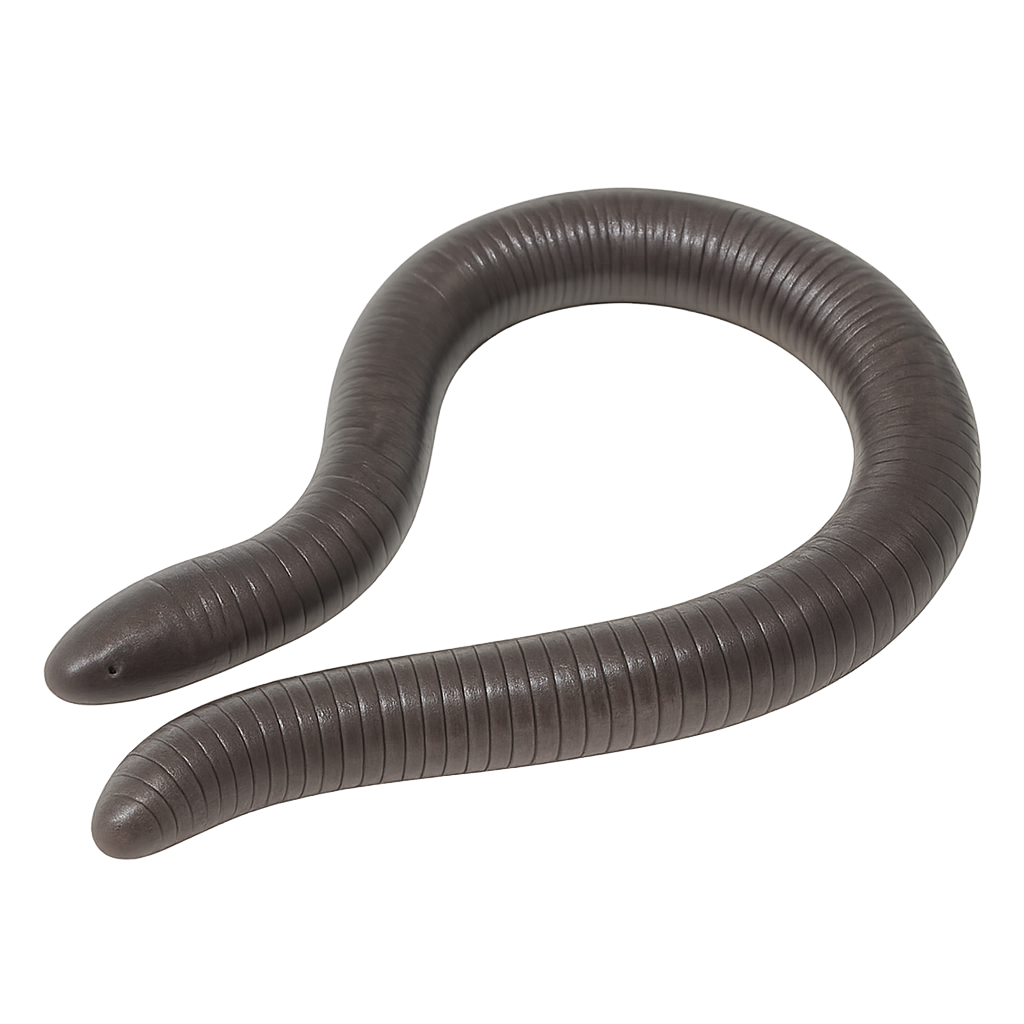
The Dermophis mexicanus, or Mexican burrowing caecilian, is a burrowing amphibian characterized by its elongated, limbless body, resembling an earthworm. Its smooth, segmented skin allows it to move easily underground. Primarily nocturnal, this species feeds on small invertebrates found in the soil. It has keen senses to detect prey in the dark. Mexican caecilians inhabit moist environments, often near rivers or in tropical forests. They are ovoviviparous, meaning the young develop in eggs inside the mother's body until hatching. Though discreet, they play a crucial role in the ecosystem by regulating invertebrate populations.
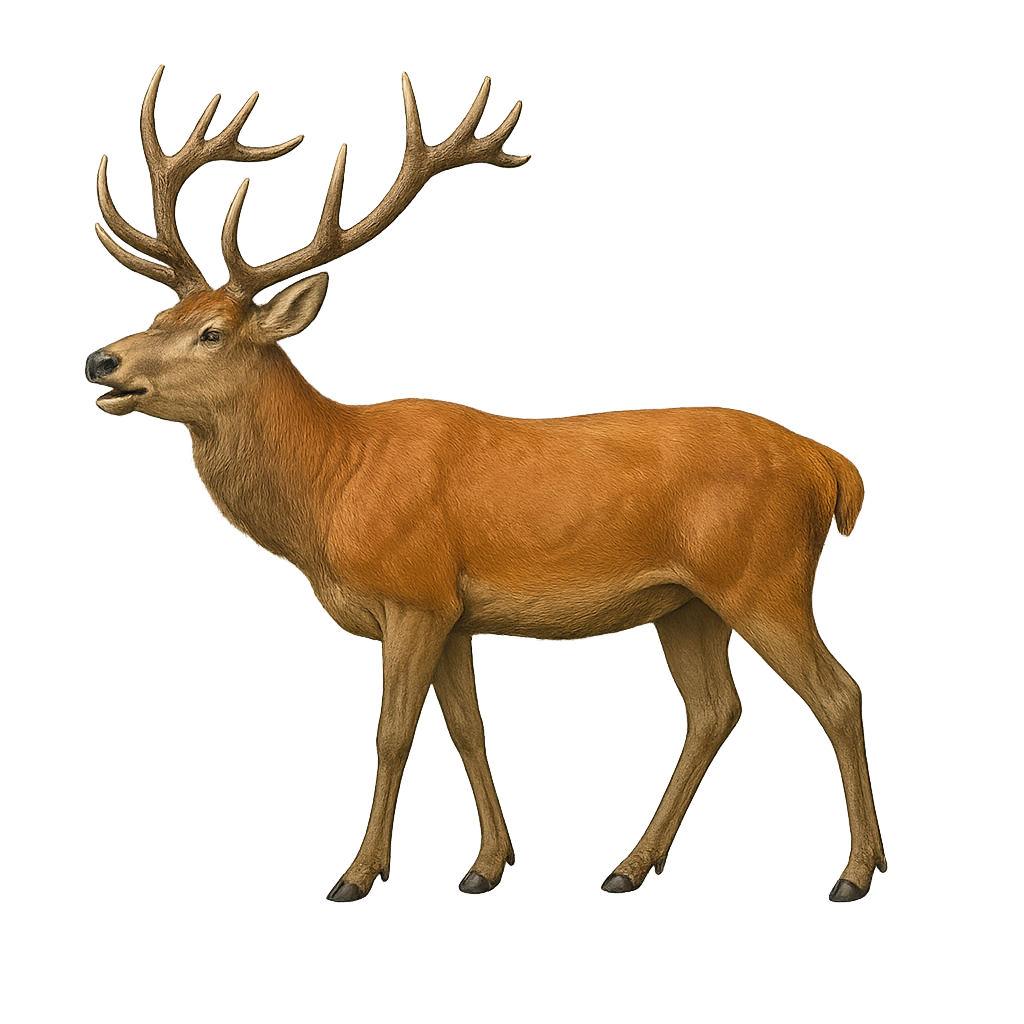
The Maral Red Deer, a subspecies of the red deer, is a majestic cervid primarily inhabiting the mountainous and forested regions of Central Asia. Recognizable by its large size and impressive antlers, the maral symbolizes power and grace. Its coat ranges from brown to gray, lightening in winter. Males sport magnificent branched antlers, which they shed annually after the rutting season. The maral is a gregarious animal, living in herds, especially outside the breeding season. It primarily feeds on grasses, leaves, and young shoots. Although its habitat is threatened by human expansion, the maral remains an iconic species of Asian wildlife.
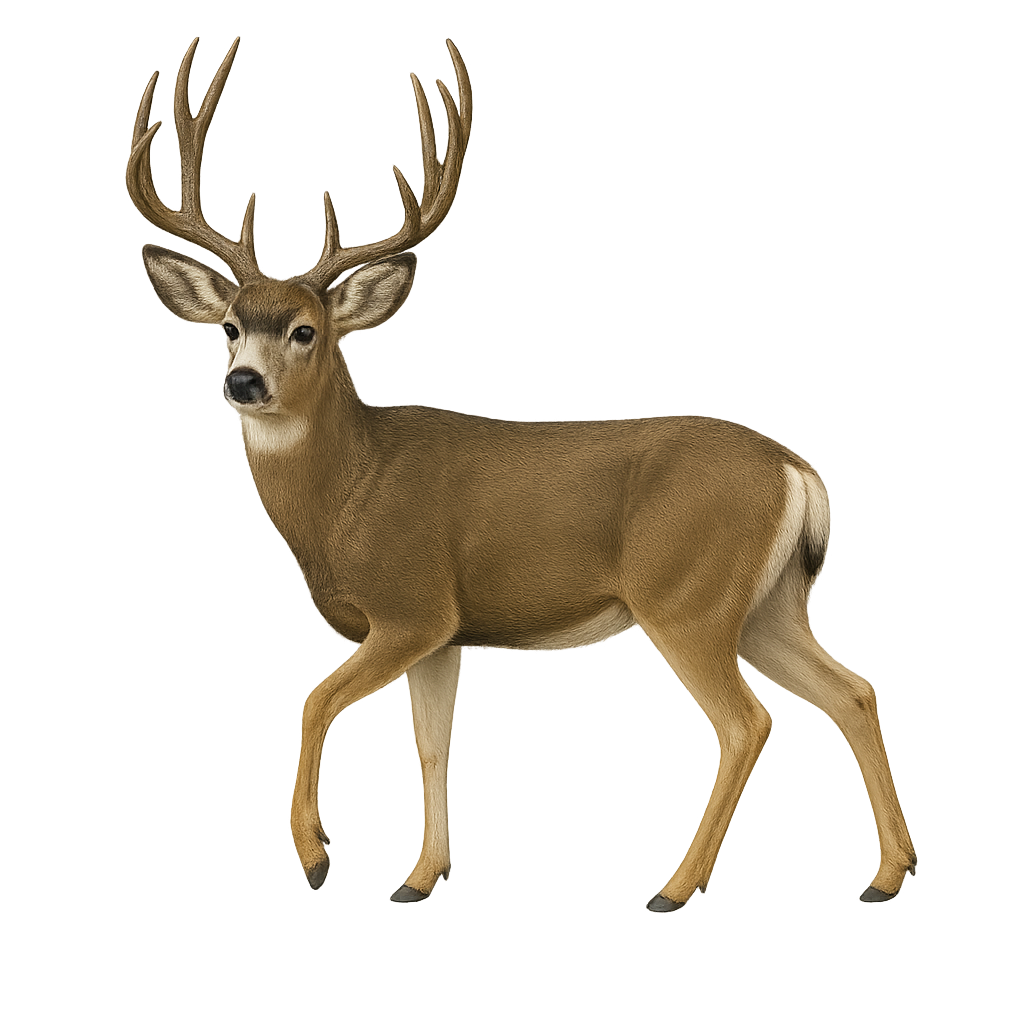
The mule deer is a North American deer species known for its large, mule-like ears. Its coat ranges from gray to brown, becoming lighter in winter. Males have branched antlers that they shed annually. Adapted to rugged terrain, they prefer mountainous and open forest habitats. Primarily herbivorous, they feed on leaves, grasses, and young shoots. Mule deer are social animals, often forming small groups, especially in winter. They are generally wary, making them challenging to approach.
The Mountain Goat is a robust mammal well adapted to life in the rugged mountains and rocky terrain of North America. This herbivore is easily recognizable by its white or cream-colored coat, which helps it blend into the snow and rocks. Its legs are specially adapted for climbing, with wide and rigid hooves that provide excellent traction on steep slopes.
The Mountain Goat feeds primarily on herbaceous plants, lichens, and moss, which it finds in rocky slopes and alpine meadows. While it is often perceived as a hardy species, it faces threats from habitat loss, poaching, and diseases transmitted by domestic animals. The population of Mountain Goats is closely monitored, and efforts are underway to protect this iconic species of the mountains.
