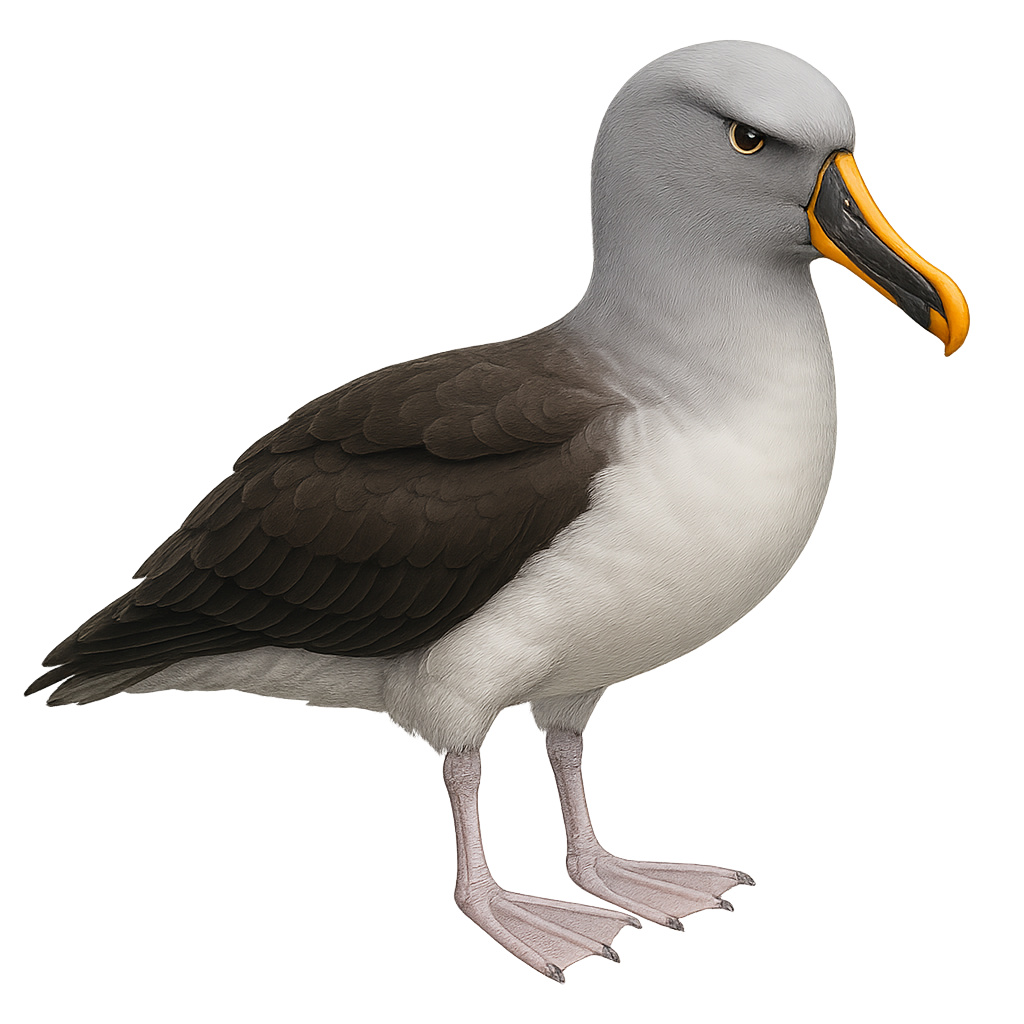
The Grey-headed Albatross, or Thalassarche chrysostoma, is a majestic seabird known for its grey head and bright yellow bill. It primarily inhabits the southern hemisphere's oceans, favoring cold and temperate waters. This albatross is an excellent glider, using air currents to travel long distances with minimal effort. It feeds mainly on fish, squid, and crustaceans, which it skillfully captures by diving. Breeding occurs on remote islands, where it builds mound-shaped nests. Although sociable at sea, it becomes territorial during the breeding season. Unfortunately, the species is threatened by longline fishing and climate change, which affect its food resources and nesting sites.
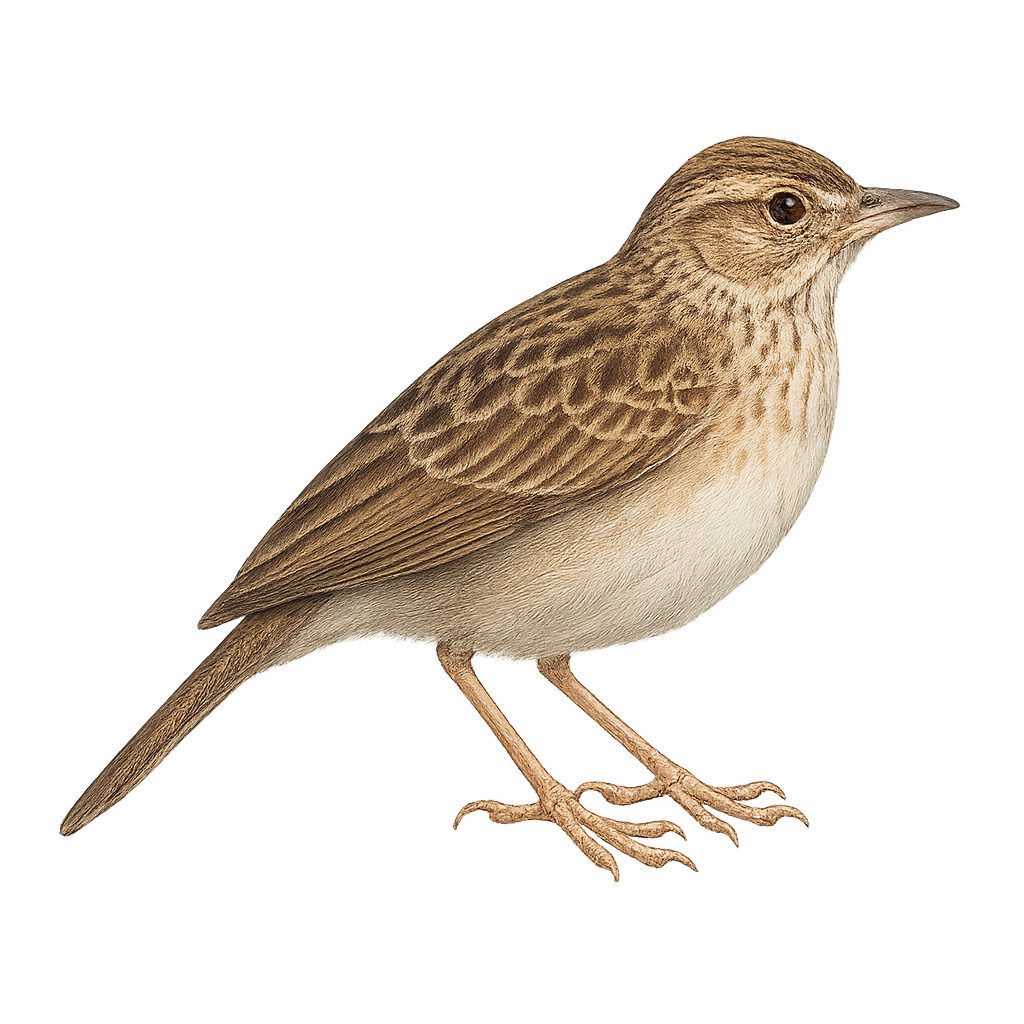
The Gillett's Lark (Calendulauda gilletti) is a discreet and little-known bird belonging to the Alaudidae family. It is mainly found in the arid and semi-arid regions of East Africa, particularly in Ethiopia and Somalia. This medium-sized bird has a sandy-brown plumage, perfect for blending into its desert environment. Its melodious and varied song is often heard at dawn and dusk, when it is most active. The Gillett's Lark primarily feeds on seeds and insects, which it finds by foraging on the ground. It builds its nest directly on the ground, hidden among dry grasses and shrubs.
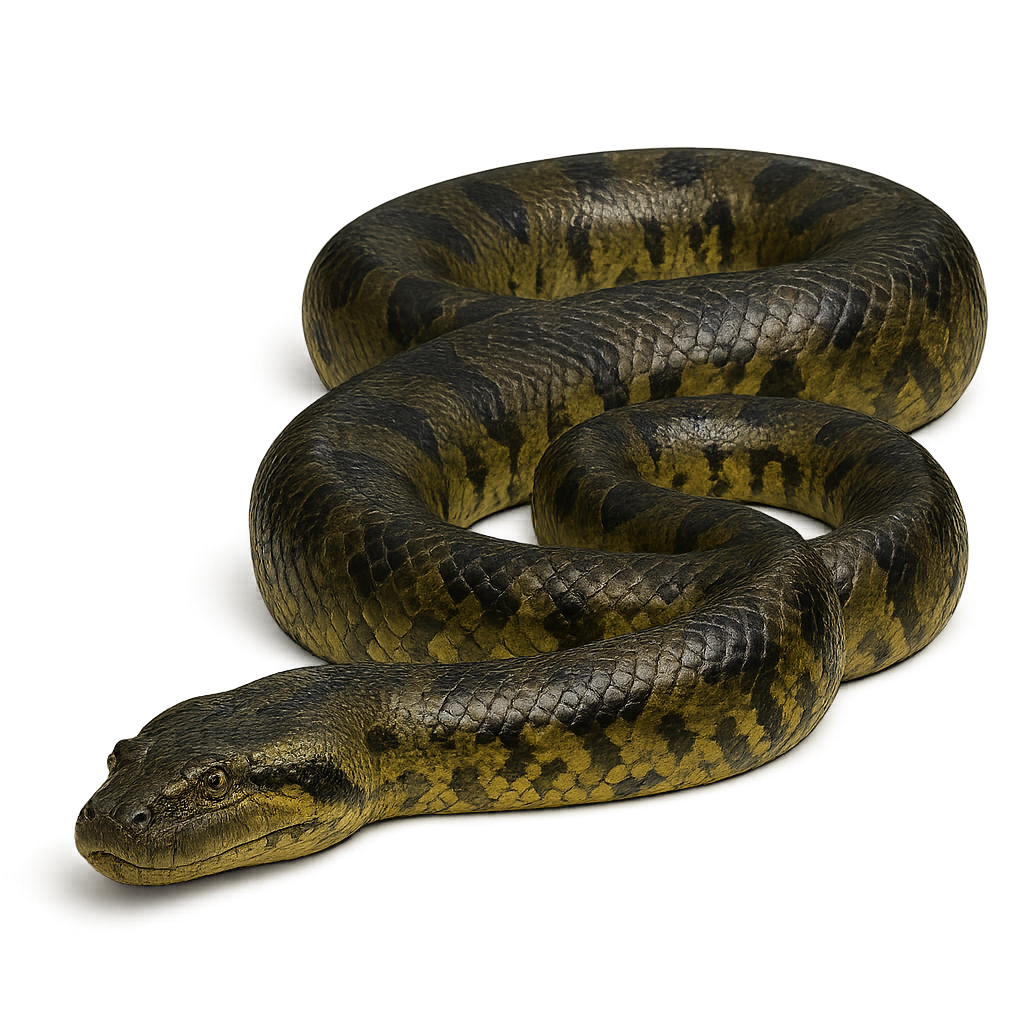
The Green Anaconda is one of the largest and most powerful snakes in the world, known for its impressive size, which can exceed 8 meters in length. This semi-aquatic snake lives in the rivers and swamps of the tropical forests of South America, where it preys on animals as large as caimans, deer, and fish. With its muscular body and constriction technique, the Anaconda can immobilize and swallow prey much larger than itself. It spends most of its time in the water, where it moves with remarkable agility.
