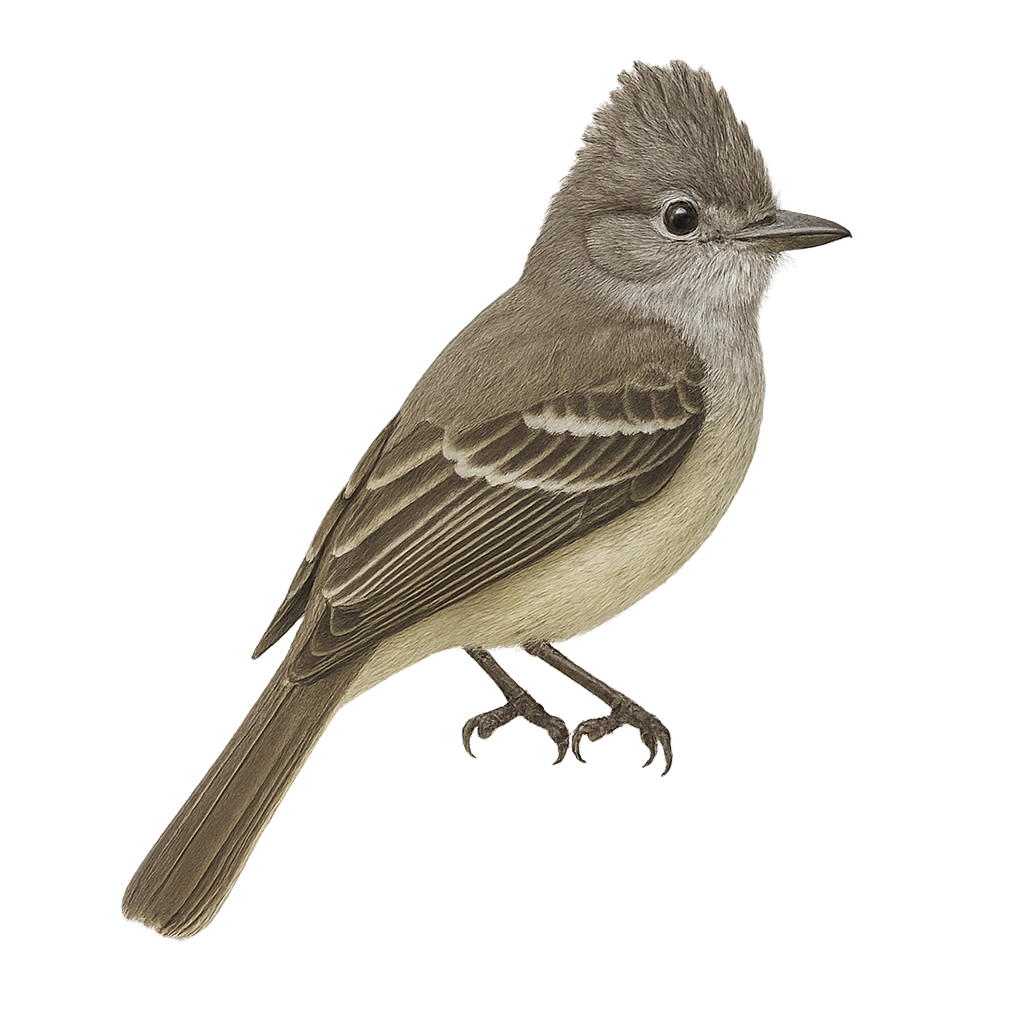
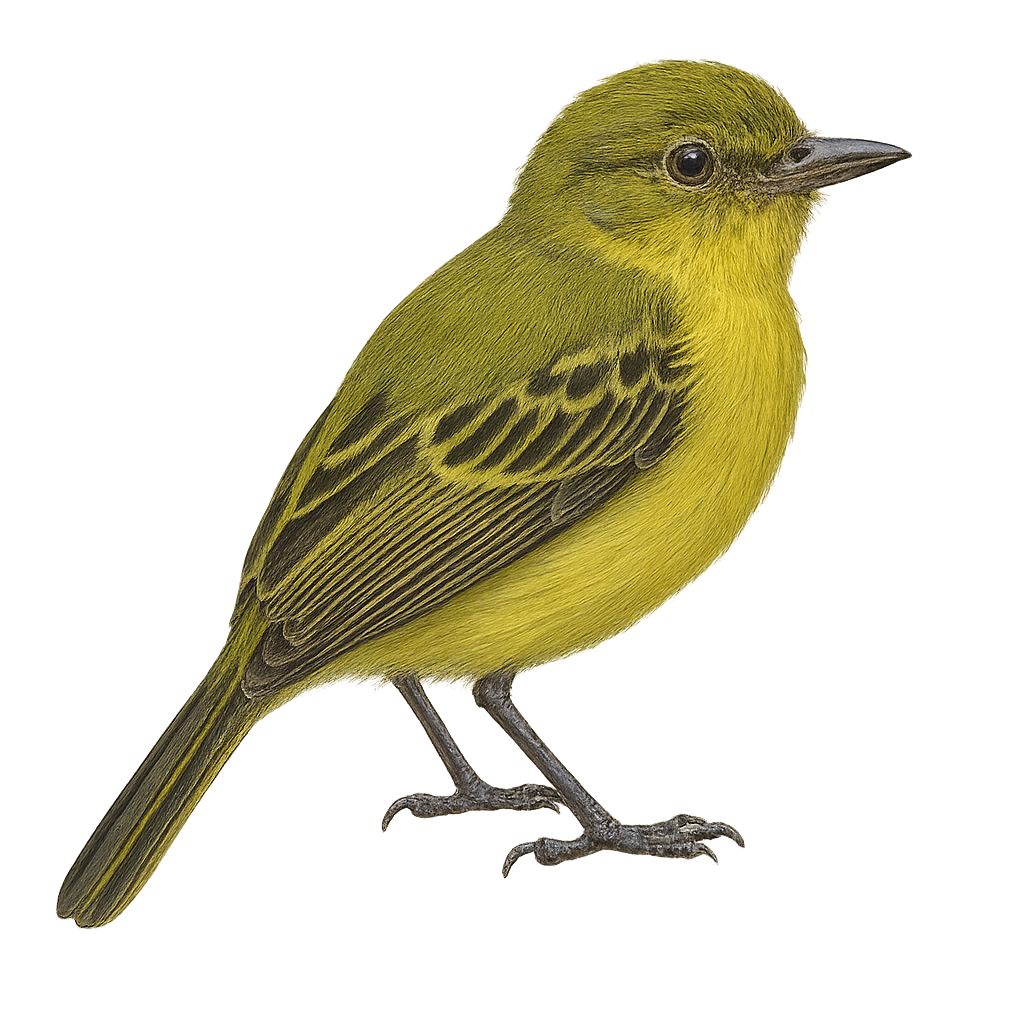
The Yellow-bellied Elaenia is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. This bird is easily recognizable by its bright yellow belly contrasting with its dull olive back. It has a subtle crest and slightly white-striped wings. It is primarily found in tropical and subtropical forests but also adapts to open woodlands and savannas. Its song is distinctive, often described as a melodious whistle. The elaenia is a diurnal bird, active mainly in the morning and late afternoon. It feeds primarily on insects and fruits, which it captures in flight or by foraging through foliage.
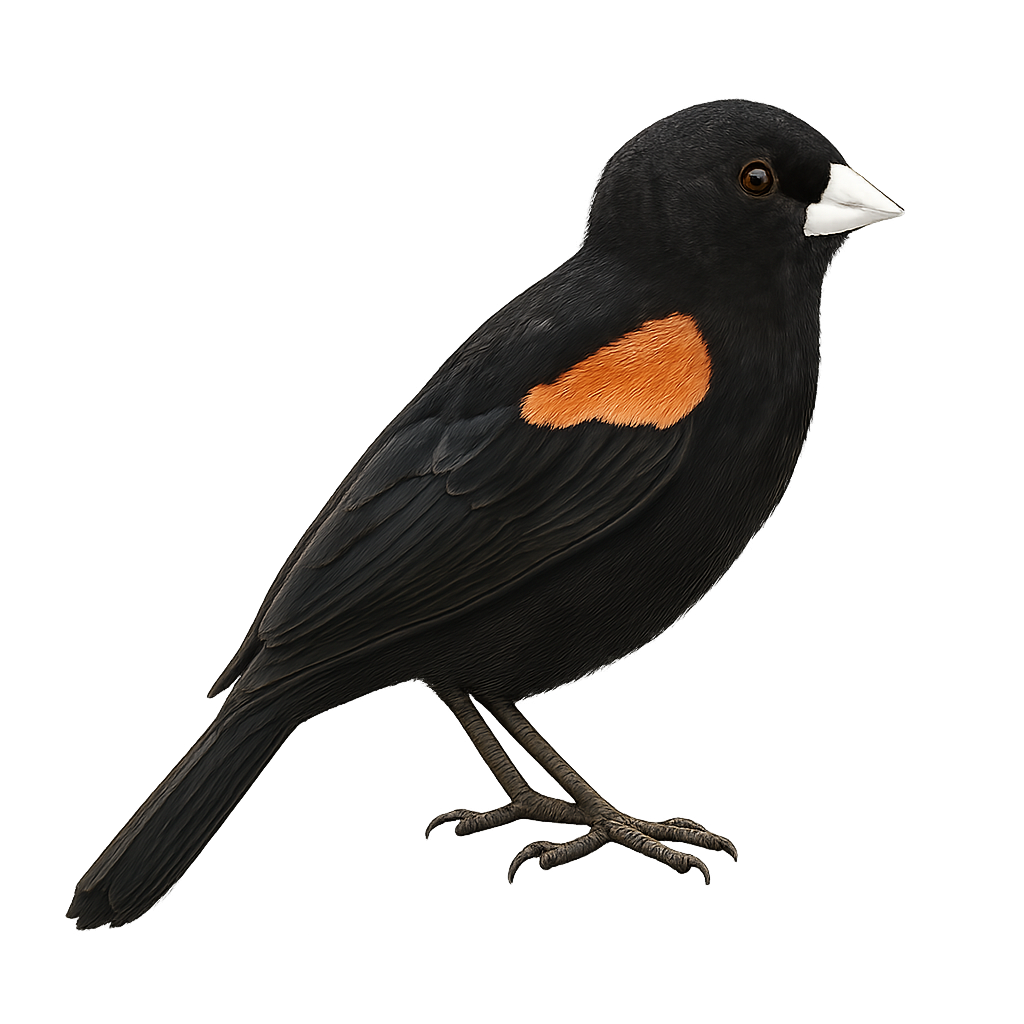
The Yellow-shouldered Widowbird is a small bird from the Ploceidae family, predominantly found in the humid regions of sub-Saharan Africa. This passerine is notable for the male's glossy black plumage with striking yellow shoulder patches, while the female is more subdued in brown tones. Males are particularly eye-catching during the breeding season, displaying long tail feathers to attract females. They live in flocks and are often seen in wet grasslands, marshes, and agricultural areas. Their diet mainly consists of seeds, but they also eat insects. Although their population is stable, habitat destruction remains a potential threat.