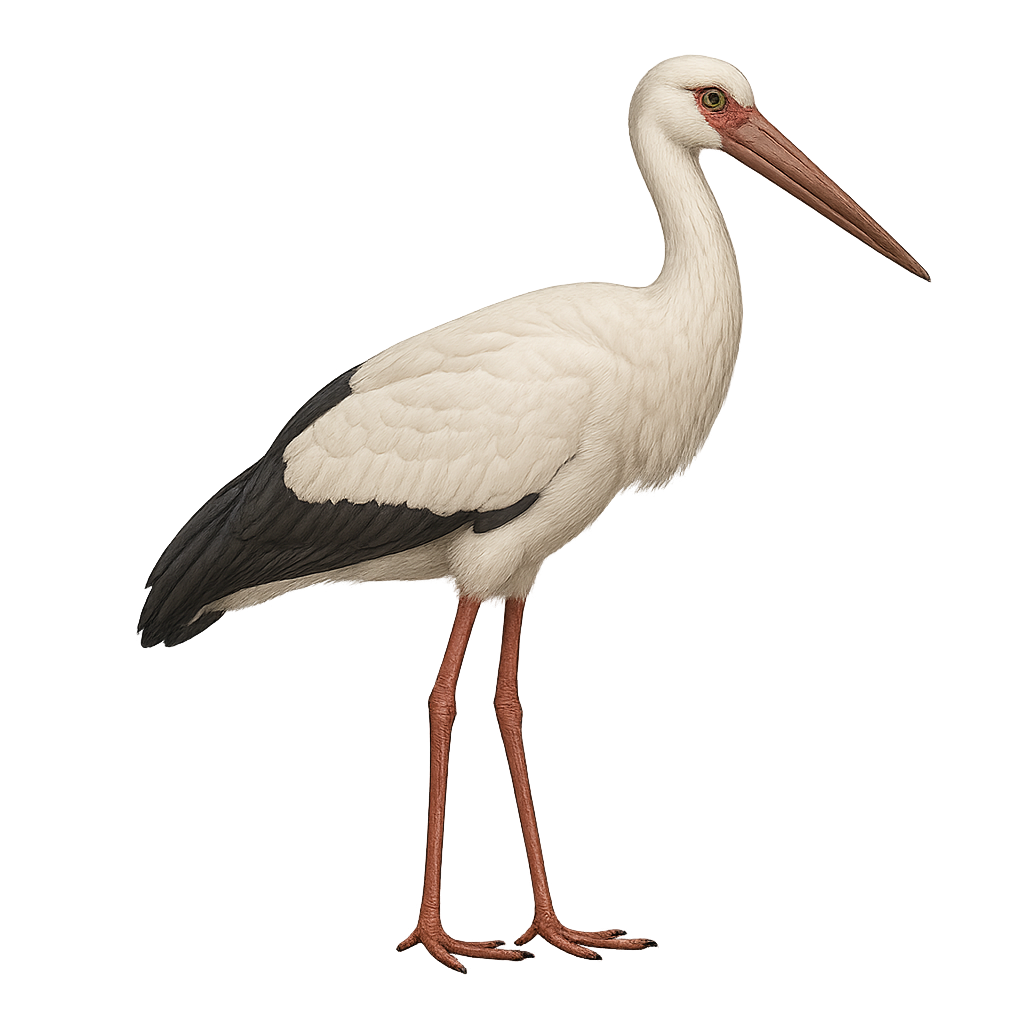
The Maguari Stork, or Ciconia maguari, is a large wading bird known for its striking white plumage and black wings. It has a long reddish bill and slender legs, allowing it to move gracefully through wetlands. Predominantly found in South America, it inhabits marshes, flooded grasslands, and riverbanks. The Maguari Stork is a gregarious bird, often seen in small groups. It primarily feeds on fish, amphibians, and aquatic insects. Although its conservation status is currently "least concern," habitat destruction poses a potential threat.
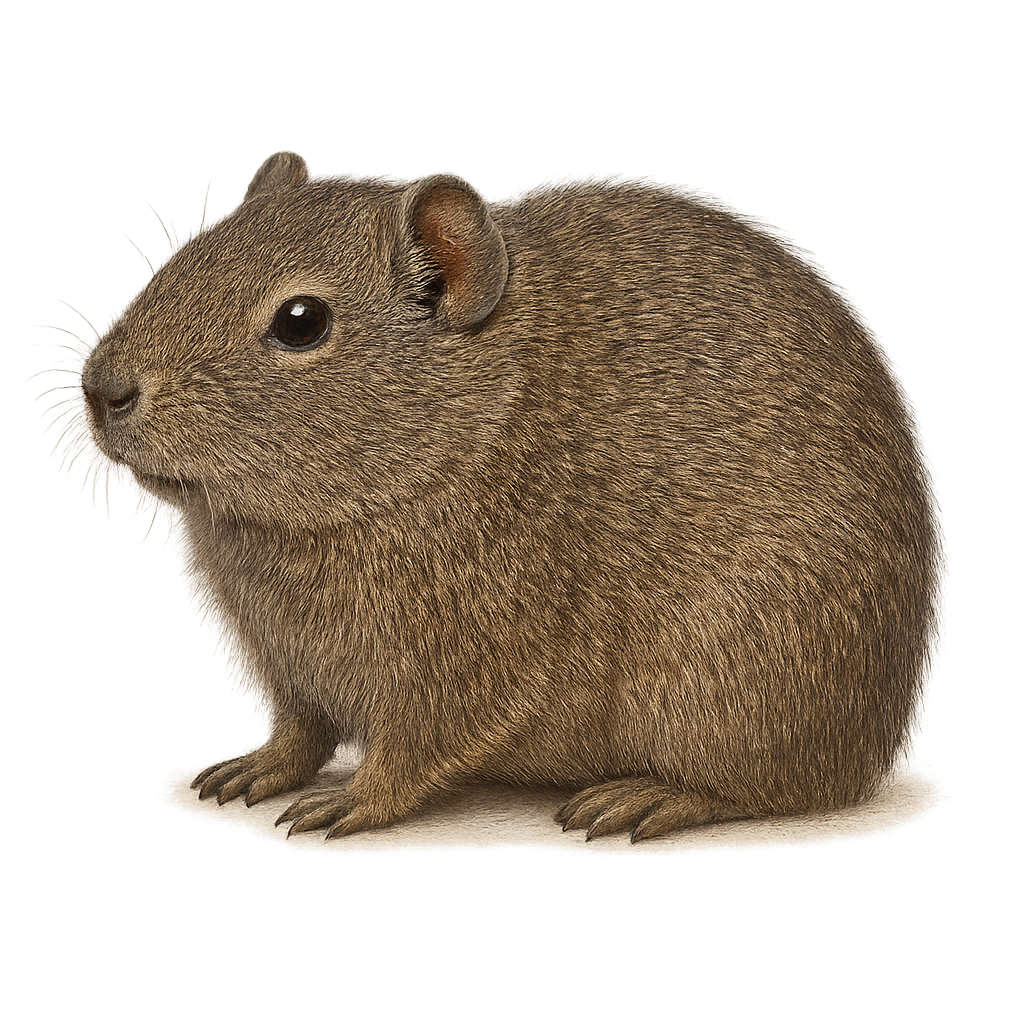
The Galea musteloides, or mountain cavy, is a small rodent native to the Andean regions of South America. Often mistaken for the guinea pig, it is smaller and exhibits different behavioral and ecological traits. This rodent typically lives in social groups in varied habitats such as grasslands, forests, and rocky areas. It is primarily herbivorous, feeding on grasses, leaves, and fruits. Its fur is short and dense, usually brown-gray, allowing it to blend effectively into its natural environment. The Galea musteloides plays an important role in its ecosystem as prey for many predators and contributes to seed dispersal.
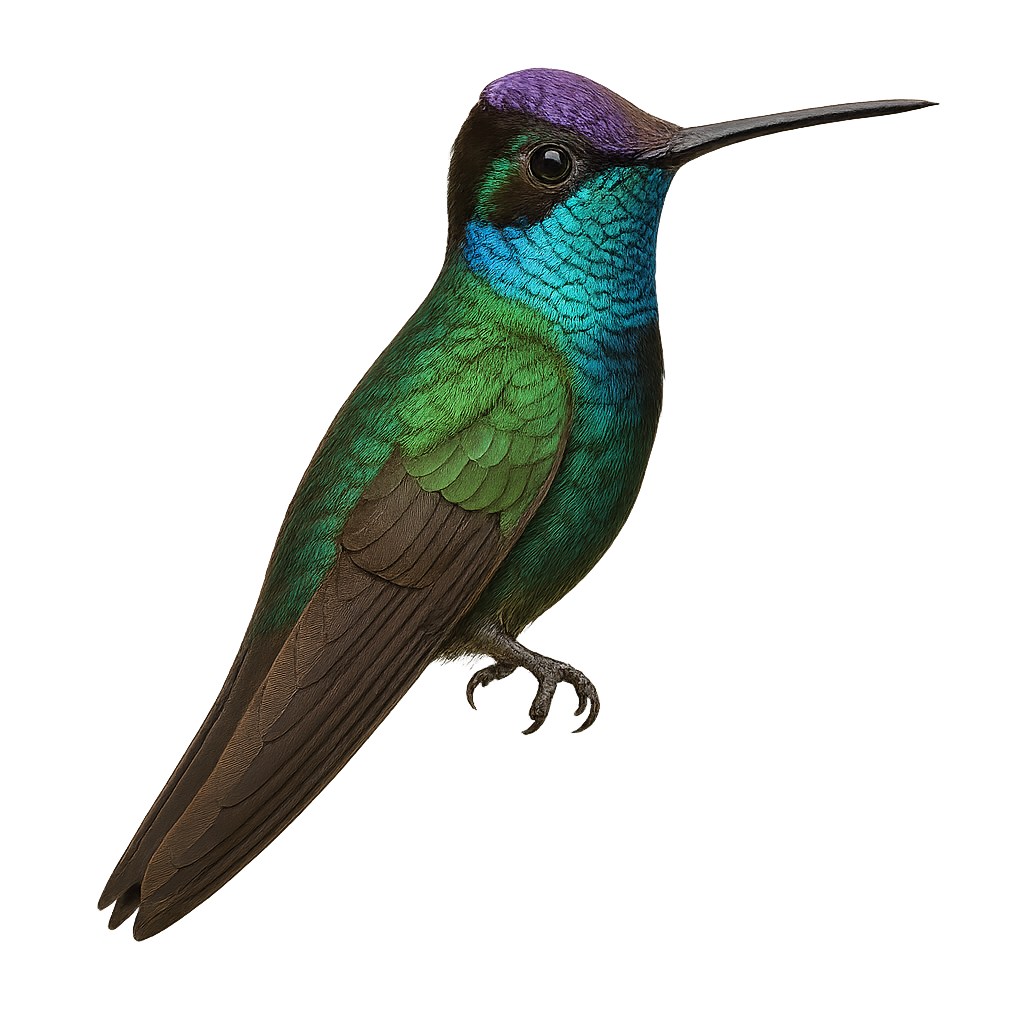
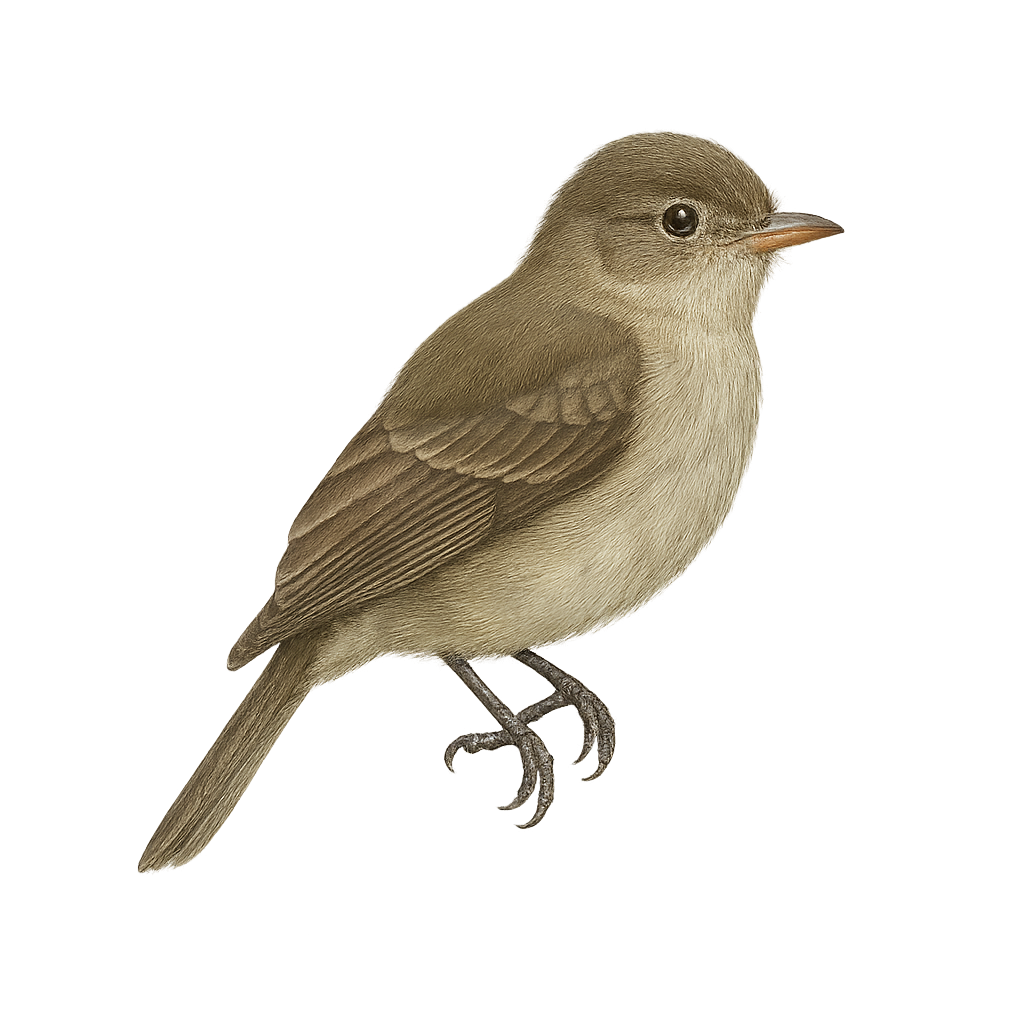
The Magnificent Hummingbird, scientifically known as Eugenes fulgens, is a medium-sized bird, measuring about 13 cm in length. It is renowned for its striking plumage, featuring metallic green hues and an iridescent throat that can appear violet or blue depending on the light. Males boast a brilliant green crown, while females are duller, with grayish tones. This hummingbird primarily inhabits mountain forests and woodland edges, where it feeds on nectar and insects. Its fast and agile flight allows it to maneuver easily between flowers. Although often solitary, it can be seen in small groups during the breeding season.
