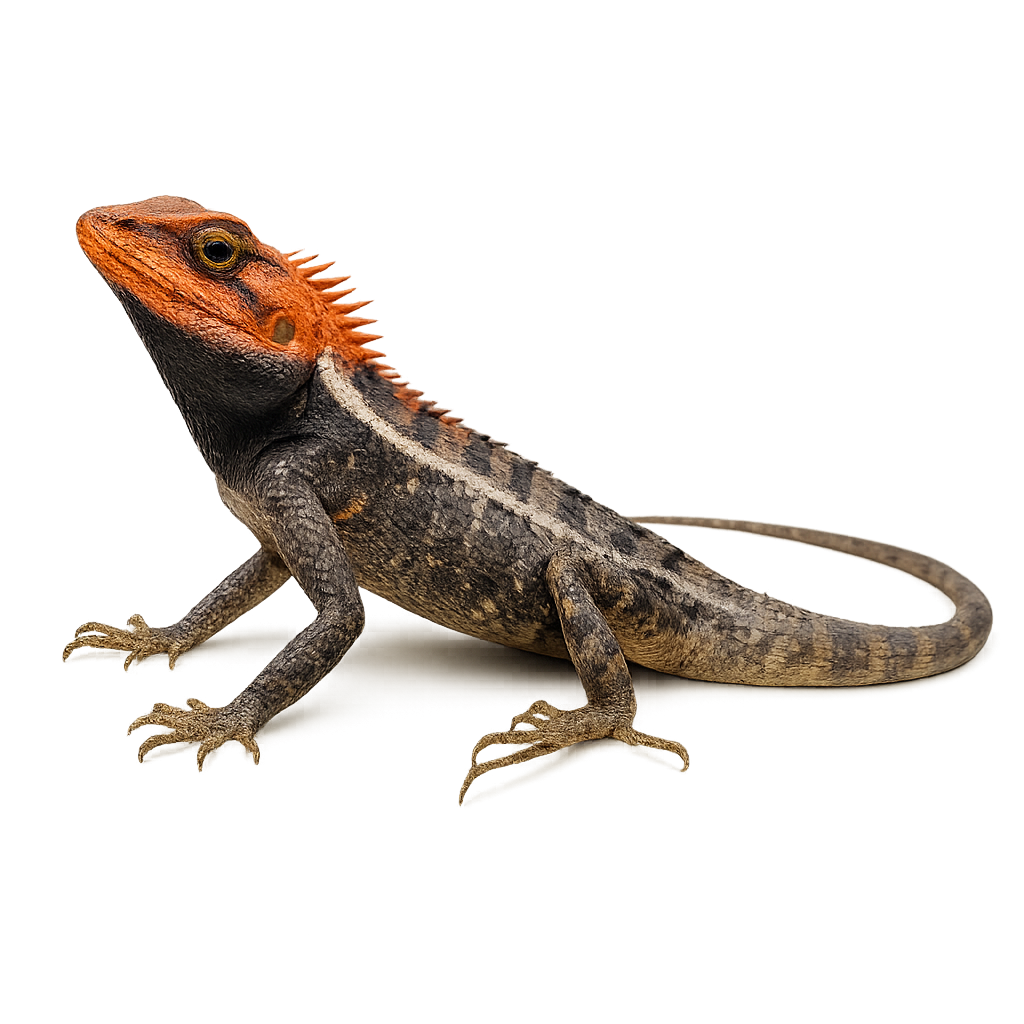
The Calotes emma, or Forest Garden Lizard, is an arboreal lizard native to Southeast Asia, particularly found in Thailand, Vietnam, and Cambodia. This reptile is known for its ability to change color to blend into its surroundings. It typically displays green and brown hues, allowing it to camouflage within the dense vegetation of tropical forests. The Emma Gray's Forest Lizard measures about 25 to 30 cm in length, including its tail. It is primarily insectivorous, feeding on various insects and arachnids. Its behavior is rather territorial, often seen perched on tree branches, keeping watch over its domain.
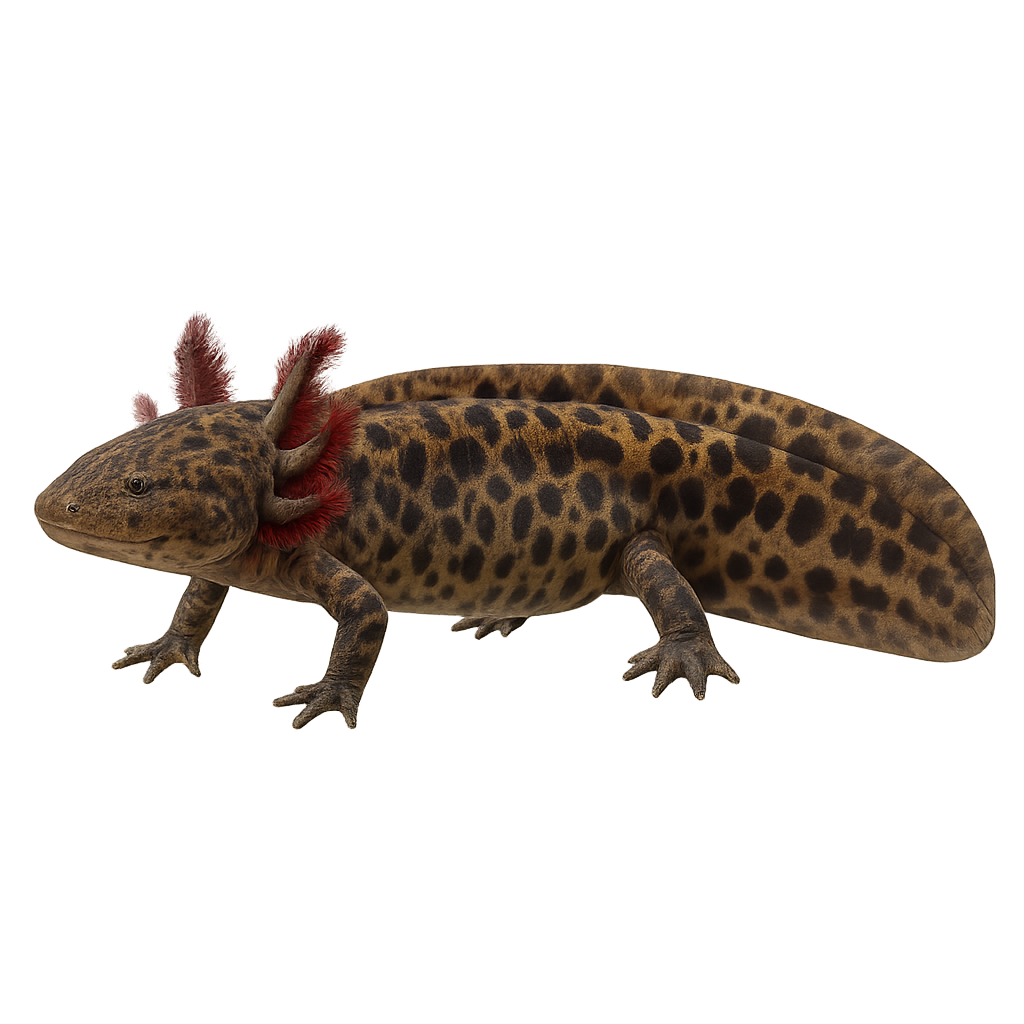
The Fisher’s salamander is an urodele amphibian endemic to the Lake Pátzcuaro basin (Michoacán, Mexico). It inhabits hot springs, marshes and wet meadows at 2030–2120 m elevation. Strictly nocturnal, it feeds on aquatic insects and small crustaceans. During the breeding season (July to September), males become territorial and perform body-undulation displays before egg‐laying.
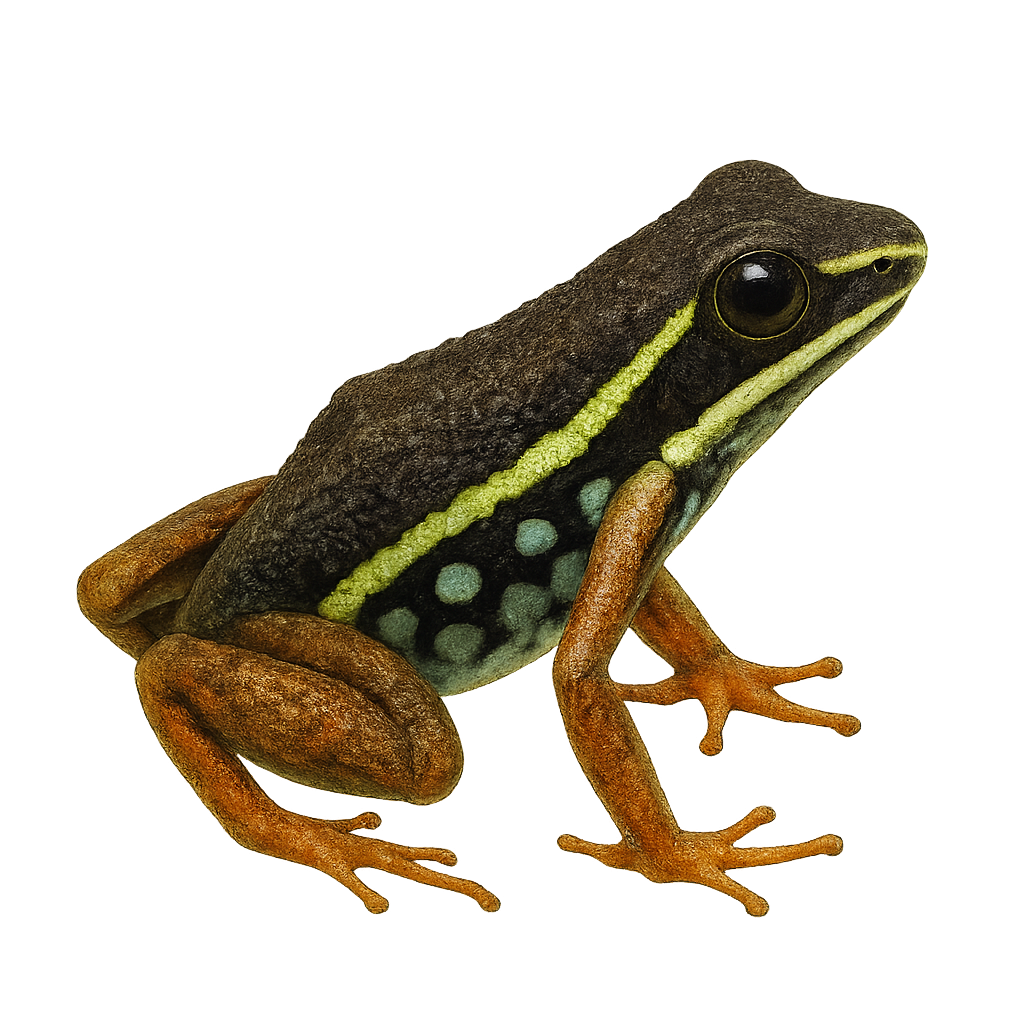
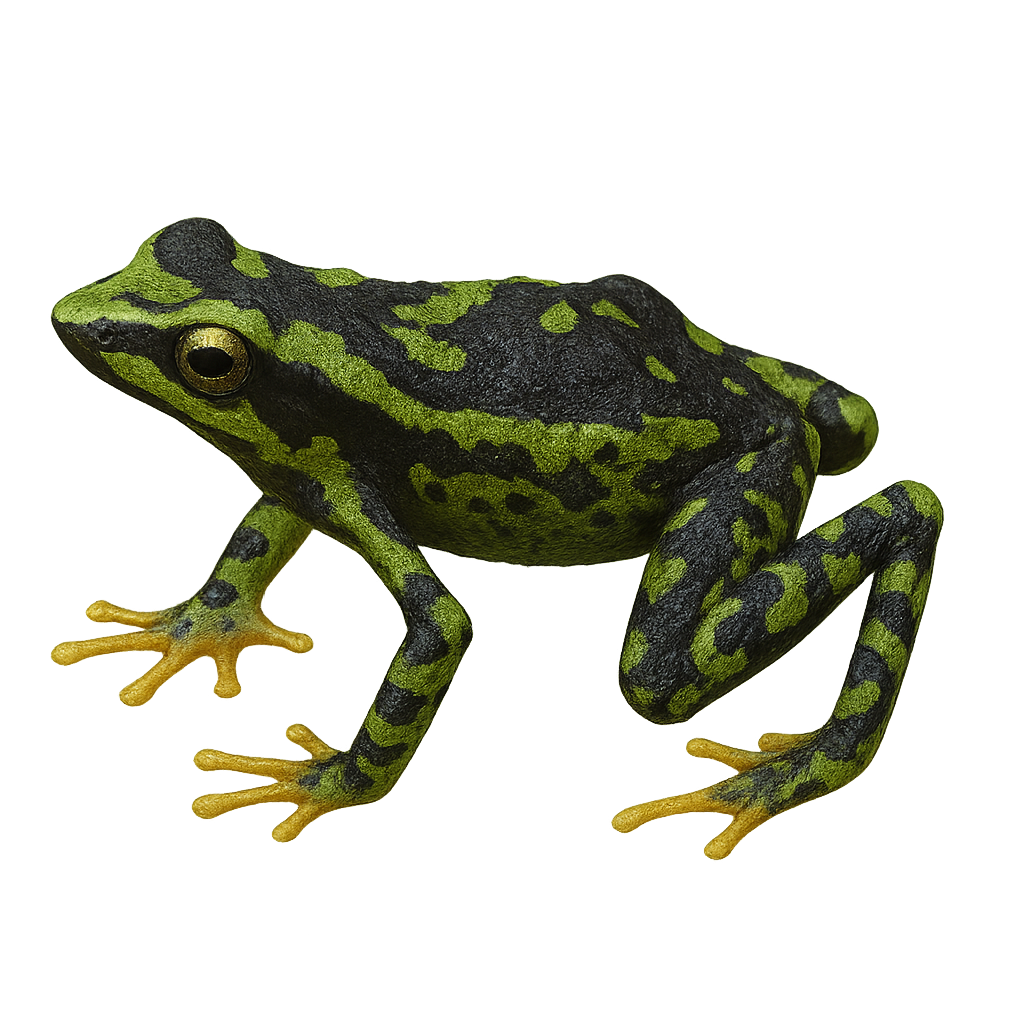
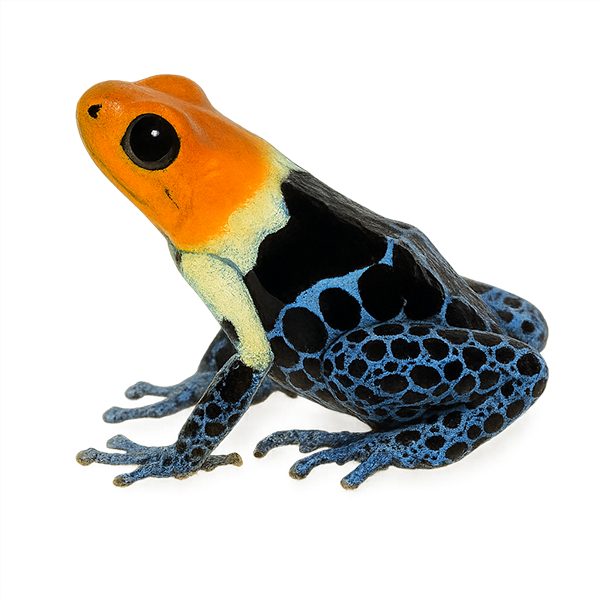
The Ameerega ignipedis, commonly known as the Fire-legged Poison Frog, is a brightly colored frog species native to the humid tropical forests of South America. It is particularly recognizable by its vivid red legs, which contrast with its black or dark brown body. This diurnal frog is often observed on the forest floor, where it primarily feeds on small insects. Although its bright coloration