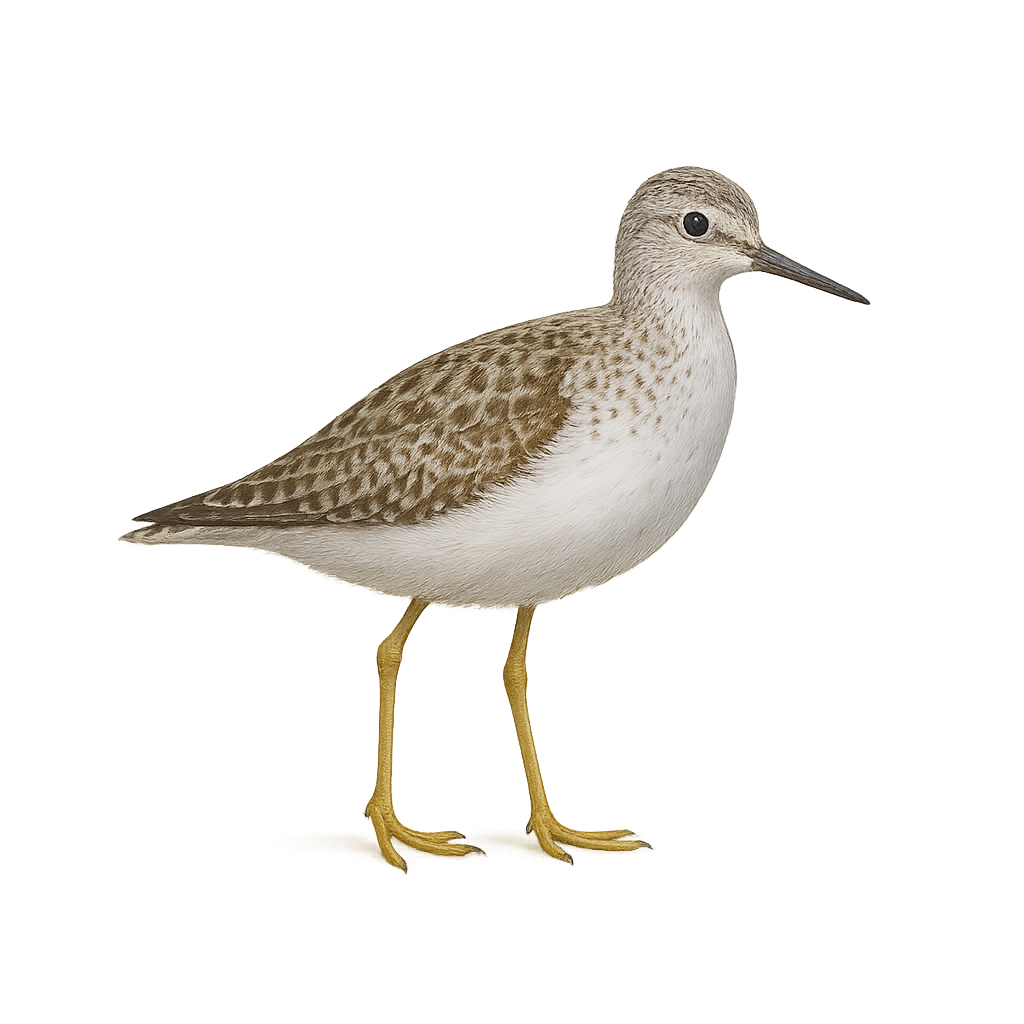
The Marsh Sandpiper is a medium-sized wader, easily identifiable by its plumage marked with gray-green and white, with darker patterns on the wings and head. During the breeding season, it displays brighter colors, with shades of vibrant green and distinct markings. Outside the breeding season, its plumage is more subdued, generally gray-brown and more muted. This wader is primarily observed in shallow wetlands such as marshes, lagoons, and estuaries, where it feeds on aquatic invertebrates, small fish, and occasionally worms.
The Marsh Sandpiper is a migratory bird that travels relatively short distances between its breeding grounds in Eastern Europe and its wintering sites in North Africa and Asia. While its population remains stable in some regions, it is threatened by the loss of its wetland habitats and water pollution. The species benefits from protections in areas where it is found, but it remains vulnerable in certain regions due to urbanization and intensive agriculture.
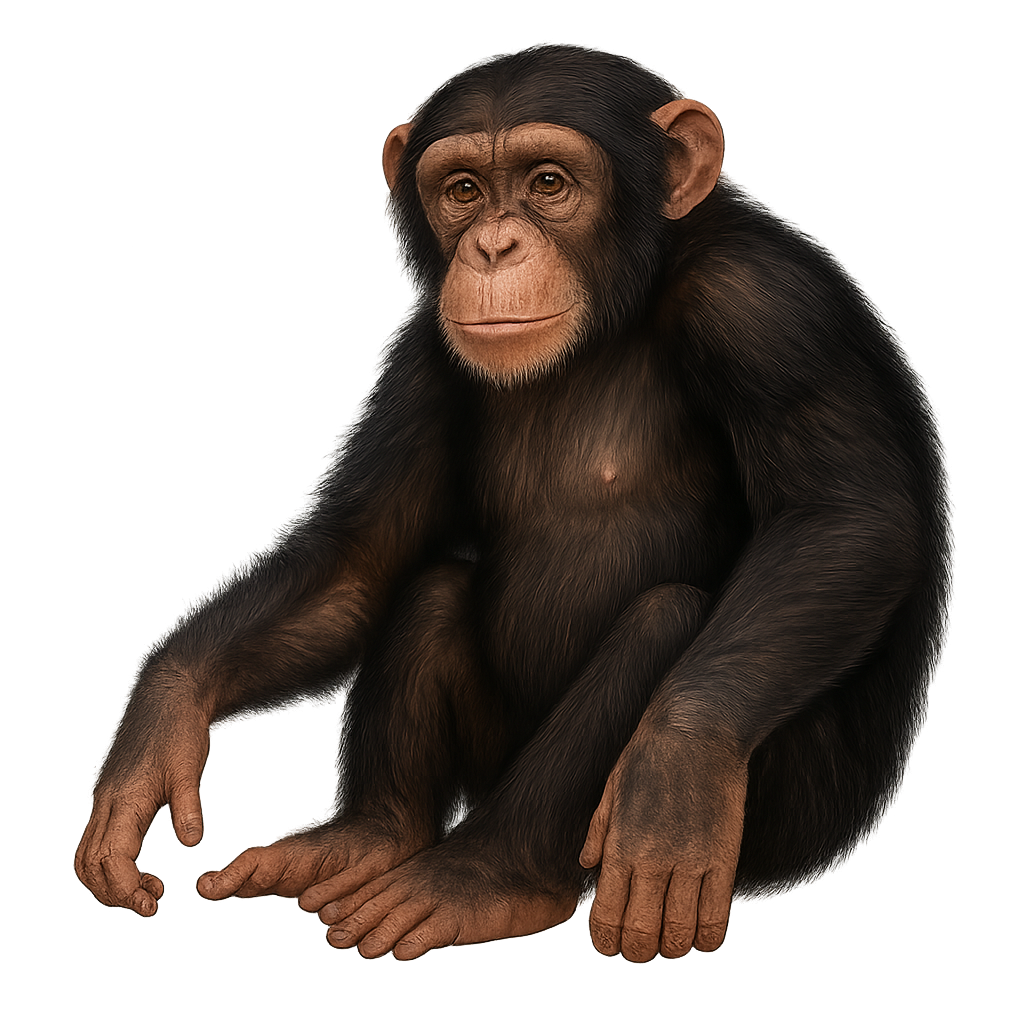

The Chimpanzee is one of humans' closest relatives, sharing about 98% of its DNA with humans. This large primate is easily recognizable by its expressive face, dark or brown skin, and sharp eyes. It has a powerful body, although it is smaller and less robust than other large primates like the gorilla. The Chimpanzee primarily inhabits tropical forests and savannas in West and Central Africa, where it forms complex social groups, called communities, which can include several dozen individuals.
An omnivore, the Chimpanzee feeds on a wide range of foods, including fruits, leaves, insects, and sometimes meat. It is also known for its use of tools, such as sticks to extract termites or stones to crack nuts. This primate has exceptional intelligence, capable of solving complex problems, communicating in sophisticated ways, and adopting cultural behaviors. However, it is threatened by deforestation, poaching, and habitat loss, leading to a decline in its wild populations. The chimpanzee is classified as an endangered species.
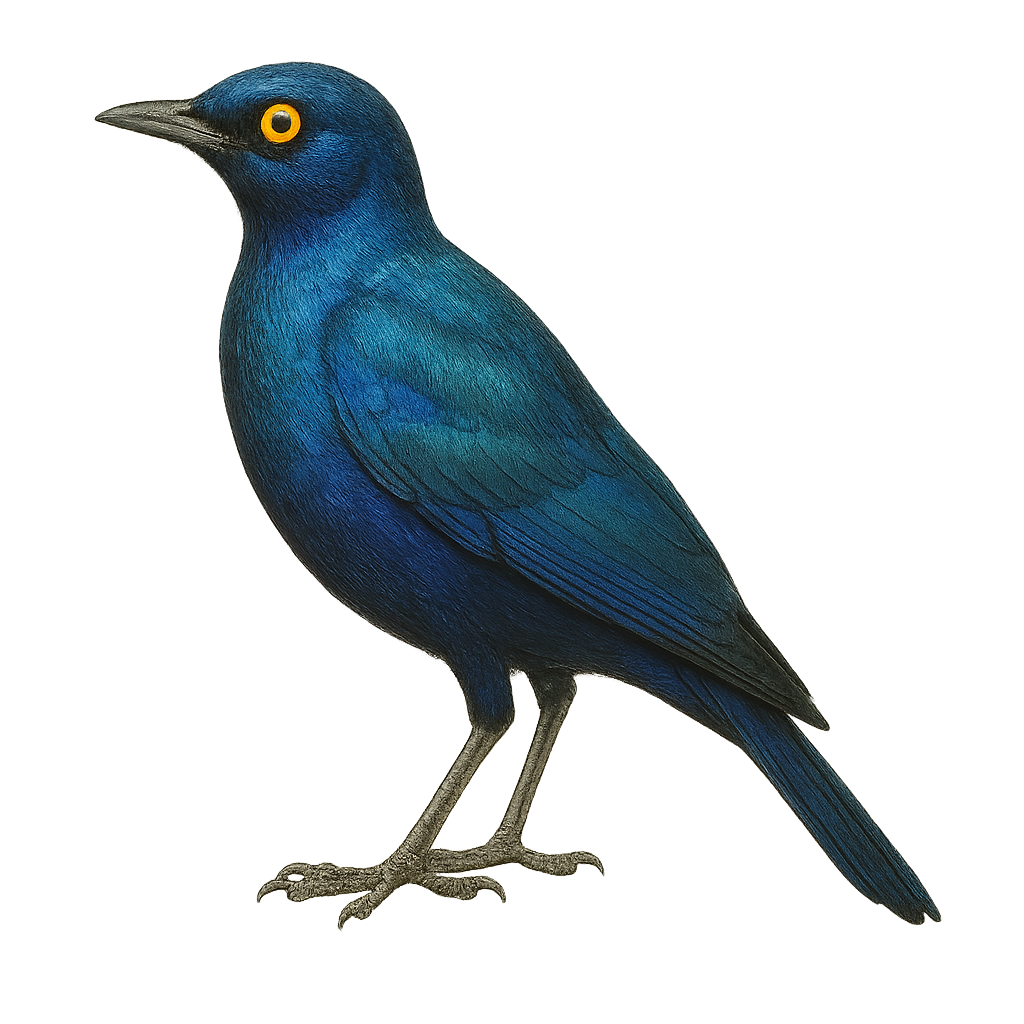
The Cape Starling, or Lamprotornis nitens, is a bird with dazzling plumage, mainly metallic blue-green, with iridescent reflections that catch the sunlight. Its yellow eyes contrast with its plumage, adding a touch of mystery to its appearance. This bird is often seen in small groups, feeding on fruits, insects, and nectar. It is known for its melodious and varied song, which it uses to communicate with its peers. It is mainly found in savannas, open forests, and agricultural areas of sub-Saharan Africa. Although generally tolerant of humans, it can be suspicious if threatened.
