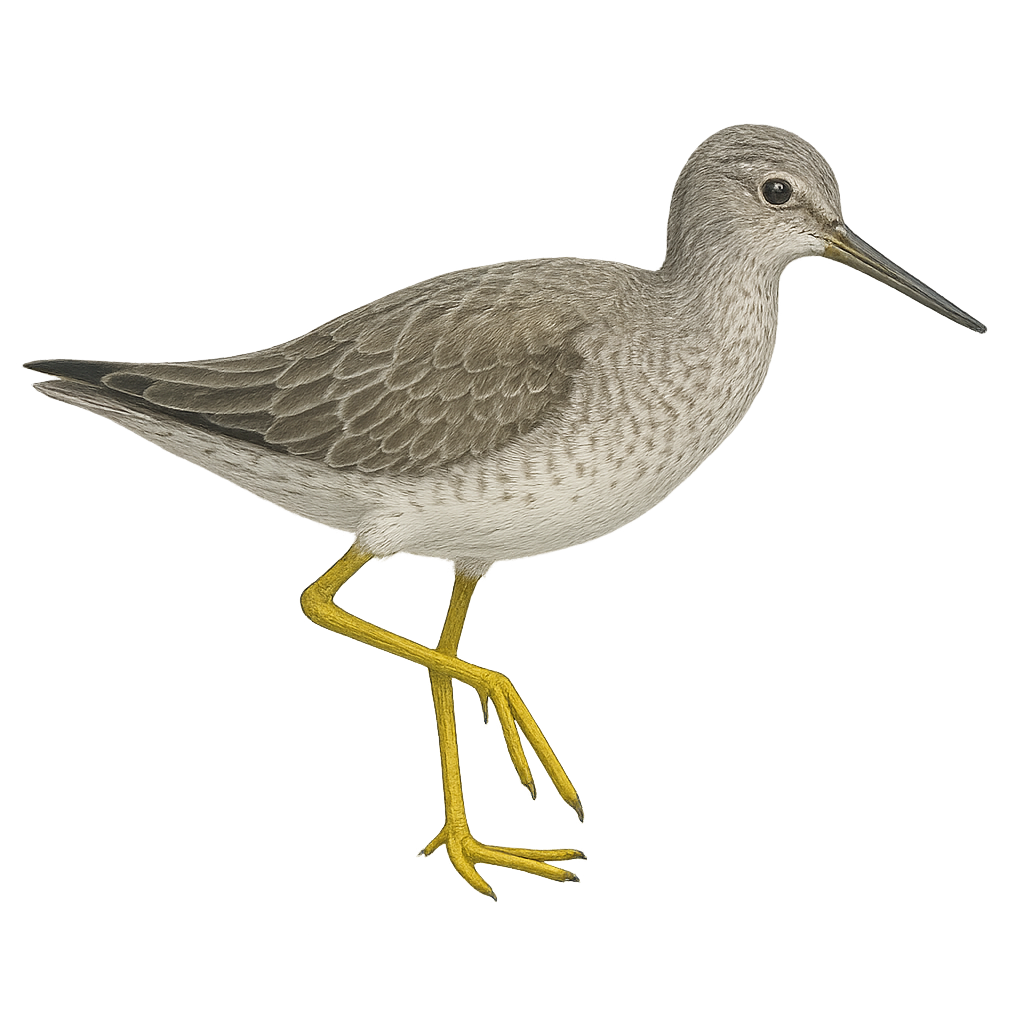
The Grey-tailed Tattler, or Tringa brevipes, is a medium-sized wader, measuring about 25 cm in length. It is easily recognizable by its grey plumage on the back and wings, contrasting with a lighter belly. Its bill is straight and relatively long, adapted for foraging in mudflats and shores. During the breeding season, it displays dark streaks on its chest. This migratory bird mainly frequents the coasts and estuaries of Asia and Australia. It feeds primarily on small invertebrates, which it captures by probing the wet ground. Although its conservation status is currently considered of least concern, habitat degradation could pose a long-term threat.
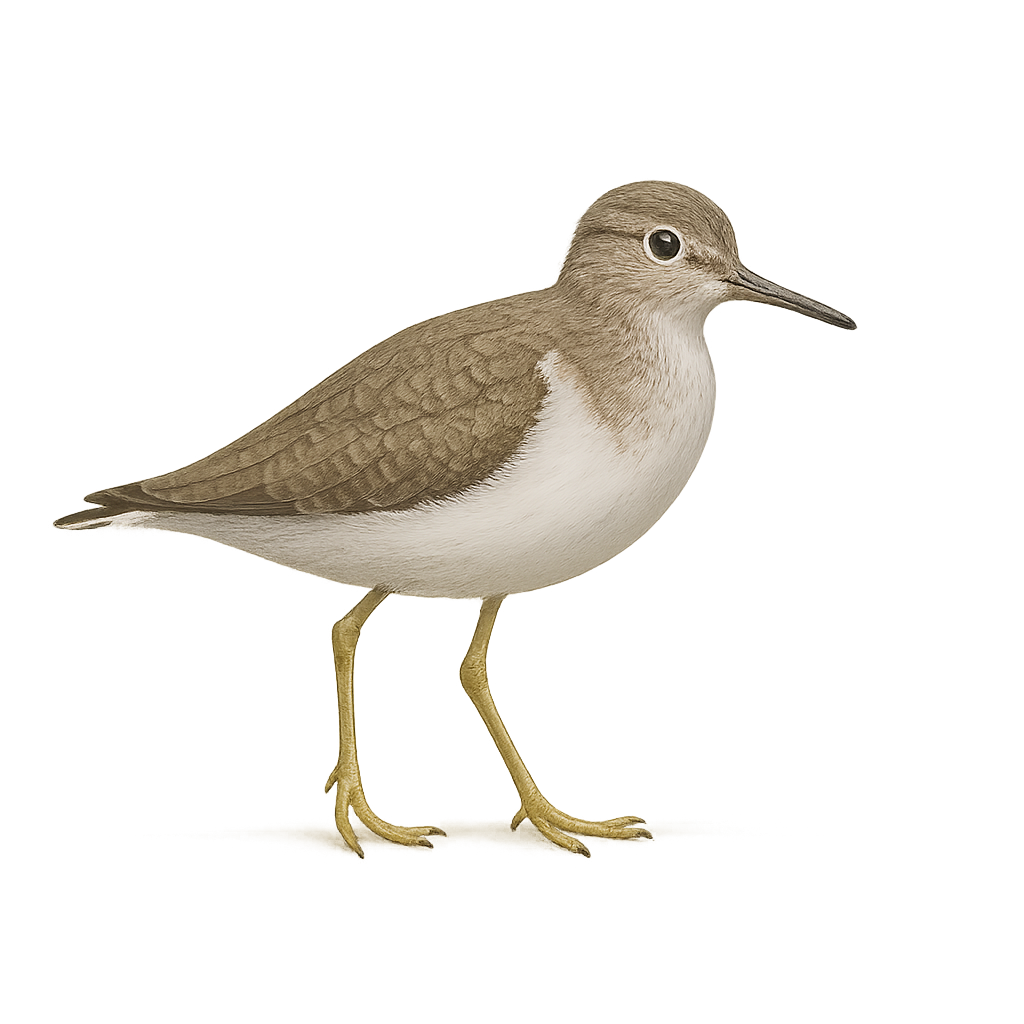
The Common Sandpiper is a small, agile, and active wader, easily recognizable by its light brown plumage, speckled with darker spots, and its long, slender legs. It is also distinguished by its short, straight bill and its energetic and nervous behavior. It is commonly found along riverbanks, estuaries, marshes, and lakes, where it hunts by running along the shores, capturing small insects, worms, and crustaceans found in the mud and shallow water.
This migratory bird typically breeds in temperate regions of Europe and Asia and migrates to North Africa for the winter. While the population of the Common Sandpiper remains stable in many regions, the species is threatened by the loss of wetland habitats and the effects of climate change, which alters aquatic ecosystems. The species is protected in some areas where it is found.
The Great Grey Owl is a large nocturnal raptor, easily recognizable by its broad facial disc and piercing yellow eyes. Its plumage is primarily gray and brown, with lighter markings on the belly and wings. It has a massive build, a round head, and long wings that allow it to fly silently. This raptor primarily inhabits boreal forests and northern regions of Europe, Asia, and North America.
The Great Grey Owl primarily hunts small mammals, such as hares, rodents, and birds. It has a remarkable ability to locate its prey with its keen hearing and silent flight. It is a solitary owl, preferring dense forests where it can hide during the day. While its population remains generally stable, it is threatened by deforestation, habitat loss, and human disturbances. It is protected in many areas to ensure the preservation of its forest habitats.
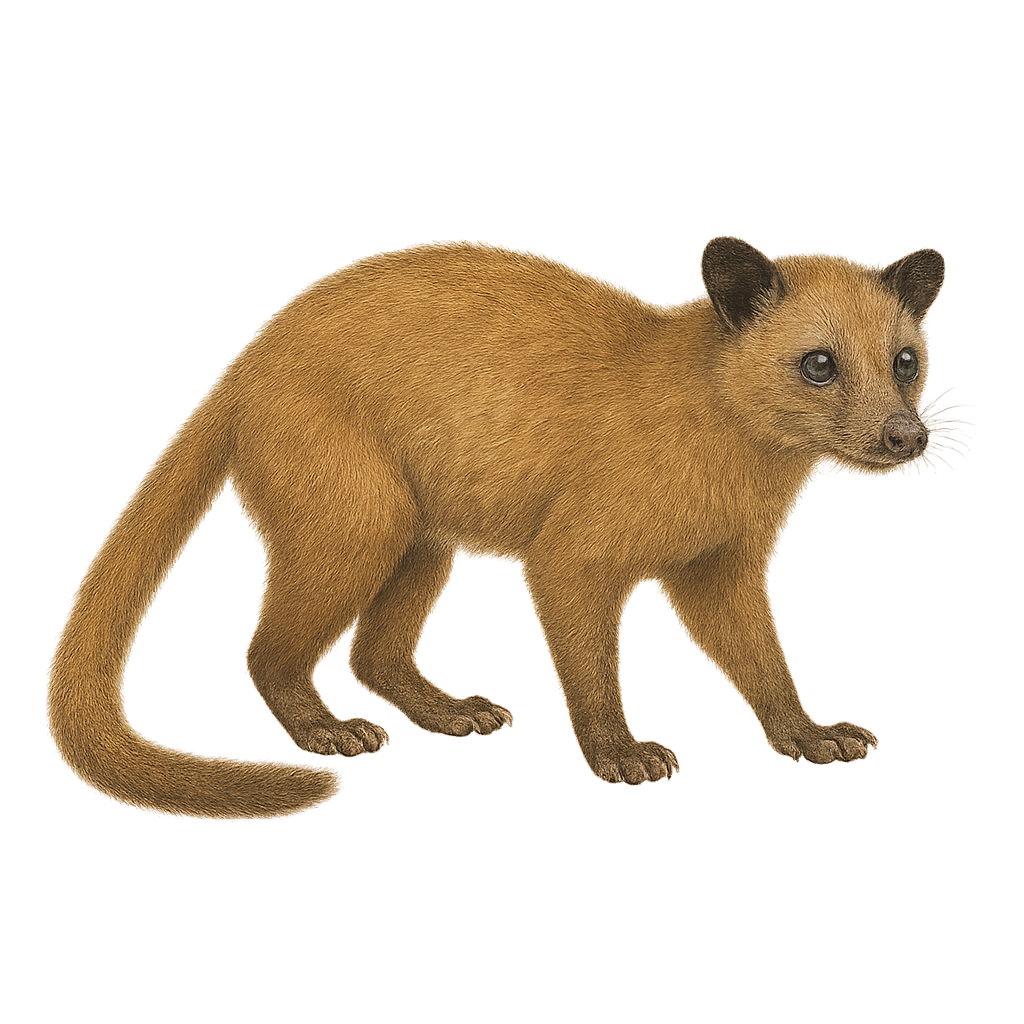
The Golden Palm Civet, or Paradoxurus zeylonensis, is a nocturnal mammal endemic to Sri Lanka. Belonging to the Viverridae family, it is primarily found in tropical rainforests, tea plantations, and wooded areas. This species is recognizable by its golden fur and bushy tail. It is omnivorous, feeding on fruits, insects, and small vertebrates. Although elusive, it plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, contributing to the biodiversity of its habitat. Unfortunately, deforestation and habitat loss threaten its survival, classifying it as vulnerable according to the IUCN.