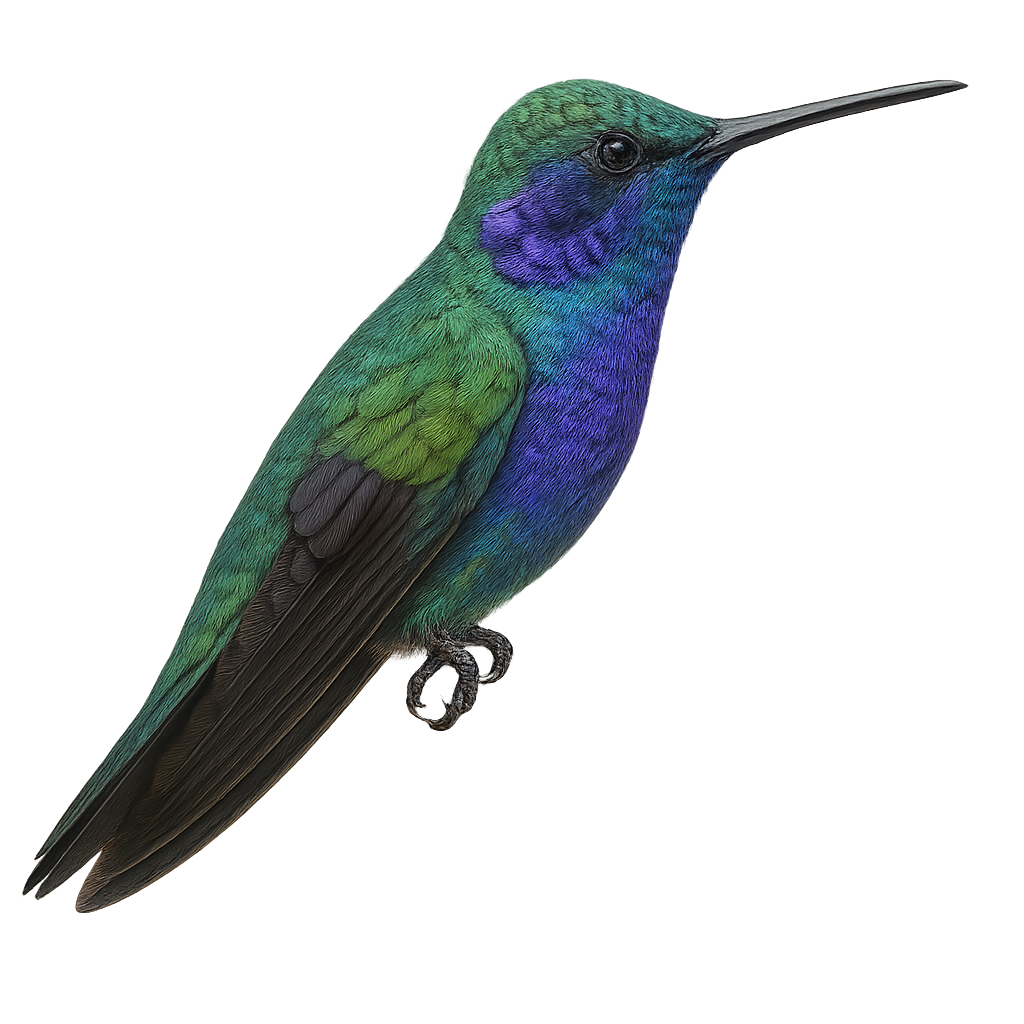
The Mexican Violetear is a small, brightly colored bird, primarily emerald green with metallic sheens. It is recognizable by its violet patches on the sides of its head and slightly forked tail. This hummingbird frequents humid forests and forest edges, often at high altitudes. It feeds mainly on nectar but supplements its diet with small insects. Its flight is fast and agile, allowing it to maneuver easily between flowers. The Mexican Violetear is a solitary bird, except during the breeding season. It is known for its spectacular courtship displays, where the male showcases his colorful feathers to attract the female.
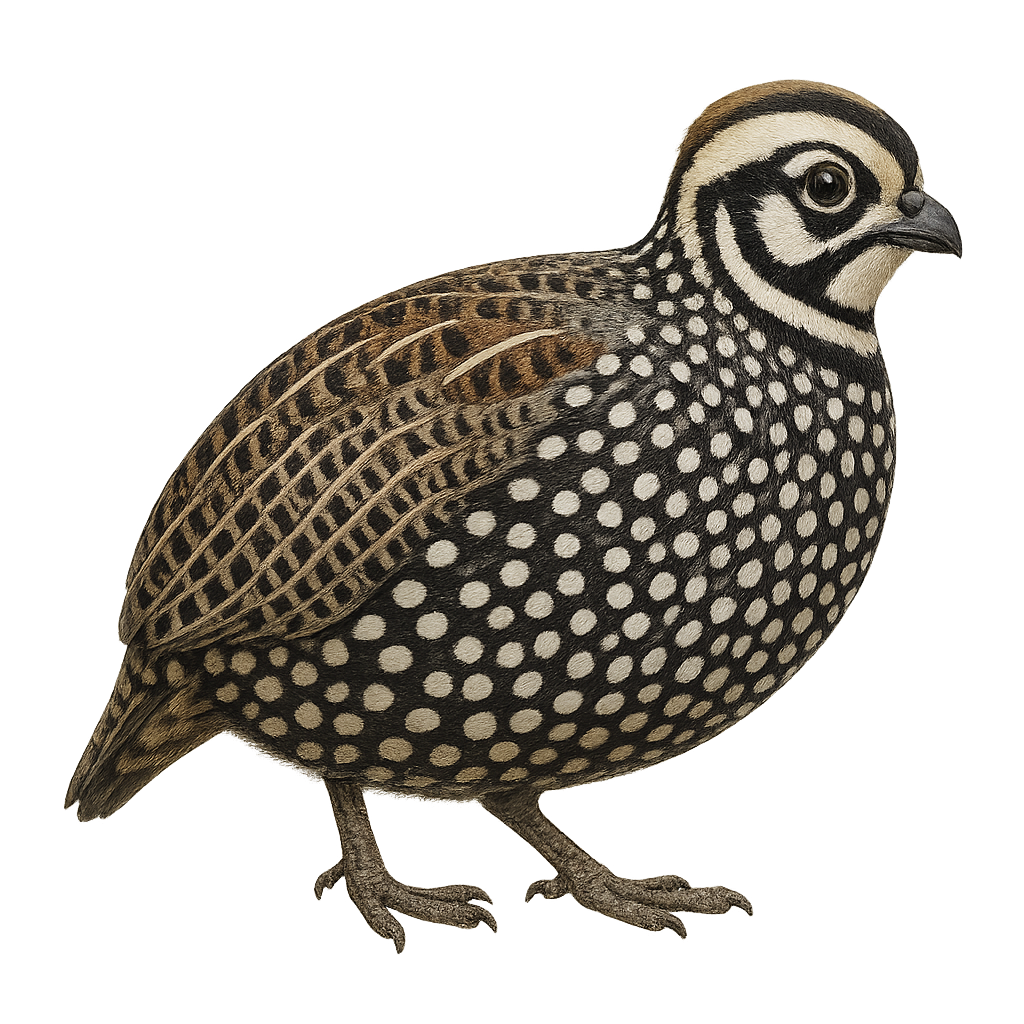
The Montezuma Quail is a medium-sized ground bird, known for its distinctive and colorful plumage. Males feature a striking black and white head with mask-like patterns, while females have a more subdued brown and speckled appearance. These birds are primarily found in the mountainous regions of the southwestern United States and Mexico, inhabiting grasslands and wooded areas. They feed mainly on seeds, insects, and bulbs, which they dig up with their strong legs. The Montezuma Quail is a discreet bird, often difficult to spot due to its shy behavior and ability to blend into its surroundings.
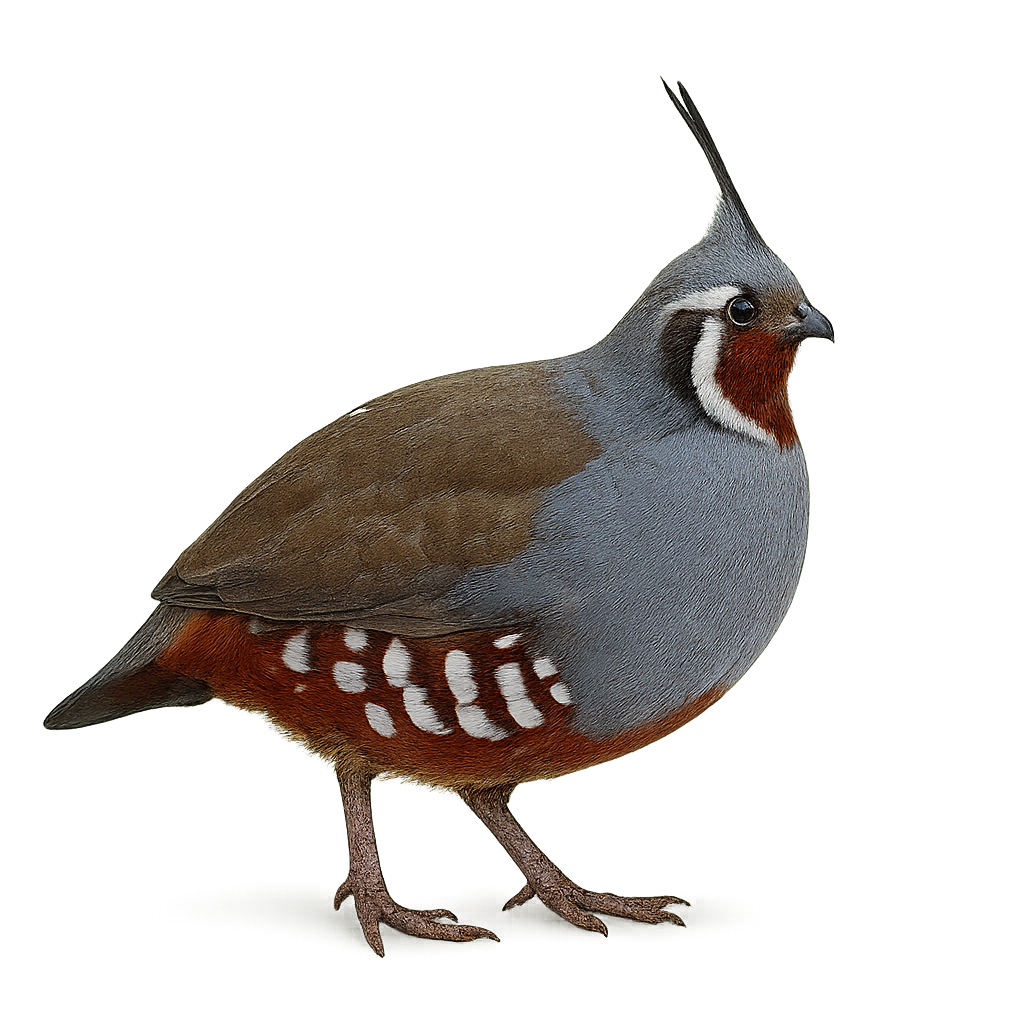
The Mountain Quail, or Oreortyx pictus, is a medium-sized ground-dwelling bird distinguished by its prominent crest and varied plumage of brown, gray, and white hues. It is primarily endemic to the mountainous regions of the western United States, where it inhabits coniferous forests and shrublands. This bird is particularly adapted to rugged terrains and primarily feeds on seeds, berries, and insects. Although capable of flight, it generally prefers to run to evade predators. The Mountain Quail is known for its elusive nature and shy behavior, making it difficult to observe in its natural habitat.
