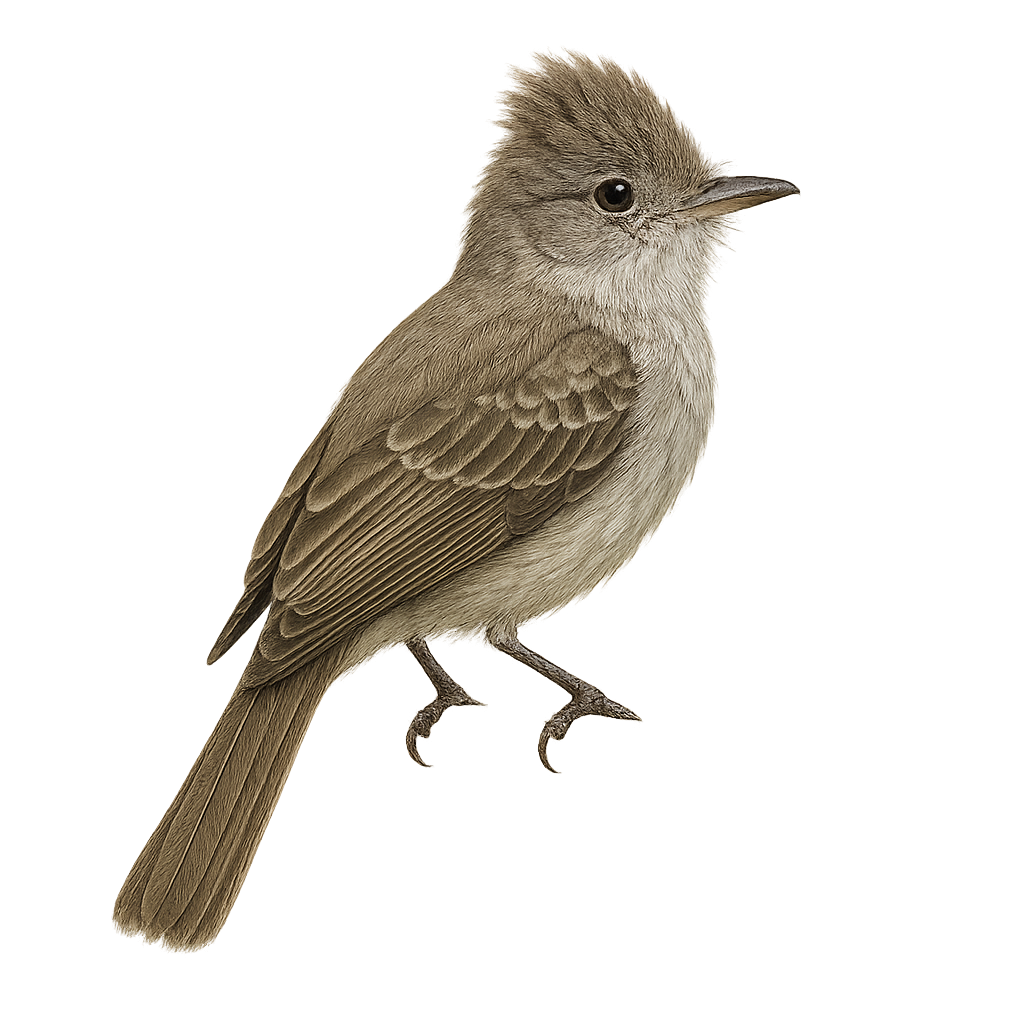
The Greater Elaenia is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is characterized by its olive-gray plumage on the back and lighter underparts, with a subtle crest on its head. This bird is mainly found in the tropical rainforests and wooded areas of South America, particularly in Colombia, Venezuela, and Brazil. Its song is a melodious whistle often heard at dawn and dusk. The Greater Elaenia is a migratory bird, moving seasonally to find food resources. It primarily feeds on insects and small fruits, which it catches in flight or by foraging through foliage.