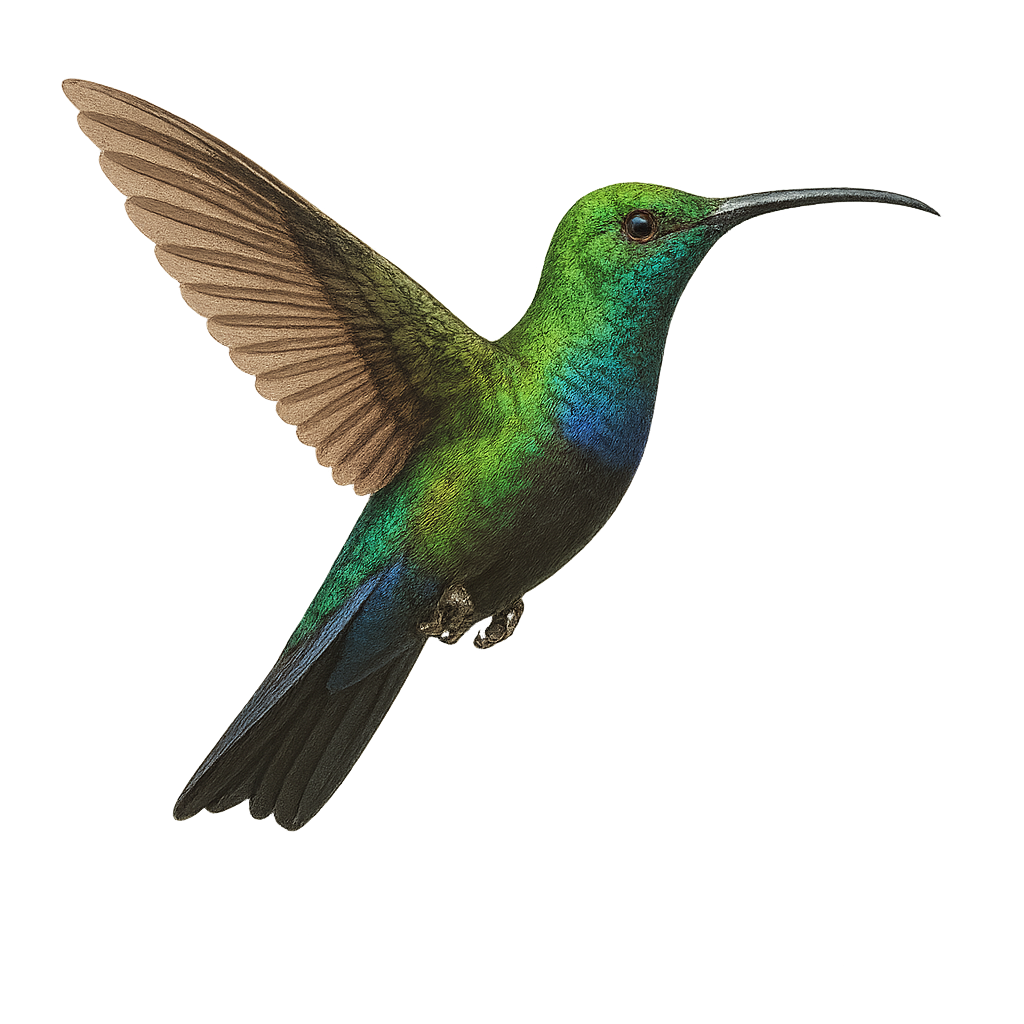
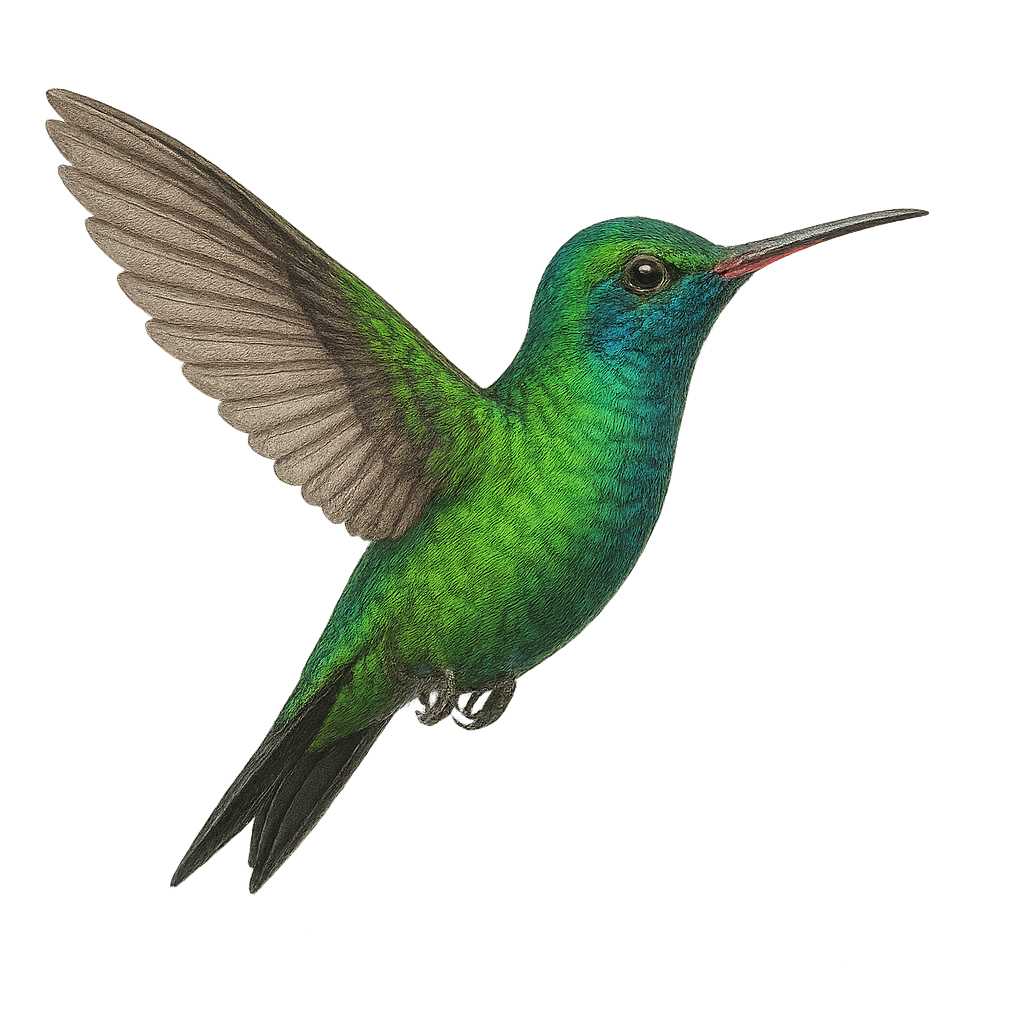
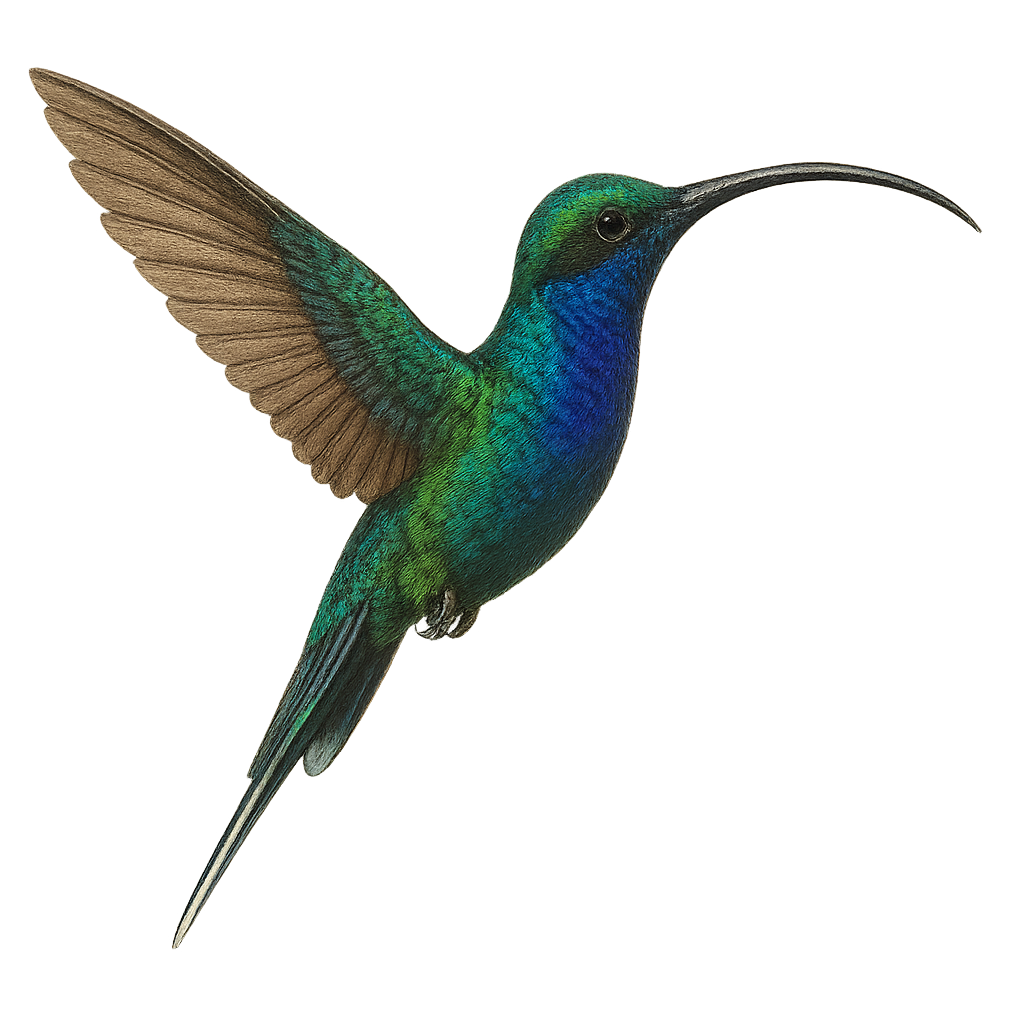
The Green-throated Carib, Eulampis holosericeus, is a captivating bird native to the Caribbean, known for its vibrant and iridescent plumage. This medium-sized hummingbird features a shimmering green throat and a body with metallic hues. It is commonly found in tropical forests, gardens, and coastal areas, where it primarily feeds on nectar, supplemented by insects. The Green-throated Carib is an essential pollinator, playing a crucial role in the reproduction of flowering plants. Its rapid and agile flight allows it to maneuver easily among flowers, while its territorial behavior drives it to vigorously defend its food sources.