serves as a warning to potential predators, indicating its toxicity, it is nonetheless vulnerable to habitat loss due to deforestation. Its reproduction typically occurs during the rainy season when conditions are ideal for tadpole development.
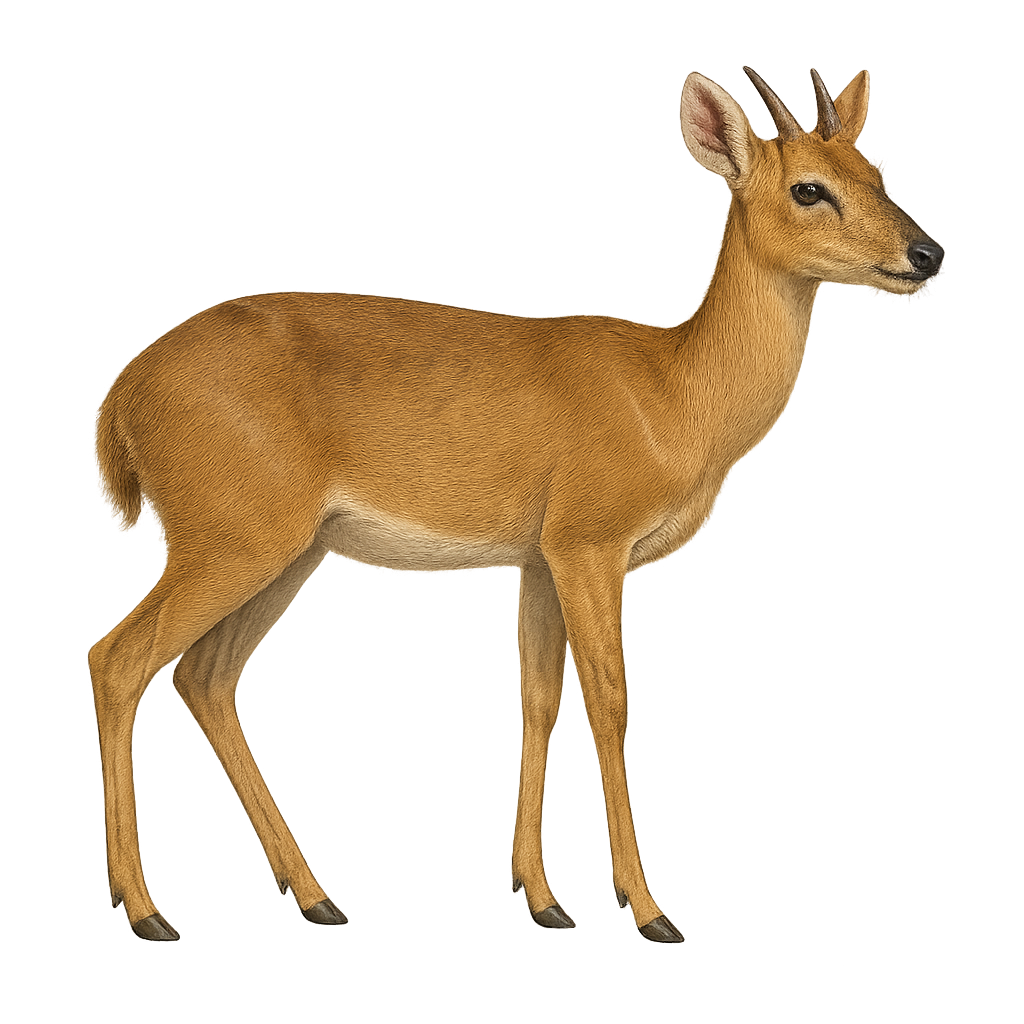
The four-horned antelope, or Tetracerus quadricornis, is a unique small ruminant, primarily due to its distinctive four horns. Native to the Indian subcontinent, this species prefers dry forests and scrublands where it can blend into the landscape to escape predators. It stands about 55 to 64 cm at the shoulder and weighs between 17 and 22 kg. Its coat ranges from light to dark brown, with a lighter belly. Males sport two pairs of horns, the longest reaching up to 12 cm. The four-horned antelope is a solitary animal, except during the breeding season. It is primarily herbivorous, feeding on leaves, fruits, and young shoots.
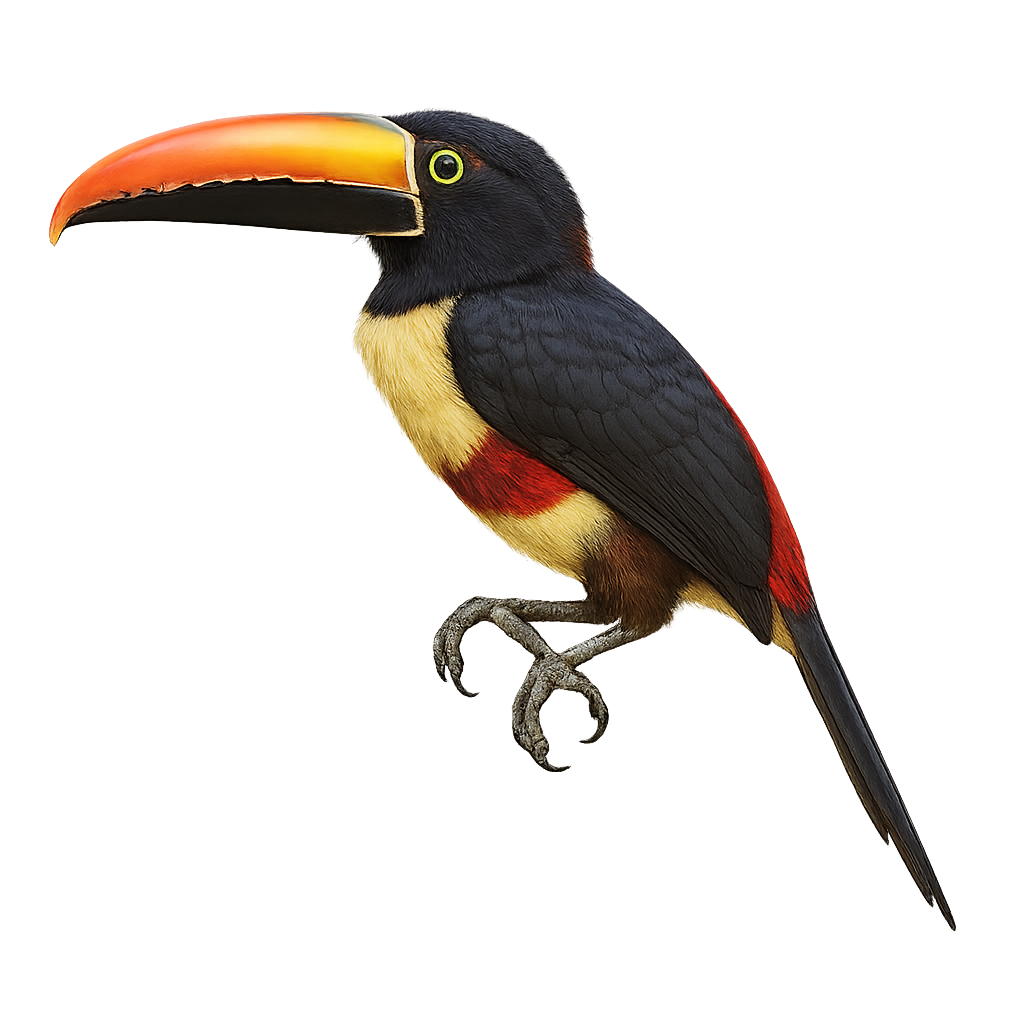
The Fiery-billed Aracari is a colorful and fascinating bird, endemic to the humid tropical forests of Costa Rica and western Panama. It is distinguished by its large, colorful bill, primarily orange-red with a black base. Its plumage is a vibrant mix of green, yellow, and red, making it easily recognizable. This bird measures about 40 cm in length and weighs between 200 and 250 grams. It typically lives in small groups and primarily feeds on fruits, but it can also consume insects and small vertebrates. The Fiery-billed Aracari plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, thus contributing to forest regeneration.
