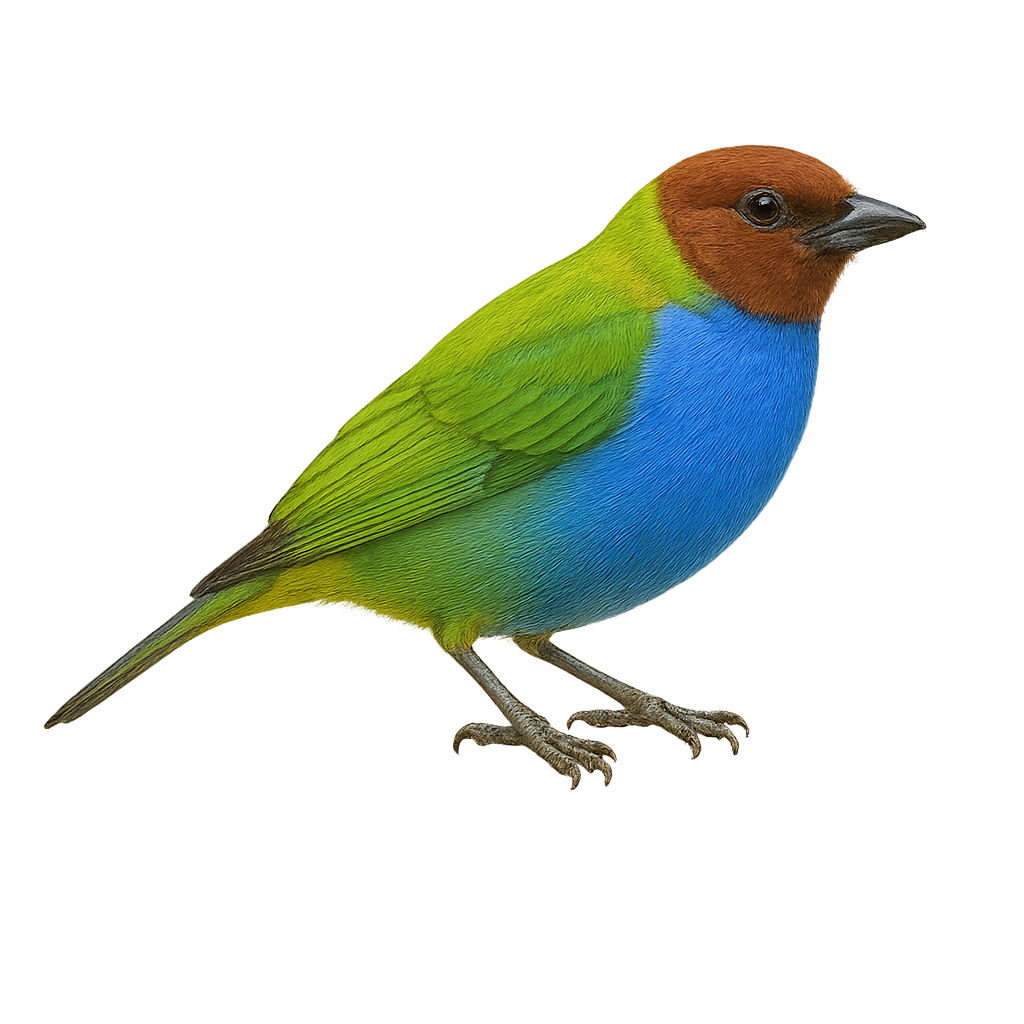
The Bay-headed Tanager, scientifically known as Tangara gyrola, is a vibrant bird native to the tropical forests of Central and South America. It is easily identified by its striking green head, which contrasts with its body adorned in shades of blue, red, and yellow. This bird measures about 14 cm in length and weighs between 19 and 22 grams. Its diet consists mainly of fruits, but it also consumes insects and nectar. Bay-headed Tanagers live in small groups and are often seen actively moving through the canopy. Their song is a soft warble, and they play a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding forest regeneration.
The Red-necked Tanager, or Tangara fastuosa, is a bird from the Thraupidae family, endemic to Brazil. It is known for its striking plumage, featuring a bright red head, a vibrant green body, and blue wings. This small bird measures about 13 to 14 cm in length and weighs between 18 and 21 grams. It primarily inhabits the humid tropical forests of eastern Brazil, where it feeds on fruits, insects, and nectar. The Red-necked Tanager is often seen in small groups or pairs, actively moving through the canopy. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it is currently classified as "Near Threatened" by the IUCN.
The Red-shouldered Tanager, or Tangara velia, is a vibrant bird found in the tropical forests of South America. It is easily identifiable by its striking plumage: a bright red back contrasting with a black belly and blue wings. This small passerine, measuring about 14 cm in length, is often seen in pairs or small groups. It primarily feeds on fruits, but also insects, which it catches with agility. Its melodious and varied song is a delight for birdwatchers. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, the Red-shouldered Tanager remains relatively common within its range.
The Green-and-gold Tanager, or Tangara labradorides, is a small tropical songbird from the humid forests of South America, recognizable by its bright green plumage with metallic blue hues and agile form. It is mainly found in the Andes, from Venezuela to Peru, at elevations between 1000 and 2500 meters. Highly active, it often moves in flocks through the canopy, feeding on fruits, insects, and nectar. Though discreet, its vivid colors make it a favorite among bird photographers. The species is considered stable in terms of population.
The Hartert's Camaroptera is a small passerine bird belonging to the Cisticolidae family, predominantly found in sub-Saharan Africa. It is characterized by its olive-green back and pale grey underparts, with a short, often cocked tail. Known for its melodious and complex song, this bird is often heard before it is seen. It primarily inhabits dense undergrowth, secondary forests, and thickets. Its ability to blend into its surroundings makes it challenging to spot. The camaroptera is a territorial bird, often living in pairs or small family groups. It feeds mainly on insects and small invertebrates, which it captures by foraging through dense foliage.
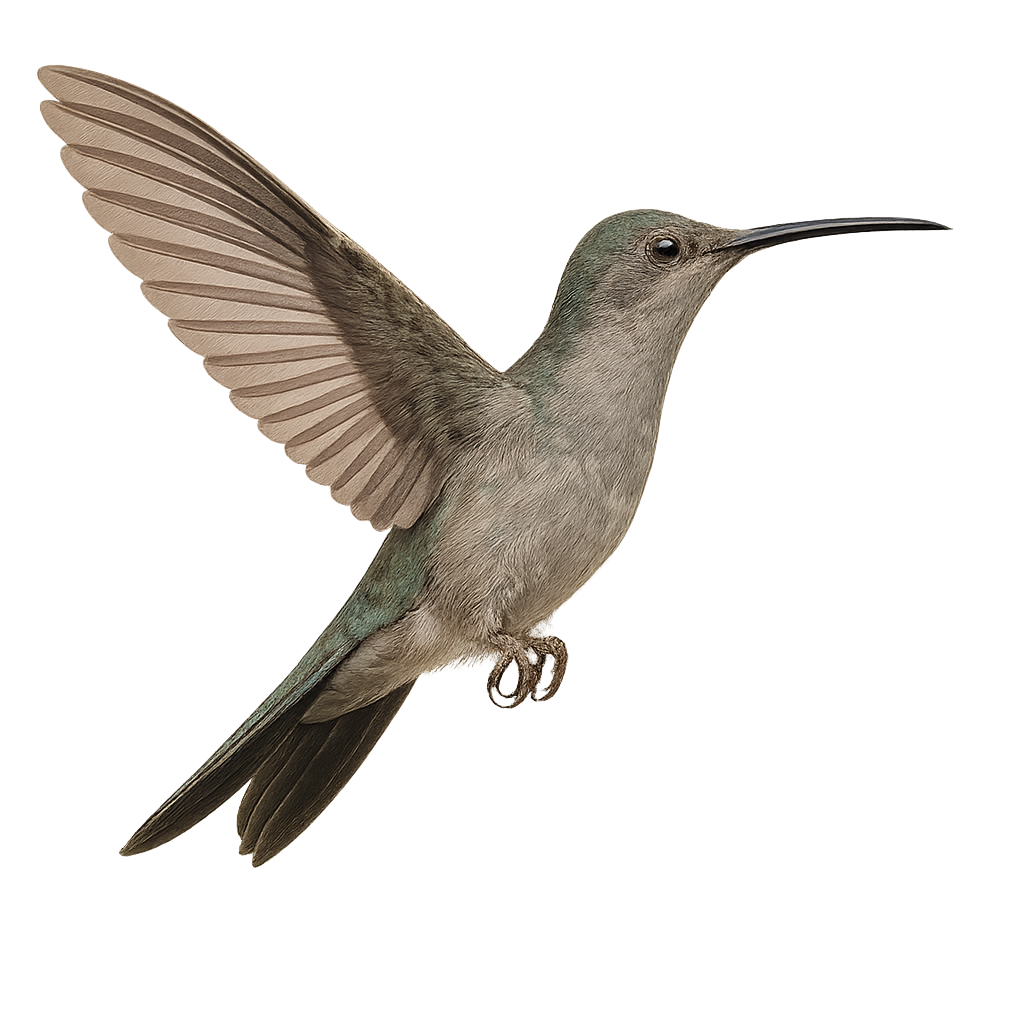
The Grey-breasted Sabrewing, scientifically known as Campylopterus largipennis, is a medium-sized hummingbird found mainly in the tropical rainforests of South America. This stunning bird is noted for its iridescent plumage, with shades of green and blue on its back and a grayish breast. Its tail is broad and slightly forked, giving it a distinctive silhouette in flight. Males and females are similar, although females may have slightly duller colors. This hummingbird is often seen feeding on nectar, using its long bill to reach tubular flowers. It plays a crucial role in the pollination of plants within its habitat.
