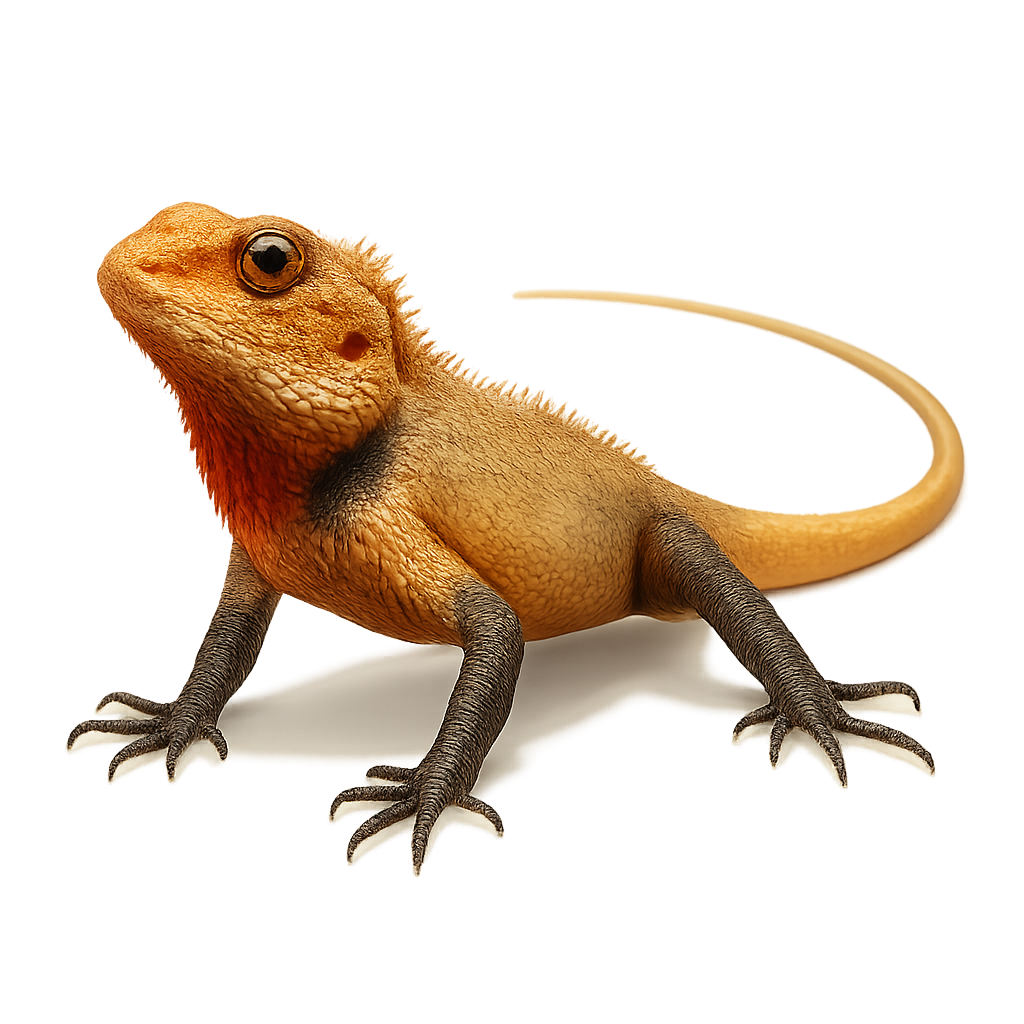
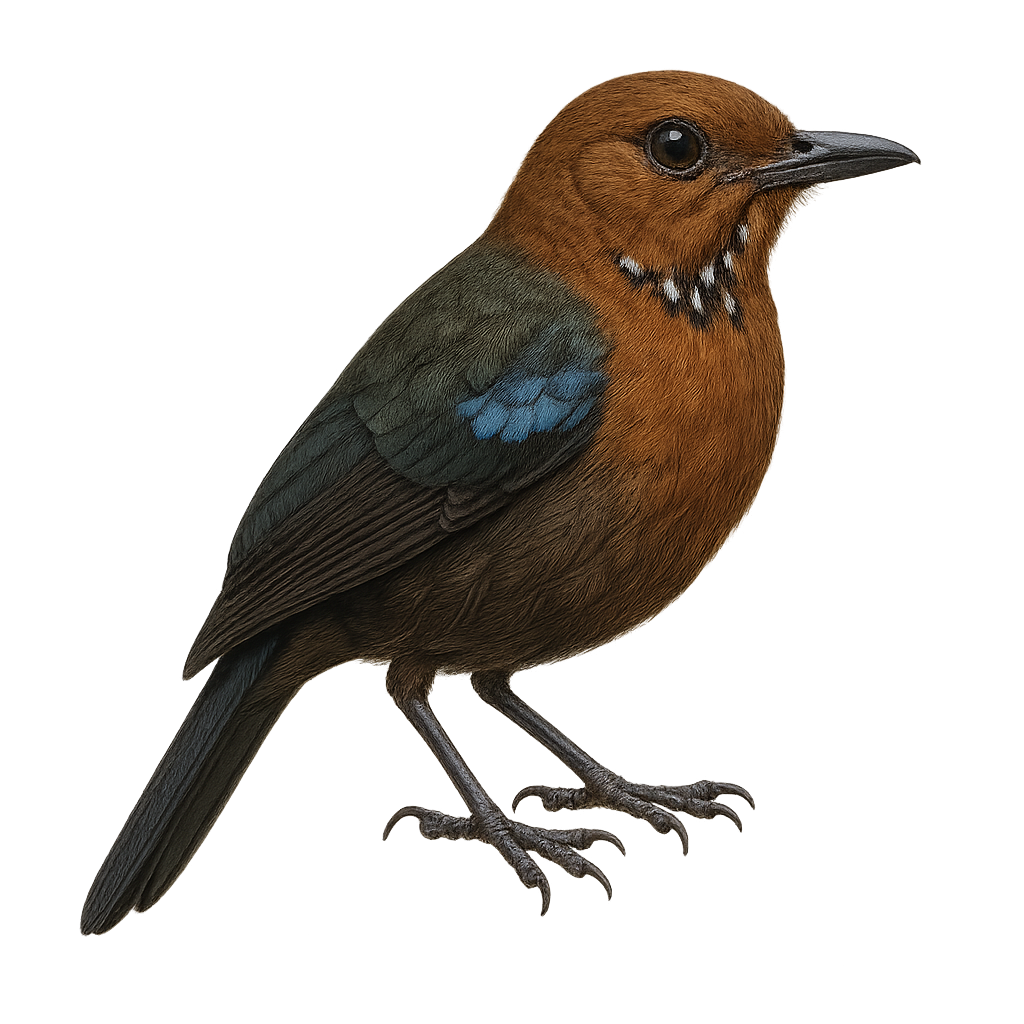
The Changeable Lizard, or Calotes versicolor, is a widespread lizard in South and Southeast Asia. It is easily recognizable by its ability to change color, shifting from brown to green, and sometimes bright red, especially during the breeding season. This diurnal lizard prefers open habitats such as gardens, light forests, and urban areas. It primarily feeds on insects but can also consume small vertebrates. Males often display a reddish throat during the breeding season to attract females. Although frequently seen in inhabited areas, it remains wary and quickly flees when threatened.
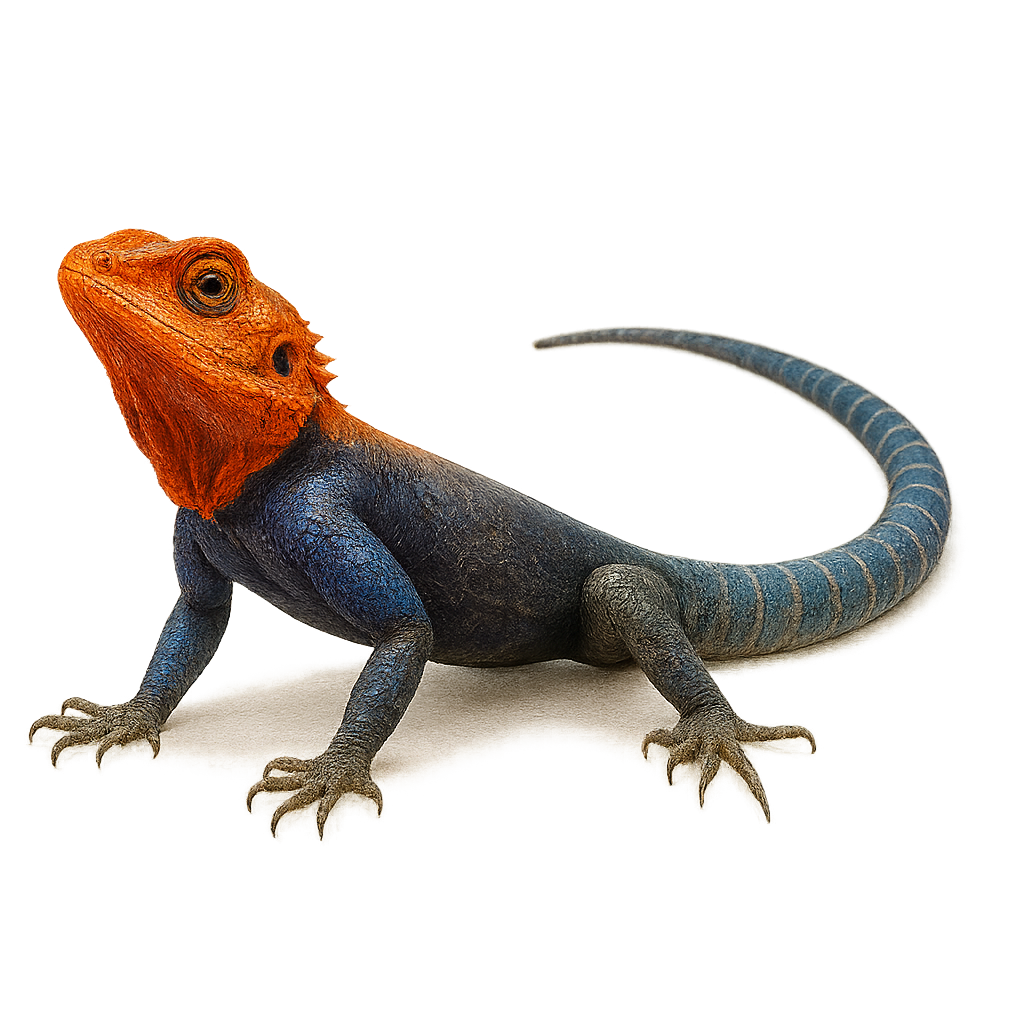
The Common Agama, or Agama agama, is a colorful and fascinating lizard found primarily in sub-Saharan Africa. This reptile is known for its ability to change color, especially males who display bright hues of blue and orange during the breeding season. Typically measuring between 25 and 30 cm in length, it has a long, slender tail. The Common Agama is a diurnal animal that prefers warm, dry environments such as savannas, rocky areas, and villages. It primarily feeds on insects but can also consume small vertebrates and plants. This lizard is social and lives in hierarchical groups, where a dominant male controls several females and subordinates.
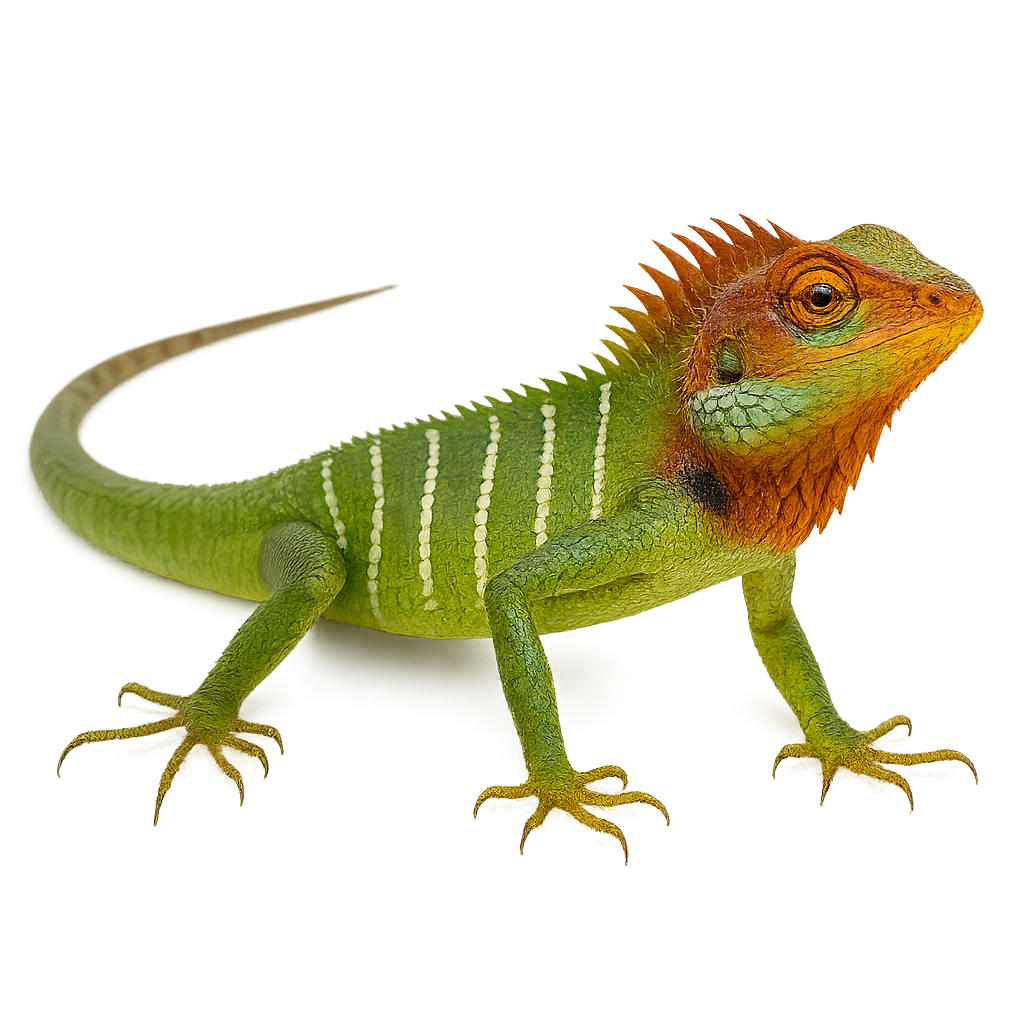
The Common Green Forest Lizard, Calotes calotes, is an arboreal lizard native to Sri Lanka and southern India. It is recognizable by its bright green color, although its hue can vary depending on its environment and mood. Males often display a more pronounced dorsal crest and brighter colors than females, especially during the breeding season. This diurnal lizard primarily feeds on insects but can also consume fruits and small vertebrates. It is often seen in gardens, forests, and wooded areas, where it skillfully camouflages among the foliage.
