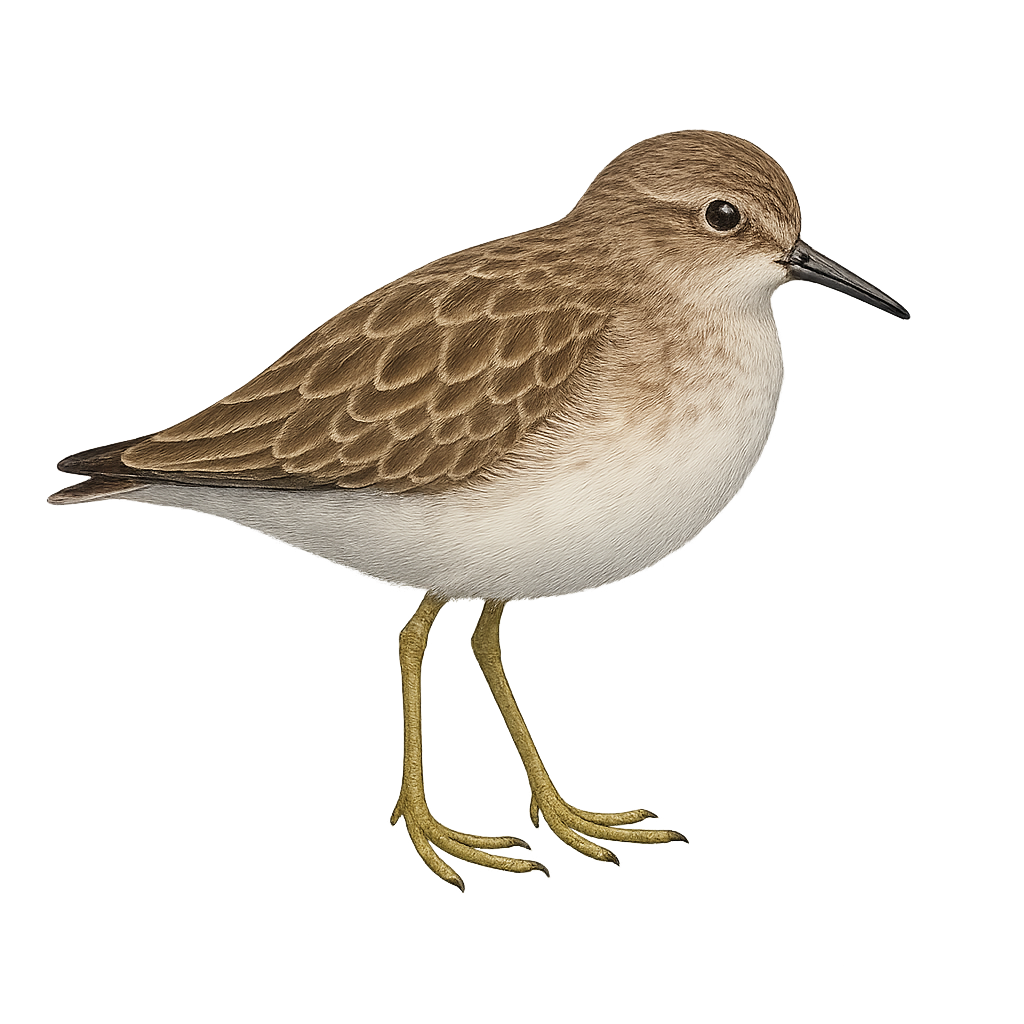
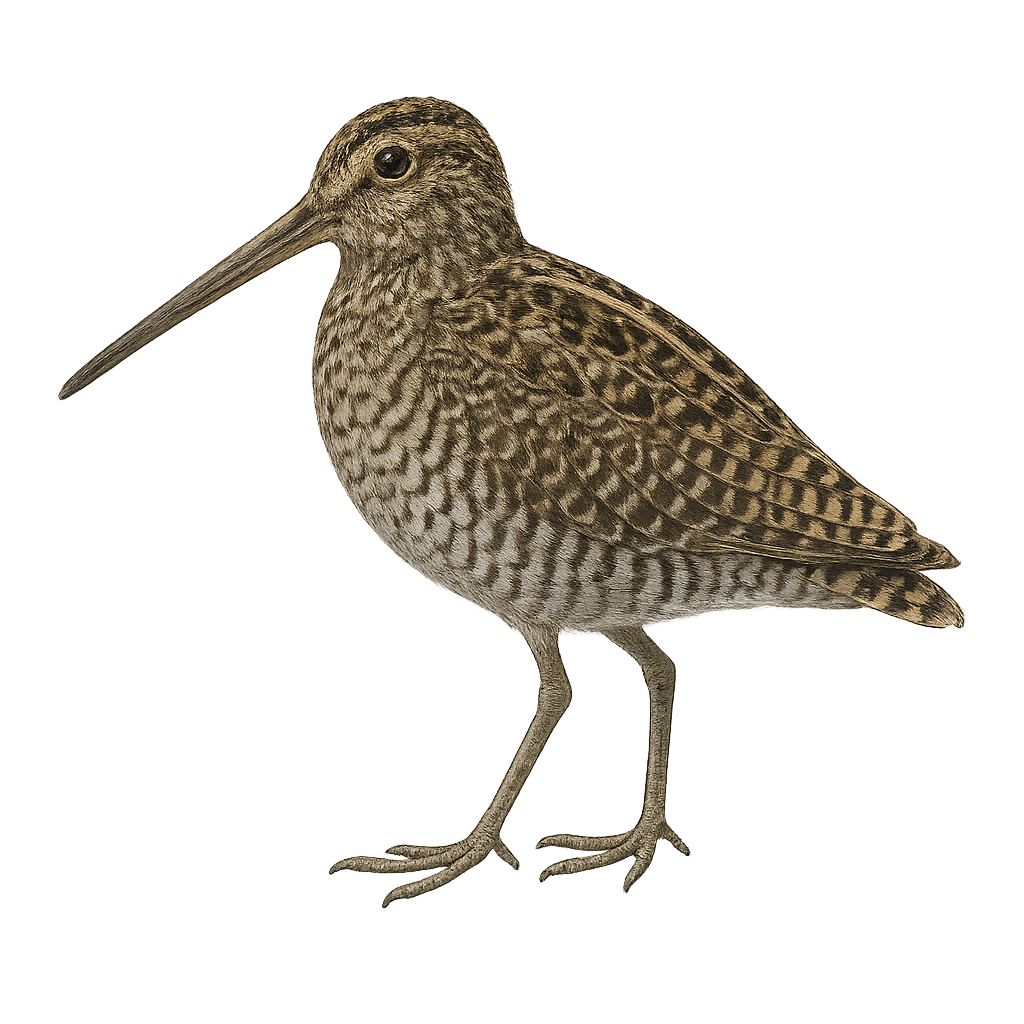
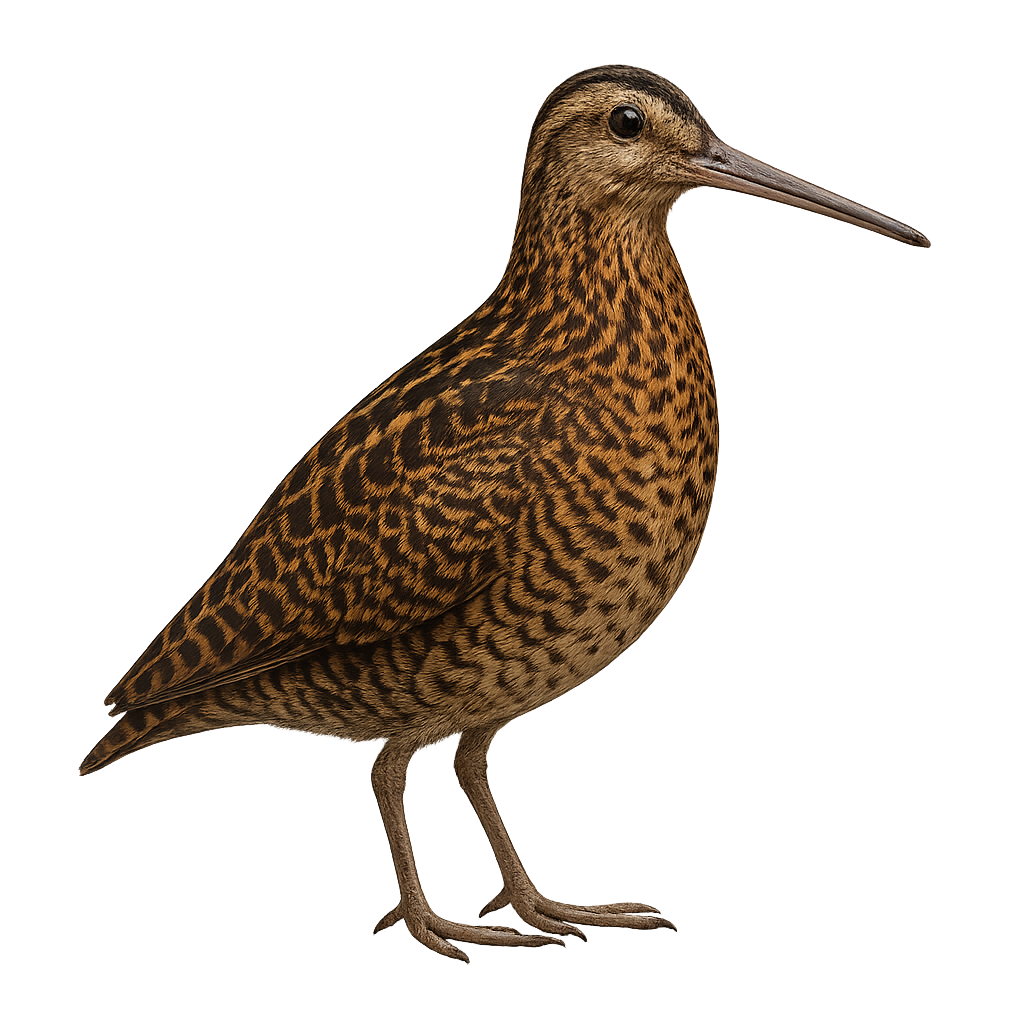
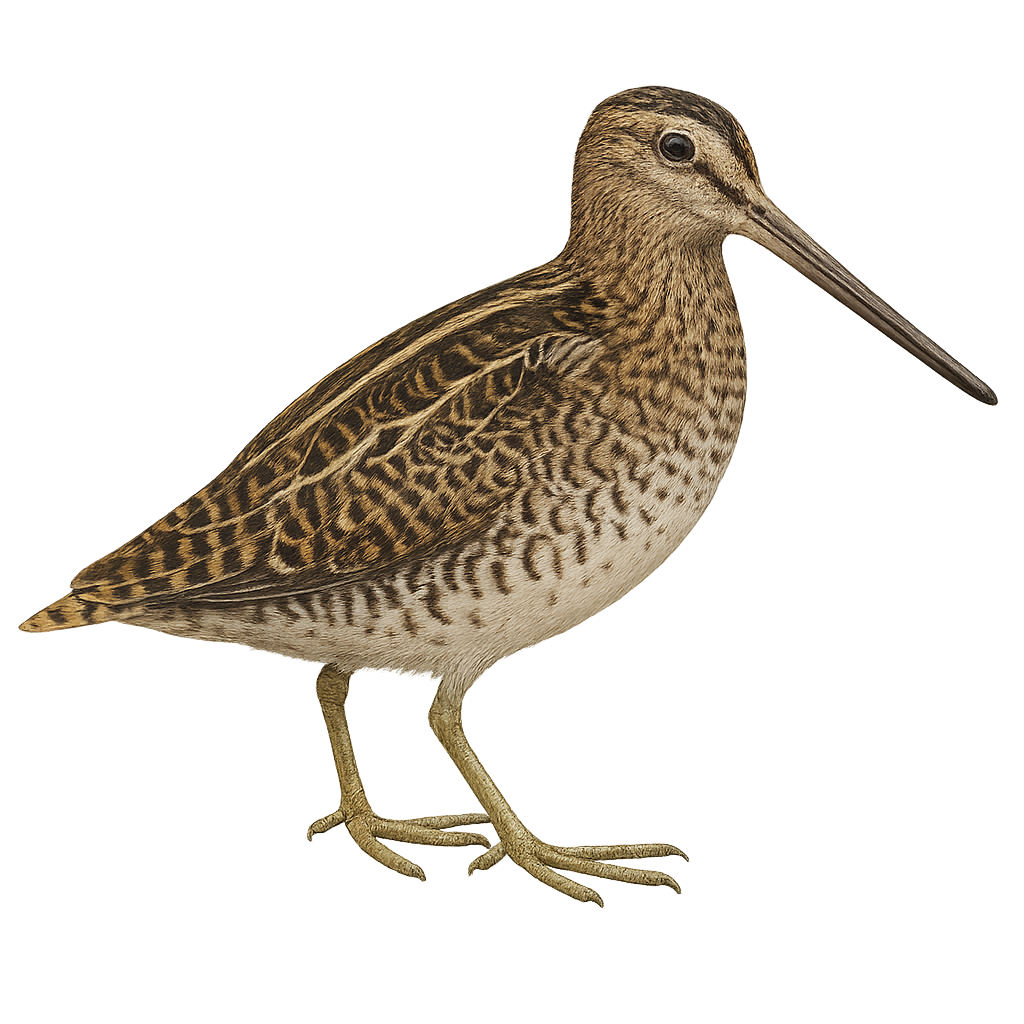
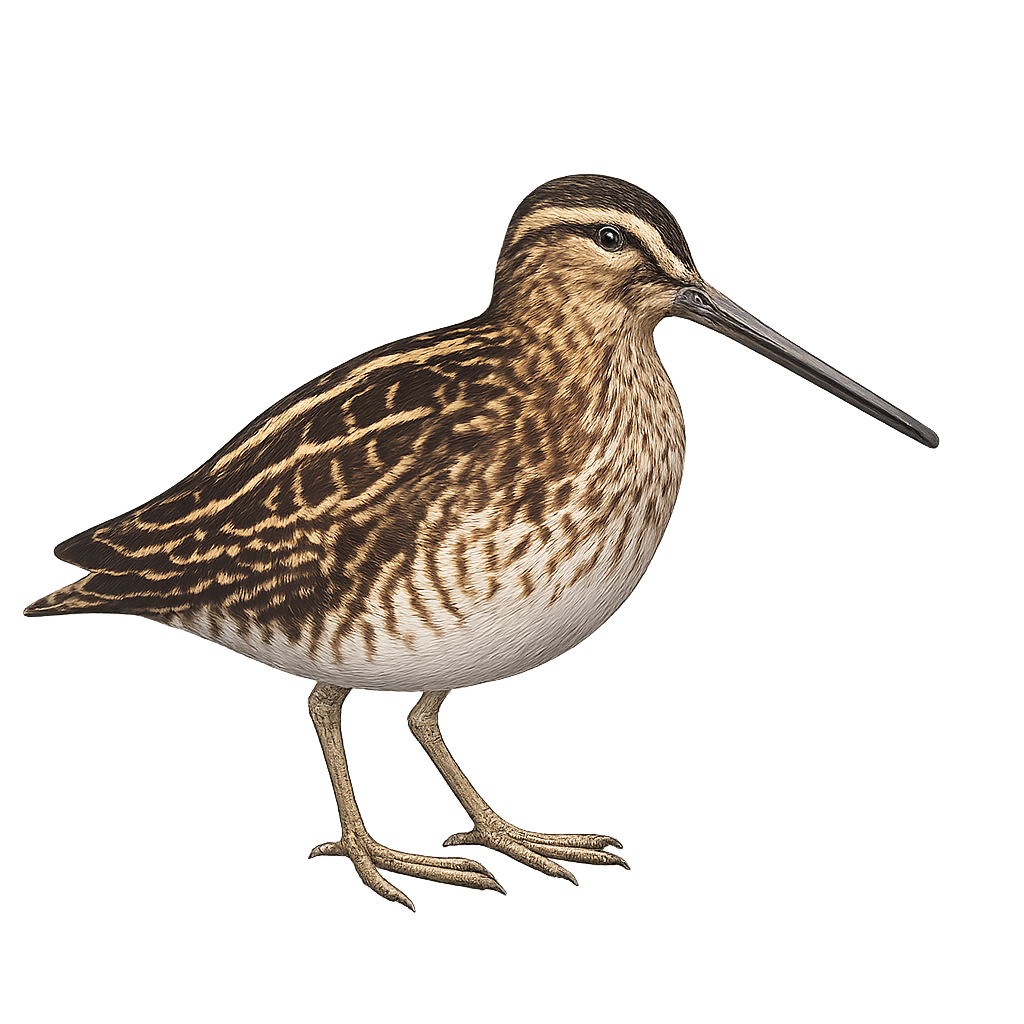
The Least Sandpiper, Calidris minutilla, is the smallest shorebird, measuring about 13 to 15 cm in length with a wingspan of 28 to 32 cm. It has a predominantly brown plumage with lighter underparts and yellowish legs. This bird inhabits wetlands, marshes, and muddy shores, feeding mainly on insects, crustaceans, and mollusks. It breeds in the Arctic tundra and migrates to the southern United