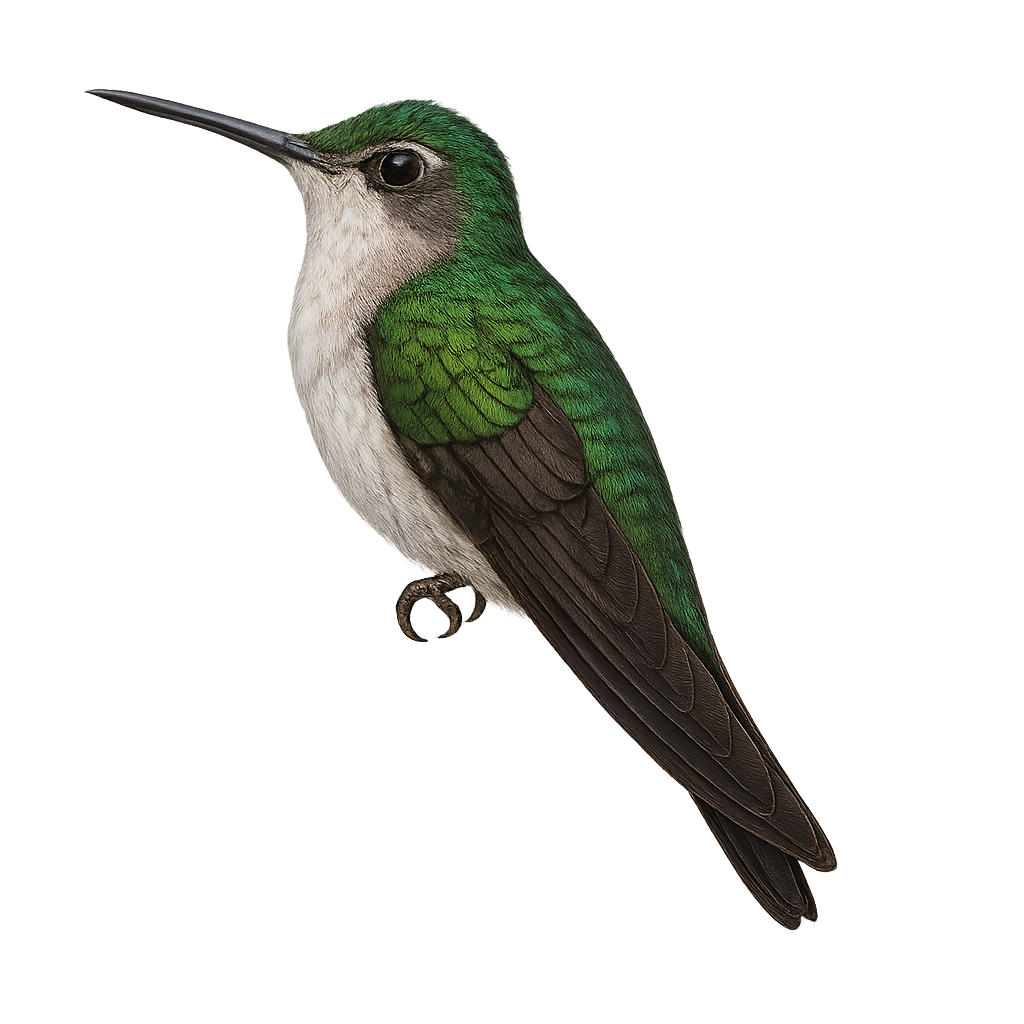
The Curve-winged Sabrewing, scientifically known as Pampa curvipennis, is a medium-sized hummingbird found primarily in the tropical and subtropical forests of Mexico. It is characterized by its curved wings and relatively long tail. The plumage is generally green with metallic sheens, and it features a contrasting white throat. Both males and females look similar, although males are slightly larger. They primarily feed on nectar but also consume small insects to supplement their diet. Their fast and agile flight allows them to move easily between flowers.
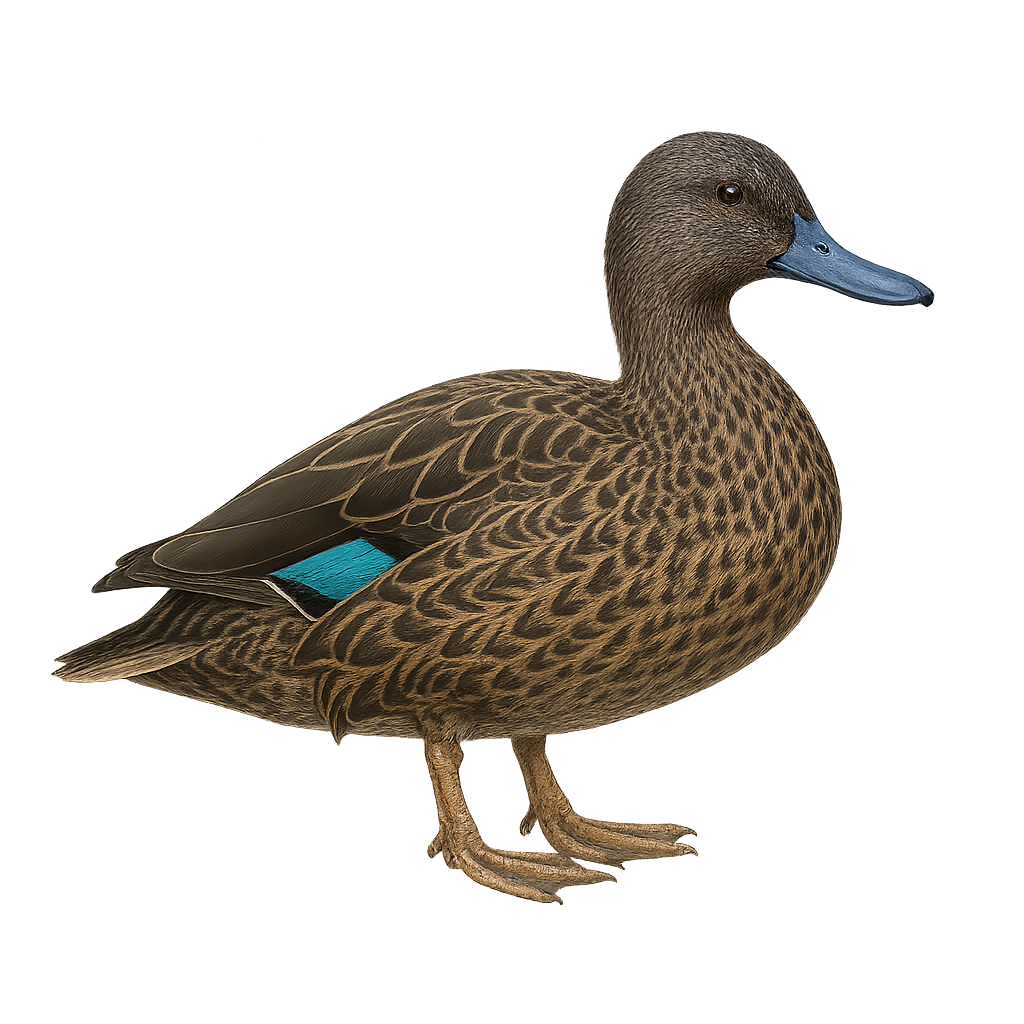
The White-winged Duck, Asarcornis scutulata, is a rare and endangered species in the Anatidae family. It is notable for its dark plumage with striking white wings visible in flight. Primarily nocturnal, it inhabits dense forests and wetlands in Southeast Asia. Its population is declining due to habitat loss and hunting. This duck is often solitary or found in small groups. It feeds on aquatic plants, insects, and small fish. Conservation of its natural habitat is crucial for its survival, with protection efforts including the establishment of nature reserves and awareness programs.
The Yellow-billed Duck, Anas undulata, is a medium-sized duck species known for its bright yellow bill and greyish-brown plumage with wavy patterns. It is primarily found in sub-Saharan Africa, inhabiting lakes, rivers, and marshes. This duck is often seen in small groups but can form large flocks outside the breeding season. It feeds mainly on aquatic plants, seeds, and aquatic insects. Although generally discreet, it can be quite noisy, producing nasal calls. The Yellow-billed Duck is an adaptable species, capable of living in various aquatic habitats, allowing it to maintain stable populations despite environmental pressures.