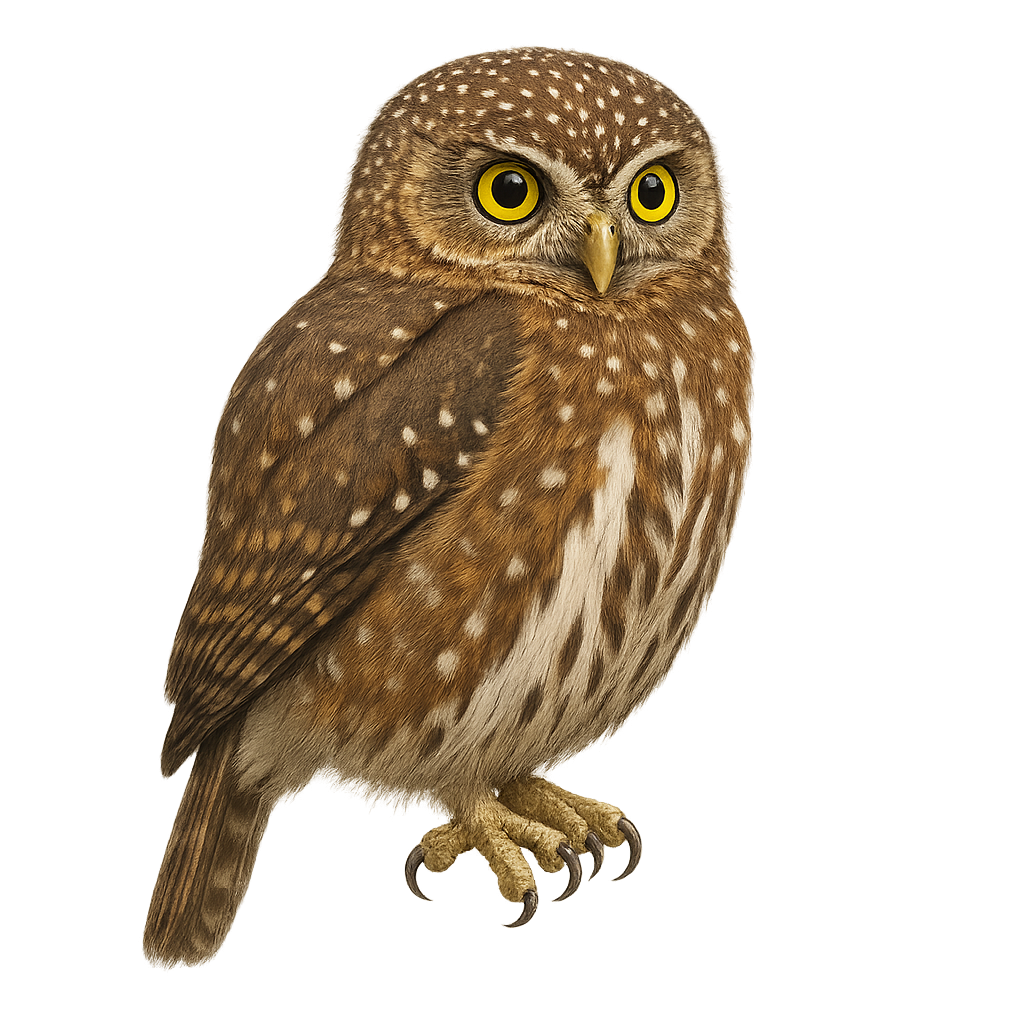
The Costa Rican Pygmy Owl, or Glaucidium costaricanum, is a small nocturnal bird of prey found mainly in the mountainous forests of Costa Rica and Panama. It measures about 15 cm in length and is characterized by its brown plumage speckled with white, piercing yellow eyes, and round head. This species is known for its ability to hunt small mammals, birds, and insects, thanks to its exceptional night vision and silent flight. Although primarily nocturnal, it can sometimes be seen at dawn or dusk. The Costa Rican Pygmy Owl is a territorial, often solitary bird that uses tree cavities for nesting.
The Chattering Cisticola is a small passerine bird belonging to the Cisticolidae family. It is primarily found in the humid regions of Central and West Africa. This small bird is characterized by its brownish plumage and relatively short tail. Chattering Cisticolas are often identified by their distinctive song, a rapid and repetitive chirping. They mainly feed on insects and small invertebrates, which they find in tall grasses and bushes. Their behavior is generally suspicious, making them difficult to observe closely. They build ball-shaped nests, often well hidden in dense vegetation.
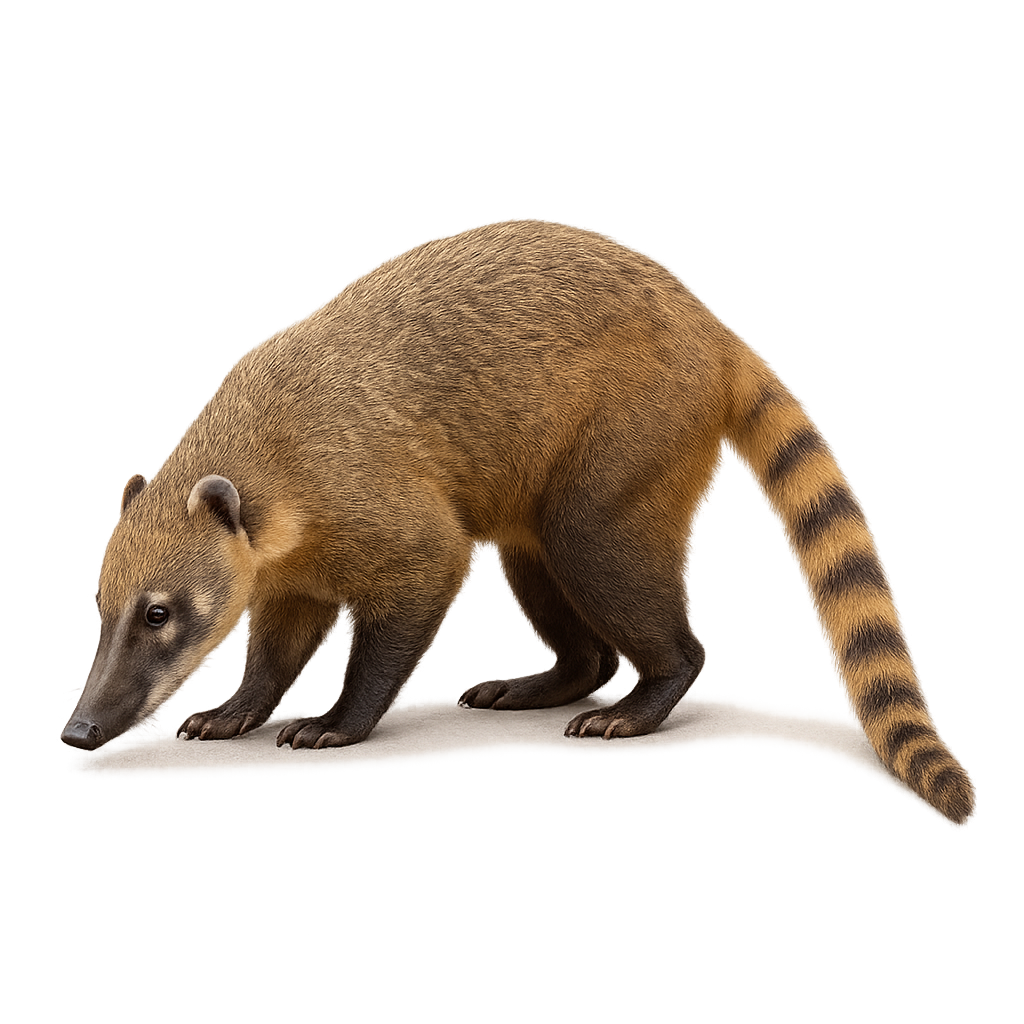
The Coati roux is a mammal belonging to the raccoon family, easily recognized by its long ringed tail and elongated snout shaped like a trunk. Its fur is typically light brown to reddish-brown, with darker markings on the face and back. This small carnivore is known for its great agility, especially in trees where it moves with ease in search of food. It primarily inhabits tropical and subtropical forests in Central and South America.
The Coati roux is omnivorous and feeds on a wide variety of foods, including fruits, insects, small vertebrates, and eggs. It is often seen in family groups, especially females, while adult males tend to live alone. Although the Coati roux is a relatively adaptable animal, it is threatened by deforestation, hunting, and habitat loss. It plays an important role in seed dispersal and regulating populations of insects and small animals.
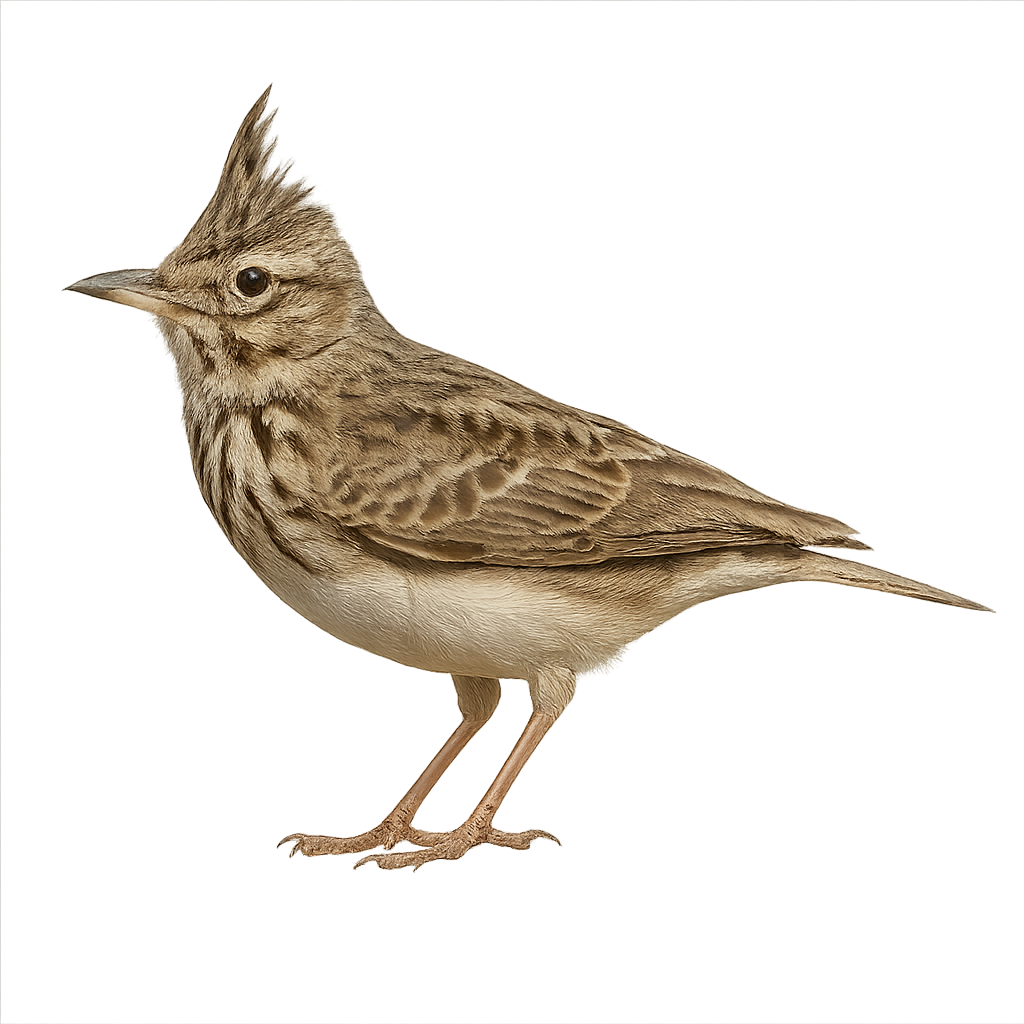
The crested lark is a small passerine, 16–18 cm long, with streaked brown plumage and an erectile crest. It inhabits open farmland, steppes, and embankments, often near human settlements across Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia. It feeds mainly on insects and seeds, walking and hopping on the ground. During the breeding season, the male performs a song flight over its territory, uttering a sharp trill while fluttering its wings before landing to attract the female.
