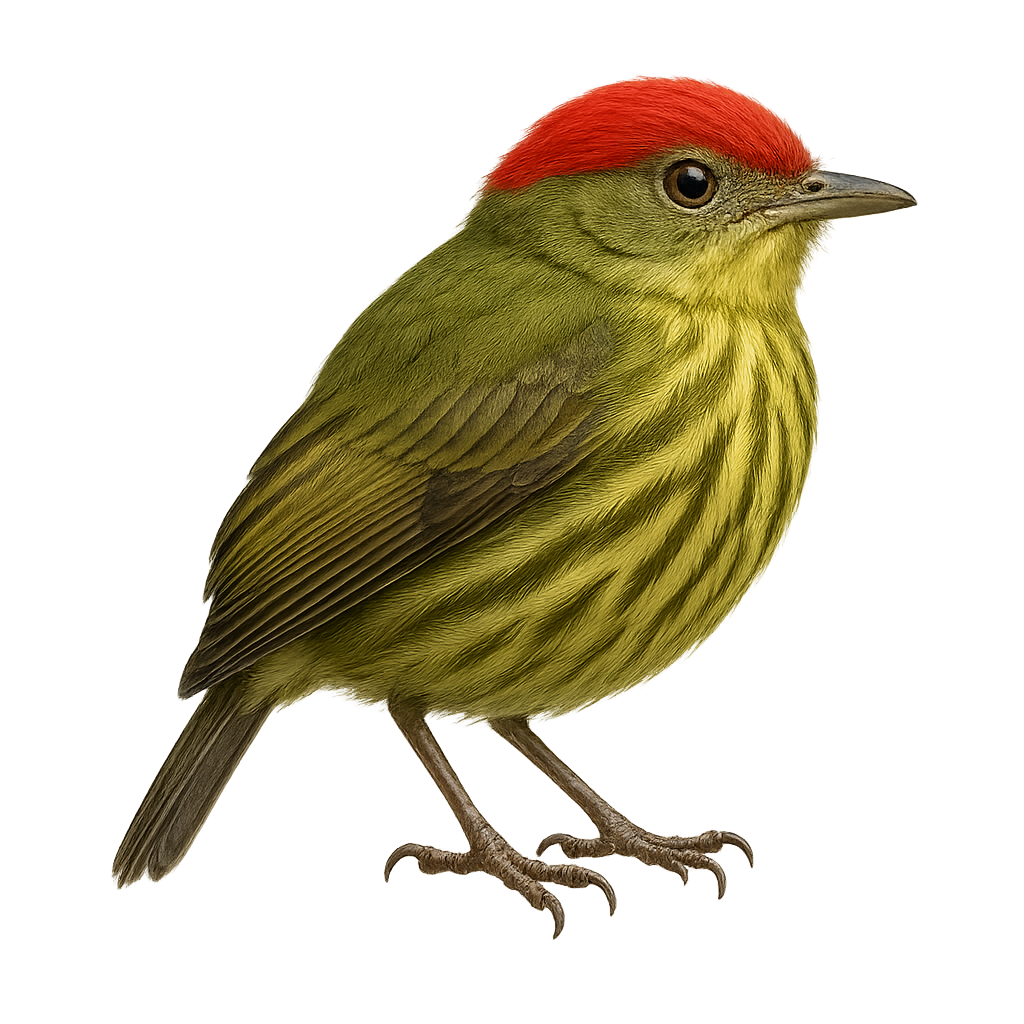
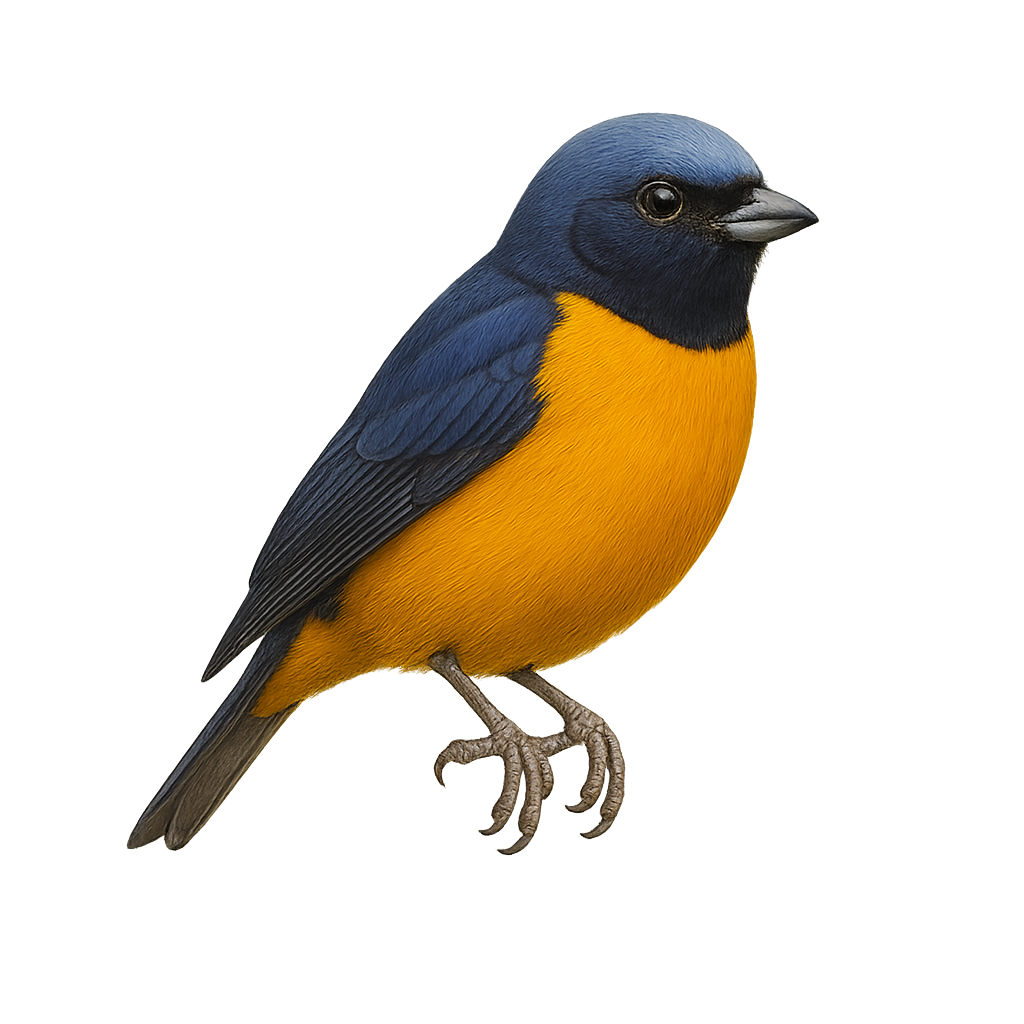
The Eckelberry's Manakin is a small, colorful bird belonging to the Pipridae family. It is primarily found in the lowland humid forests of Peru. This manakin is distinguished by its vibrant plumage, with shades of green, yellow, and red, allowing it to blend into its dense environment. Males are particularly known for their complex courtship displays, which include unique dances and vocalizations to attract females. These birds are generally solitary, except during the breeding season. They primarily feed on fruits and insects, thus contributing to seed dispersal in their habitat. Their song is often an indicator of their presence in the dense forest.
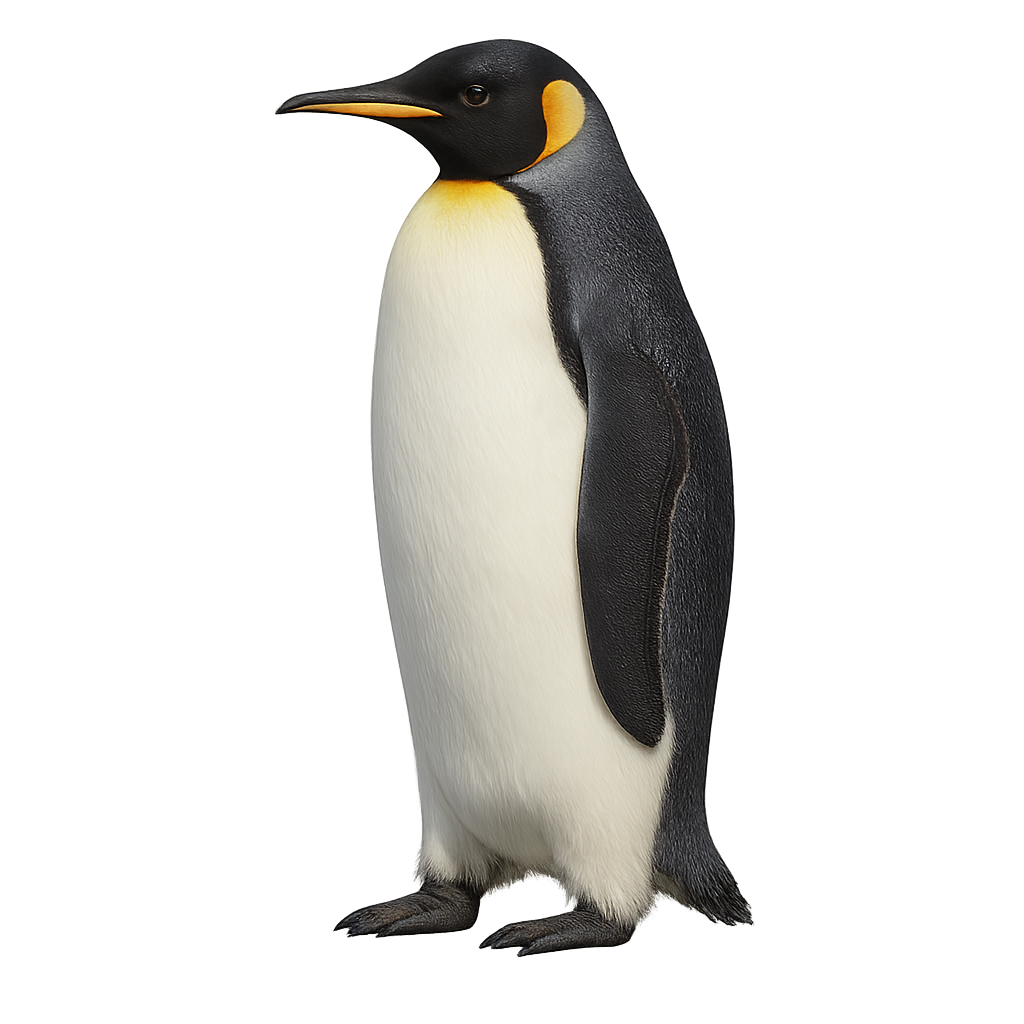
The emperor penguin is the largest penguin species, standing 1.1–1.3 m tall and weighing 22–45 kg, with striking black-and-white plumage, a pale yellow breast and orange patches at the bill’s base. Endemic to Antarctica, it breeds on sea ice during the austral winter, forming vast colonies to shelter from cold and marine predators. Following courtship displays in April–May, the female lays a single egg which she transfers to the male for incubation before returning to sea to feed.