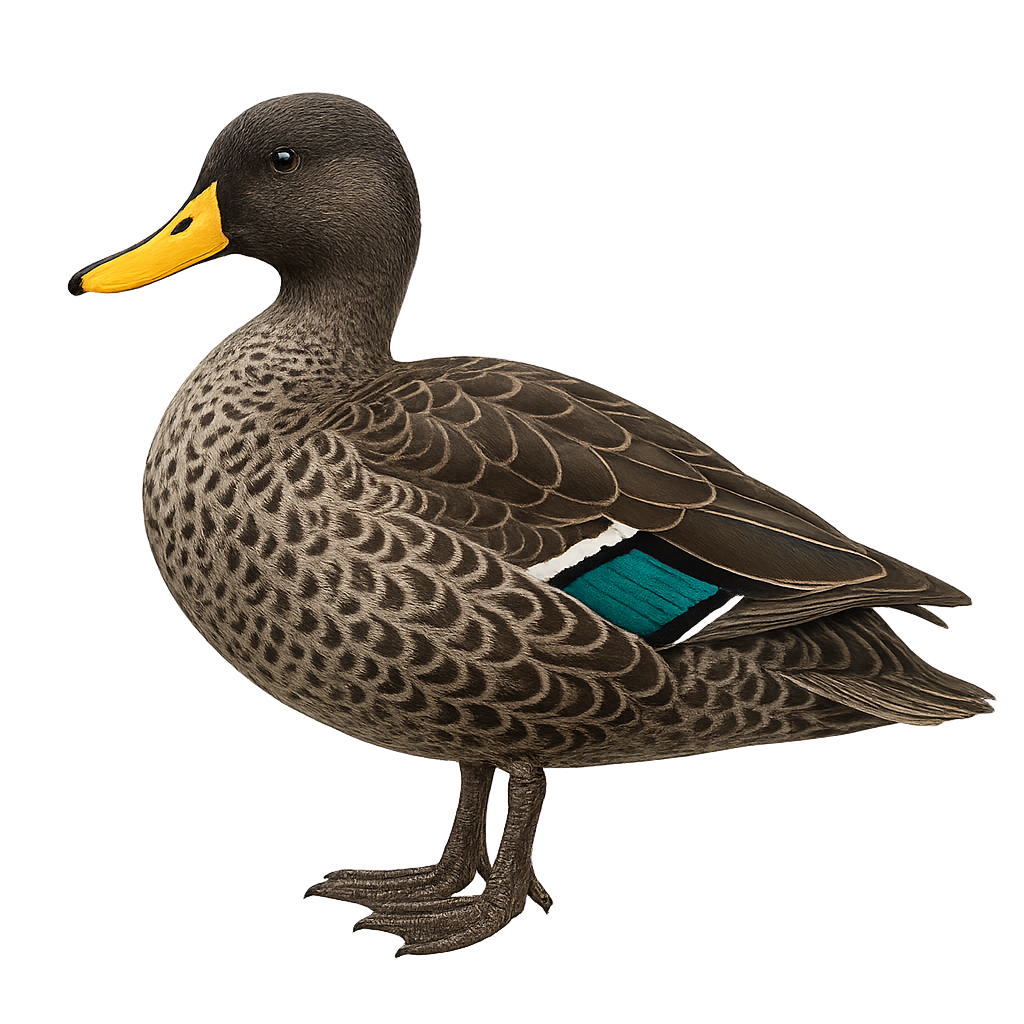
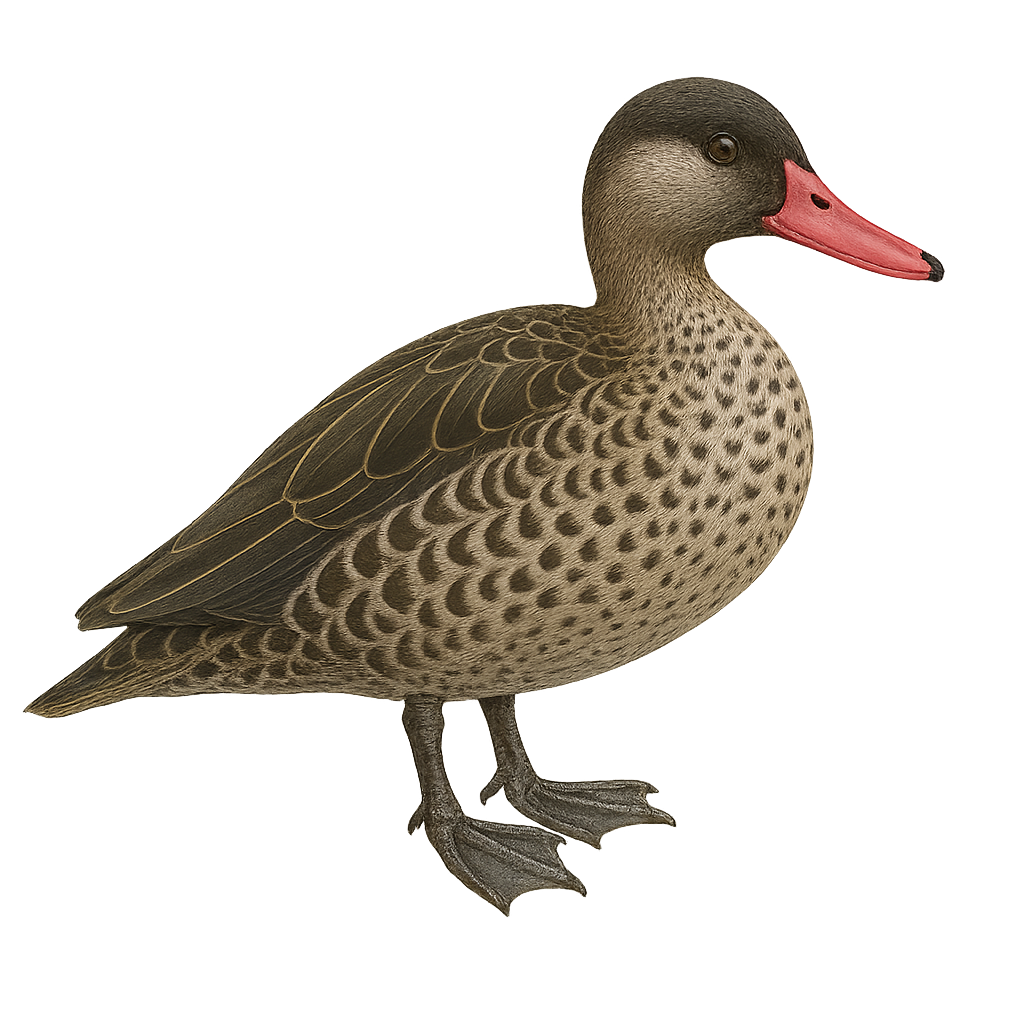
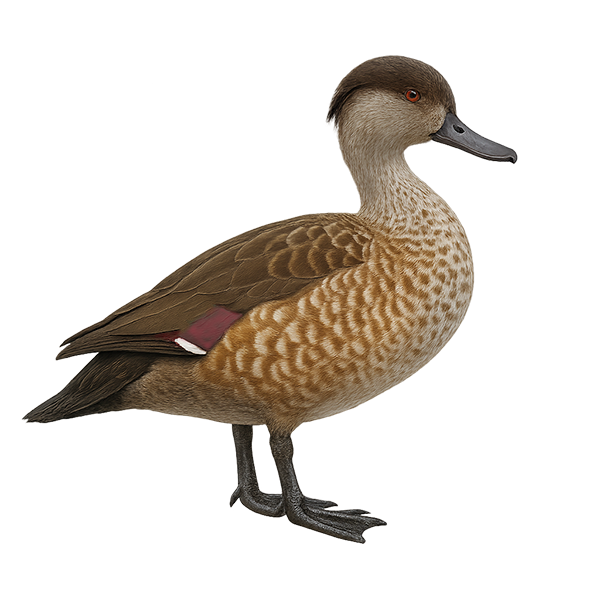
The Red-billed Teal, Anas erythrorhyncha, is a medium-sized waterfowl known for its distinctive bright red bill. Its plumage is mostly brown with lighter patterns on the belly and grayish reflections on the wings. It inhabits the wetlands of sub-Saharan Africa, favoring lakes, marshes, and rivers. This duck is often seen in small groups but can form large gatherings outside the breeding season. It primarily feeds on aquatic plants, seeds, and insects. Although generally discreet, it can be approached closely in some areas where it is accustomed to human presence.
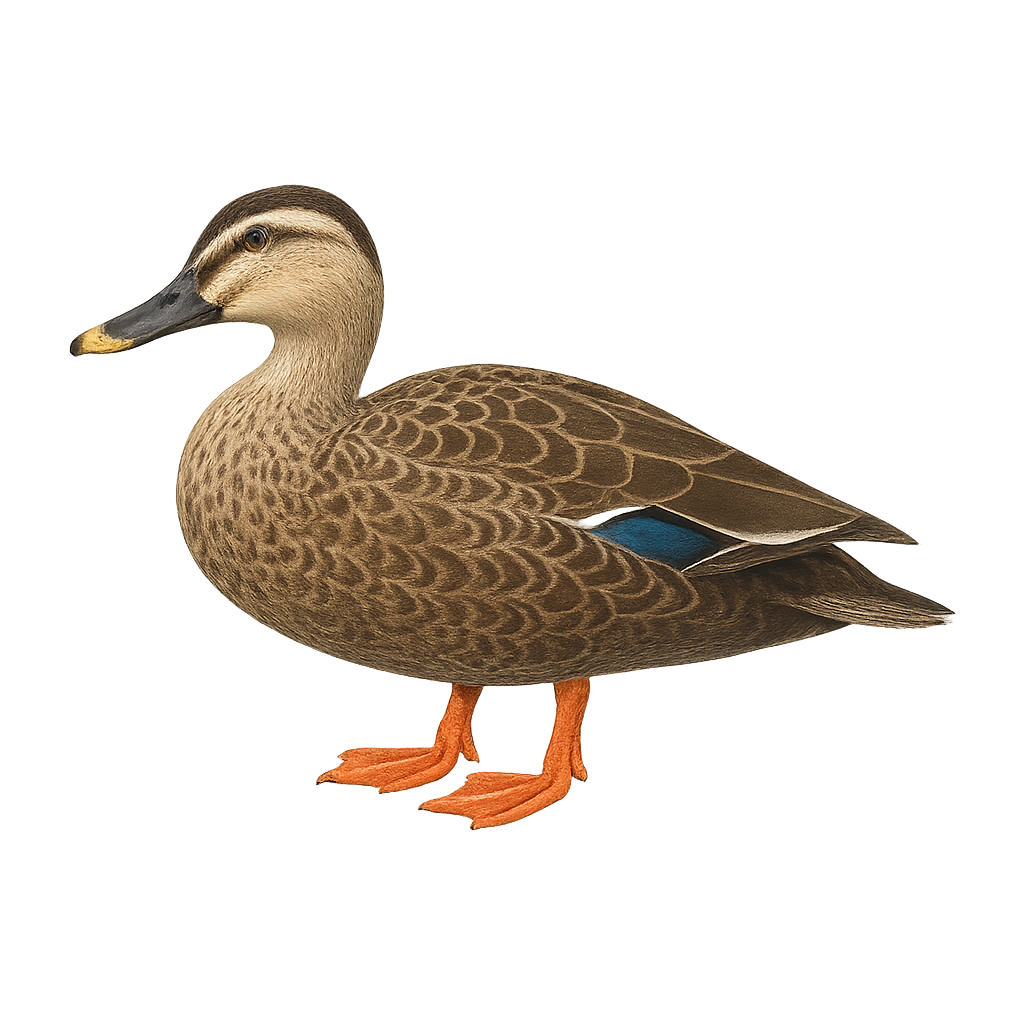
The Eastern Spot-billed Duck, Anas zonorhyncha, is a medium-sized waterfowl native to East Asia. It is easily recognized by its light brown plumage, iridescent wing patches, and distinctive yellow-tipped black bill. Preferring wetlands, lakes, and rivers, it feeds on aquatic plants, insects, and small crustaceans. This sociable duck often mingles with other duck species. Although generally tolerant of human presence, it can become wary if disturbed. Its adaptability to various habitats allows it to thrive in diverse environments, from coastal plains to mountainous regions.