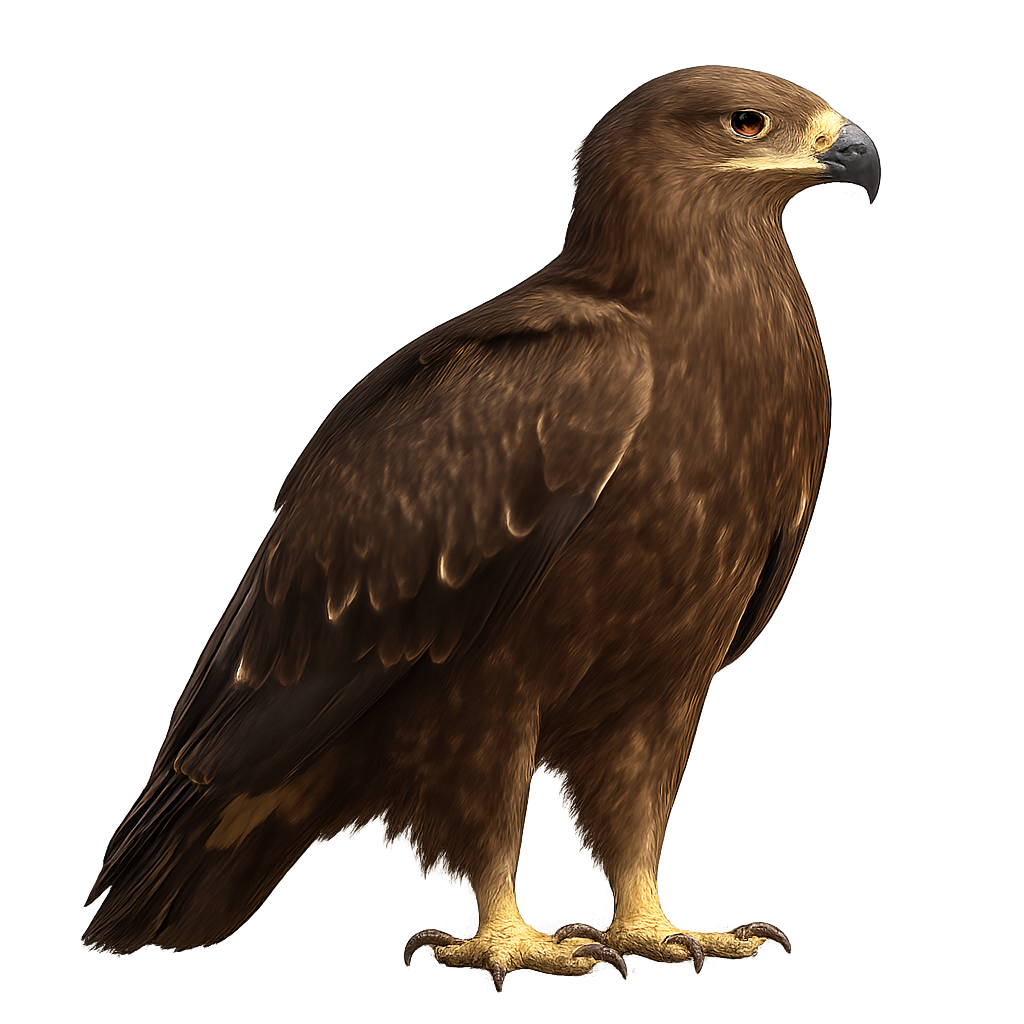
The Greater Spotted Eagle is an imposing raptor, recognizable by its dark plumage and robust silhouette. This large eagle is mainly found in Eastern Europe and Asia, where it hunts large mammals, birds, and sometimes even reptiles. It mainly inhabits open landscapes such as meadows, steppe areas, and marshes. Its powerful call, which is the source of its name, is often seen as a symbol of strength and sovereignty in local cultures.
During the breeding season, the Greater Spotted Eagle performs majestic flights and powerful calls to mark its territory and attract a mate.
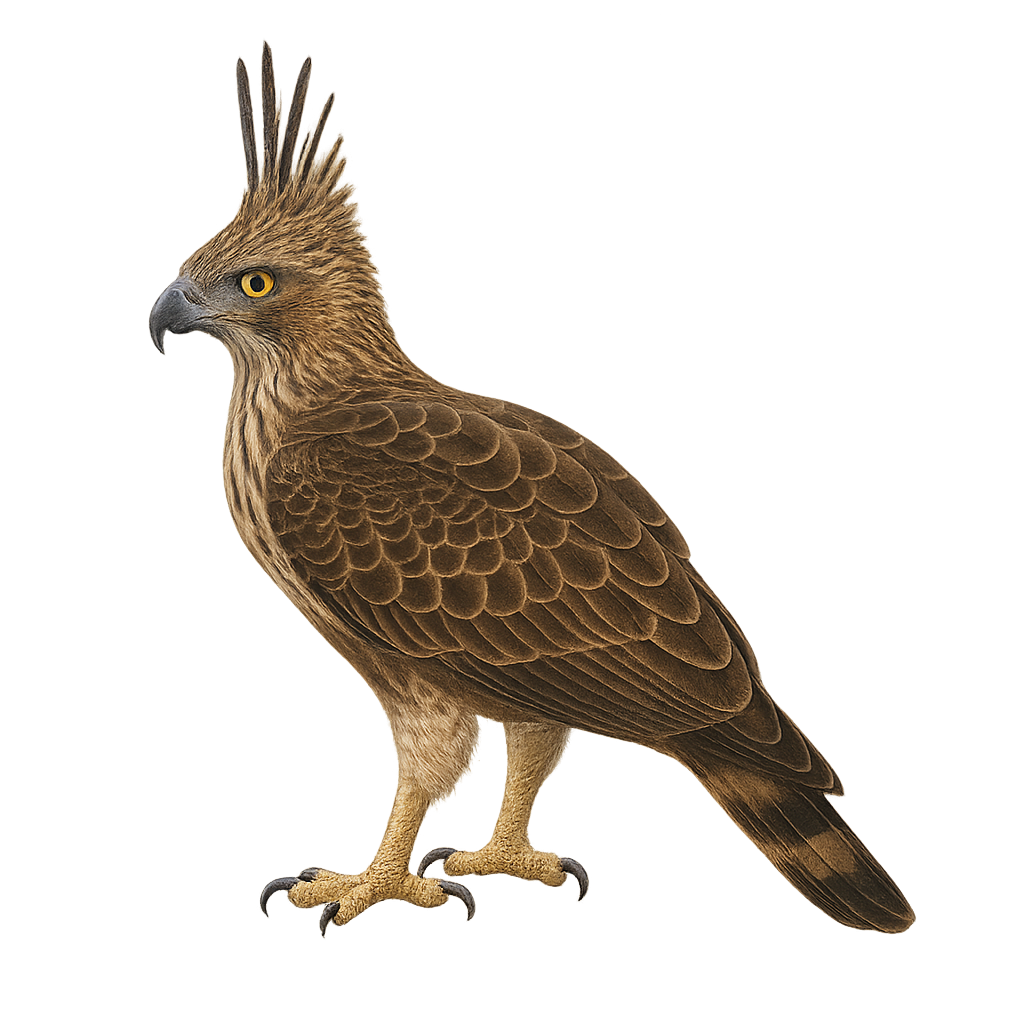
The Changeable Hawk-Eagle, or Nisaetus cirrhatus, is a majestic bird of prey found primarily in South and Southeast Asia. It is recognizable by its distinctive crest and dark brown plumage with lighter patterns on the belly. This raptor is often observed in dense forests, where it hunts a variety of prey, ranging from small mammals to birds. Its flight is powerful and graceful, allowing it to soar at great heights. Although generally solitary, it can sometimes be seen in pairs, especially during the breeding season. The Changeable Hawk-Eagle is a symbol of power and freedom in many local cultures.
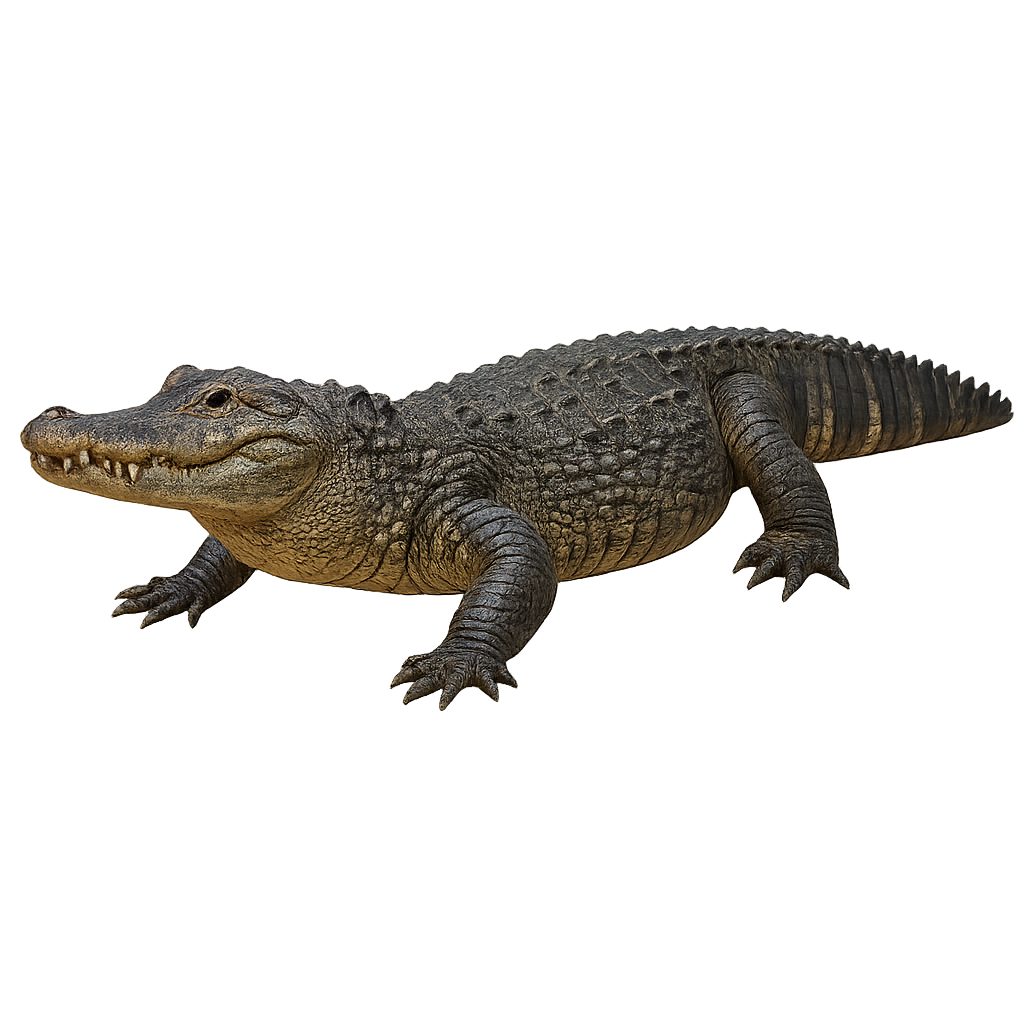
Native to the rivers and swamps of the Yangtze in China, the Chinese alligator is one of the rarest and most endangered alligator species in the world. It has a smaller size compared to the American alligator, with a maximum length of around 2.5 meters. This reptile primarily feeds on fish, crustaceans, and small mammals. Due to habitat loss and hunting, the Chinese alligator is now classified as critically endangered.