The Lesser Elaenia is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is mainly found in tropical and subtropical regions of Central and South America. This bird is characterized by its inconspicuous plumage, usually olive green on the back and lighter on the belly, with slightly darker wings. It inhabits open forests, edges, and shrublands, often at varying altitudes. Its song is a key identification feature, consisting of soft, repetitive notes. The Lesser Elaenia is a diurnal bird, active mainly in the morning and late afternoon. Although it is relatively not very shy, it remains cautious and prefers areas with dense vegetation cover.
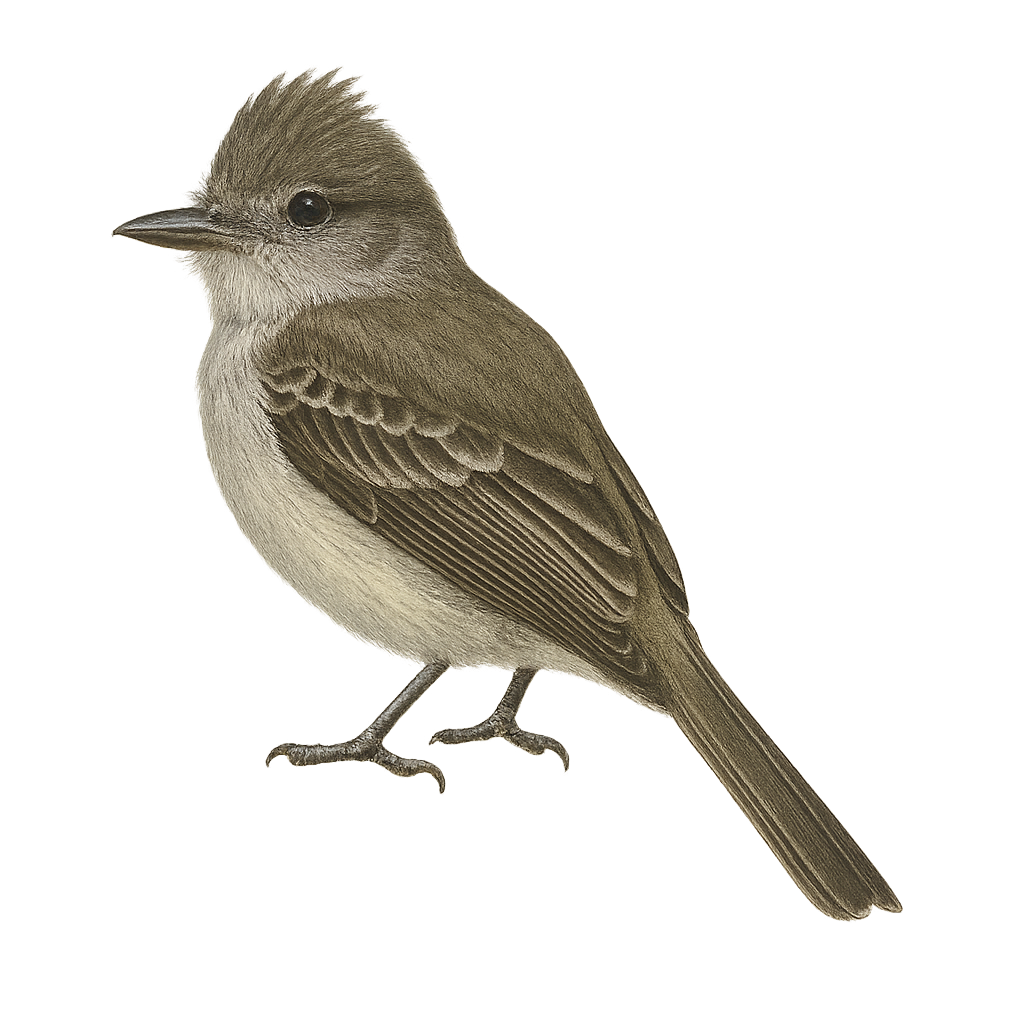
The Mountain Elaenia is a small passerine bird from the Tyrannidae family, primarily found in the montane forests of Central America. It is recognizable by its olive-gray plumage and lighter chest. This bird is often seen foraging for insects and fruits in the undergrowth. It is particularly active during the day, searching for food in dense foliage. Although generally suspicious, it can be observed from a reasonable distance without much difficulty. Humid forests and wooded areas at high altitudes are its preferred habitats.