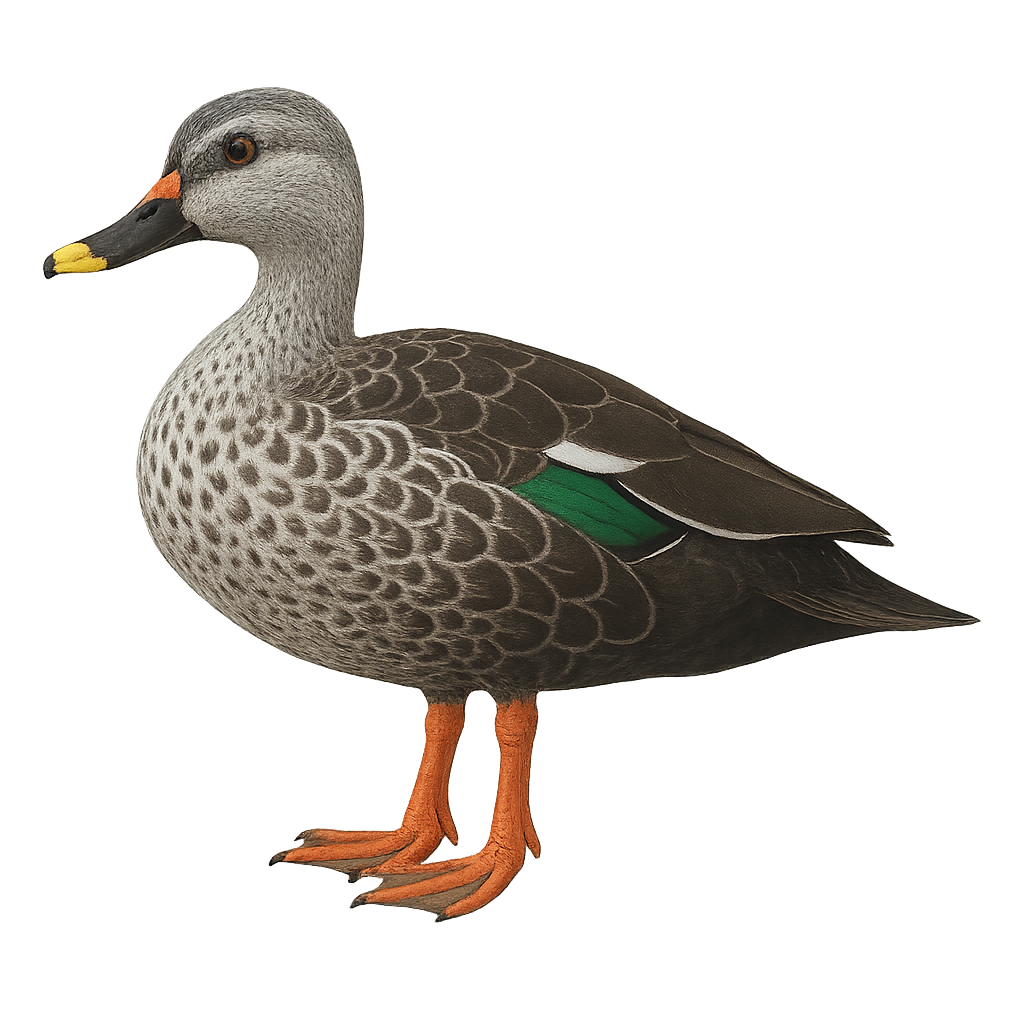
The Indian Spot-billed Duck, Anas poecilorhyncha, is a medium-sized waterfowl known for its distinctive bill marked with yellow and black spots. Its plumage is primarily brown with lighter shades on the belly and darker patterns on the back. The wings feature a green iridescent speculum, visible in flight. This duck primarily inhabits wetlands, lakes, and rivers in South and Southeast Asia. It is often seen in small groups, feeding on aquatic plants, insects, and small invertebrates. Although generally not very shy, it can be suspicious in areas where it is hunted.
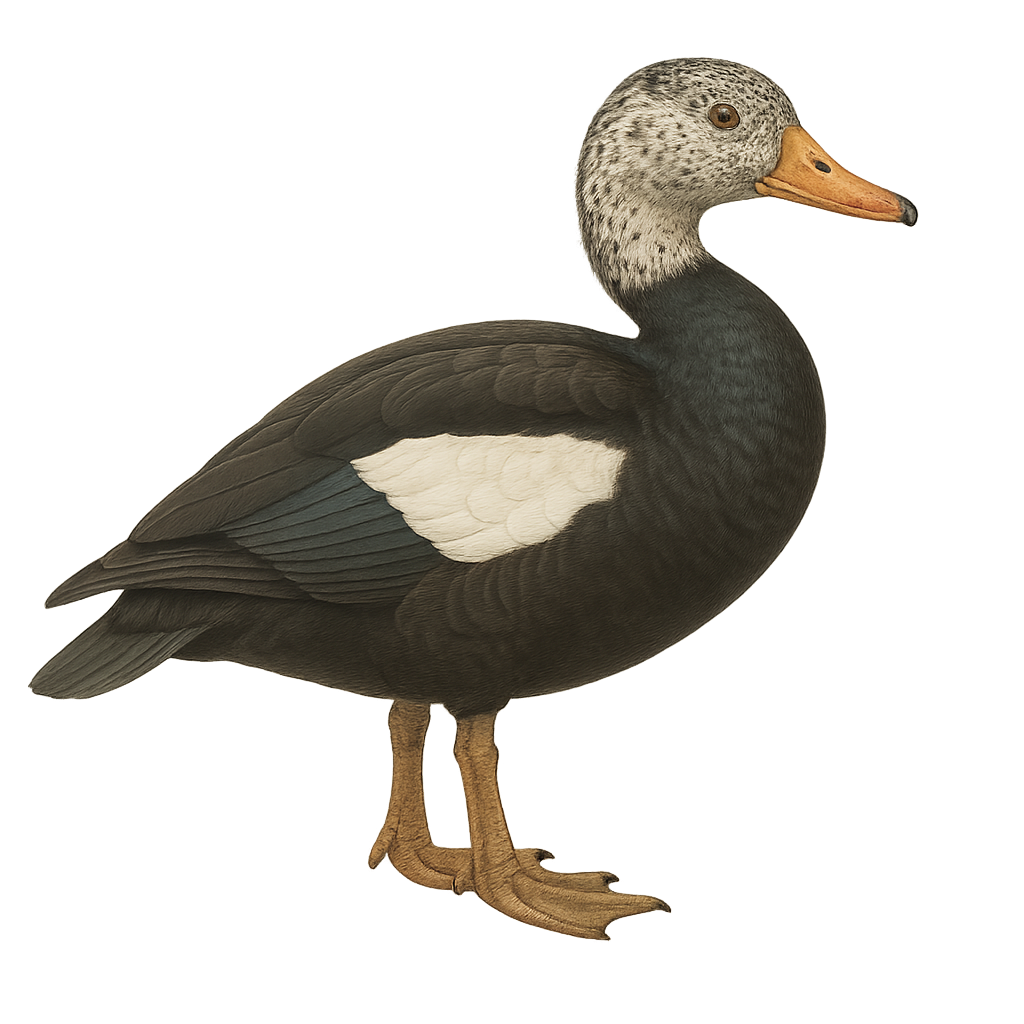
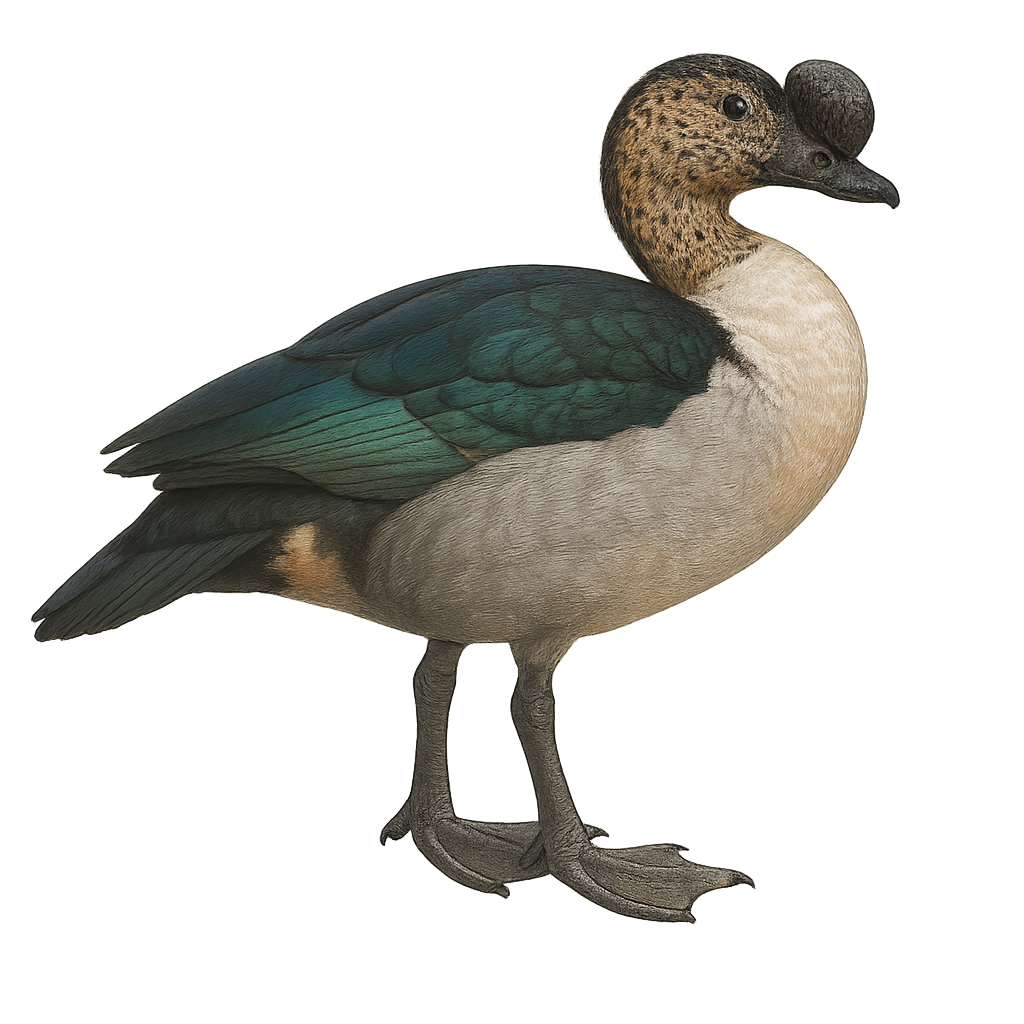
The Comb Duck, Sarkidiornis melanotos, is a medium-sized waterfowl easily identified by the prominent knob on its bill, particularly in males. It features a distinctive black and white plumage with metallic sheen on its wings. This duck primarily inhabits wetlands, lakes, and slow-flowing rivers in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia. Social by nature, it is often seen in small groups. Its diet mainly consists of aquatic plants, seeds, and insects. Although generally tolerant of humans, it can become wary if disturbed. Conservation of its habitat is crucial for its survival, as it is vulnerable to environmental changes.