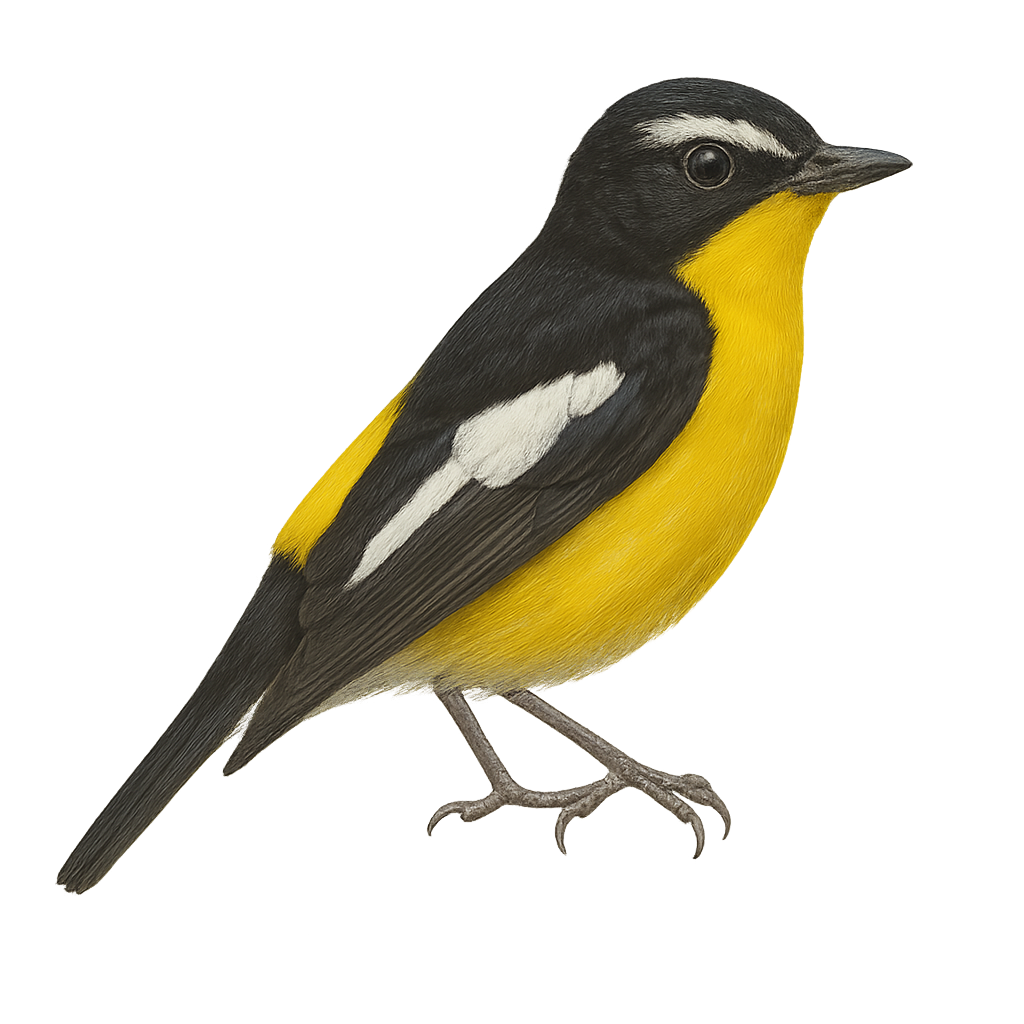
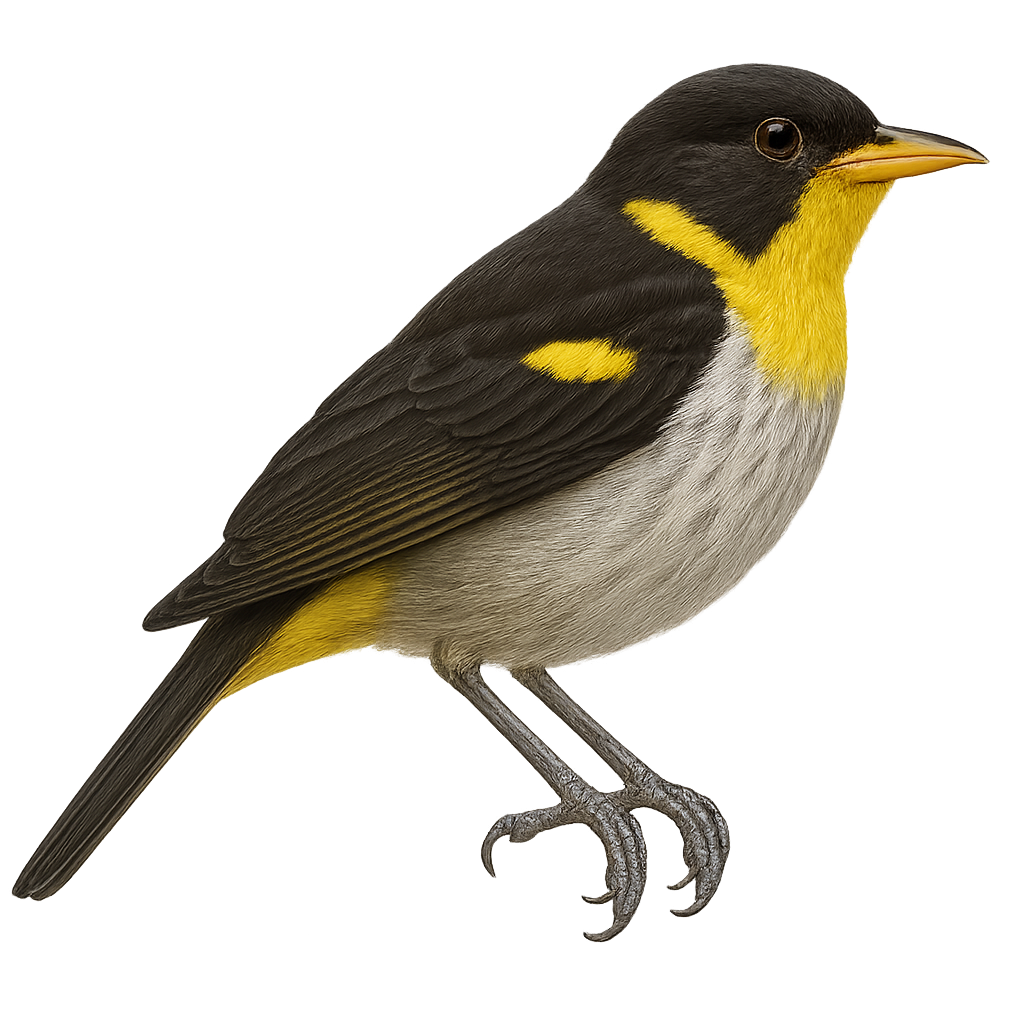
The Yellow-rumped Flycatcher, or Ficedula zanthopygia, is a small passerine bird belonging to the Muscicapidae family. Males are easily identified by their striking black and yellow plumage, with a bright yellow belly and a distinctive white wing patch, while females are more subdued in brown and yellow tones. This migratory bird breeds in the temperate forests of East Asia, including China, Korea, and Russia, before migrating south to winter in Southeast Asia. It inhabits forests, parks, and gardens, feeding primarily on insects. Its melodious song and spectacular courtship displays make it a favorite among birdwatchers.
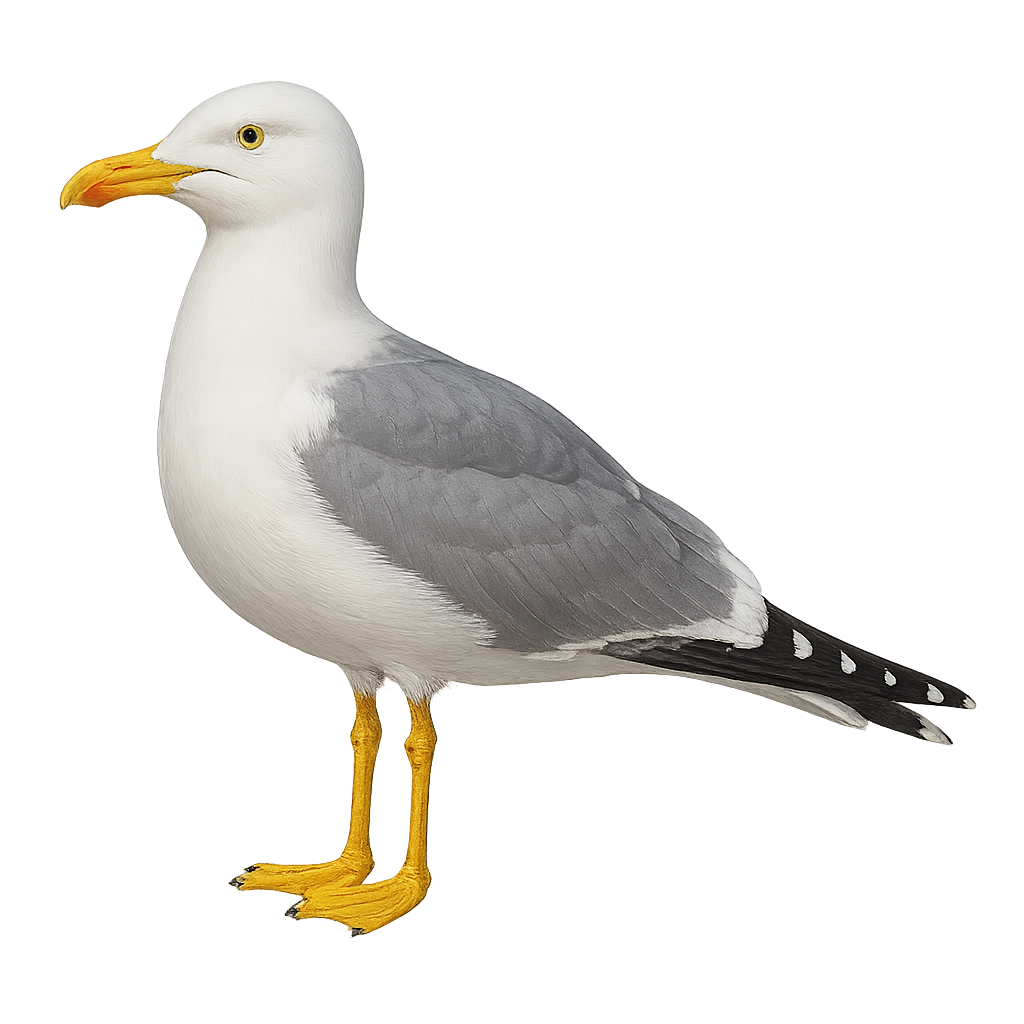
The yellow-legged gull is a large seabird found primarily along the Mediterranean and Atlantic coasts. It is easily recognized by its white plumage, gray wings, and yellow legs. This gull is omnivorous and feeds on fish, marine invertebrates, and food waste, making it an opportunist. It is also known for its nesting behaviors on rocky coastlines and cliffs and can occasionally be seen in urban areas.