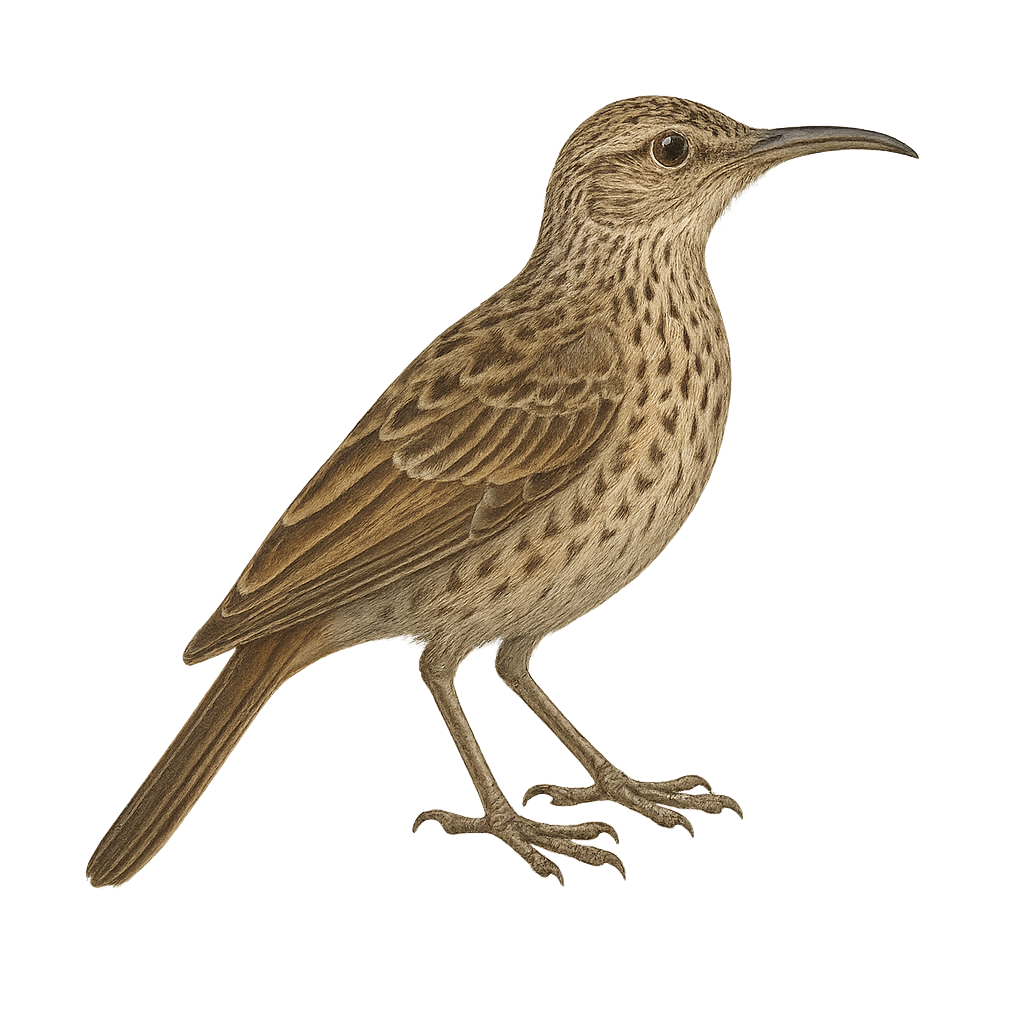
The Cape Long-billed Lark is a bird endemic to South Africa, well adapted to arid and semi-arid environments. It is characterized by its long, curved bill, which it uses to probe the ground for insects and seeds. Its plumage is generally brown with lighter shades on the belly, providing excellent camouflage in its natural habitat. Often seen alone or in small groups, it moves quickly on the ground. Although discreet, it is known for its melodious song, often delivered from a high perch. Its adaptability to harsh conditions makes it a resilient species, although its habitat is threatened by agricultural expansion.
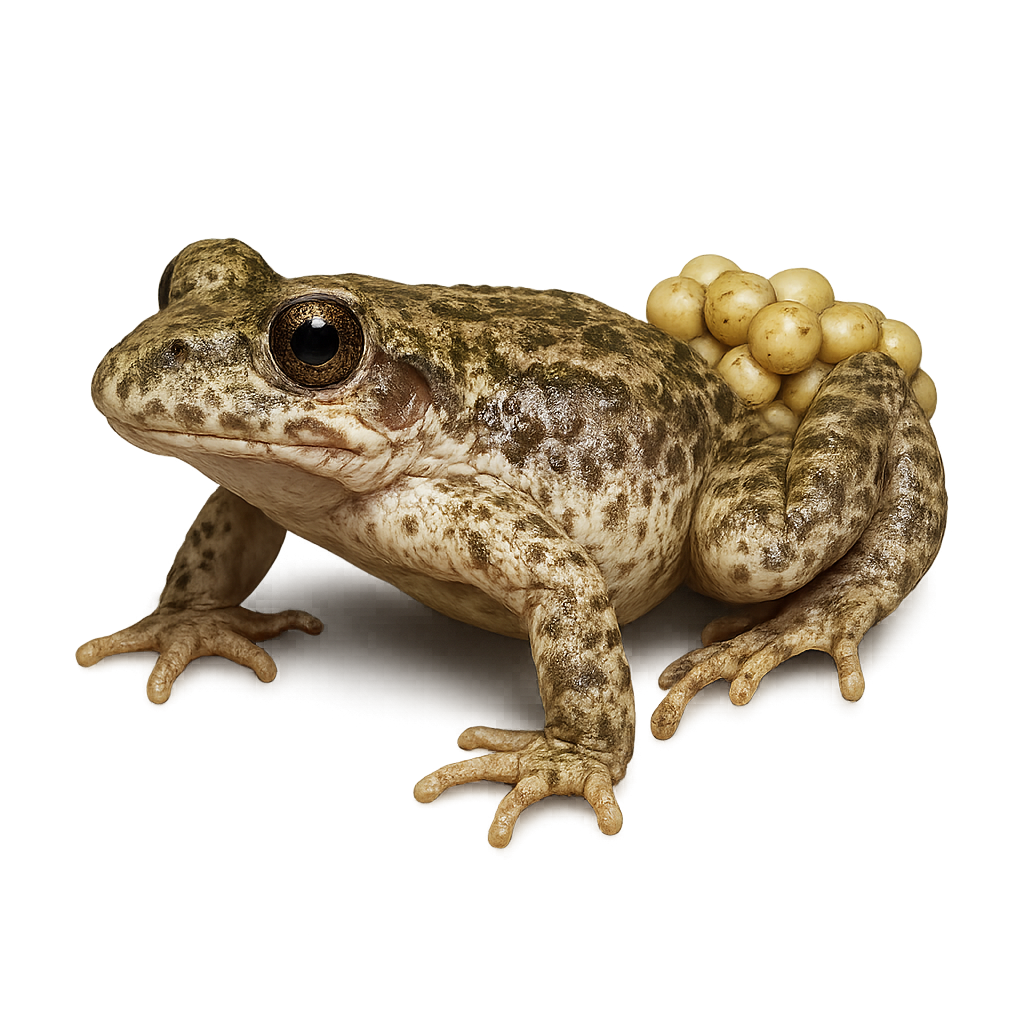
The common midwife toad is a stocky amphibian of 5–6 cm, with smooth olive-grey dorsal skin and a spotted throat. A terrestrial species of temperate Europe, it inhabits forest edges, meadows and urban areas near water bodies, where females lay eggs that males carry in strands until hatching.
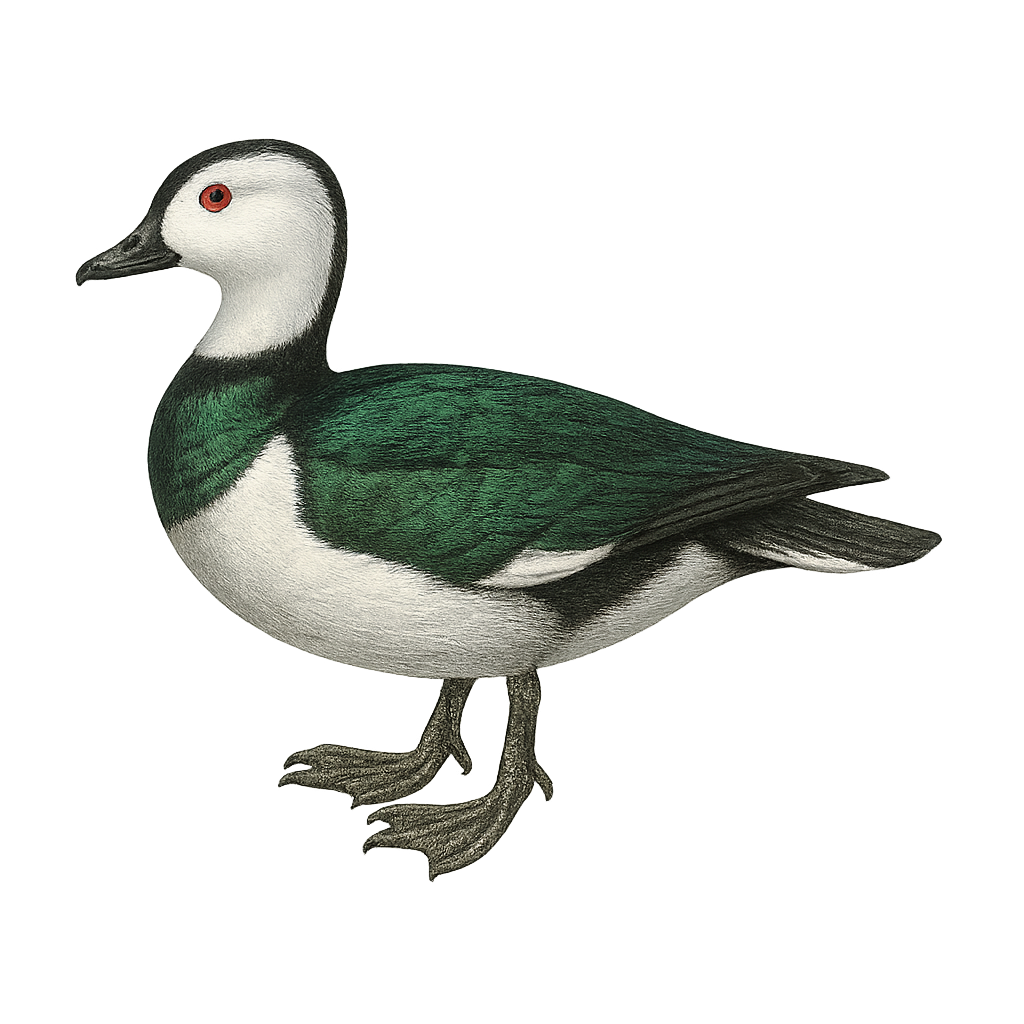
The Cotton Pygmy Goose is a small, tree-dwelling duck often mistaken for a goose due to its English name. It is identifiable by the male's striking black and white plumage, while the female displays more subdued shades of brown and grey. It primarily inhabits the wetlands of South and Southeast Asia, feeding on aquatic plants and small invertebrates. Its small size allows it to navigate dense vegetation with ease. Although its flight is swift and direct, it spends much time swimming on the water's surface. The species is generally discreet but can be seen in small groups.