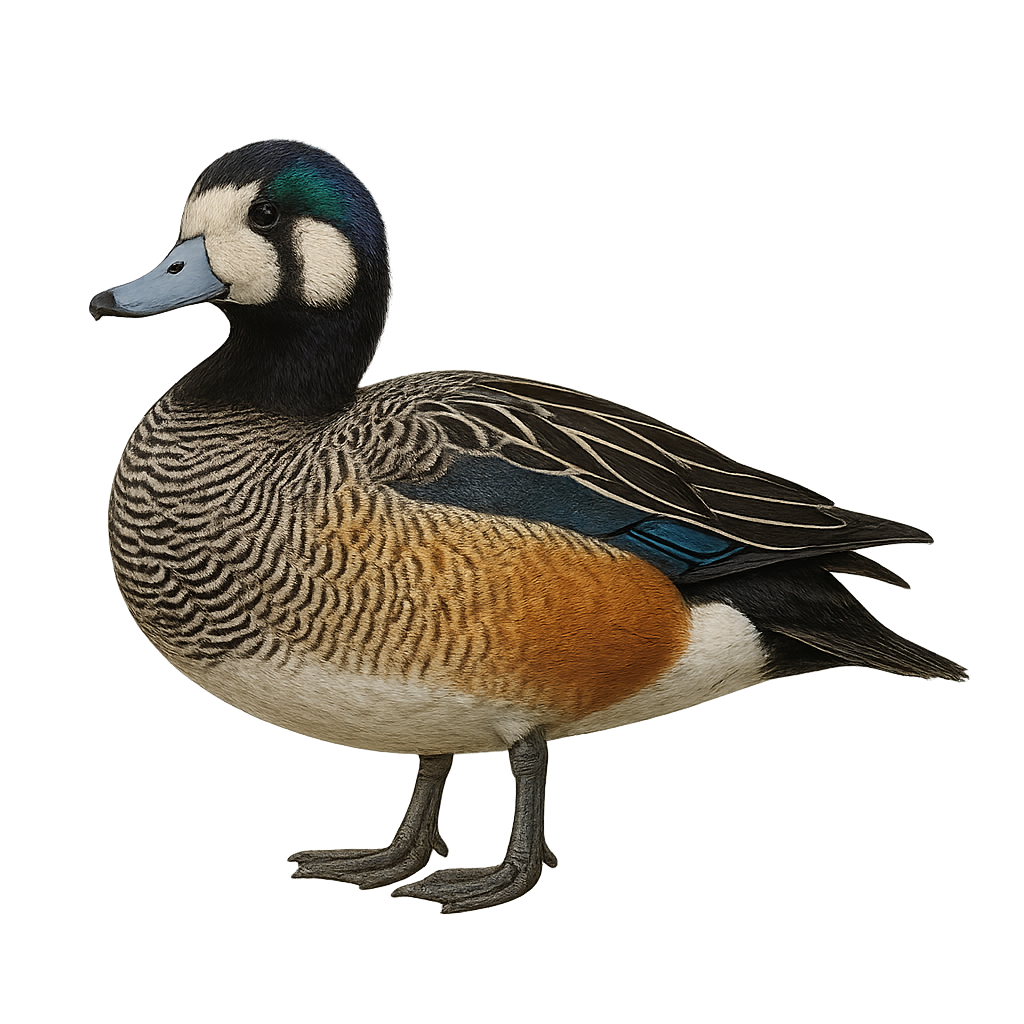
The Chiloe Wigeon, or Anas sibilatrix, is a medium-sized waterfowl known for its distinctive plumage. It features a white head with metallic green bands, a brown back, and a white belly. Its bill is blue-gray with a black tip. Native to South America, it primarily inhabits wetlands, lakes, and rivers. This duck is often seen in small groups and feeds mainly on aquatic plants, insects, and small crustaceans. Although generally not very shy, it can be cautious in the presence of threats. Its breeding season typically extends from spring to summer, and it builds its nest near water, often hidden in dense vegetation.
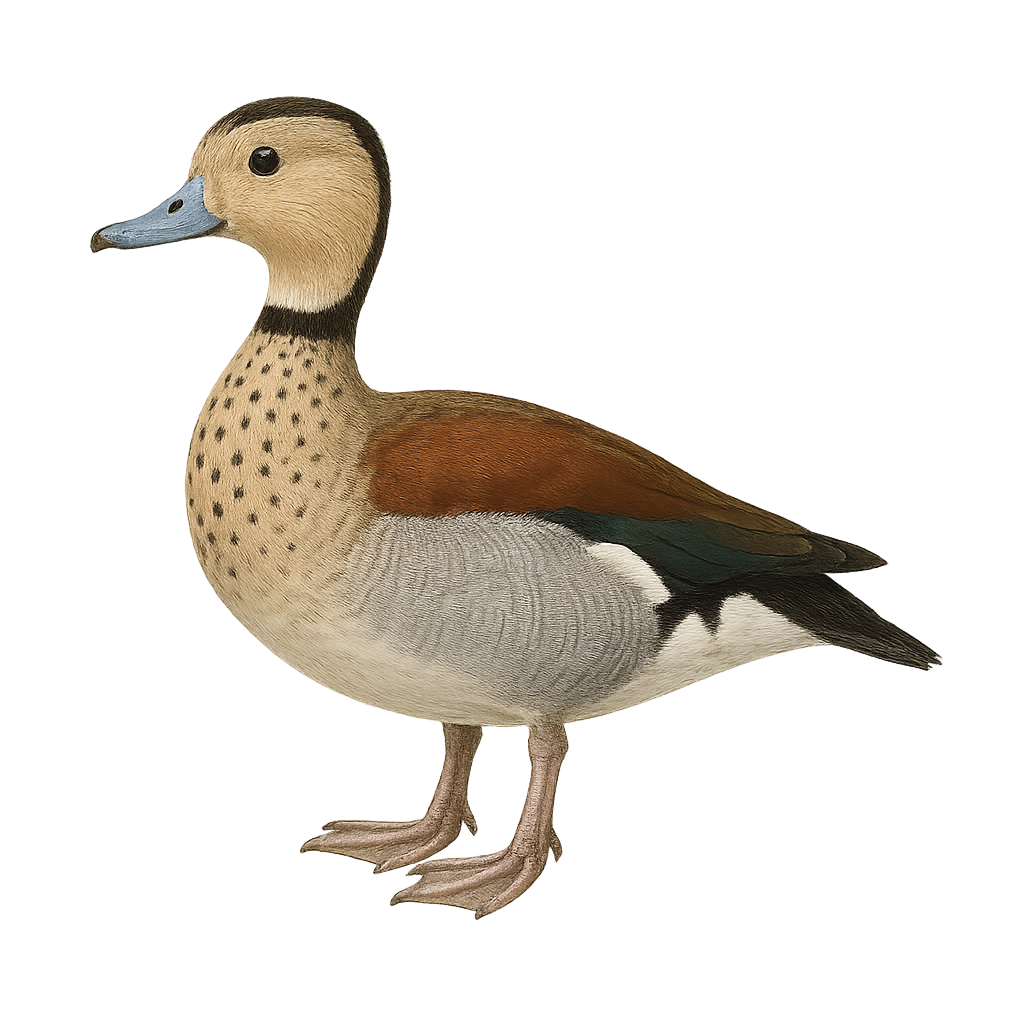
The Ringed Teal, Callonetta leucophrys, is a small, elegant duck native to South America, primarily found in the wetlands of Paraguay, Brazil, and Argentina. It is distinguished by its colorful plumage: males have a reddish-brown head with a distinctive white band around the neck, while females display a more subdued brown-gray plumage with delicate patterns. These ducks prefer wetlands, marshes, and lakes with dense vegetation, where they primarily feed on seeds, aquatic plants, and insects. Although generally discreet, they can be observed in small groups, often in pairs. Their behavior is rather suspicious, but they can become accustomed to human presence in protected areas.
The Australian Wood Duck, Chenonetta jubata, is a waterfowl native to Australia, known for its distinctive plumage and crest of feathers on its head. Males have a dark brown head and grey body, while females display a more subdued plumage with speckled patterns. These ducks prefer wetlands, rivers, and lakes but can also be found in grasslands and urban parks. They primarily feed on aquatic plants, seeds, and insects. Their social behavior is interesting, as they often form family groups. Although generally tolerant of humans, they can become wary if disturbed.
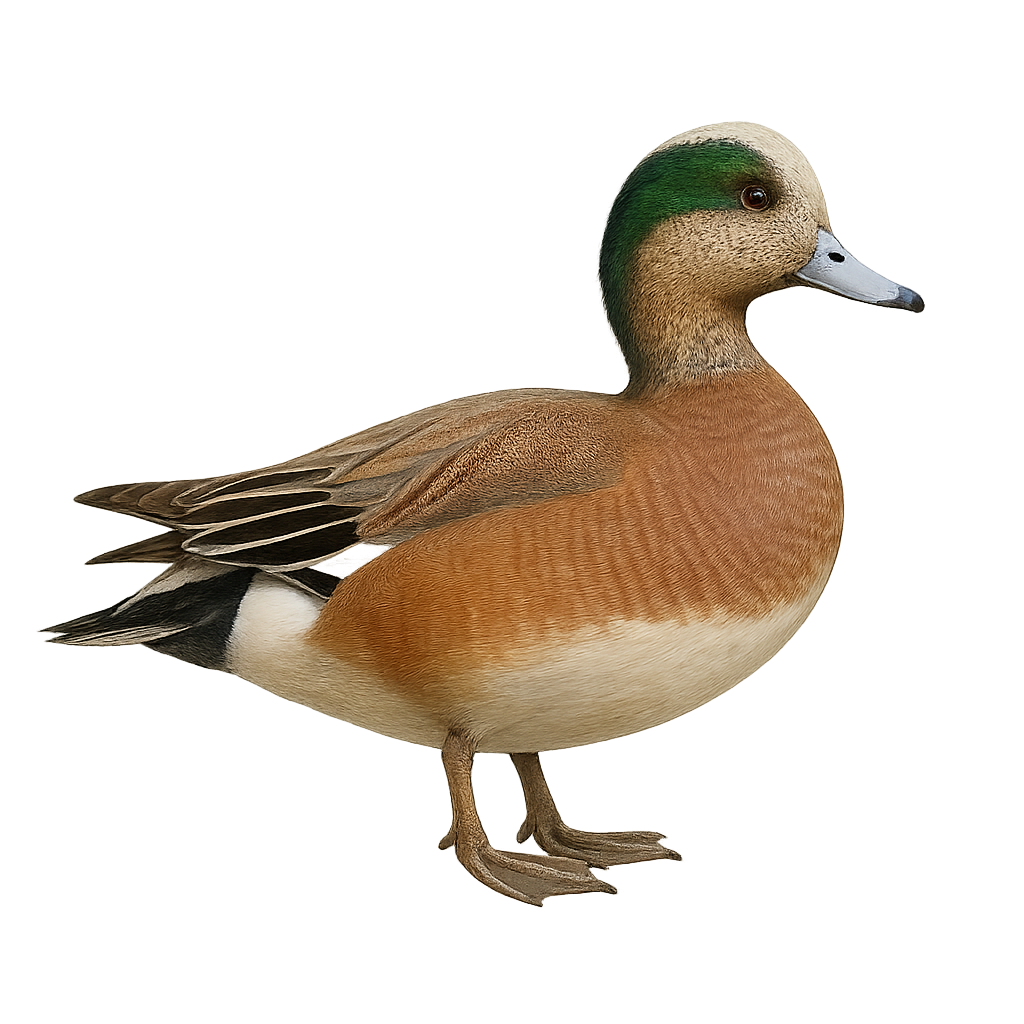
The American Wigeon, Mareca americana, is a dabbling duck species known for its striking plumage and feeding habits. The male features an iridescent green head with a distinctive white forehead stripe, while the female has a more subdued brown-gray plumage. These ducks are commonly found in wetlands, lakes, and marshes, feeding primarily on aquatic plants. They are migratory, spending summers in northern North America and wintering further south. Their flight is fast and direct, often seen in large flocks. Although generally wary, they can become accustomed to human presence in protected areas.