Although often feared, the Green Anaconda is a discreet predator, preferring to camouflage itself in dense vegetation while waiting for prey.
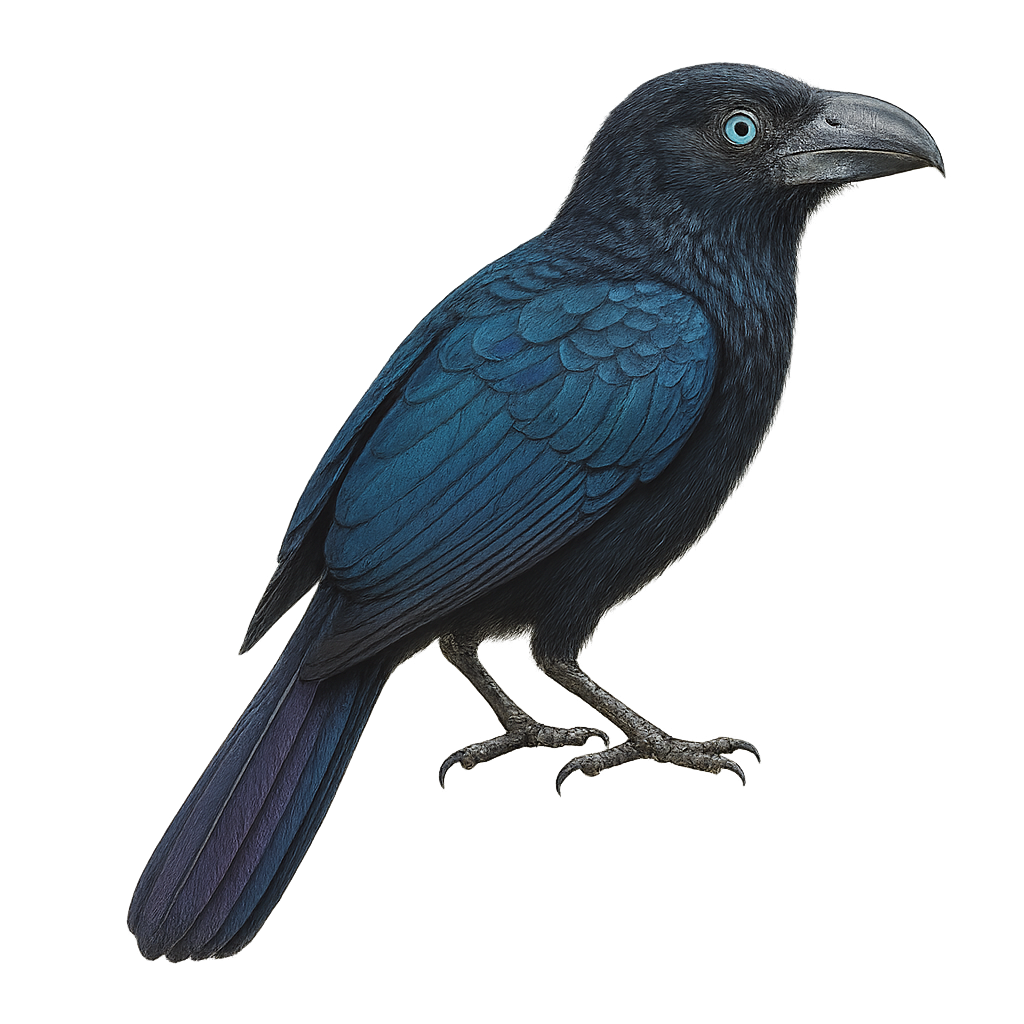
The Groove-billed Ani is a medium-sized bird, easily identified by its glossy black plumage and distinctive grooved bill. It is primarily found in tropical and subtropical regions of Central and South America. This sociable bird lives in family groups and feeds mainly on insects, fruits, and small vertebrates. It is often seen in open areas, grasslands, and forest edges. Its call is a mix of whistles and chirps. Although generally not very shy, it can be suspicious in the presence of potential threats.
The Greater Ani, scientifically known as Crotophaga major, is a bird belonging to the Cuculidae family, predominantly found in South America. It is recognized by its glossy black plumage and thick, curved bill. This bird measures about 48 cm in length and is often seen in noisy groups. It inhabits wetlands, swamps, and flooded forests. The Greater Ani is a social bird that builds communal nests where multiple females lay their eggs. Its diet mainly consists of insects, small vertebrates, and fruits. Although relatively common within its range, it is sometimes threatened by the destruction of its natural habitat.
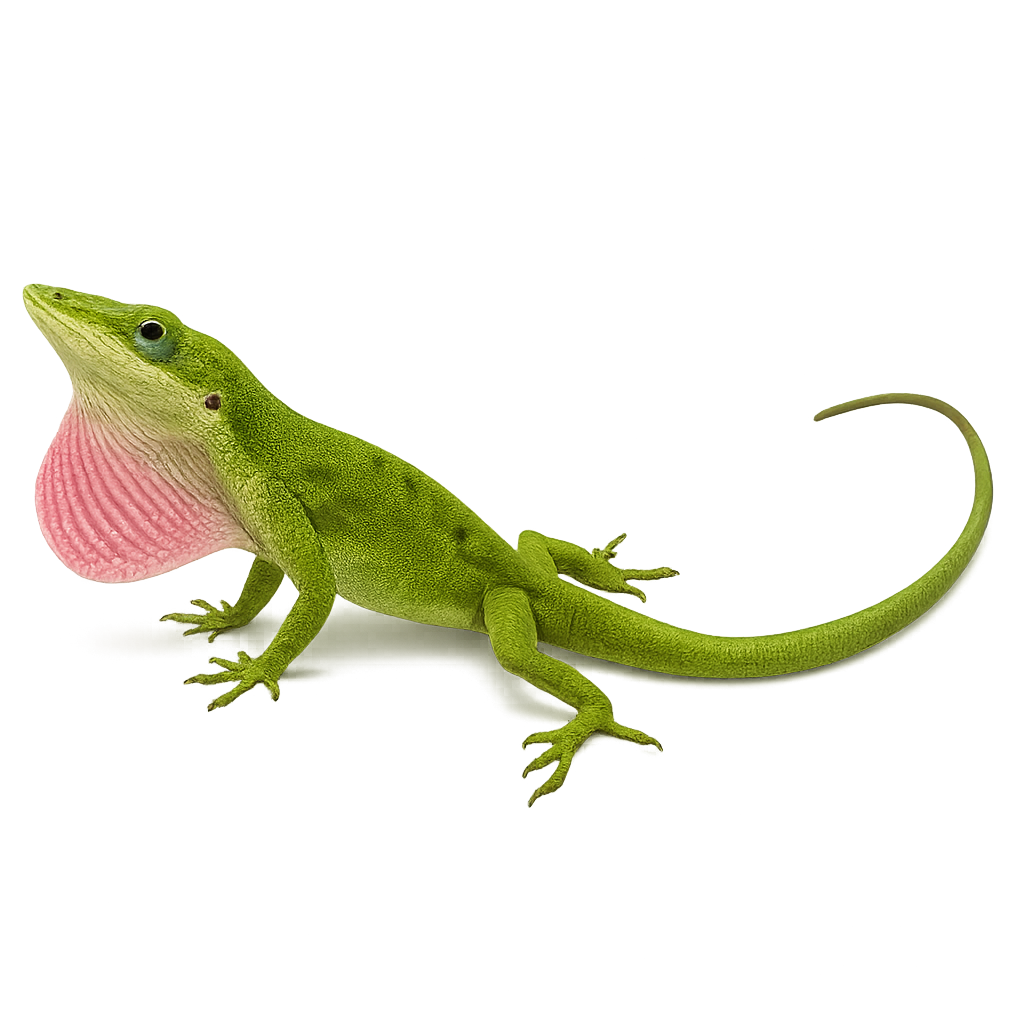
The Anolis carolinensis, commonly known as the green anole, is a small arboreal lizard native to the southeastern United States. It is easily recognizable by its bright green color, although it can change to brown depending on its mood or environment. Typically measuring between 12 and 20 cm, this anole has a long tail and adhesive toes that allow it to climb easily. It primarily feeds on insects and plays an important role in controlling pest insect populations. The green anole is often seen in gardens, forests, and urban areas, where it adapts well to human presence.