The Atelopus planispina, known as the Flat-spined Atelop, is a rare and fascinating amphibian endemic to the humid tropical forests of Ecuador. This toad is distinguished by its smooth skin and vibrant colors, ranging from green to yellow with black patterns. It typically measures between 3 and 5 cm in length. Adapted to terrestrial life, it prefers areas near water bodies where it can breed. Unfortunately, this species is threatened by habitat loss due to deforestation and climate change. Conservation efforts are crucial for its survival. Due to its rarity and beauty, it is often sought after by photographers and naturalists.
The Flightless Steamer Duck, or Tachyeres pteneres, is a waterfowl species endemic to the coasts of Patagonia in South America. Recognizable by its grayish plumage and large size, it is flightless, setting it apart from other ducks. This duck is mainly observed along rocky shores, where it feeds on mollusks and crustaceans. Males are generally larger than females and have a bright orange bill. Their territorial behavior is pronounced, especially during the breeding season. Although they are not very shy, they prefer isolated areas away from human disturbances. Their population is stable, but their habitat is vulnerable to environmental changes.
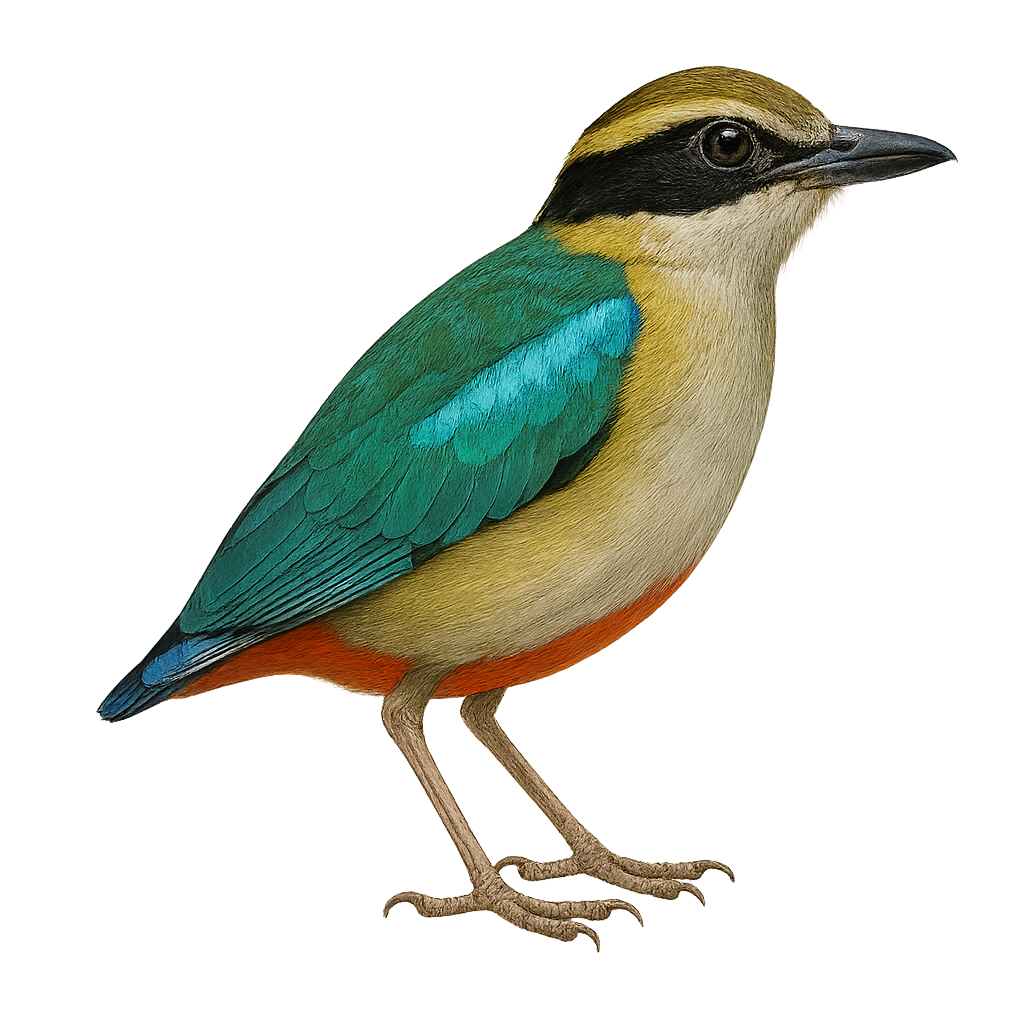
The Fairy Pitta, known scientifically as Pitta nympha, is a medium-sized bird renowned for its dazzling plumage that features shades of blue, green, red, and black. This migratory bird is primarily found in East Asia, particularly in China, Japan, and Korea. It prefers dense, humid forests where it feeds mainly on insects and small invertebrates. The Fairy Pitta is often difficult to spot due to its elusive behavior and dense habitat. It is currently classified as vulnerable due to habitat loss and increasing deforestation in its breeding and wintering areas.
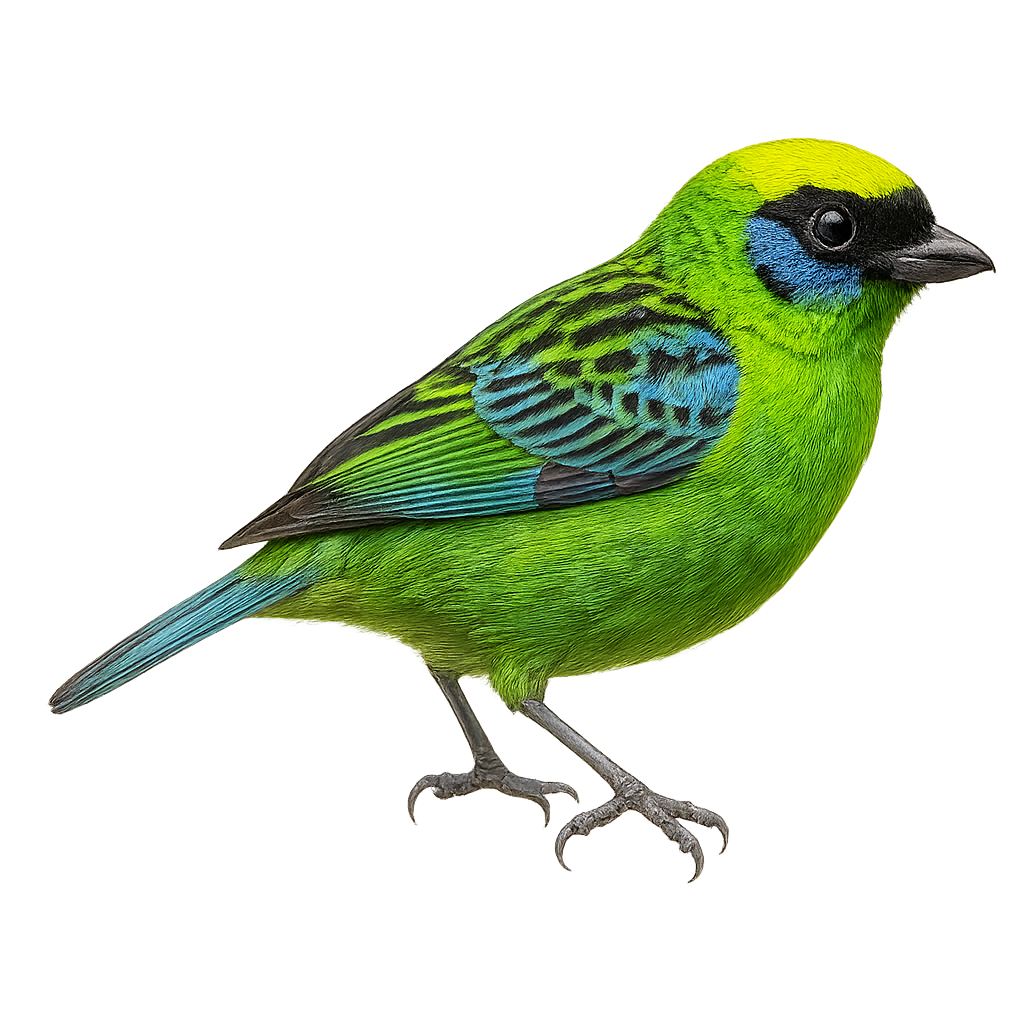
The Flame-faced Tanager, Tangara schrankii, is a vibrant bird found in the tropical forests of South America. It is easily identified by its bright orange head contrasting with its blue-green body. This small passerine measures about 13 cm in length and weighs between 18 and 22 grams. It primarily inhabits lowland and mid-elevation humid forests, feeding on fruits, insects, and nectar. Its song is melodious, consisting of clear, repeated notes. The Flame-faced Tanager is often seen in small groups, sometimes alongside other tanager species. Although relatively common in its natural habitat, deforestation poses a threat to its population.