The Magellanic Cormorant, or Leucocarbo magellanicus, is a medium-sized seabird, predominantly black with a white chest and metallic sheen on its back. It is commonly found along the rocky coasts of South America, particularly in Patagonia. This cormorant is known for its fast, direct flight and its ability to dive deep to catch fish and crustaceans. It nests in colonies on cliffs, using various materials to build its nest. Although generally tolerant of human presence, it can become suspicious if overly disturbed.
The Madagascar Pond-Heron, Ardeola idae, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Ardeidae family. It is primarily found in the wetlands of Madagascar, but also in some regions of East Africa. This bird is notable for its striking white breeding plumage, contrasting with its duller, brownish non-breeding plumage. It has a yellow bill and greenish legs. The Madagascar Pond-Heron feeds mainly on small fish, insects, and crustaceans, which it catches in shallow waters. It is often solitary or in small groups and typically breeds during the rainy season, building its nest in trees or shrubs near water.
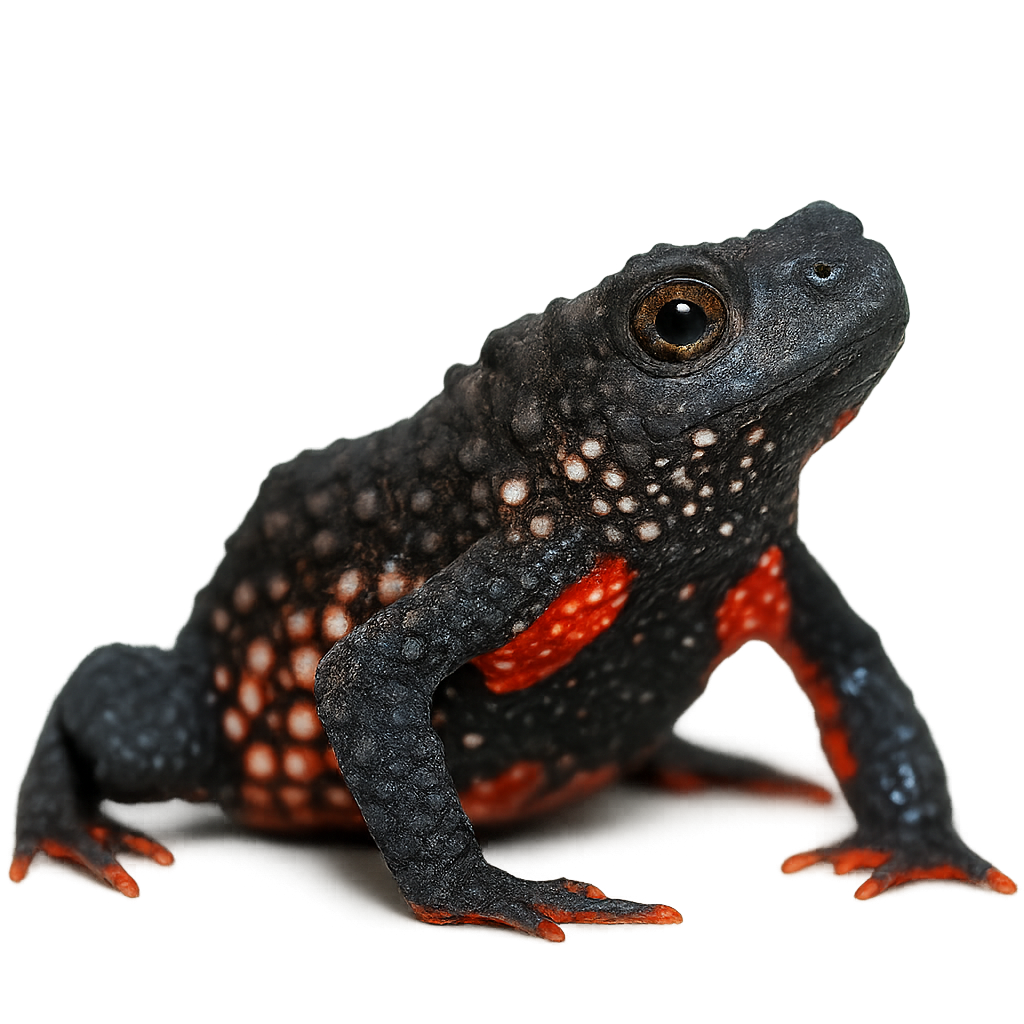
The Melanophryniscus moreirae, or Maldonado Redbelly Toad, is a species of toad endemic to the mountainous regions of Brazil. This small amphibian, typically measuring between 2 and 3 cm, is notable for its rough skin and bright colors, often a mix of black, red, and yellow. These vivid colors serve as a warning signal to potential predators, as the Maldonado Redbelly Toad secretes potent skin toxins. It primarily inhabits high-altitude grasslands and cloud forests, where it feeds on insects and other small invertebrates. Although its habitat is limited, it plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by controlling insect populations.
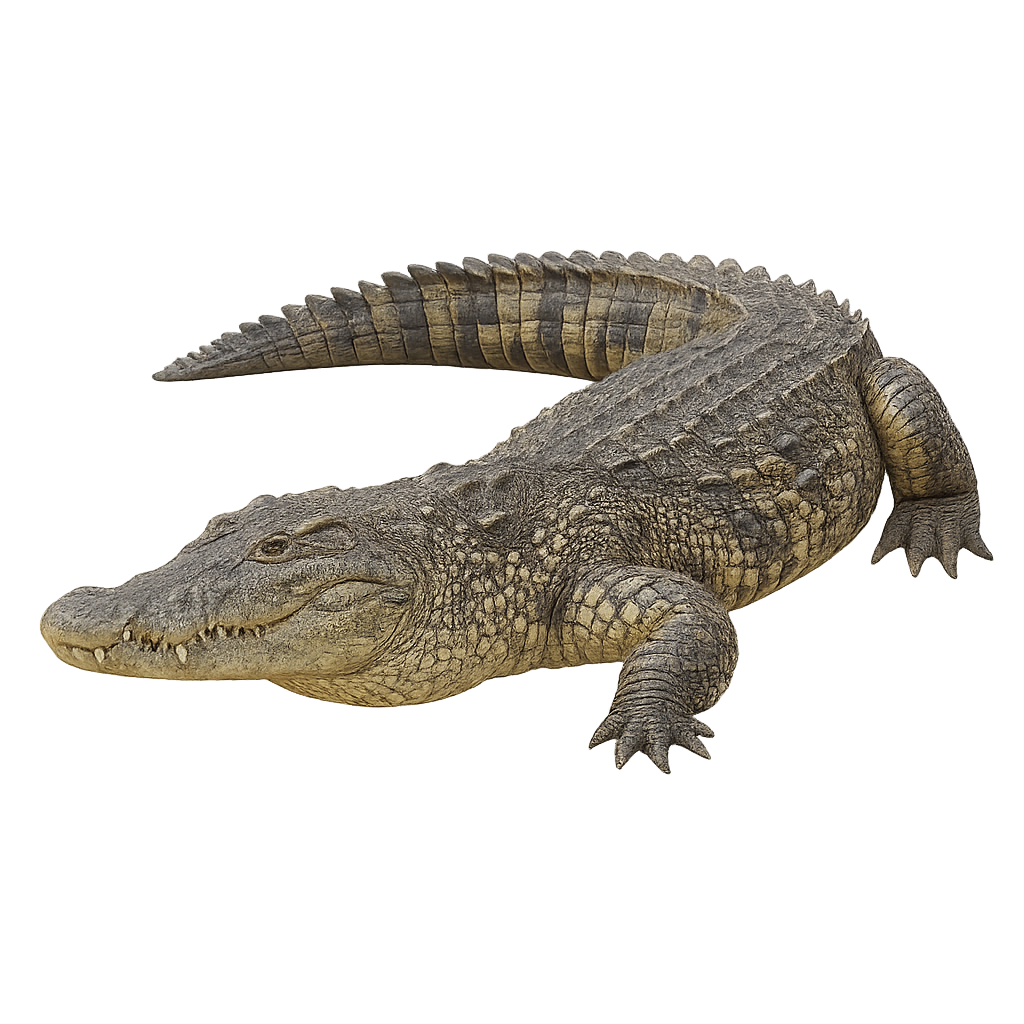
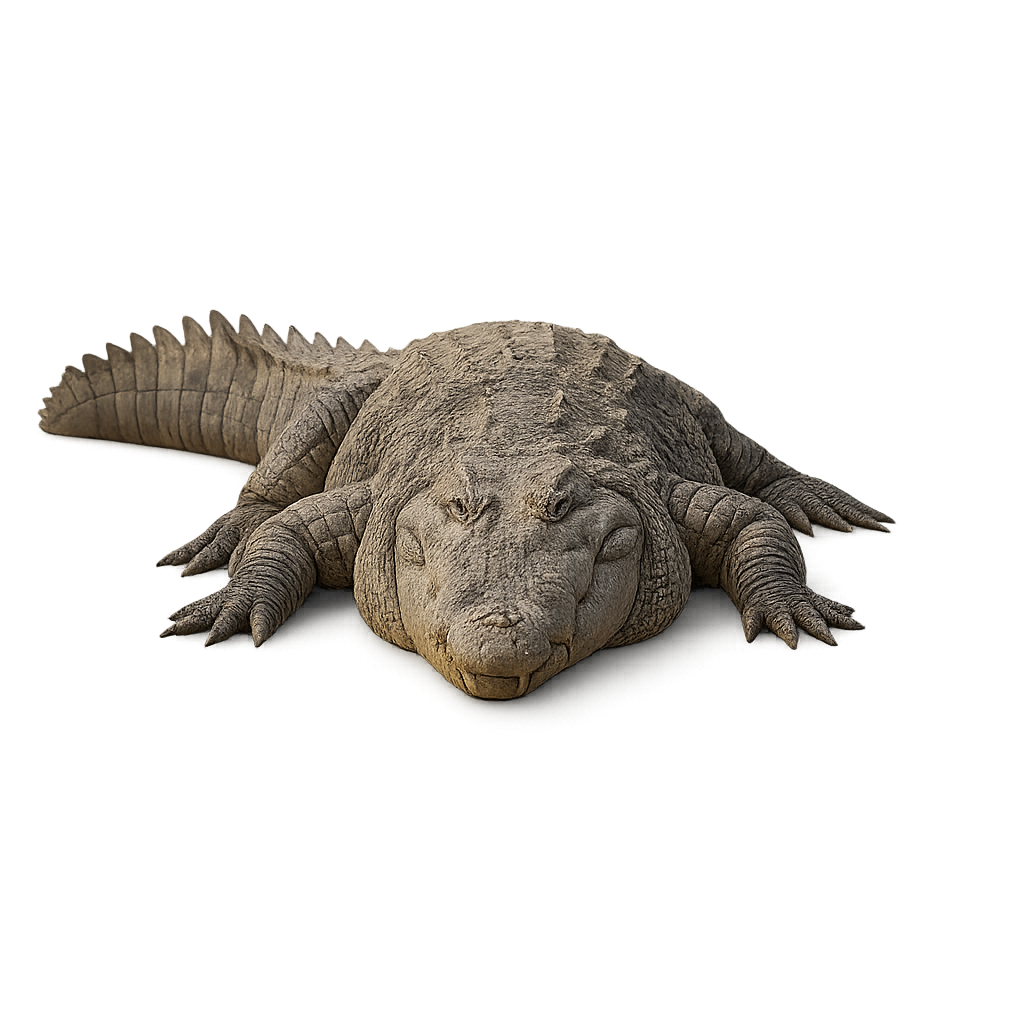
The Morelet's crocodile is a large aquatic reptile in the family Crocodylidae, measuring 2–3 m in length, with a robust body, greenish-brown scaly skin and a broad head. It inhabits coastal lakes, rivers, swamps and freshwater lagoons, occasionally brackish waters, feeding mainly on fish, birds and small mammals. During nesting, the female builds a mound of vegetation debris on the shore and lays 20–45 eggs, which she guards for about 80 days.