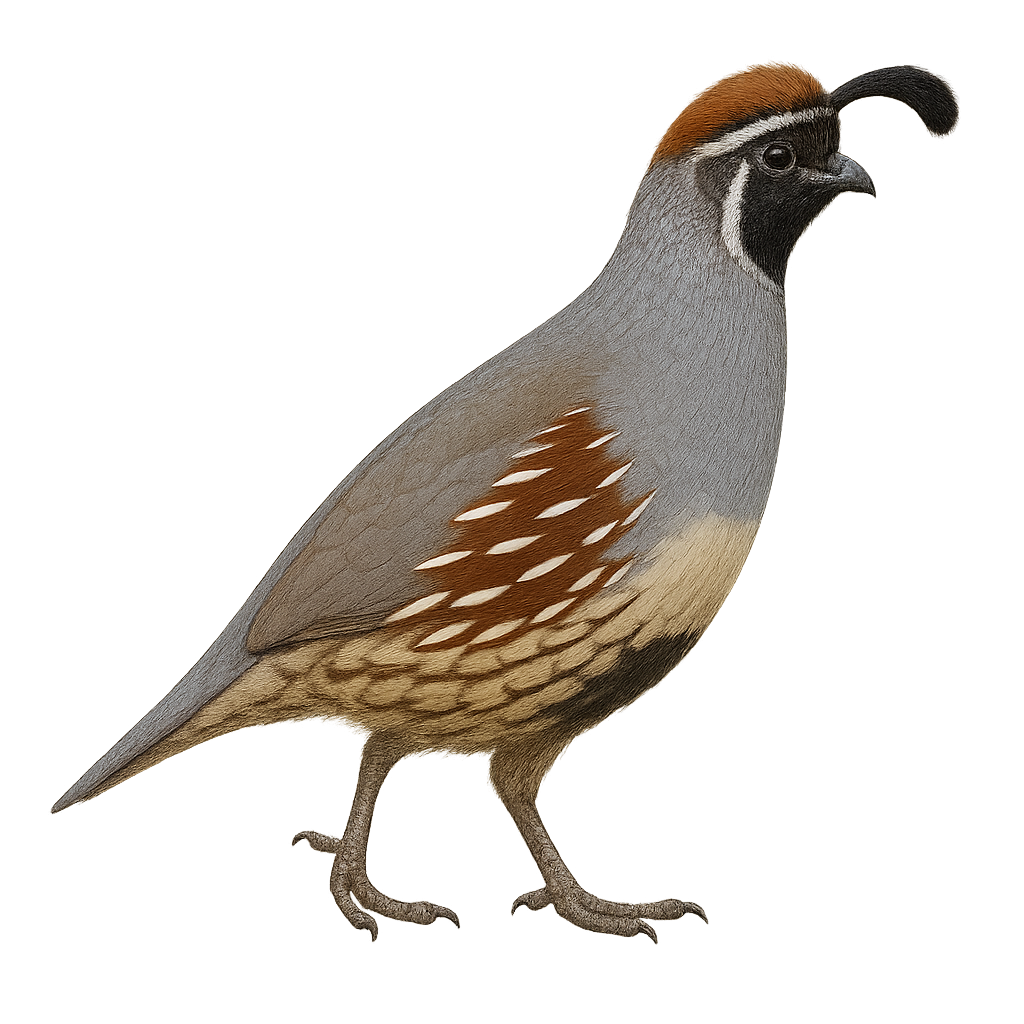
The Gambel's Quail, scientifically known as Callipepla gambelii, is a medium-sized ground-dwelling bird recognized for its distinctive comma-shaped topknot and bluish-gray plumage with black and white markings. It inhabits the arid regions of the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. This bird favors desert and semi-desert habitats, feeding primarily on seeds, leaves, and insects. Social by nature, Gambel's Quail often forms groups called "coveys". During the breeding season, males perform courtship displays to attract females. Although capable of flight, it prefers to run to evade predators.
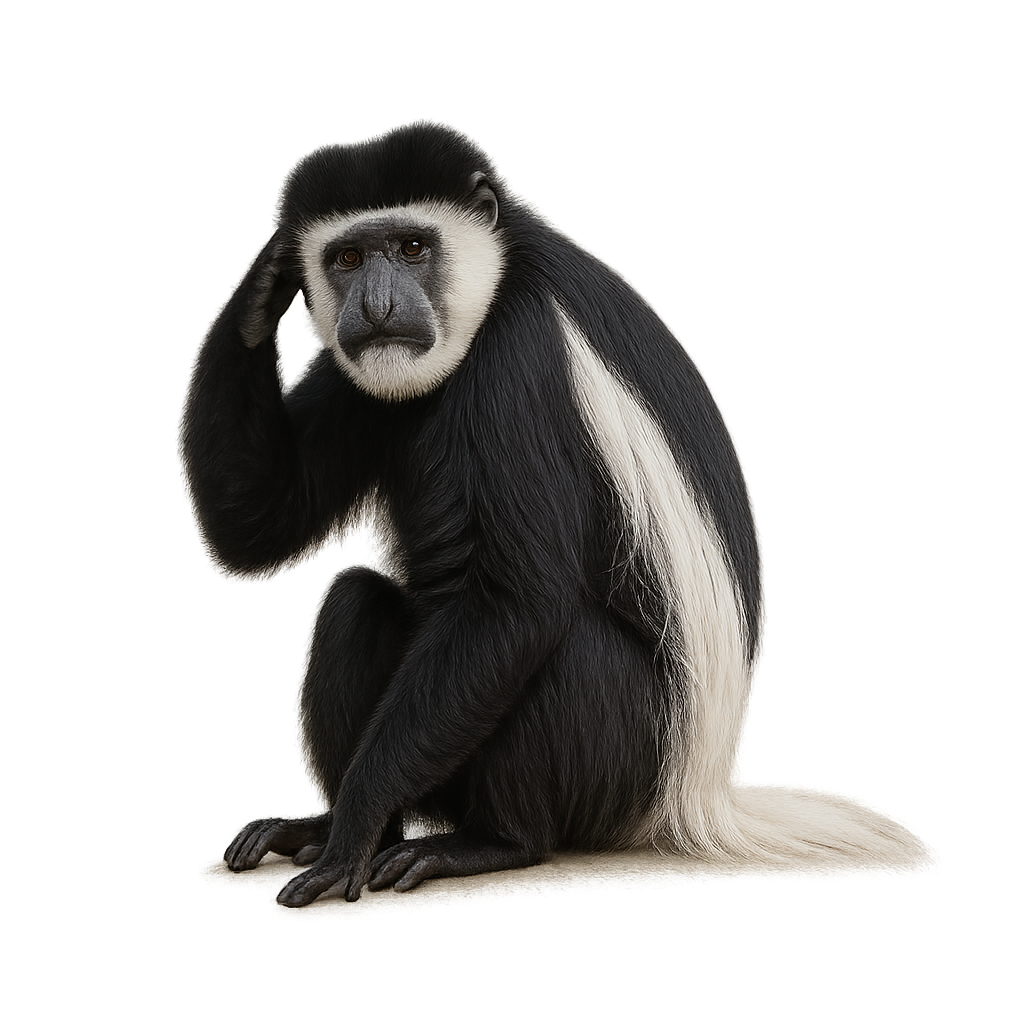
The Guereza Colobus is a large primate belonging to the family Cercopithecidae, easily recognized by its distinctive black and white fur. It has a white mane around its face, white limbs, and a long, bushy tail that helps it stabilize in the trees. Its black body is contrasted by tufts of white fur along the sides and back, making it one of the most elegant primates of the forest. It primarily lives in the tropical and subtropical forests of East Africa, spending most of its time in the trees.
The Guereza Colobus is primarily herbivorous, feeding on leaves, fruits, seeds, and flowers. With its specialized stomach, it can digest tough, fibrous leaves that other animals cannot consume. It lives in social groups led by a dominant male and is generally very calm, moving gracefully and agilely through the forest canopy. Although its population remains stable in some protected areas, it faces threats due to deforestation and hunting, causing some populations to be classified as vulnerable.
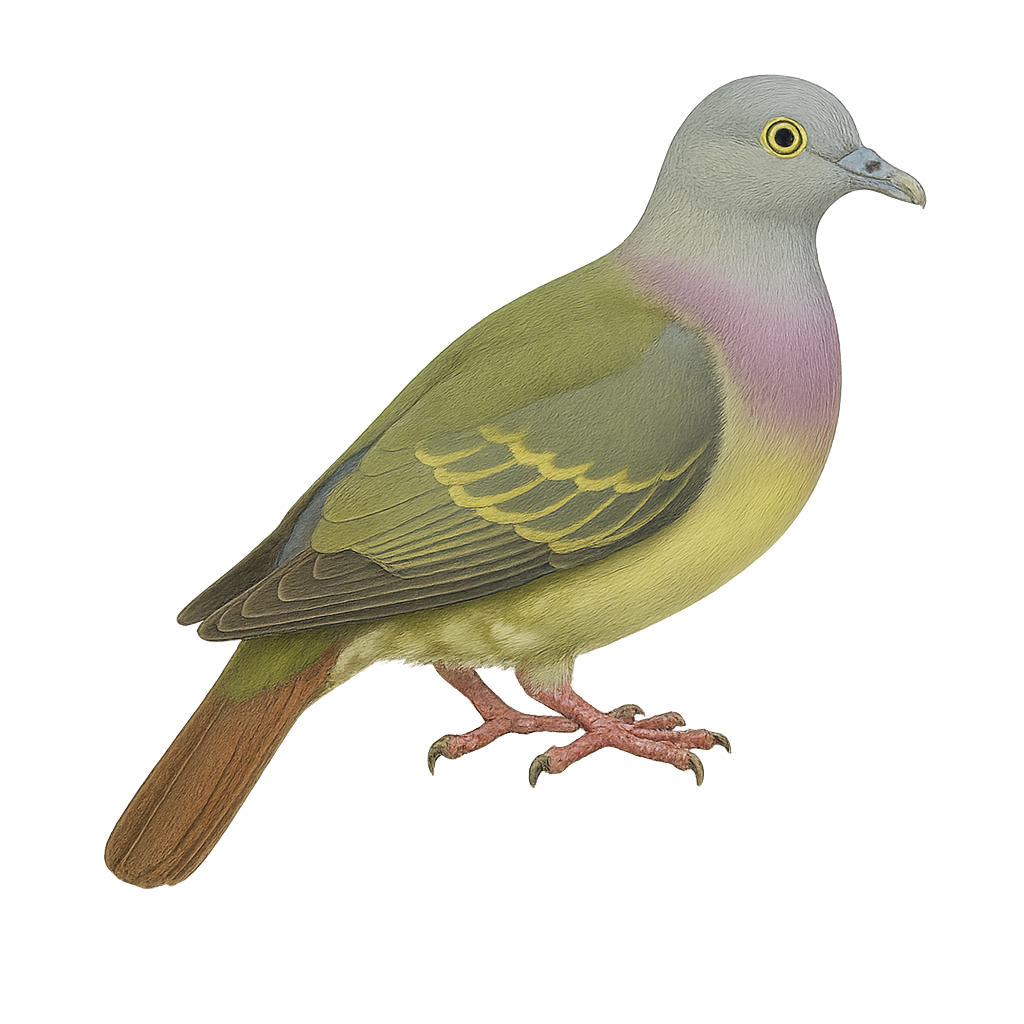
The Grey-cheeked Green Pigeon, Treron griseicauda, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Columbidae family. It is characterized by its vibrant green plumage, with a distinctive grey head and tail. This bird is primarily arboreal, inhabiting tropical and subtropical moist forests. It feeds mainly on fruits, playing a crucial role in seed dispersal. Its call is soft and melodious, often heard at dawn and dusk. Although generally discreet, it can be observed in small groups, especially near food sources. Its population is stable, but deforestation poses a potential threat to its natural habitat.
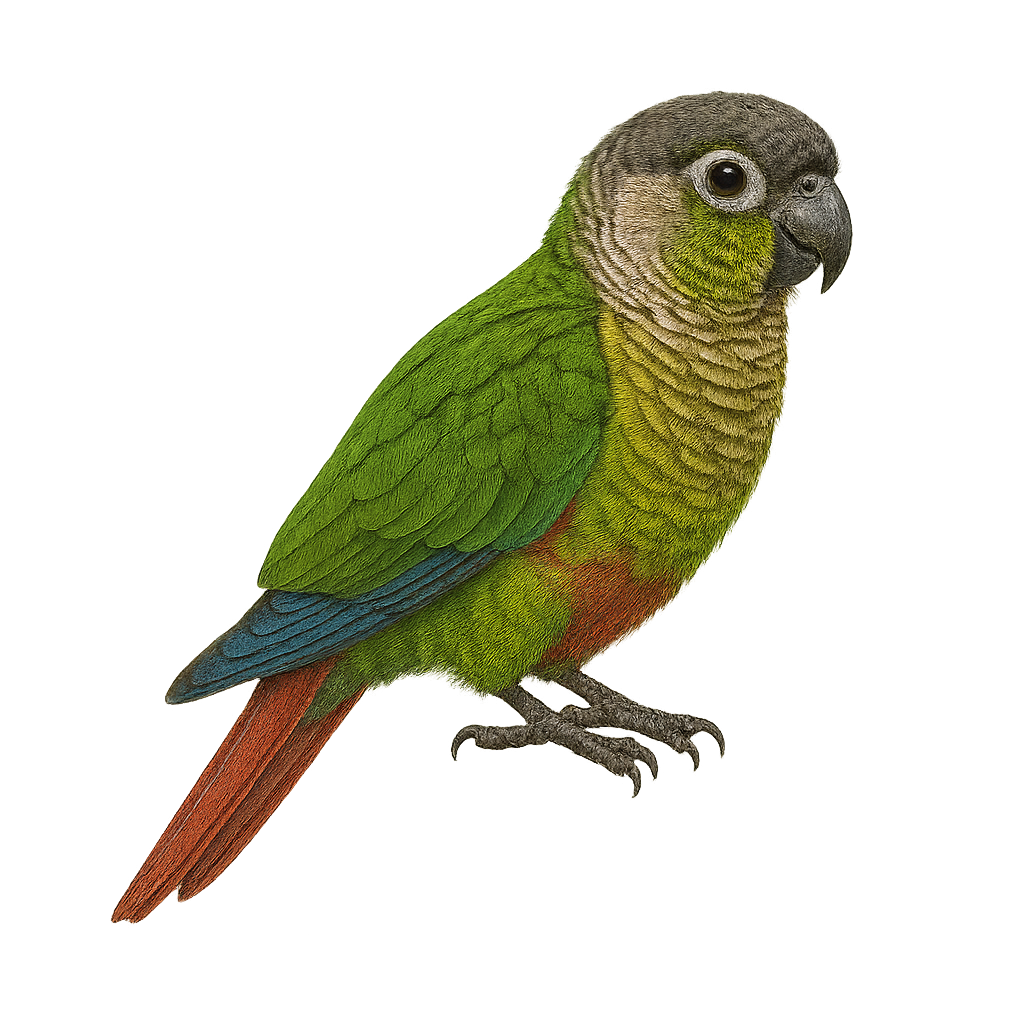
The Green-cheeked Parakeet, or Pyrrhura molinae, is a small parrot native to South America, particularly the tropical forests of Brazil, Bolivia, and Argentina. It is recognizable by its bright green plumage, green cheeks, and reddish tail. Measuring about 26 cm in length, it is appreciated for its curious and sociable personality. It lives in groups and primarily feeds on fruits, seeds, and flowers. In captivity, it is often chosen as a pet due to its playful and affectionate nature. Although it can be noisy, it is generally less vocal than other parrots.