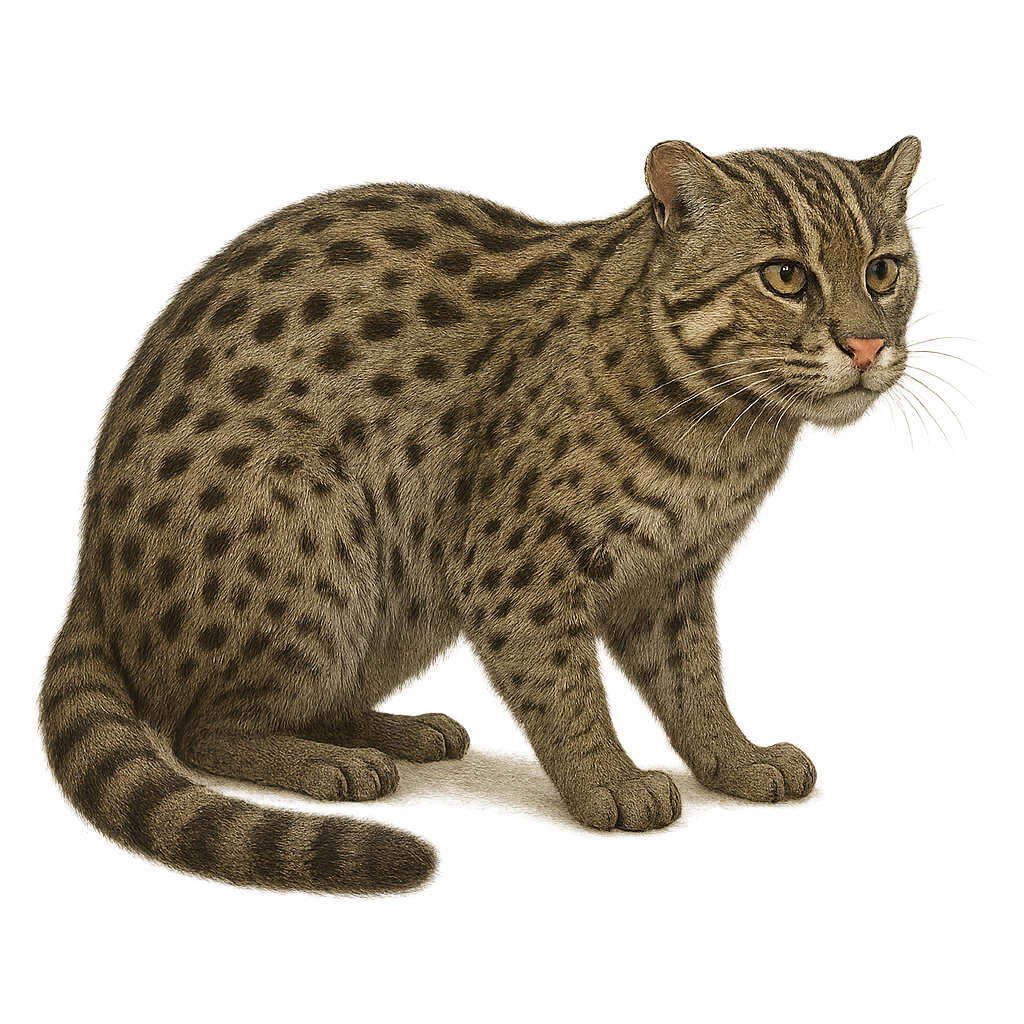
The fishing cat, or Prionailurus viverrinus, is a medium-sized feline primarily found in South and Southeast Asia. It is well adapted to aquatic life, with partially webbed feet that allow it to swim efficiently. Its coat is grayish with dark spots, providing excellent camouflage in marshy habitats. The fishing cat is an opportunistic predator, feeding mainly on fish, but also on small mammals, birds, and insects. Unfortunately, it is threatened by habitat loss due to human expansion and wetland pollution. Its population is declining, making it a vulnerable species according to the IUCN.
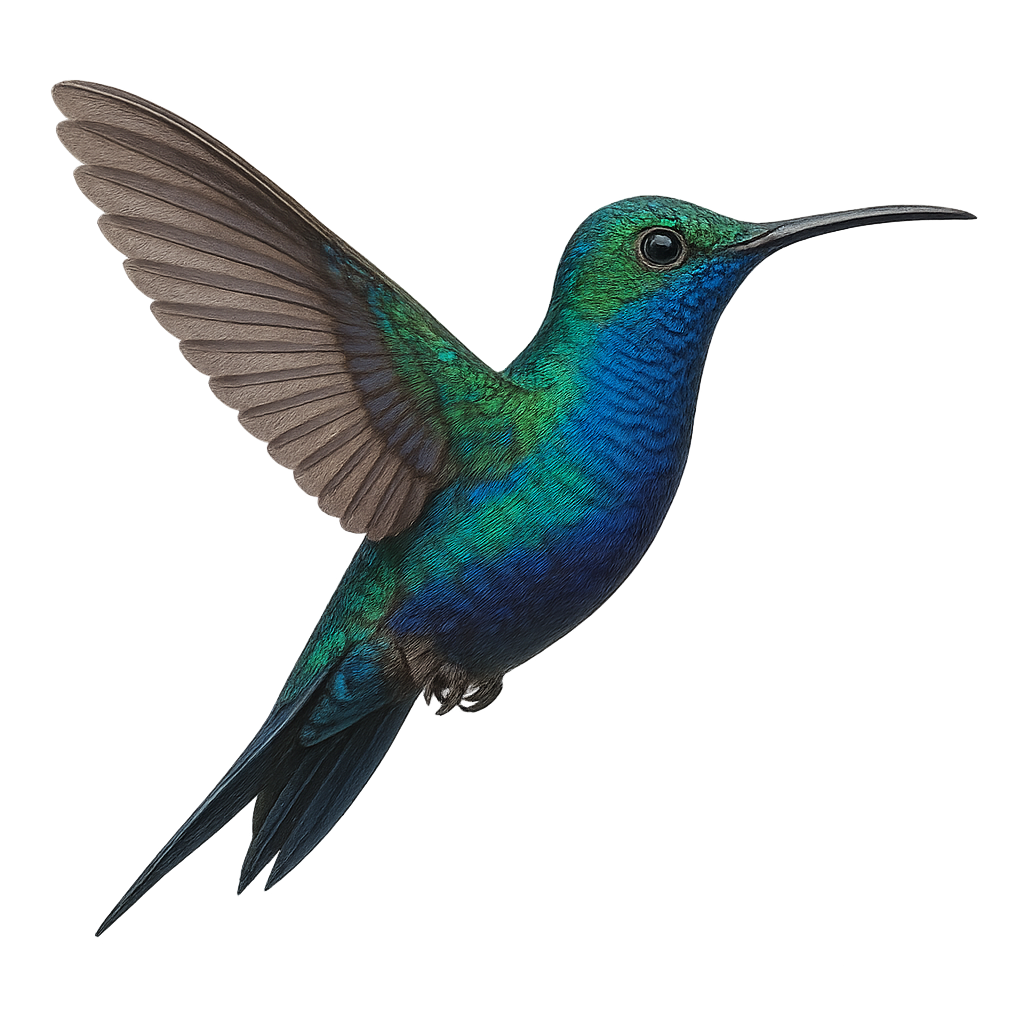
The Fork-tailed Woodnymph, or Thalurania furcata, is a captivating bird found in the tropical forests of South America. This small hummingbird is known for its dazzling plumage, featuring metallic green and blue hues. Males display a distinctive forked tail, while females have a more subdued appearance. They primarily feed on nectar, which they extract while hovering from flower to flower, but they also consume small insects to supplement their diet. Their fast and agile flight allows them to maneuver easily among branches and flowers. These birds are often seen in dense undergrowth and tropical gardens, where they play a crucial role in plant pollination.
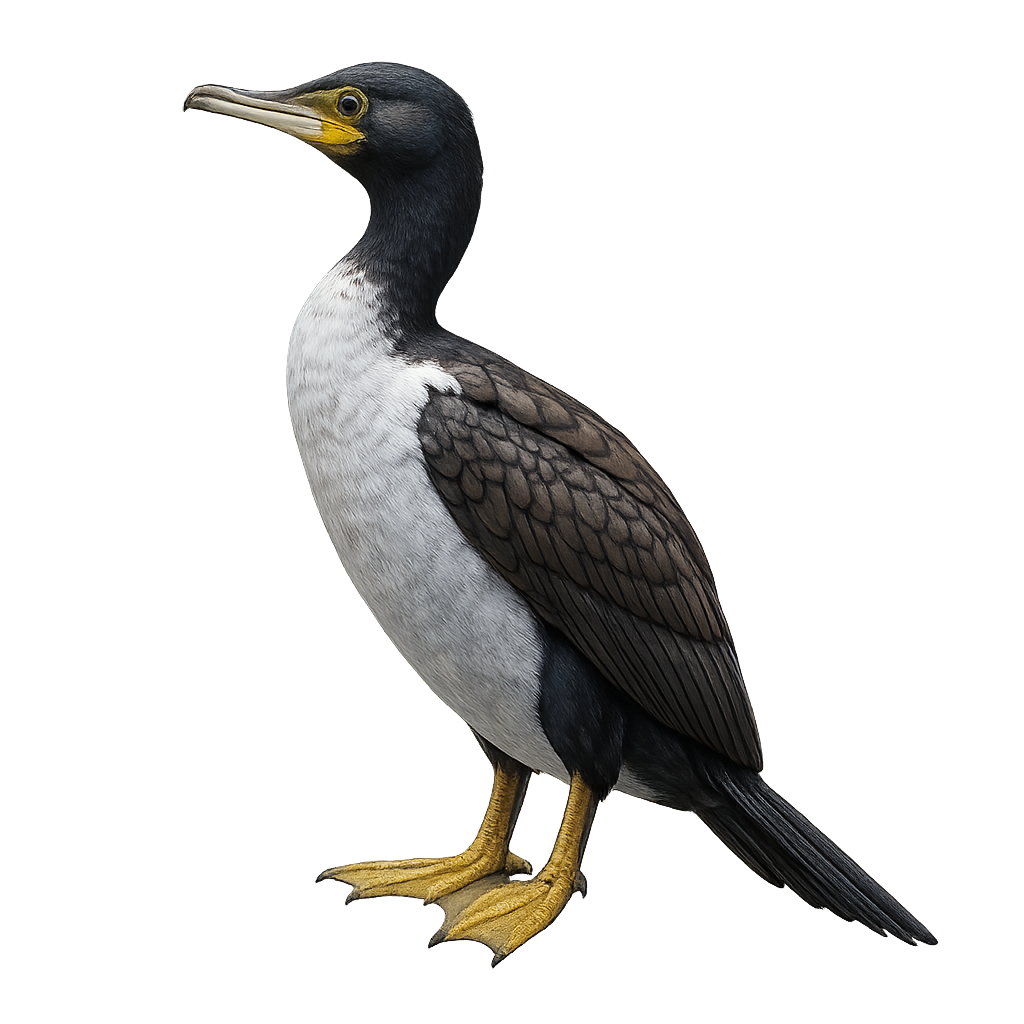
The Featherston's Shag is a marine bird species endemic to certain coastal regions of New Zealand. It is characterized by its glossy black plumage, often with metallic sheens, and striking blue eyes. This cormorant is typically seen in small groups, nesting on steep cliffs or rocky islets. It primarily feeds on fish and small marine invertebrates, which it skillfully captures by diving underwater. Although its flight is powerful and direct, it spends much time resting on rocks, wings spread to dry its feathers. This species is considered vulnerable due to its limited distribution and threats to its natural habitat.