The Marsh Crocodile, also known by the scientific name Crocodylus palustris, is a medium-sized reptile that can reach about 4 to 5 meters in length. Its body is typically olive to brown, with darker patterns that allow it to effectively blend into the swamps, rivers, and lakes of its habitat. This crocodile is primarily carnivorous and feeds on fish, birds, and small mammals, but it can also hunt larger animals when they venture too close to the water. The Marsh Crocodile is known for its patience and discretion when hunting, often remaining still for hours before seizing its prey. In terms of distribution, it is found in the Indian subcontinent, particularly in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka. Although primarily sedentary, it can move short distances in search of new habitats. This species is listed as vulnerable due to habitat loss and hunting for its skin. Major threats include the draining of swamps, water pollution, and conflicts with human communities.
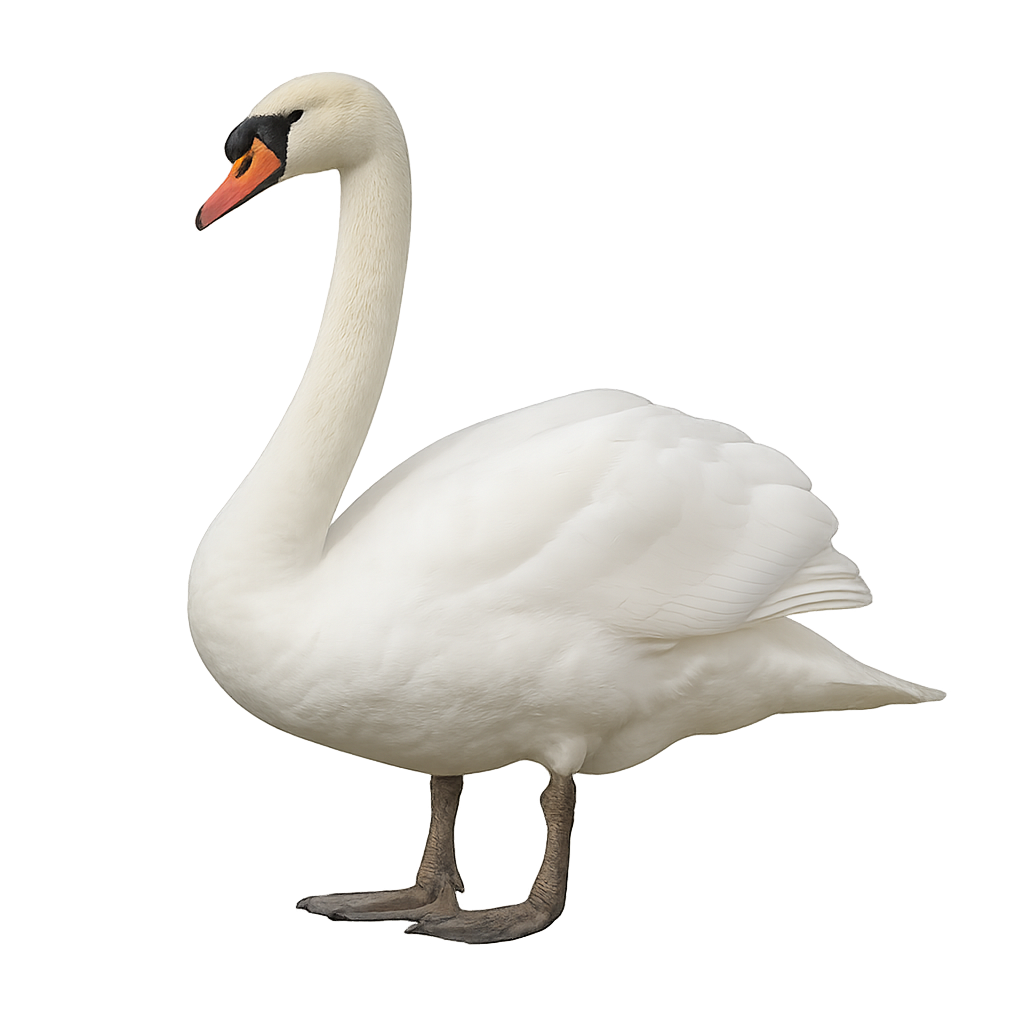
The mute swan is a large waterbird found in lakes, rivers, and ponds across Europe and Asia. It is easily recognized by its bright white plumage, long graceful neck, and the black knob on its beak. This bird is known for its majestic flight and territorial behavior, especially when protecting its territory or young. Mute swans primarily feed on aquatic vegetation but can also eat small invertebrates.
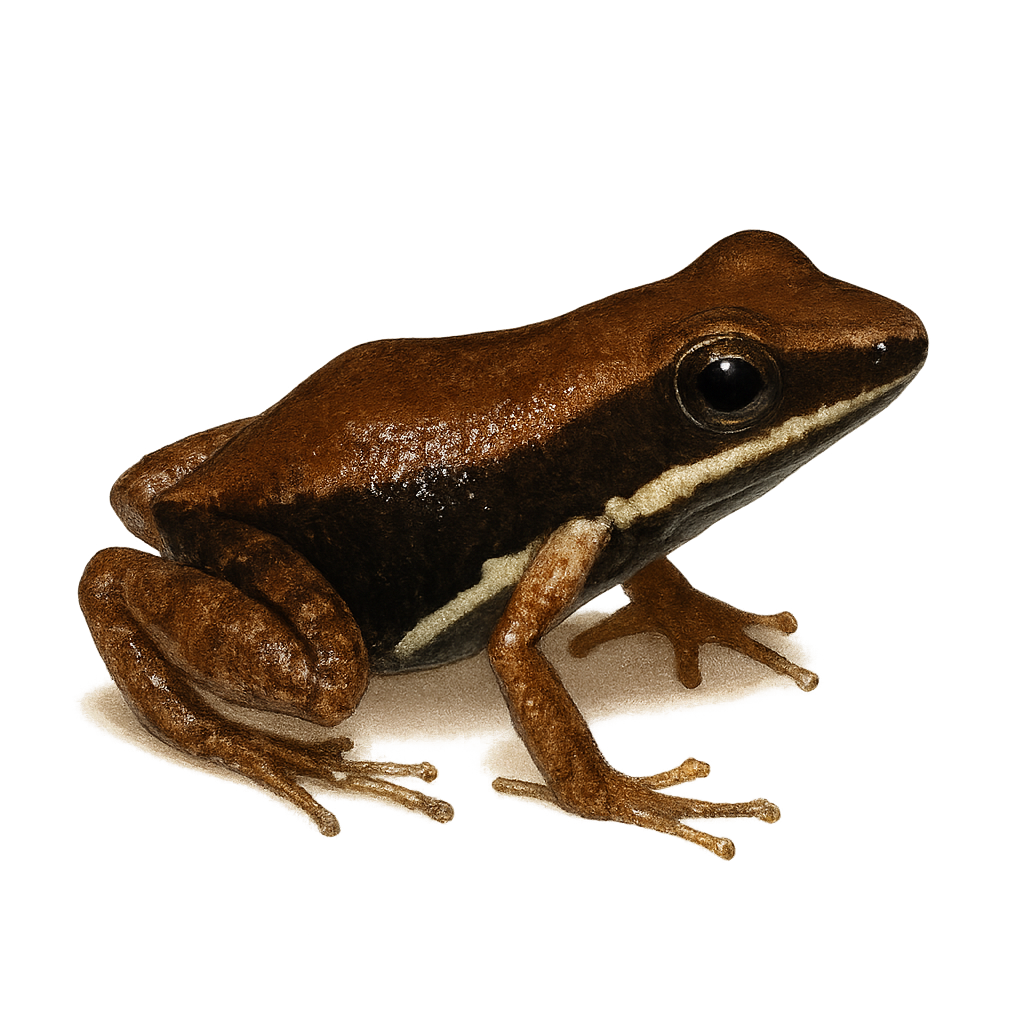
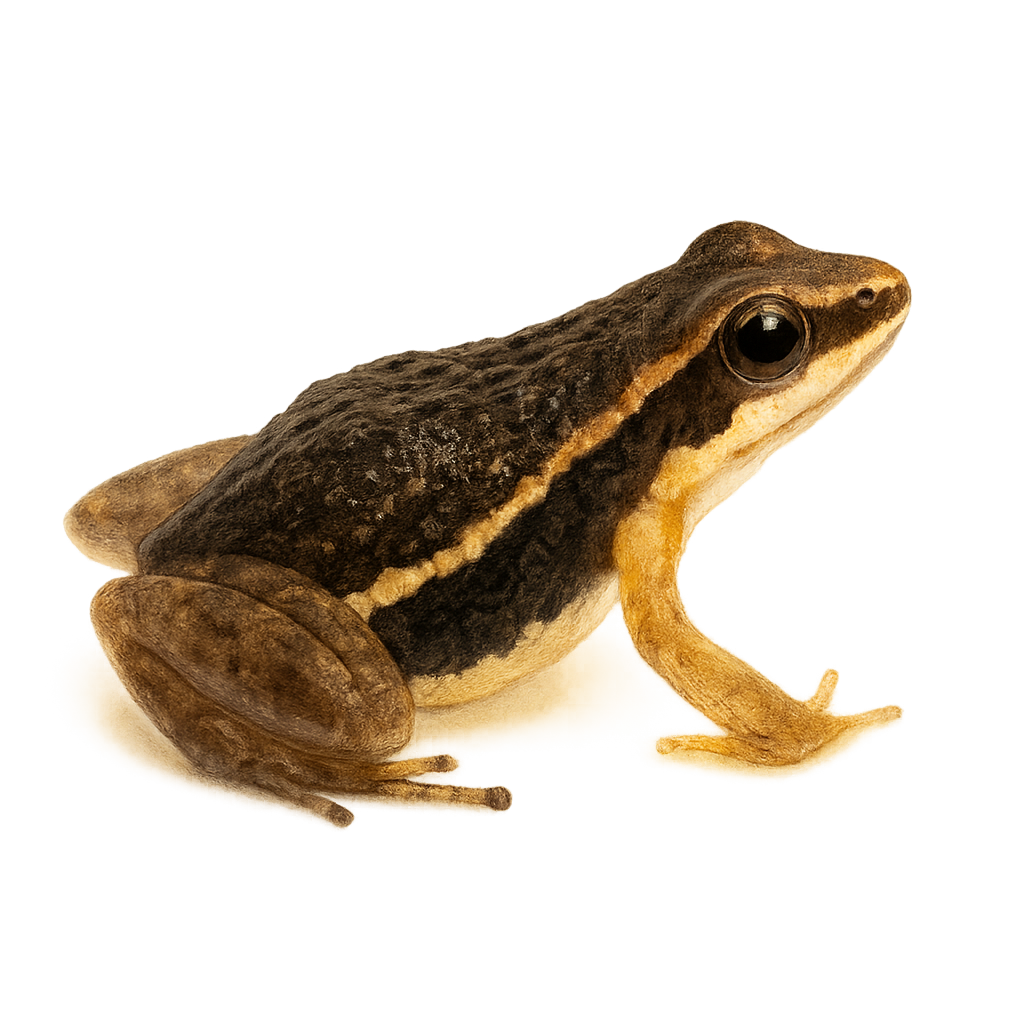
Marbled poison frog is a small, brightly colored frog native to the humid tropical forests of South America, mainly in Ecuador and Colombia. It is easily recognizable by its smooth skin and vivid patterns of red, orange, and black. This species is known for its toxicity, producing potent alkaloids that deter predators. It typically inhabits moist undergrowth, feeding primarily on small insects. Males are territorial and use vocalizations to attract females and ward off rivals. Reproduction occurs in temporary aquatic environments, where tadpoles develop before becoming adult frogs.