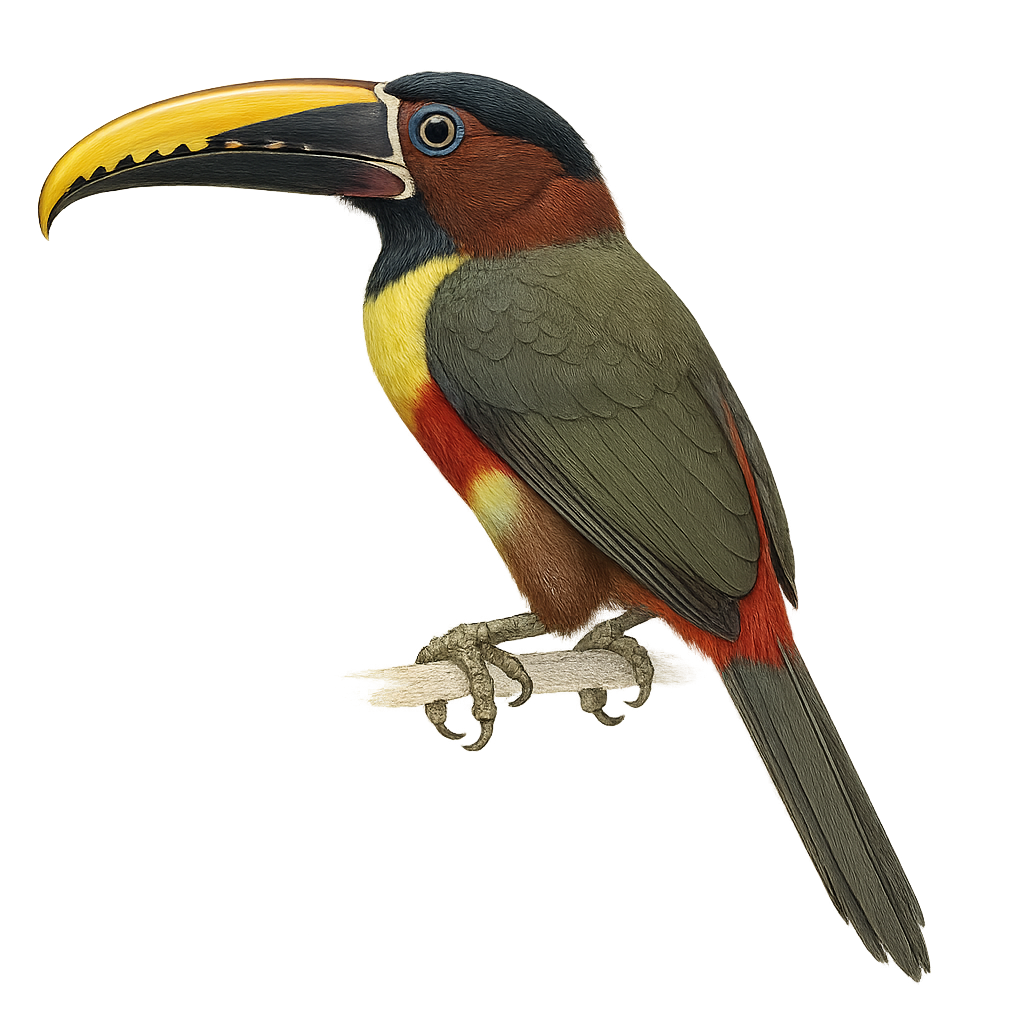
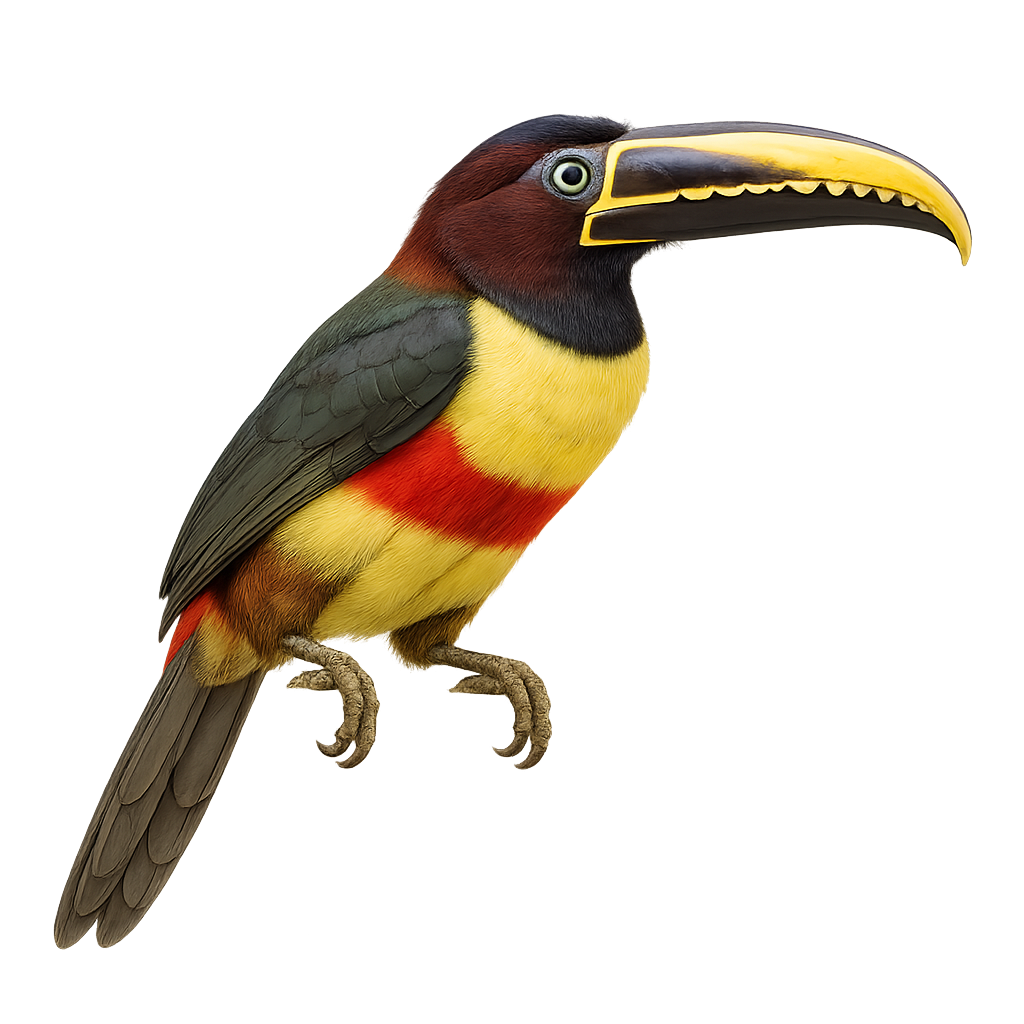
The Chestnut-eared Aracari is a colorful bird from the Ramphastidae family, known for its vibrant plumage and distinctive bill. It features bright colors with shades of green, yellow, and red, along with its characteristic chestnut-colored ear patches. This bird measures about 34 to 45 cm in length. It primarily inhabits the tropical rainforests of South America, notably in Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay, and Argentina. The Chestnut-eared Aracari is a social bird, often seen in small groups. It mainly feeds on fruits, but also consumes insects and small vertebrates. Its presence is an indicator of the health of tropical forests, as it plays a crucial role in seed dispersal.
The Curl-crested Aracari is a captivating bird belonging to the Ramphastidae family. It is distinguished by its vibrant plumage and a unique curly crest on its head, giving it a distinctive appearance. Its long, colorful bill, typical of toucans, plays a crucial role in its diet, which mainly consists of fruits, but also includes insects and small vertebrates. This bird primarily inhabits the tropical rainforests of South America, particularly in Brazil. It is often seen in small groups, moving agilely among the trees. Although its conservation status is concerning due to deforestation, it remains a vibrant symbol of Amazonian biodiversity.
The Collared Aracari is a colorful bird from the toucan family, recognizable by its long, curved beak adorned with distinctive patterns. It features primarily black plumage with a red chest band and a bright yellow belly. This bird measures about 40 to 45 cm in length and weighs between 190 and 275 grams. It inhabits the tropical rainforests of Central and South America, feeding on fruits, insects, and occasionally small vertebrates. Sociable by nature, it often moves in small family groups. Although relatively common, deforestation poses a threat to its natural habitat.
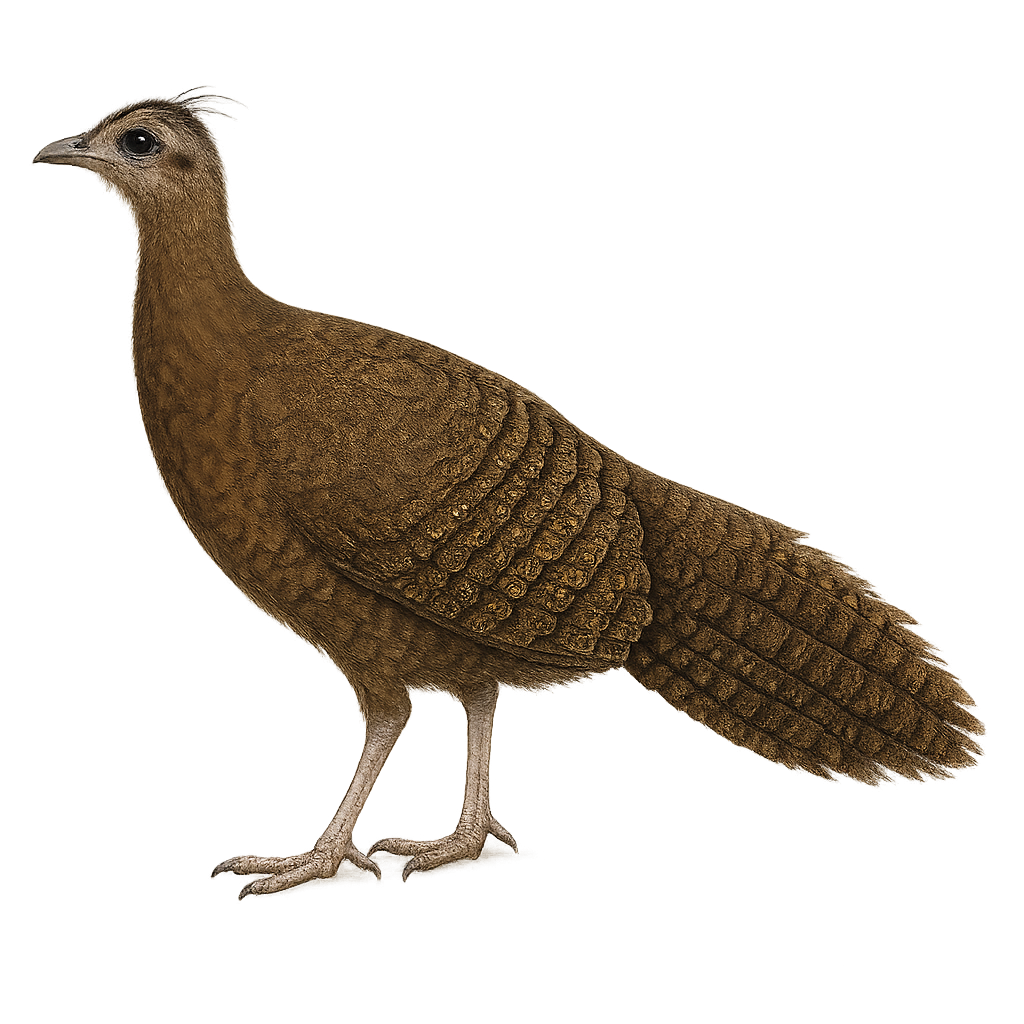
The Crested Argus, or Rheinardia ocellata, is a fascinating bird belonging to the Phasianidae family. This large pheasant is primarily known for its spectacular plumage and long tail feathers adorned with eye-like patterns reminiscent of a peacock. Males, larger than females, can reach up to 2 meters in length, including the tail. They sport a brown plumage with intricate patterns, while females are more discreet with brown and gray hues. The Crested Argus inhabits the dense tropical forests of Southeast Asia, particularly in Vietnam, Thailand, and Malaysia. This bird is mainly terrestrial, feeding on seeds, fruits, and insects. Unfortunately, it is threatened by deforestation and hunting, leading to a decline in its populations.
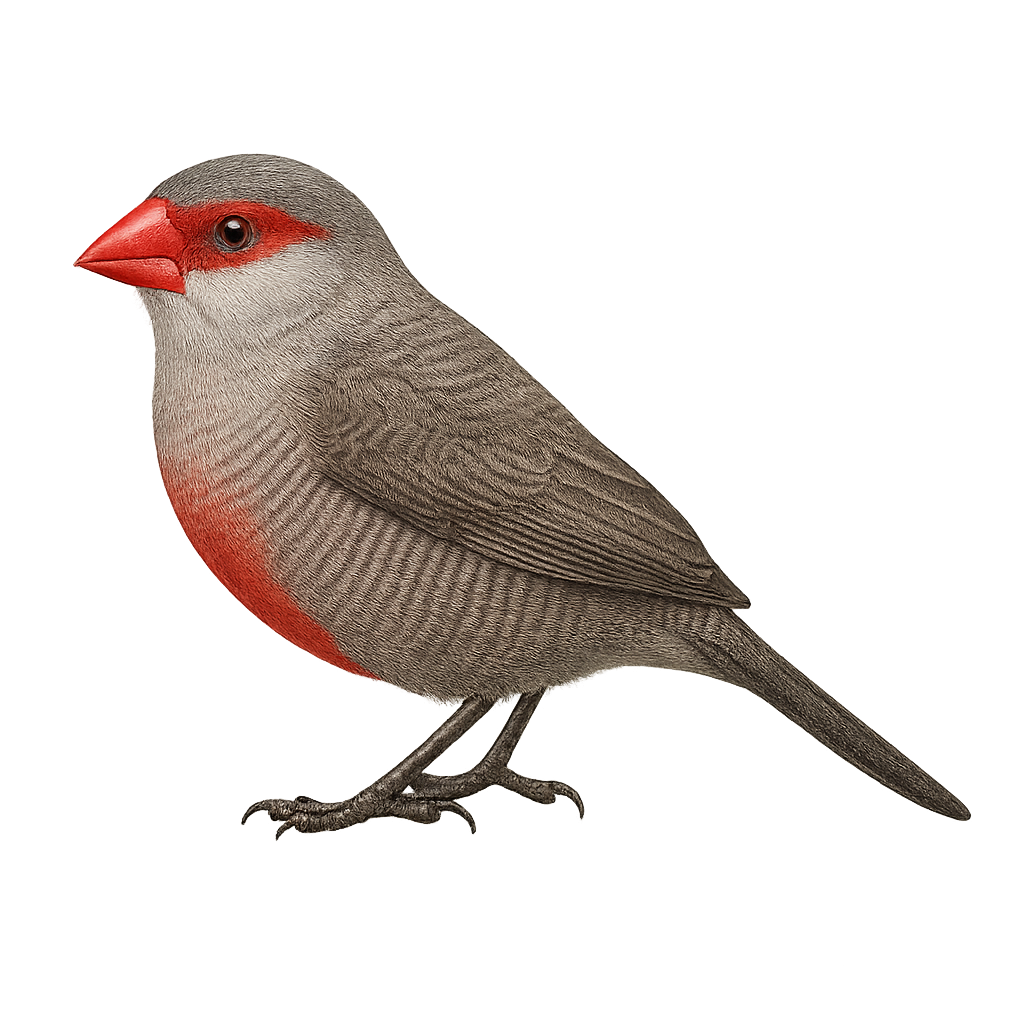
The common waxbill, or Estrilda astrild, is a small exotic bird native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is easily recognizable by its grey-brown plumage with a bright red stripe on its belly and around its eyes. Measuring about 11 to 13 cm in length, this bird is often seen in groups in grassy areas, marshes, and gardens. Its conical beak is adapted to its diet mainly consisting of seeds, although it also consumes small insects. The common waxbill is appreciated for its soft and melodious song. Although often kept as an aviary bird, it has also adapted well to various environments outside its native habitat.