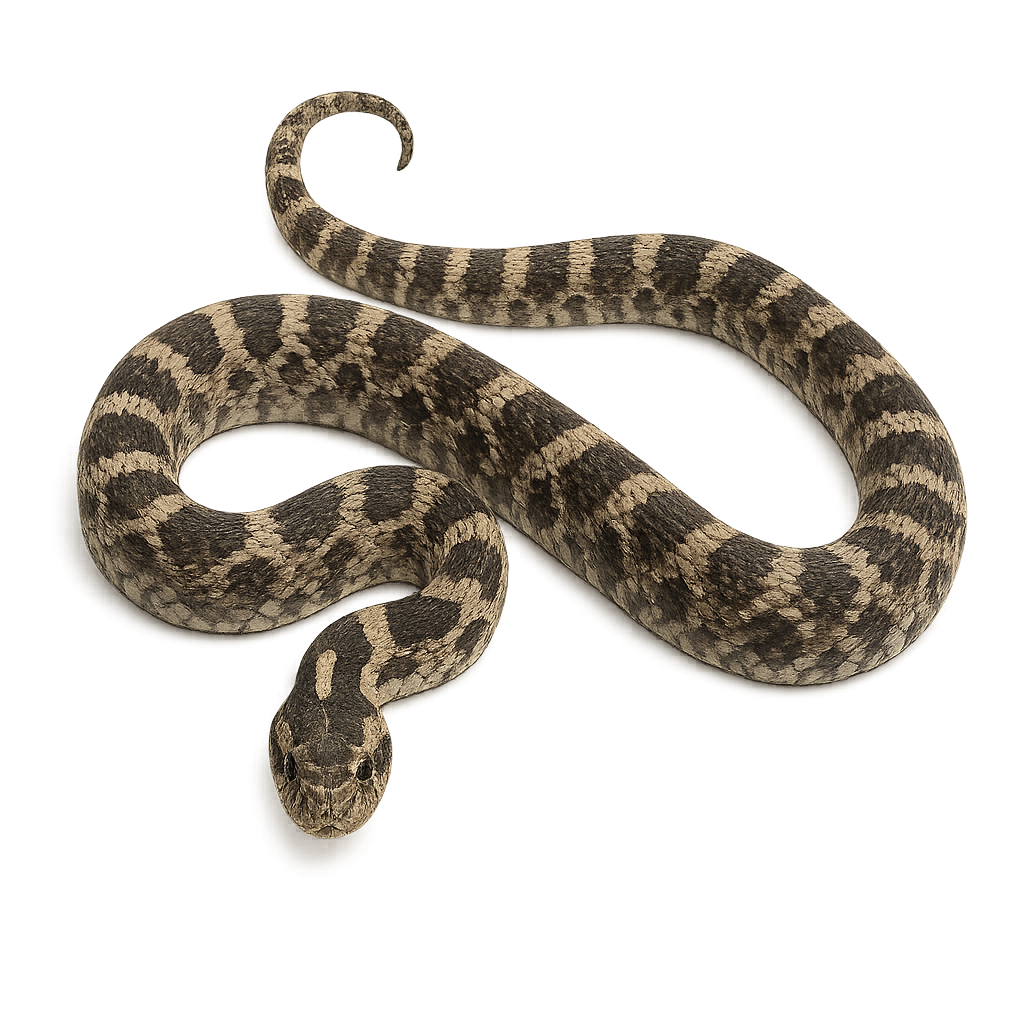
The four-lined snake, Elaphe quatuorlineata, is a non-venomous snake primarily found in southern Europe. It is recognizable by its four dark stripes running along its yellowish-brown body. Typically measuring between 100 and 200 cm, it is one of the largest snake species in Europe. It prefers dry, rocky habitats, open woodlands, and agricultural areas. Although terrestrial, it is also a good climber. It mainly feeds on small mammals, birds, and eggs. Its behavior is generally calm, but it can become defensive if threatened.
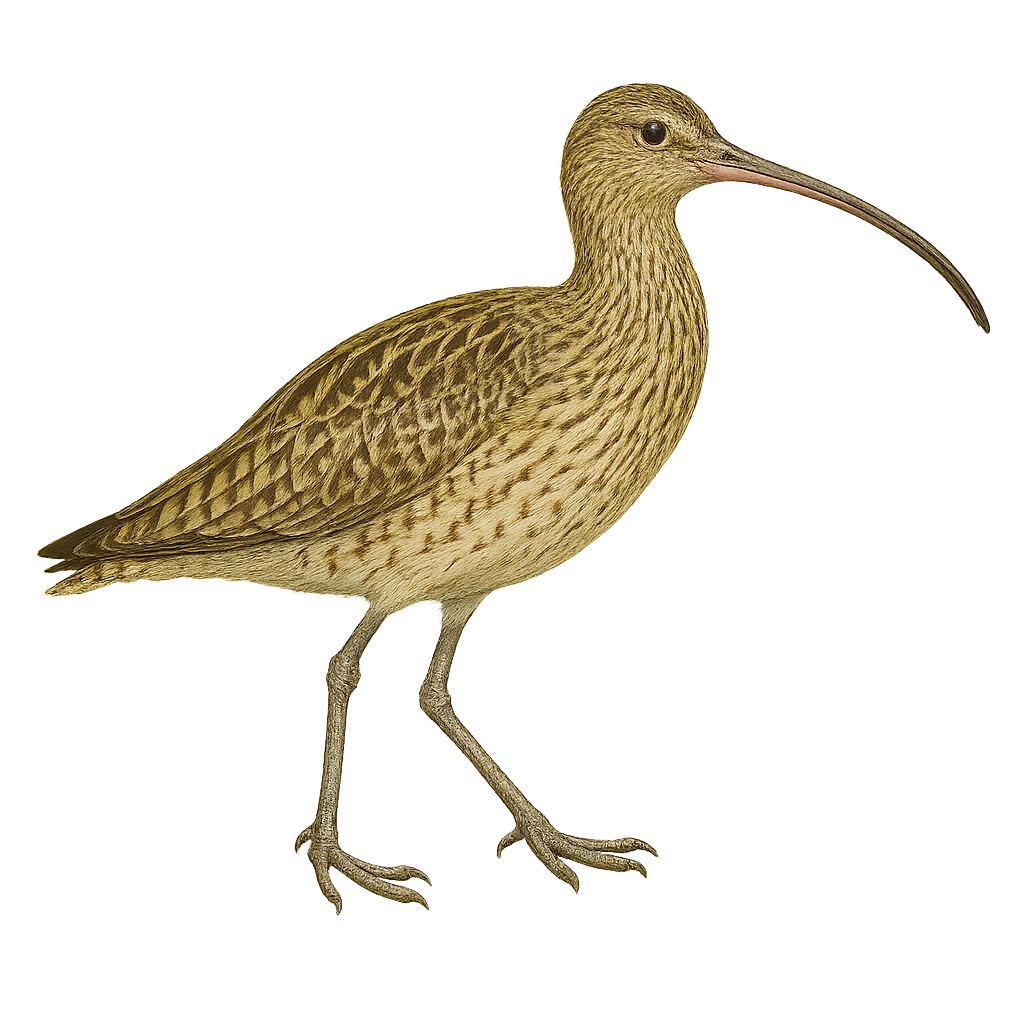
The Far Eastern Curlew, or Numenius madagascariensis, is a large wader with a brownish plumage and a distinctive long, downward-curved bill. This unique bill is perfect for probing mudflats for food, mainly invertebrates. It frequents coastal wetlands and estuaries, often seen in small flocks. As a migratory bird, it travels long distances between its breeding grounds in Siberia and its wintering areas in Australia and Southeast Asia. Unfortunately, this species is threatened by habitat loss, primarily due to urbanization and agriculture. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure its long-term survival.

The Fallow Deer, also known by the scientific name Dama dama, is a medium-sized cervid native to Europe and Asia Minor. It stands between 90 and 120 cm tall at the withers and can weigh between 30 and 100 kg, depending on sex and environment. Its coat, usually brown or gray, is spotted with white during the summer season, helping it blend into its forest habitat. The Fallow Deer primarily inhabits forests and woodlands, where it feeds on a variety of vegetation, including grasses, leaves, fruits, and bark. It is also known for its habit of moving in herds, often forming separate groups of males or females. The Fallow Deer is a ruminant herbivore that is primarily active at dawn and dusk. Although it is mostly sedentary, it can travel long distances in search of food or new habitats. During the breeding season, males fight for females, producing characteristic sounds such as roars. This species is listed as of least concern, but it can be threatened by habitat loss and excessive hunting.
The Ranitomeya fantastica, or fantastic poison frog, is a small, colorful frog native to the rainforests of Peru. Known for its striking patterns and vibrant colors, ranging from yellow to red, often with black spots, these frogs typically measure between 1.5 and 2 cm in length. They primarily inhabit humid undergrowth and feed on small insects. Their skin secretes toxic alkaloids, a natural defense against predators. Although fascinating, their habitat is threatened by deforestation, making them vulnerable. They play a crucial role in the ecosystem by controlling insect populations and serving as bioindicators of environmental health.
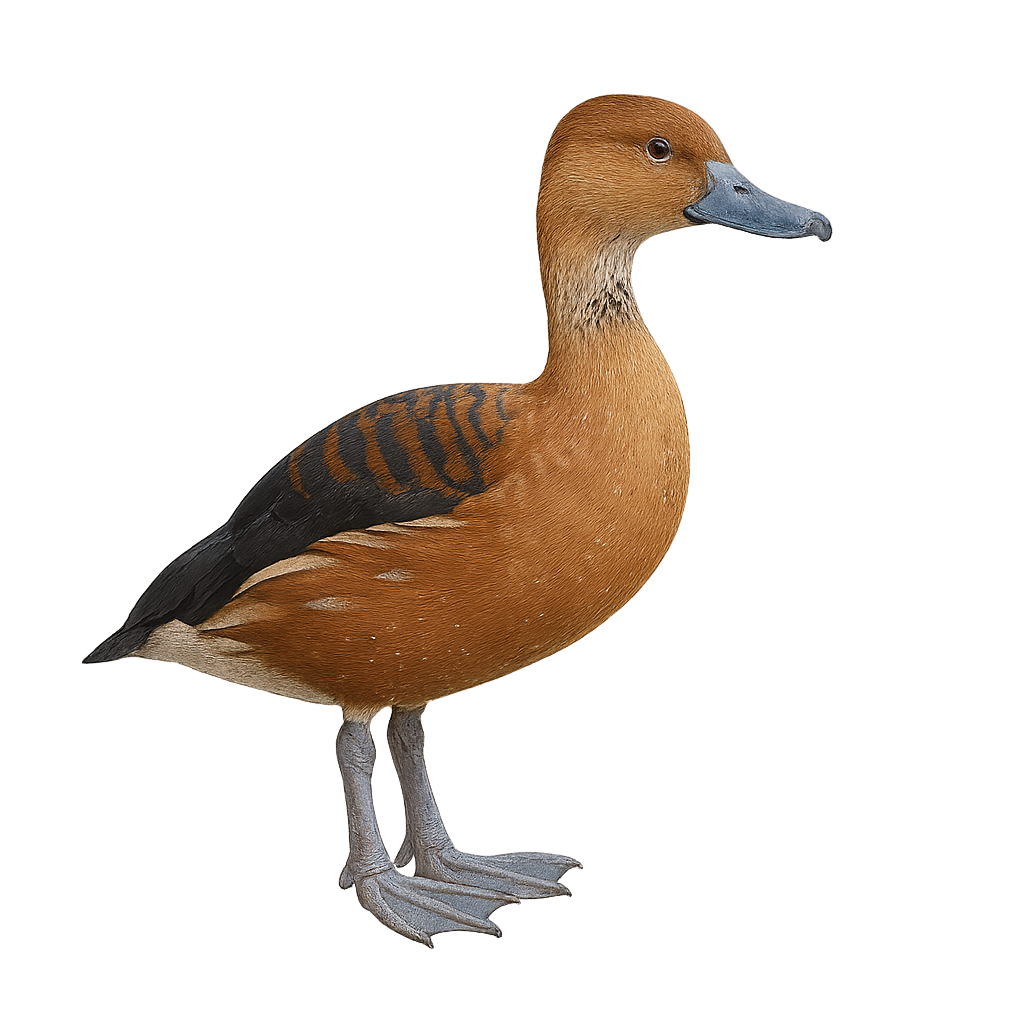
The Fulvous Whistling Duck is a medium-sized waterfowl, recognizable by its tawny-brown plumage and darker wings. It features a long neck and gray legs and is known for its distinctive whistling call. It is primarily found in wetlands, such as marshes and rice fields, where it feeds on seeds, aquatic plants, and insects. Social in nature, it often forms large flocks, especially outside the breeding season. Its geographical range includes tropical regions of America, Africa, and Asia. Although generally not very shy, it can be cautious in the presence of potential threats.