The Machalilla Poison Frog is a small, brightly colored frog endemic to the humid forests of Ecuador. It is characterized by its smooth skin and vibrant color patterns, often red and black, which serve as a warning to potential predators of its toxicity. This species is typically found in the undergrowth, where it primarily feeds on small insects. It plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by controlling insect populations. Unfortunately, deforestation and habitat loss threaten its survival. Conservation efforts are essential to protect this unique species and its natural habitat.
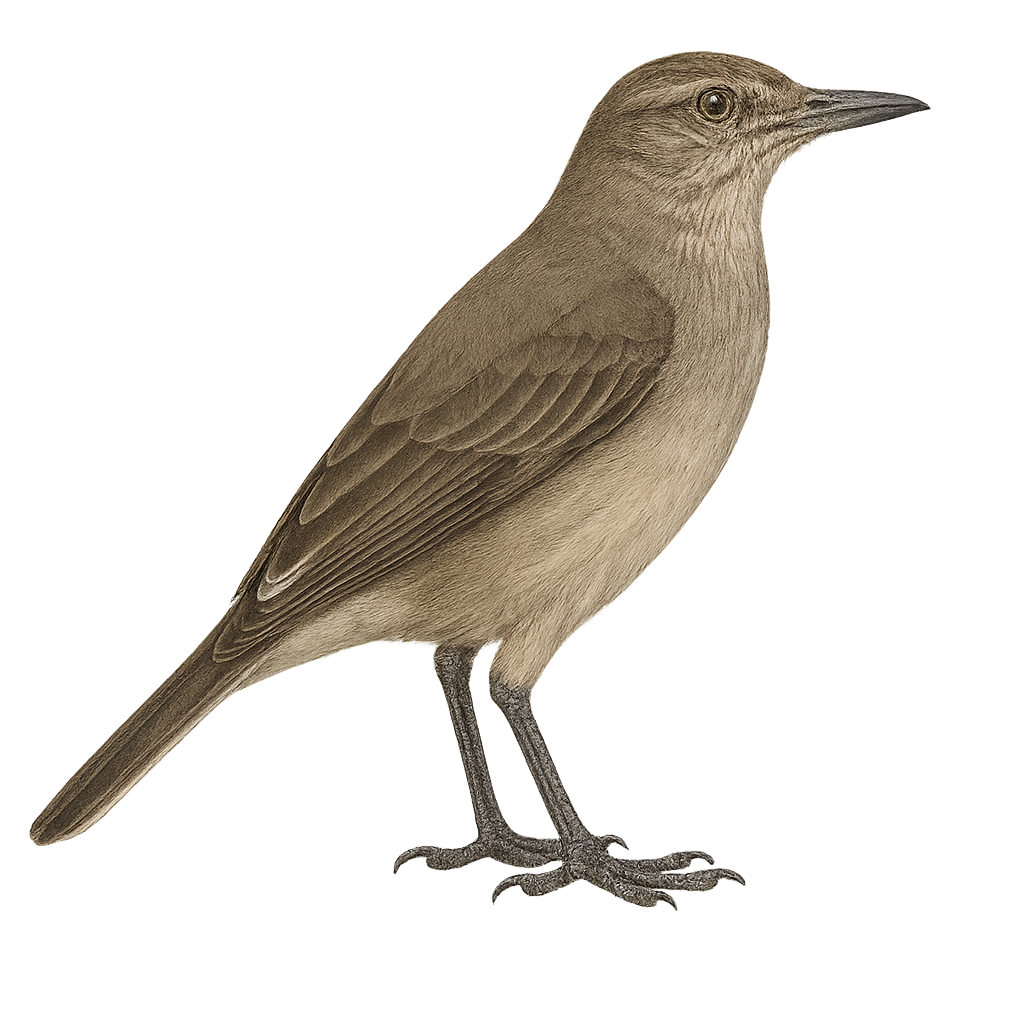
The Mountain Shrike-Tyrant, or Agriornis montanus, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in the mountainous regions of South America, particularly in the Andes. This bird is characterized by its gray-brown plumage, with lighter shades on the belly and slightly darker wings. It has a sturdy beak, adapted to its diet mainly consisting of insects and small invertebrates. The Mountain Shrike-Tyrant is often seen perched on branches or rocks, from where it monitors its territory. Its song is discreet but plays an important role in communication between individuals. Although relatively tolerant of human presence, it prefers less frequented areas.
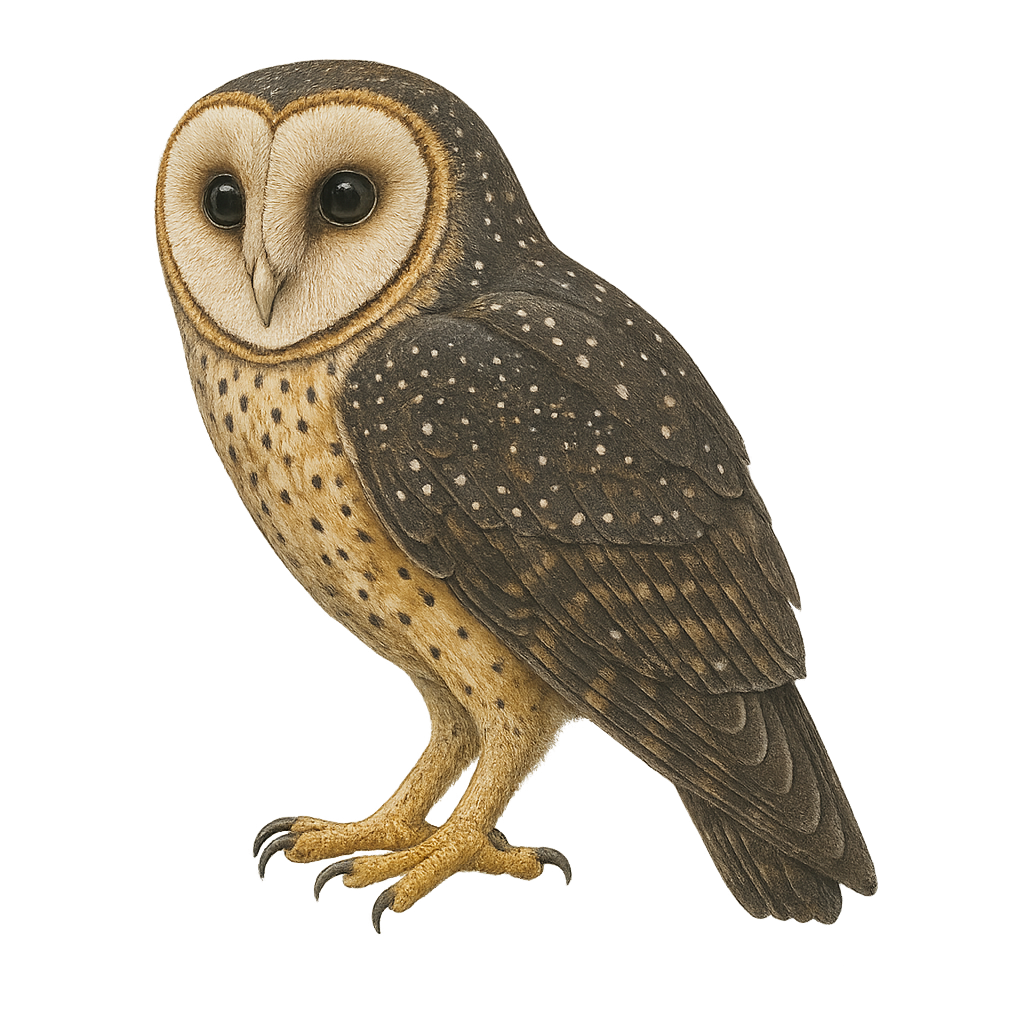
The Masked Owl, or Tyto novaehollandiae, is a medium-sized nocturnal bird of prey native to Australia and some surrounding islands. It is characterized by its heart-shaped facial disc, often white or cream, bordered by a dark edge. Its plumage is generally brown with white spots, allowing it to blend effectively into its natural habitat. It primarily inhabits forests, open woodlands, and agricultural areas but can also be found in urban zones. A nocturnal hunter, it feeds mainly on small mammals, birds, and insects. Although its conservation status is concerning in some areas, it remains relatively widespread.
The Moose is a large deer found primarily in North America, particularly in coniferous forests and wetlands. It can reach up to 2 meters in height at the withers and weigh between 350 and 600 kg. Males are distinguished by their large antler racks, which can reach a span of 1.8 meters. Their coat is typically dark brown to black, with a lighter belly and a small mane of hair under the neck. The Moose is a herbivore, feeding mainly on leaves, branches, bark, fruits, and aquatic plants. It is an excellent swimmer and spends a great deal of its time feeding in lakes and rivers. While its population remains stable, it is threatened by habitat loss and hunting.
The Mountain Elaenia is a small passerine bird from the Tyrannidae family, primarily found in the montane forests of Central America. It is recognizable by its olive-gray plumage and lighter chest. This bird is often seen foraging for insects and fruits in the undergrowth. It is particularly active during the day, searching for food in dense foliage. Although generally suspicious, it can be observed from a reasonable distance without much difficulty. Humid forests and wooded areas at high altitudes are its preferred habitats.
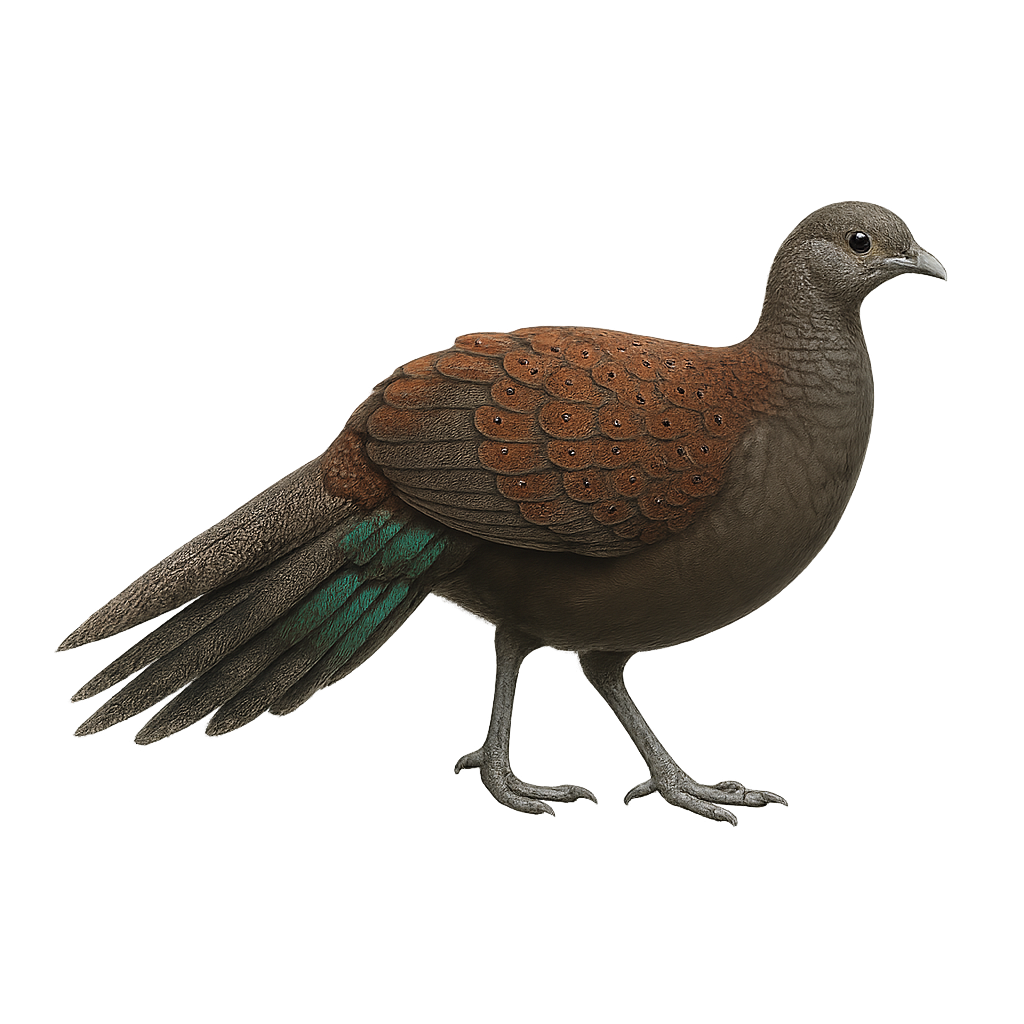
The Mountain Peacock-Pheasant, or Polyplectron inopinatum, is a fascinating bird native to the mountainous forests of Malaysia. This medium-sized pheasant is notable for its brown plumage adorned with iridescent ocelli patterns, giving it a majestic appearance. Males display a long tail which they fan out during courtship displays to attract females. These birds are generally solitary or live in small family groups. Their diet mainly consists of insects, small invertebrates, and seeds. Although their habitat is threatened by deforestation, they are still found in several nature reserves. Their discreet behavior and ability to blend into their environment make them challenging yet rewarding to observe for bird enthusiasts.