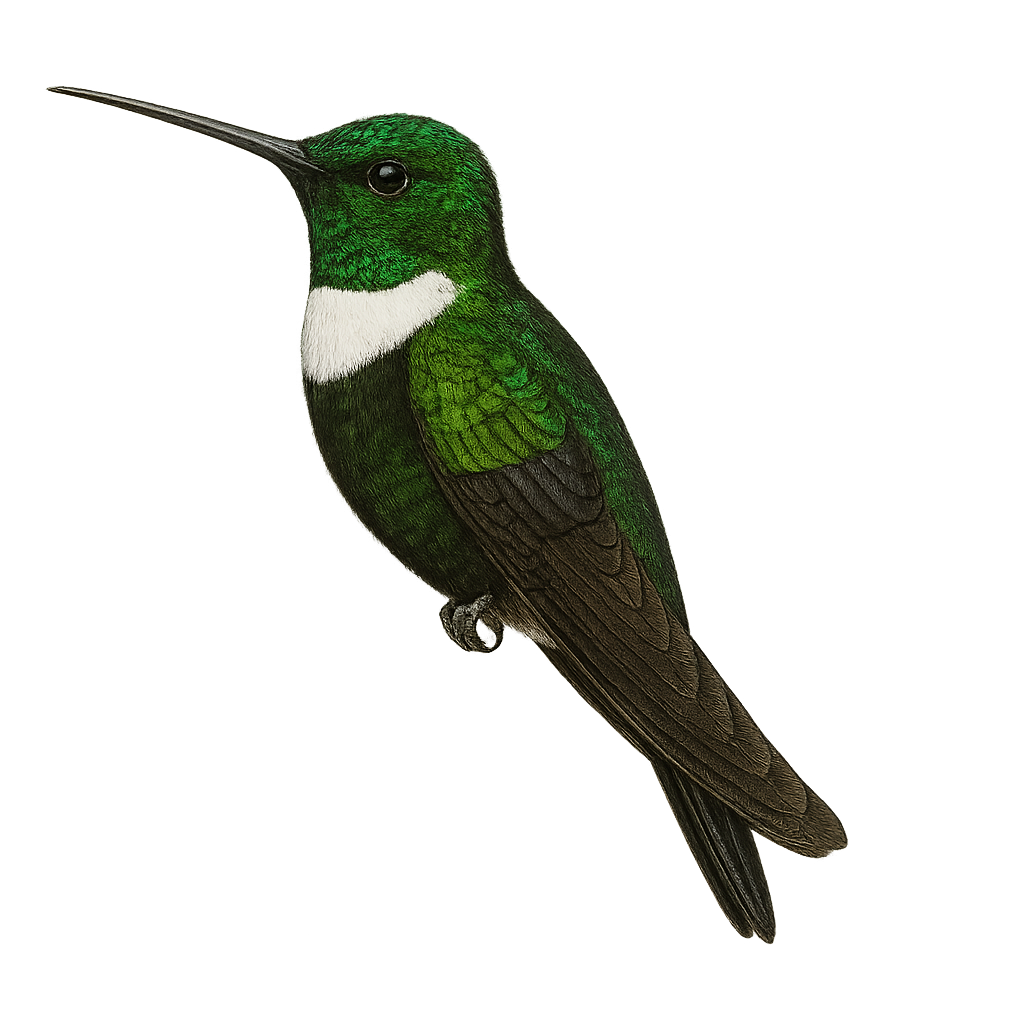
The Collared Inca, or Coeligena torquata, is a captivating bird of the Andes, easily identifiable by its glossy black plumage and distinctive white collar. It inhabits humid forests and forest edges, where it primarily feeds on nectar. Its swift and agile flight allows it to move effortlessly between flowers. This hummingbird plays a crucial role in the pollination of Andean plants. Although generally solitary, it can be seen in small groups during abundant flowering. Its adaptability to various habitats makes it a resilient species, although deforestation may threaten local populations.
The Coppery-headed Emerald is a small hummingbird endemic to Costa Rica, measuring about 8 cm. The male is notable for his metallic coppery crown, bright green throat, and white underparts. The female is duller in color, with a bronzy head and pale throat. It inhabits humid mid-elevation forests, woodland edges, and flower-rich gardens. This hummingbird feeds on nectar from various flowers and catches small insects. It is threatened by deforestation, as its range is very restricted.
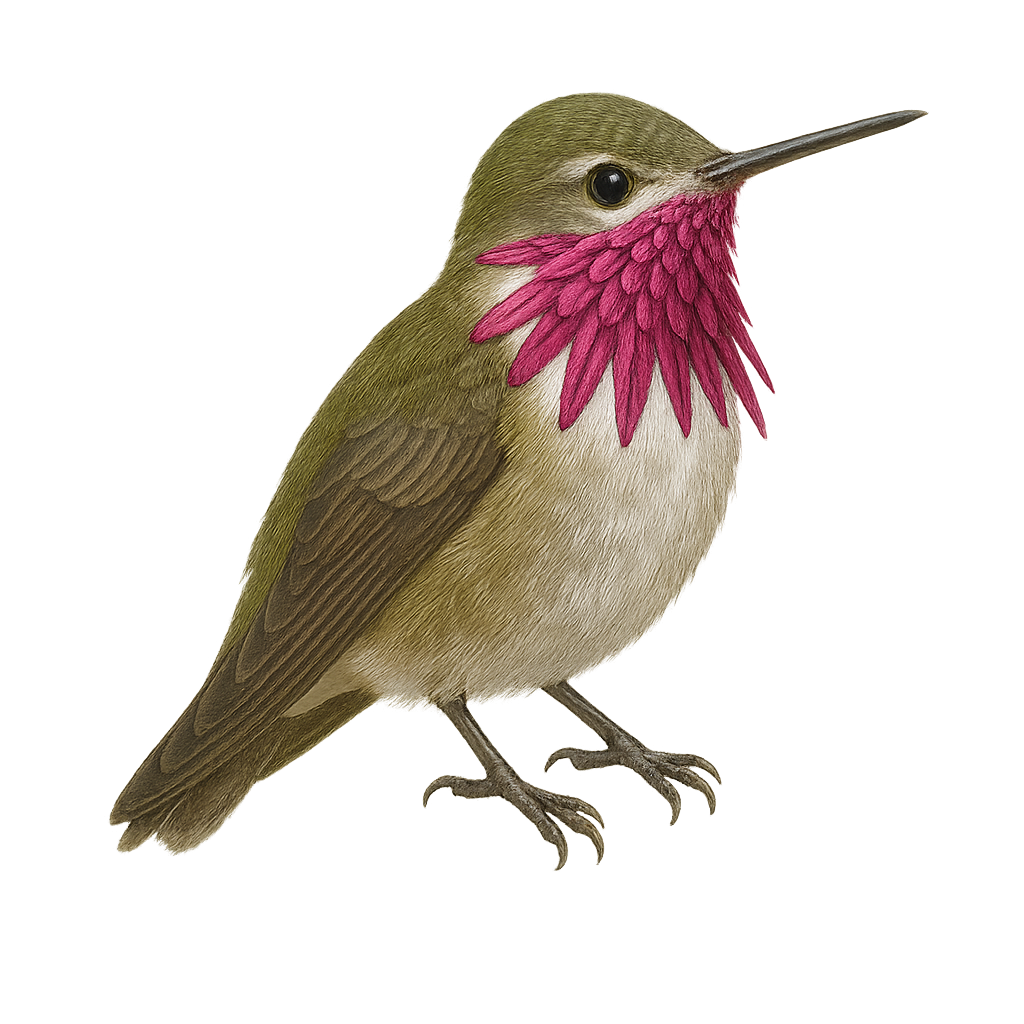
The Calliope Hummingbird is the smallest bird in North America, measuring about 7 to 10 cm in length. It is easily recognizable by the iridescent purple throat of the male, while the female has a white throat with green streaks. This hummingbird primarily inhabits coniferous forests, alpine meadows, and shrublands. It feeds mainly on nectar but also consumes insects to supplement its diet. During the breeding season, the male performs spectacular aerial displays to attract the female. The Calliope Hummingbird migrates to the southern United States and Mexico for the winter.
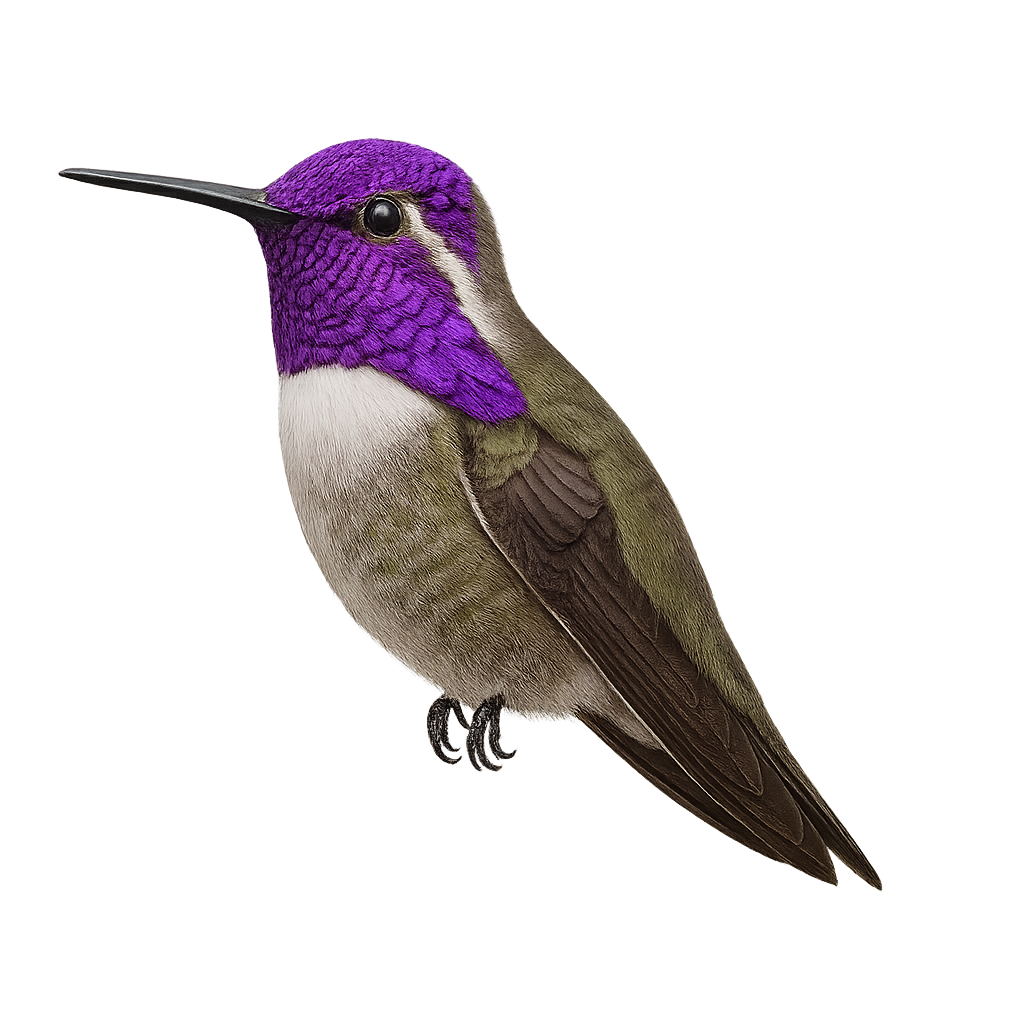
The Costa's Hummingbird, or Calypte costae, is a small, captivating bird known for its vibrant plumage and ability to fly backward. This hummingbird measures about 8 to 9 cm in length and weighs between 2 and 3 grams. Males display a striking violet head and throat, contrasting with their metallic green body. Females are more subdued with shades of green and gray. It is primarily found in the arid and semi-arid regions of the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. It feeds mainly on nectar but also consumes small insects. Its rapid and agile flight allows it to move easily between flowers.