The Spectacled Duck, or Speculanas specularis, is a waterfowl species native to the southern regions of South America, primarily in Chile and Argentina. This duck is characterized by its dark brown plumage with metallic green sheen on the wings and a distinctive white ring around its eyes, giving it its name. It inhabits lakes, rivers, and marshes, often at high altitudes. Although relatively tolerant, it remains cautious around humans. Its population is stable, but it is sensitive to habitat disturbances. The Spectacled Duck is an excellent diver, feeding mainly on aquatic plants and invertebrates.
The Pacific Black Duck, or Anas superciliosa, is a dabbling duck species found mainly in Australia, New Zealand, and some Pacific islands. It is easily recognizable by its dark brown plumage with lighter patterns and a distinctive eyebrow stripe. This duck is often seen in wetlands, lakes, and rivers, where it primarily feeds on aquatic plants, insects, and small invertebrates. Although generally not very shy, it can become wary in areas where it is hunted. The Pacific Black Duck is an excellent swimmer and diver, using these skills to evade predators and forage for food.
The Patagonian Steamer Duck, Tachyeres patachonicus, is a flightless waterbird native to the southern coasts of South America, particularly Patagonia. It is easily identified by its greyish plumage and reduced wings, which it uses to paddle swiftly across the water. Often seen in small groups, this duck feeds on mollusks and crustaceans found in shallow waters. While generally discreet, it can become territorial during the breeding season. Males and females look alike, though males are slightly larger.
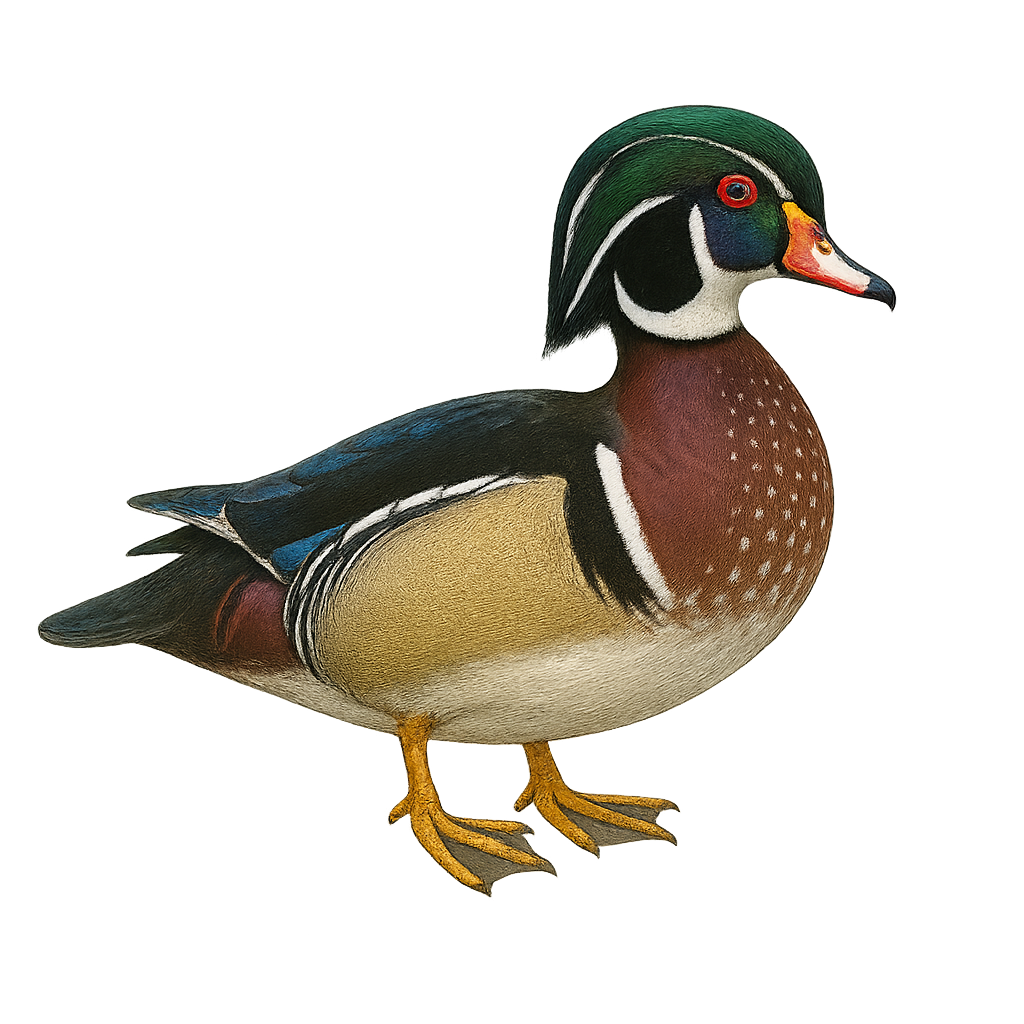
The Wood Duck, Aix sponsa, is a striking waterfowl known for its vibrant plumage and unique habits. The male displays bright colors with an iridescent green head, red eyes, and distinctive white patterns, while the female has a more subdued brown-gray plumage with white eye markings. Found primarily in North America, this duck frequents wooded areas near lakes, rivers, and swamps. It is known for its ability to nest in trees, often using natural cavities or artificial nest boxes. The Wood Duck is an excellent swimmer and diver, feeding on aquatic plants, insects, and small fish.
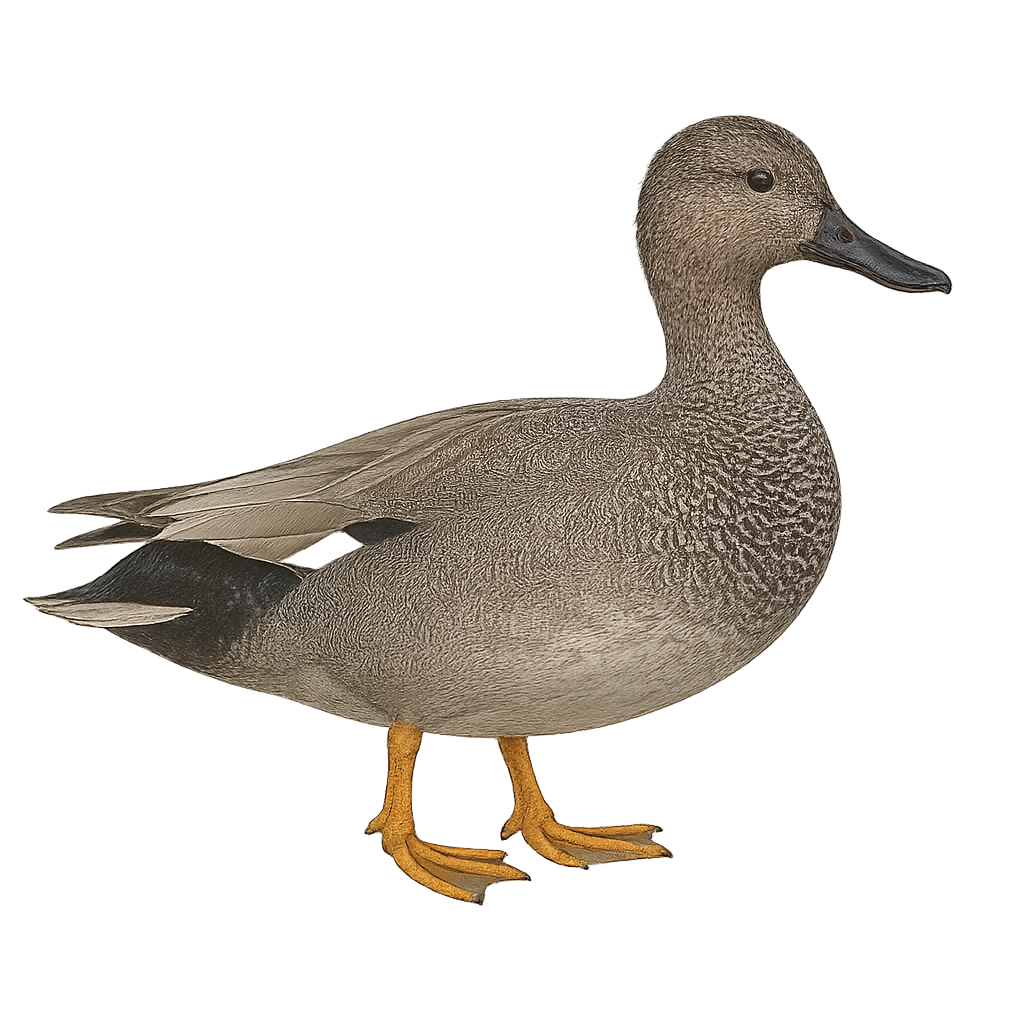
The Gadwall is a medium-sized dabbling duck, measuring between 46 and 56 cm in length with a wingspan of 78 to 90 cm. The male has finely patterned gray plumage with a distinctive white wing patch visible in flight, a black rump, and a dark bill. The female is mottled brown with an orange-edged dark bill. This species inhabits wetlands such as marshes, ponds, lakes, and flooded meadows rich in aquatic vegetation. It feeds mainly on leaves, stems, and seeds of aquatic plants, but also consumes aquatic invertebrates, especially during the breeding season. The Gadwall is a partial migrant, breeding in Eurasia and North America, and wintering in more southern regions. Although listed as Least Concern by the IUCN, it is sensitive to wetland degradation and pollution.