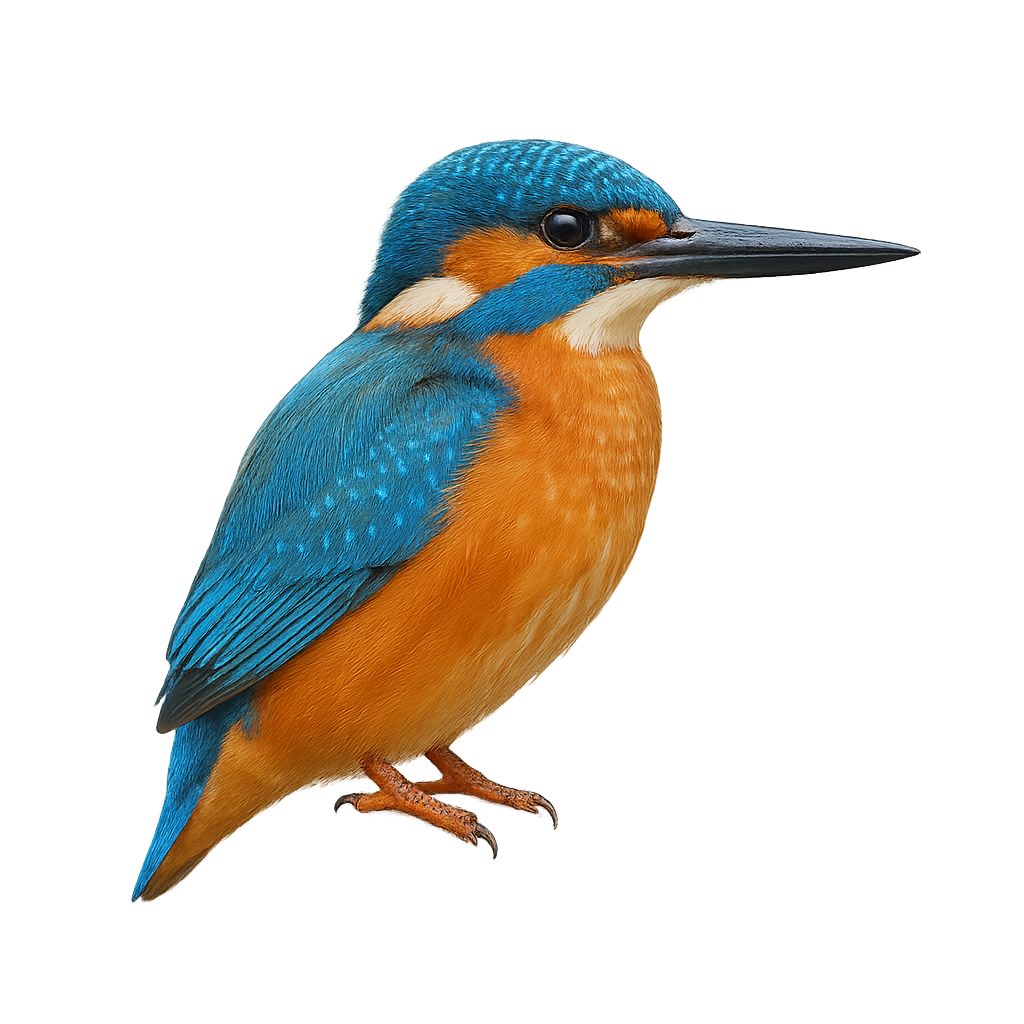
The European Kingfisher is a small aquatic bird, easily recognized by its vivid plumage and bright colors. It measures about 17 to 19 cm in length and weighs between 30 and 40 g. Its back is a brilliant metallic blue, while its belly is a bright orange. Its bill is long, straight, and pointed, perfectly suited for catching fish and aquatic insects. This kingfisher primarily lives along rivers, lakes, and canals in Europe, where it perches on branches or rocks near the water. When hunting, it dives quickly in a headfirst plunge to capture its prey, often using its excellent vision to locate fish underwater. The European Kingfisher is a solitary bird, defending its territory by emitting a sharp call. While it is relatively common in many parts of Europe, it can be threatened by water pollution and habitat destruction.
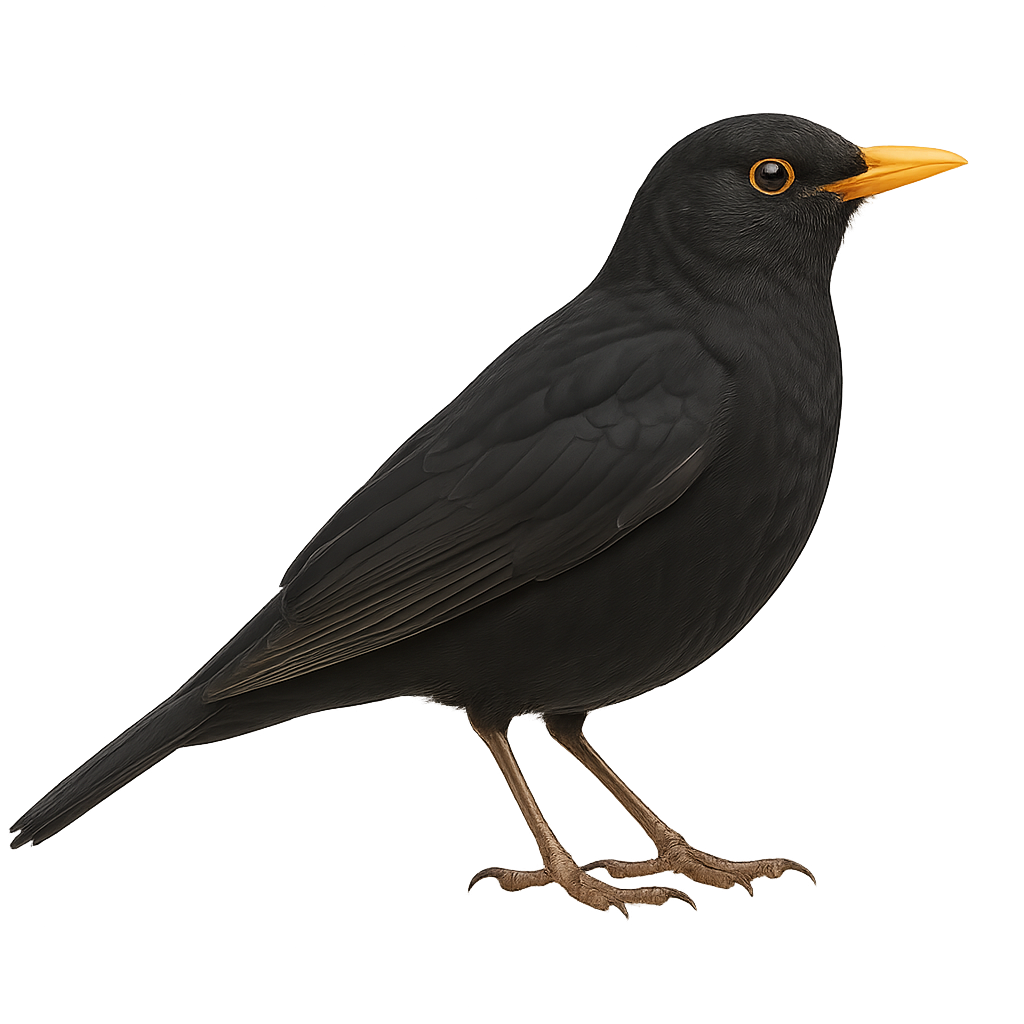
The European blackbird is a very common passerine bird found throughout Europe, Asia Minor, and North Africa. It is easily recognized by its glossy black plumage and bright yellow beak. This passerine primarily feeds on earthworms, insects, and fruit. Although it is often seen in gardens and urban parks, it remains a relatively discreet bird. It is also highly regarded for its melodious song, especially in spring.