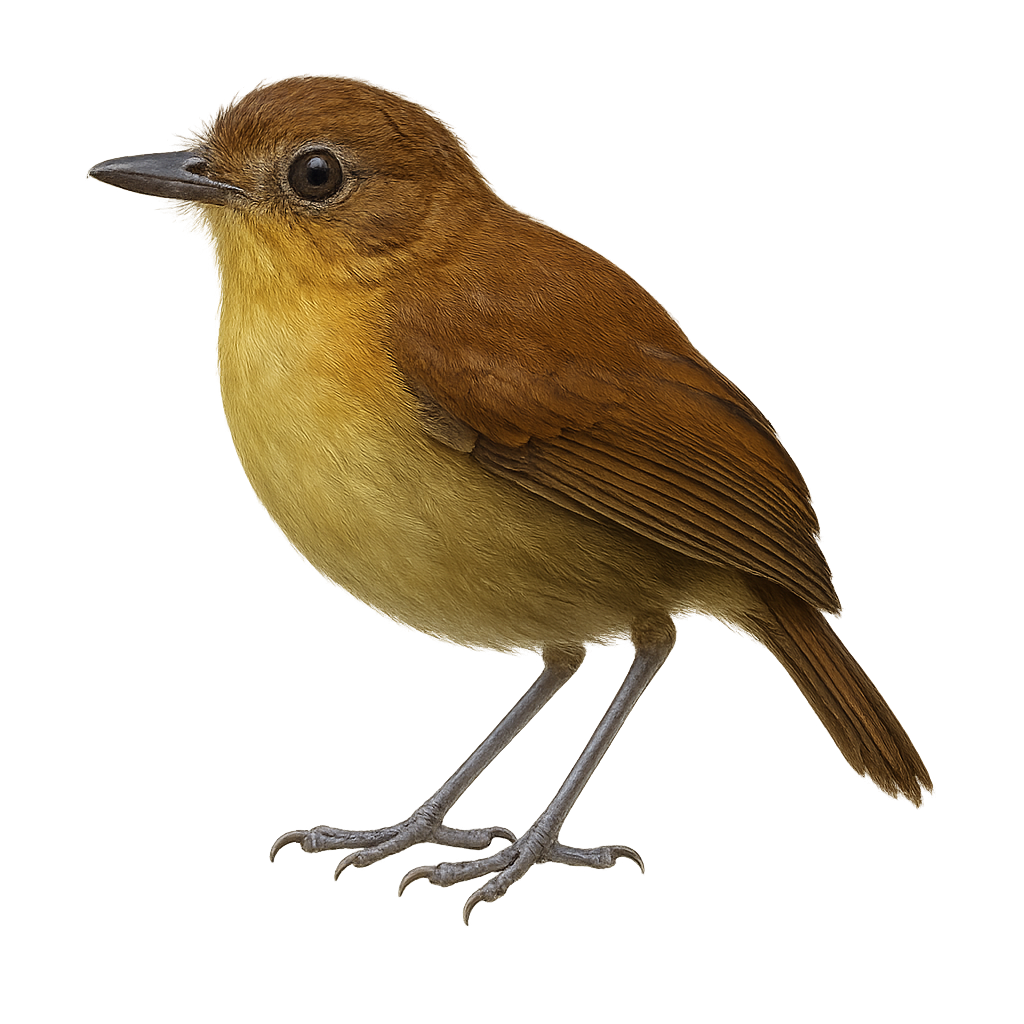
The Yellow-breasted Antpitta is a discreet and fascinating bird belonging to the Grallariidae family. It is primarily found in the humid forests of the Andes, often hiding in dense vegetation. Its plumage is characterized by a tawny hue on the breast, contrasting with an olive-brown back. This bird is known for its melodious song, often heard before being seen. It primarily feeds on insects and other small invertebrates found by foraging on the forest floor. The Yellow-breasted Antpitta is a solitary bird, rarely seen in groups. Its shy nature and difficult-to-access habitat make it a challenge for birdwatchers.
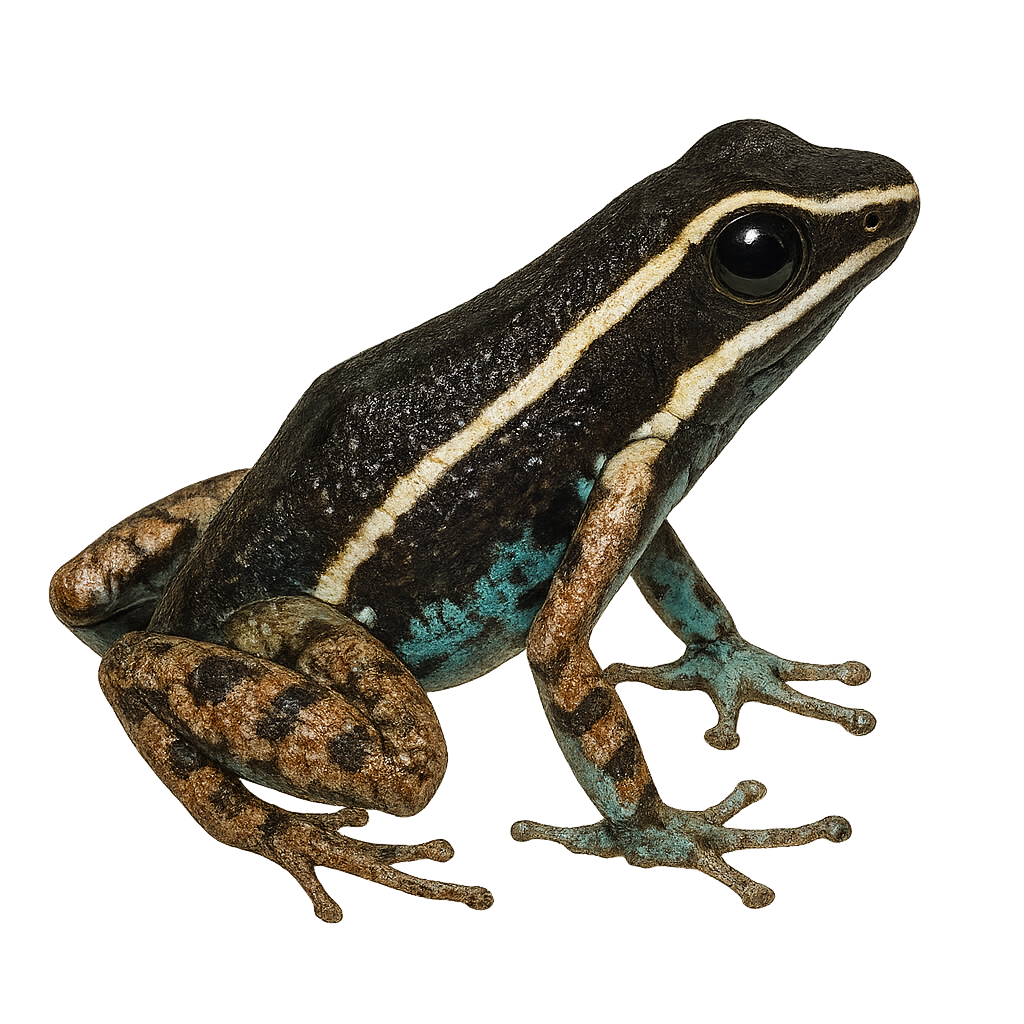
The Yurimaguas poison frog, Ameerega hahneli, is a small, brightly colored frog species belonging to the Dendrobatidae family. It is primarily found in the humid tropical forests of the Amazon, notably in Peru, Colombia, and Brazil. This frog is known for its vivid colors, which serve as a warning to potential predators of its toxicity. It typically measures between 20 and 25 mm in length. Ameerega hahneli are diurnal and spend most of their time foraging for food, mainly insects. They are also known for their distinctive call, used to attract mates and mark their territory. Although their population is stable, they are threatened by deforestation and habitat loss.
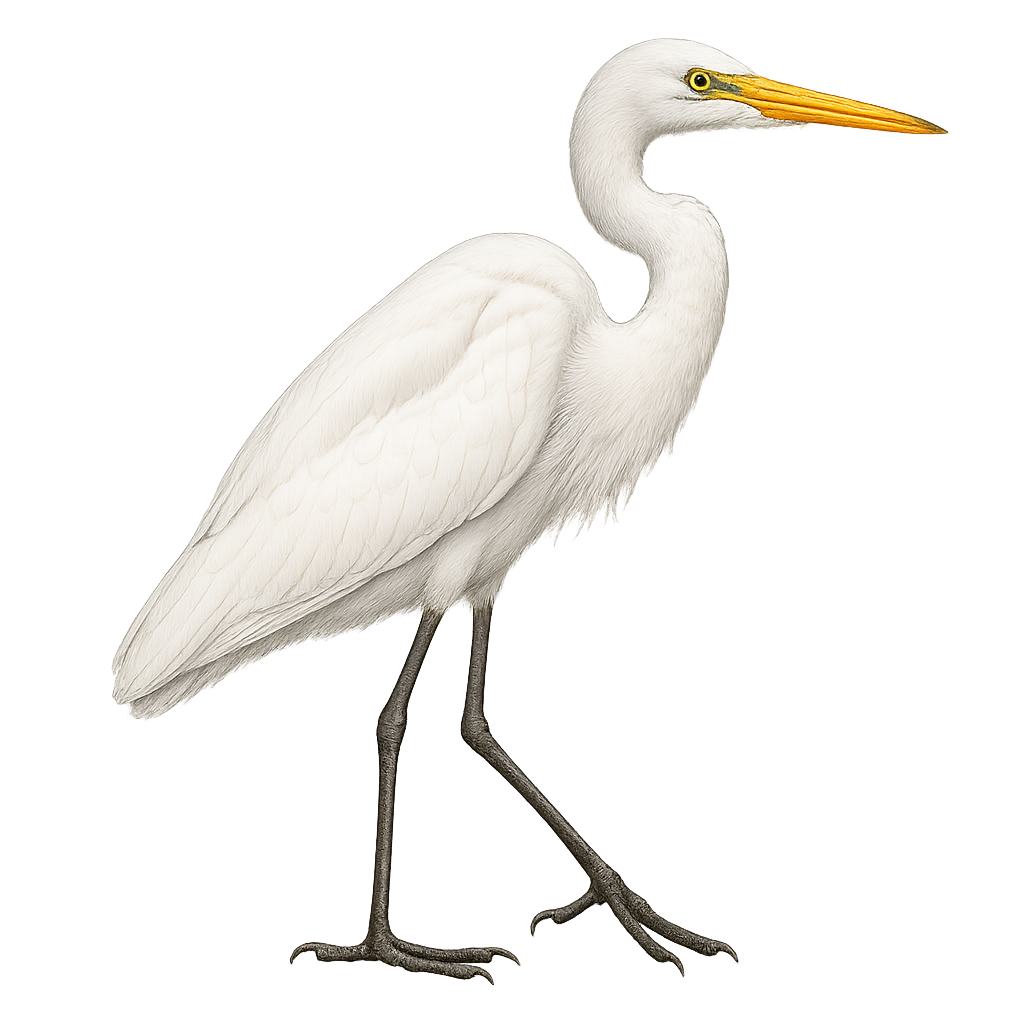
The Yellow-billed Egret, or Ardea brachyrhyncha, is a graceful and slender bird, primarily white with a distinctive yellow bill. It primarily inhabits the wetlands of sub-Saharan Africa, favoring marshes, rivers, and lakes. Its immaculate white plumage contrasts with its long black legs, ideal for wading in shallow waters in search of prey. This heron is an opportunistic hunter, feeding mainly on fish, amphibians, and aquatic insects. Although generally solitary, it can be seen in small groups during the breeding season. Its flight is graceful, with slow wing beats and a retracted neck.
The Ctenosaura defensor, or Yucatán Spiny-tailed Iguana, is a lizard species endemic to Mexico, primarily found in arid and semi-arid regions. This reptile is recognizable by its tail covered with spiny scales, providing it with a unique appearance and protection against predators. Its coloration ranges from gray to brown, with darker patterns that allow it to blend effectively into its natural environment. The spiny-tailed iguana is mainly herbivorous, feeding on leaves, flowers, and fruits, although it may occasionally consume insects. It is diurnal and spends most of its time basking in the sun to regulate its body temperature.