States, Central America, and South America for the winter. Its breeding season runs from May to July, typically laying four eggs.
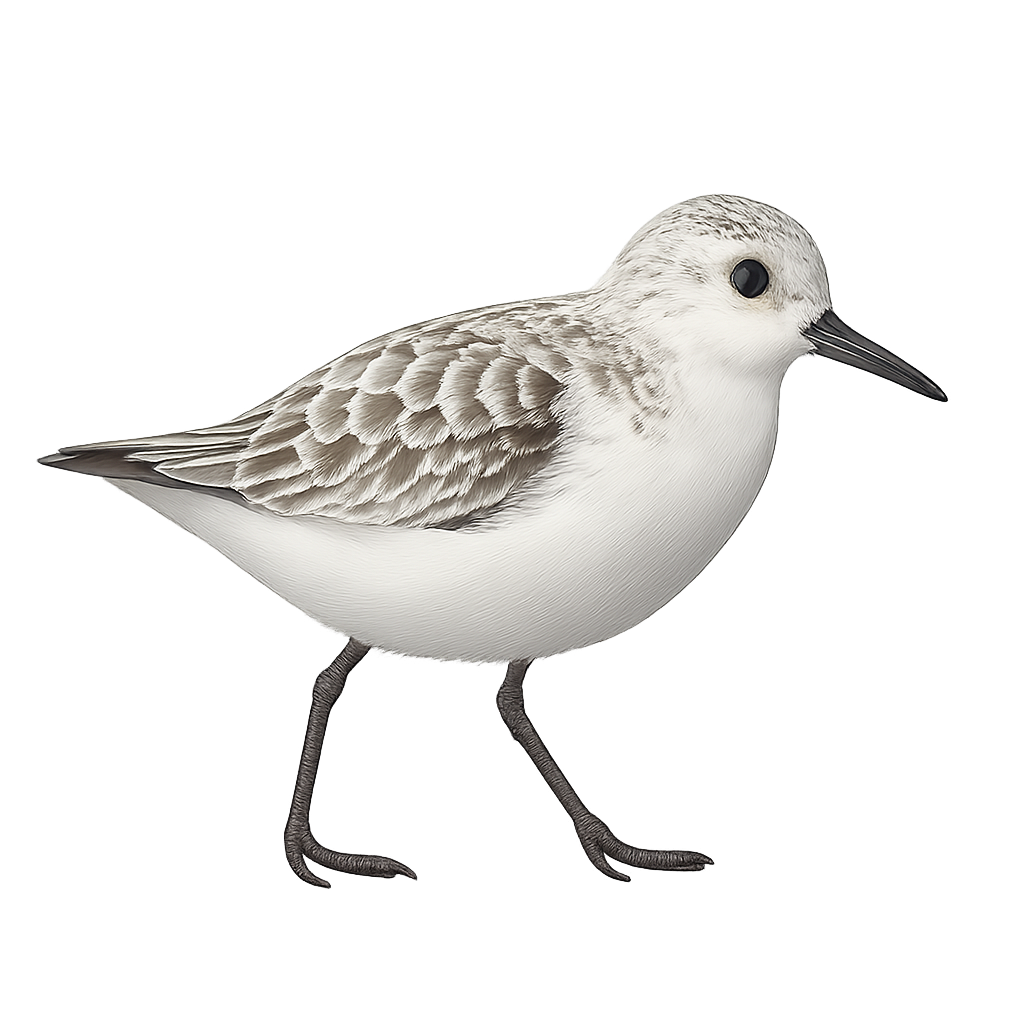
The Sanderling is a small wader with a subtle plumage, mostly white and light gray, known for its quick movements along the shore to capture marine insects, crustaceans, and mollusks. This small migratory bird inhabits beaches and coastal areas of Europe, Asia, North America, and South America, primarily feeding at low tide. The Sanderling is often seen in groups, moving in perfect synchronization, a fascinating sight to observe.