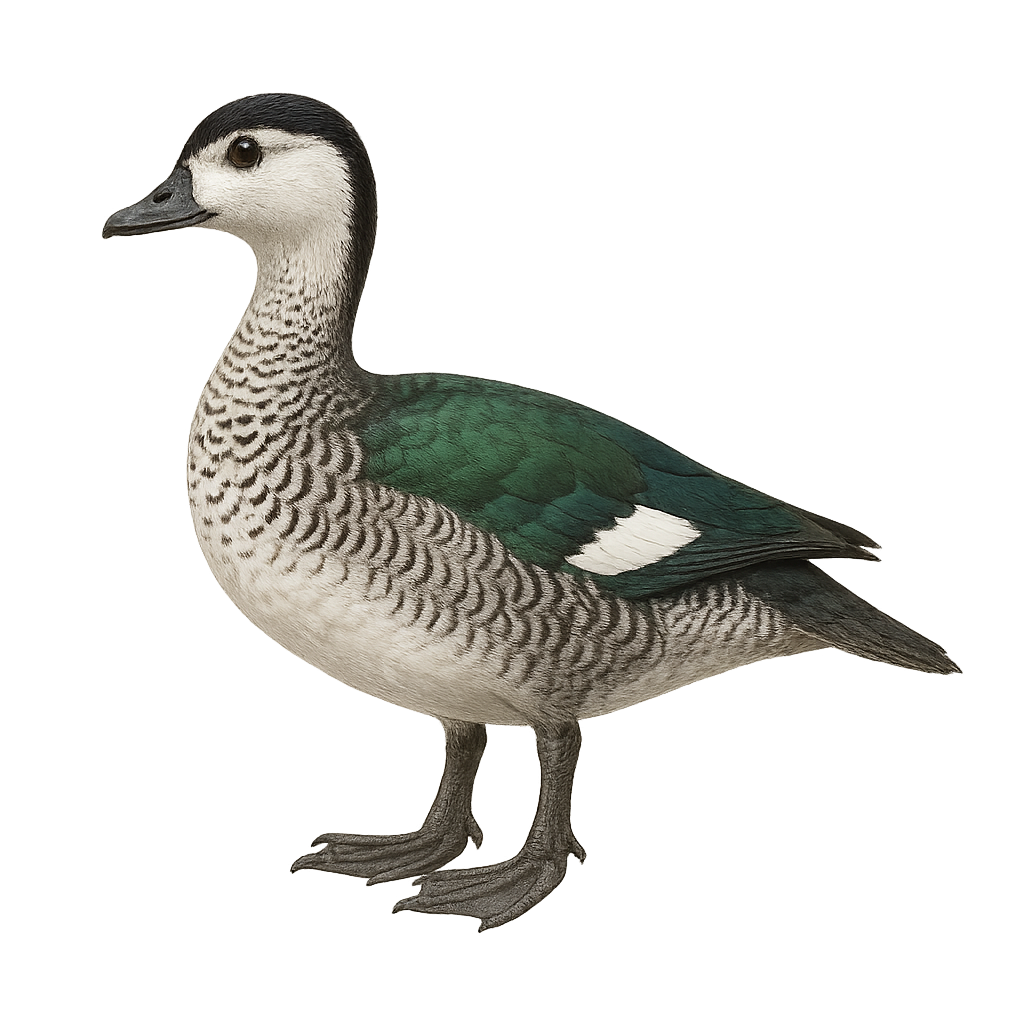
The Green Pygmy Goose, or Nettapus pulchellus, is a tiny, vibrantly colored duck found in northern Australia and New Guinea. Its plumage features metallic green, white, and dark brown tones, with a compact body and short bill. It inhabits lagoons, swamps, and flooded woodland areas. Omnivorous, it feeds on seeds, aquatic plants, and small invertebrates. Usually shy and solitary, it can also be seen in small groups. Its population is considered stable, although it relies heavily on healthy wetland ecosystems.
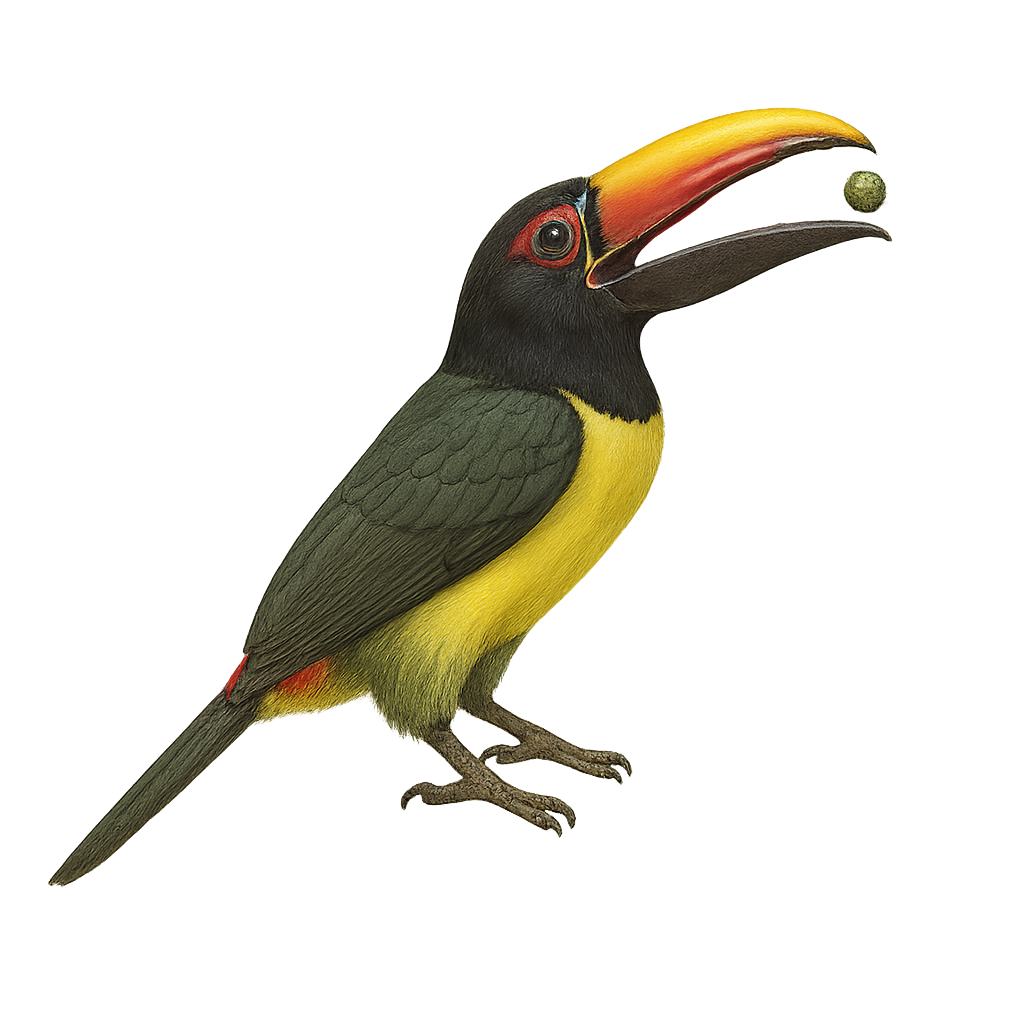
The Green Aracari, Pteroglossus viridis, is a colorful bird from the Ramphastidae family. It is distinguished by its bright green plumage, large bill, and red and yellow markings on its head and neck. This bird measures about 30 to 35 cm in length and weighs between 110 and 160 grams. It primarily inhabits the tropical rainforests of South America, particularly in Venezuela, Guyana, and northern Brazil. Arboreal, it mainly feeds on fruits but also consumes insects and small vertebrates. Sociable, it often lives in small family groups. Its call is a series of high-pitched, repetitive cries. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, the species is currently classified as "Least Concern" by the IUCN.
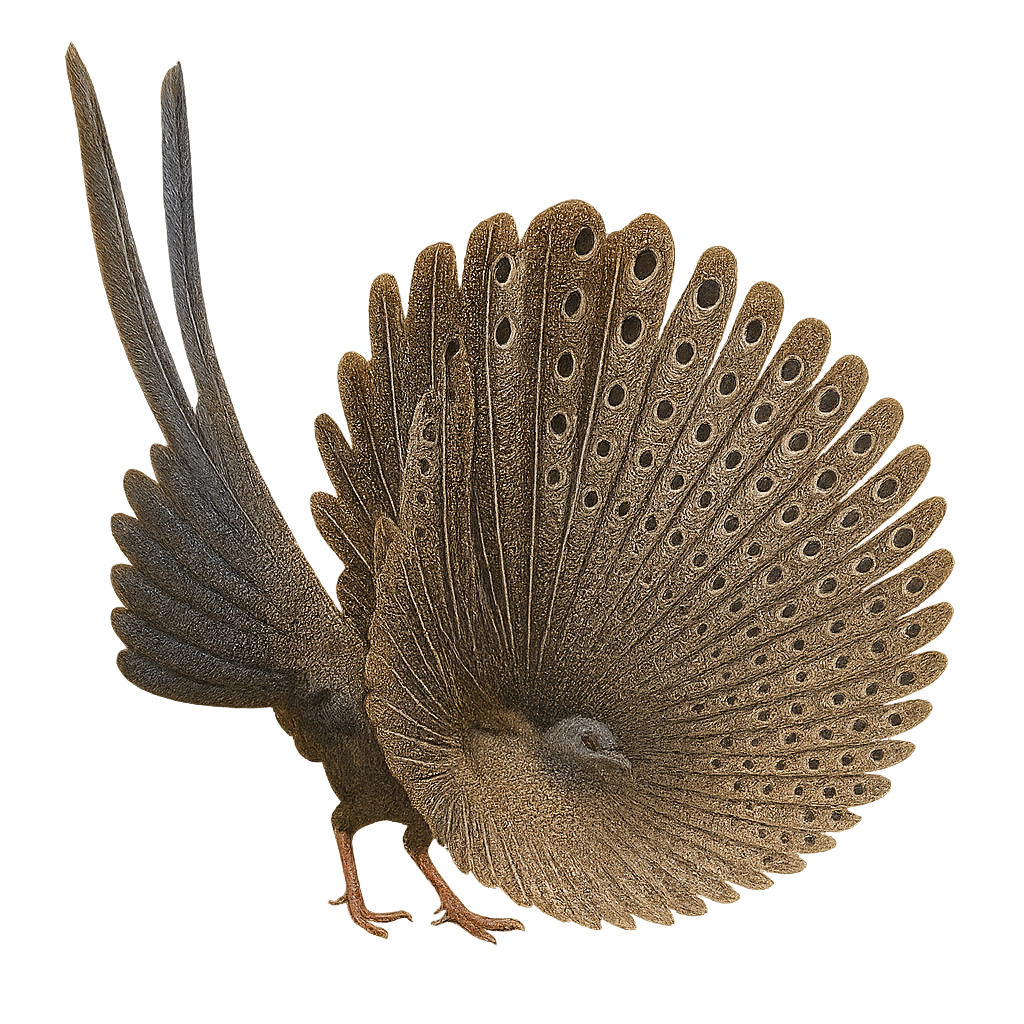
The Great Argus, or Argusianus argus, is a remarkable bird from the Phasianidae family, renowned for its spectacular plumage and fascinating courtship displays. Native to the tropical forests of Southeast Asia, this bird is distinguished by its long, ocellated feathers adorning its wings and tail. The male, larger than the female, uses these feathers to attract mates during elaborate courtship rituals. Primarily terrestrial, it prefers dense habitats where it can blend in. Although the Great Argus is a shy bird, it is sometimes seen in clearings searching for food, mainly fruits, insects, and small invertebrates. Its population is threatened by deforestation and hunting, leading to its classification as near threatened by the IUCN.
The Northern Goshawk is an elegant and powerful raptor, known for its slender silhouette and rapid, erratic flight through dense forests. This medium-sized hawk primarily inhabits temperate forests in Europe, Asia, and North America, where it hunts birds, primarily wood pigeons, doves, and sometimes smaller prey. The Northern Goshawk is an exceptional hunter, using its speed and precise aerial maneuvers to catch its prey.
Despite its remarkable flying skills, the Northern Goshawk is discreet and often difficult to spot, preferring to blend into its forest environment. While not currently threatened, habitat loss and human disturbance pose risks to its population.