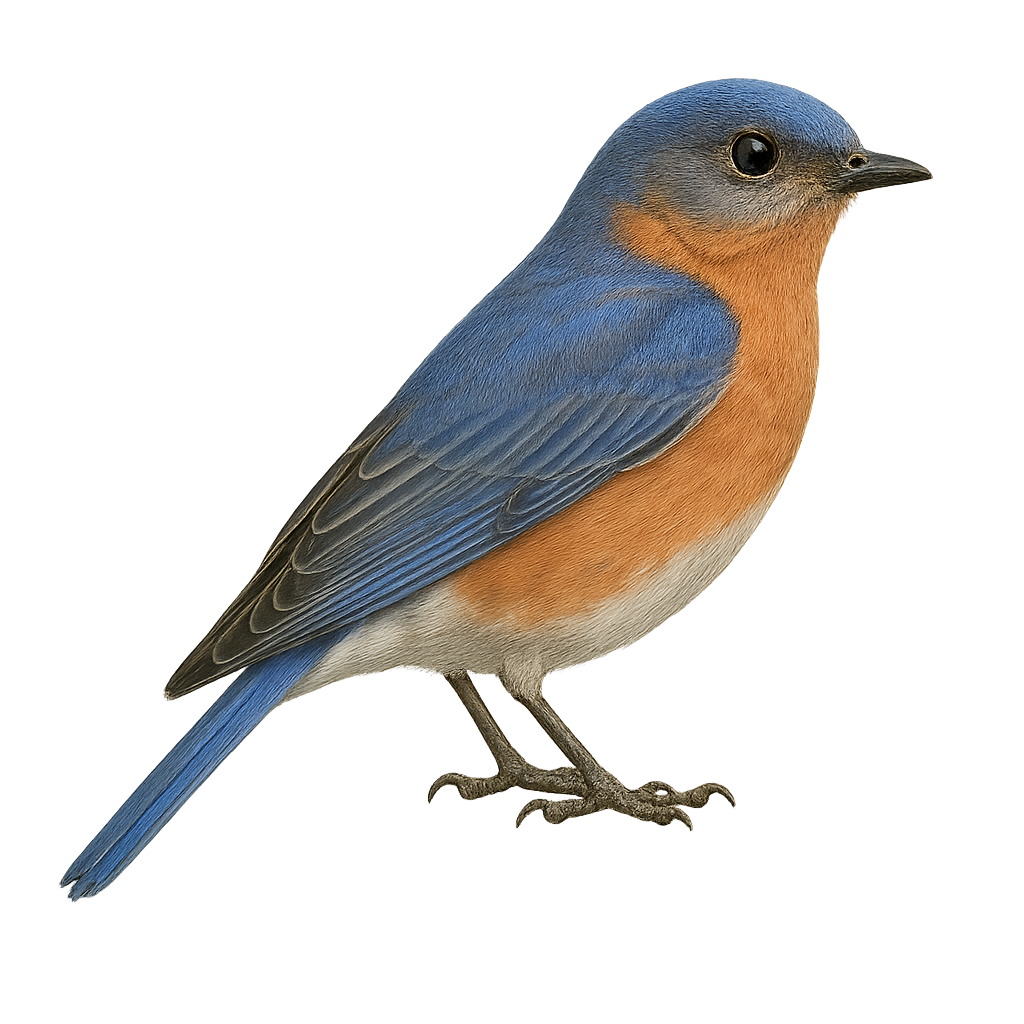
The Eastern Bluebird, or Sialia sialis, is a small songbird belonging to the Turdidae family. It is easily recognizable by its bright blue plumage on the back and wings, contrasting with a reddish-orange chest and white belly. Males display more vibrant colors than females, who have duller plumage. This bird primarily feeds on insects but also consumes berries, especially in winter. It inhabits open fields, orchards, and sparse woodlands. The Eastern Bluebird is known for its melodious song and its ability to adapt to artificial nest boxes, which has helped stabilize its populations after a decline due to habitat loss and competition with introduced species.
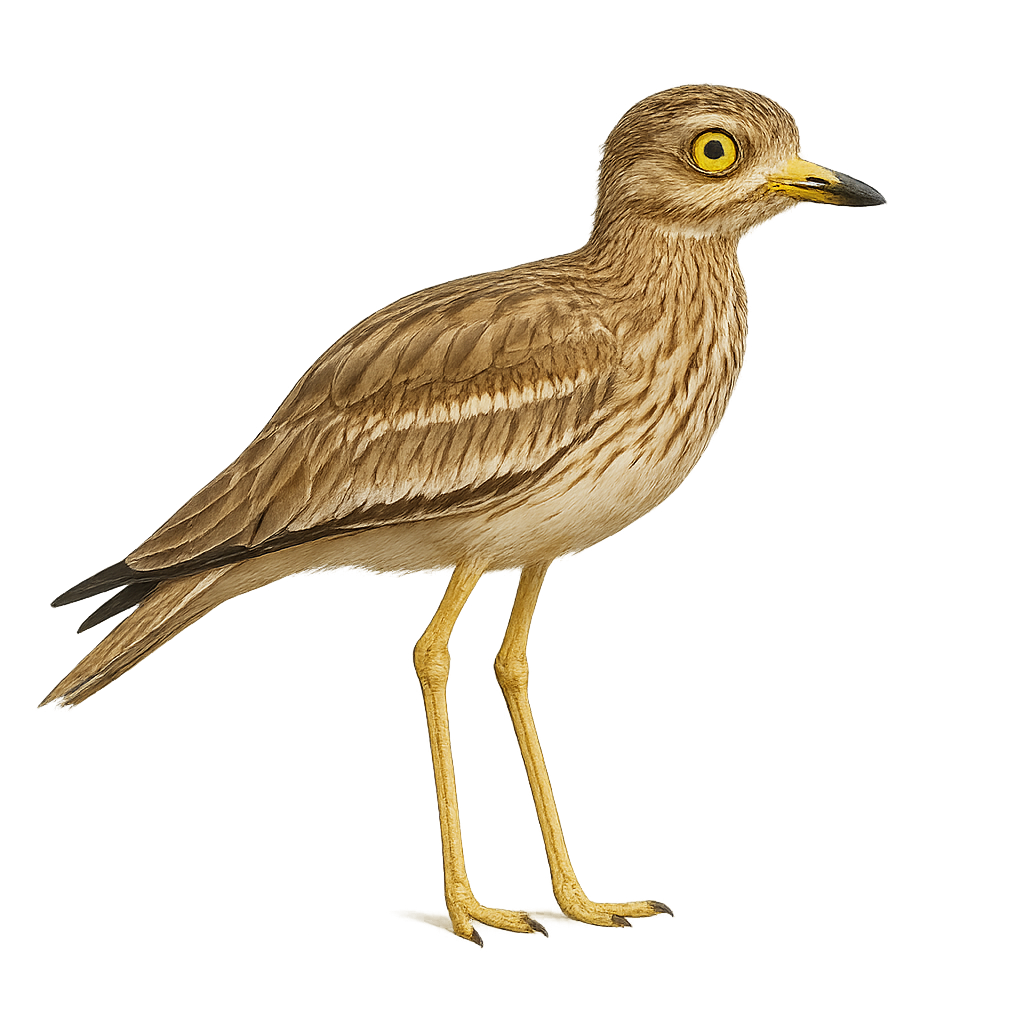
The Stone-curlew is a large, ground-dwelling bird primarily found in open and arid regions of Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa. It measures about 40 to 45 cm in height and weighs between 350 and 500 g. What distinguishes the Stone-curlew is its cryptic plumage, generally brown-gray in color, allowing it to blend effectively among vegetation or rocks. It has large yellow eyes and a distinctive call, which is often heard during the night, hence its name. This bird primarily feeds on insects, worms, and small invertebrates found on the ground. The Stone-curlew is mostly active at dusk and at night, feeding slowly while scanning its surroundings. While not in immediate danger, it faces threats from habitat loss, intensive agriculture, and human disturbance.
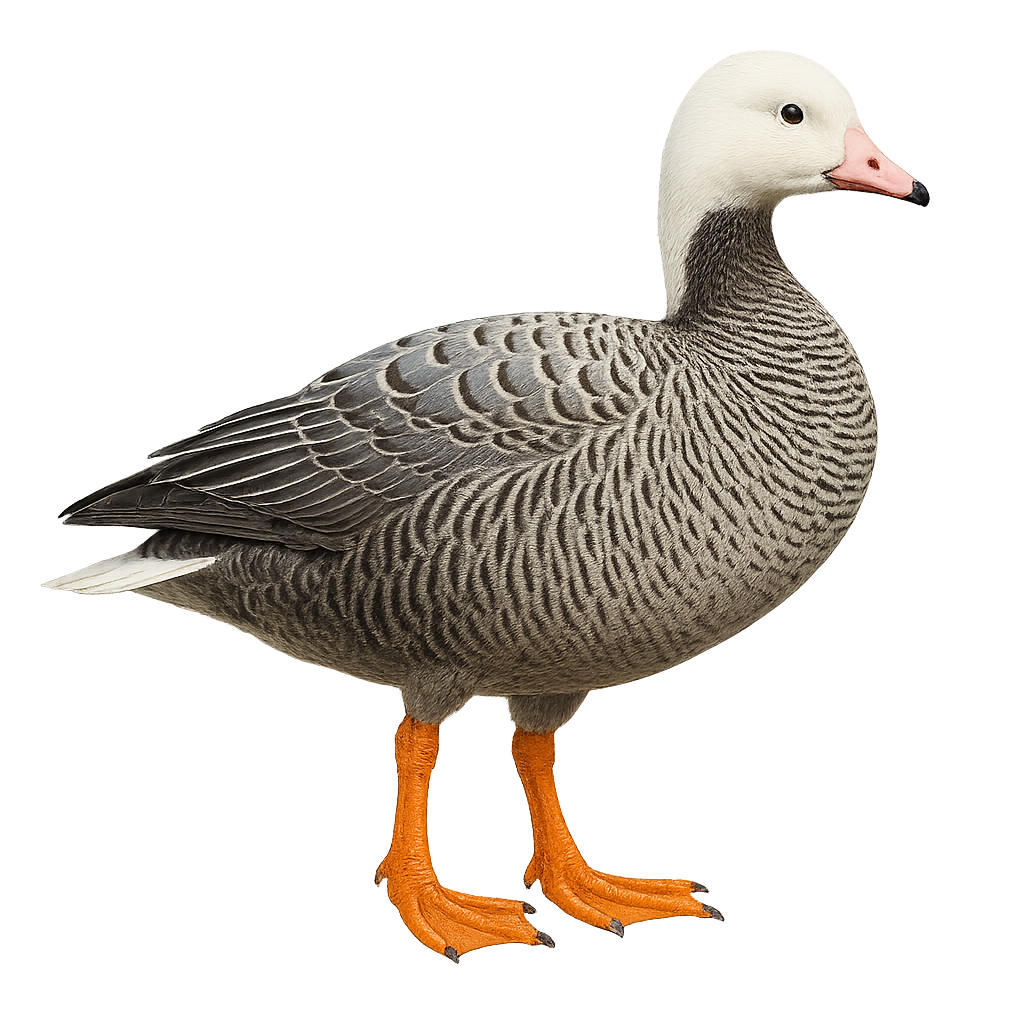
The Emperor Goose, Anser canagicus, is a medium-sized waterfowl species known for its bluish-gray plumage and distinctive white head. It features a pink bill and bright orange legs. Primarily found in Alaska and Siberia, it inhabits coastal areas and estuaries. The Emperor Goose is a migratory species that moves south for the winter. Often seen in groups, it feeds on aquatic plants, seeds, and small invertebrates. Although its conservation status is concerning, it is protected by international laws. Its beauty and social behavior make it a favored subject for birdwatchers.