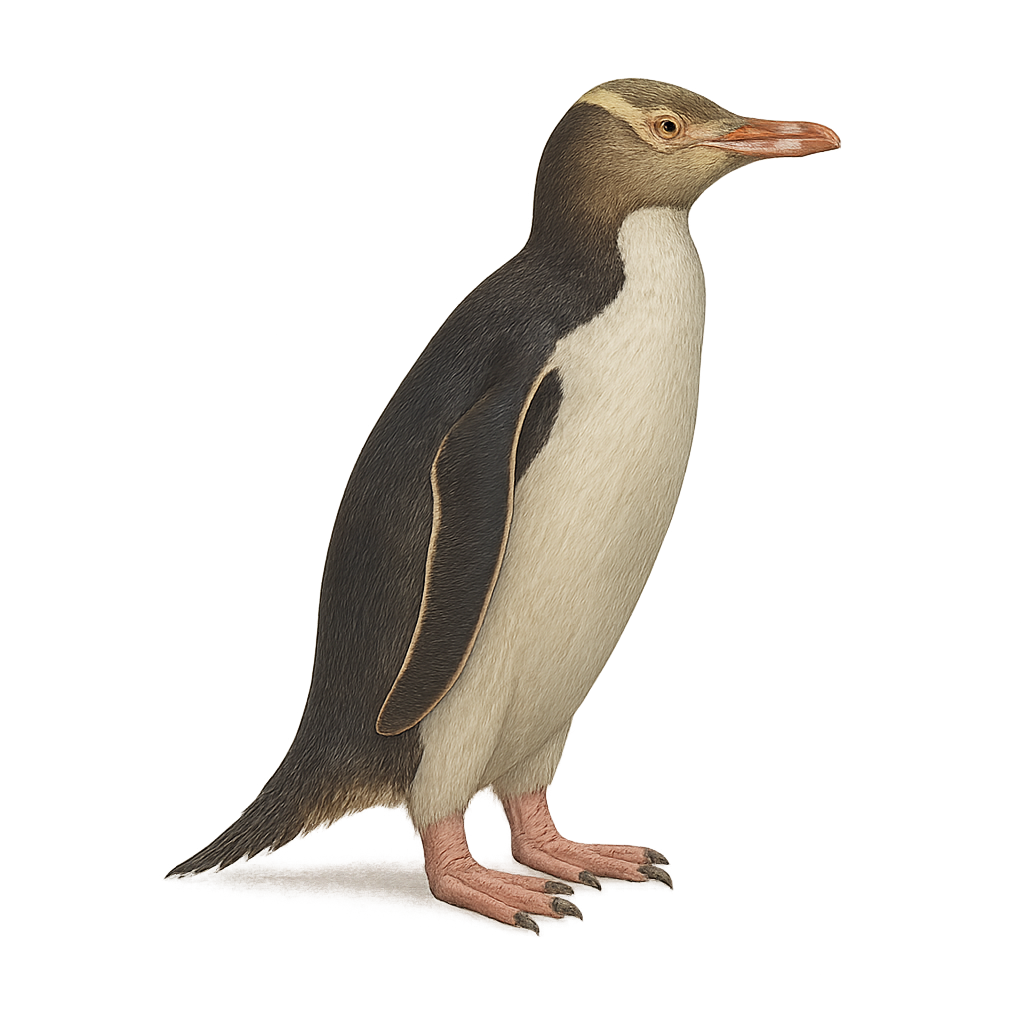
The yellow-eyed penguin, native to New Zealand, is easily identified by its striking yellow eyes and the yellow band of feathers around its head. This medium-sized penguin stands about 65 to 70 cm tall and weighs between 5 and 8 kg. It inhabits rocky shores and coastal forests, feeding primarily on fish and squid. Sadly, it is critically endangered due to habitat loss, predation by introduced species, and human disturbance. Conservation efforts are vital for its long-term survival.
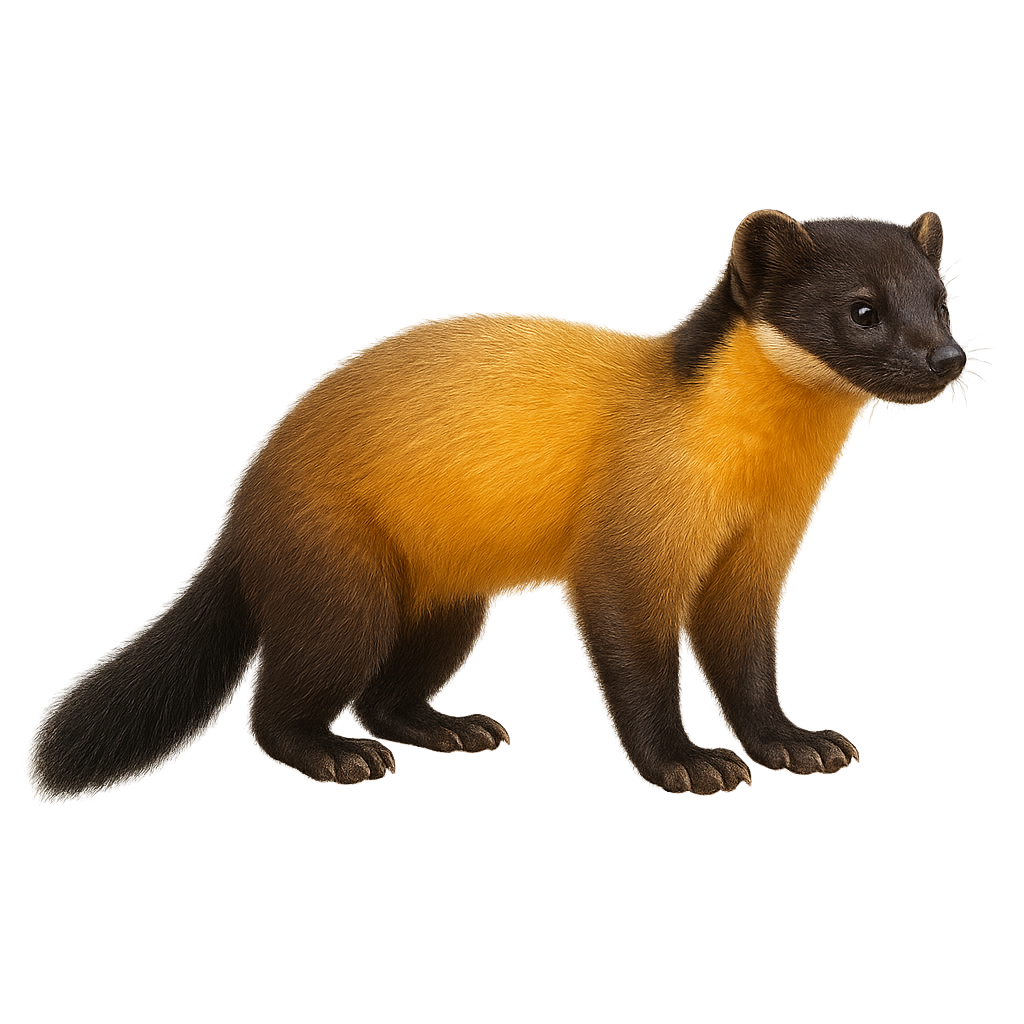
The Yellow-throated marten, Martes flavigula, is a mustelid with a distinctive yellow throat contrasting with its dark brown body. Agile and fast, it moves easily through the dense forests of Southeast Asia and the Himalayas. Omnivorous, it feeds on small mammals, birds, fruits, and insects. Its climbing ability and natural curiosity make it an effective predator. Although primarily terrestrial, it is also comfortable in trees. The yellow-throated marten is known for its relative sociability compared to other martens, often seen in small groups. It plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by regulating prey populations and dispersing seeds.
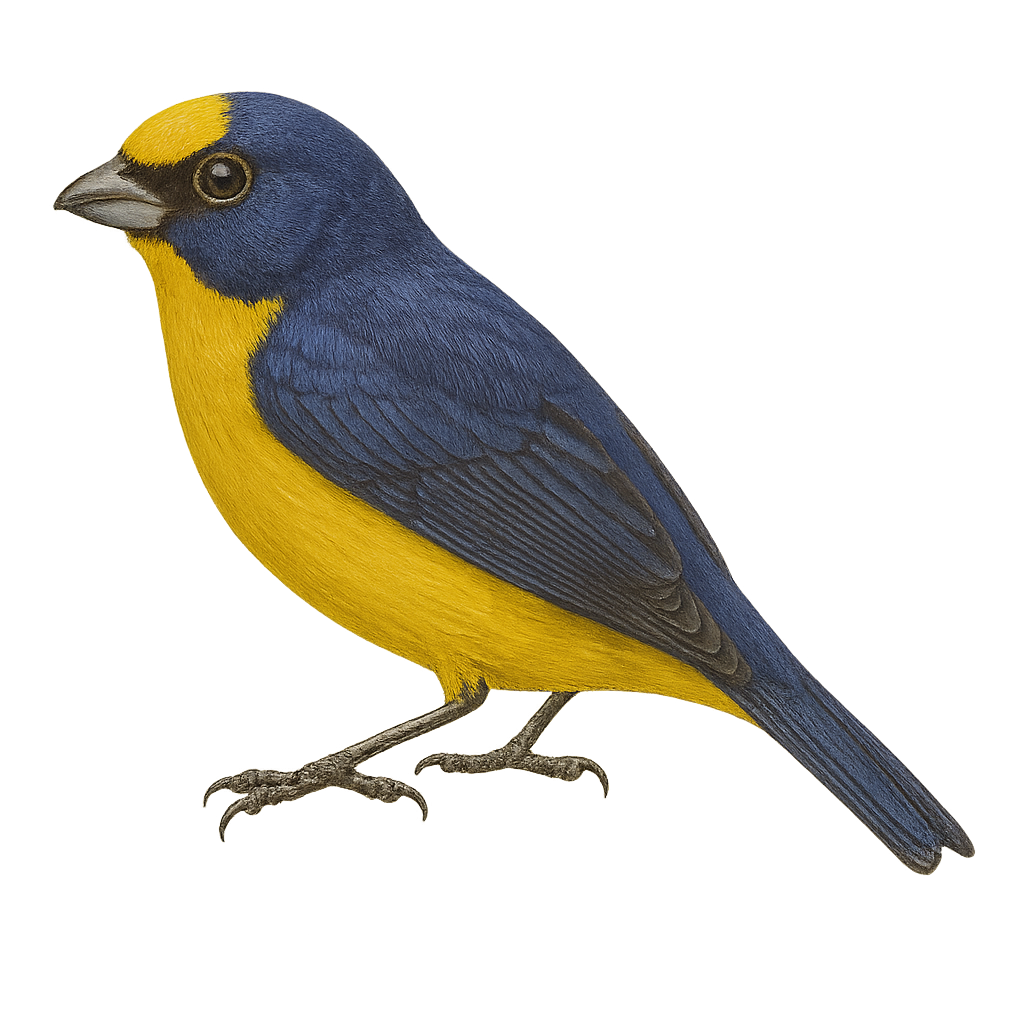
The Yellow-throated Euphonia, or Euphonia hirundinacea, is a small, colorful bird found primarily in Central America, from southern Mexico to Panama. It is easily recognizable by its bright yellow throat contrasting with its dark blue back and yellow belly. Males and females exhibit sexual dimorphism, with females generally being duller with olive-green hues. This bird measures about 11 cm in length and weighs between 10 and 15 grams. It inhabits tropical rainforests, forest edges, and gardens, where it primarily feeds on fruits and berries. Its melodious song is often heard before it is seen.
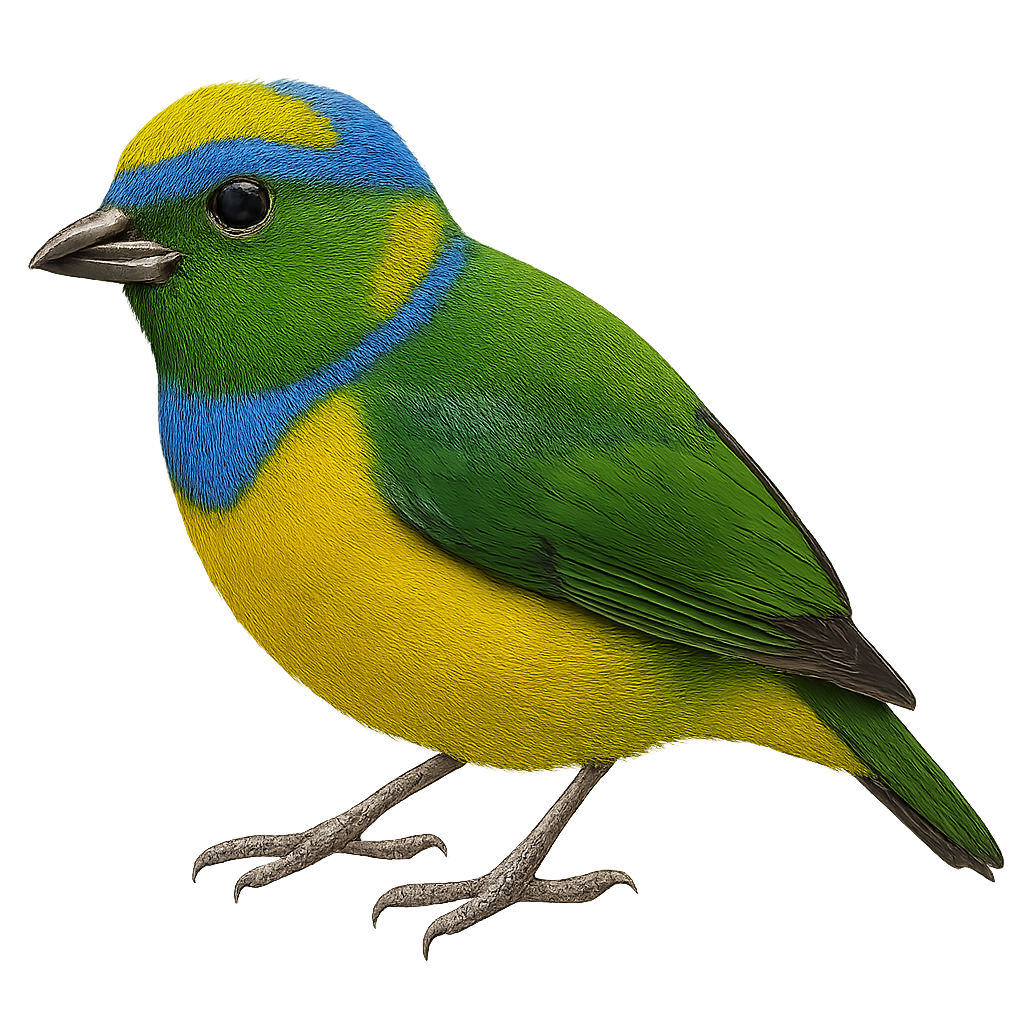
The Yellow-collared Chlorophonia, or Chlorophonia callophrys, is a small, vibrantly colored bird found primarily in the montane rainforests of Central America. Its plumage is a striking mix of emerald green, blue, and yellow, making it easily recognizable. Both males and females exhibit similar colors, although males are often slightly more vibrant. This bird primarily feeds on fruits but can also consume insects and seeds. It is often observed in small groups or pairs, actively moving through the canopy in search of food. Although its habitat is relatively restricted, it is not currently considered threatened.