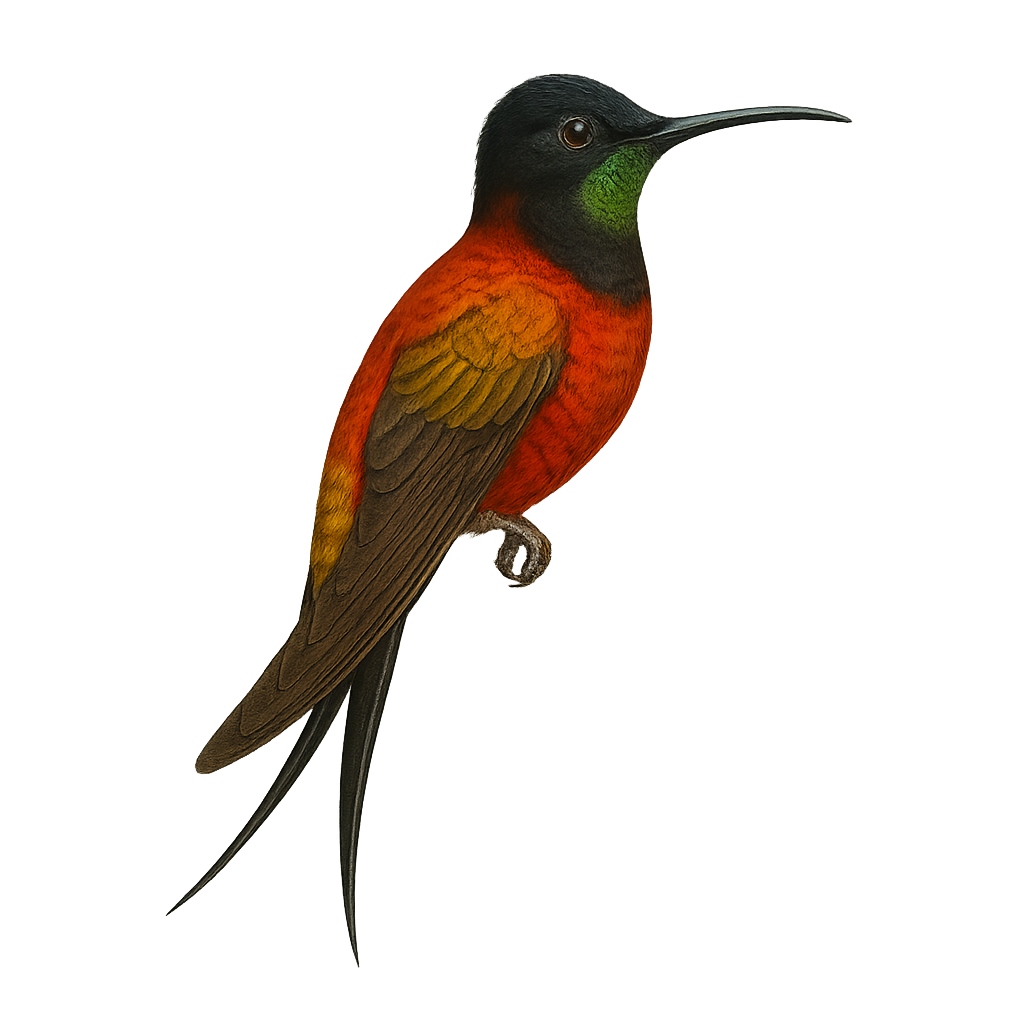
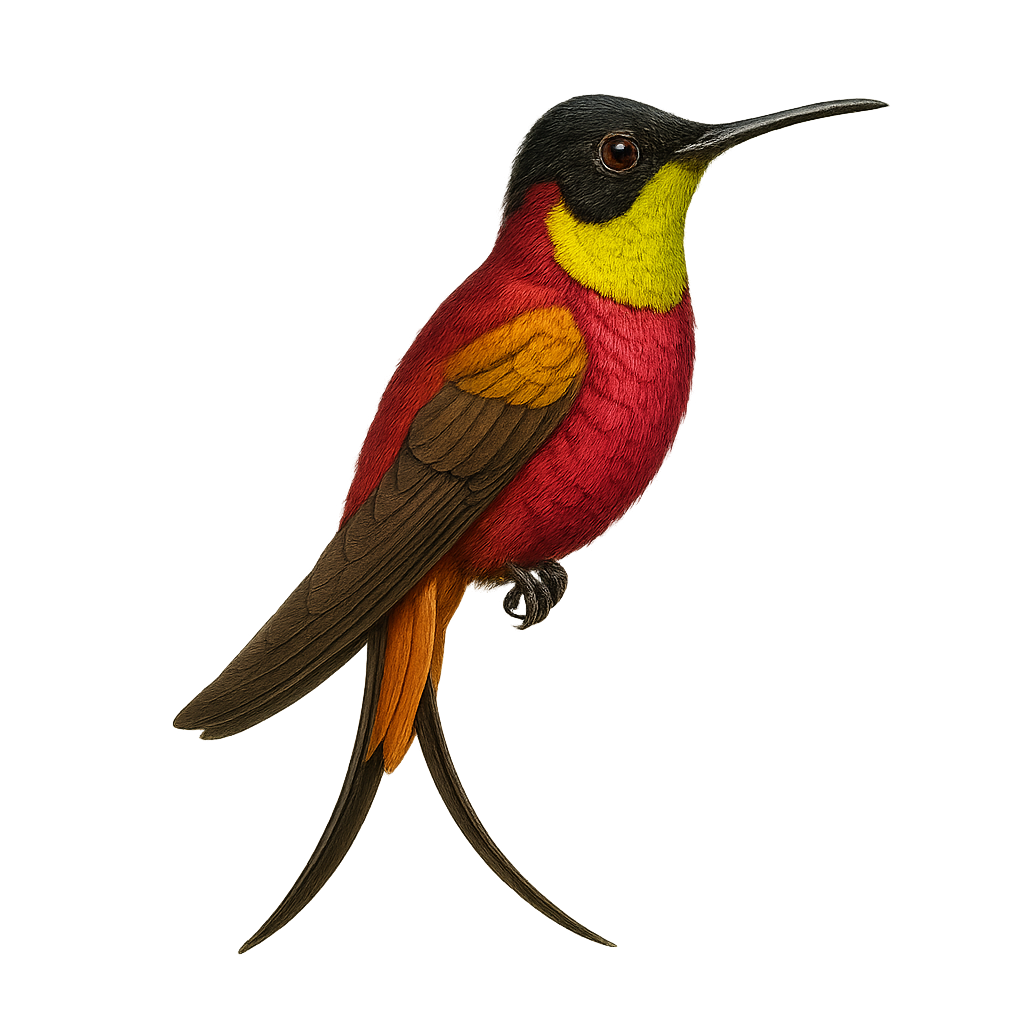
The Crimson Topaz, or Topaza pyra, is a captivating bird found in the tropical forests of South America, particularly in Guyana, Brazil, and Venezuela. This hummingbird is known for its striking plumage, featuring shades of red, orange, and metallic green. Males have long, forked tails that enhance their elegance during courtship displays. They primarily feed on nectar but also consume small insects to supplement their diet. Their rapid and agile flight allows them to move easily between flowers. Although their habitat is relatively stable, deforestation poses a potential threat to their survival.
The Crimson Topaz, or Topaza pella, is a fascinating bird found in the tropical forests of South America, particularly in Guyana, Brazil, and Venezuela. This hummingbird is notable for its striking plumage, with red and golden hues that catch the light spectacularly. Males have a long forked tail, enhancing their elegance in flight. They primarily feed on nectar but also consume small insects to supplement their diet. Crimson Topazes are often observed in dense undergrowth and near watercourses, where they find an abundance of flowers. Their fast and agile flight allows them to move easily between flowers, playing a crucial role in pollination.
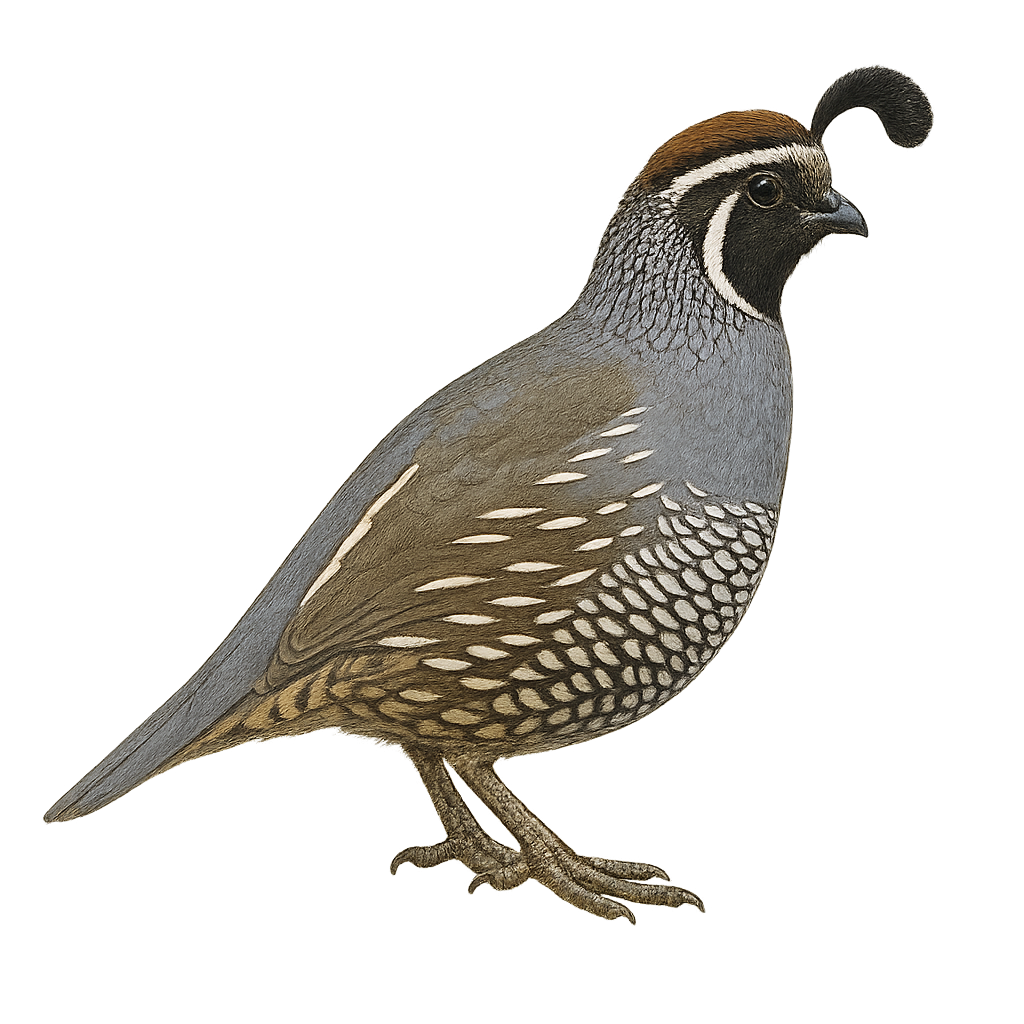
The California Quail, Callipepla californica, is a charming and distinctive bird, easily recognized by its teardrop-shaped plume adorning its head. This bird is primarily found in the western United States, particularly in California, where it inhabits scrublands, open forests, and grasslands. The quail's plumage is a blend of gray, brown, and white, with scaled patterns on the belly. Males are generally more colorful than females. Sociable by nature, it often lives in groups called "coveys," especially outside the breeding season. The California Quail feeds mainly on seeds, leaves, and insects. It is known for its distinctive and melodious calls, often heard at dusk.