The Elegant Euphonia, or Chlorophonia elegantissima, is a small, colorful bird from the Fringillidae family, primarily found in the tropical and subtropical forests of Central America. It is easily recognizable by its vibrant plumage, featuring a bright blue head, yellow belly, and olive-green back. Both males and females have similar colors, although females are slightly duller. These birds are often seen in pairs or small groups, feeding mainly on fruits and berries. Their melodious and varied song is a distinctive feature of their behavior, often used to mark their territory or attract a mate. Although they are relatively tolerant of human presence, they prefer dense wooded areas where they can hide among the foliage.
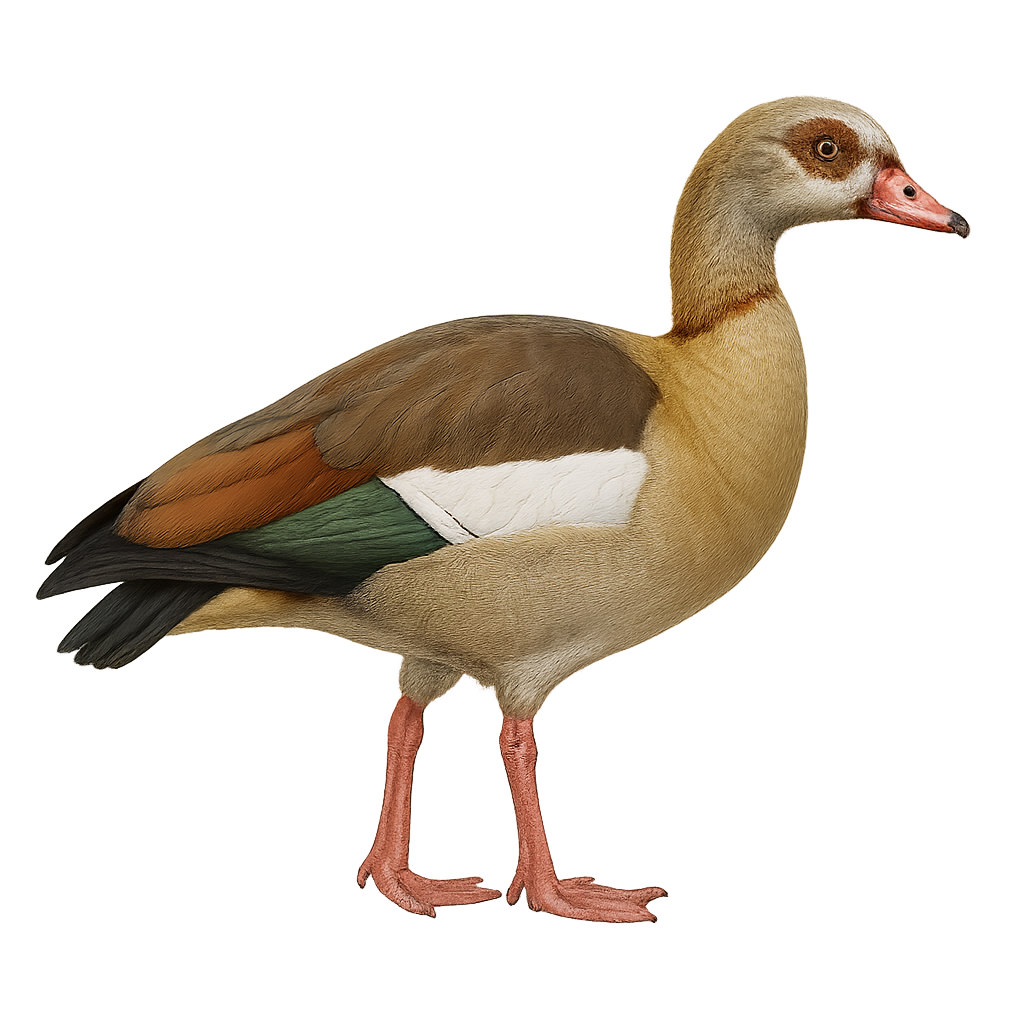
The Egyptian Goose, Alopochen aegyptiaca, is a medium-sized waterbird known for its distinctive brown, white, and black plumage, with red markings around the eyes. Native to sub-Saharan Africa, it has been introduced to various regions in Europe. It prefers habitats near freshwater, such as lakes, rivers, and marshes. This bird is often seen in pairs or small family groups. Although primarily herbivorous, it also feeds on insects and small invertebrates. The Egyptian Goose is known for its territorial behavior, especially during the breeding season. It is capable of adapting to various environments, which explains its growing presence in urban areas.
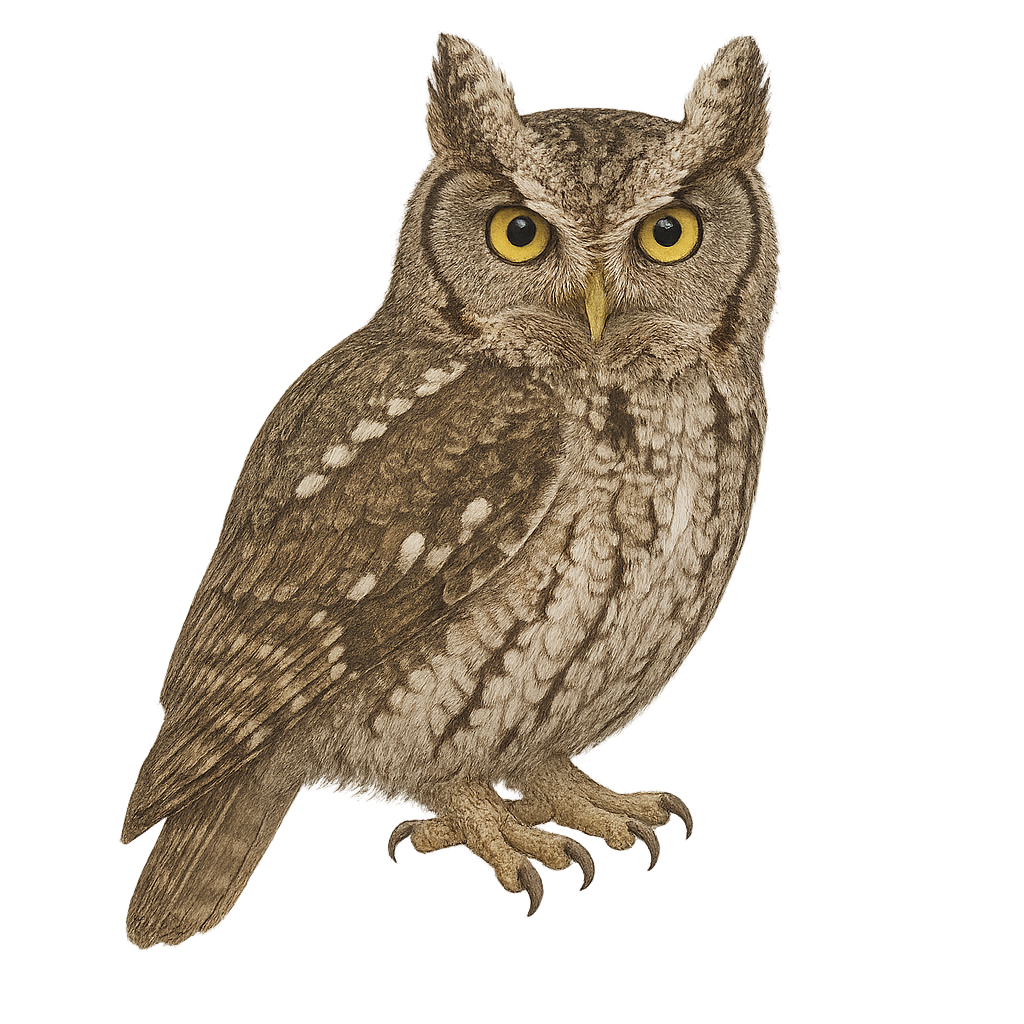
The Eastern Screech Owl, Megascops asio, is a small owl native to eastern North America. It inhabits forests, parks, and suburban areas, and is known for its excellent camouflage, with plumage ranging from gray to reddish-brown. Measuring about 16 to 25 cm in length with a wingspan of 46 to 61 cm, it primarily feeds on insects, small mammals, and occasionally small birds. Its call, a soft, monotone trill, is often heard at dusk and during the night.
The Three-toed Woodpecker is a small bird from the woodpecker family, primarily found in coniferous forests of Europe and Asia. It measures about 20 cm in length, with a wingspan of 40 to 45 cm, and weighs between 50 and 70 g. Its plumage is primarily black and white, with a distinctive yellow patch on the top of its head, and white streaks on its wings. What distinguishes the Three-toed Woodpecker is the presence of three toes on each foot, which allows it to climb with great agility. It primarily feeds on insect larvae, which it extracts from the bark of trees using its strong beak. The Three-toed Woodpecker lives in old forests and dense wooded areas, and although it is not currently threatened, it is vulnerable to habitat loss and human disturbance.