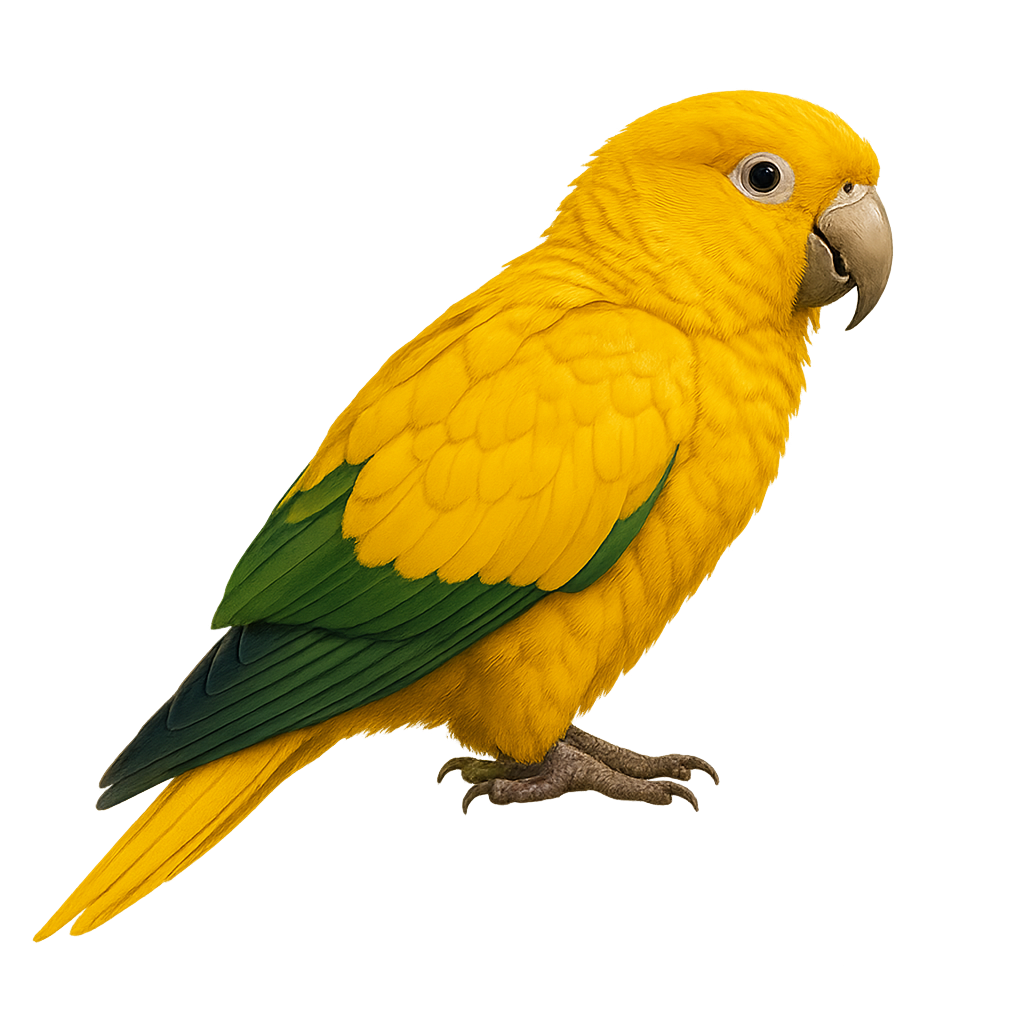
The Golden Parakeet, or Guaruba guarouba, is a medium-sized bird known for its bright yellow plumage and green wings. Native to the Amazon rainforest in Brazil, it is often seen in noisy flocks. This species is threatened by deforestation and illegal trade. It primarily feeds on fruits, seeds, and flowers. Its social behavior is characterized by strong interaction within groups, and it is known for its curious and playful nature. The Golden Parakeet is a symbol of Amazonian biodiversity and the importance of conserving natural habitats.
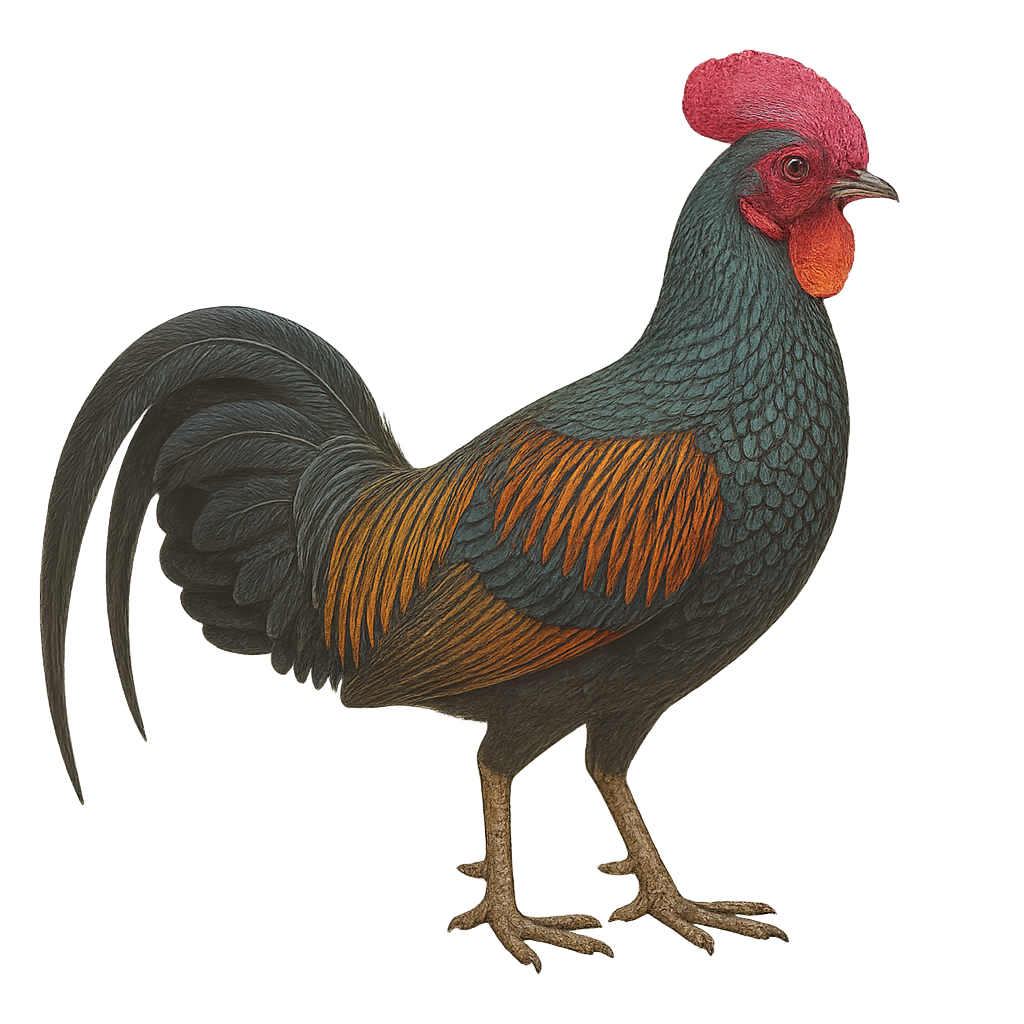
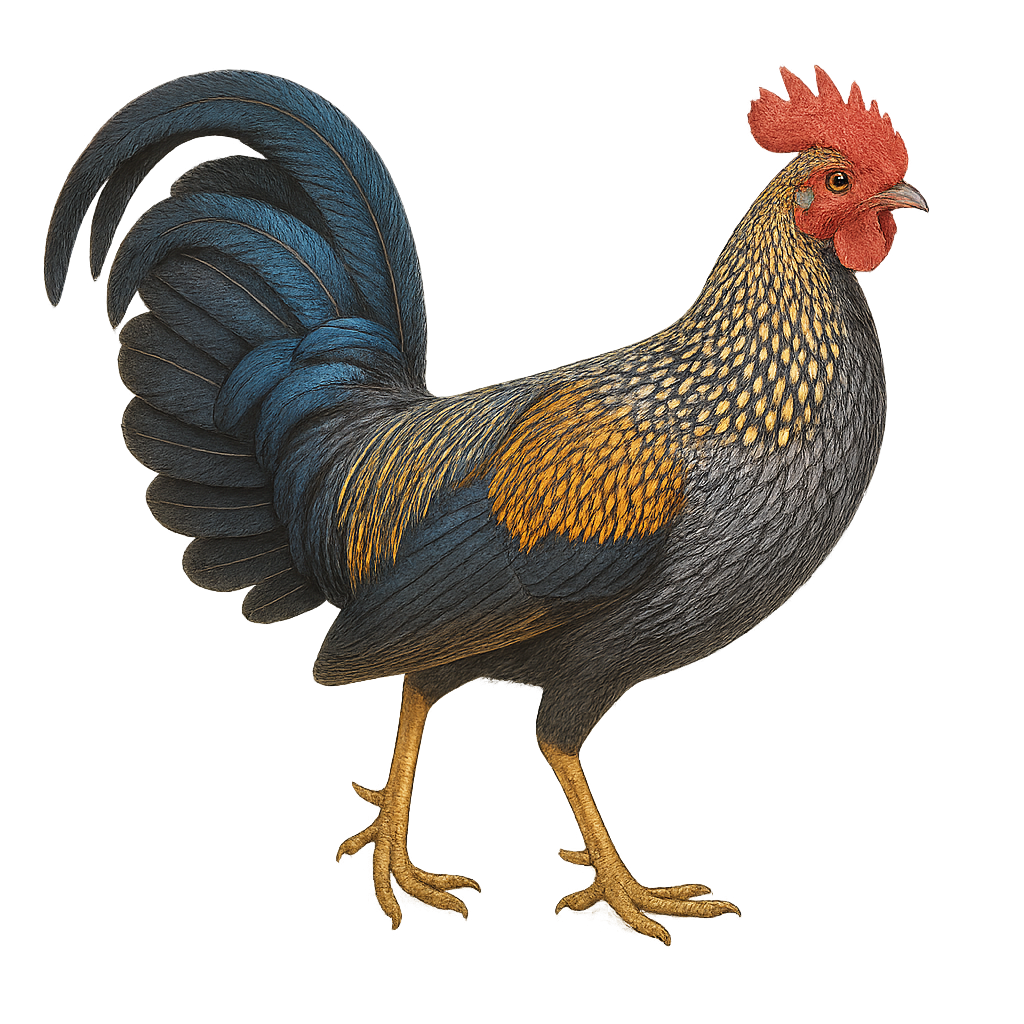
The Green Junglefowl, or Gallus varius, is a gallinaceous bird species native to the Indonesian islands of Java, Bali, and Lombok. This striking bird is known for its vibrant plumage, featuring shades of green, blue, and black with metallic sheen. The male boasts a bright red comb and distinctive facial wattles. It primarily inhabits tropical forests, savannas, and agricultural areas, feeding on seeds, insects, and small invertebrates. The Green Junglefowl is a social bird, often seen in small groups. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it is currently listed as least concern by the IUCN.