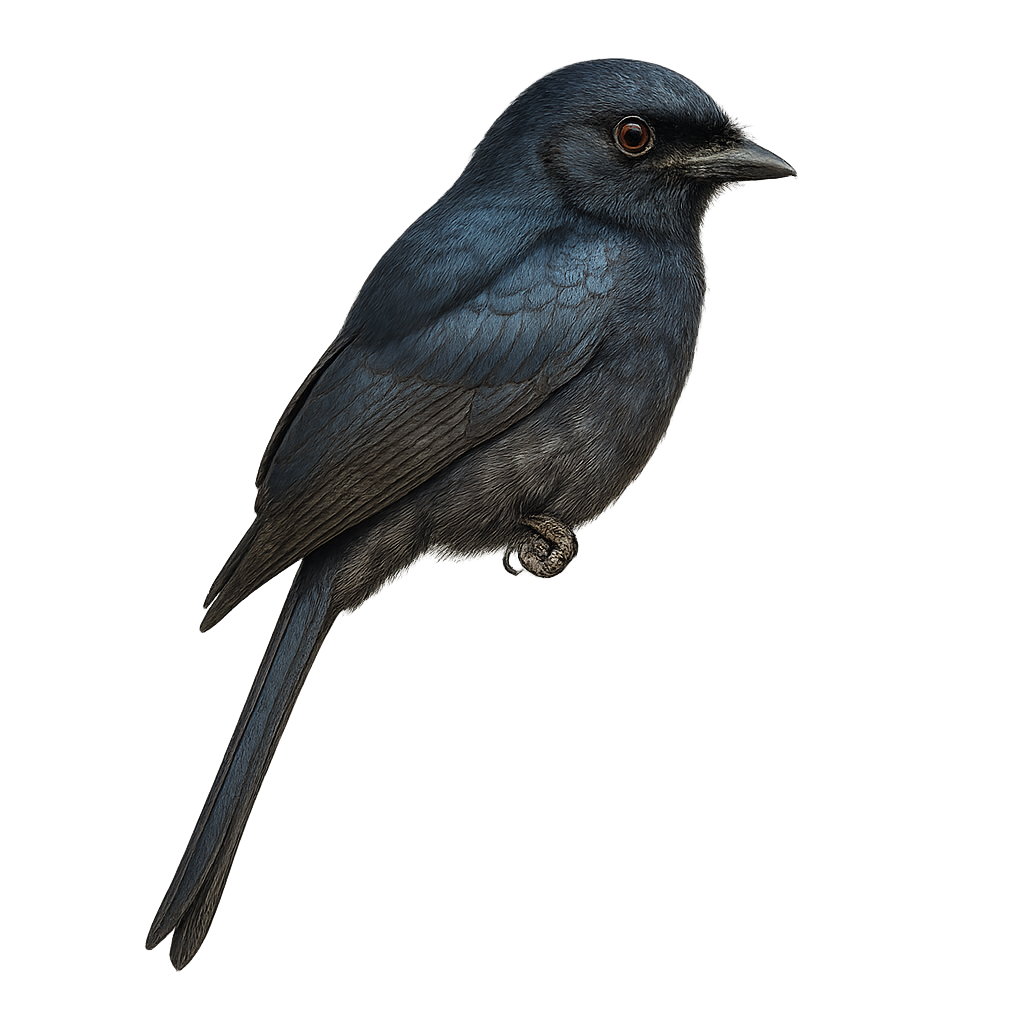
The Fork-tailed Drongo, Dicrurus adsimilis, is a medium-sized bird known for its glossy black plumage and distinctive forked tail. It is commonly found in open forests, savannas, and agricultural areas across sub-Saharan Africa. This drongo is noted for its bold and aggressive behavior, often attacking larger predators to defend its territory. It primarily feeds on insects but can also consume small vertebrates. Its varied and melodious song is often heard at dawn and dusk. The Fork-tailed Drongo is also famous for its ability to mimic the calls of other birds, allowing it to deceive competitors and steal their food.
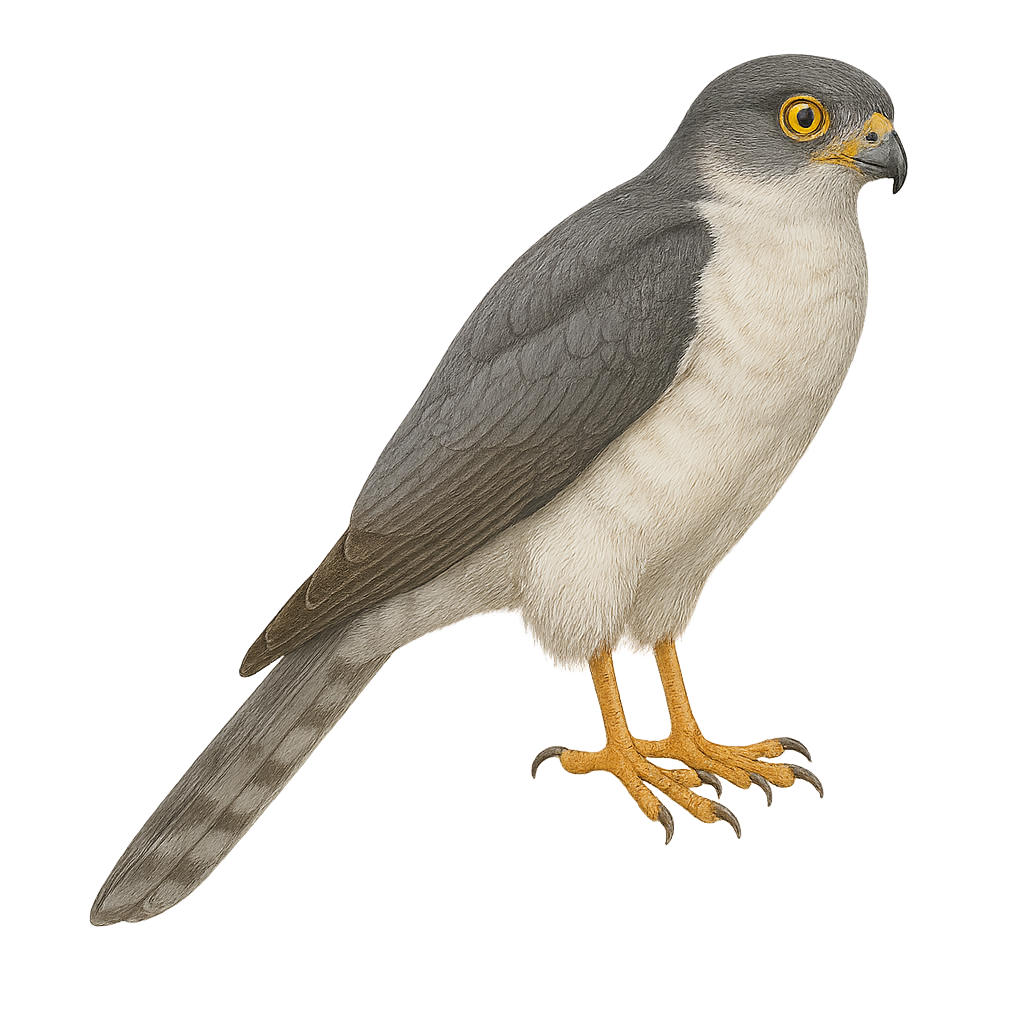
The Frances's Sparrowhawk, or Accipiter francesiae, is a small raptor endemic to Madagascar. This agile predator is recognizable by its slender silhouette and short, rounded wings, ideal for maneuvering through dense forests. Its plumage is generally gray on top and white with brown streaks underneath, allowing it to blend into its environment. It primarily feeds on small birds, insects, and occasionally small mammals. The Frances's Sparrowhawk is a discreet bird, often difficult to observe due to its shy behavior. It plays a crucial role in controlling the populations of its prey, thus contributing to the ecological balance of its habitat.

The Fennec is a small fox, easily recognized by its large ears, which can measure up to 15 cm long, nearly a third of its body size. It measures about 24 to 41 cm in length, with a tail measuring 18 to 30 cm, and weighs between 0.8 and 1.5 kg. Its fur is light beige to sandy, allowing it to blend perfectly into its desert environment. The large ears of the Fennec are not only a distinctive feature but also play a crucial role in regulating its body temperature by dissipating excess heat. The Fennec primarily inhabits the deserts and semi-desert regions of North Africa, especially the Sahara. It is a nocturnal animal, hunting primarily at night to avoid the intense heat of the day. Its diet is omnivorous, consisting of small mammals, insects, fruits, and roots. Thanks to its digging skills, it is able to find water beneath the sand, allowing it to survive in an environment where water is scarce. While the Fennec is not currently threatened, it may face risks related to habitat destruction and illegal capture for the pet trade.
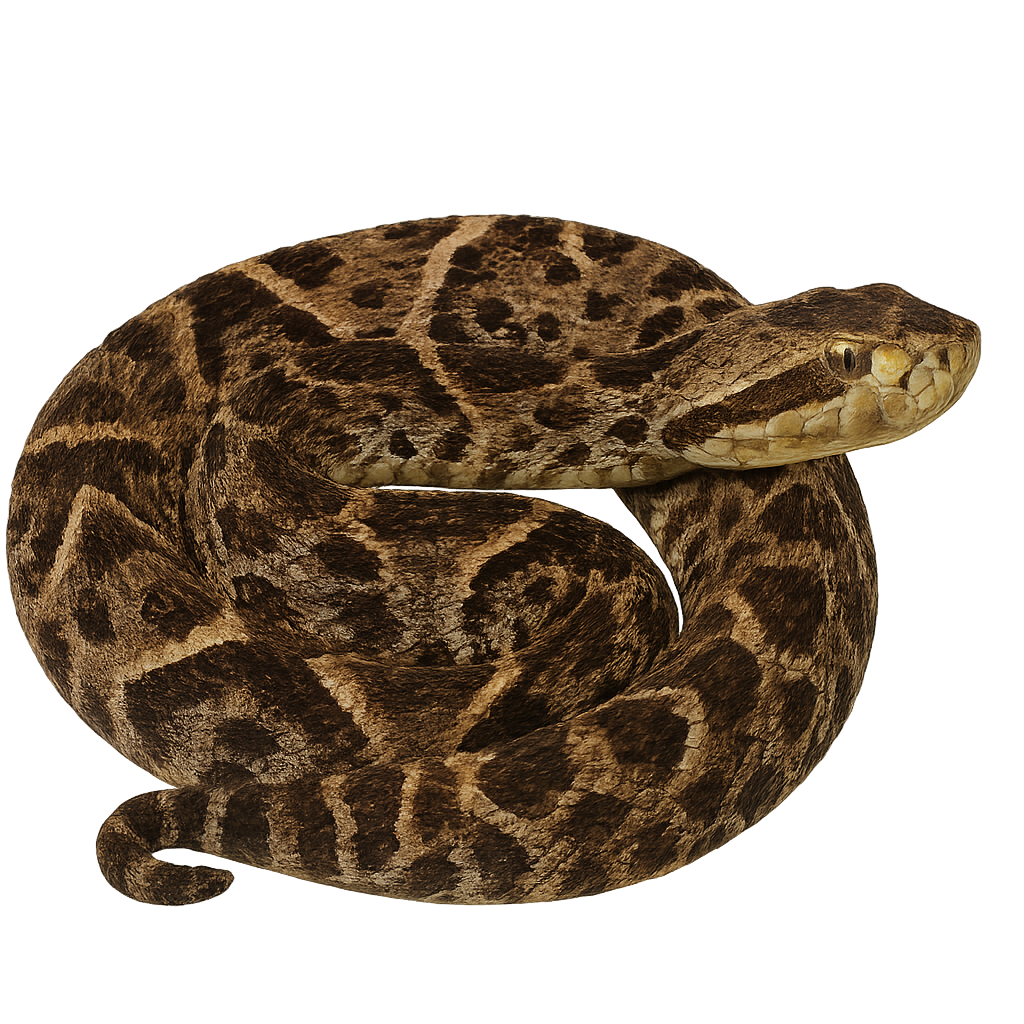

The Barba amarilla is a venomous viper found primarily in the rainforests of Central and South America. It is a medium to large snake, typically measuring between 1.5 and 2.5 meters in length, although some individuals can reach up to 3 meters. Its body is robust, and its color ranges from brown, gray, to olive, with diamond-shaped patterns along its back, which helps it blend into its environment. Its head is triangular and distinct from the body, with characteristic scales that give it a "spearhead" appearance. This snake is primarily terrestrial and often hides under leaves or in underbrush to hunt or rest. The Barba amarilla is an opportunistic predator, feeding mainly on small mammals, birds, and frogs. Its venom is extremely potent and can cause severe injury or death if antivenom is not administered quickly. It usually strikes by surprise, launching itself at its prey or an intruder. While it is an important predator in its ecosystem, it faces threats related to deforestation and habitat loss.