During migration, it covers long distances, leaving the cold regions of winter to reach temperate or tropical beaches where it finds food. While not currently threatened, it is sensitive to human disturbance and the loss of its coastal habitats.
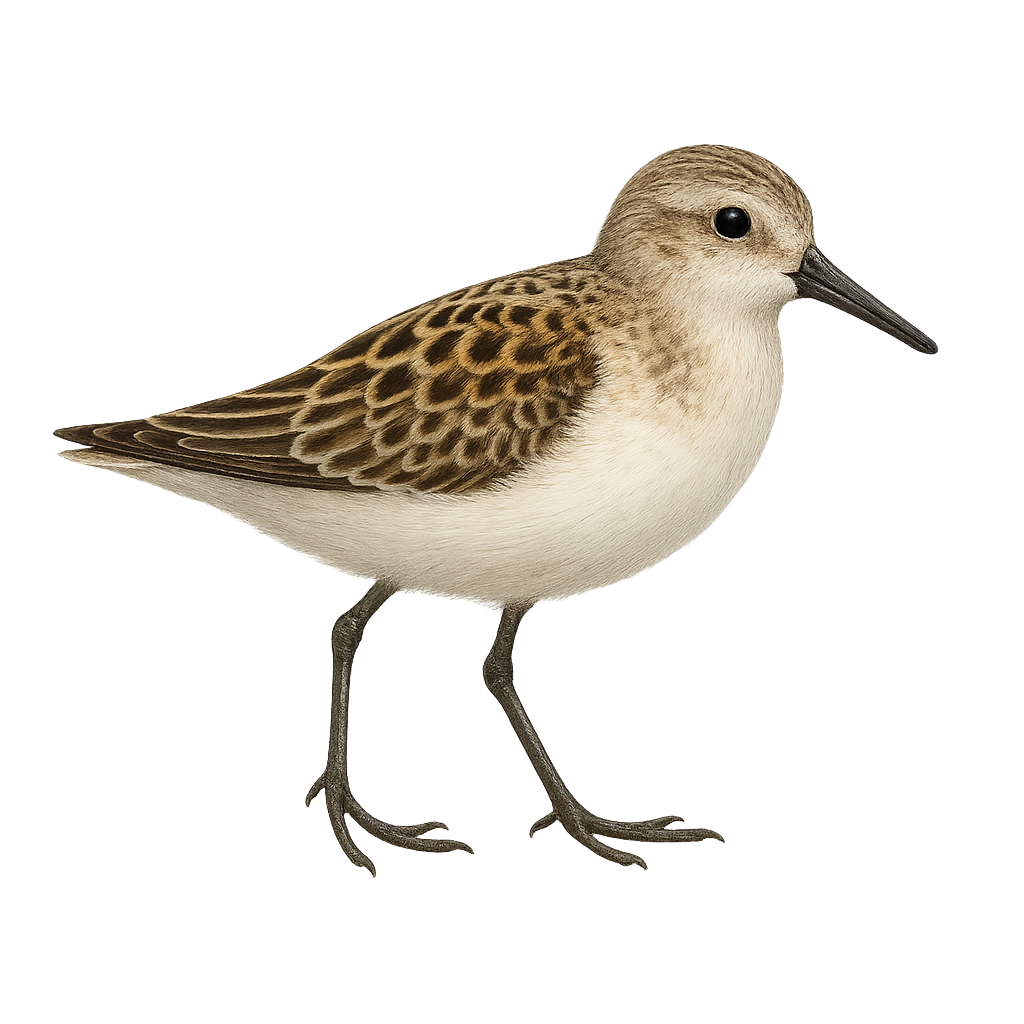
The Semipalmated Sandpiper is a small migratory bird belonging to the Scolopacidae family. It measures about 13 to 15 cm in length with a wingspan of 28 to 30 cm. Its plumage is mainly brownish on the top with lighter shades on the belly. During the breeding season, it displays more vivid and contrasting colors. This bird is known for its long migrations, traveling thousands of kilometers between its breeding grounds in the Arctic and its wintering areas in South America. It primarily frequents wetlands, beaches, and mudflats where it feeds on small invertebrates. Its ability to adapt to different environments makes it a resilient bird, although some populations are threatened by habitat loss.
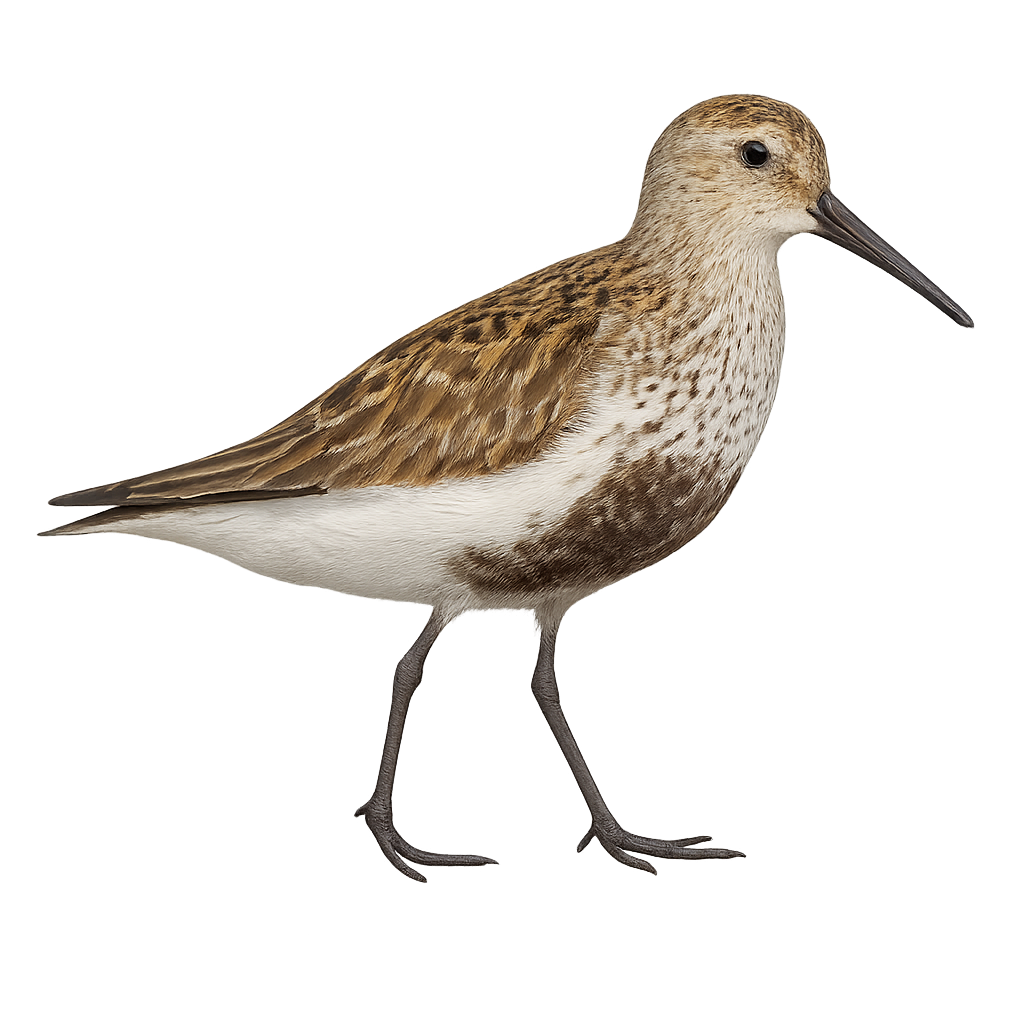
The Dunlin is a small, graceful wader, easily recognizable by its plumage that changes with the seasons, transitioning from gray-brown in winter to more contrasting black and white tones during breeding. This small bird primarily inhabits coastal areas of Europe, Asia, and North America, where it feeds on marine invertebrates, primarily worms and mollusks, which it finds by probing the sand and mud. The Dunlin exhibits social behavior and is often seen in groups, especially during migration.
This migratory wader covers long distances, leaving the cold regions of winter to reach more temperate or tropical areas for feeding and breeding. While relatively common, it can be affected by the disturbance of its coastal habitats.
The Purple Sandpiper is a small wader distinguished by its plumage, which features shades of gray, brown, and purple, especially visible during the breeding season. This small bird primarily inhabits the Arctic coasts of Europe and North America, feeding on small marine invertebrates, mainly crustaceans and mollusks, which it finds in the mud and sand of beaches. The Purple Sandpiper is a long-distance migrant, covering vast distances between its breeding grounds in the Arctic regions and its wintering areas in more temperate zones.
The social behavior of the Purple Sandpiper is also noteworthy, often seen in large groups during migration. While this species is still relatively abundant, it can be affected by disturbance to its coastal habitats and climate change.
The Long-billed Dowitcher is a medium-sized shorebird known for its long, straight bill and mottled brown plumage. It primarily inhabits wetlands, such as marshes and mudflats, where it probes the mud for food, mainly aquatic invertebrates. This migratory bird travels long distances between its breeding grounds in Alaska and its wintering areas in Central and South America. In flight, it is distinguished by its pointed wings and rapid flight. Although its habitat is threatened by wetland destruction, it is currently classified as "Least Concern" by the IUCN.
The Asian Dowitcher is a medium-sized wader bird, identifiable by its long straight bill and partially webbed feet. Its plumage is mainly brown with lighter patterns on the belly, allowing it to blend into the wetland habitats it frequents. It is often seen in coastal areas, estuaries, and salt marshes in Asia, where it feeds on small invertebrates by probing the mud with its bill. As a migratory bird, it travels long distances between its breeding sites and wintering grounds. Although its conservation status is concerning, efforts are underway to protect its habitats and ensure its survival.