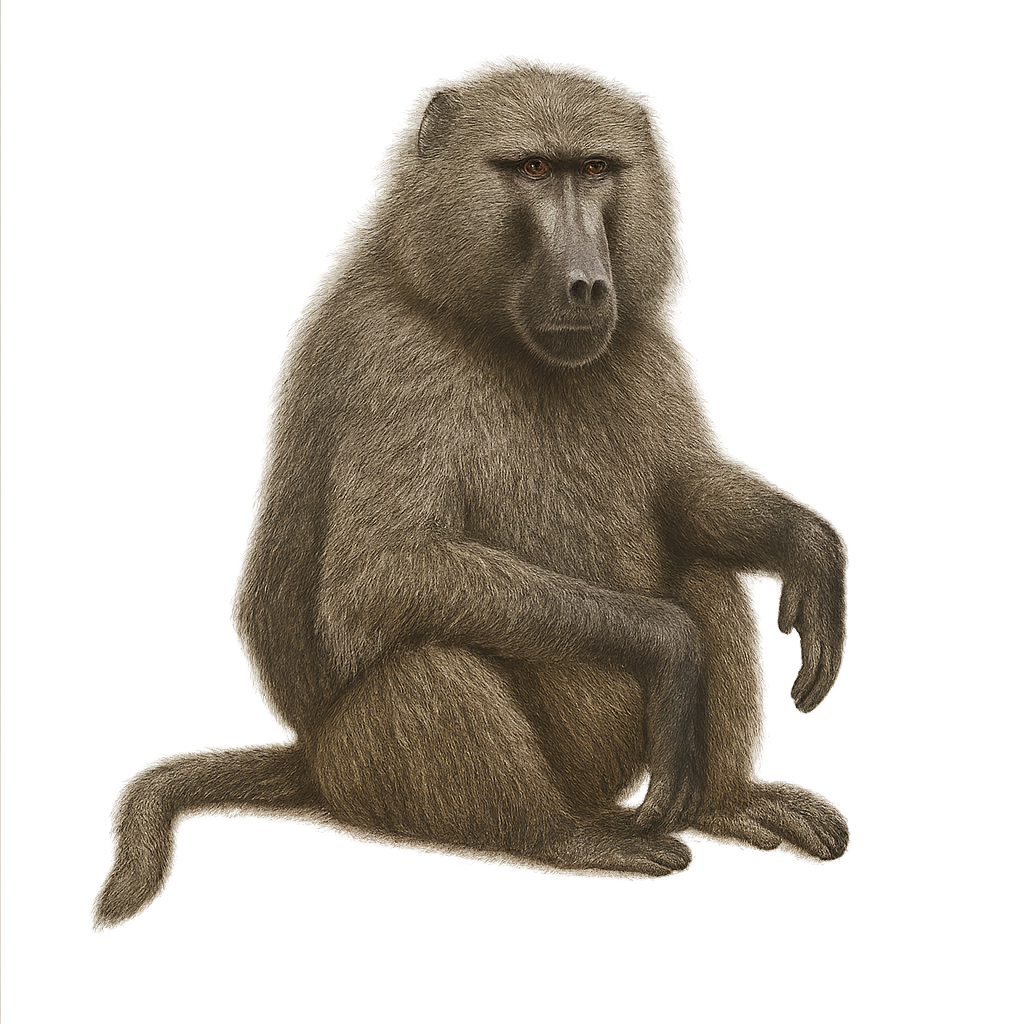
The chacma baboon, Papio ursinus, is a primate from the Cercopithecidae family, widely found in southern Africa. It is recognizable by its gray-brown fur and dark face, often surrounded by a lighter mane in males. Chacma baboons live in complex social groups that can number up to 100 individuals. They are omnivorous, feeding on fruits, seeds, insects, and small vertebrates. Their habitat ranges from savannas to open forests and rocky areas. Known for their intelligence, they can adapt to various environments, including urban areas. Although sometimes considered pests, they play a crucial role in their ecosystem.
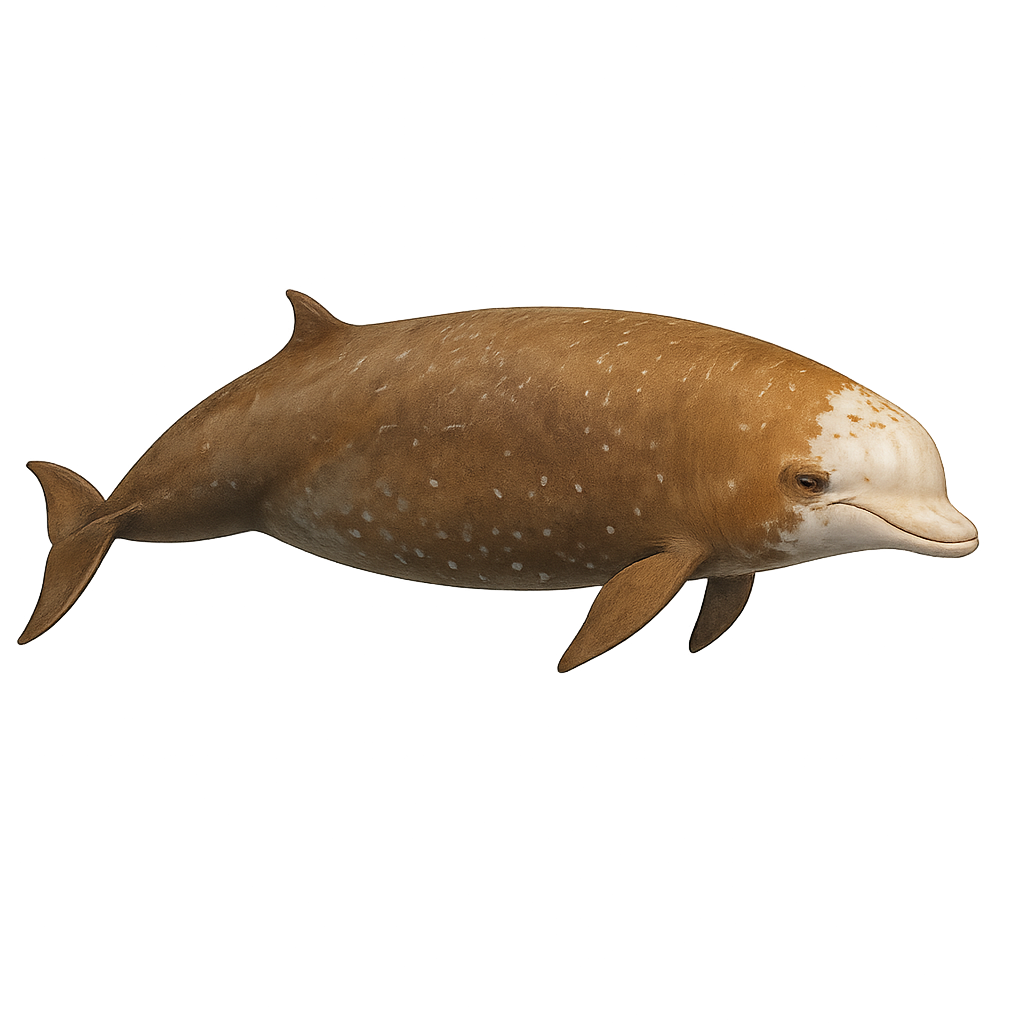
Cuvier's beaked whale, also known as the Cuvier's whale, is a deep-diving cetacean found primarily in tropical and temperate oceans worldwide. It is easily recognized by its elongated head and prominent beak. This cetacean is one of the deepest diving whales, capable of descending more than 2000 meters in search of food. Its diet primarily consists of squid and deep-sea fish. Although it is a difficult animal to observe due to its deep habitat, it is sometimes seen at the surface to breathe. Cuvier's beaked whale is known for its long dives and mysterious behaviors.
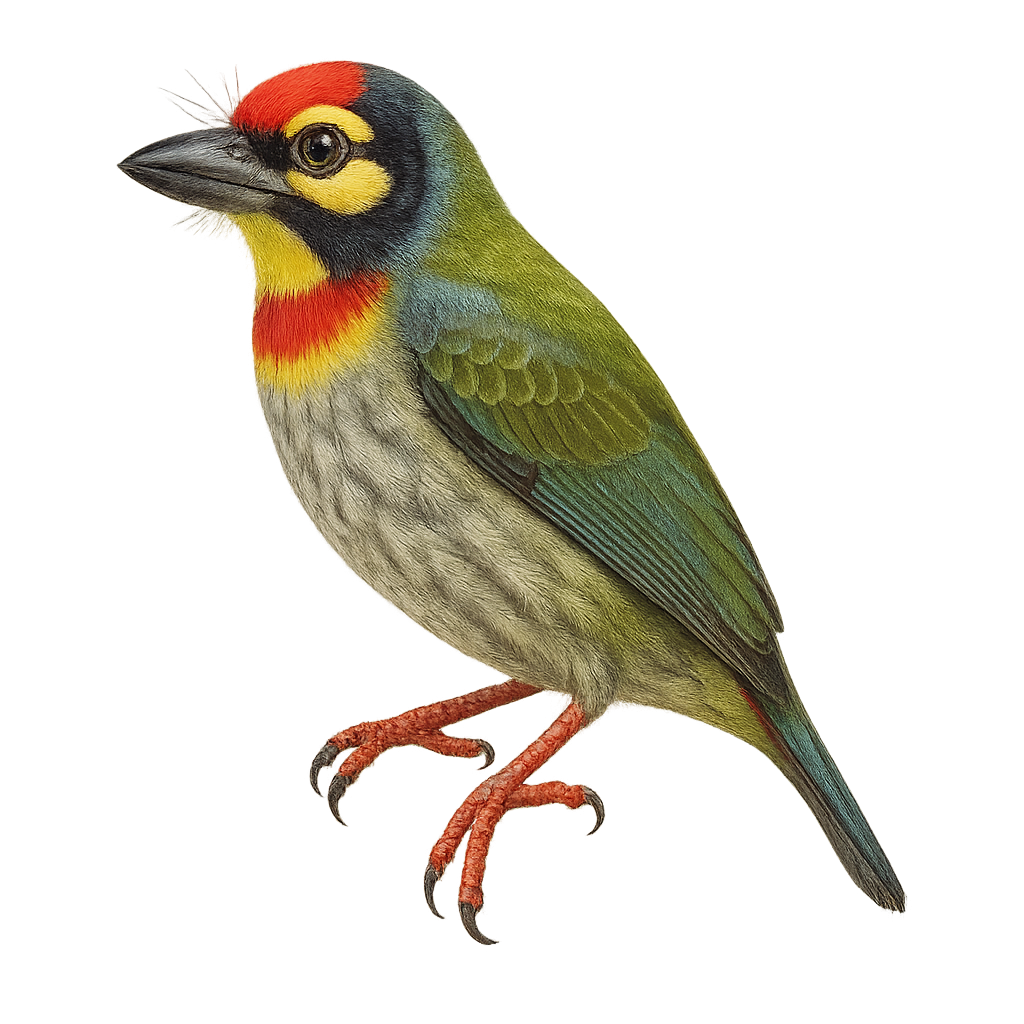
The Psilopogon haemacephalus, commonly known as the Coppersmith Barbet, is a small, colorful bird from the Megalaimidae family. It is easily recognized by its bright red head, yellow belly, and green wings. This barbet is often found in the tropical and subtropical forests of South and Southeast Asia. It is famous for its repetitive call that resembles the sound of a hammer striking metal, hence its English name "Coppersmith". These birds are primarily frugivorous but also consume insects. They nest in tree cavities, which they excavate with their strong beaks. Although generally solitary, they can be seen in small family groups.