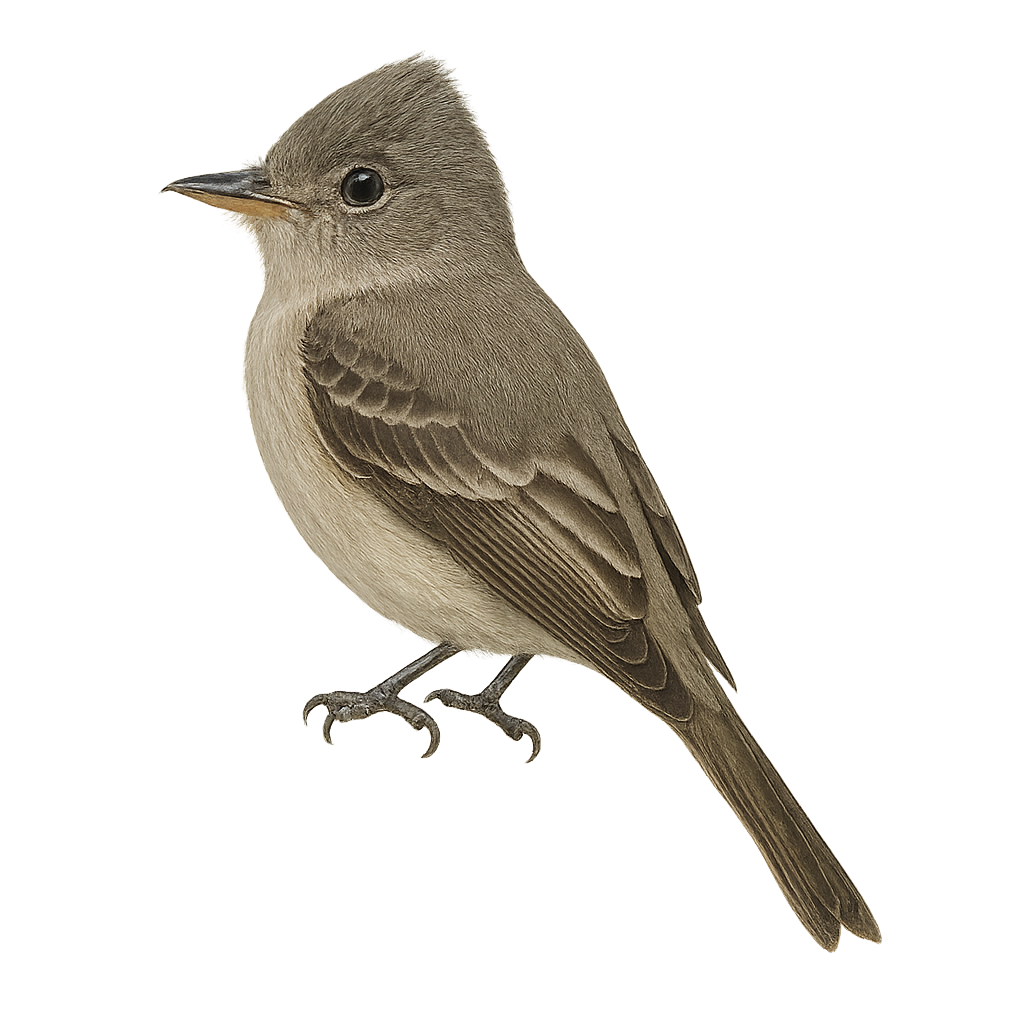
The Eastern Wood-Pewee, or Contopus virens, is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in the deciduous and mixed forests of North America, where it is recognized for its melodious and repetitive song. Modest in size, it features an olive-gray plumage on its back and lighter on its belly, with wings slightly barred with white. This migratory bird winters in Central and South America. It mainly feeds on insects, which it catches in flight with its skilled aerial acrobatics. The Eastern Wood-Pewee is often solitary and vigorously defends its territory during the breeding season. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it is currently classified as Least Concern by the IUCN.
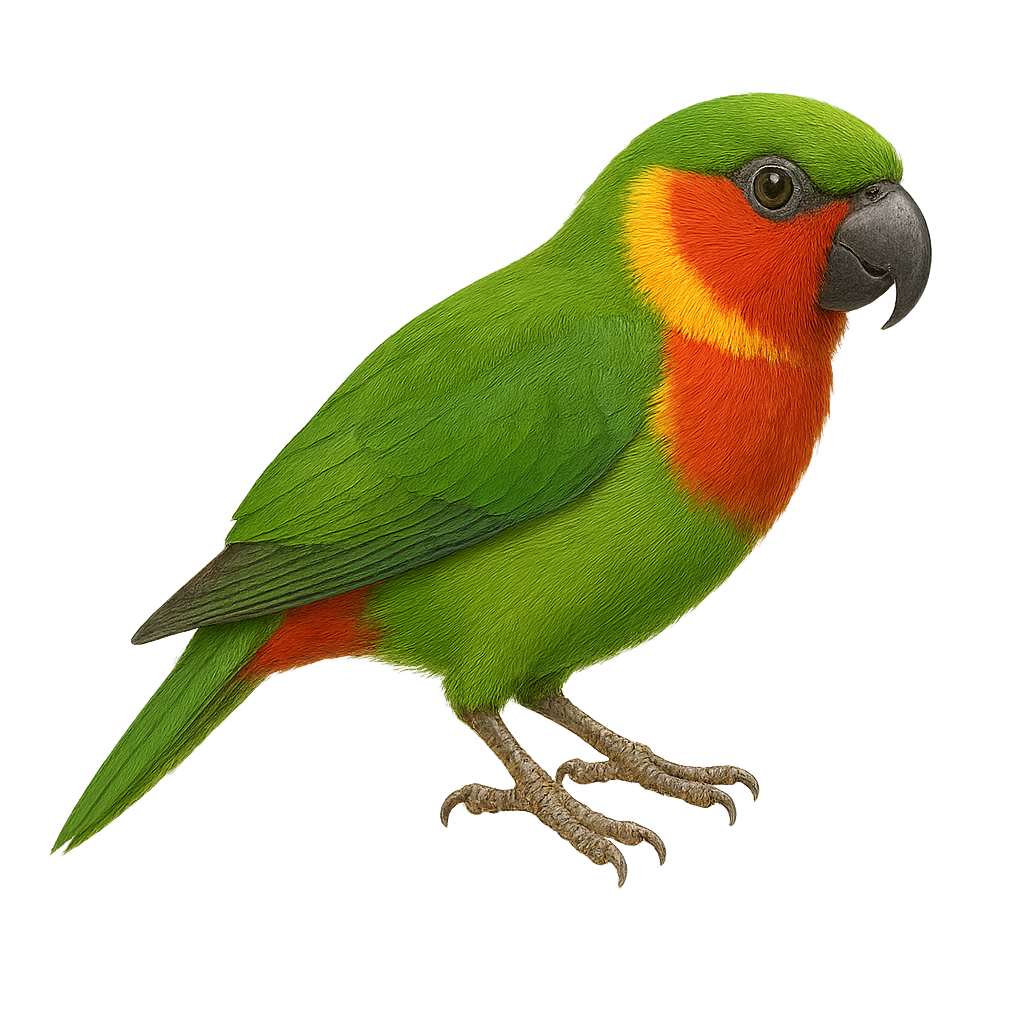
The Edwards's Fig Parrot is a medium-sized parrot species endemic to New Guinea. It is characterized by its bright green plumage, with shades of blue and red around the head and neck. This parrot primarily inhabits tropical rainforests, where it feeds on fruits, seeds, and flowers. It is often seen in small groups or pairs, moving nimbly among the branches. Although its habitat is relatively stable, it is sometimes threatened by deforestation. Its song is melodious, consisting of whistles and chirps.
The European Polecat is a small carnivore found primarily in Europe, inhabiting a variety of environments such as forests, meadows, and agricultural areas. It measures about 45 to 60 cm in length, with a tail of 20 to 30 cm, and weighs between 0.8 and 1.5 kg. Its fur is generally light brown or gray, with lighter underparts and a distinctive black mark on its face, surrounding its eyes. The European Polecat is a nocturnal and opportunistic predator, primarily feeding on small mammals, birds, eggs, as well as fruits and insects. While it is often perceived as a pest by farmers, it plays an important role in regulating populations of small animals. Its population is generally stable, but it can be threatened by habitat loss and road collisions.