The Short-billed Dowitcher, Limnodromus griseus, is a medium-sized shorebird, measuring about 23 to 32 cm in length. It is recognizable by its long straight bill and brownish plumage with lighter patterns on the belly. During the breeding season, its plumage turns more rufous, hence its name. It primarily inhabits wetlands, marshes, and mudflats, probing the soil for worms, crustaceans, and insects. A migratory bird, it breeds in the northern regions of North America and migrates south for the winter. Its call is a soft "tu-tu-tu," often heard during flights.
The Swinhoe's Snipe, or Gallinago megala, is a discreet and well-camouflaged bird often seen in the wetlands of Asia. It is distinguished by its brown mottled plumage and long pointed tail. This migratory bird frequents marshes, wet meadows, and rice fields, where it primarily feeds on insects and small invertebrates. Its ability to blend into its environment makes it difficult to spot. The Swinhoe's Snipe is known for its fast and zigzagging flights, a behavior that helps it evade predators. Although its conservation status is concerning, it remains relatively widespread in its range.
The Wilson's Snipe, Gallinago delicata, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Scolopacidae family. It is characterized by its mottled brown plumage, long legs, and straight, slender bill, perfect for probing wet soils for food. This bird is often found in marshy areas, wet meadows, and lake edges. Its flight is rapid and zigzagging, making it difficult to track. The Wilson's Snipe is known for its distinctive call, often heard during the breeding season. It primarily feeds on insects, worms, and small crustaceans. Although discreet, it is a fascinating sight for birdwatching enthusiasts.
The Common Snipe is an elegant small wader, easily recognized by its long, slender bill and mottled brown and beige plumage. This bird primarily inhabits marshes, wet meadows, and riverbanks in Europe, Asia, and North Africa, where it feeds on aquatic invertebrates, mainly worms, insects, and mollusks. The Common Snipe uses its long, flexible bill to probe the mud in search of food.
It is a migratory bird, leaving the cold regions of winter to move to more temperate zones for breeding. While its population is relatively stable, the Common Snipe is sensitive to habitat changes and water pollution.
The Jameson's Snipe is a discreet and well-camouflaged bird, belonging to the Scolopacidae family. It is primarily found in the wetlands and high-altitude grasslands of the Andes in Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. This medium-sized bird, measuring about 25 to 28 cm in length, is distinguished by its mottled brown plumage, which allows it to blend into its surroundings. Its long, straight bill is ideal for probing the ground for worms and insects. Although not extensively studied, this species is considered to have a stable population but remains vulnerable to changes in its natural habitat.
The Great Snipe is an elegant wader, easily recognized by its mottled brown and beige plumage and two long white bands visible on its wings, from which it gets its name. This species, slightly larger than the Common Snipe, inhabits marshes, wetlands, and riverbanks in Europe and Asia, where it primarily feeds on worms, insects, and small crustaceans found in the mud. The Great Snipe is a particularly discreet bird, often blending into its environment.
Migratory, it covers long distances between its breeding grounds in Europe and its wintering sites in North Africa and Asia. Although less abundant than other waders, the Great Snipe is affected by habitat loss and changes in the hydrological regime in its breeding areas.
The Imperial Snipe, or Gallinago imperialis, is a rare and elusive bird mainly found in the Andes. It is characterized by its dark brown plumage with intricate patterns that allow it to blend into its marshy surroundings. Its long, straight bill is perfectly adapted for probing the ground in search of worms and insects. This bird is most active at dawn and dusk, making it difficult to spot. The Imperial Snipe is often solitary, although it can sometimes be seen in small groups. It prefers wetland habitats and peat bogs located at high altitudes, between 2000 and 3000 meters. Its population is declining, mainly due to the loss of its natural habitat.
The Madagascar Snipe, or Gallinago macrodactyla, is an endemic bird of Madagascar, primarily found in the island's wetlands. It is characterized by its long legs and slender, elongated bill, typical of snipes. Its plumage is mainly brown with streaked patterns, allowing it to blend seamlessly into its natural habitat. It inhabits marshes, rice paddies, and wet meadows, feeding mainly on insects, worms, and small mollusks. Although discreet, it is sometimes seen probing the ground for food. The Madagascar Snipe is currently classified as a vulnerable species due to habitat loss and wetland degradation in Madagascar.
The Jack Snipe is a small, discreet wader, often difficult to spot due to its cryptic plumage that blends perfectly with its environment. This small bird, with its brown and mottled plumage, primarily inhabits marshes and bogs in Northern Europe and Asia. It feeds on invertebrates, mainly worms, insects, and mollusks, which it finds by probing the mud with its short, straight bill.
The Jack Snipe adopts a stealthy behavior and is often observed hiding in dense vegetation or freezing when threatened. While more difficult to observe due to its discretion, it is threatened by habitat loss and changes in the hydrological regime in its breeding areas.
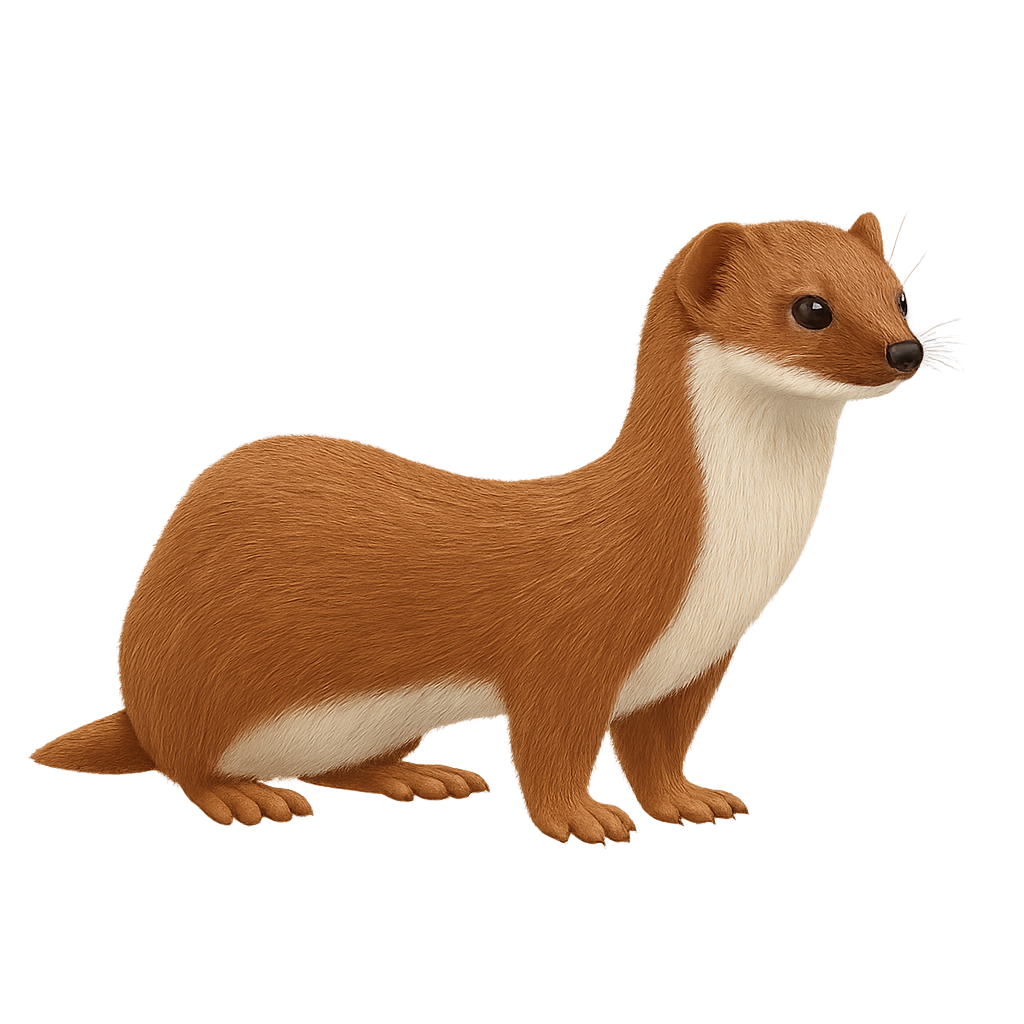
The European Weasel is the smallest carnivore in Europe, easily recognizable by its tiny size and brown coat with a white throat and belly. It primarily inhabits a variety of environments such as forests, meadows, and agricultural areas, where it hunts small mammals, birds, insects, and eggs. Agile and fast, the European Weasel is a stealthy hunter, capable of slipping into tight spaces to capture its prey.
Solitary and territorial, the European Weasel is active both day and night, and it uses its own burrows or those of other animals to hide and rest. Though small, it is a formidable predator, often seen as beneficial for regulating small rodent populations. However, it can be threatened by habitat destruction and changes in agricultural practices.