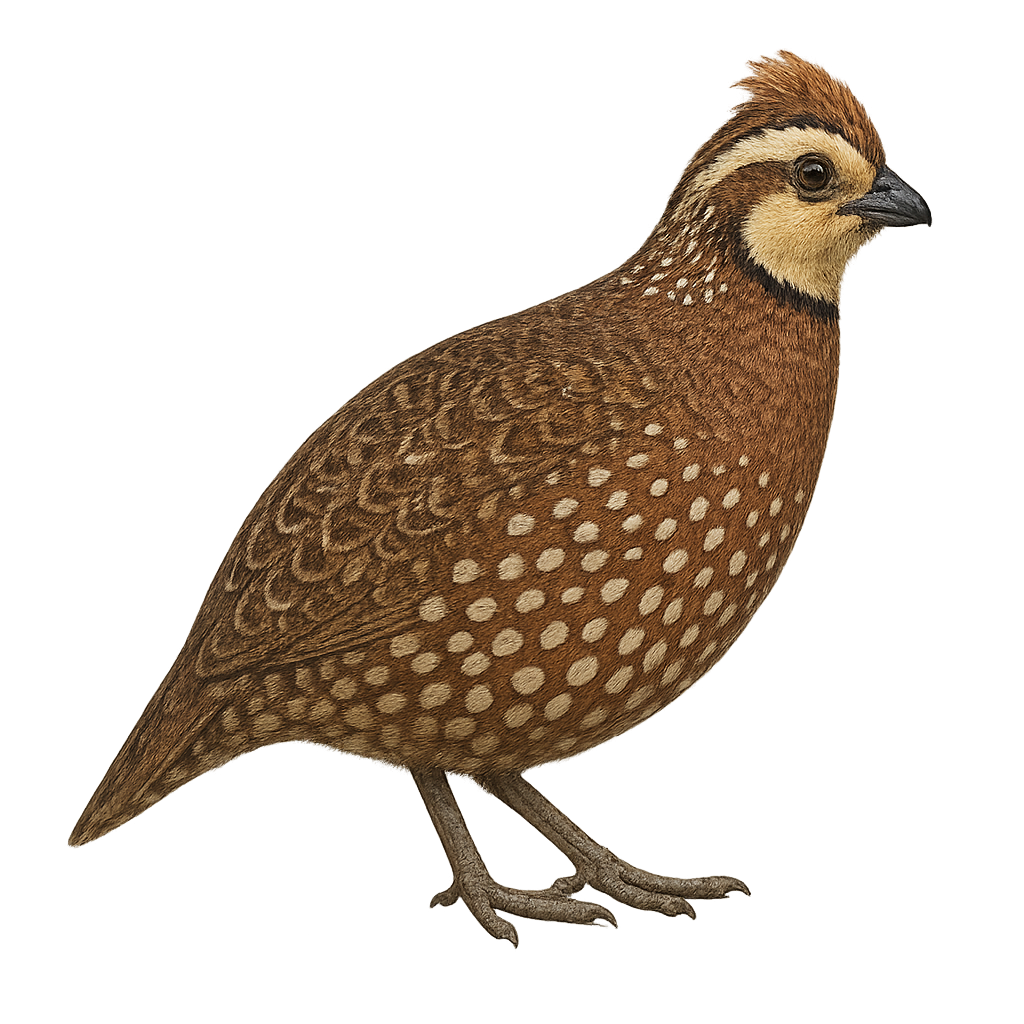
The Crested Bobwhite, Colinus cristatus, is a bird from the Odontophoridae family, recognizable by its distinctive crest. It measures about 22 to 25 cm in length and weighs between 140 and 180 grams. Its plumage is mainly brown with white and black patterns on the head and neck. Males and females are similar, although males often have brighter colors. This bird is primarily terrestrial and prefers open habitats such as grasslands and savannas. It feeds mainly on seeds, insects, and small fruits. The Crested Bobwhite is known for its distinctive calls, often heard at dusk. It forms family groups and is generally monogamous.
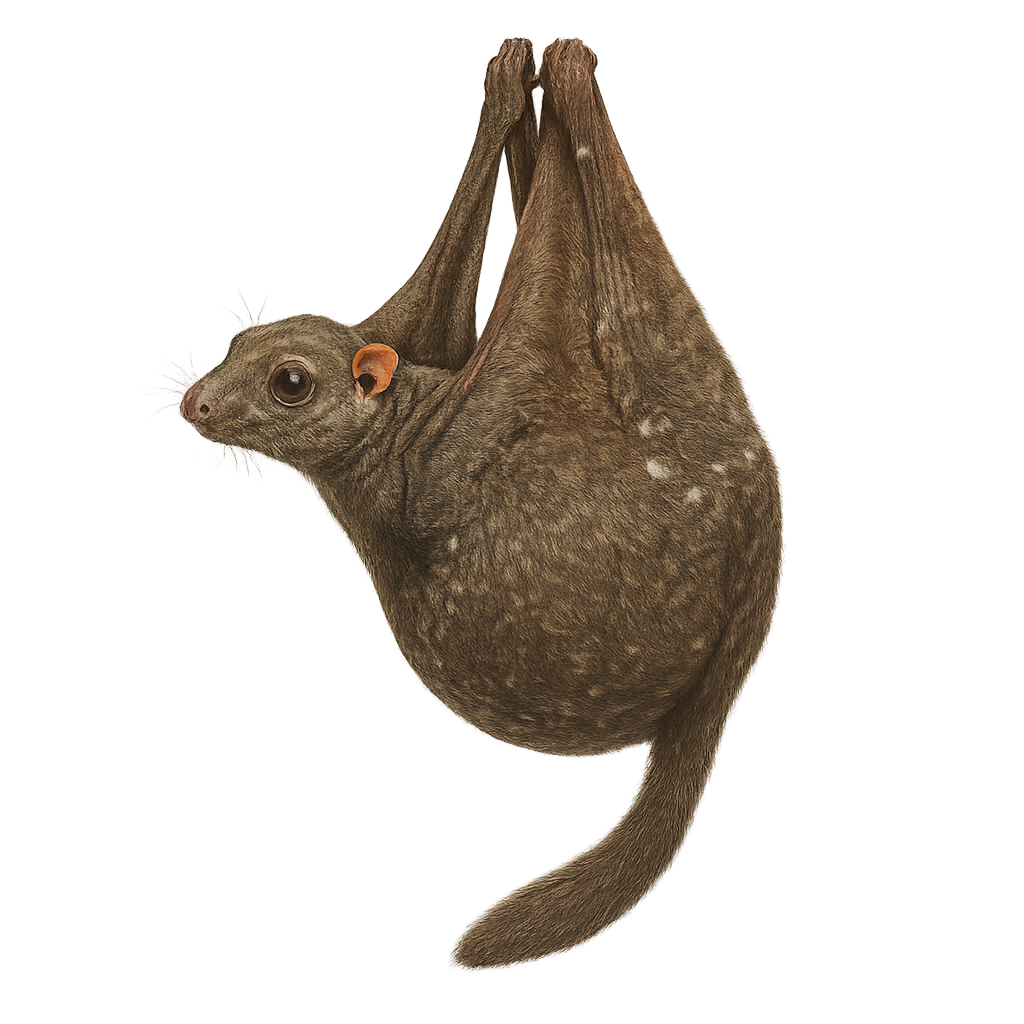
The Colugo, also known as the flying lemur, is a small tree-dwelling mammal native to Southeast Asia. While not a true lemur, it is often called so due to its gliding abilities, which it performs using a thin membrane of skin that connects its limbs to its body. This gliding allows it to move efficiently from tree to tree in search of food, primarily consisting of leaves, fruits, and flowers. The Colugo is a nocturnal and rather discreet animal, using its dense fur and camouflage to blend into the forest environment.
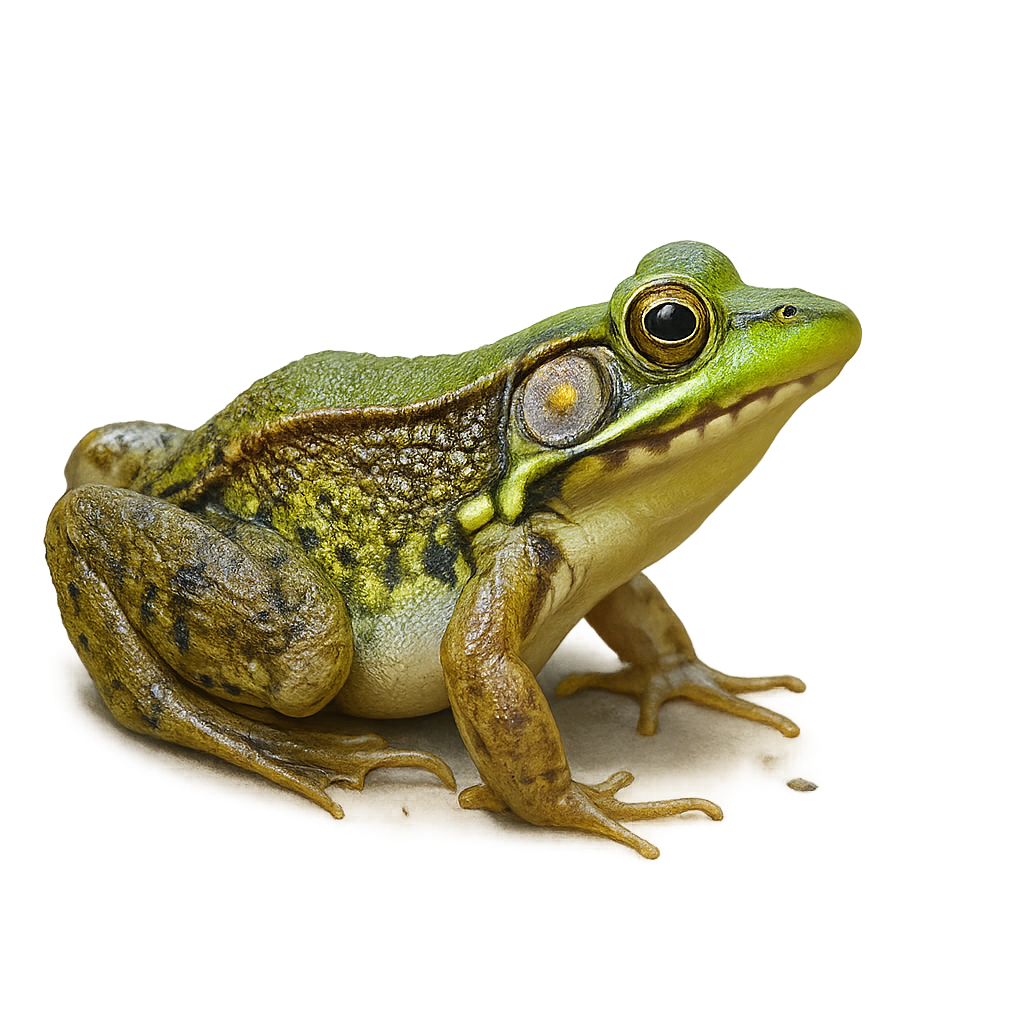
The Common rocket frog, scientifically known as Colostethus inguinalis, is a small amphibian species distinguished by its vibrant coloration. It features a bright yellow belly contrasting with a brownish back, often speckled with dark spots. This frog is primarily terrestrial and inhabits the humid tropical forests of Central and South America. It is often observed near water bodies where it breeds. Its distinctive call is an essential means of communication, especially during the breeding season. Although discreet, it plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by regulating insect populations.