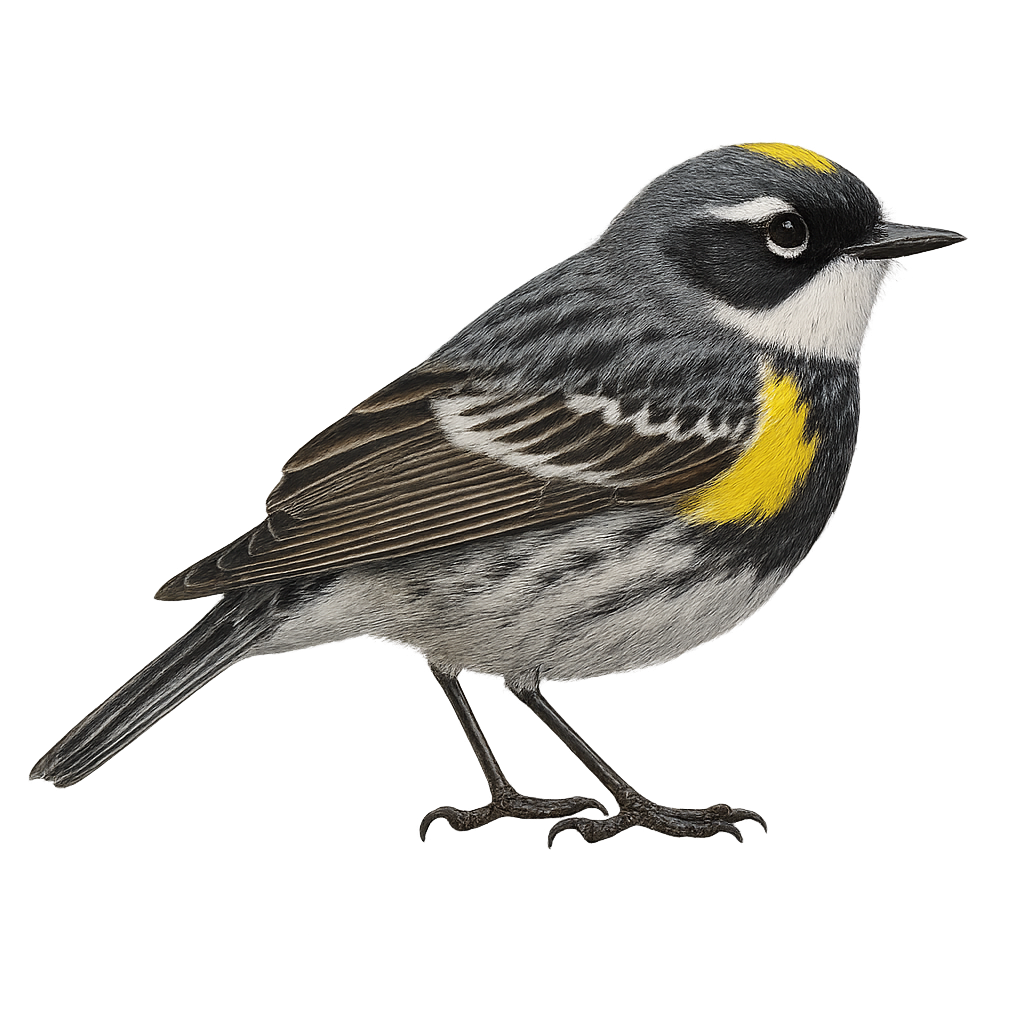
The Yellow-rumped Warbler, Setophaga coronata, is a small songbird belonging to the Parulidae family. Easily identifiable by its bright yellow rump, this feature gives the bird its name. Males display a striking blue-gray plumage with black markings and white flanks, while females and juveniles are duller. Widely distributed across North America, this migratory species breeds in the boreal forests of Canada and winters in the temperate regions of the United States and Mexico. It inhabits various environments, including coniferous forests, mixed woodlands, and shrubby areas. Primarily insectivorous, it feeds on small insects and spiders, but also consumes berries, especially in winter.
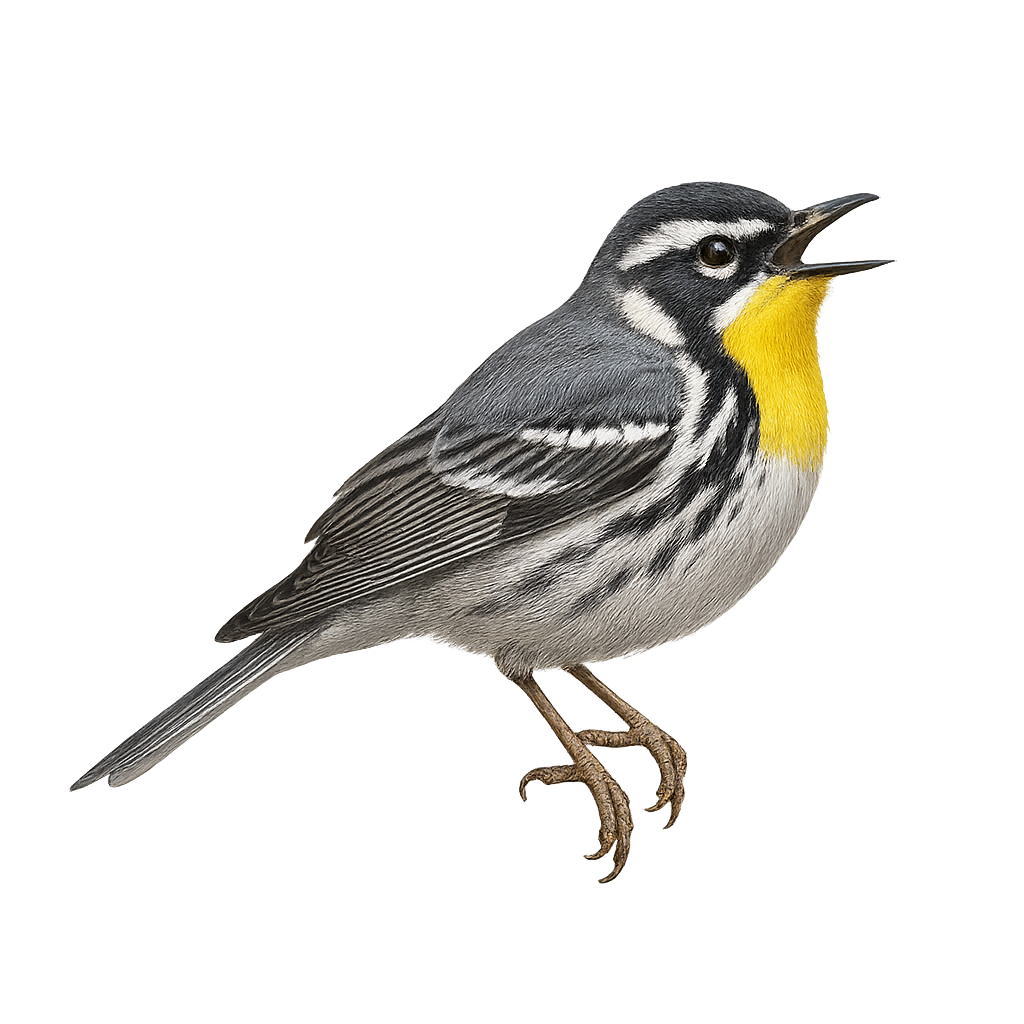
The Yellow-throated Warbler, Setophaga dominica, is a small songbird in the Parulidae family. It is easily recognizable by its bright yellow throat contrasting with its gray and white plumage. Black stripes on its face and wings add to its distinctive appearance. It primarily inhabits coniferous forests and moist woodlands in the southeastern United States. A migratory bird, it winters in the Caribbean and Central America. Its melodious song and aerial acrobatics make it a favorite among birdwatchers. Although its habitat is sometimes threatened by deforestation, it is currently listed as Least Concern by the IUCN.
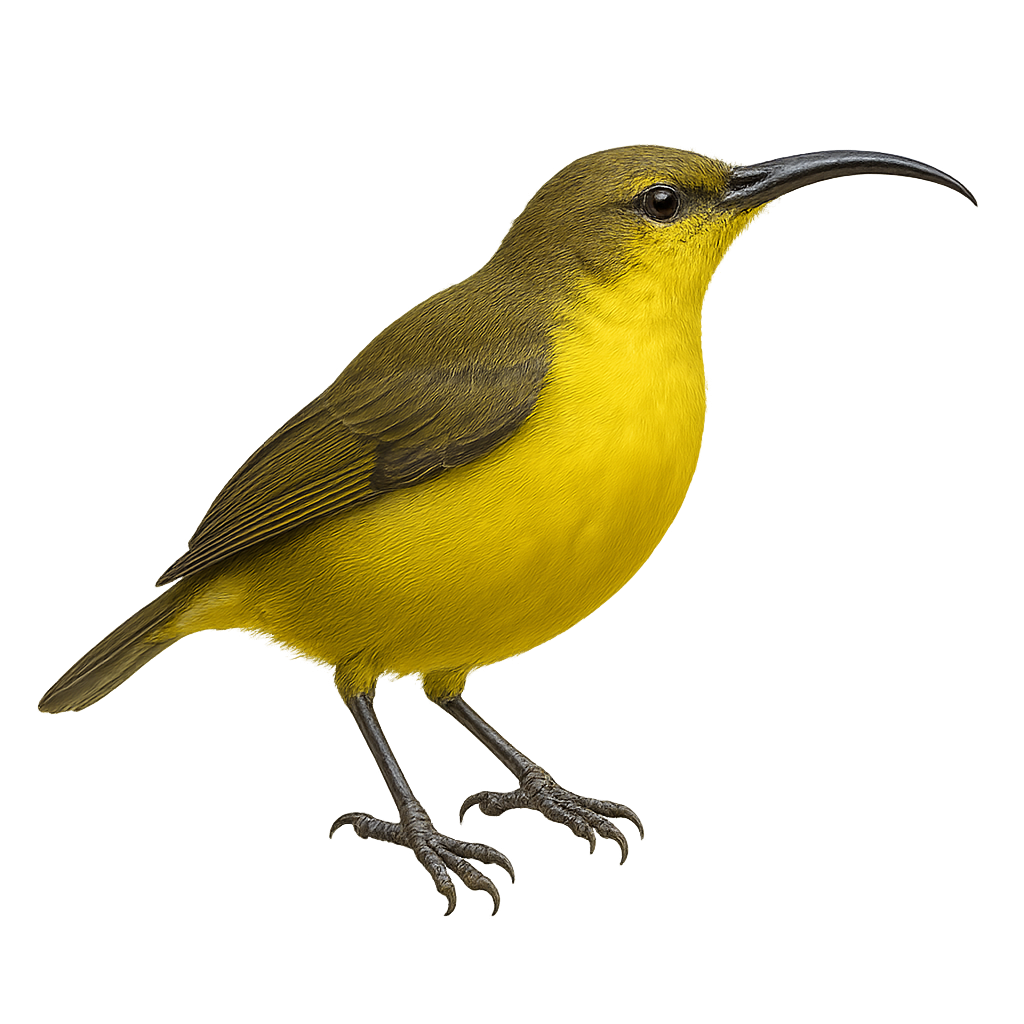
The Yellow-bellied Sunbird-Asity, or Neodrepanis hypoxantha, is a small bird endemic to Madagascar, admired for its striking plumage. It features a bright yellow belly contrasting with an olive-green back and a black head. This passerine primarily inhabits montane rainforests, feeding on nectar and insects. Its curved beak is perfectly adapted for extracting nectar from flowers. Though discreet, it plays a vital role in the pollination of local plants. Unfortunately, deforestation threatens its natural habitat, leading to a decline in its population. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure its long-term survival.