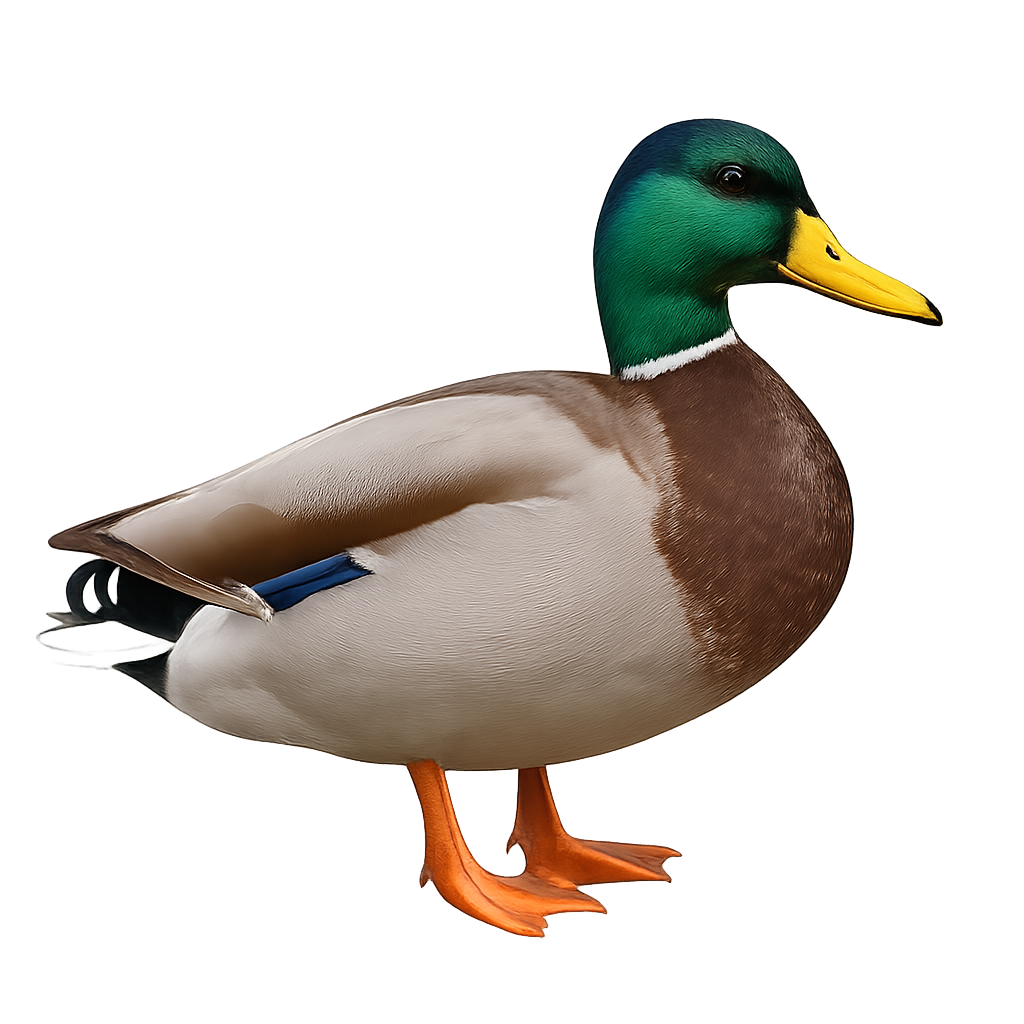
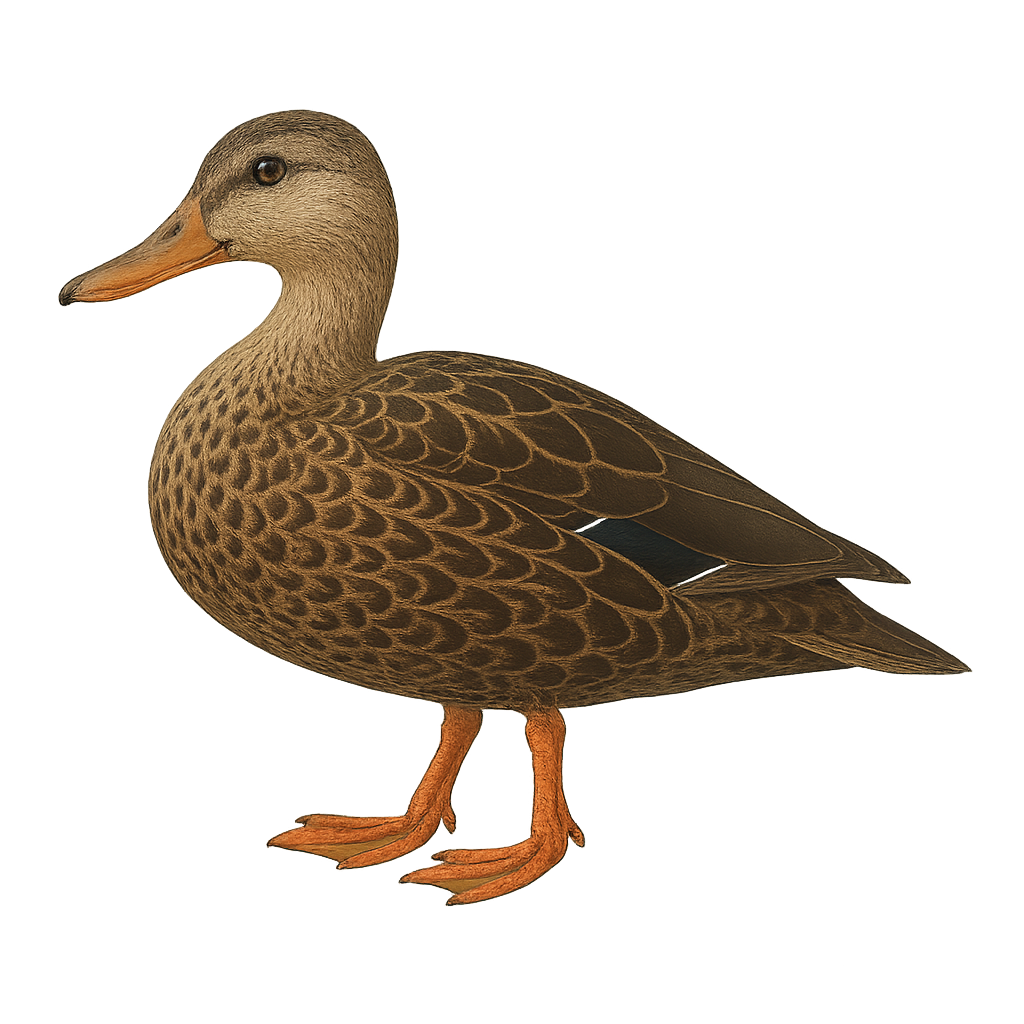
Anas platyrhynchos is a medium-sized duck species, measuring between 50 and 65 cm in length, with a wingspan of 81 to 98 cm. The male is distinguished by its iridescent green head, white neck, and brown-roux body, while the female is brown-speckled, aiding in camouflage. They primarily inhabit freshwater wetlands such as ponds, lakes, slow rivers, and marshes. They feed on a wide variety of plant and animal matter, including seeds, roots, insects, and small fish. Reproduction occurs in spring, with the female building a ground nest near water, where she typically lays 8 to 13 eggs. Incubation lasts about 27 to 28 days, and ducklings are capable of swimming and feeding themselves shortly after hatching. A very widespread species, it is classified as Least Concern by the IUCN.
The Hartlaub's Duck, or Pteronetta hartlaubii, is a little-known species of duck endemic to the tropical rainforests of Central Africa. This medium-sized duck has dark brown plumage with metallic sheen on its wings and a lighter head. It is often seen in small groups, moving quietly along rivers and swamps. Its preferred habitat includes dense forests and wetlands, where it feeds mainly on seeds, small invertebrates, and aquatic plants. Although generally discreet, it can be curious and approach silent observers. Habitat conservation is crucial for its survival, as deforestation poses a significant threat.
The Meller's Duck, Anas melleri, is an endemic species of Madagascar, often mistaken for the mallard due to its resemblance. This medium-sized duck has brown plumage with lighter shades on the belly and greenish reflections on the wings. It primarily inhabits wetlands, lakes, and rivers on the island. Its population is declining due to habitat loss and hunting. The Meller's Duck is monogamous and typically breeds during the rainy season. It plays a crucial role in the local ecosystem by aiding in seed dispersal and controlling aquatic insect populations.
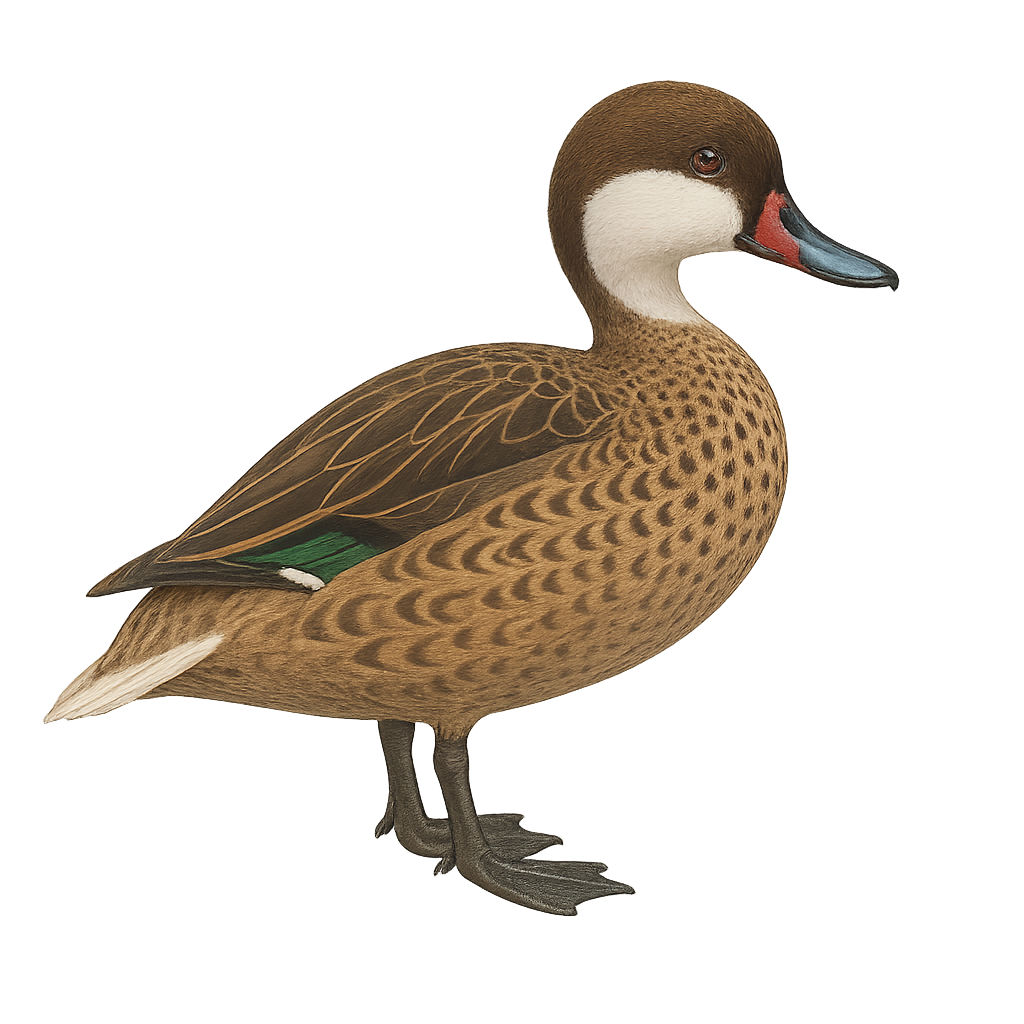
The White-cheeked Pintail, or Anas bahamensis, is a medium-sized duck known for its distinctive white head with a red spot on the bill and speckled brown plumage. It inhabits wetlands in the Caribbean, South America, and the Galápagos. Preferring shallow waters, it feeds on aquatic plants, insects, and small crustaceans. Often seen in small groups or pairs, this duck has a fast, direct flight but spends much time swimming and dabbling. Its population is stable, though habitat loss and hunting pose threats.