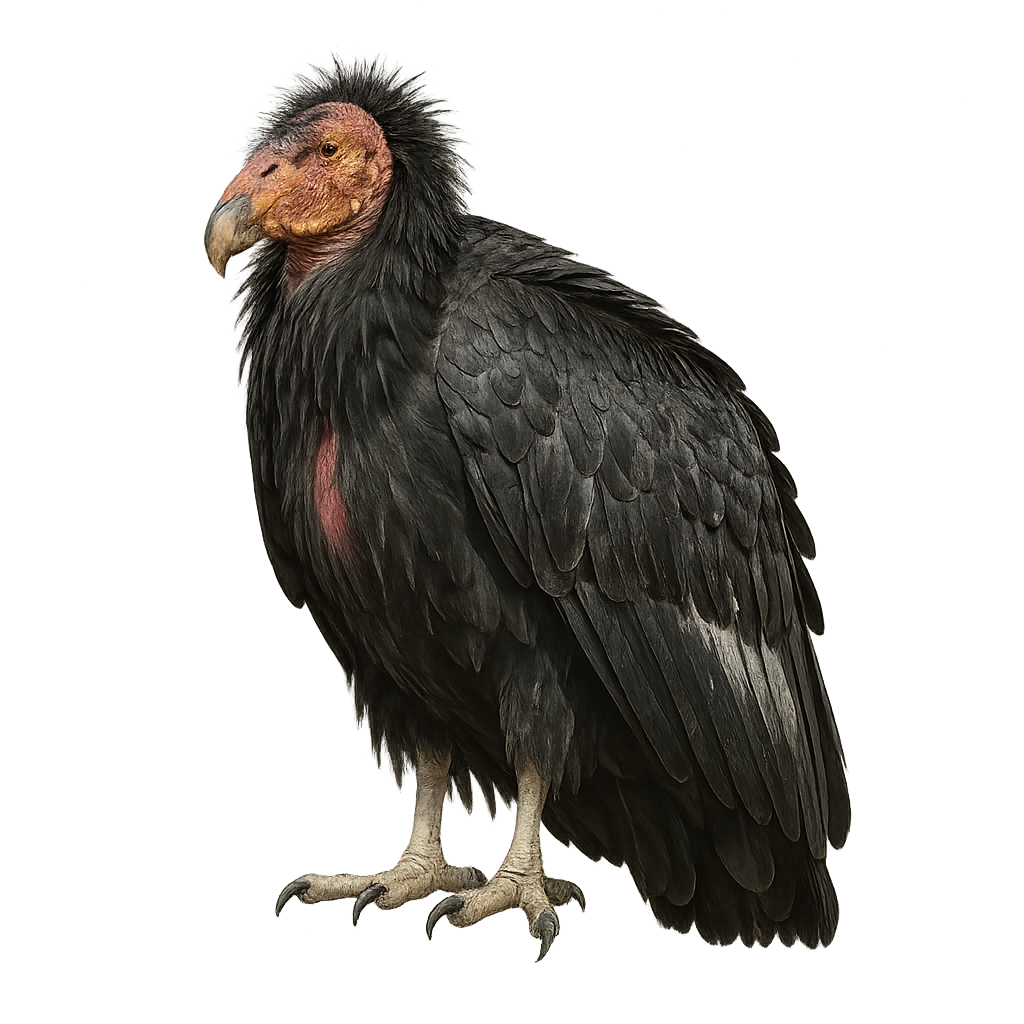
The California condor is a large terrestrial vulture in the family Cathartidae, with a wingspan of 2.7–3.2 m, black plumage and a bare head and neck. It inhabits coastal cliffs and arid canyons, feeding mainly on carrion of large mammals. Pairs nest on cliff ledges, laying one egg every other year.
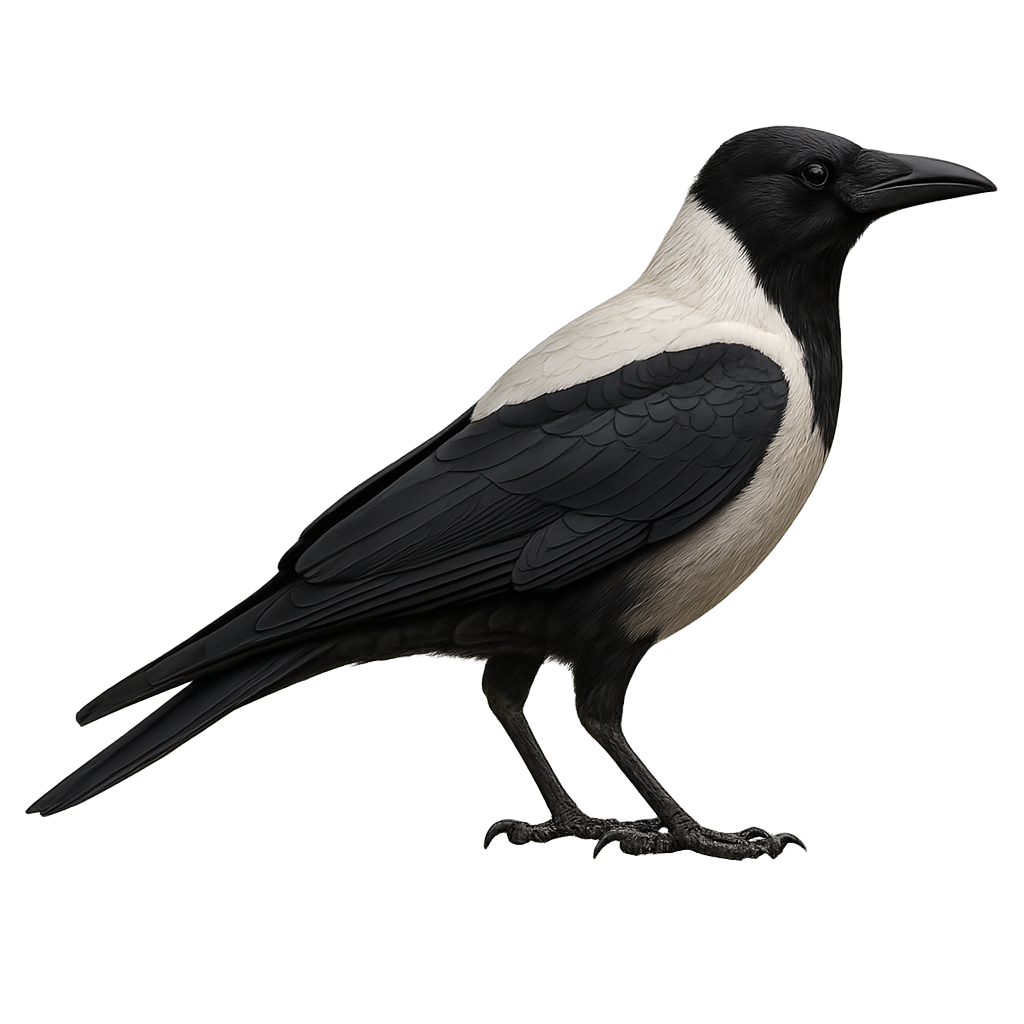
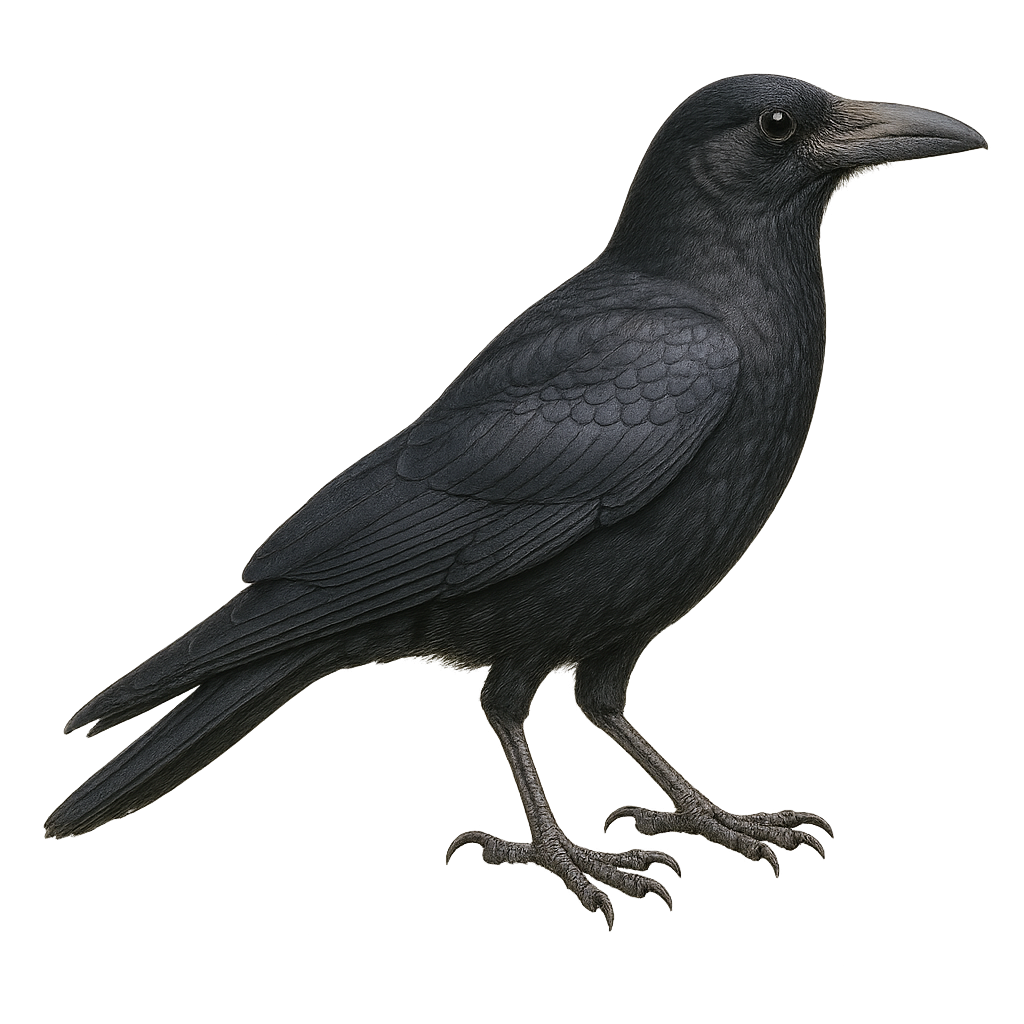
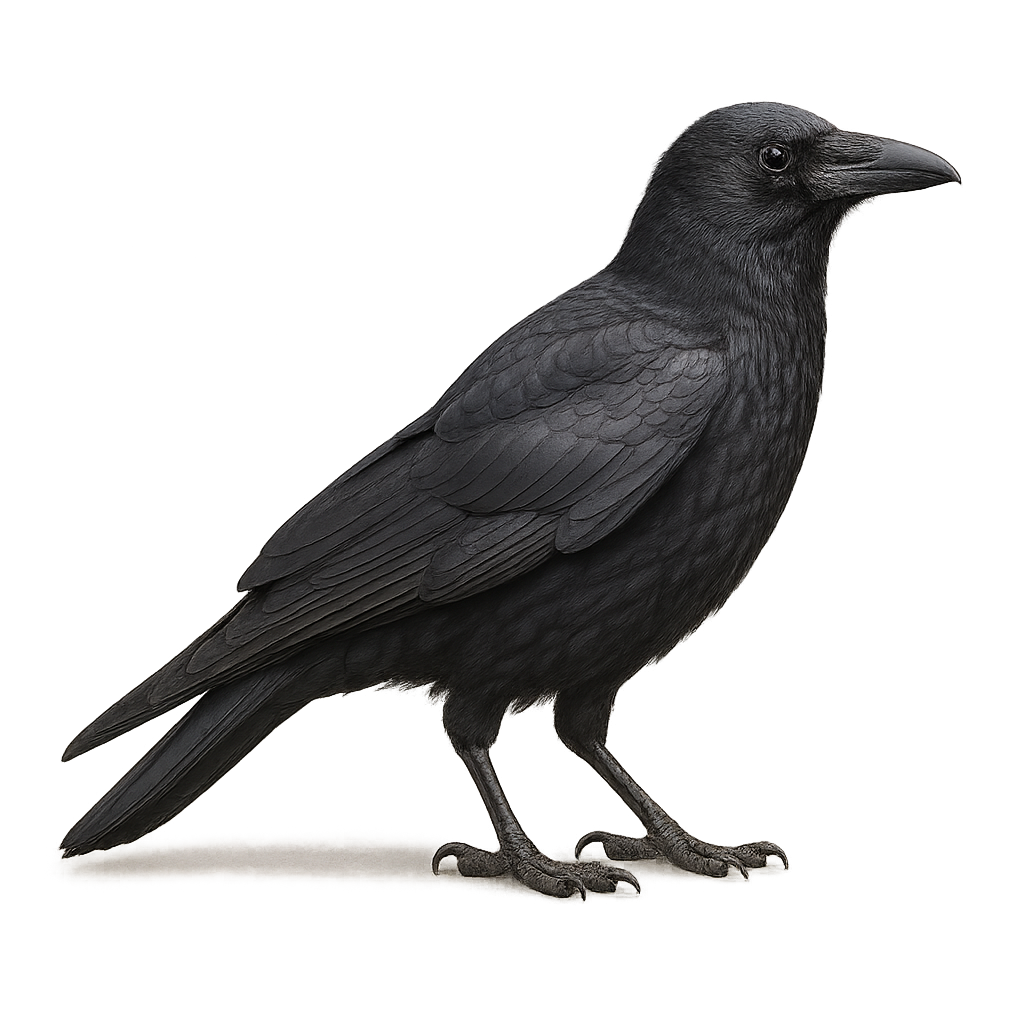
The Collared Crow, or Corvus torquatus, is a medium-sized bird known for its glossy black plumage and distinctive white collar around its neck. It primarily inhabits regions of East Asia, particularly China, where it frequents agricultural areas, open forests, and urban zones. As an opportunist, it feeds on a variety of foods, ranging from insects to small animals and human waste. Its intelligence and adaptability allow it to thrive in diverse environments. Although often solitary, it can be seen in small groups, especially when foraging. Its voice is harsh and varied, contributing to its complex social communication.
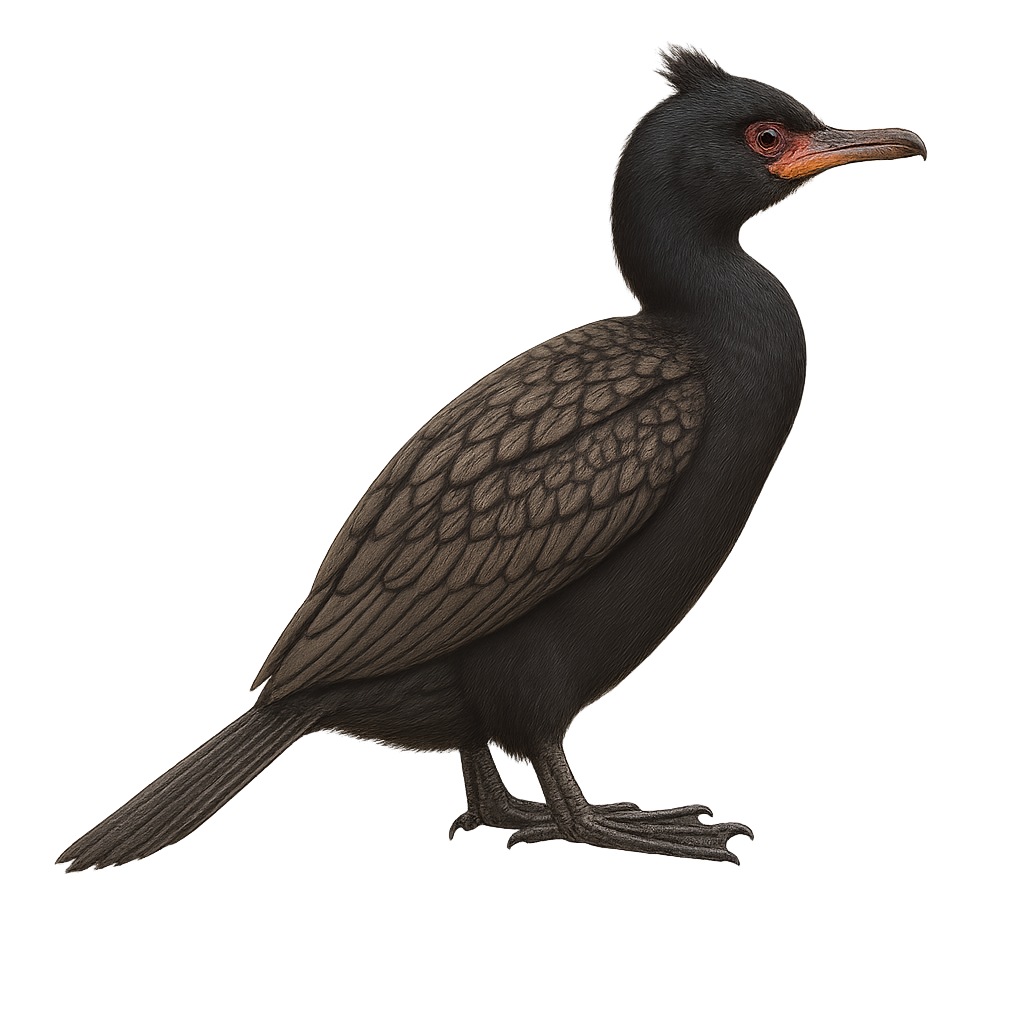
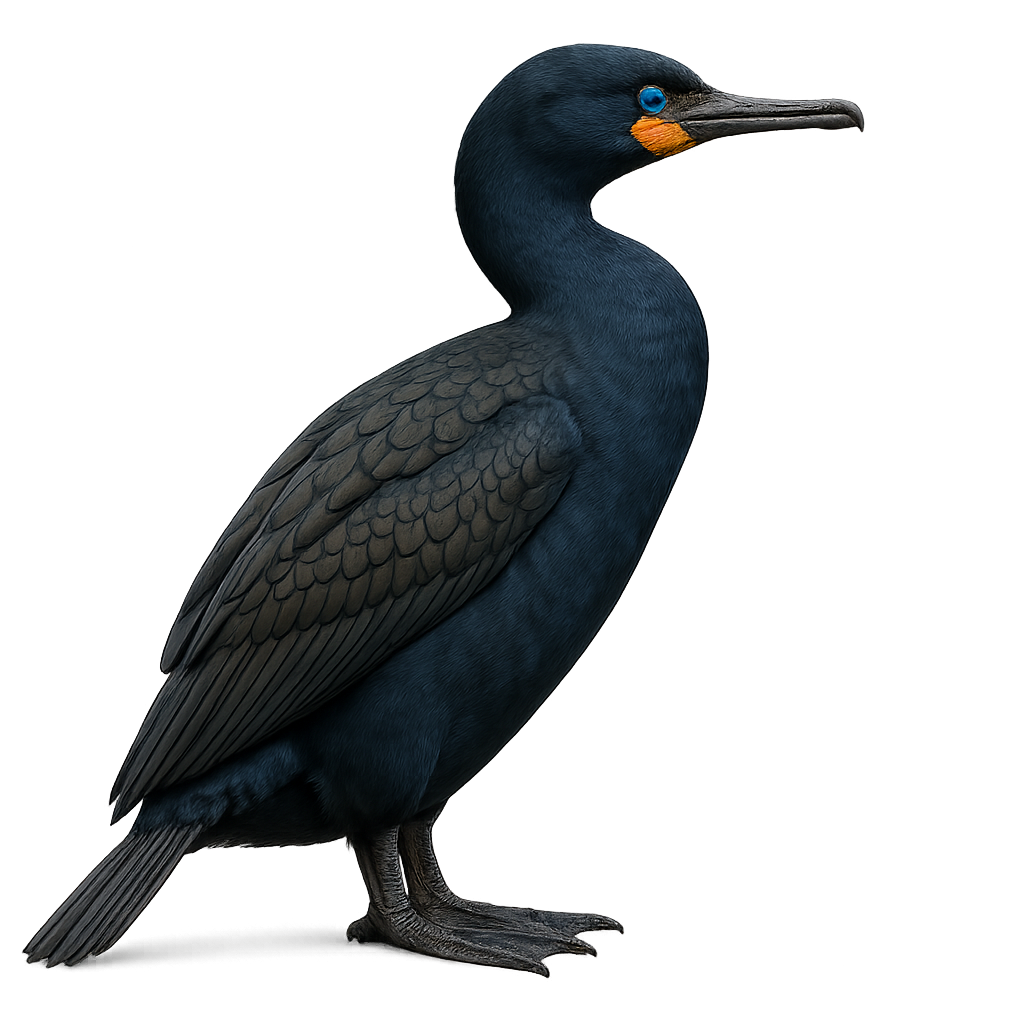
The Crowned Cormorant, Microcarbo coronatus, is a medium-sized aquatic bird primarily found along the rocky coasts of southern Africa. Its plumage is predominantly black with metallic green sheen, and it features a distinctive small crest on its head, giving it its name. This cormorant feeds mainly on small fish and crustaceans, which it skillfully catches by diving underwater. It is often seen perched on rocks, drying its wings in the sun. Although its habitat is relatively limited, it adapts well to coastal environments, allowing it to maintain a stable population. However, it remains vulnerable to human disturbances and marine pollution.
The Cape Cormorant, or Phalacrocorax capensis, is a medium-sized seabird known for its glossy black plumage and striking turquoise eyes. It is primarily endemic to the South African coast, where it frequents coastal waters and rocky islands. This cormorant is an excellent diver, capable of descending several meters to catch fish and crustaceans. It nests in dense colonies, often on cliffs or islets, where it builds rudimentary nests with seaweed and debris. Although its flight is powerful and direct, it is often seen drying its wings in the sun after fishing.