The Yellow-throated Woodpecker, or Piculus flavigula, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Picidae family. It is easily recognizable by its bright yellow throat contrasting with its olive-green plumage. This bird primarily inhabits the humid tropical forests of South America, notably in Brazil, Colombia, and Venezuela. It feeds mainly on insects, which it finds under tree bark using its strong beak. The Yellow-throated Woodpecker is a diurnal bird, often seen alone or in pairs. Its call is a mix of trills and characteristic drumming. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it is currently classified as Least Concern by the IUCN.
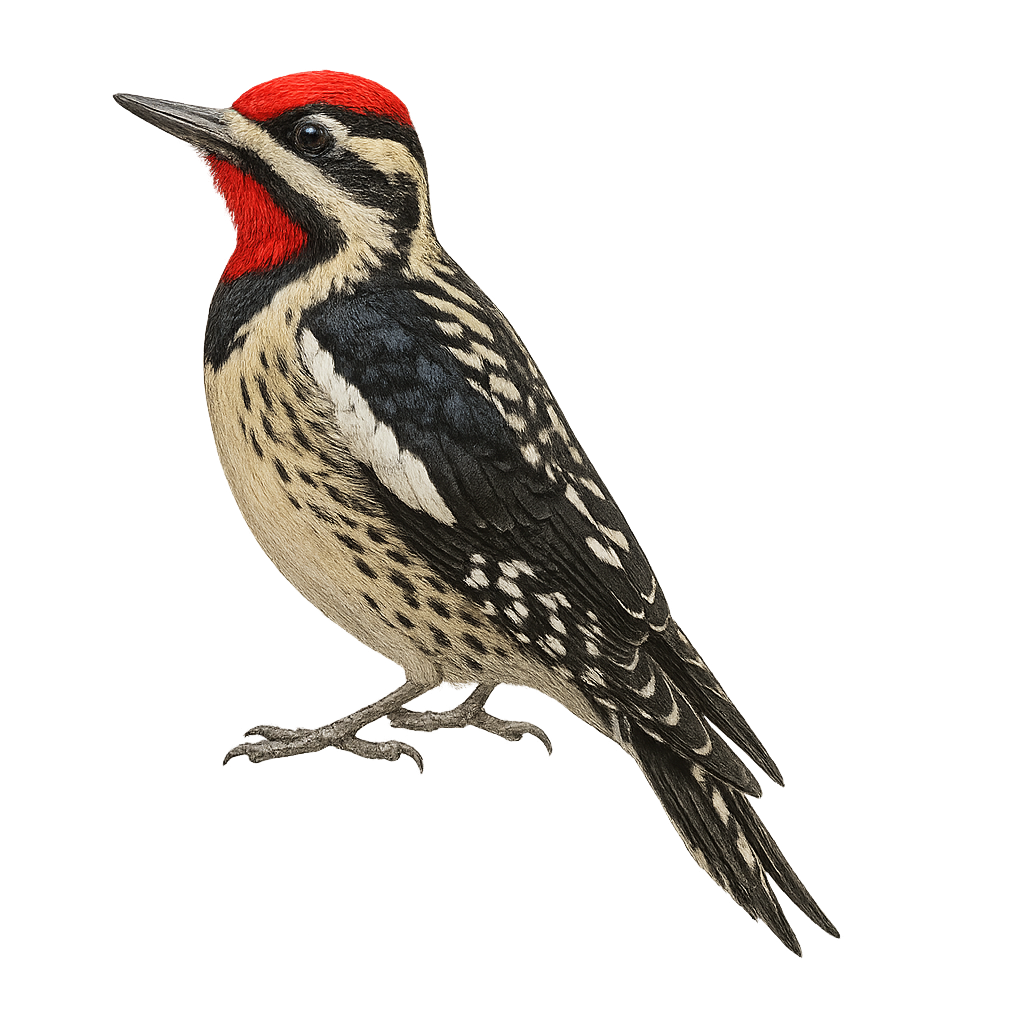
The Yellow-bellied Sapsucker, Sphyrapicus varius, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the woodpecker family. It is easily recognizable by its distinctive plumage, featuring a pale yellow belly, a head striped with black and white, and a bright red patch on the forehead. This bird primarily feeds on insects but also consumes tree sap, which it extracts by drilling holes in the bark. It is mainly found in deciduous and mixed forests of North America, where it nests in tree cavities. As a migratory bird, it winters in the southern United States and Central America. The Yellow-bellied Sapsucker plays an important ecological role by creating habitats for other species through its sap wells.
The Yellow-breasted Flycatcher is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in the tropical rainforests of Central and South America, where it is distinguished by its bright yellow belly and olive back. This bird measures about 12 to 13 cm in length and weighs between 10 and 12 grams. Its beak is relatively broad and flattened, adapted for catching insects in flight. The song of the Yellow-breasted Flycatcher is a soft and melodious whistle, often heard in the forest canopy. It is mainly insectivorous but can also consume small fruits. Its ability to blend into dense foliage sometimes makes it difficult to spot, although it is quite common in its natural habitat.
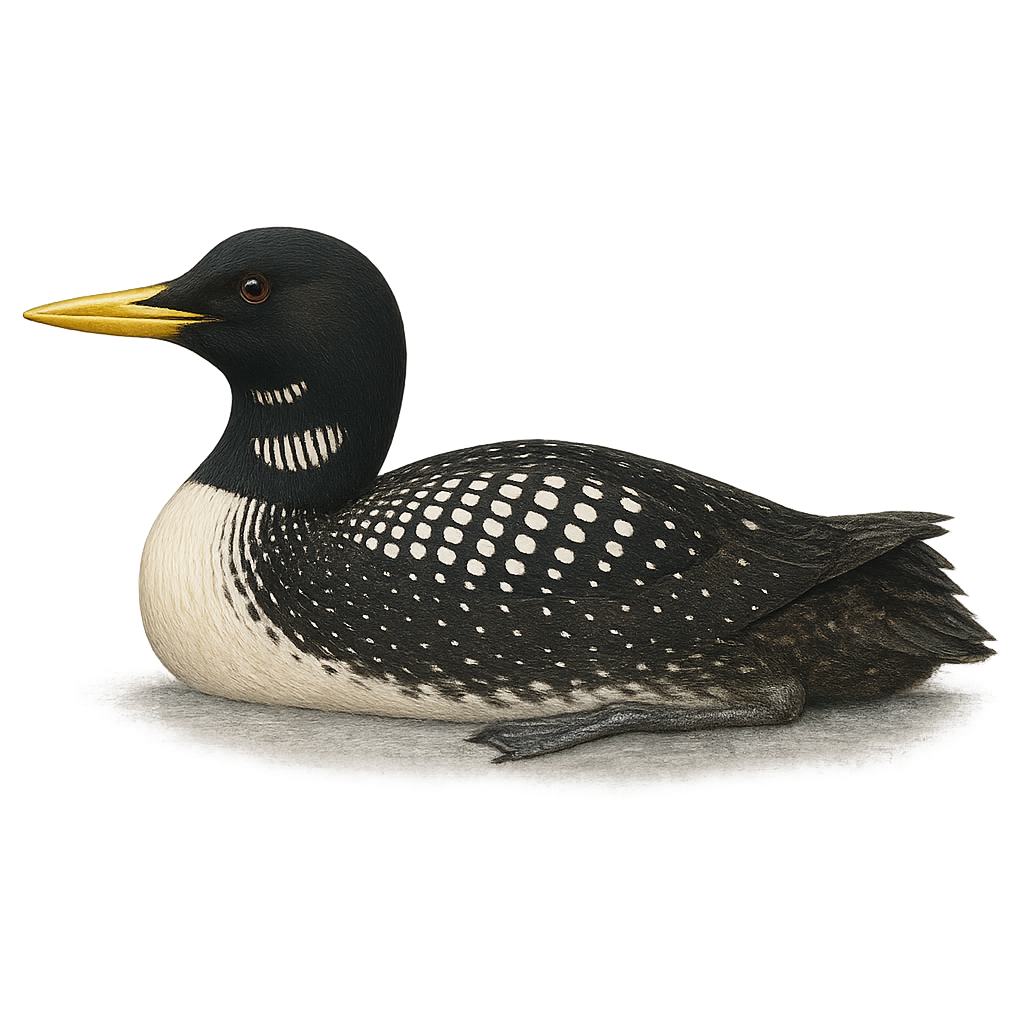
The Yellow-billed Loon, Gavia adamsii, is a majestic aquatic bird primarily inhabiting Arctic regions. It is recognizable by its distinctive pale yellow bill and black-and-white plumage. In summer, it sports a black back with white spots and a grey head, while in winter, its plumage becomes duller. This bird prefers large lakes and coastal seas to feed on fish and aquatic invertebrates. It is known for its melodious and plaintive call that echoes across northern landscapes. Although its habitat is remote, it is sometimes observed during its migrations southward.
The Yunnan snub-nosed monkey (Rhinopithecus bieti) is a large arboreal primate measuring 74–83 cm in body length (excluding tail) and weighing 14–17 kg, distinguished by its striking black-and-white coat, pink lips and flattened nose lacking nasal bones. Endemic to the alpine coniferous and mixed forests of southwestern China at elevations between 3000 and 4500 m, it feeds mainly on tree lichens, supplemented by bamboo leaves, buds and occasional fruits. This dietary specialization and dense, insulating fur enable survival in subzero temperatures. Living in cohesive troops often exceeding 400 individuals, these monkeys exhibit synchronized group displays and vocal congregations that reinforce social bonds during long, harsh winters.