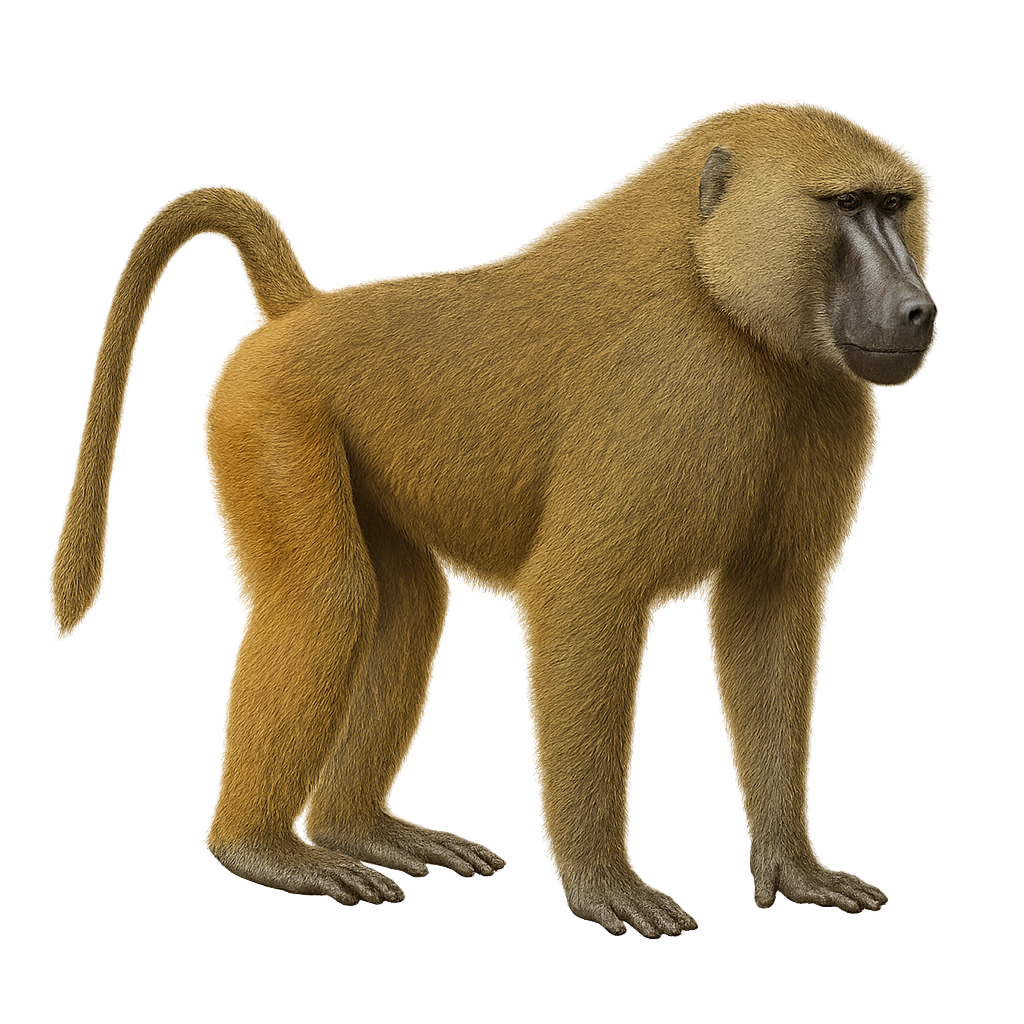
The Guinea baboon, Papio papio, is a medium-sized primate belonging to the Cercopithecidae family. It is primarily found in West Africa, particularly in Guinea, Senegal, and Gambia. This baboon is distinguished by its reddish-brown fur and black face. Males are generally larger than females and have a more developed mane. They live in complex social groups, often consisting of several dozen individuals. These primates are omnivorous, feeding on fruits, seeds, insects, and small animals. The Guinea baboon plays an important role in its ecosystem, particularly in seed dispersal.
The Greenland whale is one of the largest baleen whales, with a size that can reach 16 to 18 meters. It lives in the icy waters of the Arctic and primarily feeds on krill and small fish, filtering them through its baleen plates. It is a long-lived animal, with a lifespan that can exceed 200 years. While protected, it is threatened by climate change, pollution, and ship collisions.
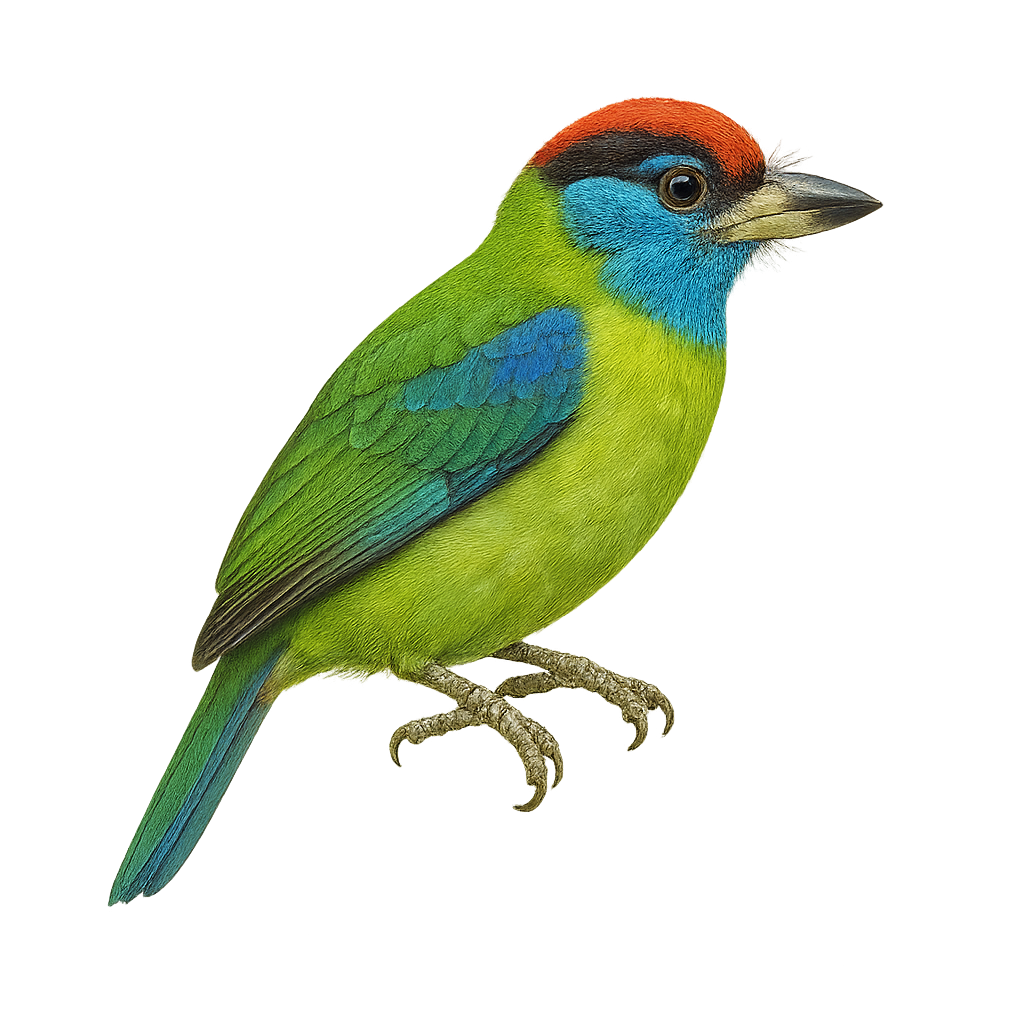
The Golden-throated Barbet, or Psilopogon franklinii, is a colorful bird from the Megalaimidae family. It is recognized by its vibrant green plumage, golden throat, and sturdy beak. This bird is primarily arboreal, feeding on fruits, insects, and occasionally small vertebrates. It inhabits the tropical and subtropical forests of Southeast Asia, particularly in mountainous regions. Its call is distinctive, often heard before the bird is seen. The Golden-throated Barbet is territorial, usually observed alone or in pairs. Although relatively common in its natural habitat, it is rarely seen outside dense forests.
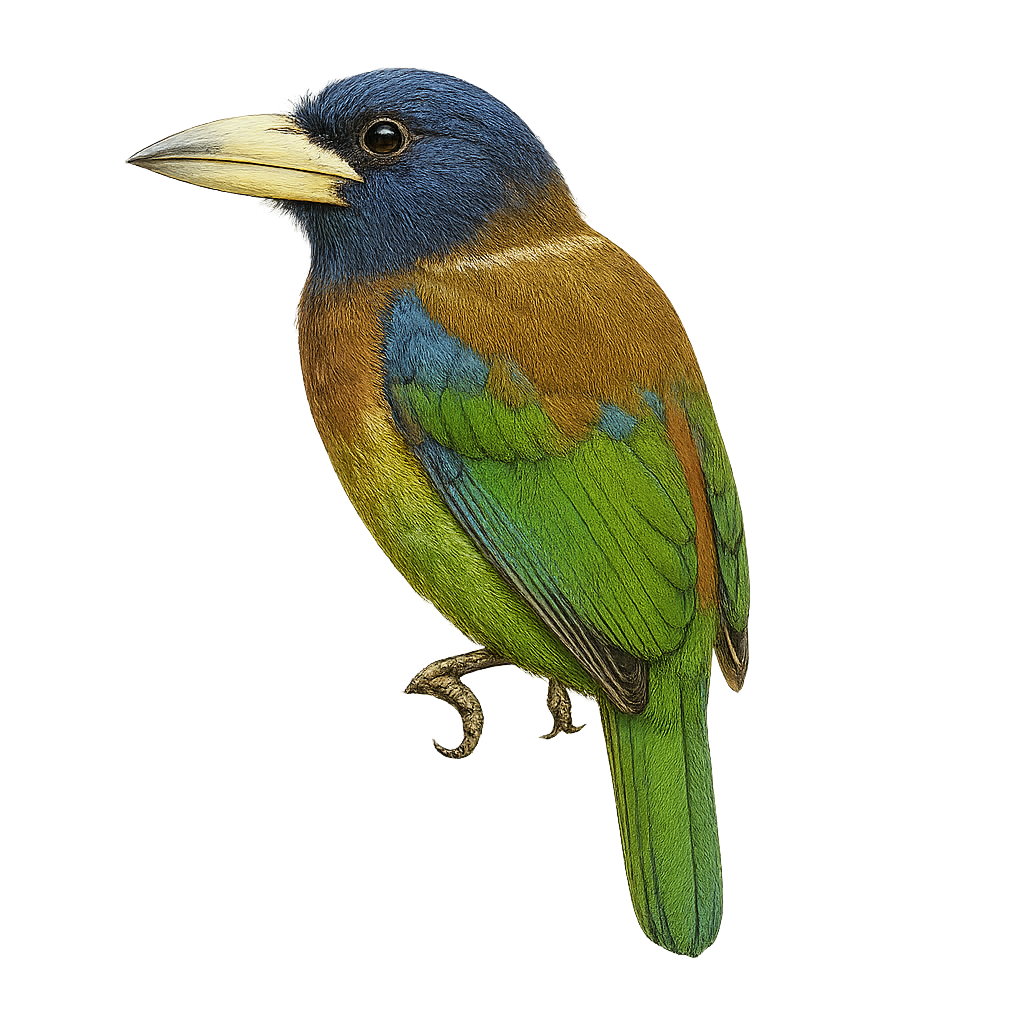
The Great Barbet, or Megalaima virens, is a colorful bird from the Megalaimidae family. It is primarily found in the tropical and subtropical forests of South and Southeast Asia, particularly in the mountainous regions of the Himalayas. This bird is distinguished by its bright green plumage, blue head, and red throat. It measures about 30 cm in length and has a robust beak adapted to its diet, which mainly consists of fruits but also includes insects. The Great Barbet is a diurnal bird, often seen alone or in small groups. It is known for its loud and repetitive call that echoes through the canopy. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it is currently classified as of least concern by the IUCN.