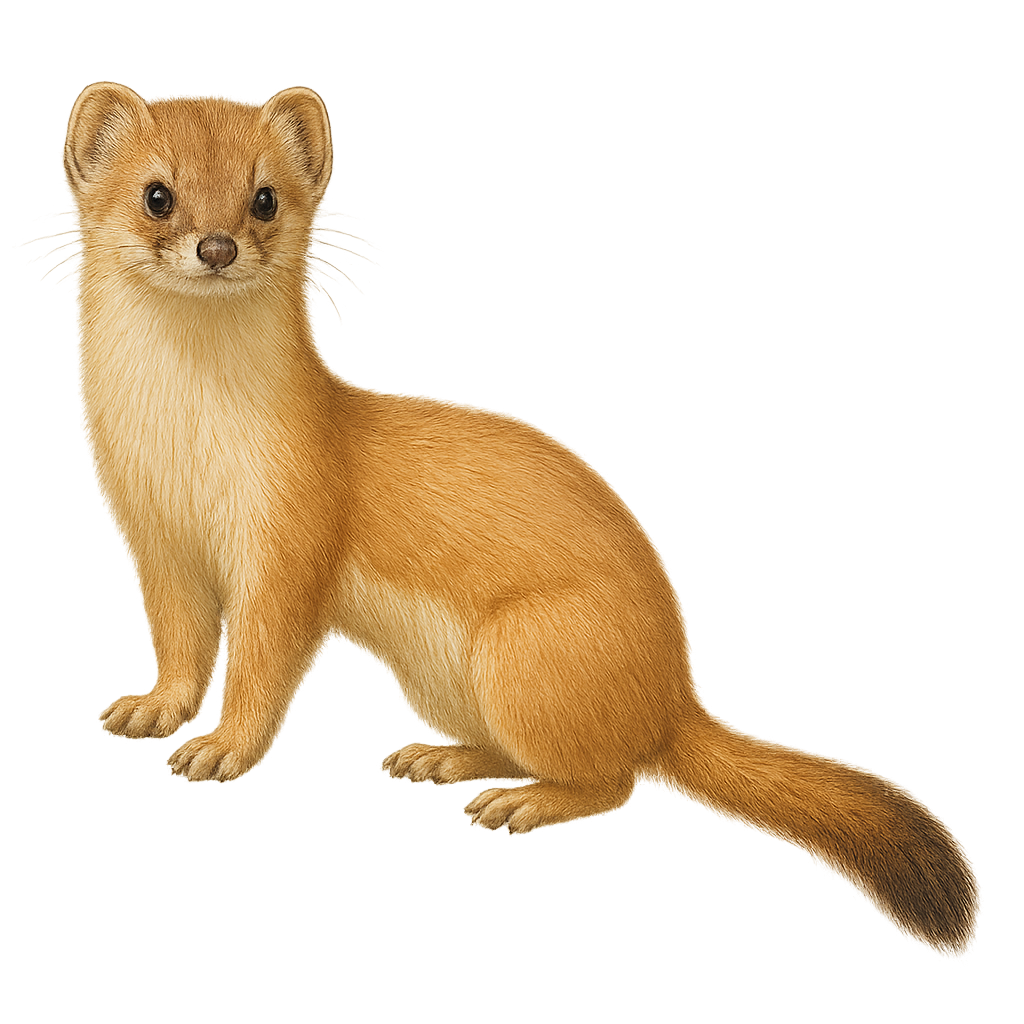
The mountain weasel, Mustela altaica, is a small mustelid native to the mountainous regions of Central Asia. It is characterized by its dense, silky fur, typically light to dark brown, with a lighter underside. Its body length ranges from 22 to 29 cm, with a tail measuring about 12 to 15 cm. Adapted to cold environments, it is often found in alpine meadows, coniferous forests, and rocky areas. As a carnivore, it primarily feeds on small mammals, birds, and insects. Although elusive, it plays a crucial role in controlling rodent populations.
The Beluga is a remarkable cetacean, easily recognizable by its immaculate white color and streamlined shape. Unlike many other dolphins, the Beluga has a rounded forehead, called a "melon," which allows it great head flexibility. What also makes the Beluga unique is its ability to produce a wide variety of sounds, which it uses to communicate and navigate in the cold waters of the Arctic seas, the North Atlantic, and rivers. It primarily feeds on fish, crustaceans, and mollusks, hunting them with its excellent echolocation ability.
Belugas live in social groups called "pods" and are known for their social behavior and interaction with humans. Despite its popularity, the Beluga is vulnerable to water pollution and climate change, which affect its natural habitats.
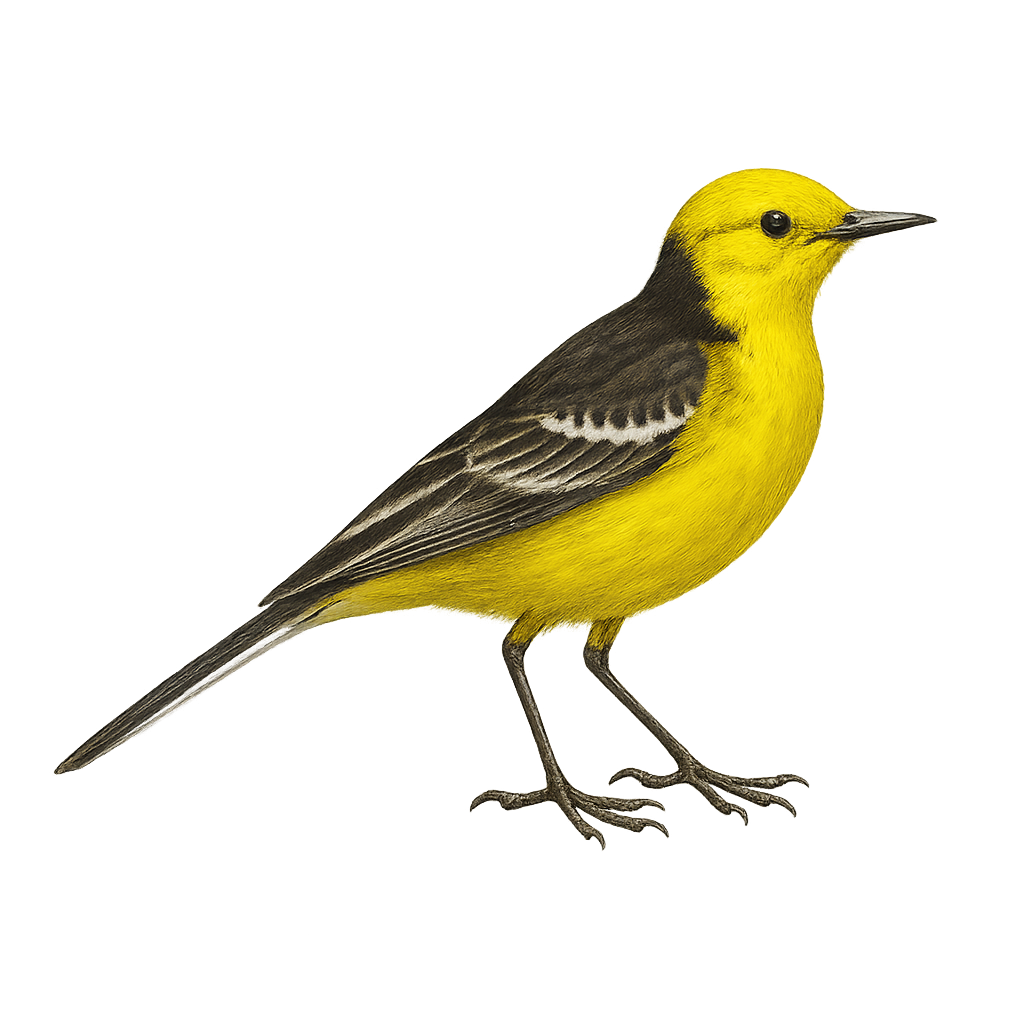
The Citrine Wagtail, or Motacilla citreola, is an elegant and colorful bird belonging to the Motacillidae family. It is distinguished by its bright yellow plumage on the belly and chest, contrasting with a gray back and a black head in males during the breeding season. Females and juveniles display duller shades, with gray and brown hues. This bird is often found in wetlands, meadows, and riverbanks, where it primarily feeds on insects and small invertebrates. A migratory species, the Citrine Wagtail breeds mainly in Central Asia and migrates to South Asia for the winter. Its characteristic gait, marked by a tail-wagging movement, makes it easily identifiable.
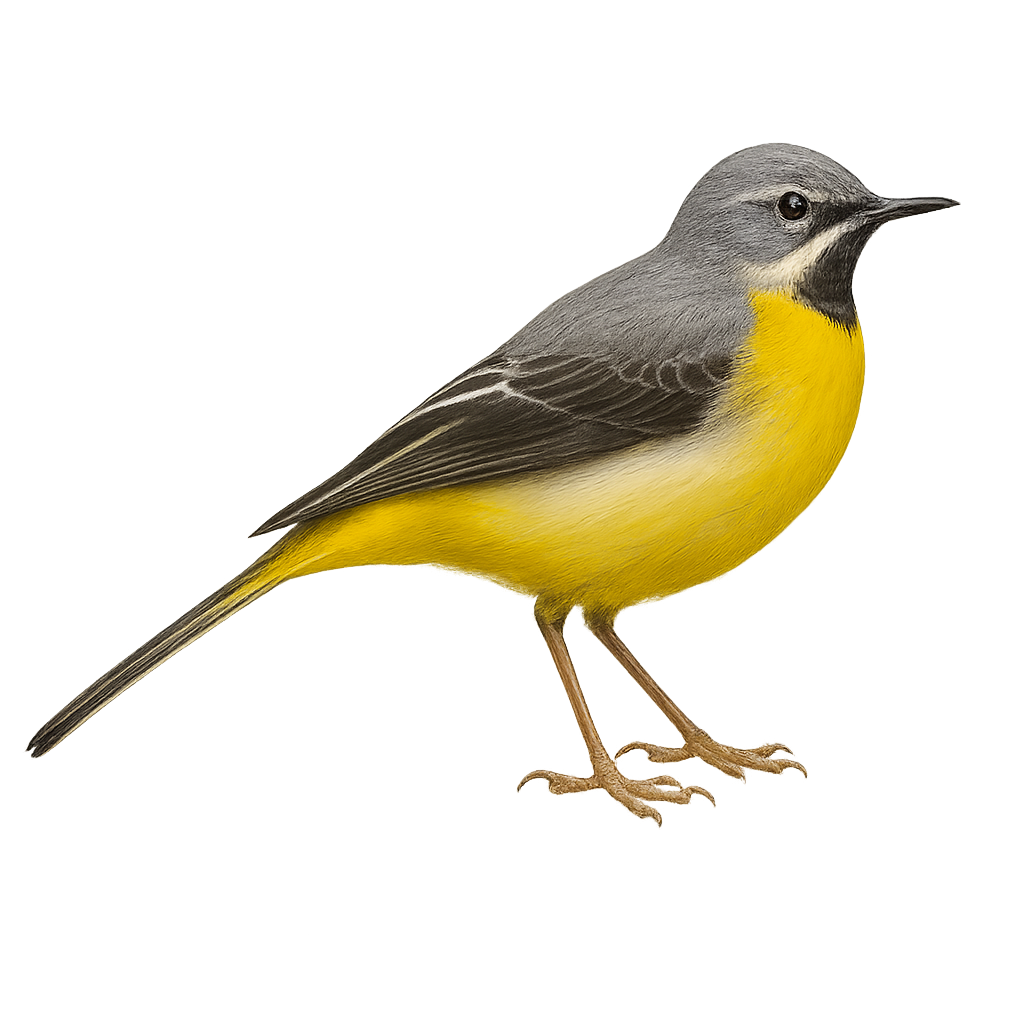
The gray wagtail is a small bird found primarily near rivers, streams, and wetlands across Europe, Asia, and northern Africa. This passerine bird is distinguished by its gray and yellow plumage, long tail, and lively, jittery movements. It primarily feeds on insects, which it catches while running along riverbanks and searching through rocks. The gray wagtail is also known for its territorial behaviors and pleasant song.