The Highland Elaenia is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is characterized by its subtle plumage, mainly olive-gray, with lighter shades on the belly. Its often-raised crest and slightly streaked wings add to its discreet charm. Found primarily in the humid forests and wooded areas of South America, it feeds on insects and fruits. Although often difficult to spot due to its discreet behavior, its melodious song reveals its presence. The Highland Elaenia is a resilient bird, capable of adapting to various habitats, but it remains vulnerable to deforestation and the loss of its natural habitat.
The Small-billed Elaenia is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in the subtropical and tropical moist forests of South America, particularly in Brazil, Argentina, and Paraguay. This bird is characterized by its olive-gray back and white belly, which gives it its name. It has a relatively short bill and dark eyes. The Small-billed Elaenia is an active bird, often seen foraging for insects and fruits in the canopy. Its song is a key element for identification, consisting of a series of high-pitched, repetitive notes. Although not currently threatened, deforestation poses a potential risk to its natural habitat.
The Large Elaenia is a bird from the Tyrannidae family, identifiable by its medium size and primarily olive-green plumage with lighter shades on the belly. Its short, robust beak is suited for its mainly insectivorous diet, although it also consumes fruits. It is primarily found in tropical and subtropical forests but also adapts to open wooded areas. Its song is a melodious trill, often heard at dawn. This bird is migratory, moving with the seasons to find food resources. It is generally solitary or seen in small family groups.
The Caribbean Elaenia is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in the Caribbean, particularly on the islands of Martinique, Guadeloupe, and Saint Vincent. This bird features an olive-gray plumage on its back and a lighter shade on its belly, with a subtle crest on its head. It is often seen in tropical forests, forest edges, and shrublands. The Caribbean Elaenia is an active insectivore, feeding mainly on insects caught in flight or on leaves. Its song is a soft, melodious whistle, often heard at dawn.
The Greenish Elaenia, Myiopagis subplacens, is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in the tropical and subtropical forests of South America, particularly in Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. This bird is characterized by its olive-green plumage on the back and lighter underparts, with slightly darker wings. Its short, straight bill is well-suited for its diet, which mainly consists of insects and fruits. The Greenish Elaenia is a diurnal bird, most active in the morning and late afternoon. It is often seen alone or in small groups, moving nimbly through the canopy in search of food.
The Greenish Elaenia is a small passerine bird from the Tyrannidae family, widely distributed across Central and South America. Its plumage is primarily olive green, with lighter shades on the belly and slightly darker wings. This bird is characterized by its subtle crest and relatively short beak. It mainly inhabits tropical and subtropical forests but can also be found in open woodlands and forest edges. The Greenish Elaenia is an active insectivore, often seen catching insects in flight or foraging among foliage. Its song is a key aspect of its territorial behavior, often heard before seen.