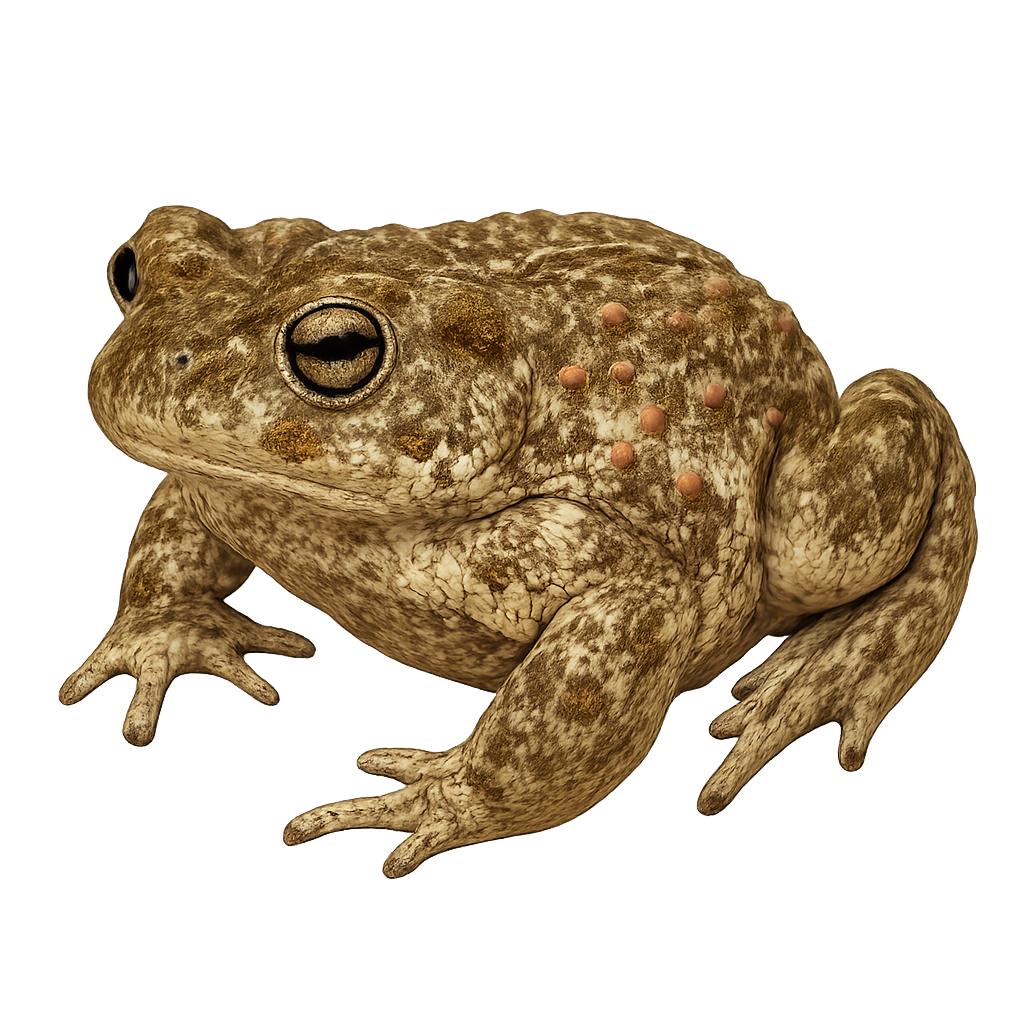
The yellow-bellied toad is a small amphibian 30–40 mm long, with olive-brown dorsal coloration and bright yellow belly mottled with black. It inhabits temporary shallow wetlands at forest edges and meadows, feeding on insects, spiders and worms. During breeding, males emit high-pitched calls near shallow pools and females lay clusters of eggs on aquatic vegetation.
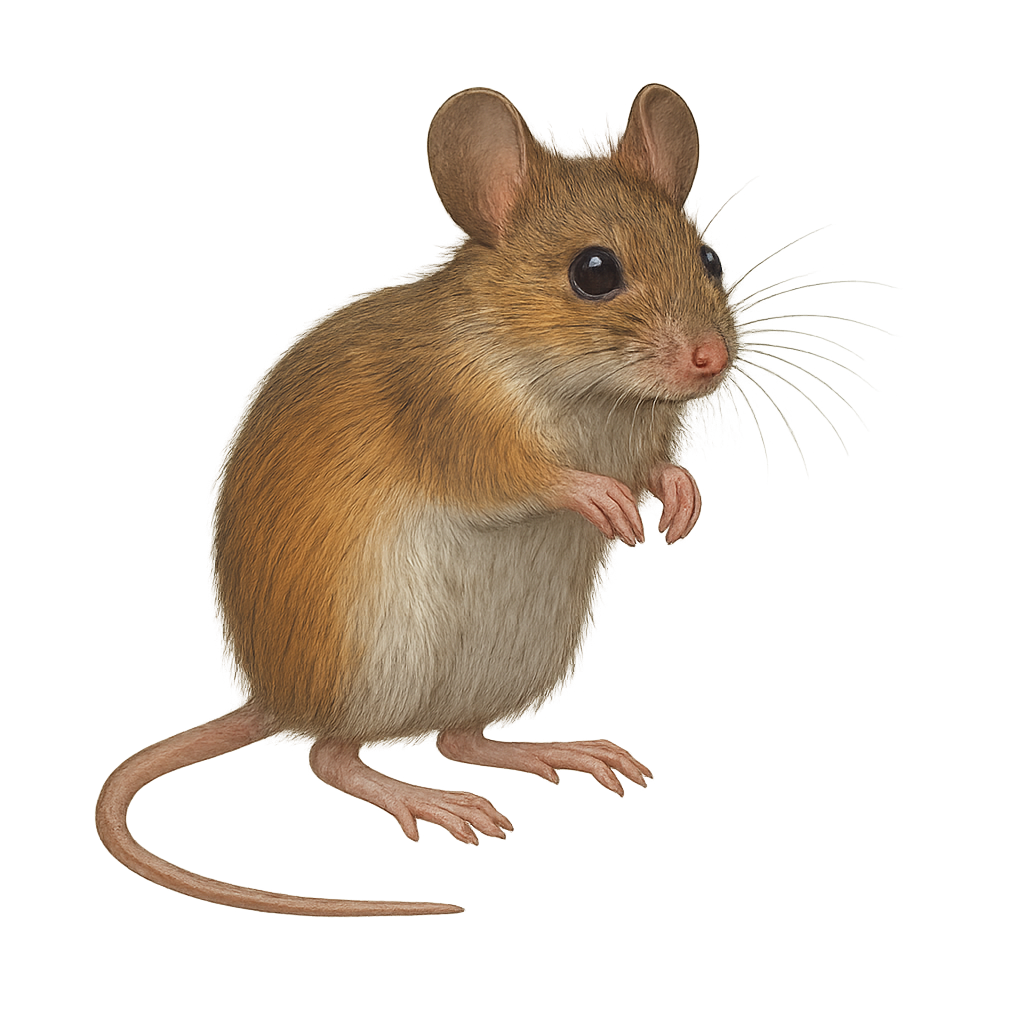
The yellow-necked mouse, Apodemus flavicollis, is a small rodent belonging to the Muridae family. It is characterized by a distinctive yellow band around its neck, contrasting with its reddish-brown back and white belly. Primarily nocturnal, it inhabits forests, hedgerows, and sometimes gardens. Its diet includes seeds, fruits, and insects. Agile and fast, it can evade predators effectively. It reproduces several times a year, with litters of 4 to 7 young. Although common, it plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by dispersing seeds and controlling insect populations.
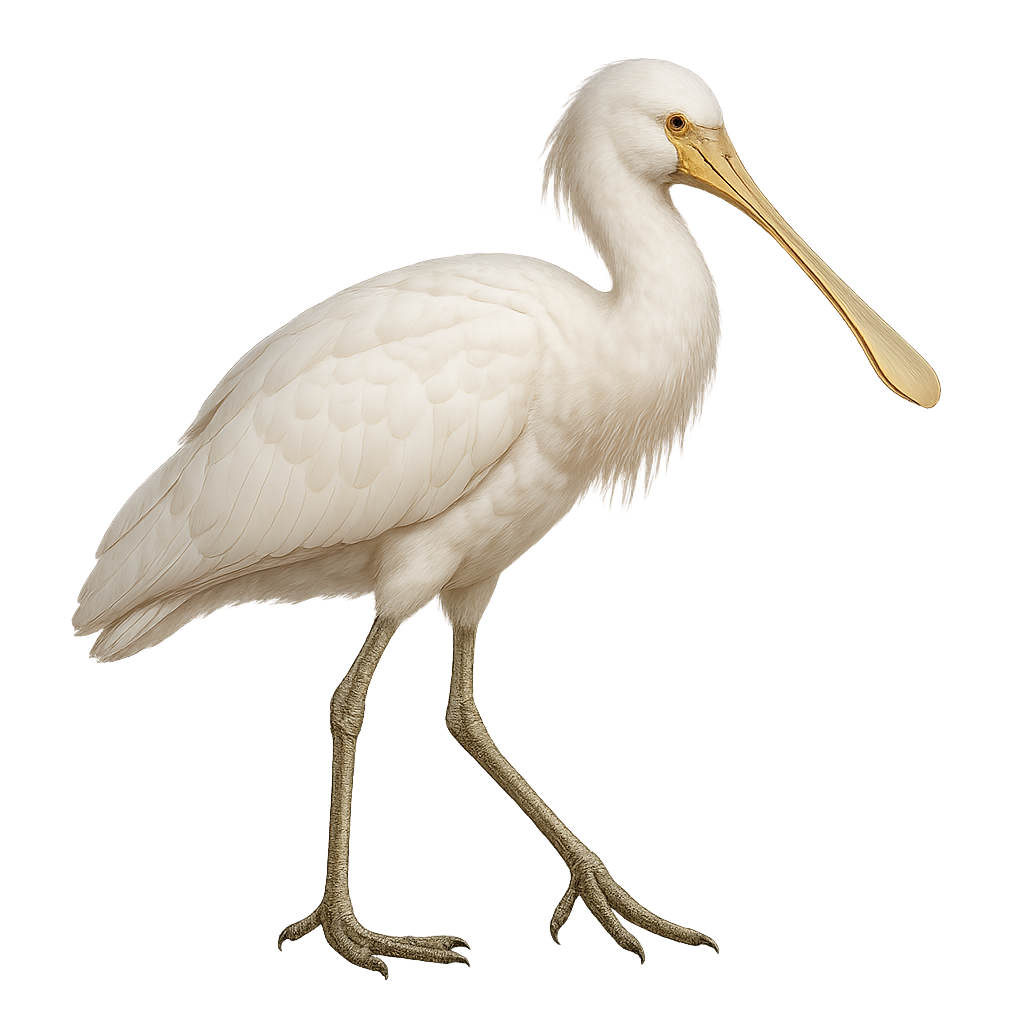
The Yellow-billed Spoonbill, Platalea flavipes, is a medium-sized aquatic bird known for its long, flat, yellow bill. It has a striking white plumage, sometimes tinged with pink during the breeding season. This bird is primarily found in Australia, where it inhabits wetlands, marshes, and lake edges. The Yellow-billed Spoonbill feeds mainly on small fish, aquatic insects, and crustaceans, which it captures by sweeping its bill through the water. It is often seen in small groups but can also be solitary. Although its habitat is threatened by wetland degradation, it is currently classified as of least concern by the IUCN.