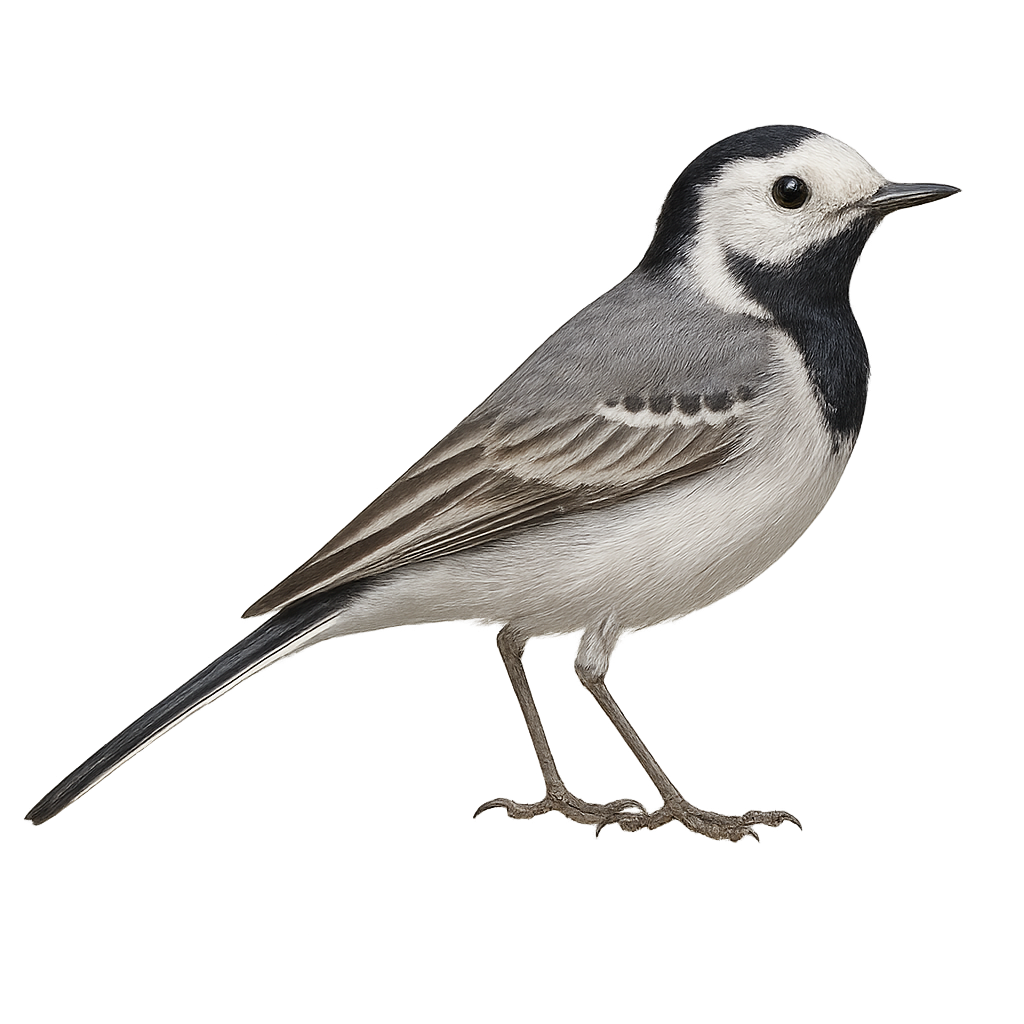
The white wagtail is a small passerine bird found primarily in open areas such as fields, roadsides, and riverbanks across Europe and Asia. It is easily recognized by its black and white plumage and distinctive wagging tail, especially when it runs or forages on the ground. This small bird primarily feeds on insects and small invertebrates, which it captures while running or rummaging through low vegetation.
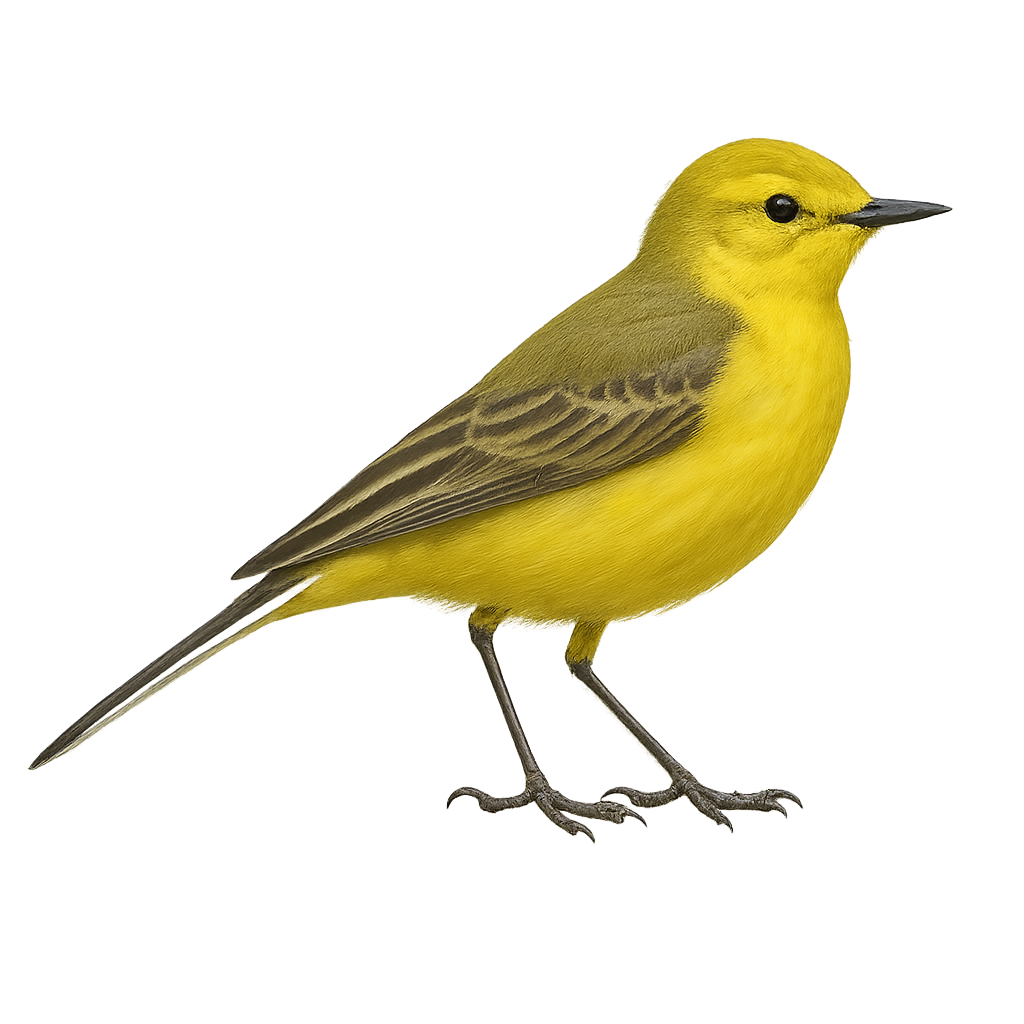
The yellow wagtail is a small migratory passerine bird found primarily in meadows, cultivated fields, and riverbanks across Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It is easily recognized by its bright yellow plumage on the belly and chest, its slender legs, and its quick movements. This bird primarily feeds on insects and invertebrates, which it captures by running on the ground or pecking at the grass.
The Point-tailed Palmcreeper is a rare and fascinating bird, endemic to the palm forests of the Amazon. With its olive-brown plumage and distinctive pointed tail, it blends seamlessly into its habitat. This bird is often seen climbing along palm trunks, searching for insects and small invertebrates. Its ability to move skillfully among the fronds allows it to feed efficiently while staying hidden from predators. Although primarily solitary, it can occasionally be seen in small family groups. Its discretion and specific habitat make observing it a real challenge for amateur and professional ornithologists alike.
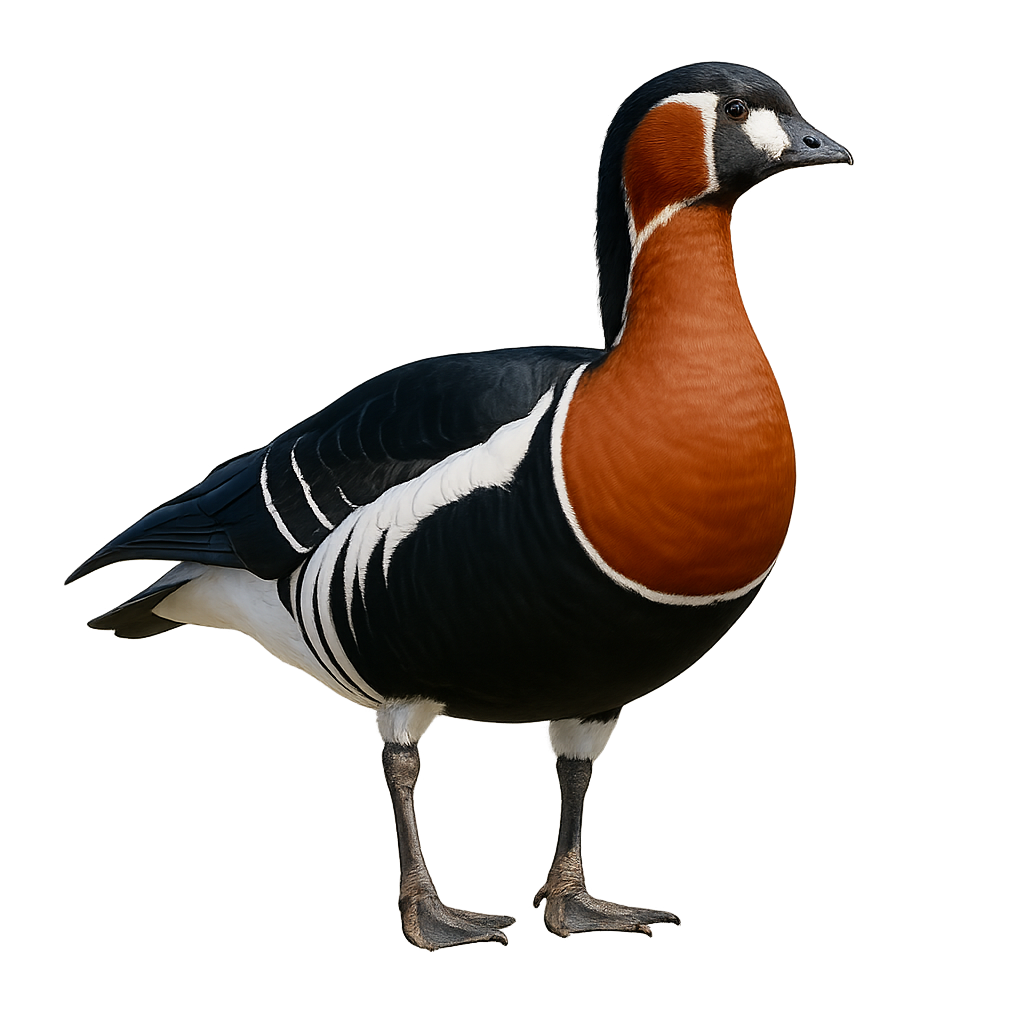
The red-breasted goose is a small migratory goose (55–65 cm wingspan) with contrasting black-and-white plumage and a bright russet breast. It breeds in Arctic coastal tundra near waterways and winters in temperate wetlands of Europe and Asia. During the breeding season, males and females actively defend their nesting territory with head-forward displays and harsh calls.