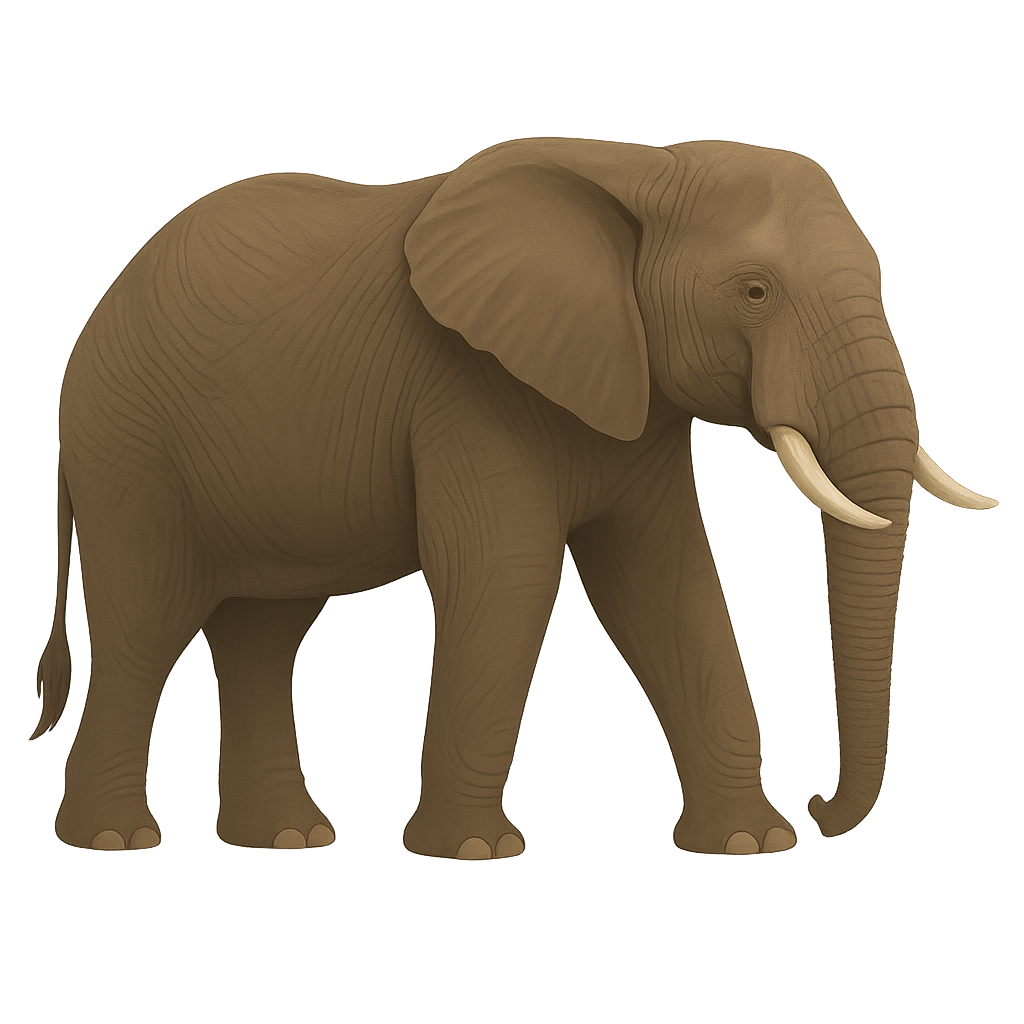
The African Savannah Elephant is the largest land mammal, and the largest of all terrestrial animals. It can stand up to 4 meters tall at the withers and weigh between 4,000 and 7,500 kg. Its coat is gray, with rough skin often covered in dust or mud to protect it from the sun and parasites. The African Savannah Elephant is easily recognizable by its large ears, shaped like the map of Africa, which help regulate its body temperature. This elephant is primarily herbivorous, feeding on leaves, bark, fruits, and plants. It inhabits savannas, grasslands, and open forests across sub-Saharan Africa. The African Savannah Elephant is a social animal, living in family groups led by an older female. It plays a crucial role in its ecosystem by creating openings in vegetation and dispersing seeds. However, the species is threatened by habitat loss, poaching for its valuable tusks, and conflicts with human communities. The African Savannah Elephant is currently listed as vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).

The Asian Elephant is a large land mammal, known for its imposing size and large rounded ears. It typically stands between 2 and 3.5 meters at the withers and weighs between 2,000 and 5,000 kg. Its coat is generally grayish, although some individuals may have a more brownish tint. The Asian Elephant differs from the African Elephant in its smaller size, narrower ears, and its trunk, which has a single "finger" at the tip. This elephant primarily inhabits tropical forests, savannas, and wetland areas in South and Southeast Asia, including India, Thailand, Sri Lanka, and Cambodia. It is herbivorous, feeding on leaves, bark, fruits, and grasses. The Asian Elephant has often been associated with human communities due to its historical role in labor, transport, and religious ceremonies. However, the species is threatened by habitat loss due to agriculture, poaching for its valuable tusks, and conflicts with human populations. It is listed as endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).