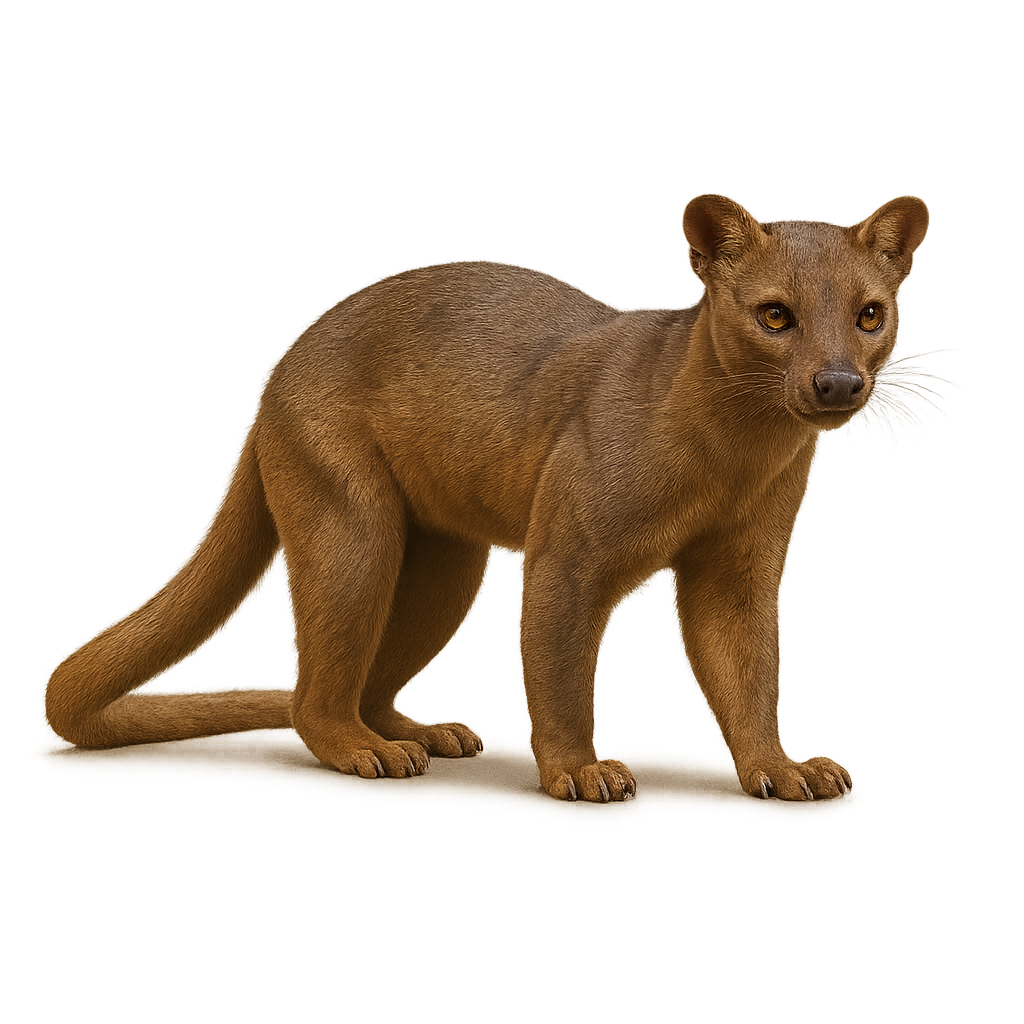
The Fossa is a carnivorous predator endemic to Madagascar, a unique mix between a feline and a mongoose, with a sleek body and a long tail. It is the largest land predator on the island, primarily feeding on lemurs, but also small mammals, birds, and reptiles. The Fossa is particularly agile and capable of climbing, but it often prefers to hunt its prey on the ground. Although secretive and difficult to observe, it plays an important role in the ecosystem of Madagascar. The Fossa is endangered due to the loss of its natural habitat.
The Forest Fody, or Foudia omissa, is a small bird endemic to Madagascar. It is primarily recognizable by its bright red plumage in males, while females display more subdued shades of brown and gray. This passerine is mainly found in the island's humid forests, where it feeds on seeds, insects, and small fruits. The Forest Fody is a sociable bird, often seen in small groups. Its breeding season coincides with the rainy season, providing an abundance of food for the young. Although relatively common, deforestation poses a threat to its natural habitat.
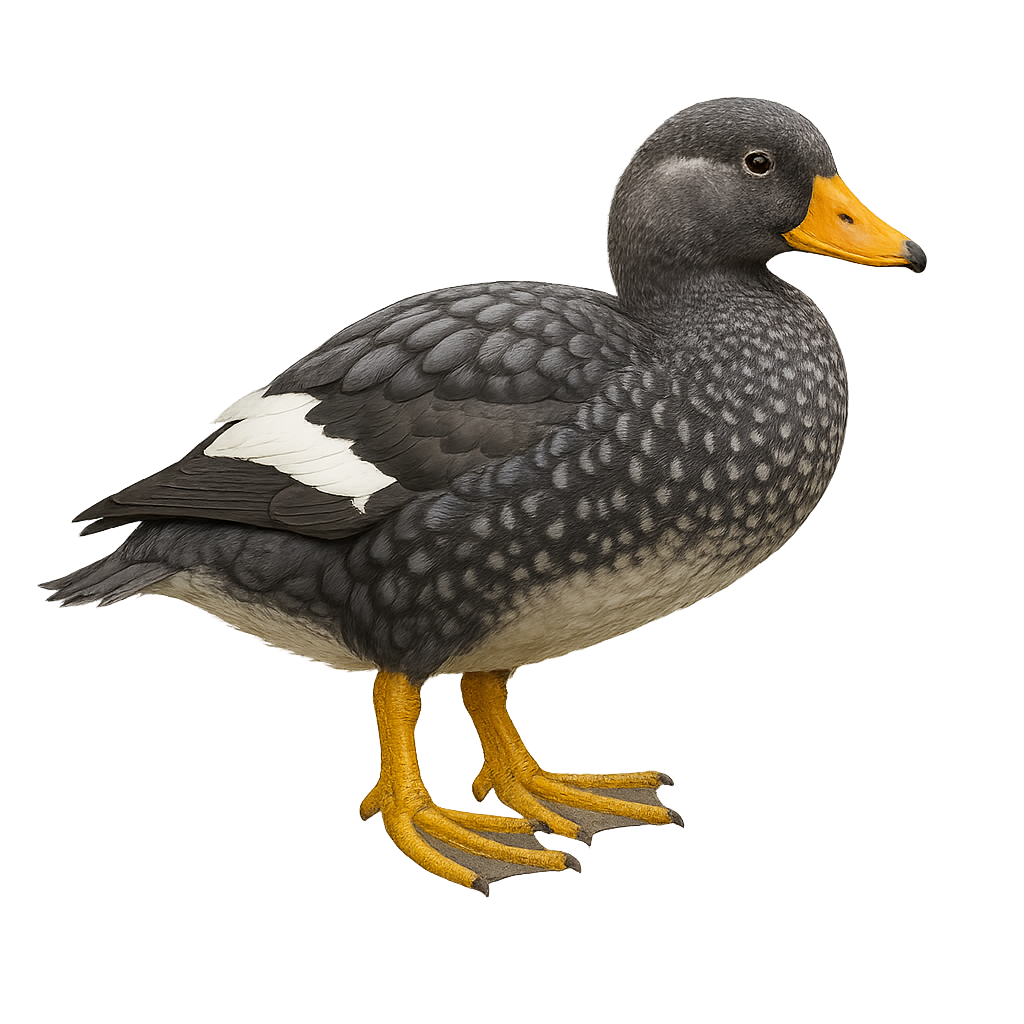
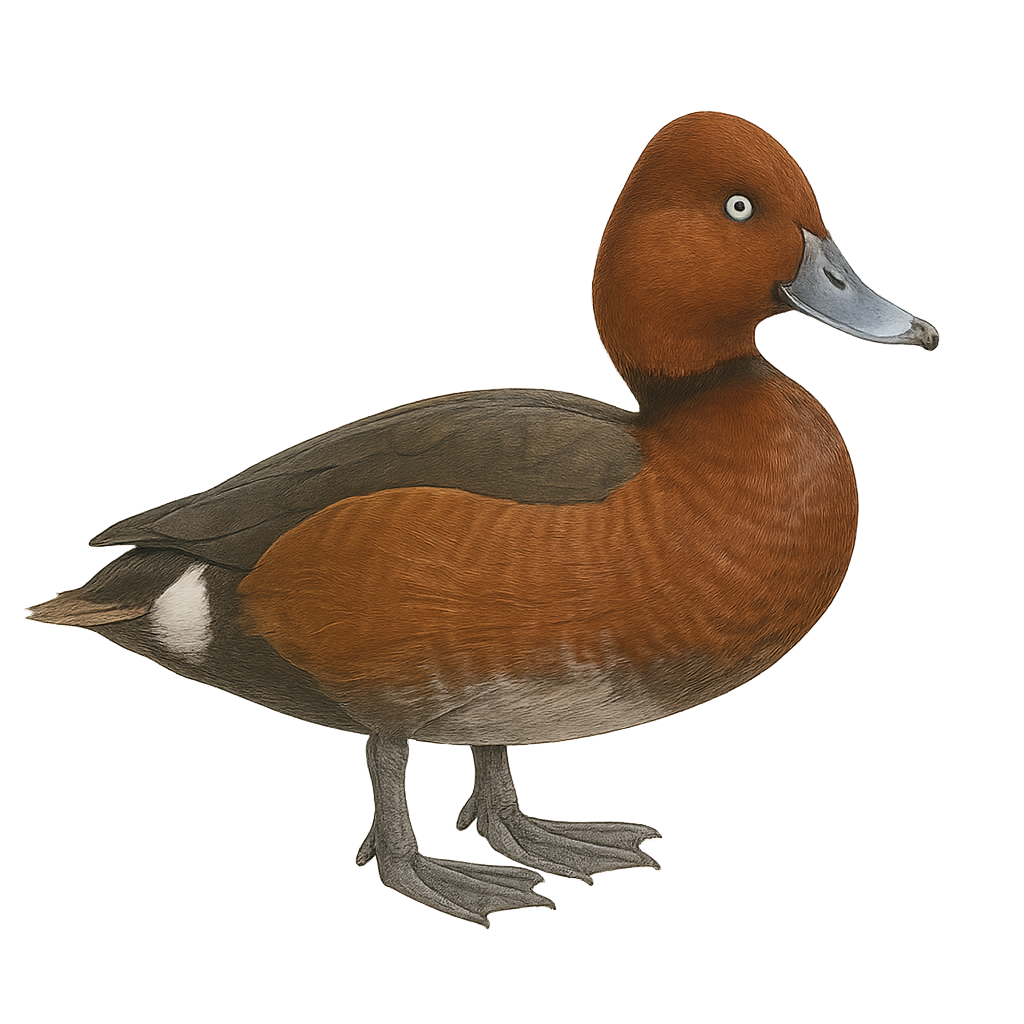
The Ferruginous Duck is a small diving duck measuring between 38 and 42 cm in length with a wingspan of 63 to 67 cm. The male has a dark chestnut plumage with white undertail coverts and distinctive white eyes. The female is duller brown with dark brown eyes. This species inhabits shallow lakes, marshes, and ponds rich in aquatic vegetation, preferring calm areas with dense reed beds. It feeds mainly on seeds and aquatic plants, supplemented by mollusks, aquatic insects, and small fish. The Ferruginous Duck is migratory, breeding in Eastern Europe and Asia, and wintering in North Africa, South Asia, and around the Mediterranean. Listed as Near Threatened by the IUCN, it faces habitat loss, pollution, and illegal hunting.