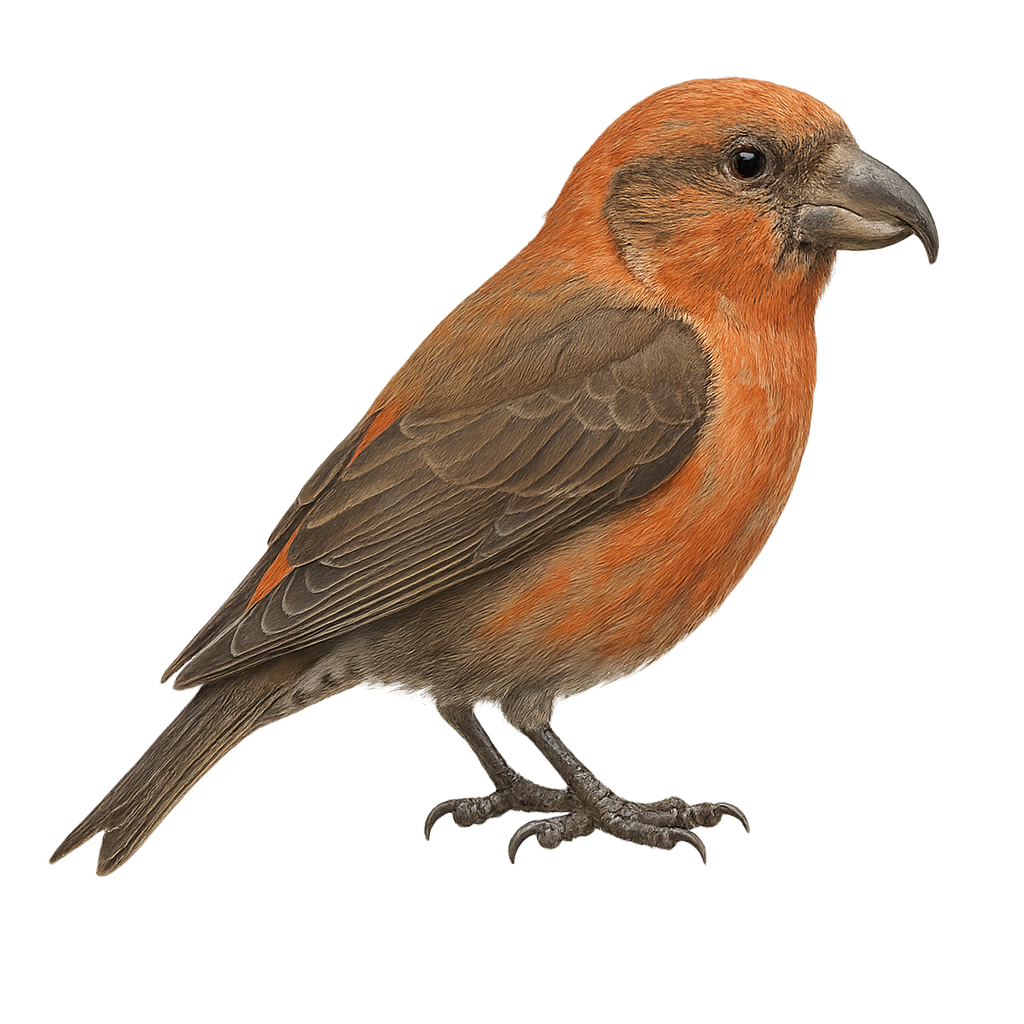
The crossbill is a passerine bird found primarily in coniferous forests across Europe, Asia, and North America. It is easily recognized by its bright red plumage in males and its crossed bill, which allows it to extract seeds from pine cones and other conifers. This small bird is often seen in groups, primarily feeding on tree seeds. It is also known for its melodious song.
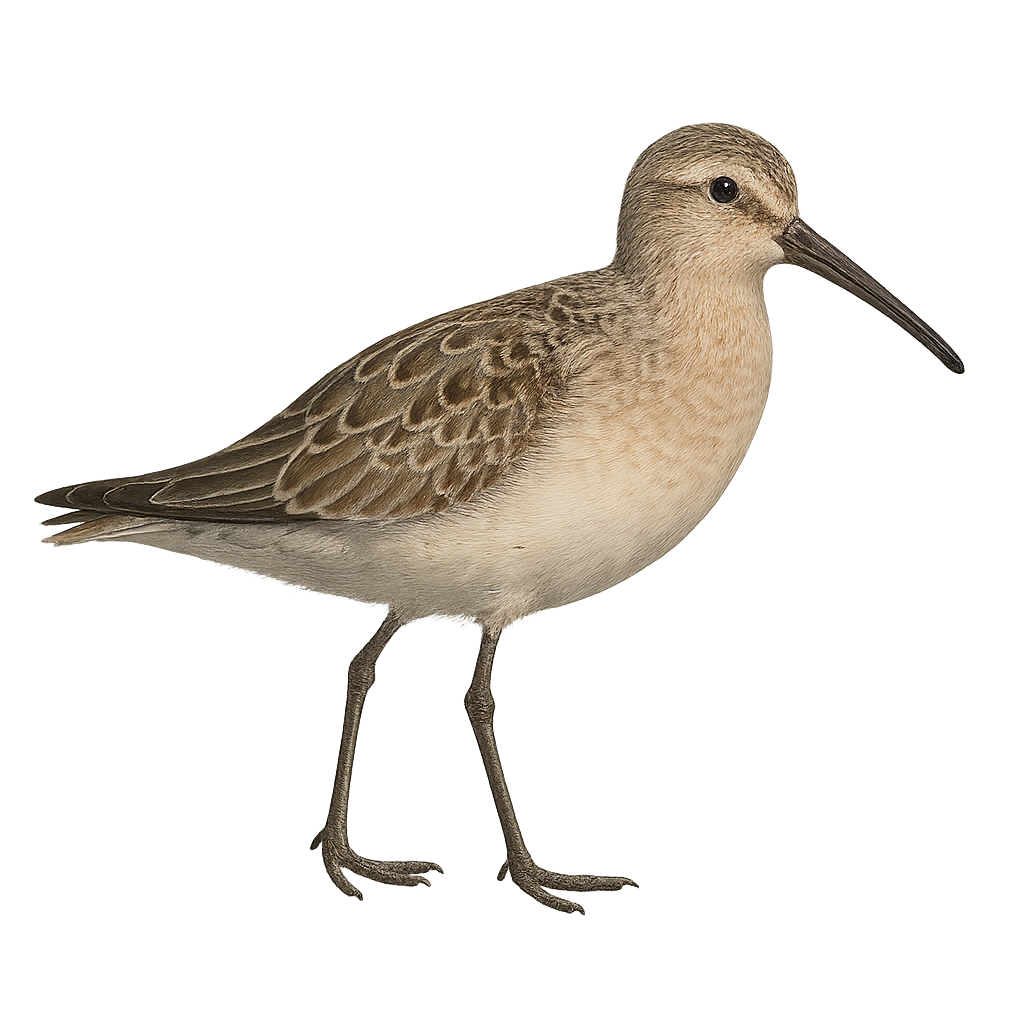
The Curlew Sandpiper, Calidris ferruginea, is a small wader belonging to the Scolopacidae family. It is easily identifiable by its reddish breeding plumage and slightly curved long bill. Outside the breeding season, its plumage turns duller with grayish tones. This migratory bird travels long distances between its breeding grounds in Siberia and its wintering areas in Africa, South Asia, and Australia. It primarily inhabits coastal wetlands, estuaries, and lagoons, feeding on small invertebrates by probing the mud with its bill. The Curlew Sandpiper is a gregarious bird, often seen in large flocks during migration.
The Common Snipe is an elegant small wader, easily recognized by its long, slender bill and mottled brown and beige plumage. This bird primarily inhabits marshes, wet meadows, and riverbanks in Europe, Asia, and North Africa, where it feeds on aquatic invertebrates, mainly worms, insects, and mollusks. The Common Snipe uses its long, flexible bill to probe the mud in search of food.
It is a migratory bird, leaving the cold regions of winter to move to more temperate zones for breeding. While its population is relatively stable, the Common Snipe is sensitive to habitat changes and water pollution.
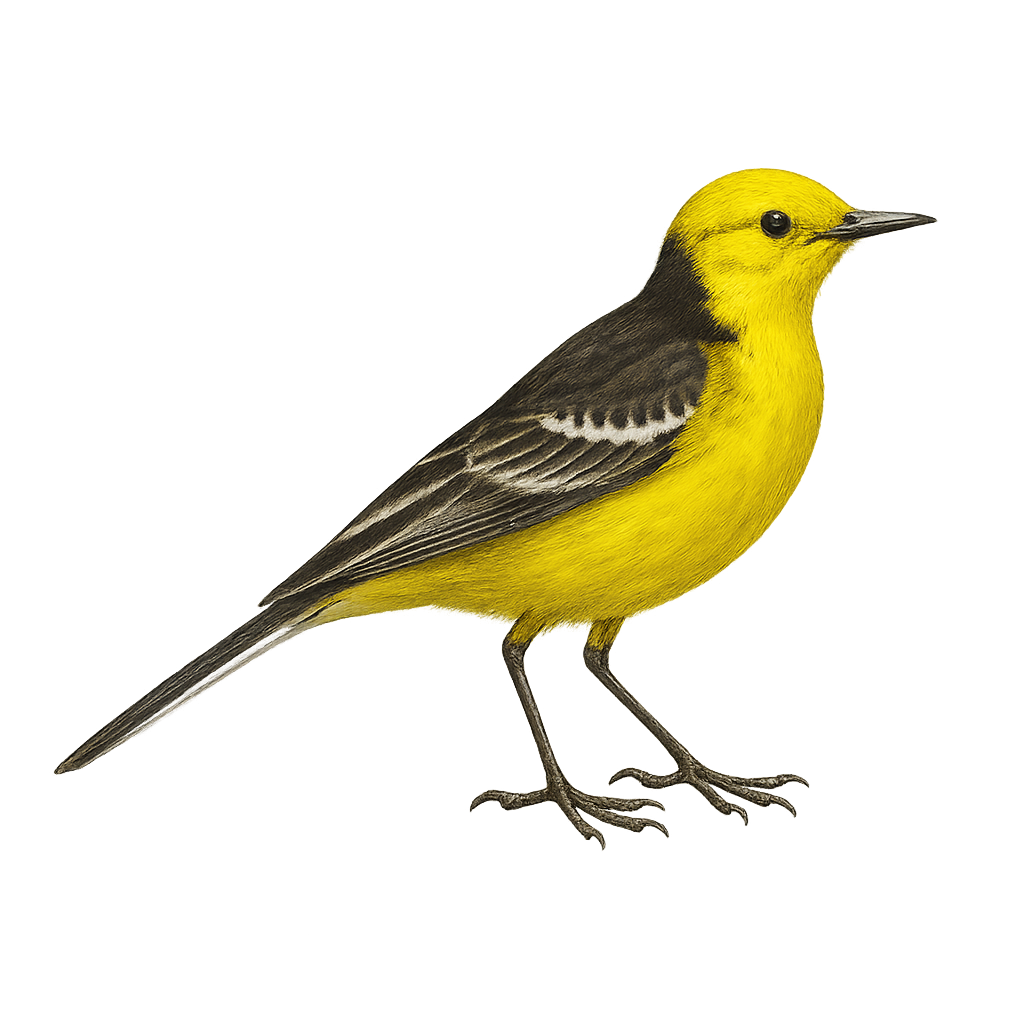
The Citrine Wagtail, or Motacilla citreola, is an elegant and colorful bird belonging to the Motacillidae family. It is distinguished by its bright yellow plumage on the belly and chest, contrasting with a gray back and a black head in males during the breeding season. Females and juveniles display duller shades, with gray and brown hues. This bird is often found in wetlands, meadows, and riverbanks, where it primarily feeds on insects and small invertebrates. A migratory species, the Citrine Wagtail breeds mainly in Central Asia and migrates to South Asia for the winter. Its characteristic gait, marked by a tail-wagging movement, makes it easily identifiable.