The Cape Crow, or Corvus capensis, is a medium-sized bird known for its glossy black plumage and sturdy beak. It is primarily found in southern Africa, where it inhabits savannas, grasslands, and agricultural areas. This crow is noted for its intelligence and adaptability to various environments. It feeds mainly on insects, small vertebrates, and seeds. The Cape Crow is often seen in groups, which helps protect it from predators. Its voice is distinctive, with harsh and varied calls. Although generally wary of humans, it can become accustomed to their presence in undisturbed areas.
The carrion crow is a 44–51 cm corvid, all black with a stout bill and strong flight. It inhabits urban areas, farmland and open woodlands across Europe and Asia, feeding on insects, small vertebrates, seeds and carrion, and scavenging human refuse. An opportunistic omnivore, it uses tools and caches food. During the breeding season (March–May), pairs defend a territory, build a large branch nest and raise 3–5 young.
The Collared Gnatwren is a small, elusive bird native to the humid tropical forests of South America. It is identifiable by its olive-brown plumage and distinctive white collar contrasting with its dark throat. Measuring about 12 cm in length, this bird is often seen skittering through dense underbrush in search of insects. It is particularly active at dusk and dawn, when it emits soft, melodious calls. Although not very shy, it remains difficult to spot due to its dense habitat and discreet nature. Its social behavior is mostly solitary, although it can sometimes be seen in small family groups.
The Coscoroba Swan is a medium-sized waterbird often mistaken for a swan due to its pure white plumage and graceful long neck. It is distinguished by its bright red bill and pinkish legs. Native to South America, it inhabits lakes, marshes, and lagoons, feeding mainly on aquatic plants, insects, and small crustaceans. Although sociable, it can be territorial during the breeding season. The Coscoroba Swan is an excellent swimmer, using its wings to propel itself on water. Its population is stable, but it remains vulnerable to environmental changes and habitat loss.
The Common Cuckoo, Cuculus canorus, is a migratory bird known for its distinctive call and brood parasitism behavior. It measures about 32 to 34 cm in length with a wingspan of 55 to 60 cm. Its plumage is primarily gray with lighter shades on the belly. The Common Cuckoo is famous for laying its eggs in the nests of other birds, leaving the foster parents to raise its young. It inhabits various environments, including forests, grasslands, and wetlands. Widely distributed across Europe and Asia, it migrates to sub-Saharan Africa for the winter. Its call, a repeated "cuckoo," is often heard in spring.
The Cuckoo Roller, or Leptosomus discolor, is a unique and fascinating bird endemic to Madagascar and the Comoros. It is the sole member of the Leptosomidae family. This bird features distinctive plumage, with males displaying bluish-grey hues and females showing brown and mottled patterns. The Cuckoo Roller is known for its graceful gliding flight and resonant calls. It primarily inhabits tropical rainforests but can also be found in drier wooded areas. Its diet mainly consists of insects, small reptiles, and occasionally fruits. Although relatively common in its natural habitat, deforestation poses a potential threat to its population.
The Cream-colored Courser, Cursorius cursor, is an elegant and swift terrestrial bird, primarily found in the arid and semi-arid regions of North Africa and the Middle East. Its slender silhouette, long legs, and light beige plumage with cream hues allow it to blend seamlessly into its desert surroundings. This bird is particularly adapted to desert life, feeding mainly on insects and small invertebrates. The Cream-colored Courser is known for its rapid running and ability to cover long distances in search of food. It typically nests on the ground in open areas, with its eggs well camouflaged among stones and sand.
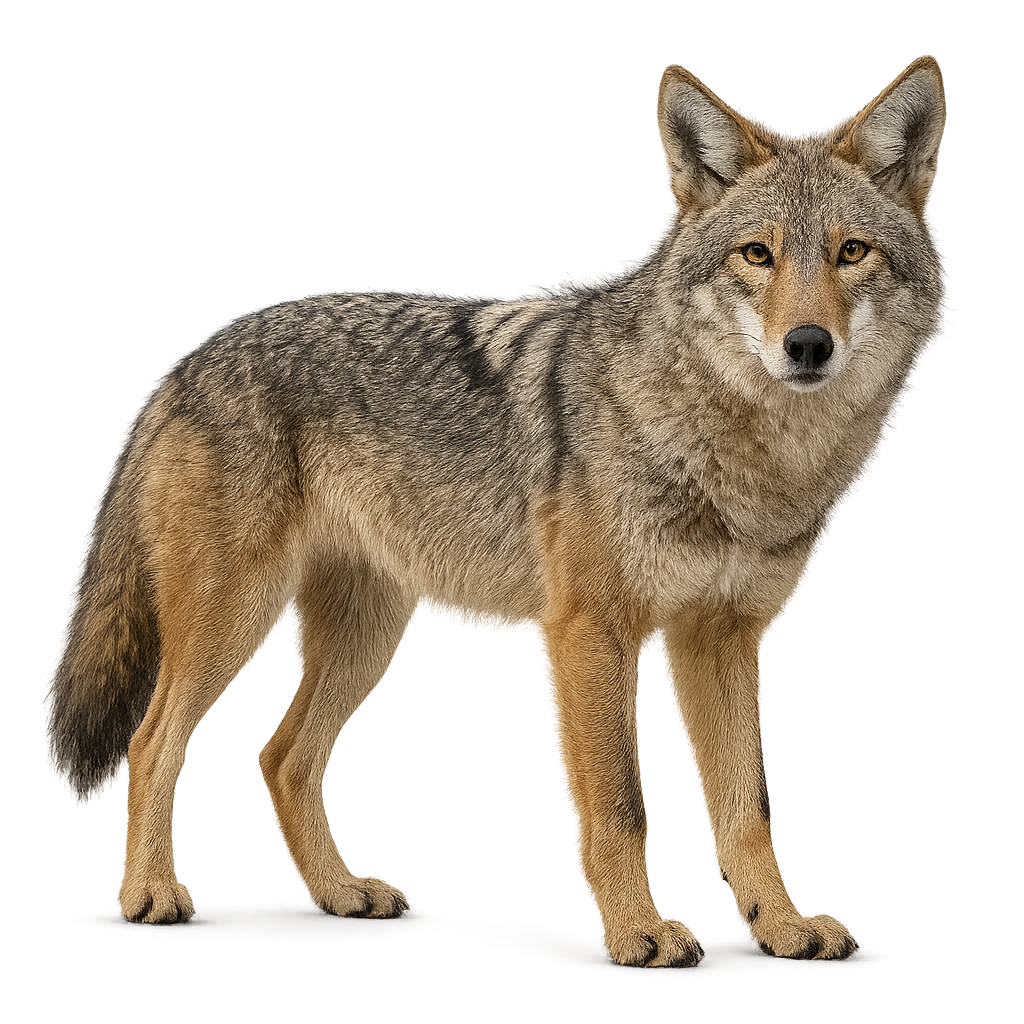

The Coyote is a medium-sized canine, very similar to the wolf but smaller and more agile. Its fur varies from gray to light brown, with a face often marked by black traits, a white chest and belly, and dark legs. The Coyote is easily recognizable by its pointed muzzle, relatively large ears, and bushy tail. It typically stands between 60 and 80 cm at the shoulder, with a total length of 75 to 90 cm for the body, excluding the tail.
This canine is an opportunistic feeder, primarily hunting small mammals such as rodents, rabbits, and sometimes birds, but it can also eat fruits and carrion. Highly adaptable, the Coyote inhabits a wide variety of environments, ranging from prairies and deserts to urban areas, and it is particularly active at dusk and during the night. Unlike other predators, the Coyote often hunts alone or in small groups. Although its population is stable across much of its range, it is sometimes seen as a nuisance in certain areas and faces threats from hunting and habitat loss.
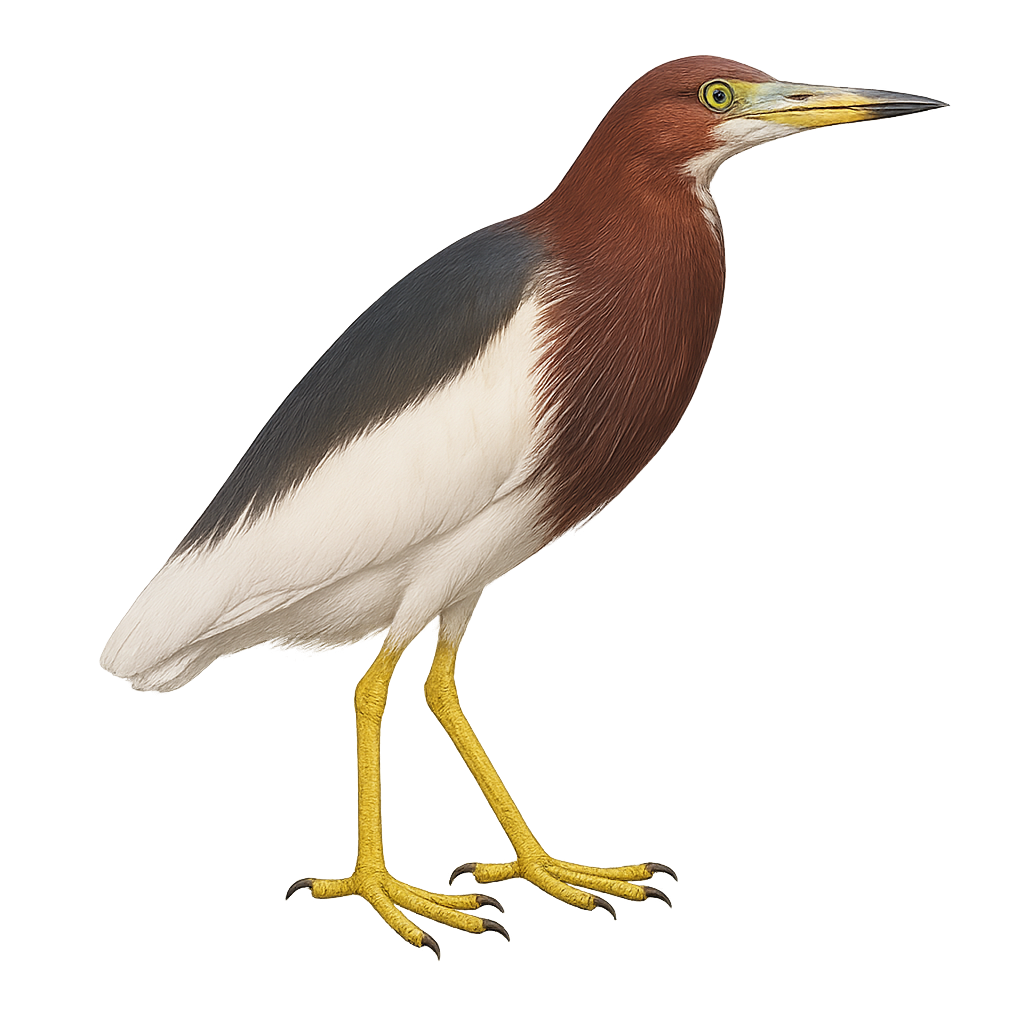
The Chinese Pond Heron, Ardeola bacchus, is a small heron with distinctive plumage. During the breeding season, it displays vibrant colors with a reddish-brown head and neck, metallic green back, and white wings. Outside this period, it appears duller with brownish hues. Found mainly in Southeast Asia's wetlands, it inhabits rice fields, marshes, and lake edges, feeding on fish, insects, and small crustaceans. Its flight is swift and direct, often at low altitudes.