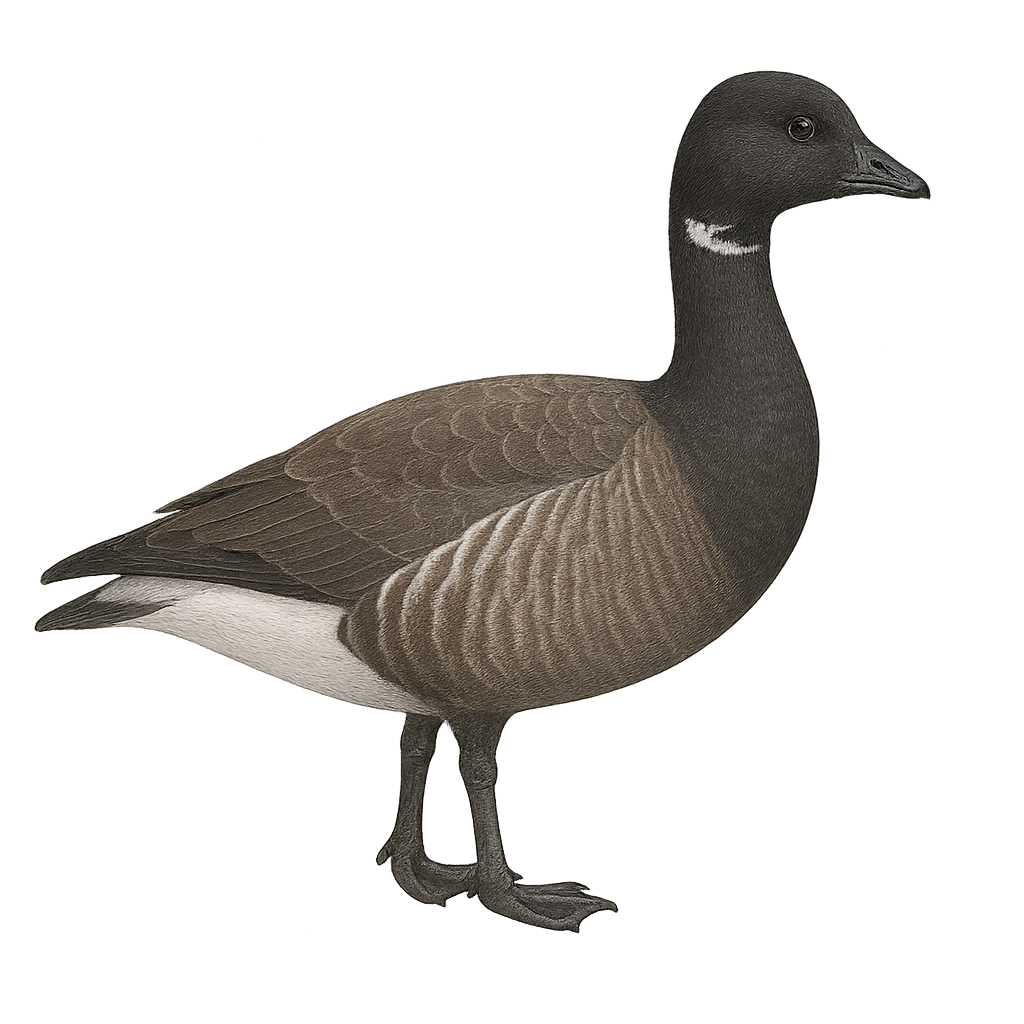
The Brant Goose is a medium-sized waterfowl belonging to the Anatidae family. It is characterized by its dark plumage, with a black head and neck, featuring a small white patch on the side of the neck. Its belly is lighter, contrasting with the rest of its body. This migratory bird breeds in Arctic regions and winters along temperate maritime coasts. It primarily feeds on aquatic plants and grasses found in intertidal zones. The Brant Goose is often seen in large flocks, which helps protect it from predators. Although generally discreet, it can become noisy when disturbed.
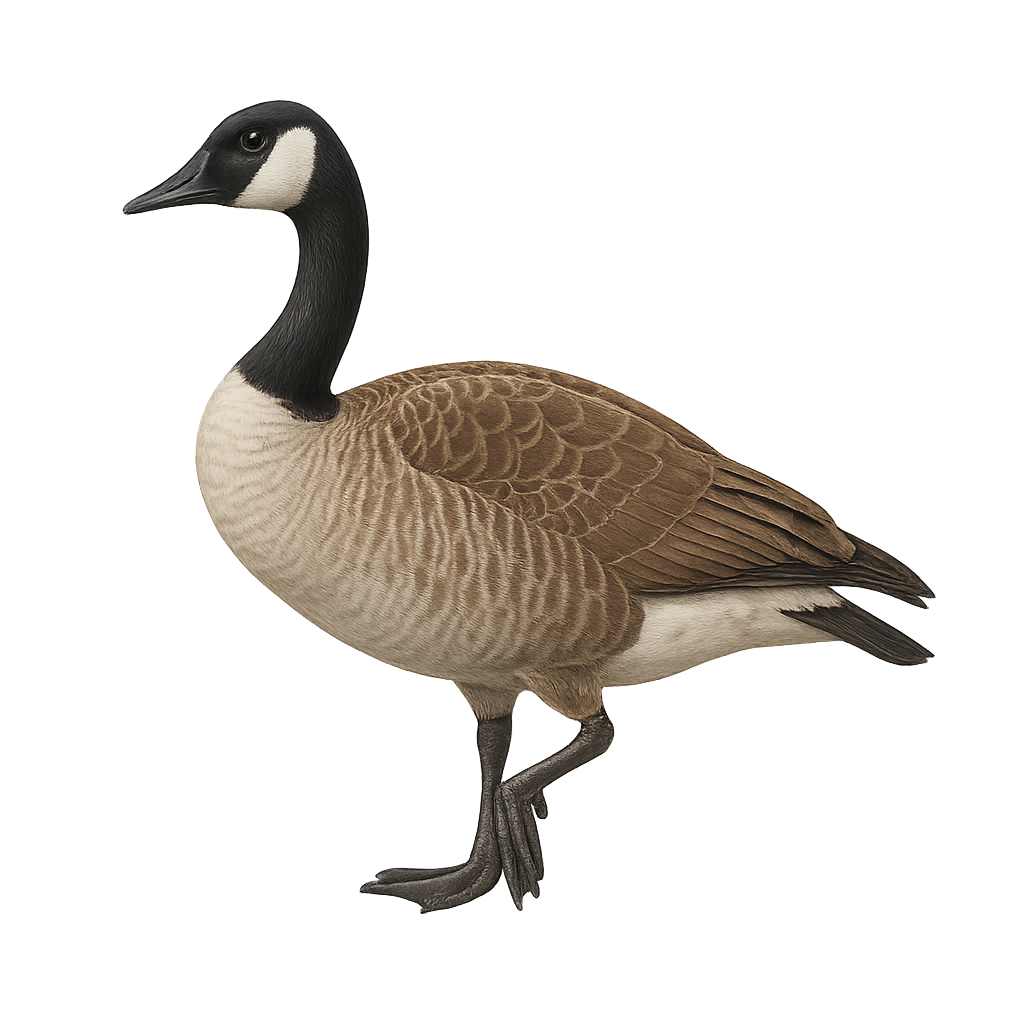
The Cackling Goose, or Branta hutchinsii, is a medium-sized waterfowl belonging to the Anatidae family. Often mistaken for the Canada Goose due to their similar appearance, it is generally smaller with a shorter bill. Its plumage is primarily gray-brown with a distinctive black head and neck, featuring a white chinstrap. It primarily inhabits wetlands, lakes, and rivers, feeding on aquatic plants, seeds, and insects. A migratory bird, it travels long distances between its breeding grounds in Alaska and Canada and its wintering areas in the United States. Although generally wary, it can become accustomed to human presence in protected areas.
The Cackling Goose, scientifically known as Branta canadensis leucopareia, is a subspecies of the Anatidae family. It is easily identified by its brown and white plumage, long black neck, and white cheeks. It primarily inhabits wetlands, lakes, and rivers. This species is known for its spectacular migrations in large V-shaped formations. Highly adaptable, it can be found in various environments, including urban parks. Although generally tolerant of human presence, it can become aggressive if threatened, especially during nesting season.