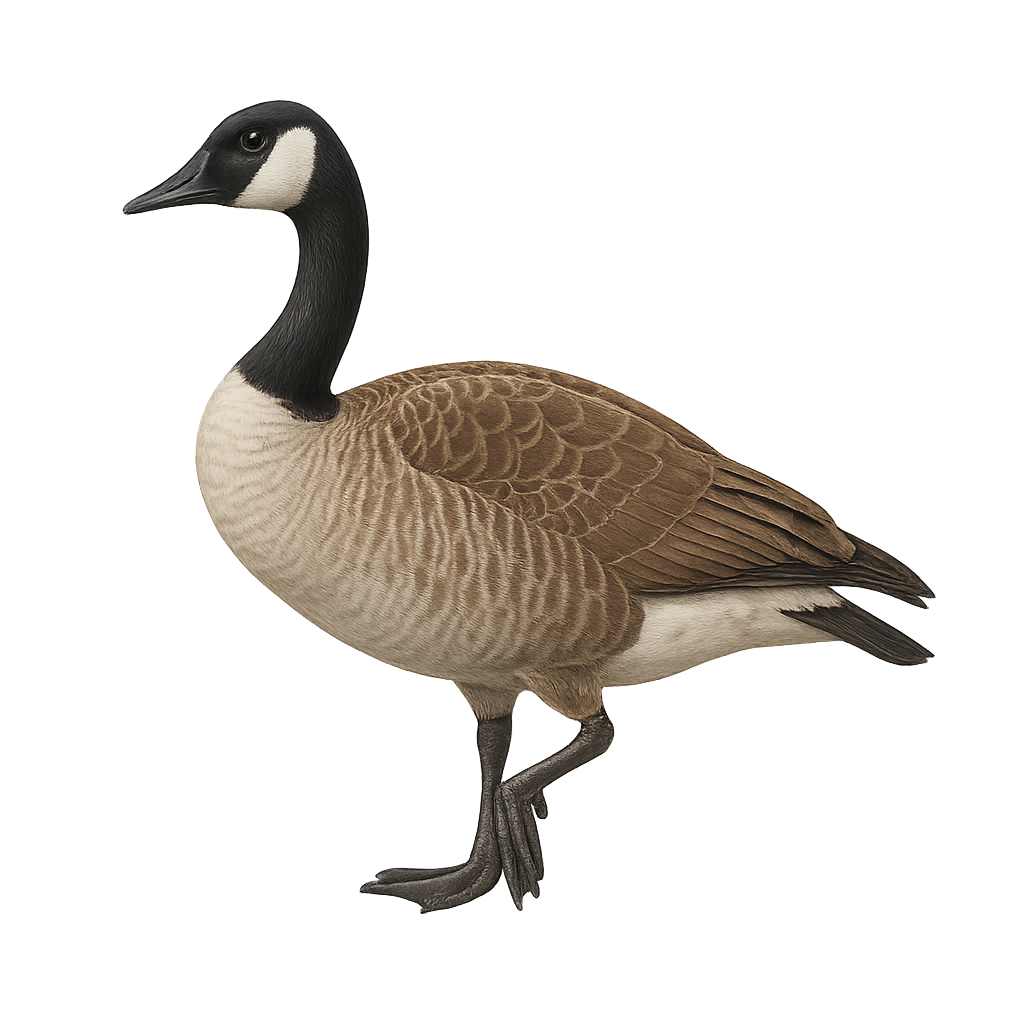
The Cackling Goose, scientifically known as Branta canadensis leucopareia, is a subspecies of the Anatidae family. It is easily identified by its brown and white plumage, long black neck, and white cheeks. It primarily inhabits wetlands, lakes, and rivers. This species is known for its spectacular migrations in large V-shaped formations. Highly adaptable, it can be found in various environments, including urban parks. Although generally tolerant of human presence, it can become aggressive if threatened, especially during nesting season.
The Cackling Goose, or Branta hutchinsii, is a medium-sized waterfowl belonging to the Anatidae family. Often mistaken for the Canada Goose due to their similar appearance, it is generally smaller with a shorter bill. Its plumage is primarily gray-brown with a distinctive black head and neck, featuring a white chinstrap. It primarily inhabits wetlands, lakes, and rivers, feeding on aquatic plants, seeds, and insects. A migratory bird, it travels long distances between its breeding grounds in Alaska and Canada and its wintering areas in the United States. Although generally wary, it can become accustomed to human presence in protected areas.
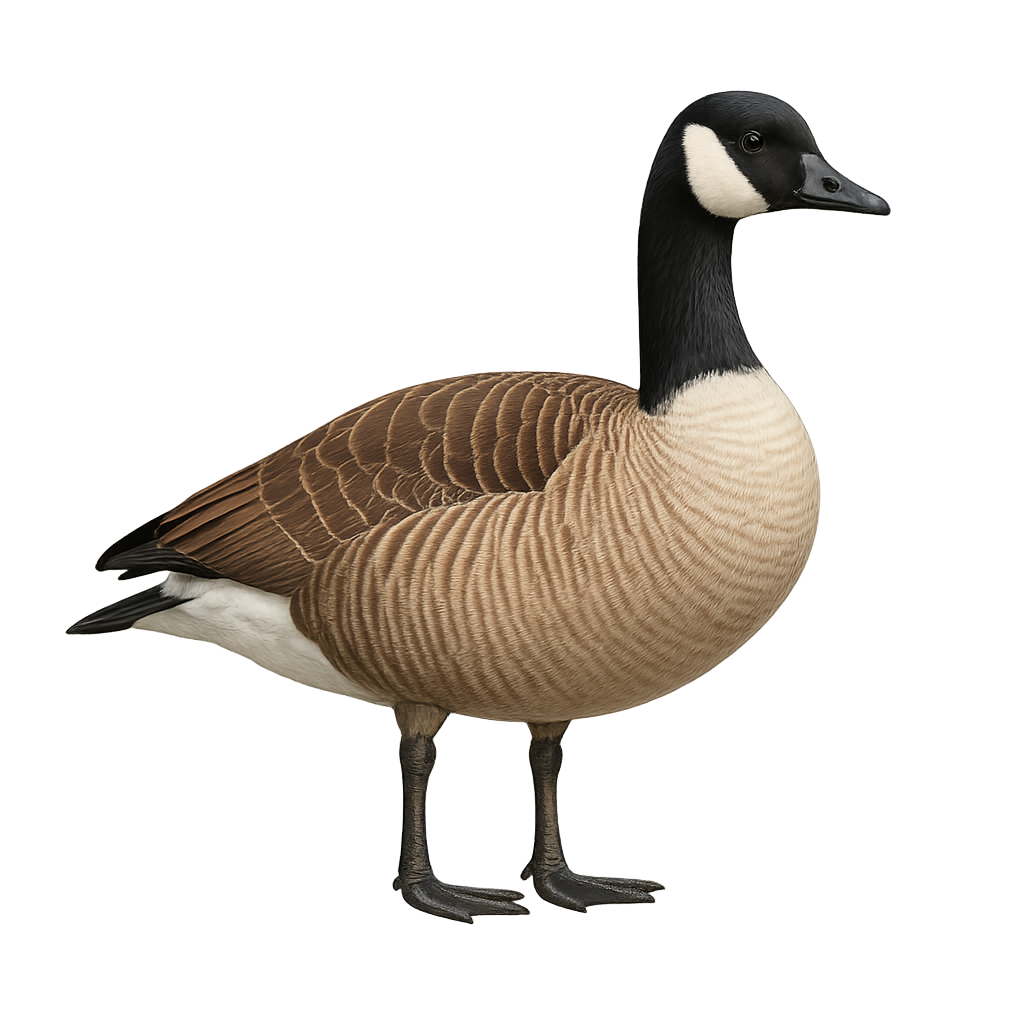
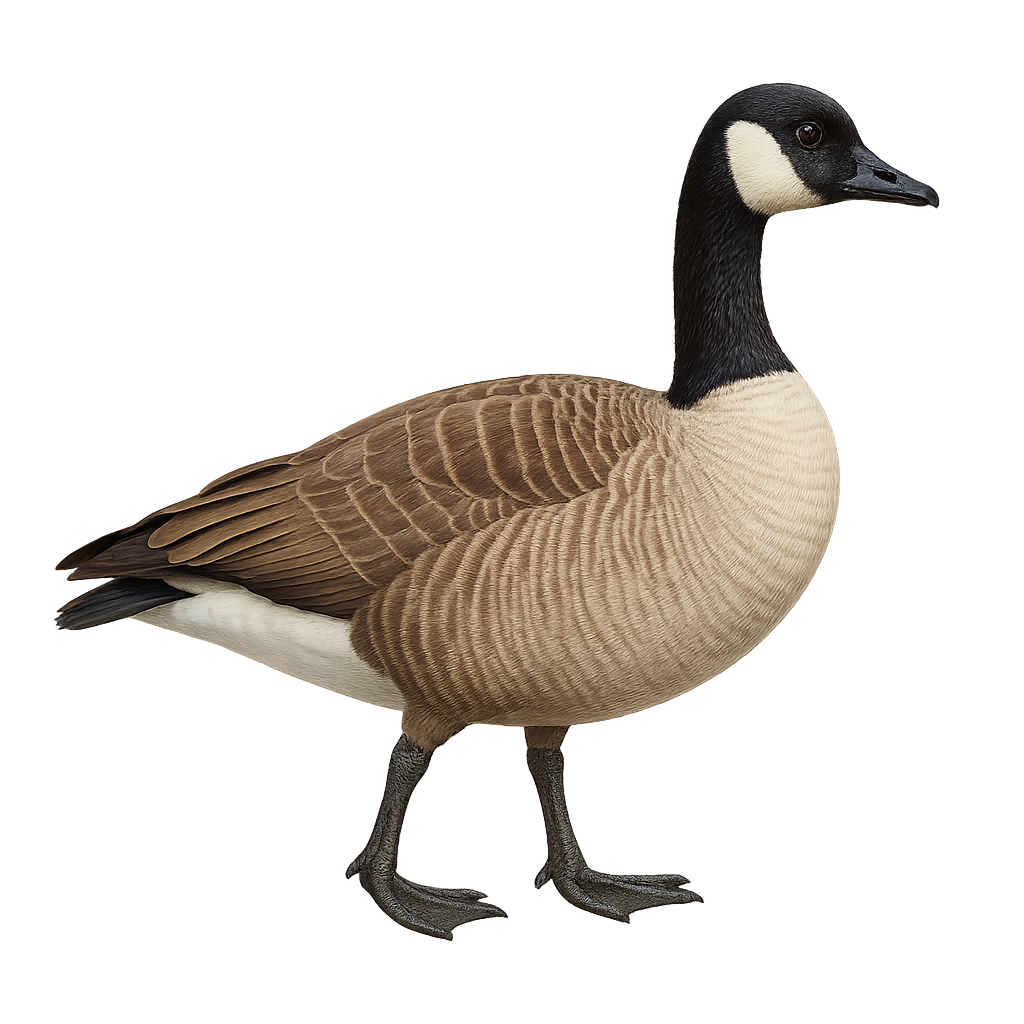
The Canada Goose is a large waterfowl species easily identified by its brown body, black head and neck, and distinctive white cheek patch. Often seen in large flocks, they form V-shaped formations during migration. These birds are highly adaptable, inhabiting a range of environments from lakes and rivers to urban parks. Their diet is diverse, including aquatic plants, seeds, and insects. While generally tolerant of humans, they can become aggressive if threatened, especially during nesting season.
The Crossley's Vanga is an endemic bird of Madagascar, belonging to the Vangidae family. It is distinguished by its colorful plumage, blending shades of blue, green, and black, and its robust, slightly hooked beak. This bird primarily inhabits the island's humid forests, where it feeds on insects and small invertebrates. Its melodious and varied song is often heard at dawn and dusk. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, the Crossley's Vanga is currently classified as "least concern" by the IUCN. However, it is essential to continue monitoring its populations to ensure its long-term conservation.