The Grey Junglefowl, or Gallus sonneratii, is a pheasant species native to the forests of southern India. Known for its striking plumage, it features shades of grey, black, and metallic sheens. Males have a vivid red comb and wattles, along with neck feathers that resemble golden filaments. These birds are primarily terrestrial, preferring dense forests and wooded areas. They feed on seeds, insects, and small invertebrates. The Grey Junglefowl plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by aiding in seed dispersal. Although relatively common in its natural habitat, it faces threats from habitat loss due to deforestation.
The Green-and-black Fruiteater, or Pipreola riefferii, is a striking bird found in Andean montane forests from Venezuela to northern Bolivia. Males show vivid green upperparts, a bold black belly, and a bright yellow throat, while females are duller with streaked underparts. This secretive species often remains motionless in the canopy or dense undergrowth, feeding primarily on fruit. It prefers humid forests between 1,500 and 3,000 meters in elevation. Usually seen alone or in small groups, the species is considered stable but can be affected by forest fragmentation.
The Giant Coua, or Coua gigas, is a bird endemic to Madagascar, belonging to the Cuculidae family. It is recognizable by its blue-gray plumage and long tail. This terrestrial bird prefers dry forests and savannas, where it feeds mainly on insects, fruits, and small reptiles. The Giant Coua is diurnal, active mainly in the morning and late afternoon. Although capable of flight, it prefers to move by running. It is known for its melodious song and varied calls. The Giant Coua plays an important role in the ecosystem as an insect predator and seed disperser.
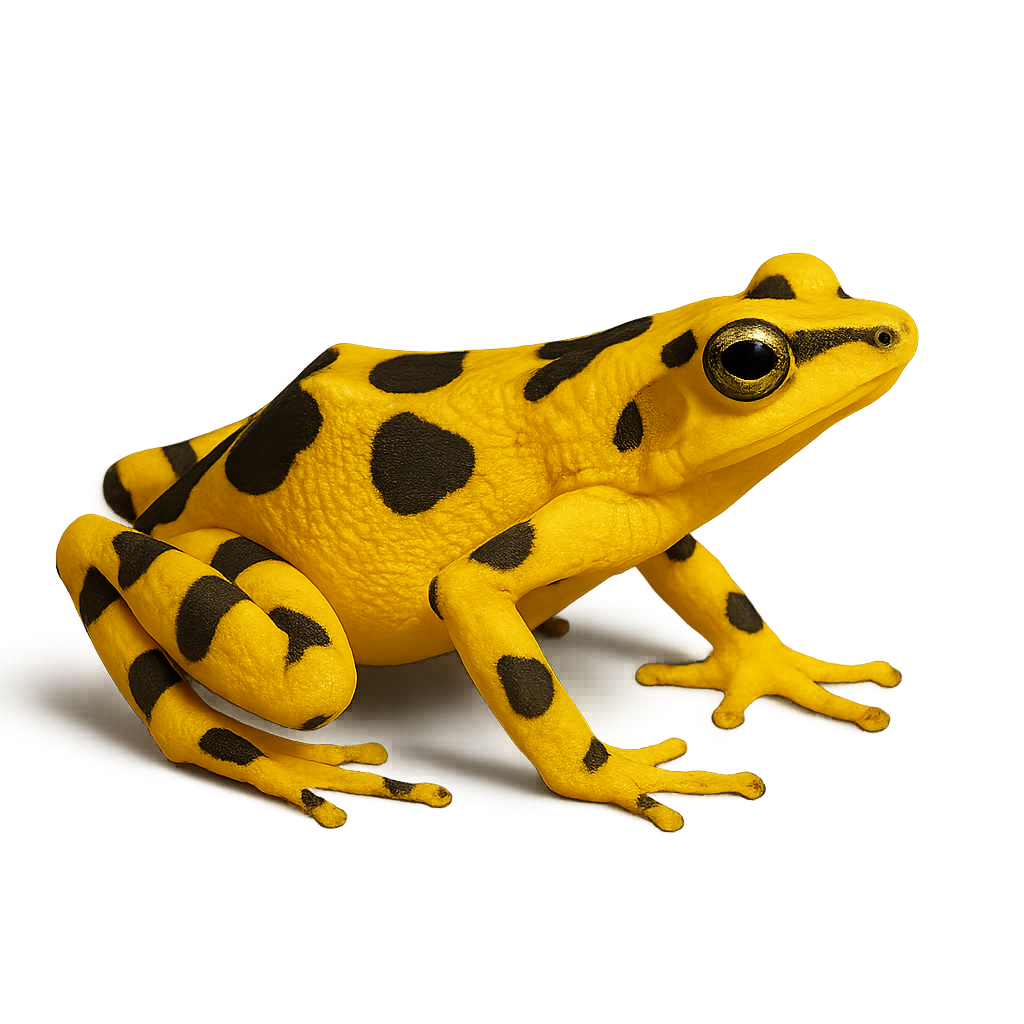
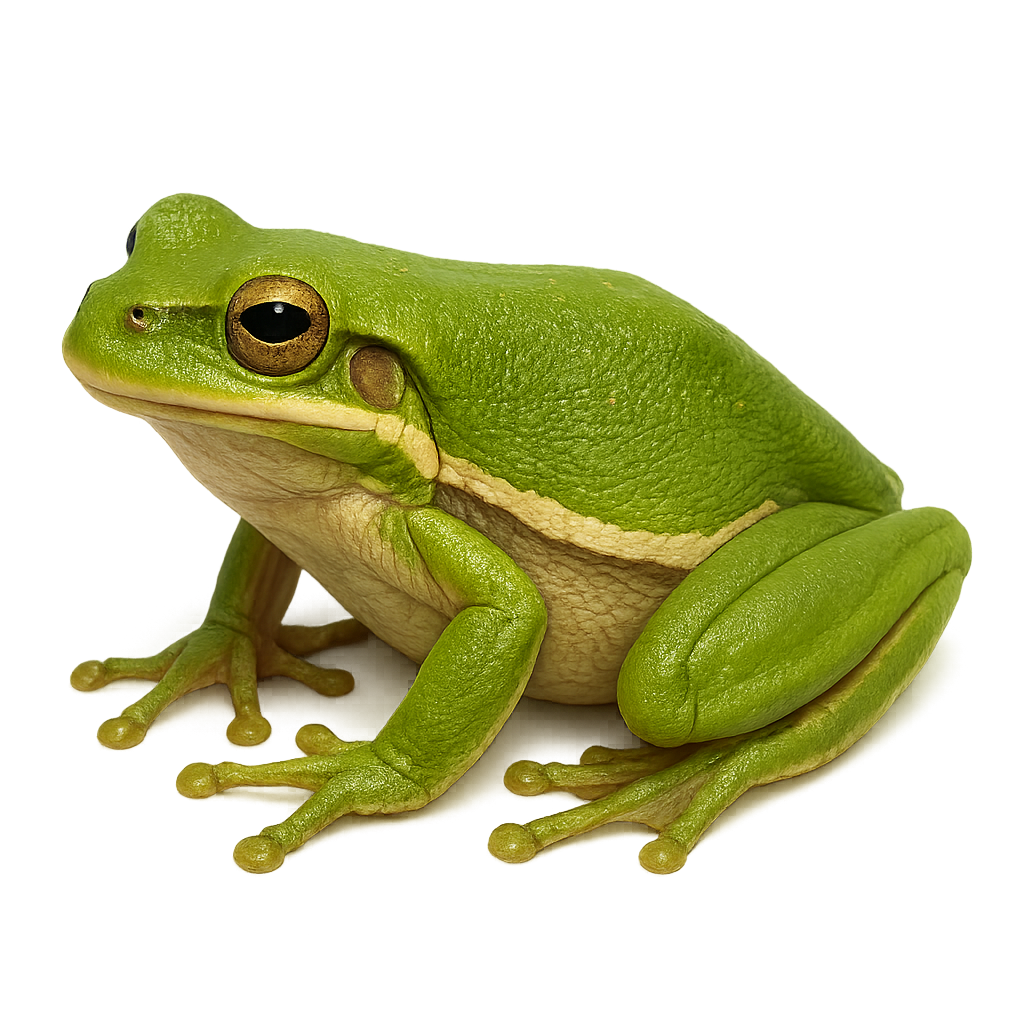
The golden poison dart frog is an iconic species of frog found in the humid tropical forests of Panama. It is famous for its vibrant golden-yellow color and is one of the most poisonous amphibians in the world. It primarily feeds on insects and small invertebrates found in its natural habitat. Unfortunately, this species is critically endangered due to habitat loss and diseases, and it is currently classified as endangered.
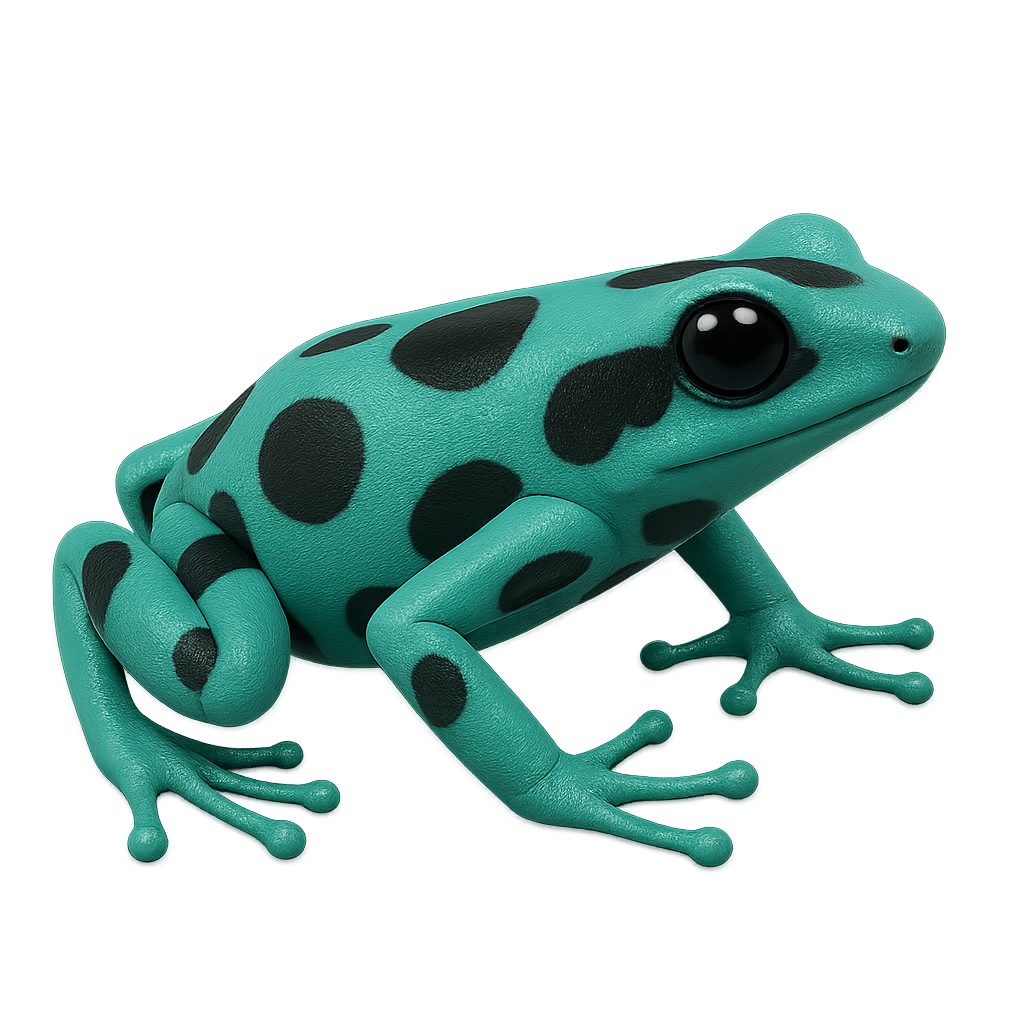
The Golden Poison Dart Frog is a small, vibrant, and colorful frog from the Dendrobatidae family. This species typically measures between 2 and 3 centimeters in length and is easily recognized by its golden skin, often speckled with black. It primarily inhabits the humid tropical forests of Central and South America, particularly in Costa Rica and Panama. The Golden Poison Dart Frog feeds mainly on small insects, ants, and mites. It is known for its toxicity, which comes from its diet, particularly from certain ants and beetles that contain alkaloids. These toxins serve as a defense mechanism against predators. This species is also known for its social behaviors and vocalizations during the breeding season. The eggs of the Golden Poison Dart Frog are laid on the forest floor, and the tadpoles develop in small pools of water or on decaying leaves. While this species is not currently endangered, it is threatened by deforestation and the destruction of its natural habitat.