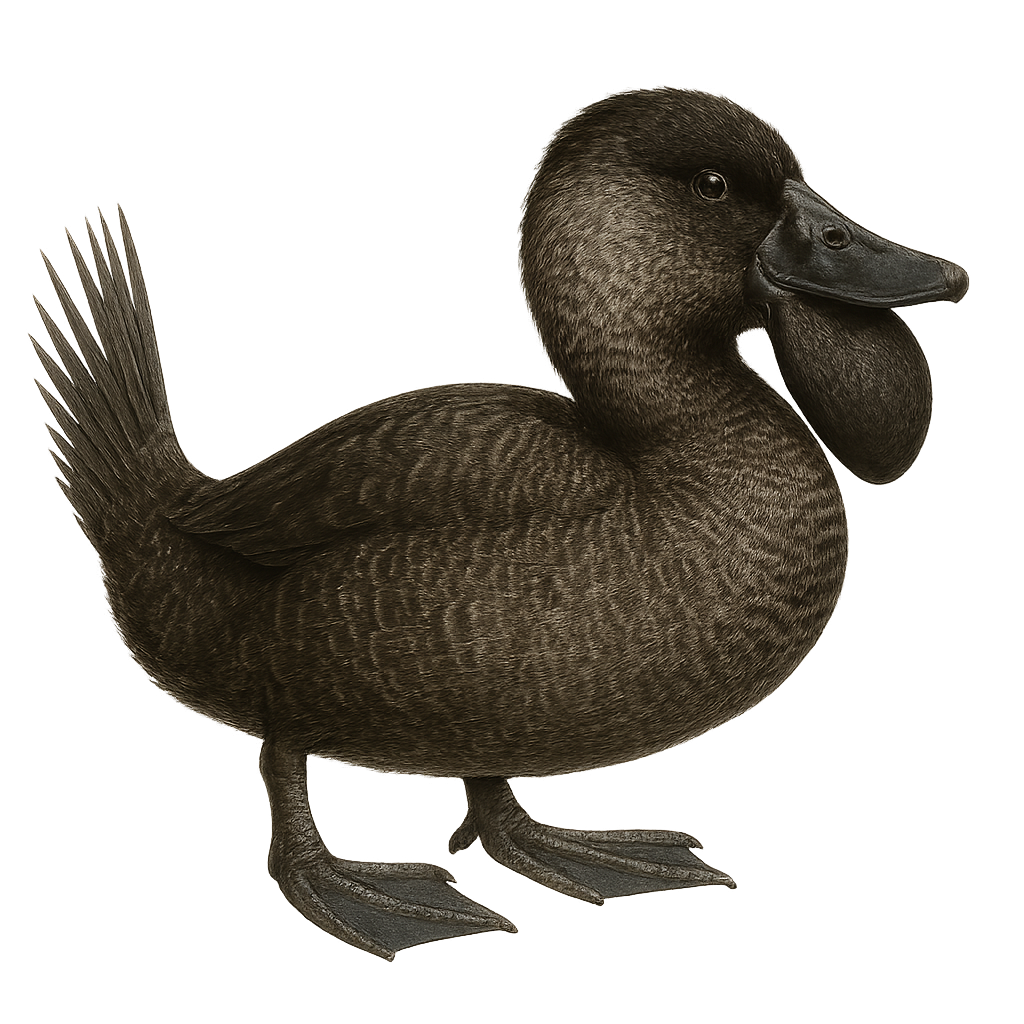
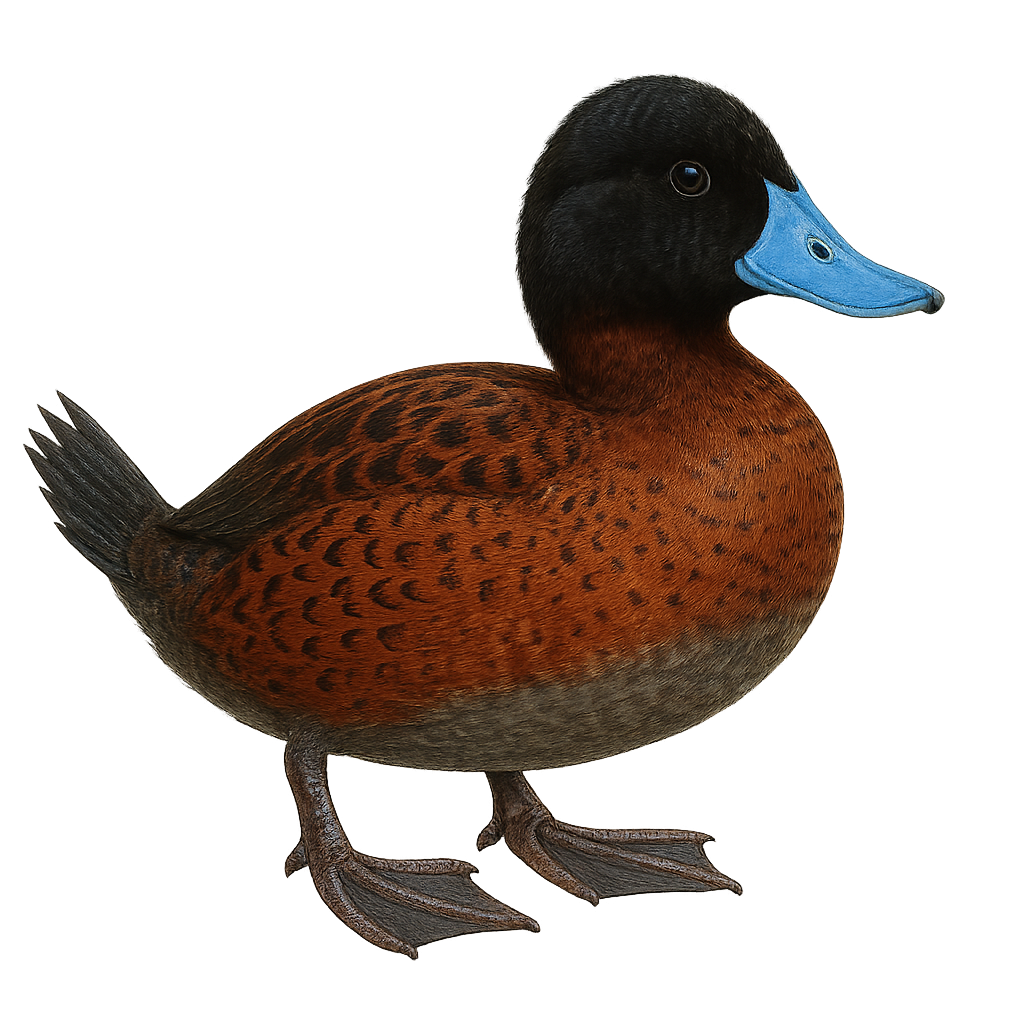
The Musk Duck, Biziura lobata, is a diving duck native to Australia, known for its broad bill and stiff tail. Males display a lobed flap under the bill during courtship displays. This duck prefers large freshwater bodies like lakes and swamps, feeding mainly on mollusks, crustaceans, and aquatic insects. Although often solitary, it can be seen in small groups. Its ability to dive deeply and stay underwater for extended periods makes it an effective hunter. The species is currently classified as Least Concern by the IUCN but is sensitive to environmental changes and habitat degradation.
The Masked Duck is a small diving duck known for its unique plumage and elusive behavior. Males display a striking rufous plumage with a black head and a distinctive white mask, while females and juveniles are duller with brownish patterns. This species prefers dense aquatic habitats such as marshes and ponds with abundant vegetation. It is primarily nocturnal, feeding on aquatic plants, insects, and small invertebrates. Although widely distributed in the Caribbean and parts of Central and South America, it remains difficult to spot due to its shy nature and habit of hiding in dense vegetation.
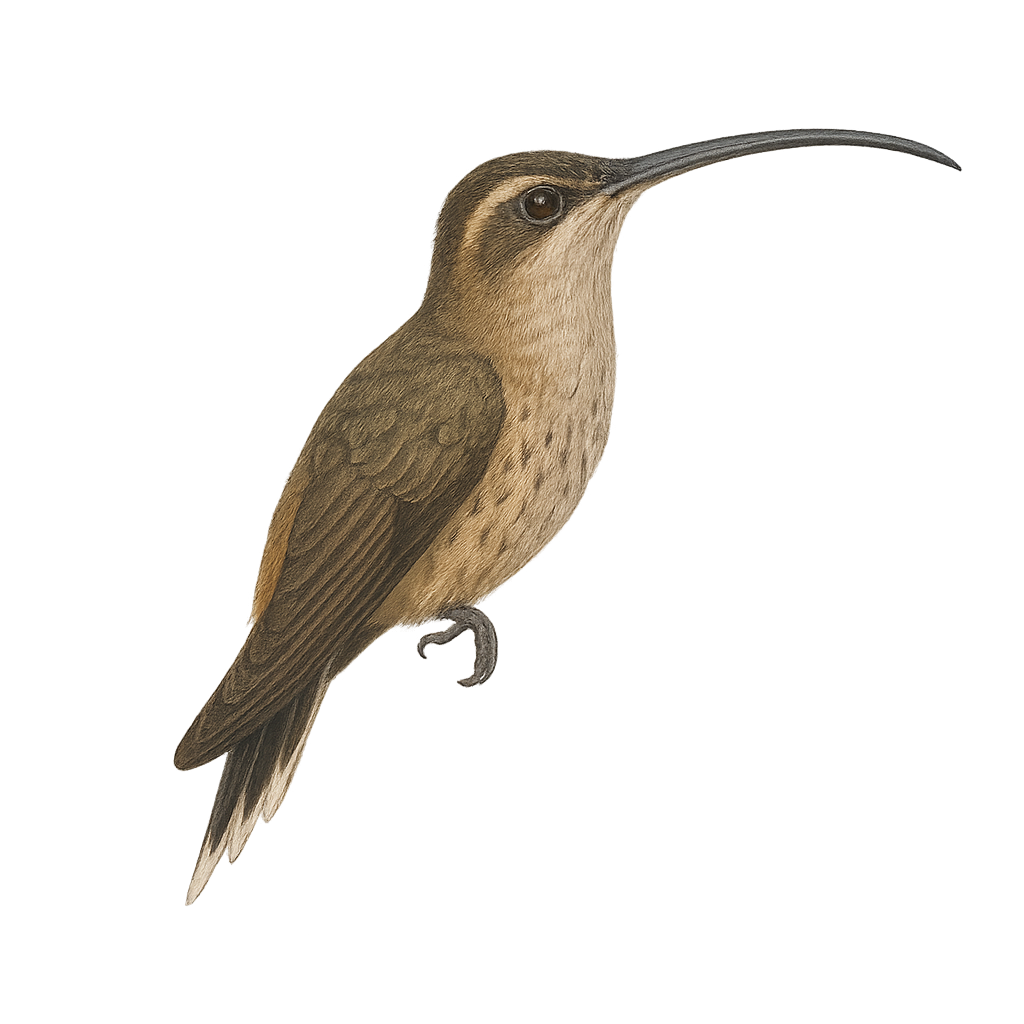
The Mexican Hermit, or Phaethornis mexicanus, is a fascinating hummingbird primarily inhabiting the tropical rainforests of Mexico and Central America. This small bird is distinguished by its brown-green plumage, long curved beak, and spatula-shaped tail. It is often seen darting swiftly from flower to flower, using its specialized beak to extract nectar. The Mexican Hermit plays a crucial role in the pollination of local plants. Although mostly solitary, it can sometimes be seen in small groups during the breeding season. Its song is a soft hum, often heard before it is seen. Despite its delicate appearance, this bird is resilient and adapts well to its environment, although it is threatened by deforestation.