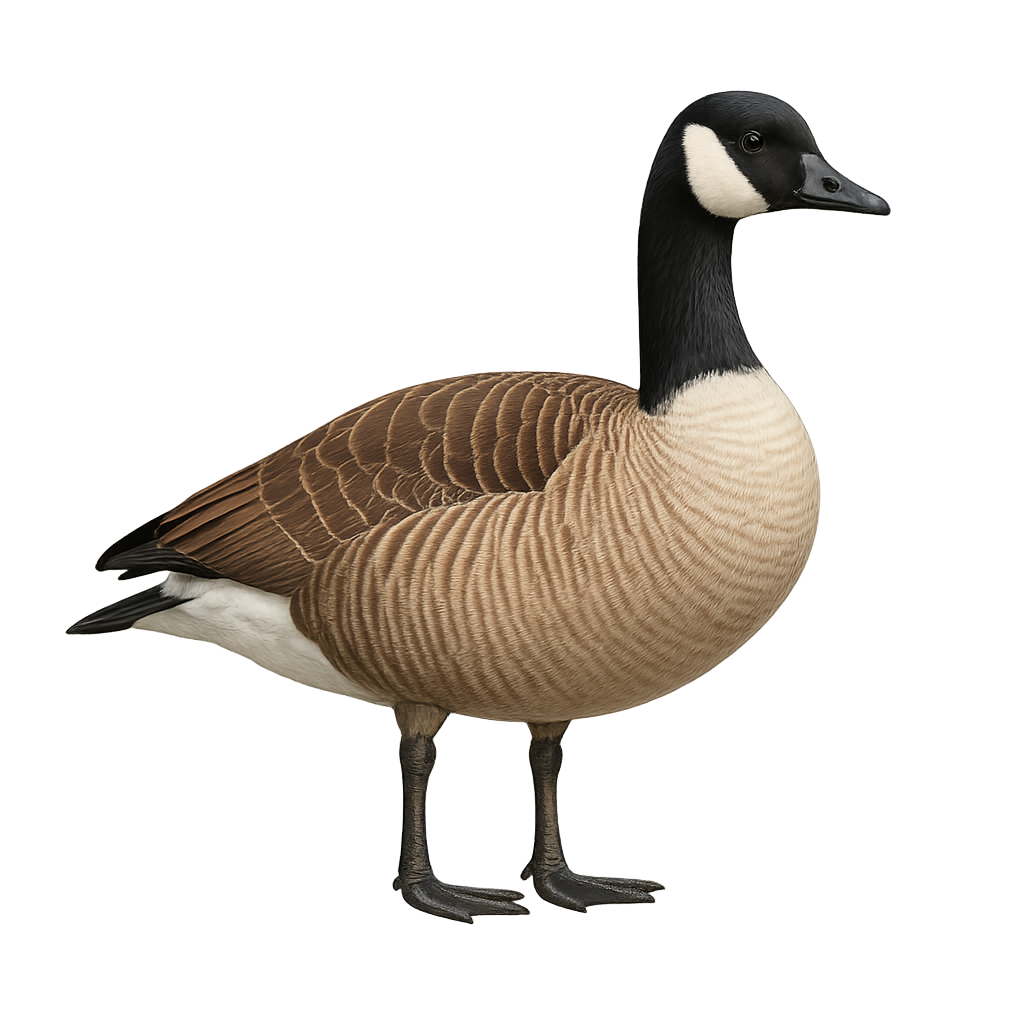
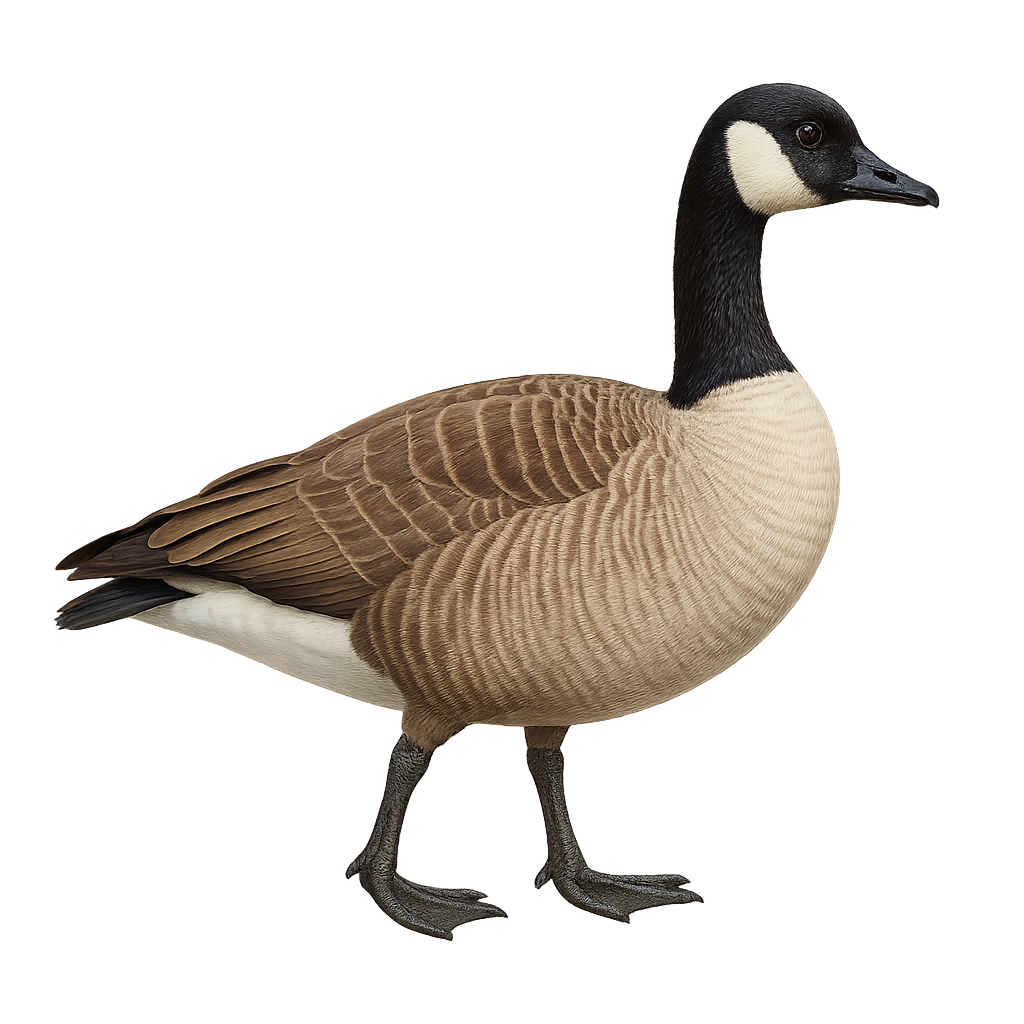
The Canada Goose is a large waterfowl species easily identified by its brown body, black head and neck, and distinctive white cheek patch. Often seen in large flocks, they form V-shaped formations during migration. These birds are highly adaptable, inhabiting a range of environments from lakes and rivers to urban parks. Their diet is diverse, including aquatic plants, seeds, and insects. While generally tolerant of humans, they can become aggressive if threatened, especially during nesting season.
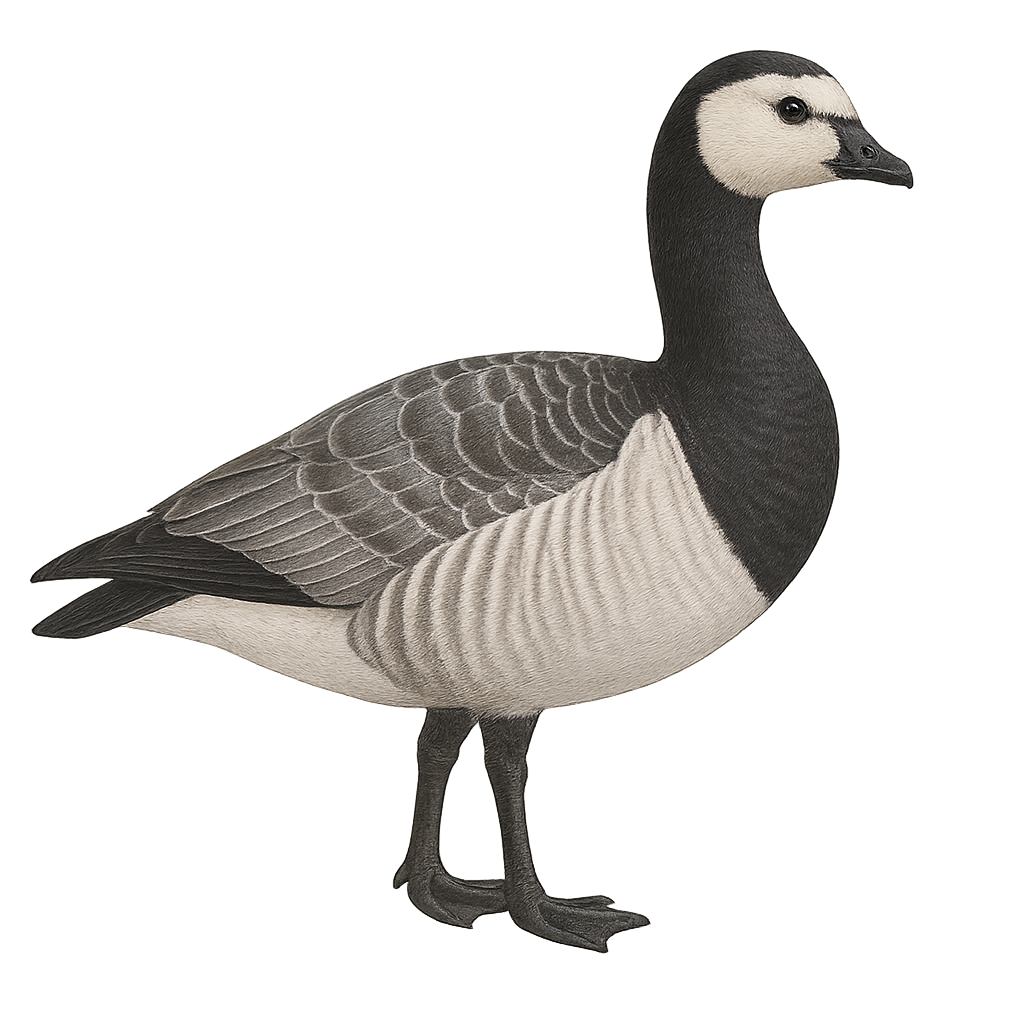
The Barnacle Goose, Branta leucopsis, is a medium-sized waterfowl belonging to the Anatidae family. It is easily recognizable by its white face contrasting with its black neck and chest. Its back is light gray, while its wings display darker gray shades. It primarily inhabits Arctic regions for breeding, migrating to more temperate areas in winter. Its preferred habitats include coastal areas, estuaries, and wet meadows. The Barnacle Goose is a gregarious bird, often seen in large flocks. It feeds mainly on aquatic vegetation, grasses, and herbs. Although its conservation status is currently assessed as "least concern," it remains vulnerable to climate change and habitat degradation.