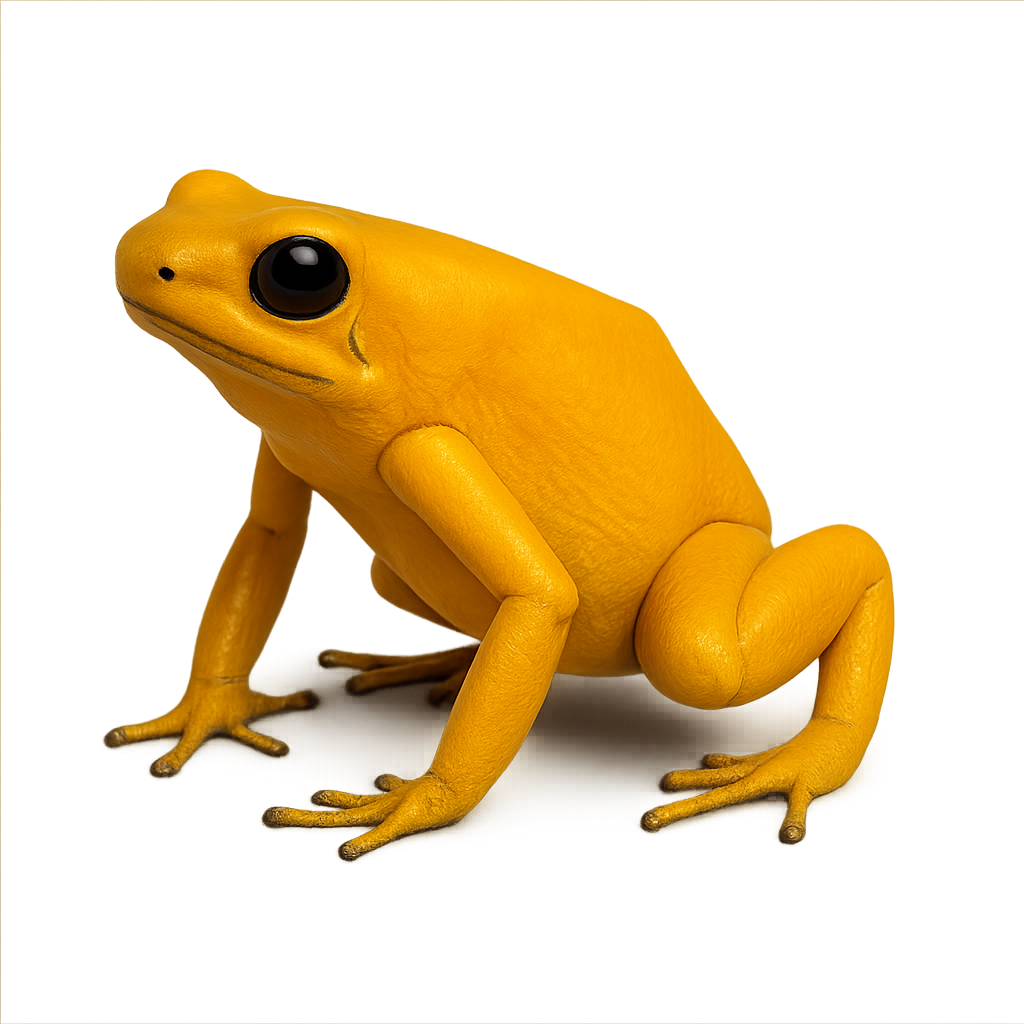
The Golden poison dart frog, also known as the Terrible Dart Frog, is considered one of the most toxic animals in the world. Native to the tropical forests of Colombia, this small frog is distinguished by its bright yellow color, which serves as a warning to predators of its toxicity. It derives its toxin from its diet, primarily consisting of insects found in its natural habitat. These frogs are not toxic in captivity as their diet changes. Despite its toxicity, it has been used by some cultures to poison the tips of their arrows, earning it the name 'poison dart frog.'
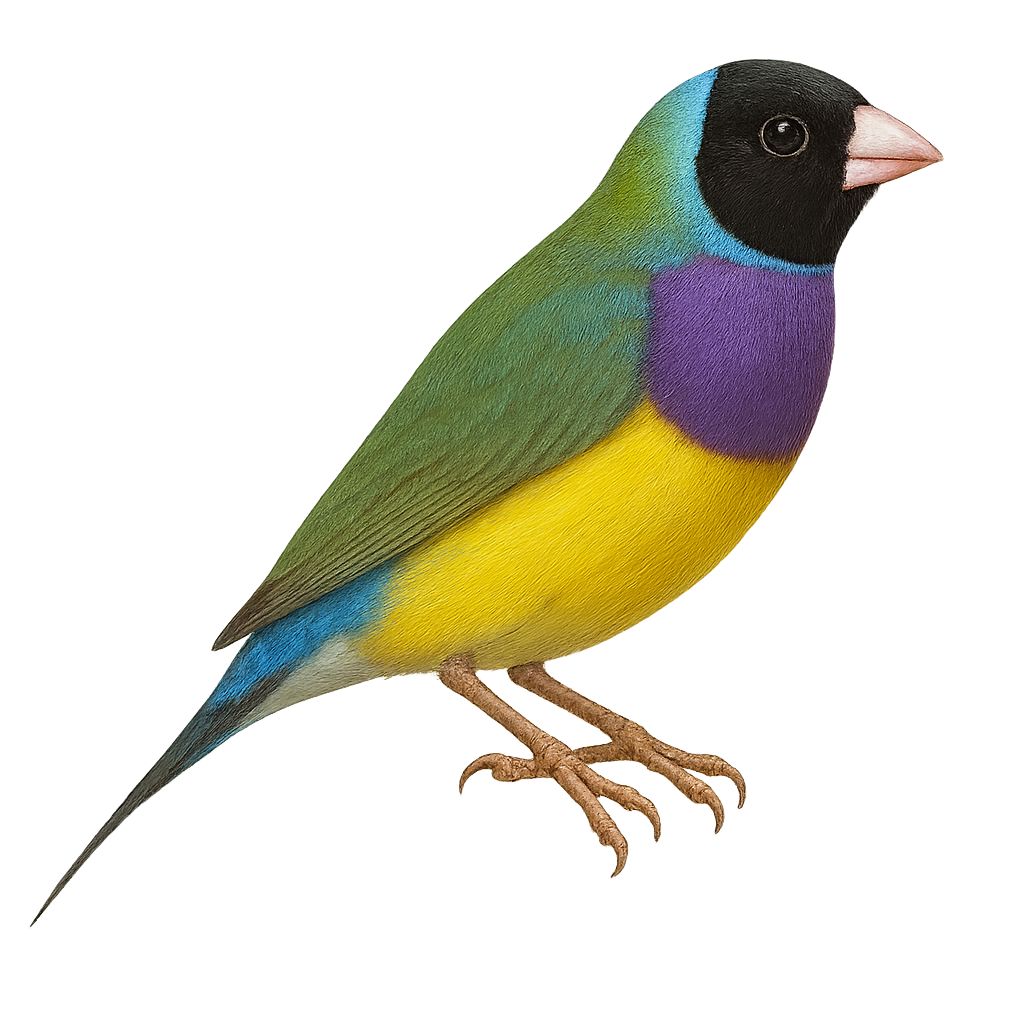
The Gouldian Finch, or Chloebia gouldiae, is a brightly colored bird native to Australia. This small passerine is renowned for its vivid plumage, featuring a mix of bright colors such as red, green, yellow, and blue. Males are generally more colorful than females, which is typical in many bird species. They primarily inhabit savannas and open grasslands, where they feed on seeds and insects. The Gouldian Finch is a social bird, often seen in small groups. However, it is considered vulnerable due to habitat loss and environmental pressures.
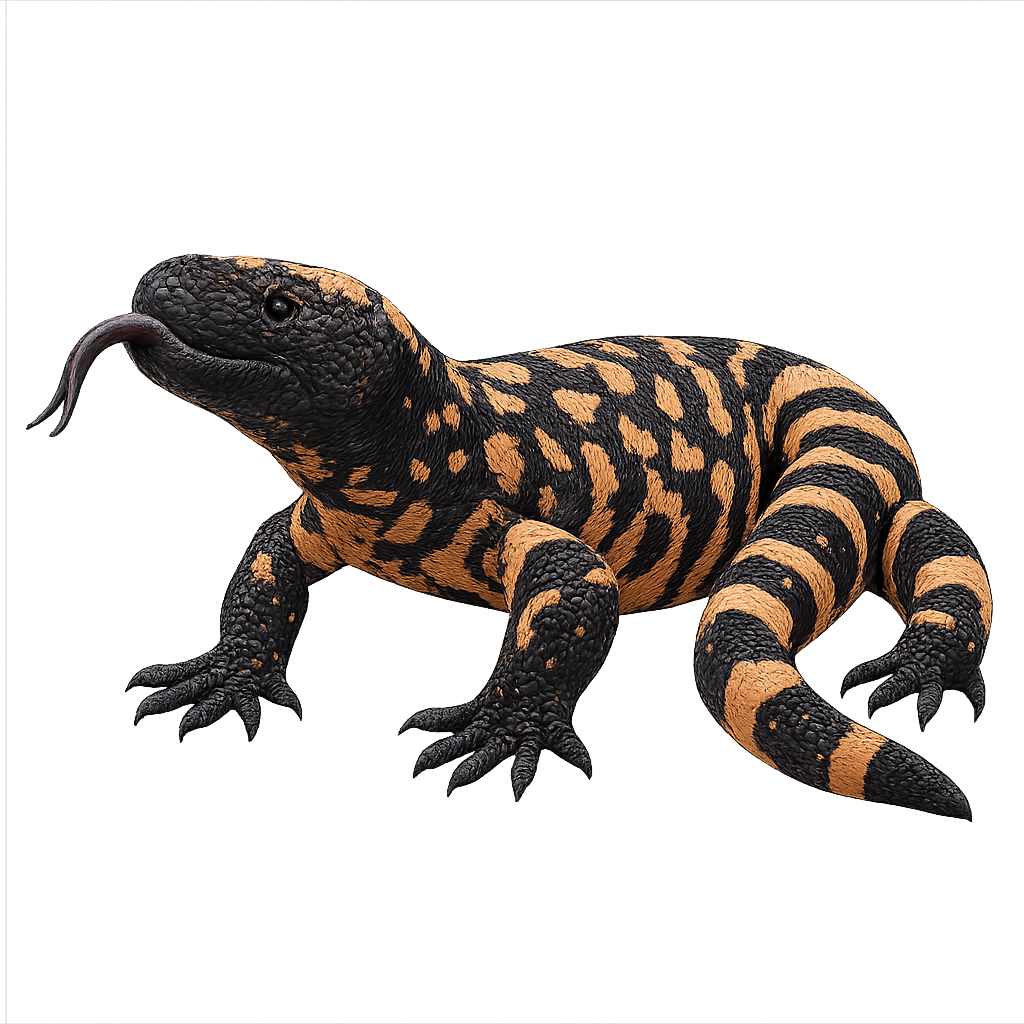
The Gila monster is a large venomous lizard, reaching 30–56 cm in length, with a robust body and bead-like scales patterned in yellow, pink, and black. Native to the deserts of the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico, it inhabits scrubland, succulent desert, and oak woodland, feeding mainly on small mammals, birds, and eggs. As the breeding season (April to June) approaches, males become territorial and exhibit dominance displays by lifting their bodies and bobbing their heads before mating.