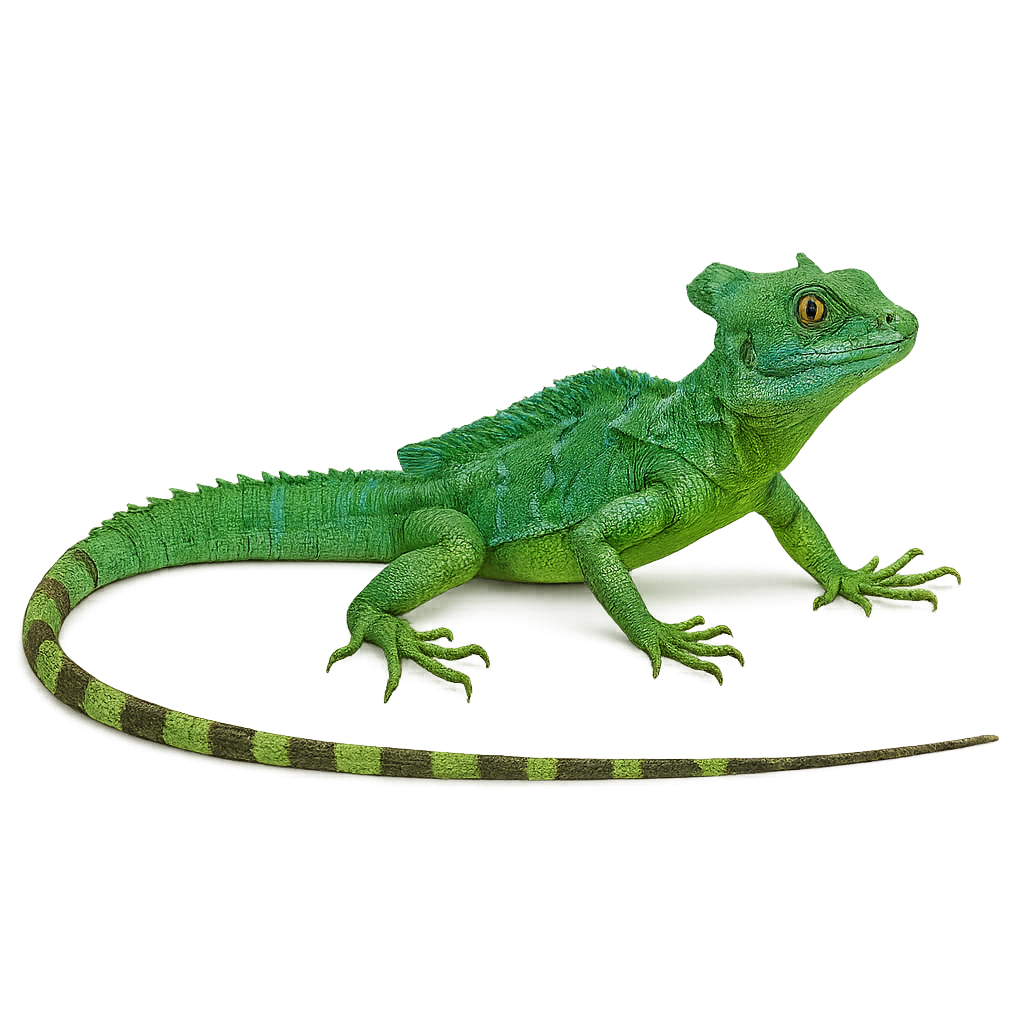
The Green Crested Basilisk is an impressive species native to the tropical forests of Central America. This lizard is famous for the distinctive crest on its head and back, as well as for its ability to run on water, earning it the nickname 'Jesus Christ lizard.' It uses this ability to escape predators by running at high speed across shallow water surfaces. Primarily arboreal, it spends much of its life in trees and bushes, where it feeds on small insects, fruits, and flowers. This lizard is also known for its bright green color and distinctive patterns.
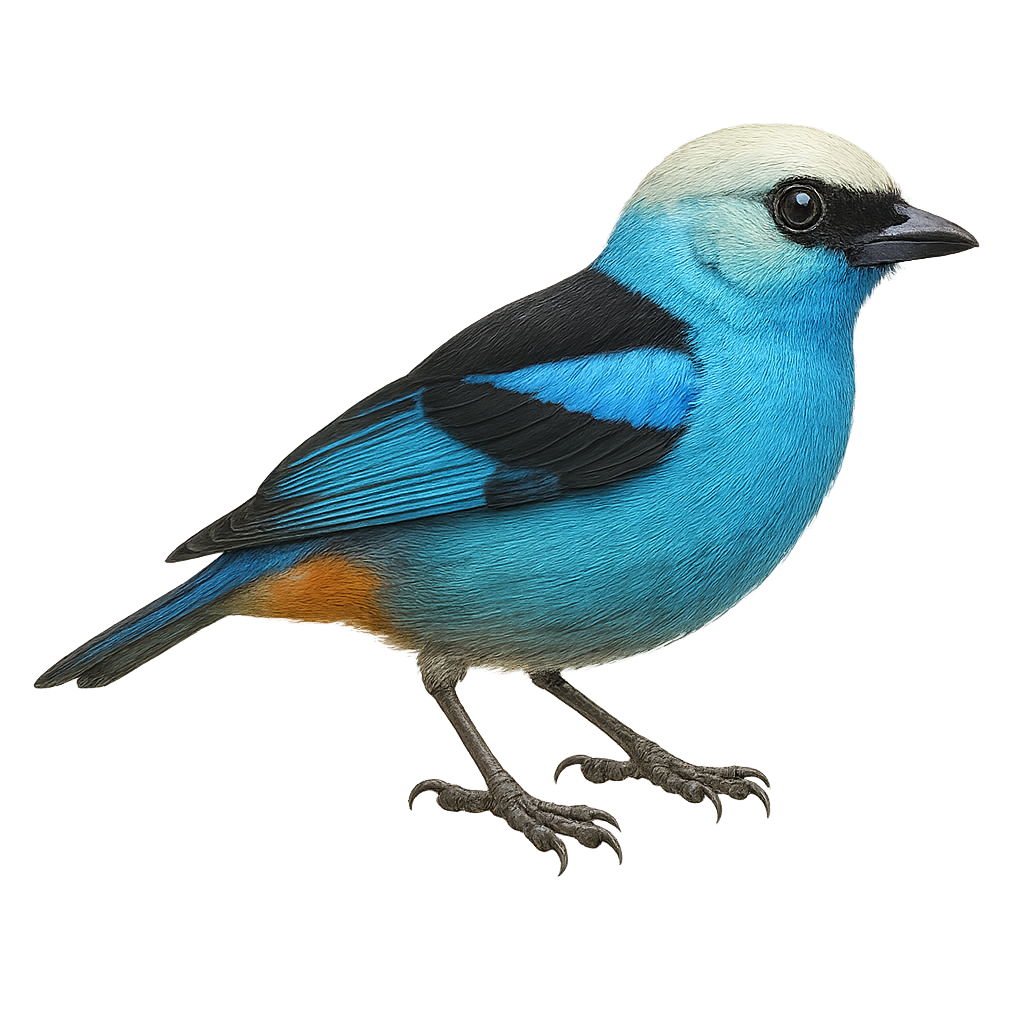
The Green-winged Pytilia, or Pytilia melba, is a small, colorful bird belonging to the Estrildidae family. It is primarily found in sub-Saharan Africa, where it inhabits savannas, open woodlands, and shrublands. This bird is distinguished by its vibrant plumage, featuring green wings, a red belly, and a brownish back. Both males and females exhibit similar colors, although males are often more vibrant. The Green-winged Pytilia is a granivorous bird, mainly feeding on seeds but also consuming insects. It is known for its melodious songs and elaborate courtship displays. Although generally not very shy, it can be suspicious when faced with potential threats.
The Great Knot is a medium-sized migratory bird belonging to the Scolopacidae family. It is recognizable by its speckled brown plumage and long, slender bill. During the breeding season, it displays more pronounced patterns on its back and chest. This bird breeds mainly in the Arctic regions of Siberia and migrates to the coasts of Australia and Southeast Asia for the winter. It frequents wetlands, estuaries, and sandy beaches where it primarily feeds on mollusks, crustaceans, and insects. The Great Knot is a vulnerable species due to habitat loss and human disturbances.
The Jack Snipe is a small, discreet wader, often difficult to spot due to its cryptic plumage that blends perfectly with its environment. This small bird, with its brown and mottled plumage, primarily inhabits marshes and bogs in Northern Europe and Asia. It feeds on invertebrates, mainly worms, insects, and mollusks, which it finds by probing the mud with its short, straight bill.
The Jack Snipe adopts a stealthy behavior and is often observed hiding in dense vegetation or freezing when threatened. While more difficult to observe due to its discretion, it is threatened by habitat loss and changes in the hydrological regime in its breeding areas.
The gray wagtail is a small bird found primarily near rivers, streams, and wetlands across Europe, Asia, and northern Africa. This passerine bird is distinguished by its gray and yellow plumage, long tail, and lively, jittery movements. It primarily feeds on insects, which it catches while running along riverbanks and searching through rocks. The gray wagtail is also known for its territorial behaviors and pleasant song.