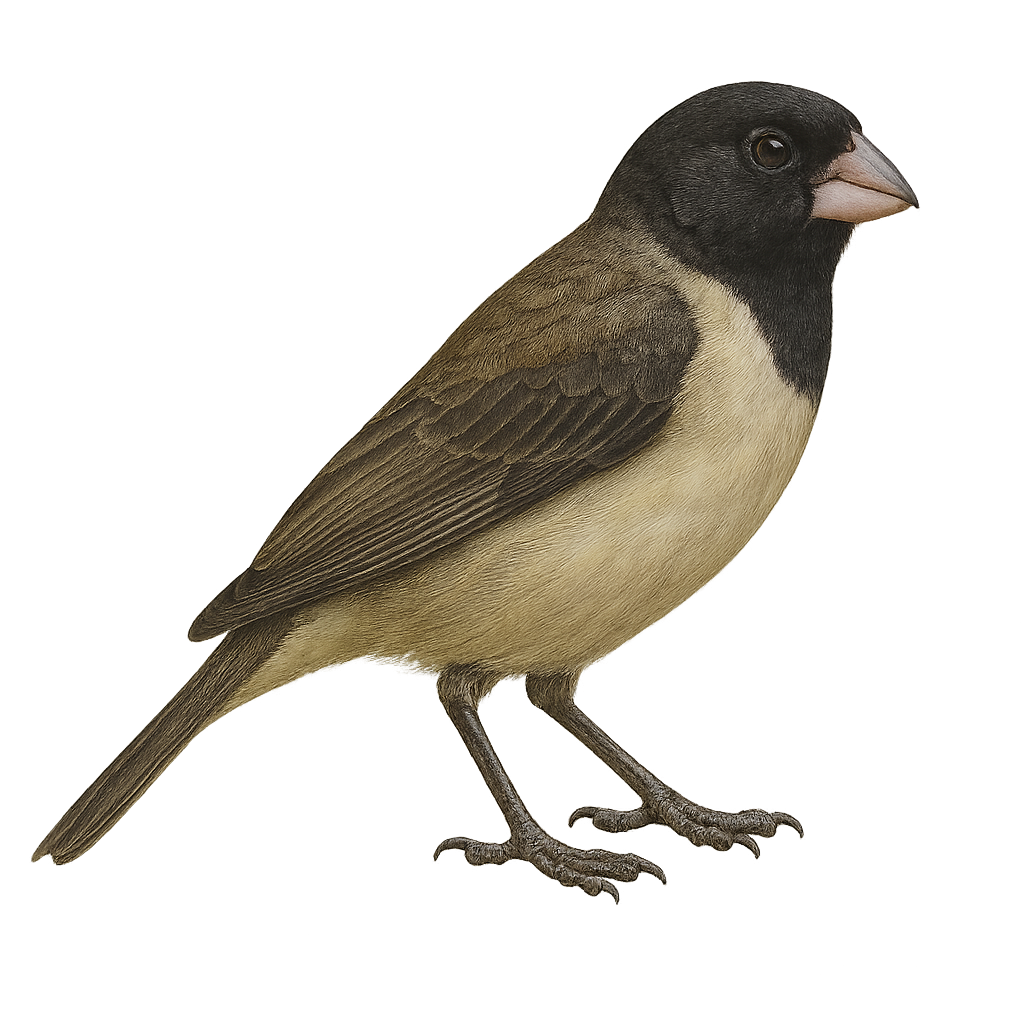
The Yellow-bellied Seedeater is a small passerine bird belonging to the Thraupidae family. It is primarily found in Central and South America, inhabiting open areas such as grasslands, cultivated fields, and forest edges. This bird is notable for its contrasting plumage: the male has a brown back, bright yellow belly, and distinctive black throat, while the female displays duller tones. The Yellow-bellied Seedeater is granivorous, mainly feeding on seeds, but it can also consume small insects. Its song is melodious and varied, making it easily identifiable. Although often solitary, it can form small groups outside the breeding season.
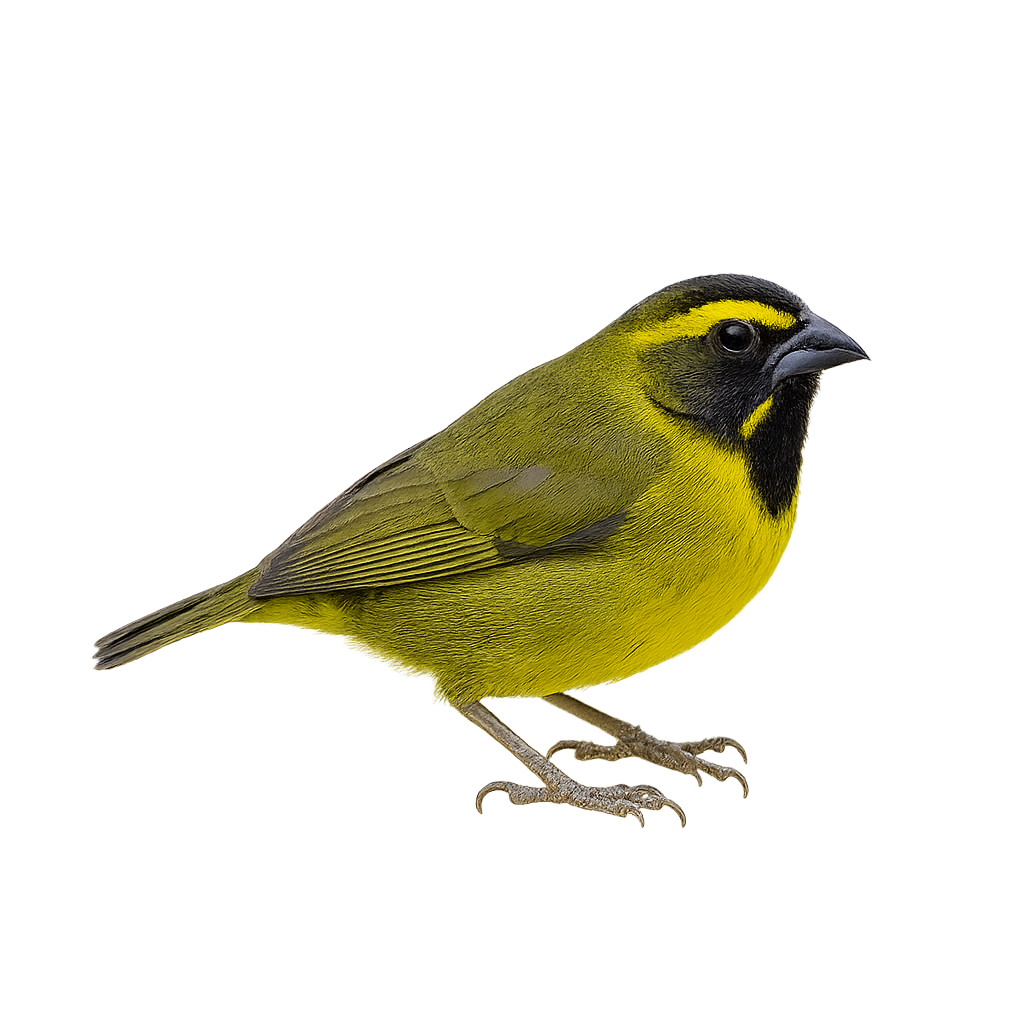
The Yellow-faced Grassquit, or Tiaris olivaceus, is a small granivorous bird found mainly in the tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas. It is easily recognizable by its olive-green plumage and bright yellow facial mask, which contrasts with its duller body. This passerine measures about 11 cm in length and weighs between 8 and 10 grams. It primarily inhabits grasslands, savannas, and shrublands, where it feeds on seeds and insects. The Yellow-faced Grassquit is a social bird, often observed in small groups. Its song is a soft and melodious trill, used to mark its territory and attract mates. Although not threatened, deforestation and habitat loss can affect its local populations.
The Yellow-rumped Tanager, or Heterospingus rubrifrons, is a small, colorful bird native to the humid Caribbean slopes of Central America, especially in Costa Rica and Panama. It is recognized by its vivid yellow rump, reddish head, and dark olive body. Found in the canopy of lowland and mid-elevation rainforests, it often joins mixed-species flocks. Active and inquisitive, it feeds on fruits, insects, and occasionally nectar. Its population is considered stable in protected areas, although deforestation could pose a local threat.
The Yellow-backed Tanager, or Hemithraupis flavicollis, is a small, lively songbird from the tropical forests of South America, easily recognized by its bright yellow back, black head (in males), and white underparts. It is found from eastern Panama through the Amazon Basin, the Guianas, and as far as southern Brazil. It lives in the canopy of humid forests, forest edges, and secondary growth. Active and sociable, it often joins mixed-species flocks and feeds on fruits, insects, and nectar. This adaptable species is common, and its population is considered stable across its range.
The Yellow-winged Tanager, or Thraupis abbas, is a colorful and fascinating bird found primarily in the tropical and subtropical forests of Central America. This medium-sized passerine boasts a striking plumage, with distinctive yellow wings contrasting against its blue-gray body. Males and females exhibit little sexual dimorphism, although males are often slightly more vibrant. The Yellow-winged Tanager is a sociable bird, often seen in small groups, feeding mainly on fruits but also on insects. Its melodious and varied song is a delight for birdwatchers. Although relatively common in its natural habitat, it is essential to preserve the forests where it resides to ensure its long-term survival.
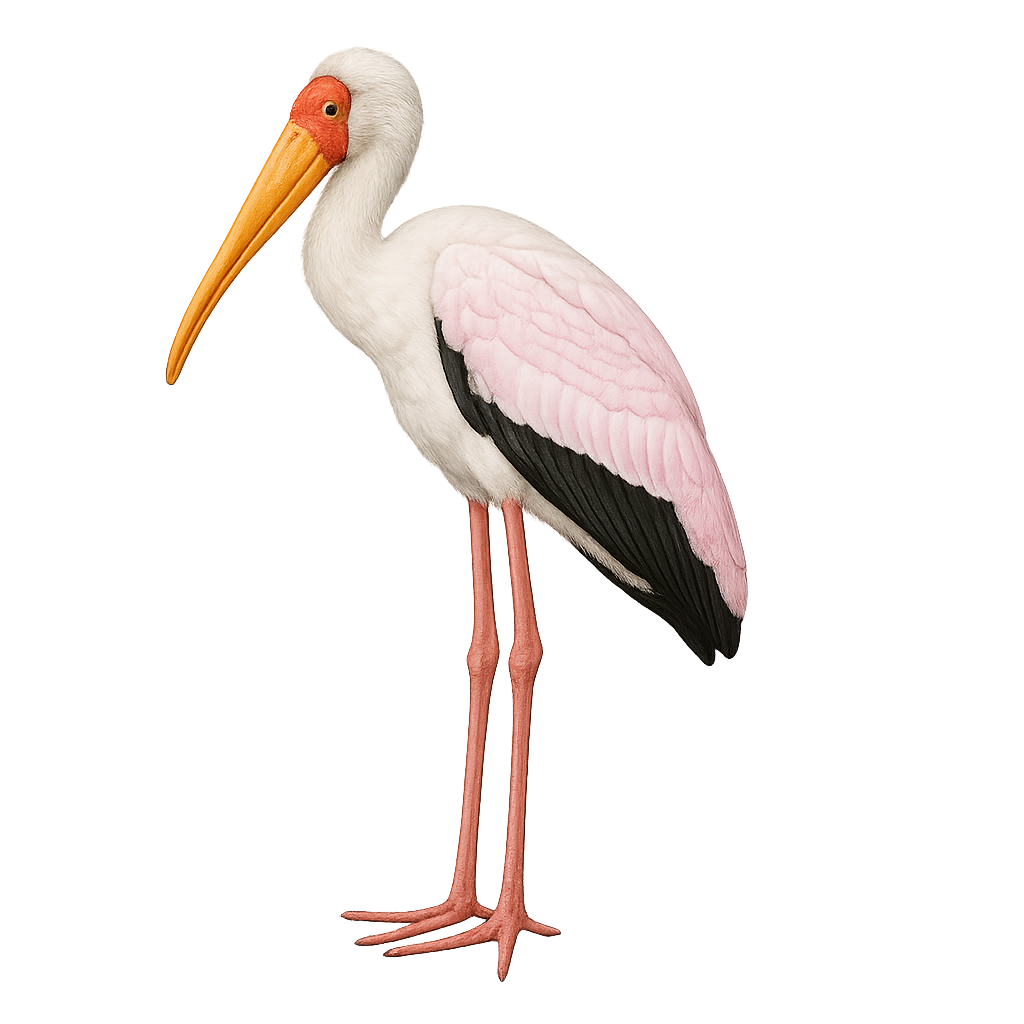
The Yellow-billed Stork, or Mycteria ibis, is a large wading bird known for its distinctive downward-curved yellow bill and predominantly white plumage with contrasting black wings. It inhabits the wetlands of sub-Saharan Africa, feeding on fish, crustaceans, and insects. This gregarious bird is often seen in groups, especially during the breeding season. The Yellow-billed Stork nests in trees, often in mixed colonies with other wading birds. Although not currently threatened, habitat degradation poses a potential risk to its populations.
The Yellow-browed Tody-Flycatcher is a small bird with distinctive plumage, primarily olive green with golden cheeks that give it its name. It inhabits the humid tropical forests of South America, particularly in the Amazon. This passerine is often seen in pairs or small groups, actively moving through the canopy in search of insects. Its song is a high-pitched, rapid trill, often heard before it is seen. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it remains relatively common in protected areas. Its small size and quick movements make it difficult to spot, but it is a prized subject for birdwatchers and nature photographers.