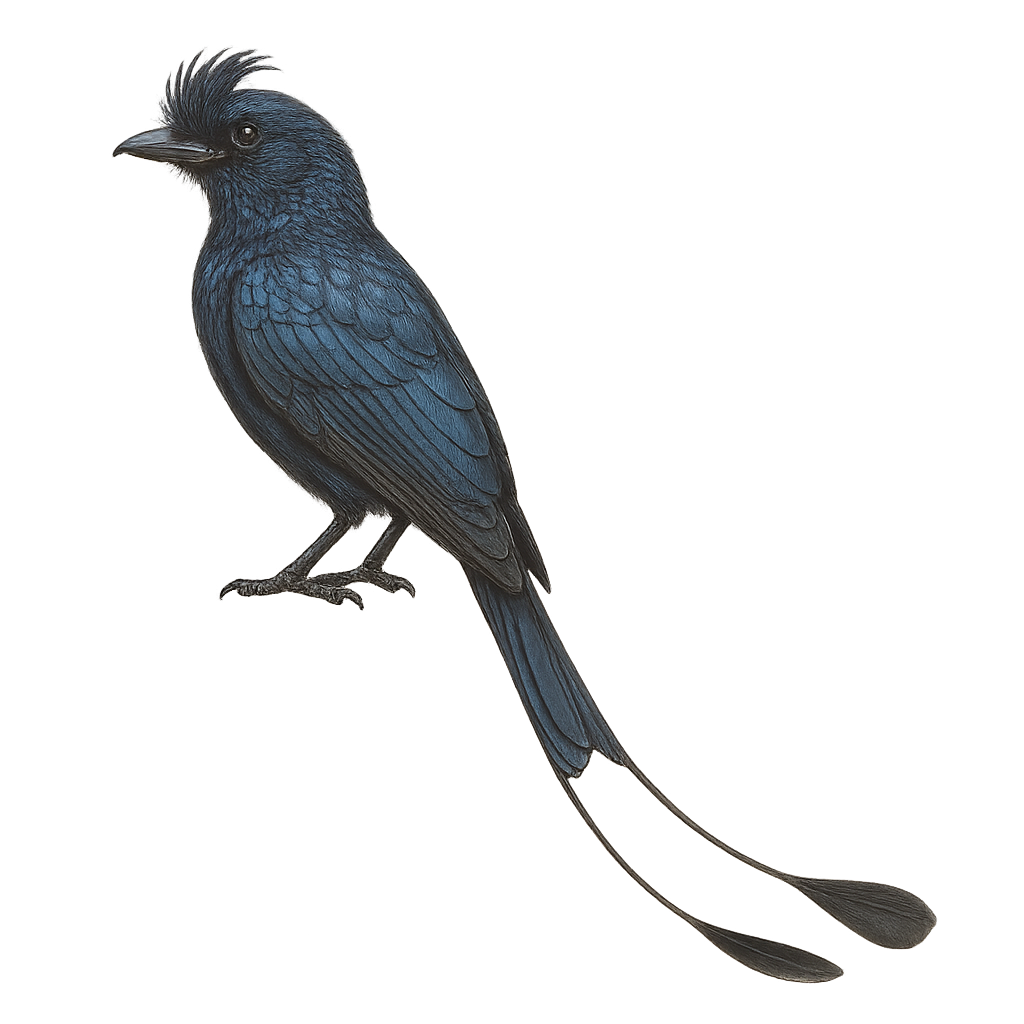
The Greater Racket-tailed Drongo, or Dicrurus paradiseus, is a striking bird known for its long tail feathers shaped like rackets. It is predominantly black with metallic blue and green sheen, and features a distinctive crest on its head. This bird is renowned for its intelligence and ability to mimic the sounds of other birds and animals. It inhabits the tropical and subtropical forests of South and Southeast Asia, where it primarily feeds on insects. The Greater Racket-tailed Drongo is often seen following groups of primates to catch insects disturbed by their movement. It is also territorial and can be aggressive towards intruders.
The green tree frog, Hyla cinerea, is a small arboreal frog native to North America. It is characterized by its bright green color, sometimes adorned with white or golden spots. Its skin is smooth, and it has long limbs adapted for climbing. Measuring about 4 to 6 cm, it is often found near stagnant water bodies like marshes and ponds. Primarily nocturnal, it emits a distinctive call during the breeding season. Although common, it is sensitive to environmental changes, particularly water pollution and habitat destruction.
The Giant Eland, or Tragelaphus derbianus, is a large, robust, and majestic antelope, easily recognizable by its spiral-shaped horns, present only in males. It measures between 1.4 and 1.7 meters at the shoulder and can reach a length of 2.5 to 3 meters, including its tail. Its weight ranges between 600 and 1,000 kg, making it one of the largest antelopes. Its coat is generally light brown to gray, with white markings on the belly and throat. The Giant Eland primarily inhabits open savannas, light forests, and mountainous regions in Central and West Africa, mainly in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Cameroon, Gabon, and Angola. Herbivorous, the Giant Eland primarily feeds on grasses, leaves, and fruits, and it is capable of consuming a wide variety of vegetation, allowing it to adapt to different environments. It is a social animal that lives in family groups or small herds. While the species is classified as of least concern, it is threatened by habitat loss and hunting.
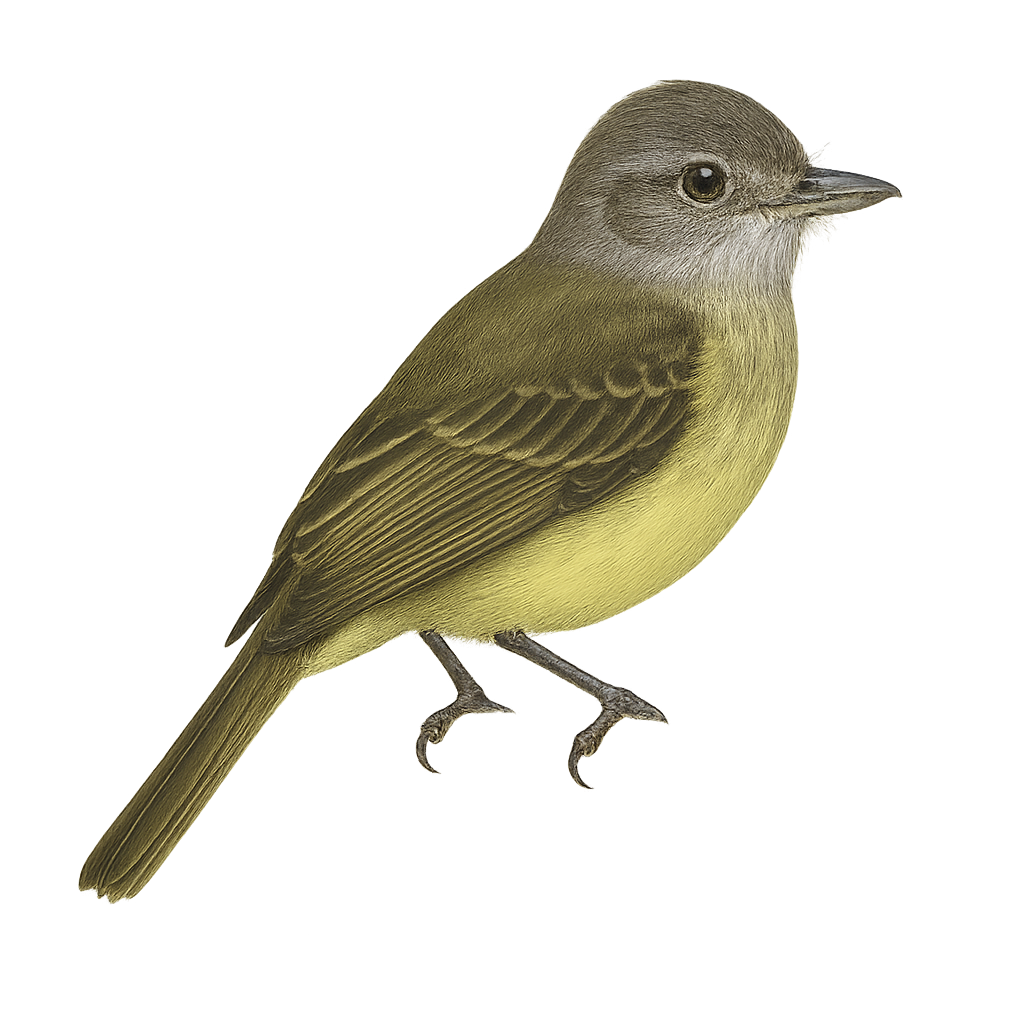
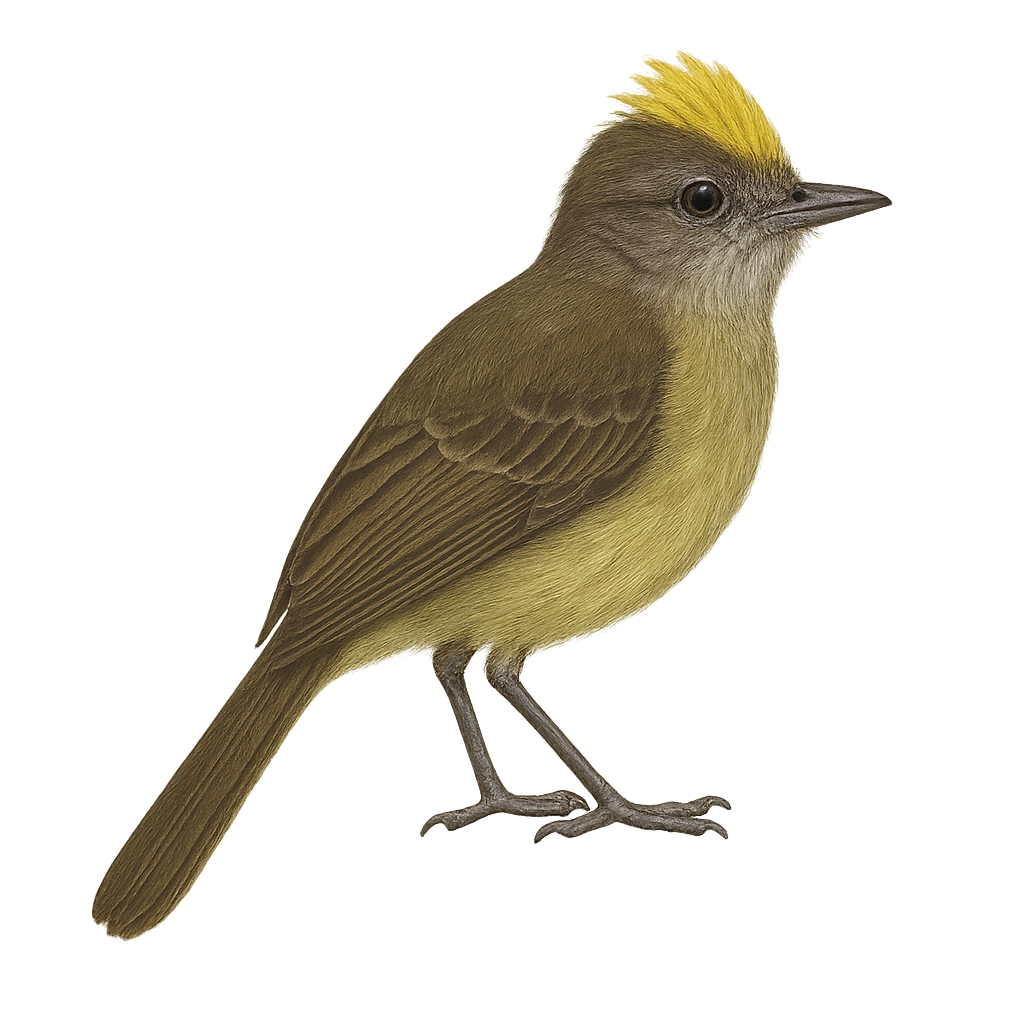
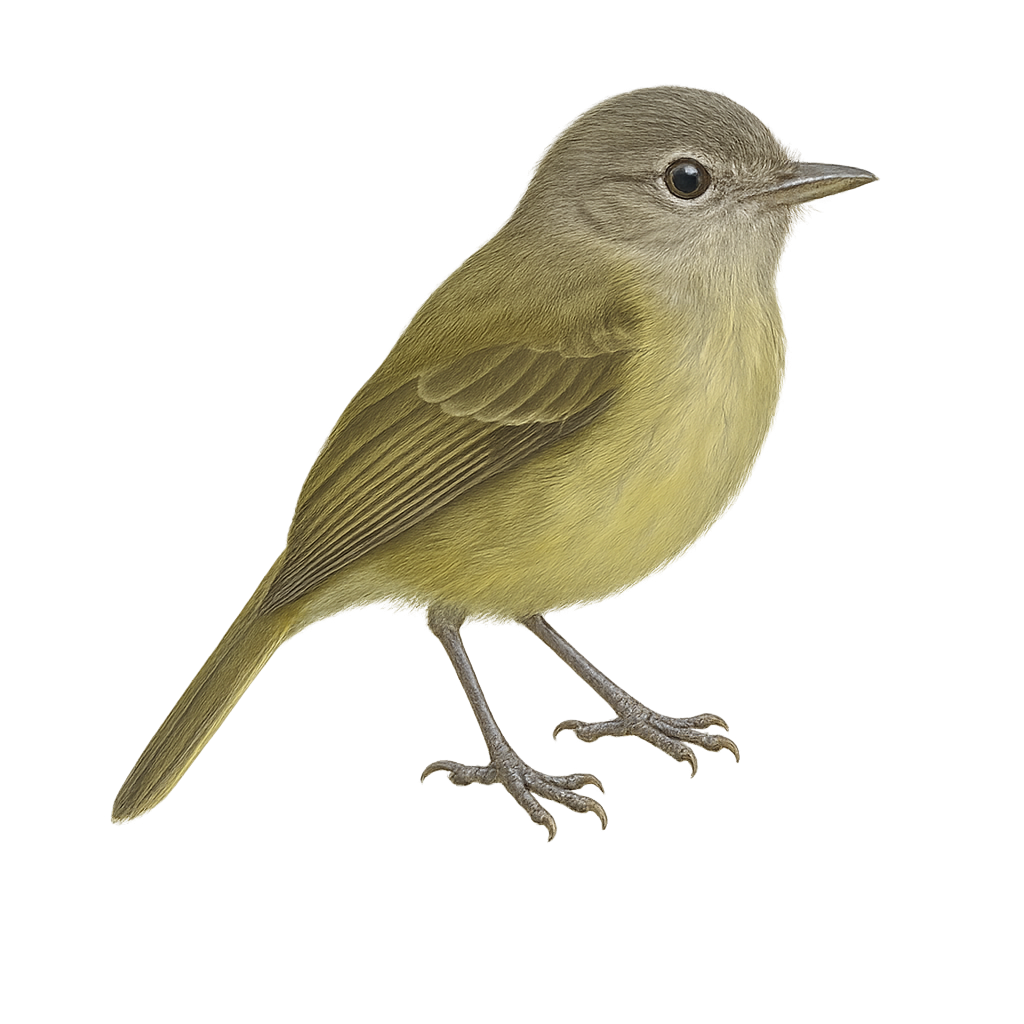
The Grey-capped Flycatcher is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in the tropical and subtropical forests of Central and South America. This bird is characterized by its grey head, white belly, and greenish wings. It is often seen catching insects in flight, thanks to its agile and swift movements. Although discreet, its melodious song can be heard throughout the canopy. The Grey-capped Flycatcher plays an important role in the ecosystem by regulating insect populations and participating in the pollination of certain plants.