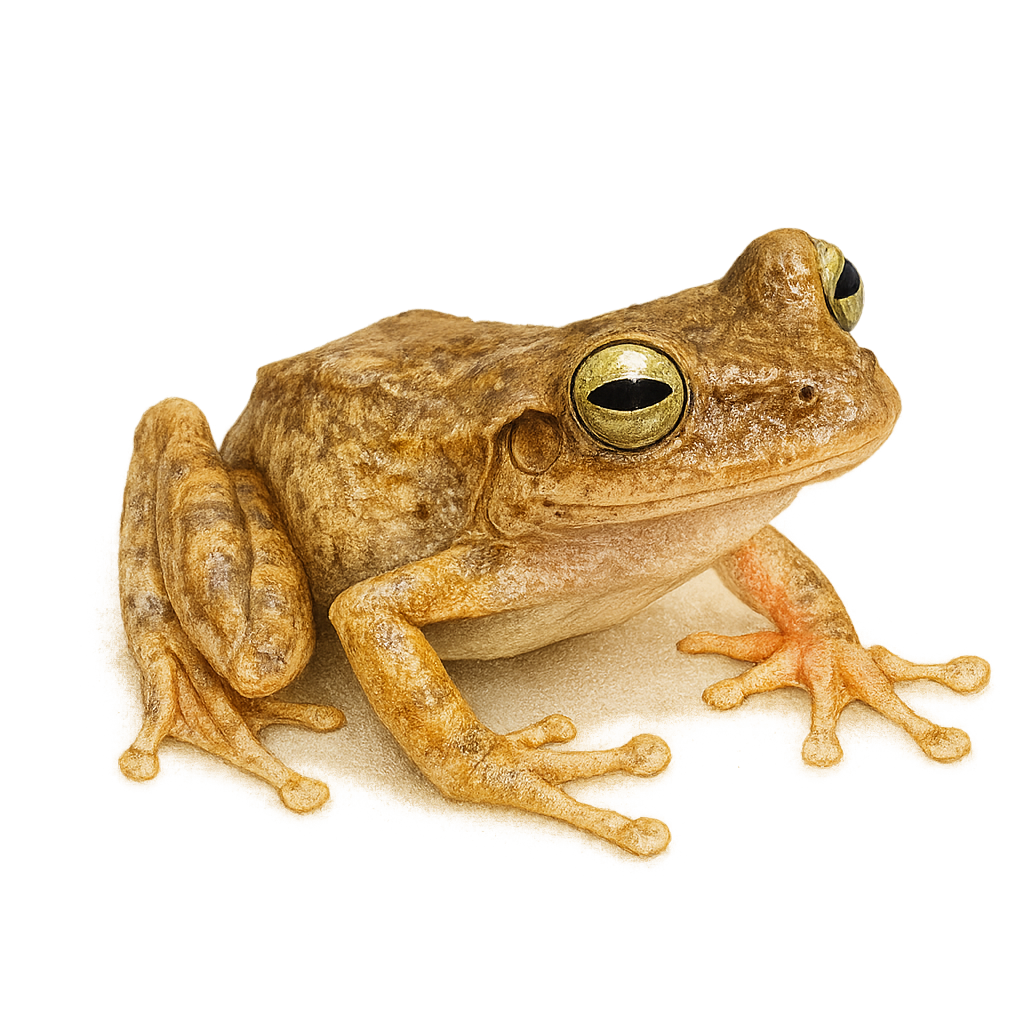
The Emerald‑eyed treefrog, scientifically known as Hypsiboas crepitans, is a tree-dwelling frog native to tropical regions of Central and South America. It is characterized by its smooth skin and green coloration, which provides excellent camouflage among leaves. Typically measuring between 3 and 5 cm, this frog has adhesive pads on its toes, aiding in climbing. It is primarily nocturnal, feeding on insects. Its distinctive call, a crepitating sound, is often heard during humid nights, especially in the rainy season.
The Boana pulchella, commonly known as the Elegant Tree Frog, is a species of amphibian in the Hylidae family. It is primarily found in South America, particularly in Argentina, Brazil, and Uruguay. This frog is recognizable by its smooth skin and vibrant colors, usually green with shades of yellow and brown. It measures about 3 to 5 cm in length. The Boana pulchella is an arboreal species that prefers humid habitats, such as tropical and subtropical forests. It is mainly active at night, feeding on insects and other small invertebrates. Although its conservation status is currently "least concern," it is threatened by the loss of its natural habitat due to deforestation and urbanization.
The European Tree Frog, or Hyla arborea, is a small arboreal frog native to Europe. It is characterized by its smooth skin and bright green color, although some may exhibit shades of brown or gray. Typically measuring between 3 and 5 cm, it has adhesive pads on its fingers, allowing it to climb easily on plants and trees. It is often found near stagnant water bodies, such as ponds and marshes, where it breeds. Its call, a loud croak, is particularly noticeable during the breeding season. Although primarily nocturnal, it can be seen basking in the sun during the day.
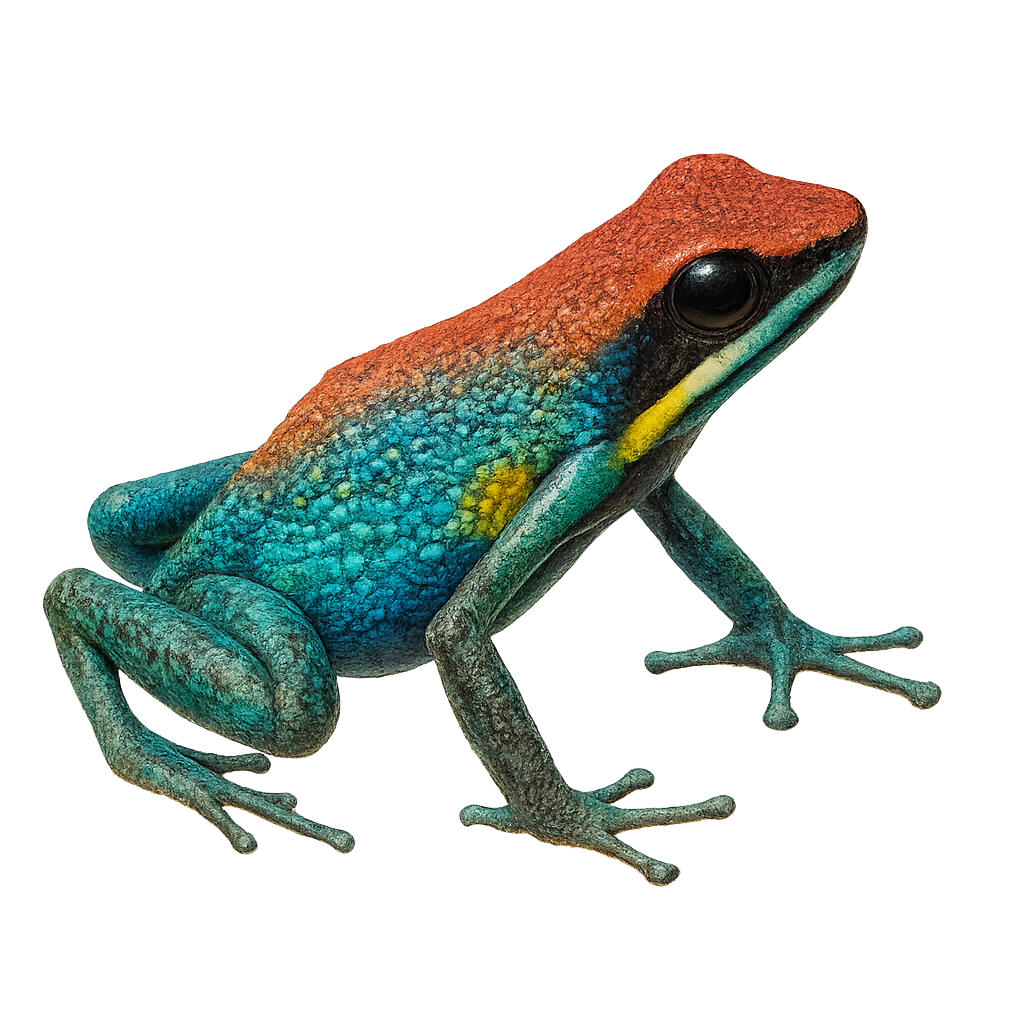
The Ecuador poison frog, Ameerega bilinguis, is a brightly colored frog species belonging to the Dendrobatidae family. It is primarily found in the humid tropical forests of Ecuador and Colombia. Known for its vivid colors, typically a mix of black, blue, and yellow, this frog uses its appearance to warn potential predators of its toxicity. It measures about 2 to 3 cm in length. Ameerega bilinguis are diurnal and primarily feed on small insects. Their skin secretes toxic alkaloids, a common trait among frogs of this family. They play a crucial role in the ecosystem by controlling insect populations and serving as prey for certain predators immune to their poison.
The Eurasian robin is a small bird from the Muscicapidae family, easily recognized by its bright red breast. It is widely distributed across Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa. This bird is mostly active during the day, feeding mainly on insects, worms, and berries. Although very territorial, it is admired by photographers for its curious nature and active behavior.
The Eurasian reed warbler is a small migratory passerine, 11–13 cm long, with olive-brown plumage and a repetitive, hiss-like song. It inhabits reed beds and freshwater marshes, feeding on insects and larvae. During the breeding season, the male sings from an exposed perch and the pair builds a vase-shaped woven nest within dense reed vegetation.
The Eastern hellbender is one of the largest salamander species in the world, growing up to 75 cm in length. It primarily inhabits clear rivers and streams in the United States, where it hides among rocks and feeds on small aquatic invertebrates. This amphibian is particularly sensitive to water pollution and habitat loss. Due to these threats, the Eastern hellbender is classified as a vulnerable species.
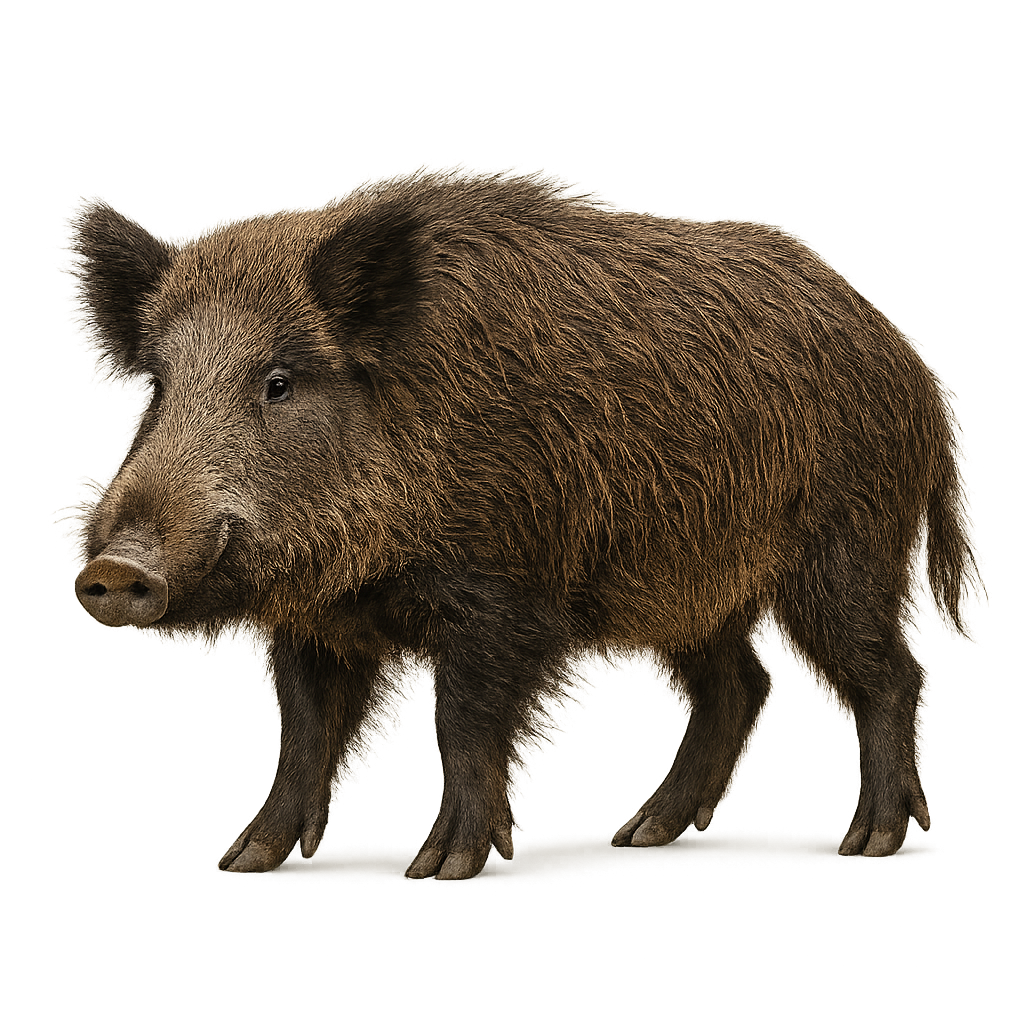
The Wild Boar is a large omnivorous mammal found primarily in forests, wooded areas, and mountains of Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It measures between 1.2 and 1.8 meters in length, with a tail of 15 to 25 cm, and weighs between 50 and 100 kg, though some specimens can reach up to 200 kg. Its fur is typically brown, with darker hair on the back and lighter on the sides. The Wild Boar is a nocturnal animal, primarily feeding on roots, fruits, seeds, insects, and small animals. While it is considered game, it can sometimes pose a threat to agricultural crops due to its tendency to root through the soil. This species is widely distributed, and its population remains relatively stable, although it is sometimes threatened by excessive hunting and habitat loss.