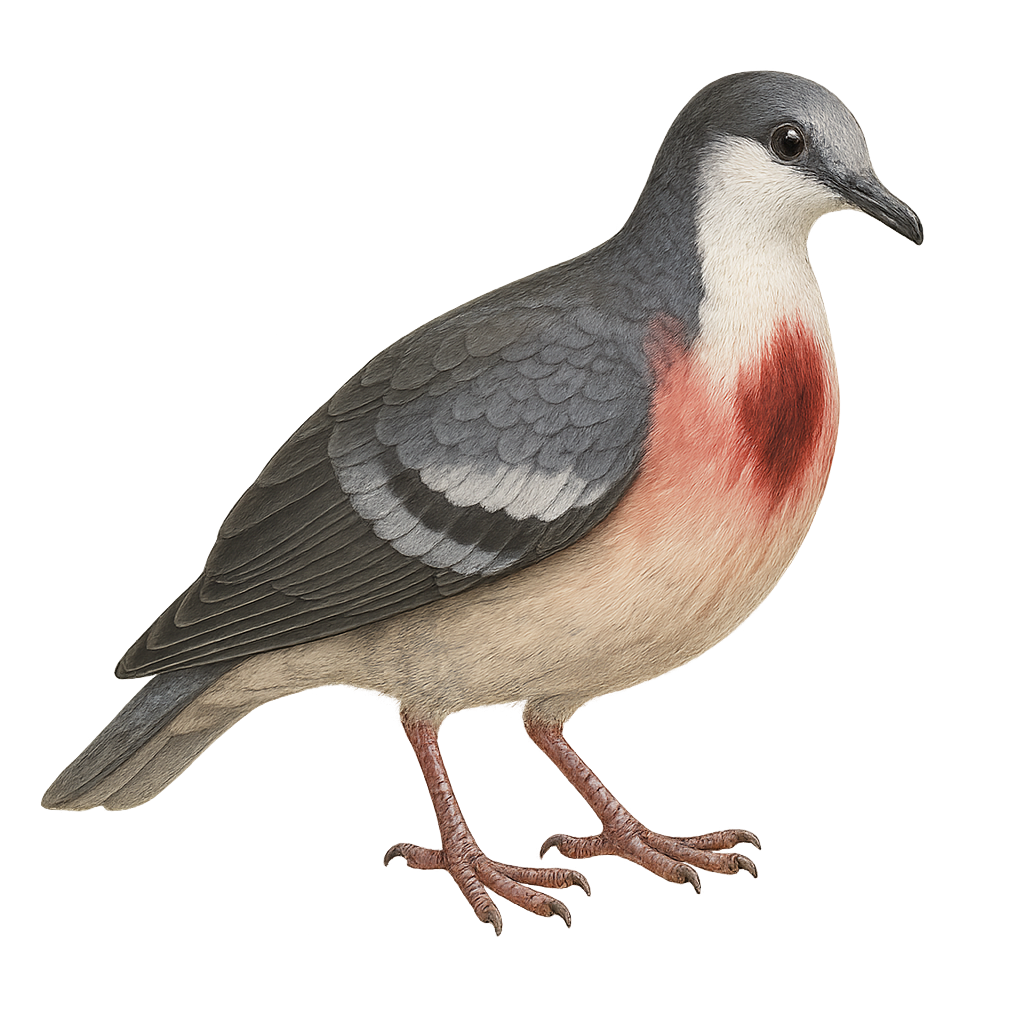
The Pampusana stairi, commonly known as the Friendly Ground Dove, is a bird species endemic to the South Pacific islands, particularly Samoa and Tonga. This medium-sized pigeon is recognizable by its grey-blue plumage with metallic sheen on the wings and a white chest. It prefers dense forests and wooded areas, where it primarily feeds on seeds and fallen fruits. Though discreet, it plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding forest regeneration. Its population is threatened by deforestation and the introduction of non-native predators, leading to its classification as a vulnerable species by the IUCN.
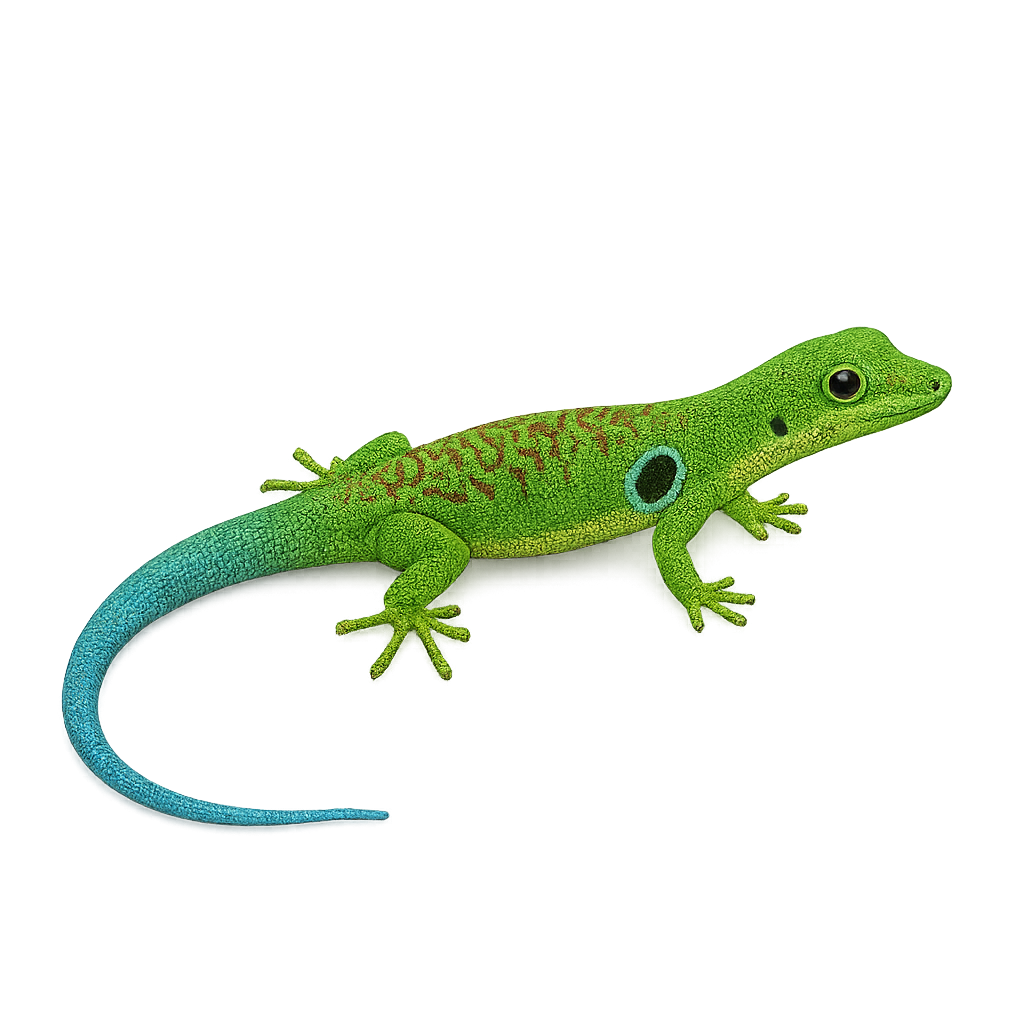
The Phelsuma quadriocellata, or four-spotted day gecko, is a small, colorful lizard native to Madagascar. It is known for its bright green skin adorned with blue and red spots, and its distinctive four black spots on the back. This diurnal gecko is often found in humid tropical forests, feeding mainly on insects and nectar. It is appreciated for its adaptability to various environments, including gardens and human dwellings. Although generally suspicious, it can become tolerant of humans over time. Its reproduction is oviparous, with a gestation period of about 40 to 45 days.
The Fiery-breasted Bushshrike is a bird with vibrant plumage, primarily bright red on the chest and belly, contrasting with an olive-green back. This passerine, belonging to the Malaconotidae family, is known for its melodious and powerful song. It primarily inhabits the humid tropical forests of Central and West Africa, where it feeds on insects and small invertebrates. Although discreet, it can be observed in pairs or small groups. Its ability to blend into dense foliage sometimes makes it difficult to spot. Its conservation status is currently stable, but deforestation could threaten its habitats in the future.
The Forbes's Plover, scientifically known as Charadrius forbesi, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Charadriidae family. It is characterized by its light brown plumage on the back and white on the belly, with a distinctive black band across the chest. Adults have a dark brown cap and a black bill. This plover is primarily found in the savannas and wet grasslands of West Africa, where it feeds on insects, worms, and small crustaceans. It is often seen in small groups, moving quickly on the ground in search of food. Although its conservation status is currently considered "least concern," habitat degradation could pose a future threat.
The Forbes's Plover, or Charadrius forbesi, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Charadriidae family. It is primarily found in West Africa, particularly in Nigeria, Ghana, and Ivory Coast. This bird prefers open habitats such as grassy plains and wetlands. It is characterized by its brown-grey plumage with a black breast band and white belly. The beak is black, and the legs are yellowish. The Forbes's Plover is a diurnal bird, often seen foraging for food, mainly insects and small invertebrates, on the ground. Although its conservation status is currently considered of least concern, habitat degradation could pose future threats.
The Finca Primavera rocket frog, scientifically known as Colostethus alacris, is a small, vibrant frog species native to the humid tropical forests of South America. It is primarily found in the mountainous regions of Colombia, where it inhabits leaf litter and areas near water streams. Its coloration ranges from brown to green, with distinctive patterns that allow it to blend effectively into its natural surroundings. This species is known for its distinctive call, used by males to attract females during the breeding season. Although its conservation status is currently concerning due to deforestation and habitat loss, it continues to fascinate herpetologists and nature enthusiasts with its unique behavior and ecology.