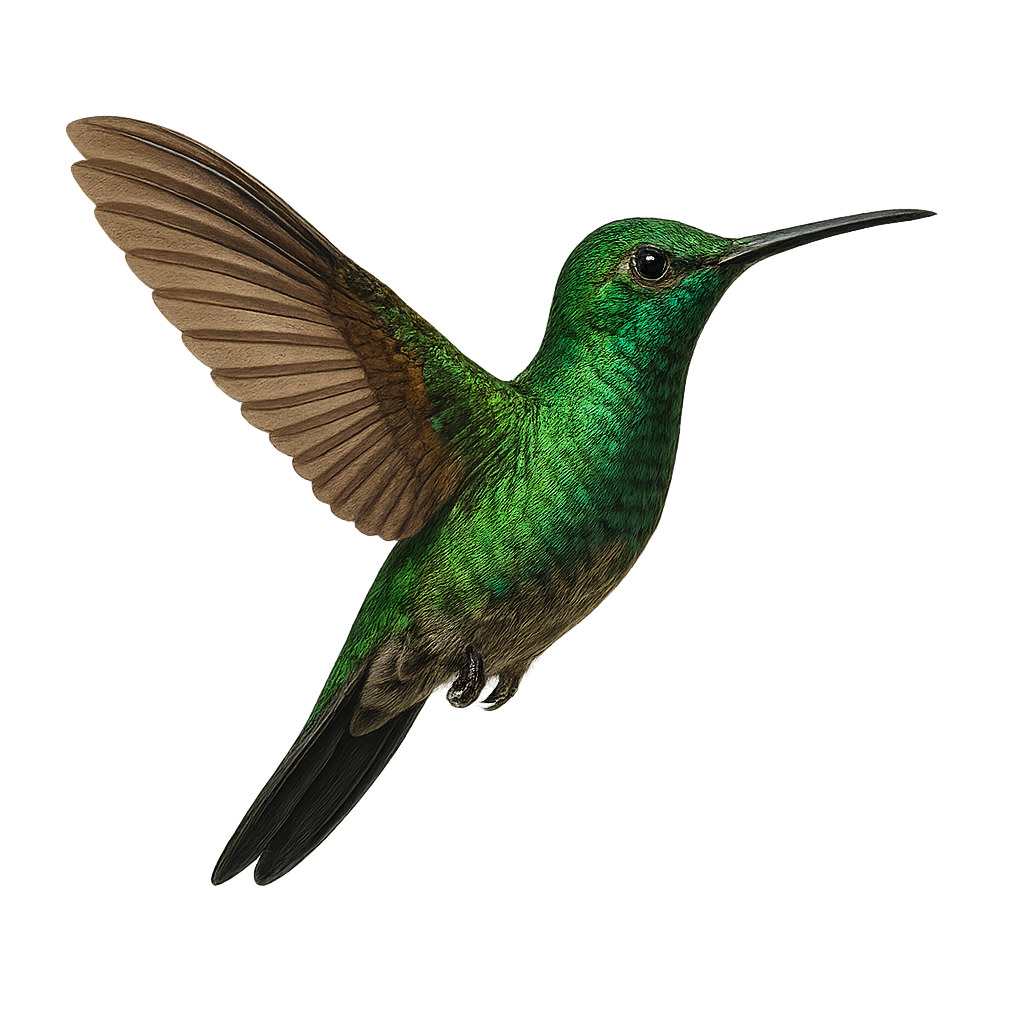
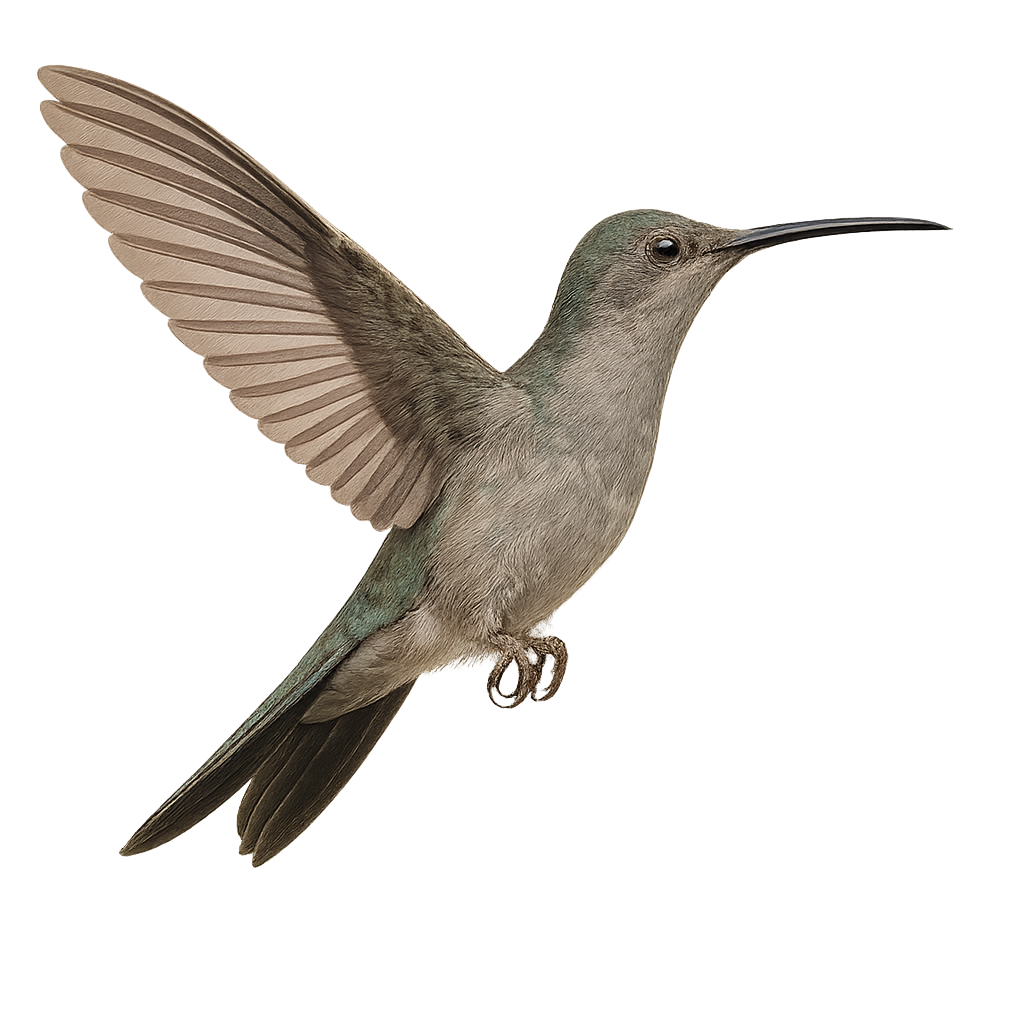
The Green-crowned Brilliant, scientifically known as Heliodoxa jacula, is a medium-sized hummingbird found in the humid forests of Central America, from Costa Rica to Panama. Measuring about 11 to 12 cm, this bird is notable for its striking metallic green plumage and emerald crown. Males have a distinctive blue-violet throat, while females feature a white throat speckled with green. Their relatively short, slightly curved beak is well-suited for nectar feeding. These birds are often seen hovering near flowers, using their agility to access nectar while playing a vital role in pollination.
Galah
Eolophus roseicapilla
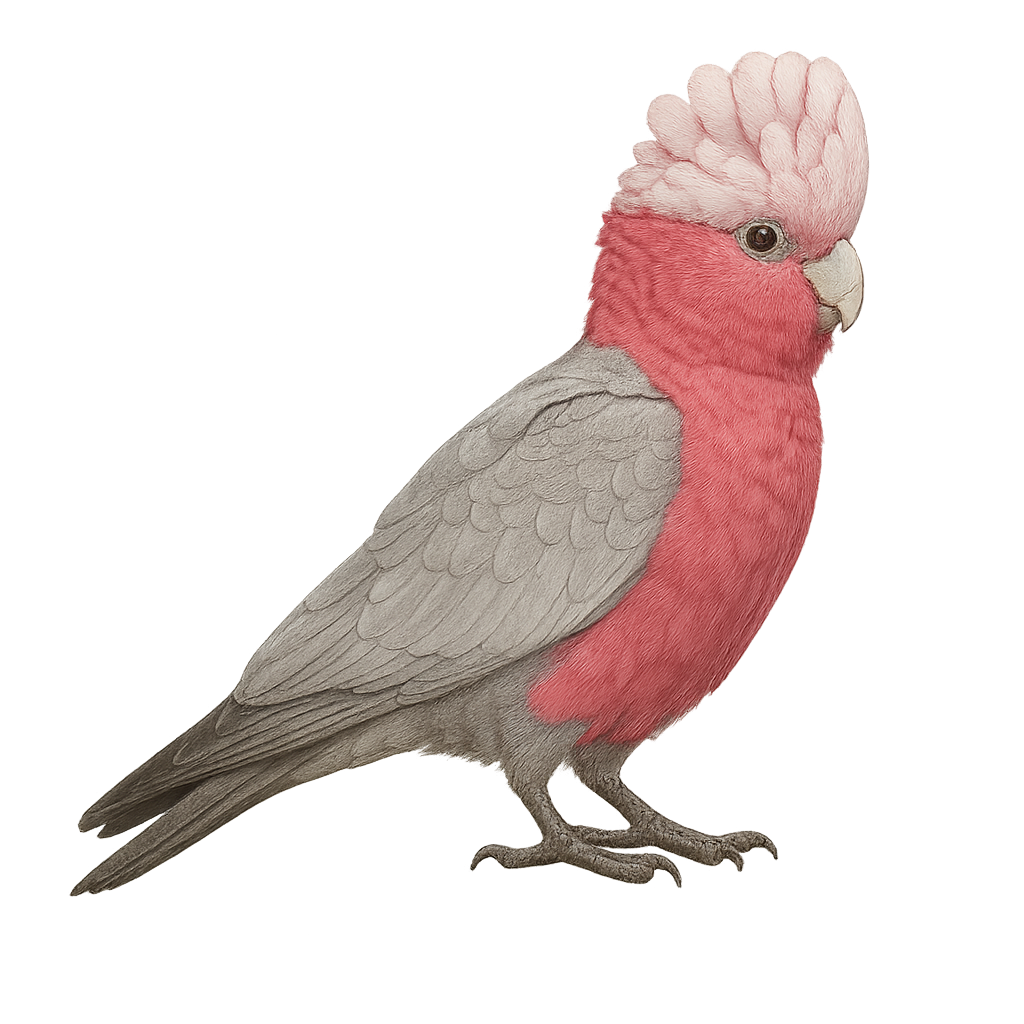
The Galah, or Eolophus roseicapilla, is a distinctive Australian bird known for its striking pink and grey plumage. It measures about 35 cm in length and weighs between 270 and 350 grams. Its strong beak is well-suited for its diet of seeds, fruits, and vegetation. Highly social and intelligent, it lives in large flocks and is often seen in open areas such as grasslands and farmlands. The Galah is famous for its aerial acrobatics and loud calls. It adapts well to captivity, making it a popular pet, although it requires significant attention and mental stimulation.