Anas crecca is the smallest dabbling duck in Eurasia, measuring between 33 and 38 cm in length with a wingspan of 53 to 58 cm. The male in breeding plumage is distinguished by a chestnut head with an iridescent green band from the eye to the nape, a white collar, and a body finely vermiculated grey. The female is brown speckled, with a light line at the eye and a light spot on the rump. It frequents shallow wetlands such as marshes, ponds, rice fields, and mudflats, often with dense aquatic vegetation. It primarily feeds on seeds of aquatic plants, algae, small invertebrates, and insect larvae. Reproduction occurs between May and July, with the female building a well-hidden nest in vegetation, where she lays 8 to 11 eggs. Incubation lasts about 21 to 23 days. A migratory species, it winters in Europe, Asia, and North Africa.
The European Snake-eyed Skink, Ablepharus kitaibelii, is a small, elusive lizard found mainly in the warm, dry regions of Southeastern Europe and Western Asia. Its skin is smooth and shiny, often bronze or golden-brown, allowing it to blend into its surroundings. This lizard is characterized by its reduced eyelids, hence its name, and snake-like eyes. It prefers rocky habitats, dry grasslands, and shrub areas. Although primarily terrestrial, it is agile and quick, moving easily among stones and grasses. Its small size and discreet behavior make it difficult to observe, but it plays an important role in the ecosystem as an insect predator.
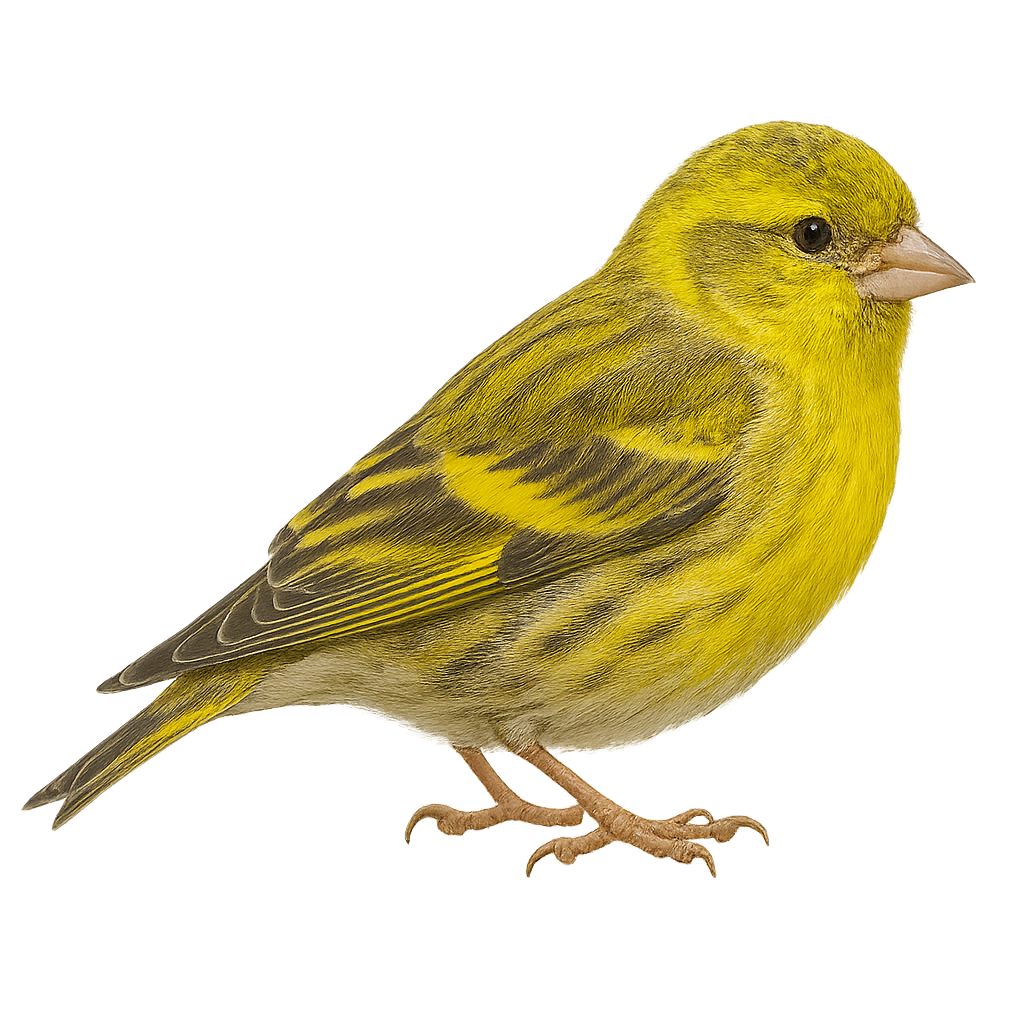
The European serin is a small passerine bird found primarily in gardens, orchards, and urban areas across Europe and the Middle East. It is distinguished by its bright yellow plumage, dark wings, and small size. This small bird primarily feeds on seeds, which it finds in trees, bushes, and grasses. It is also known for its high-pitched, melodious song, which it performs during the breeding season.
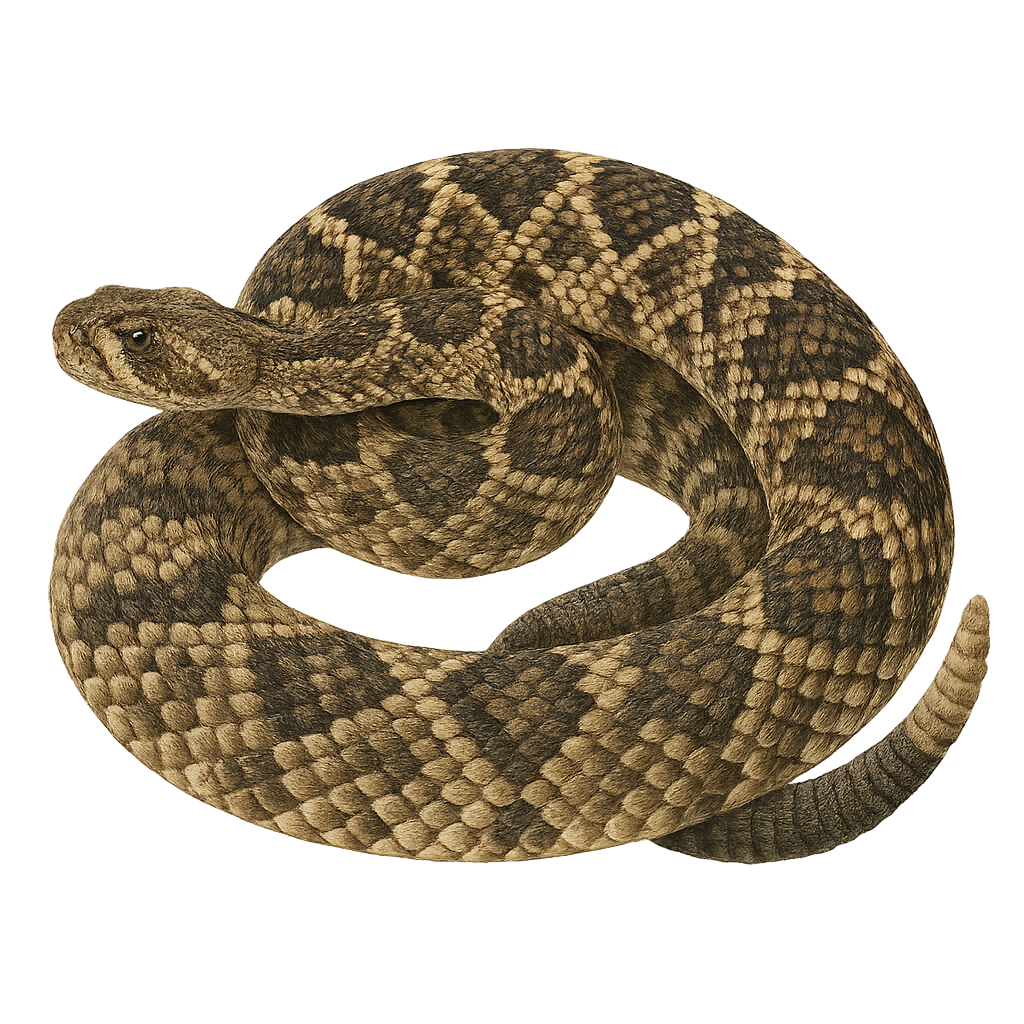
The Eastern Diamondback Rattlesnake, Crotalus adamanteus, is the largest rattlesnake species in North America, reaching lengths of up to 2.4 meters. It is easily identified by its distinctive diamond-shaped patterns along its back. This venomous snake primarily inhabits pine forests, marshes, and coastal prairies in the southeastern United States. Although feared for its potentially deadly bite, it is generally reclusive and avoids human encounters. Its coloration provides excellent camouflage in its natural habitat. The Eastern Diamondback plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by controlling small mammal populations.