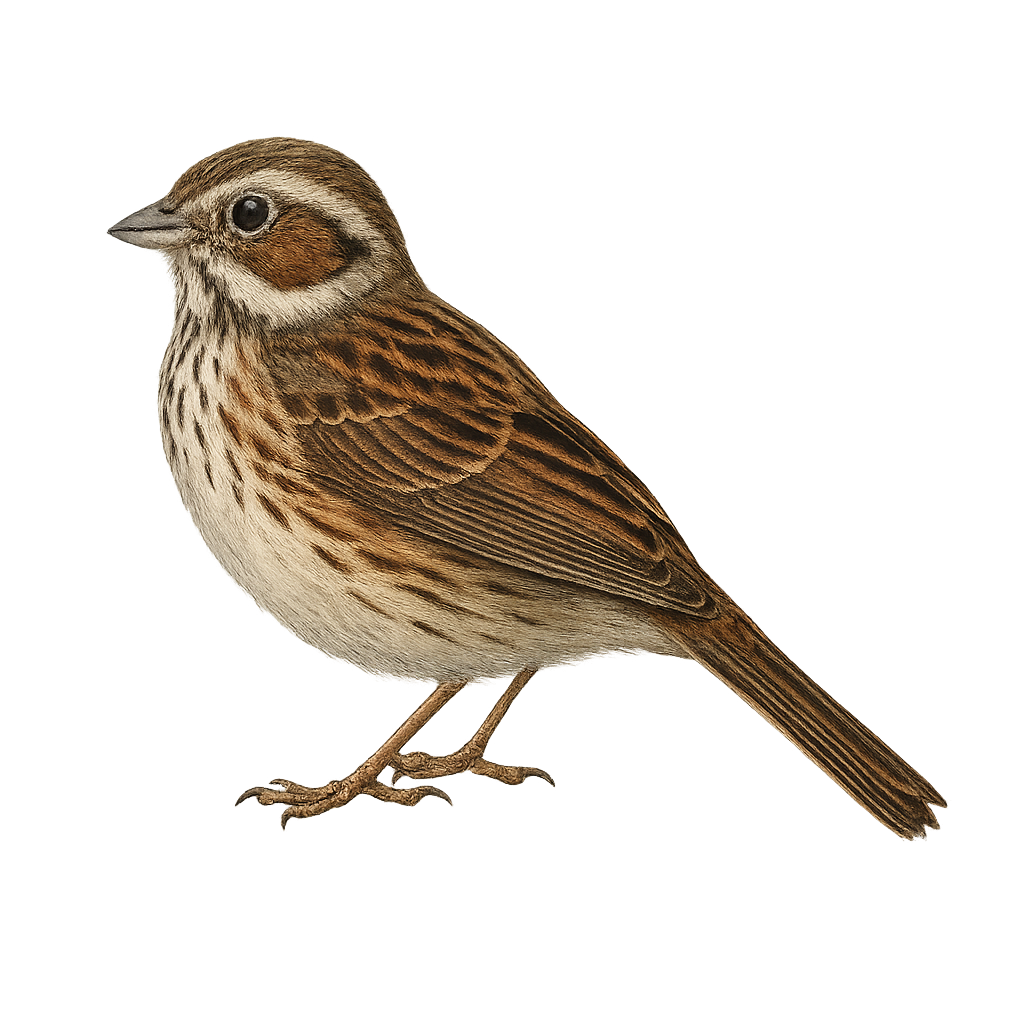
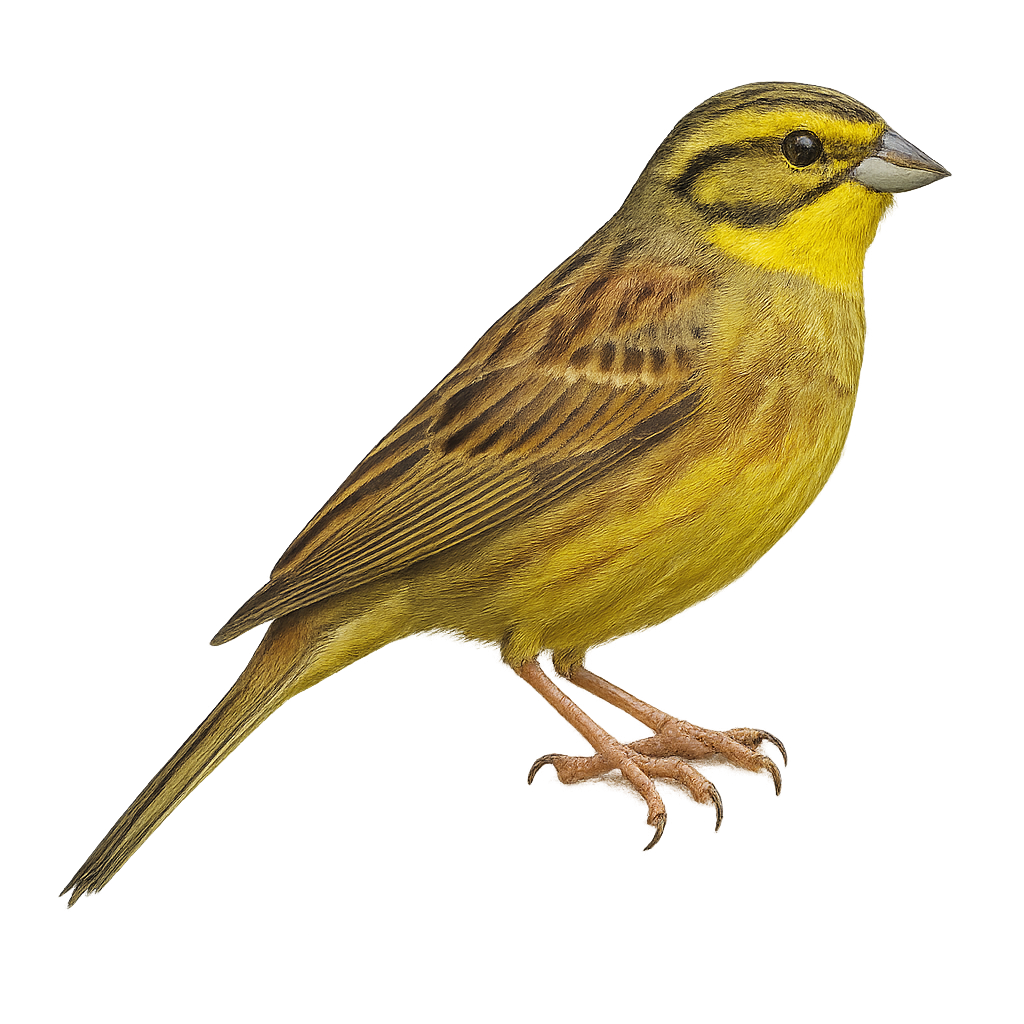
The Chestnut-eared Bunting, Emberiza fucata, is a small bird from the Emberizidae family. It is easily identifiable by its distinctive chestnut ear patches and brown and gray plumage. This passerine bird primarily inhabits open areas such as grasslands and cultivated fields, feeding on seeds and insects. It is commonly found in Asia, especially in China, Japan, and Russia. During the breeding season, the male sings to attract a mate, subsequently building a well-hidden nest in low vegetation. Although its conservation status is currently "least concern," habitat destruction could pose future threats.
The Cirl bunting is a small passerine in the bunting family Emberizidae, measuring 16–17 cm in length, with streaked brown plumage and a yellow head marked by a black crown and dark throat. It inhabits sunny grasslands, hedgerows and scrub, feeding mainly on seeds and insects. During breeding, it builds a nest in low bushes and the male sings from an exposed perch to attract the female and defend its territory.
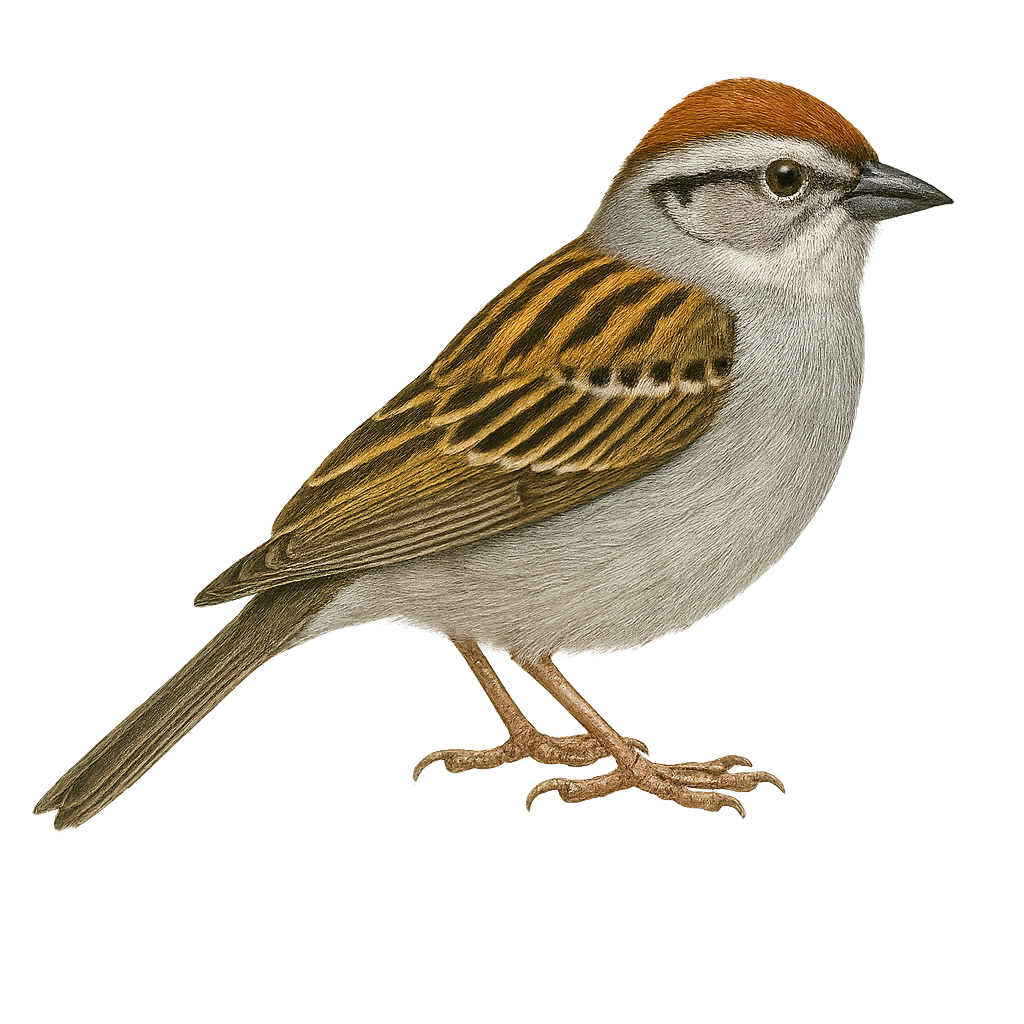
The Chipping Sparrow, or Spizella passerina, is a small songbird common in North America. It is easily identified by its rufous cap, gray cheeks, and black eye line. Its plumage is primarily brown with streaks on the back, while the underside is lighter. It inhabits open areas, gardens, and parks, often near human settlements. This sparrow is known for its simple yet melodious song, often heard in spring and summer. It primarily feeds on seeds and insects, which it finds on the ground or in shrubs. During the breeding season, it builds a cup-shaped nest in shrubs or low trees.
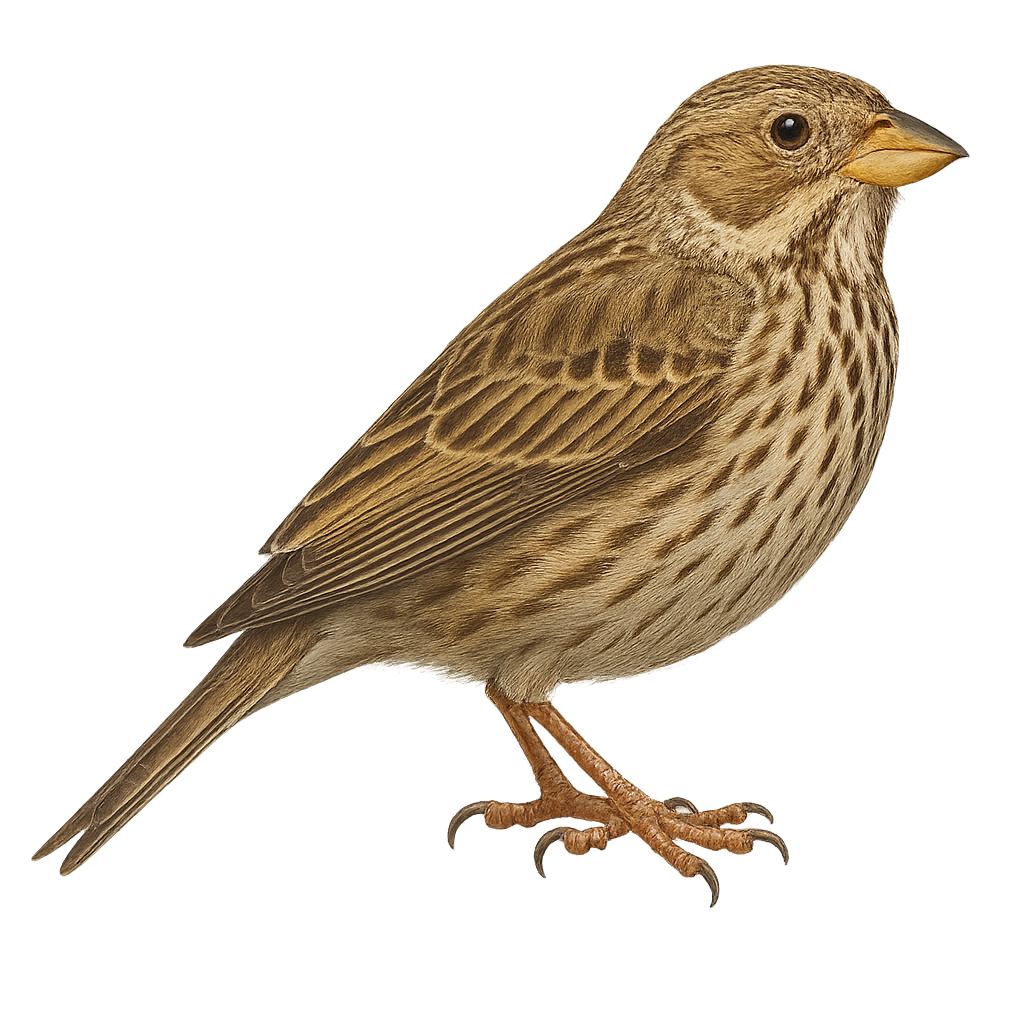
The corn bunting (Emberiza calandra) is a passerine bird in the family Emberizidae. It is a large, bulky bunting, 16–19 cm long, with heavily streaked buff-brown plumage. Found in open farmland, weedy wastelands and meadows across southern and central Europe, North Africa and Asia, it feeds mainly on seeds, supplemented by insects during the breeding season. During breeding it builds its nest on or near the ground, and the male sings from an exposed perch to attract the female and defend its territory.
The Damaliscus korrigum, commonly known as the Coke's hartebeest, is a large African herbivore belonging to the Bovidae family. It is characterized by its reddish-brown coat and lyre-shaped horns. Adapted to savannas and open grasslands, it is often seen in herds. Males are slightly larger than females and have more robust horns. They play a crucial role in the ecosystem by influencing vegetation structure. Their diet mainly consists of grasses, but they can also consume leaves and shoots. Although their population is stable in some areas, they are threatened by hunting and habitat loss.