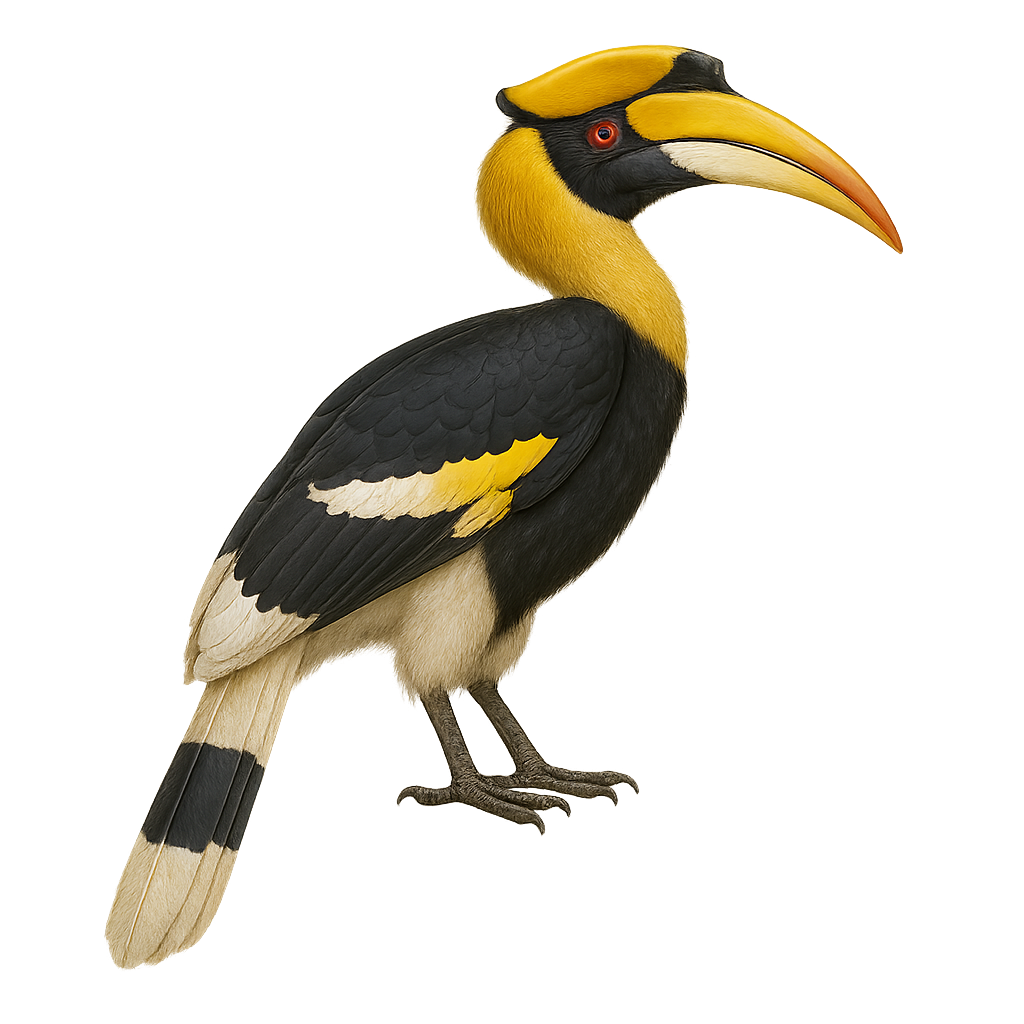
The great hornbill (Buceros bicornis) is a large forest bird (95–120 cm long, weighing 2–3.4 kg) known for its massive yellow bill topped by a hollow casque. It inhabits humid tropical and gallery forests from India to Vietnam, at elevations from sea level to 1500 m. Primarily frugivorous, it feeds on figs and various fruits, supplementing its diet with small vertebrates and insects. Monogamous and territorial, pairs remain together year-round. During the breeding season (01.01–31.05), the male and female engage in loud duets and casque-butting displays. After pairing, the female seals herself within a tree cavity and incubates 1–2 eggs for 38–40 days, receiving food through a narrow slit provided by the male.
The Golden-hooded Tanager, scientifically known as Stilpnia larvata, is a vibrant bird native to the tropical rainforests of Central America. This small passerine is easily identified by its striking blue head, contrasting with its black body and wings adorned with shades of green and yellow. Measuring about 13 cm in length, it primarily feeds on fruits, insects, and nectar. Its song is a soft warble, often heard at dawn or dusk. Although generally solitary, it can sometimes be seen in small groups. The Golden-hooded Tanager plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding in forest regeneration.
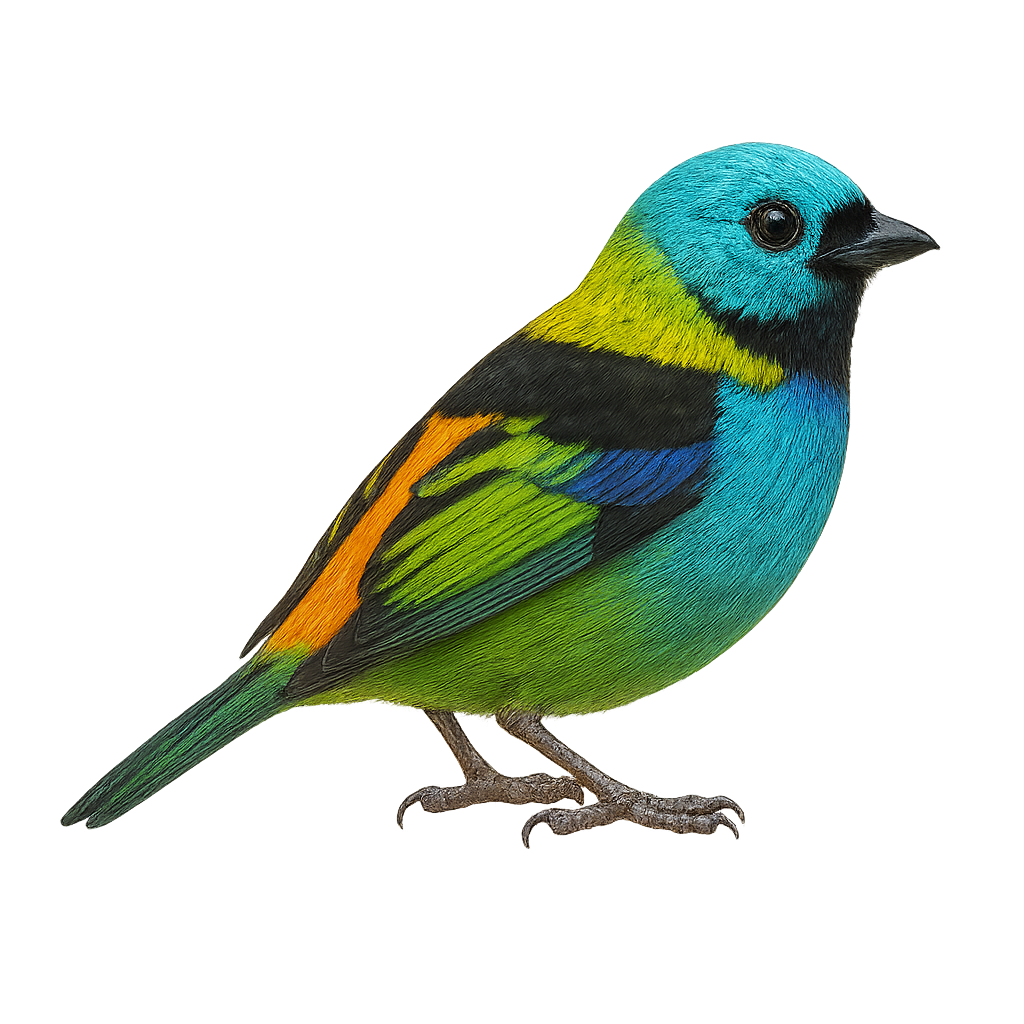
The Green-headed Tanager, or Tangara seledon, is a colorful and fascinating bird primarily inhabiting the humid tropical forests of South America, notably in Brazil, Argentina, and Paraguay. This bird is easily recognizable by its vibrant plumage, blending shades of green, blue, yellow, and black. It measures about 13 to 14 cm in length and weighs between 15 and 20 grams. The Green-headed Tanager is a sociable bird that feeds mainly on fruits, nectar, and insects. It plays an important role in seed dispersal, thus contributing to forest regeneration. Although not considered threatened, deforestation poses a potential threat to its natural habitat.
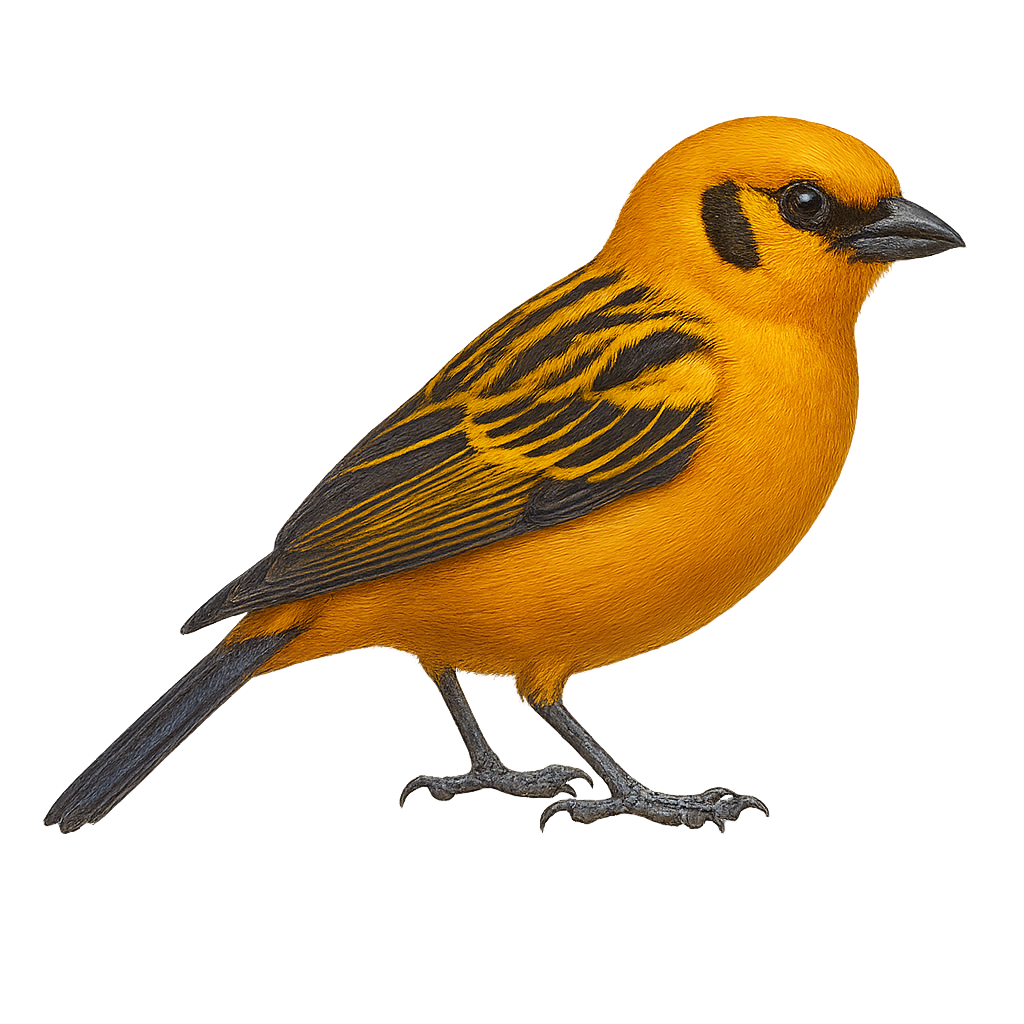
The Golden Tanager, or Tangara arthus, is a colorful and fascinating bird native to the humid tropical forests of South America. It is easily recognizable by its bright plumage, primarily golden with shades of black on the wings and tail. This small bird measures about 13 to 14 cm in length. It typically lives in groups and feeds mainly on fruits, insects, and nectar. The Golden Tanager is often observed in mountain forests, where it plays a crucial role in seed dispersal. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it is still relatively common in some areas.