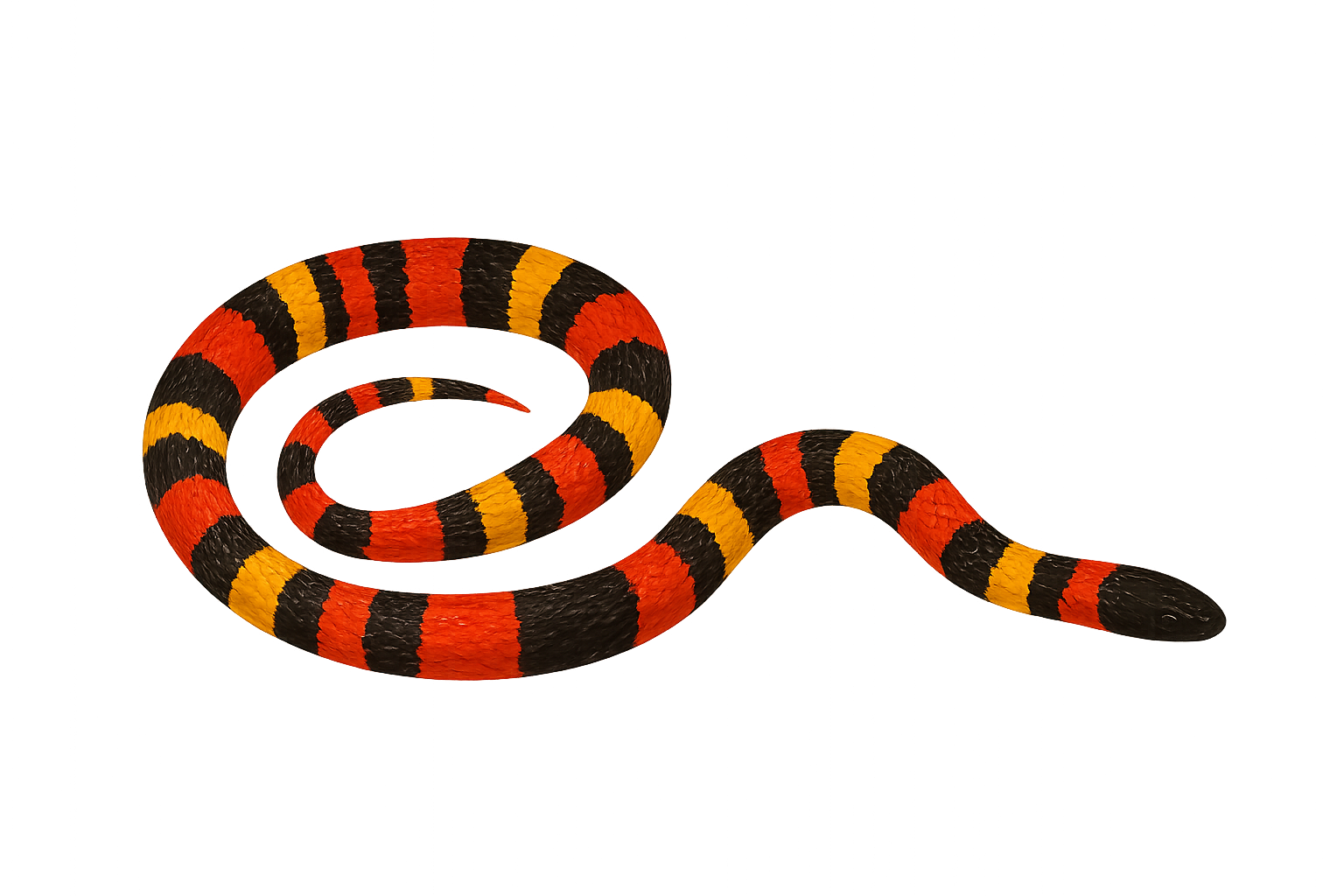
The Coral Snake is a venomous species found primarily in Central and South America, notably in Mexico, Costa Rica, Panama, and Colombia. It typically measures between 50 and 80 cm in length, although some specimens can reach up to 1 meter. It is distinguished by its red, black, and yellow rings, giving it a vibrant and easily recognizable appearance. Although coral snakes are venomous, their bite is rarely fatal due to their small size and the difficulty of delivering the bite, but it can cause severe symptoms due to their neurotoxin. These snakes typically live in tropical forests, where they hide under dead leaves or in shrubs. They primarily feed on small reptiles, amphibians, and young snakes.
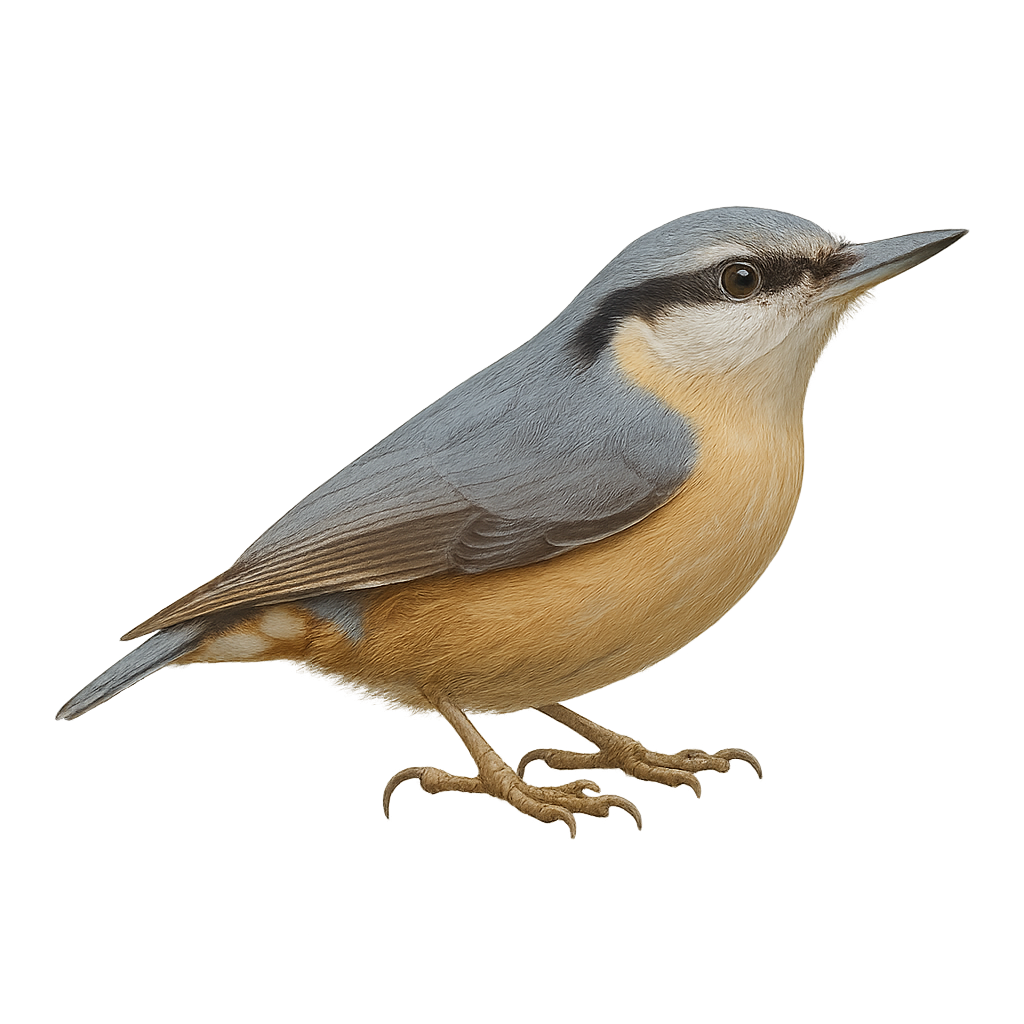
The Eurasian nuthatch is a small woodland bird found primarily in mixed and deciduous forests across Europe and Asia. It is easily recognized by its blue-grey and orange plumage, light belly, and distinctive black mask around its eyes. This bird is particularly known for its ability to climb upside down on tree trunks, allowing it to reach areas inaccessible to other birds. It primarily feeds on insects, seeds, and nuts.
The Edwards's Tanager, scientifically known as Bangsia edwardsi, is a vibrant and captivating bird native to the humid montane forests of Colombia and Ecuador. This medium-sized passerine boasts a striking plumage with shades of blue and green that catch the eye. Often seen in small groups, it primarily feeds on fruits and insects. Its natural habitat ranges from 1,200 to 2,400 meters in altitude, where it plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding forest regeneration. Although its conservation status is concerning, efforts are underway to protect its habitat and ensure its long-term survival.
The European Stonechat, Saxicola torquata, is a small passerine bird belonging to the Muscicapidae family. It is easily identifiable by its distinctive plumage: the male has a black head, white throat, and orange-brown back, while the female is duller with brownish tones. This bird is often seen perched on bushes or fences, watching for insects to feed on. It inhabits open areas such as meadows, heaths, and agricultural lands. The European Stonechat is a resident bird in temperate regions, but some populations migrate south in winter. It is known for its melodious song and short, sharp calls.