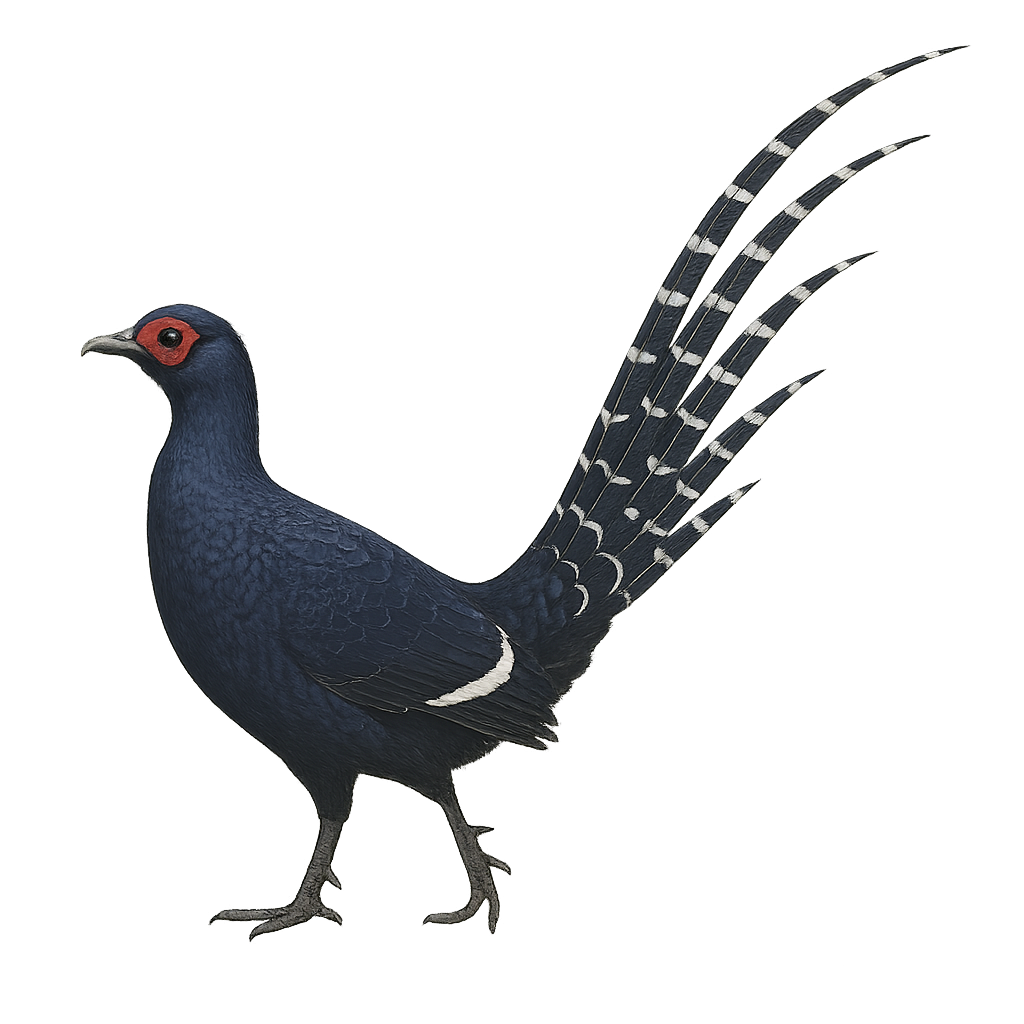
The Mikado Pheasant (Syrmaticus mikado) is an elegant and rare bird, endemic to the mountains of Taiwan. This pheasant is distinguished by its dark, glossy plumage with metallic blue-green sheen. Males feature long tail feathers, while females are more subdued with mottled brown plumage. They primarily inhabit mountain forests, feeding on seeds, fruits, and insects. The Mikado Pheasant is a culturally significant symbol in Taiwan, often associated with beauty and grace. However, it is threatened by habitat loss and illegal hunting, making it a protected species.
The Fossa fossana, also known as the Malagasy civet, is a small carnivorous mammal endemic to Madagascar. It is characterized by its grey-brown fur with black spots, which provides excellent camouflage in its natural habitat. Measuring about 50 cm in length, with a tail almost as long as its body, the Malagasy civet is primarily nocturnal. It inhabits the island's humid forests, feeding on small animals, insects, and fruits. Although often confused with the fossa, another Malagasy carnivore, the Malagasy civet belongs to a different family. Its population is threatened by deforestation and hunting, leading to its classification as near threatened by the IUCN.
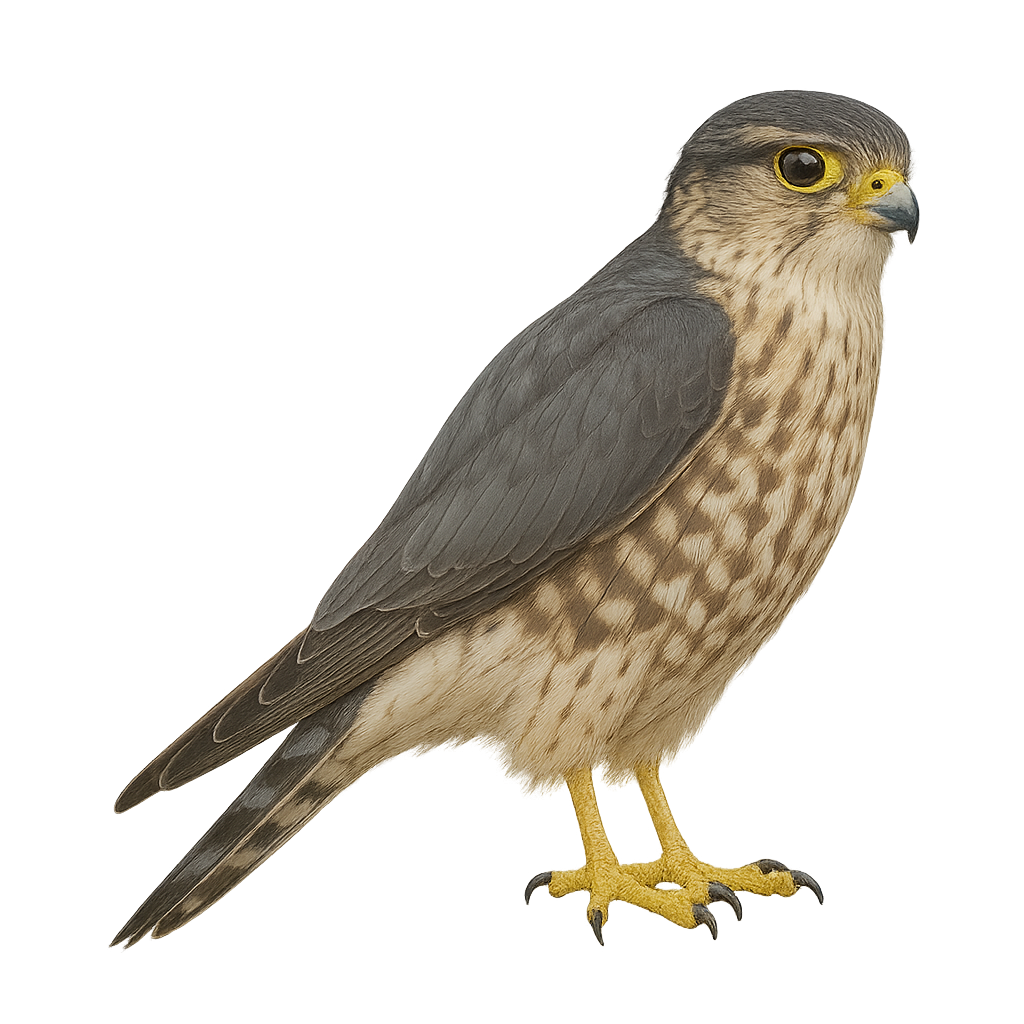
The Merlin is a small raptor, one of the fastest birds, easily recognizable by its compact plumage and vibrant colors. It measures between 28 and 34 cm in length, with a wingspan of 60 to 80 cm, and weighs between 150 and 250 g. The male has a blue-gray plumage on its back, with black wings and a head marked with black bands, while the female is generally larger and duller, with brownish hues. The Merlin is found primarily in Europe, Asia, and North America, where it inhabits a variety of habitats, from open areas such as meadows and agricultural zones to forests. This bird primarily feeds on smaller birds, small mammals, and insects. It hunts in flight, using its impressive speed to capture its prey. It is particularly known for its fast and agile aerial maneuvers. While the species is not endangered, it faces threats such as habitat loss, human disturbance, and the reduction of prey populations.
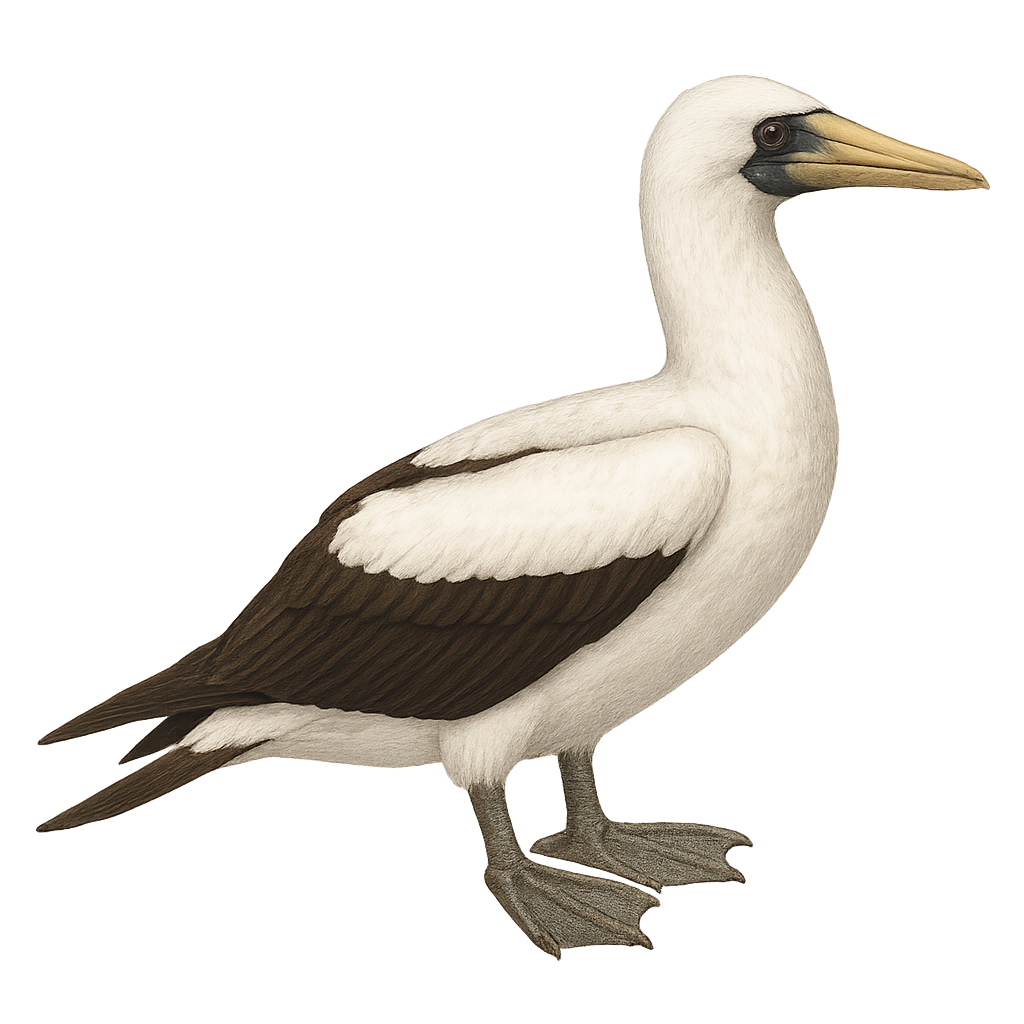
The Sula dactylatra, commonly known as the Masked Booby, is a large seabird recognized for its striking white plumage and distinctive black facial mask. Its long, slender wings allow it to glide over vast ocean expanses. It primarily feeds on fish and squid, which it catches by diving from the air. Often seen in colonies on tropical and subtropical islands, it nests on the ground. The Masked Booby is an adept diver, capable of plunging to impressive depths to catch its prey. Despite its name, it is its relatives, the Blue-footed Boobies, that have the colorful feet.