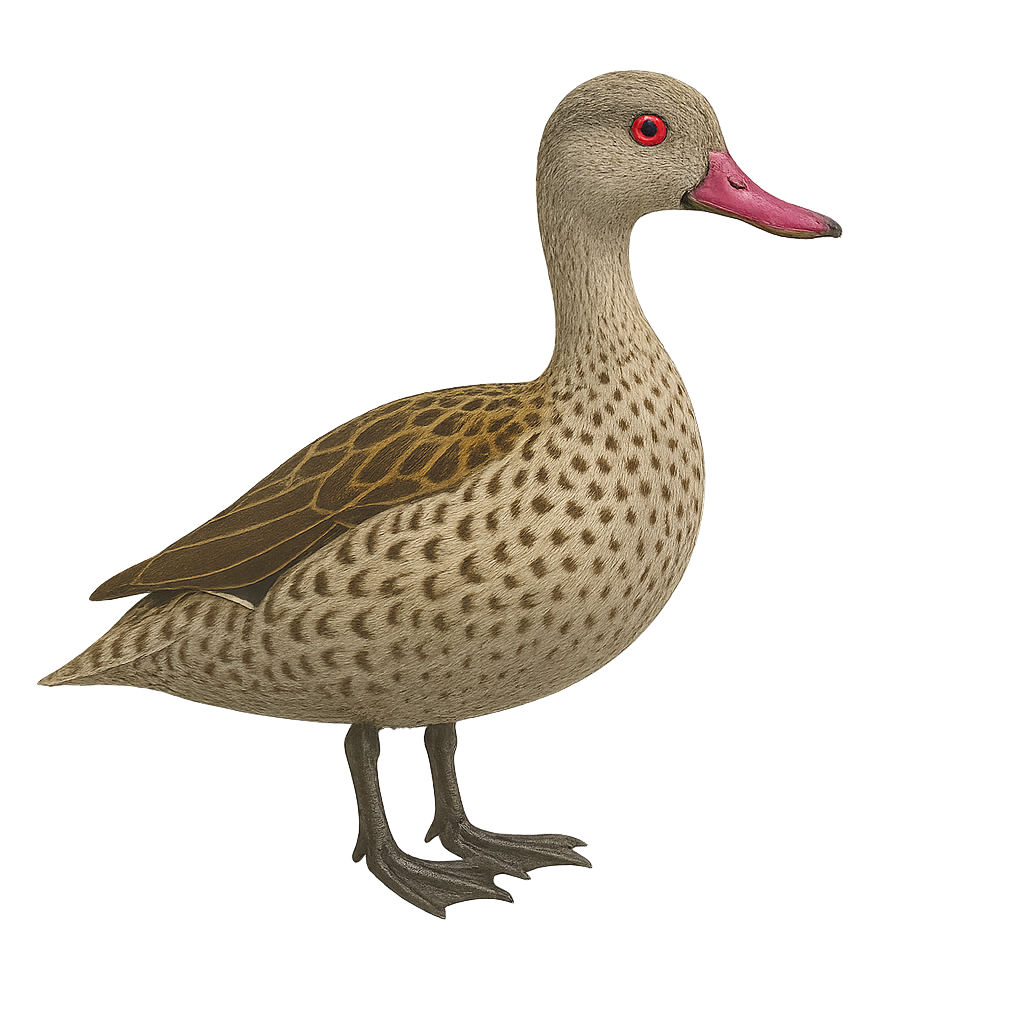
The Cape Teal, Anas capensis, is a small dabbling duck native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is easily identifiable by its bright red bill and pale grey plumage speckled with dark spots. Males and females are similar, though females are slightly smaller. This duck prefers aquatic habitats such as lakes, marshes, and slow-moving rivers. It primarily feeds on aquatic plants, seeds, and insects. Although generally discreet, it can form large flocks outside the breeding season. Its population is stable, but it is sometimes threatened by habitat loss and water pollution.
The Mexican Duck, Anas diazi, is a dabbling duck species native to the southwestern United States and Mexico. It closely resembles the Mallard but is distinguished by its more subdued and uniform plumage, lacking the Mallard's characteristic green head. Both males and females look alike, which is uncommon among ducks. They favor aquatic habitats such as lakes, ponds, and slow-moving rivers. Their diet is varied, consisting mainly of aquatic plants, insects, and small invertebrates. Although their population is stable, habitat loss and hybridization with other duck species, particularly the Mallard, pose potential threats.
The Crested Duck, or Lophonetta specularioides, is a medium-sized Andean duck, recognizable by its subtle crest and brown-gray plumage with iridescent wing highlights. It inhabits high-altitude lakes, marshes, and slow rivers, mainly in the Andes and Patagonia. Well adapted to cold, windy environments, it is omnivorous, feeding on aquatic vegetation, invertebrates, and occasionally small fish. This duck is gregarious yet discreet, often seen in small groups. Its population is considered stable overall.
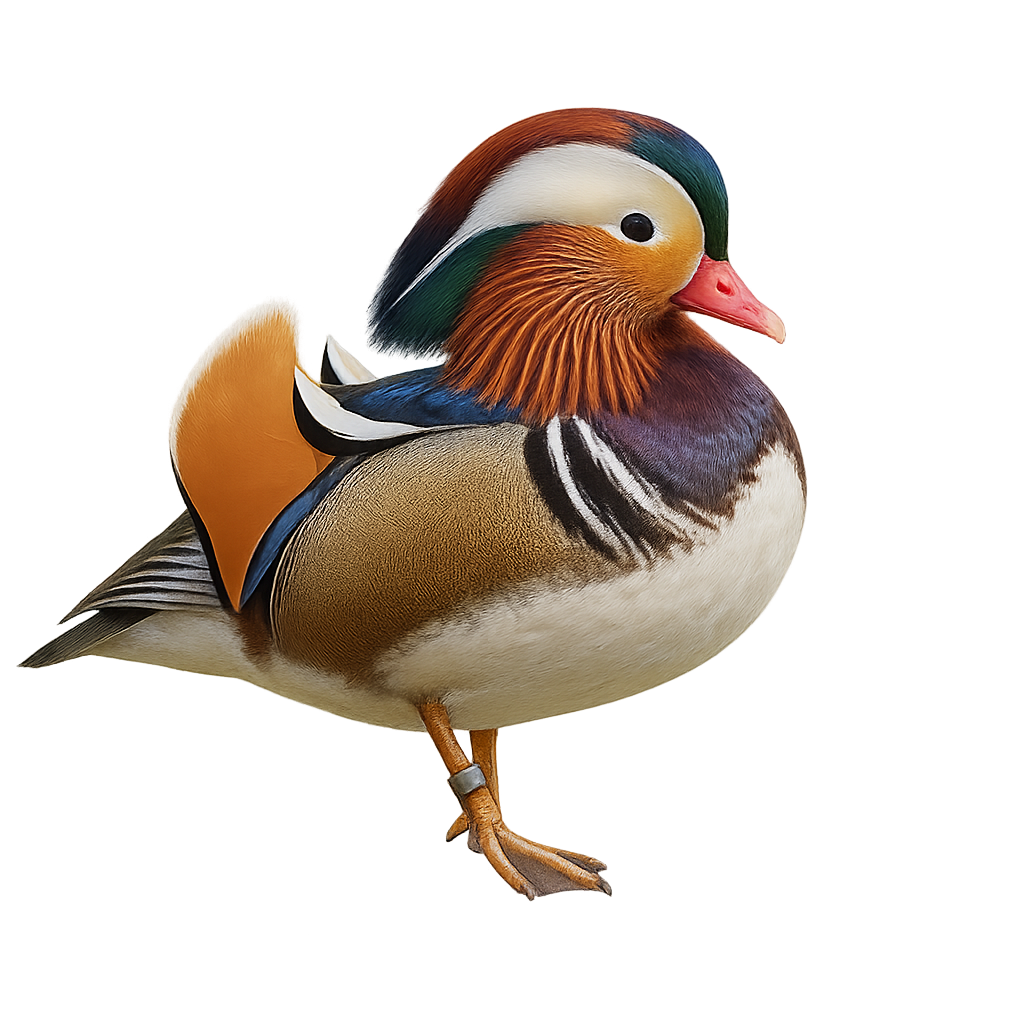
The Mandarin Duck is a spectacular waterfowl, easily recognizable by its vibrant and colorful plumage, particularly in the male. The male displays an impressive mix of bright colors, including orange, blue, and green, with a distinctive crest on the head and feathers on the sides of the neck that resemble scales. The female, more subdued, has brown plumage with subtle white accents around the eyes and bill.
Native to East Asia, the Mandarin Duck is now widely distributed in Europe and North America, often seen in parks and gardens around bodies of water. This duck prefers calm waters in lakes, ponds, and rivers, where it feeds mainly on seeds, fruits, insects, and small crustaceans. Although the Mandarin Duck is not considered endangered, its natural habitat can be threatened by pollution and the loss of wetland areas.