The Green-and-gold Tanager, or Tangara labradorides, is a small tropical songbird from the humid forests of South America, recognizable by its bright green plumage with metallic blue hues and agile form. It is mainly found in the Andes, from Venezuela to Peru, at elevations between 1000 and 2500 meters. Highly active, it often moves in flocks through the canopy, feeding on fruits, insects, and nectar. Though discreet, its vivid colors make it a favorite among bird photographers. The species is considered stable in terms of population.
The Grey-breasted Sabrewing, scientifically known as Campylopterus largipennis, is a medium-sized hummingbird found mainly in the tropical rainforests of South America. This stunning bird is noted for its iridescent plumage, with shades of green and blue on its back and a grayish breast. Its tail is broad and slightly forked, giving it a distinctive silhouette in flight. Males and females are similar, although females may have slightly duller colors. This hummingbird is often seen feeding on nectar, using its long bill to reach tubular flowers. It plays a crucial role in the pollination of plants within its habitat.
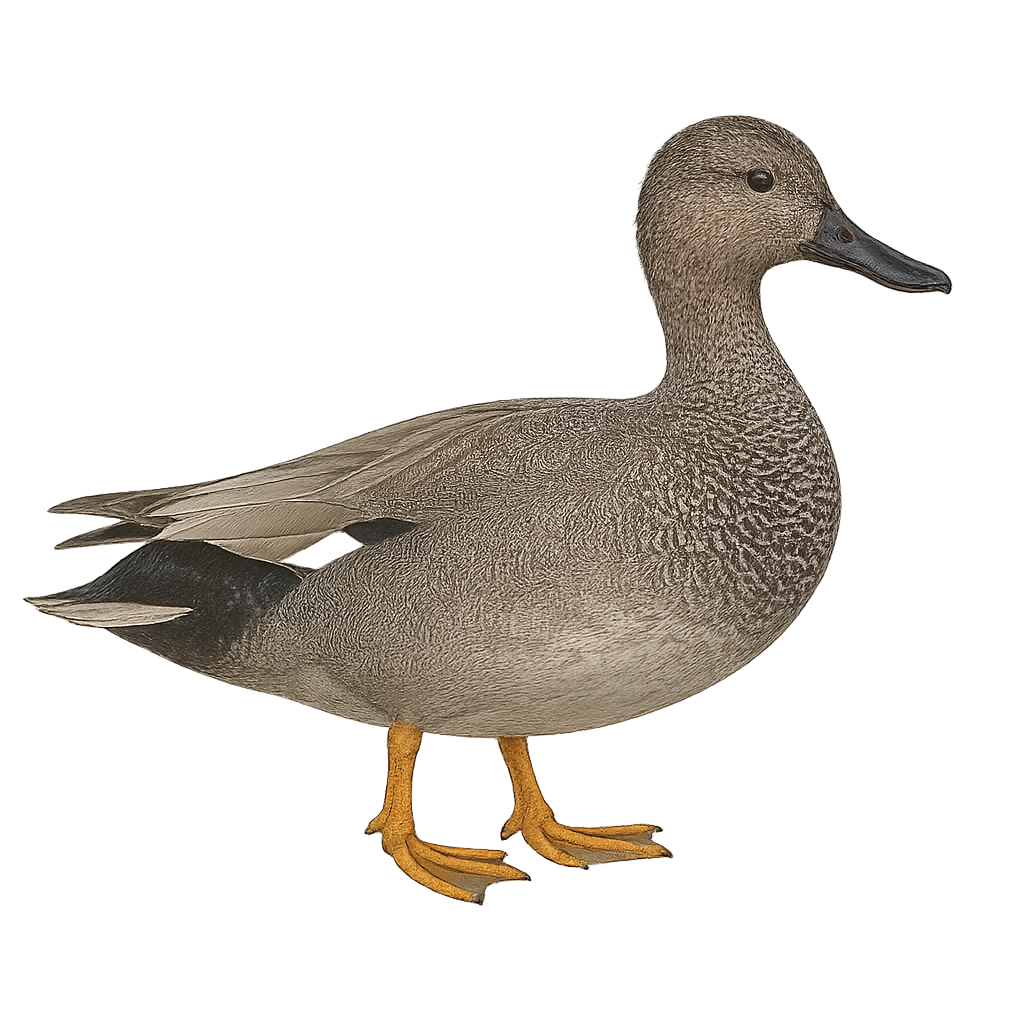
The Gadwall is a medium-sized dabbling duck, measuring between 46 and 56 cm in length with a wingspan of 78 to 90 cm. The male has finely patterned gray plumage with a distinctive white wing patch visible in flight, a black rump, and a dark bill. The female is mottled brown with an orange-edged dark bill. This species inhabits wetlands such as marshes, ponds, lakes, and flooded meadows rich in aquatic vegetation. It feeds mainly on leaves, stems, and seeds of aquatic plants, but also consumes aquatic invertebrates, especially during the breeding season. The Gadwall is a partial migrant, breeding in Eurasia and North America, and wintering in more southern regions. Although listed as Least Concern by the IUCN, it is sensitive to wetland degradation and pollution.
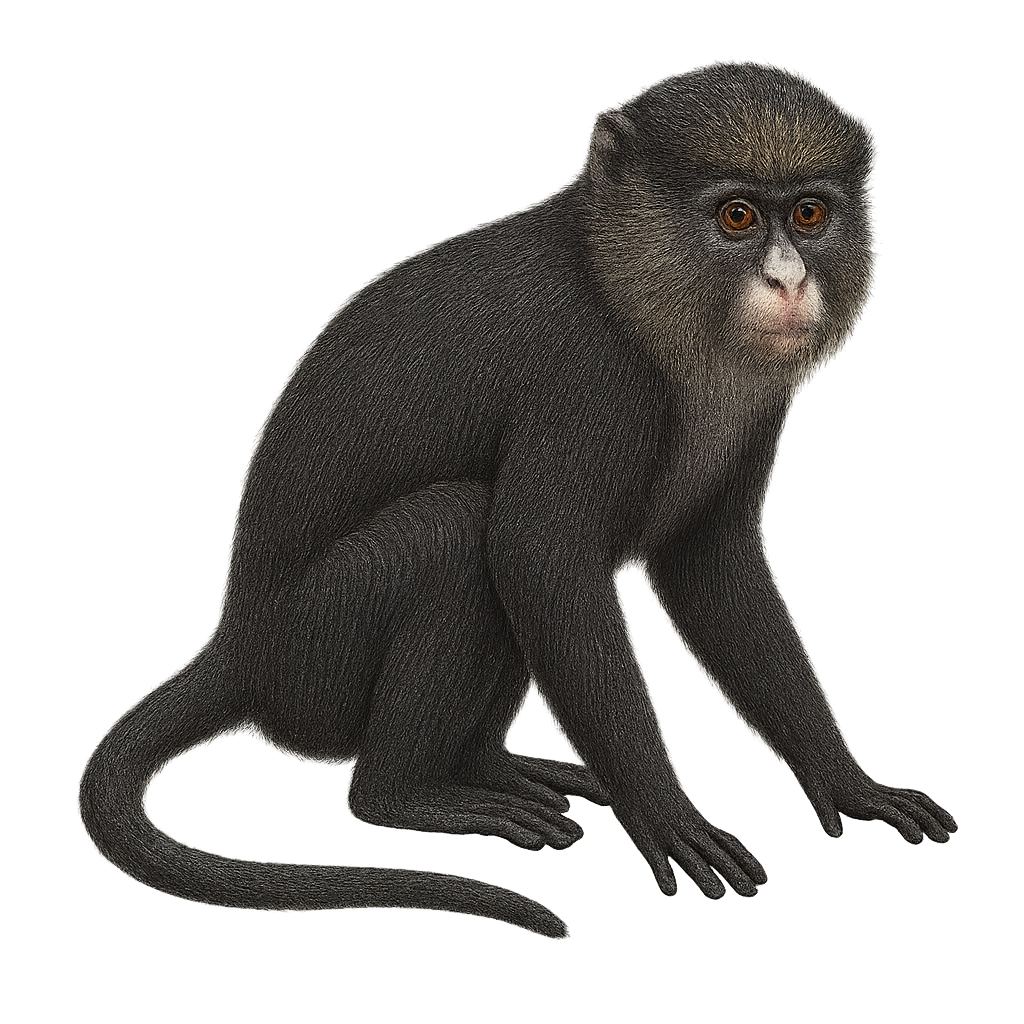
The Greater Spot-nosed Monkey, scientifically known as Cercopithecus nictitans, is a medium-sized arboreal primate found primarily in the tropical forests of West and Central Africa. It is distinguished by a characteristic white spot on its nose and a grey-green coat. This social monkey lives in hierarchical groups led by a dominant male. Omnivorous, it feeds on fruits, leaves, insects, and small animals. Its alarm call is used to warn the group of predators. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it remains relatively widespread.
The Golden Jackal is a small canid found primarily in South Asia, the Middle East, and Southeastern Europe. It is easily recognizable by its golden fur, which ranges from pale yellow to golden brown, allowing it to blend into the landscapes of grasslands, open forests, and savannas. The Golden Jackal has a more slender body and relatively long legs compared to other jackals, enabling it to be an excellent runner.
Opportunistic by nature, the Golden Jackal feeds on a wide variety of prey, ranging from small mammals and birds to fruits and carrion. Although often solitary or in small family groups, the Golden Jackal can occasionally be seen in larger groups while foraging for food. It is also known for its varied vocalizations and skilled hunting behavior. While its population remains relatively stable, it faces threats such as habitat loss and human conflict.