The Greenish Elaenia, Myiopagis gaimardii, is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in the tropical rainforests of Central and South America, where it is distinguished by its olive-green plumage and lighter belly. This bird is often observed alone or in small groups, feeding mainly on insects caught in flight. Its ability to blend into dense foliage sometimes makes it difficult to spot. Although not currently threatened, deforestation poses a potential risk to its natural habitat. The Greenish Elaenia is also known for its distinctive song, which plays a crucial role in communication between individuals, especially during the breeding season.
The Greater Elaenia is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is characterized by its olive-gray plumage on the back and lighter underparts, with a subtle crest on its head. This bird is mainly found in the tropical rainforests and wooded areas of South America, particularly in Colombia, Venezuela, and Brazil. Its song is a melodious whistle often heard at dawn and dusk. The Greater Elaenia is a migratory bird, moving seasonally to find food resources. It primarily feeds on insects and small fruits, which it catches in flight or by foraging through foliage.
The Greenish Elaenia, Myiopagis subplacens, is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in the tropical and subtropical forests of South America, particularly in Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. This bird is characterized by its olive-green plumage on the back and lighter underparts, with slightly darker wings. Its short, straight bill is well-suited for its diet, which mainly consists of insects and fruits. The Greenish Elaenia is a diurnal bird, most active in the morning and late afternoon. It is often seen alone or in small groups, moving nimbly through the canopy in search of food.
The Greenish Elaenia is a small passerine bird from the Tyrannidae family, widely distributed across Central and South America. Its plumage is primarily olive green, with lighter shades on the belly and slightly darker wings. This bird is characterized by its subtle crest and relatively short beak. It mainly inhabits tropical and subtropical forests but can also be found in open woodlands and forest edges. The Greenish Elaenia is an active insectivore, often seen catching insects in flight or foraging among foliage. Its song is a key aspect of its territorial behavior, often heard before seen.
The Glittering-bellied Emerald, or Chlorostilbon lucidus, is a small hummingbird with dazzling, predominantly green plumage with metallic sheen. This winged jewel is endemic to the subtropical and tropical regions of South America, particularly in Argentina, Brazil, and Uruguay. It inhabits open forests, savannas, and urban gardens, where it primarily feeds on nectar, playing a crucial role in plant pollination. Its rapid and agile flight allows it to move easily between flowers. Despite its small size, it is territorial and does not hesitate to chase intruders from its feeding area. Its breeding period varies by region, but it is generally active year-round.
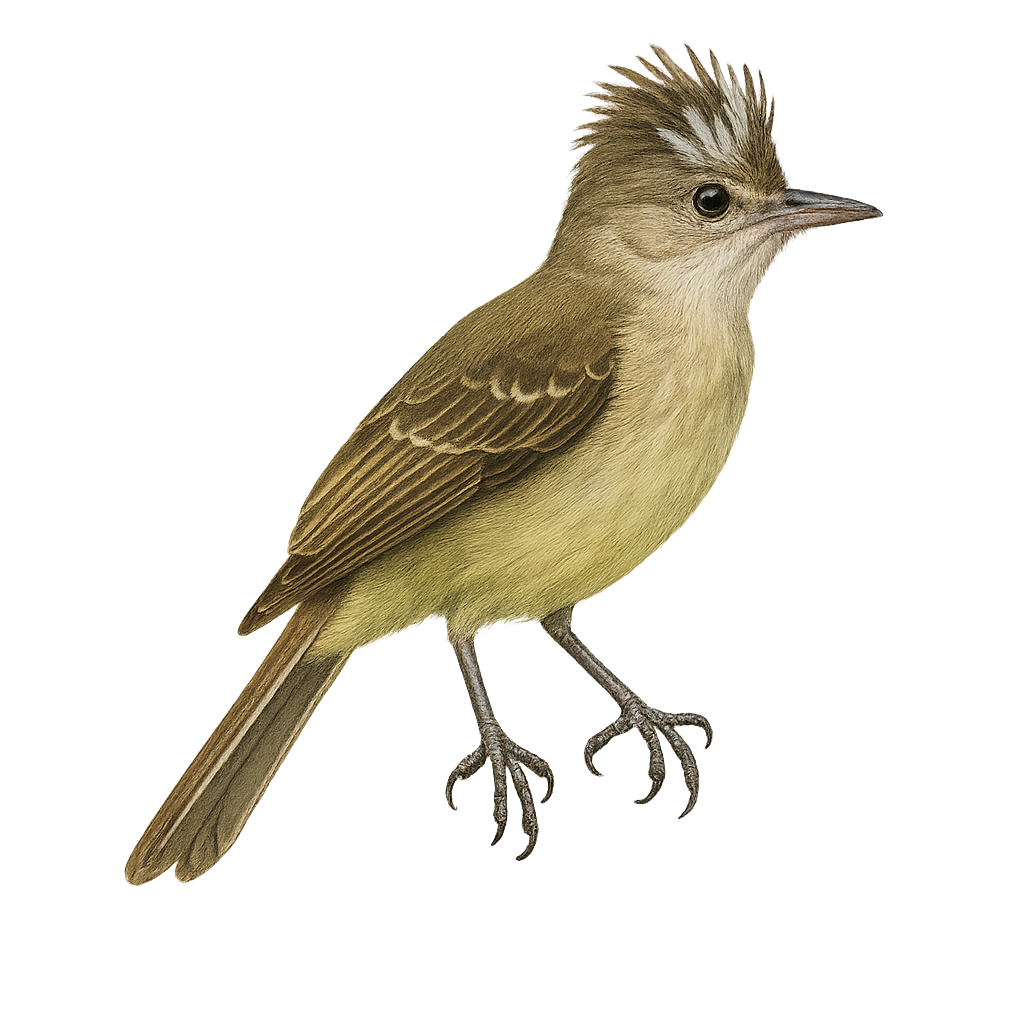
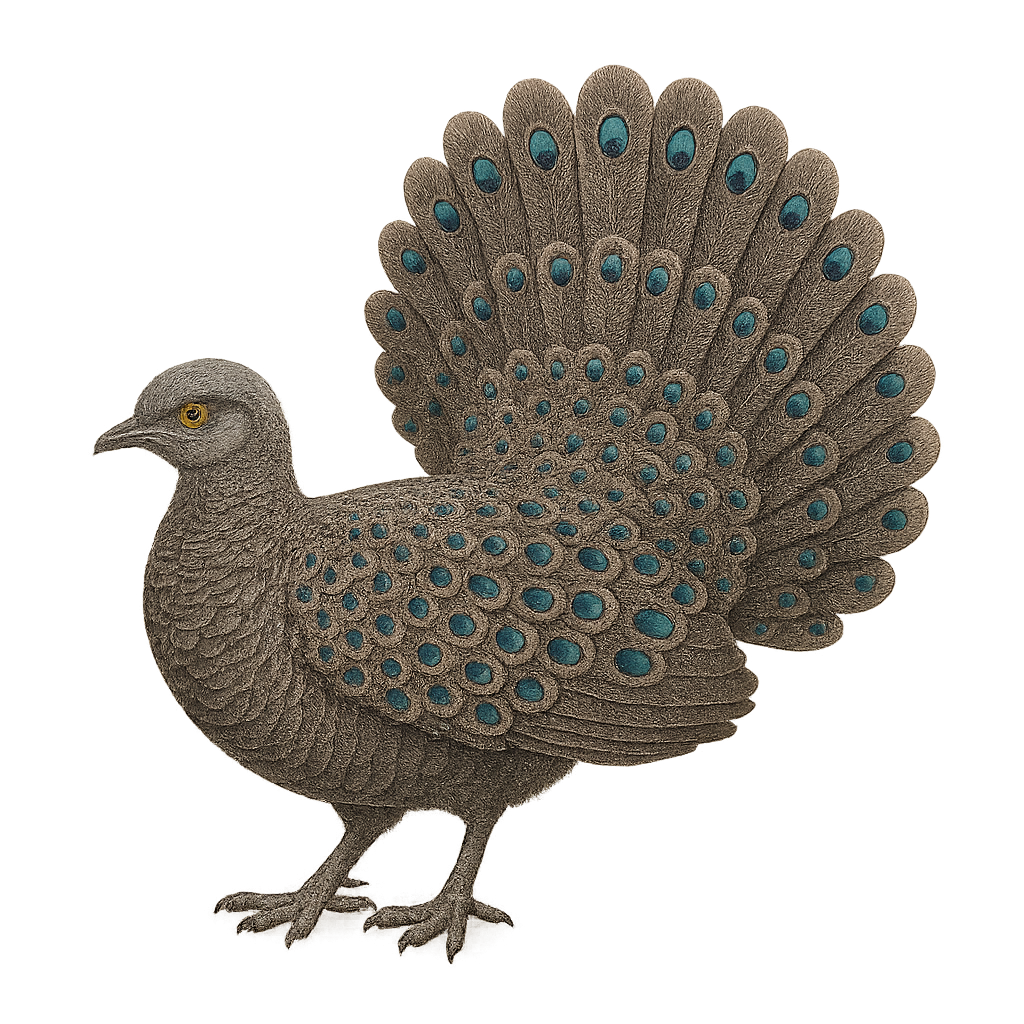
The Grey Peacock-Pheasant, or Polyplectron bicalcaratum, is a captivating bird from the Phasianidae family, native to the dense forests of Southeast Asia. It is recognizable by its grey plumage adorned with eye-like patterns, giving it a majestic appearance. Males display long tail feathers during courtship to attract females. This bird prefers forest habitats where it feeds on seeds, insects, and small invertebrates. Although discreet, it is sometimes seen in small family groups. Its ability to blend into dense vegetation makes it difficult to spot, but its melodious call often reveals its presence.
The Green Hermit, or Phaethornis guy, is a captivating hummingbird found primarily in the humid tropical forests of Central and South America. This small bird is recognizable by its bright green plumage and distinctive long tail. Both males and females exhibit similar features, although males often have longer tails. They primarily feed on nectar, using their long curved bills to reach tubular flowers. In addition to nectar, they also consume small insects to supplement their diet. Green Hermits are known for their territorial behavior, vigorously defending their food sources against intruders. Their fast and agile flight is a spectacle to behold, especially as they move from flower to flower.