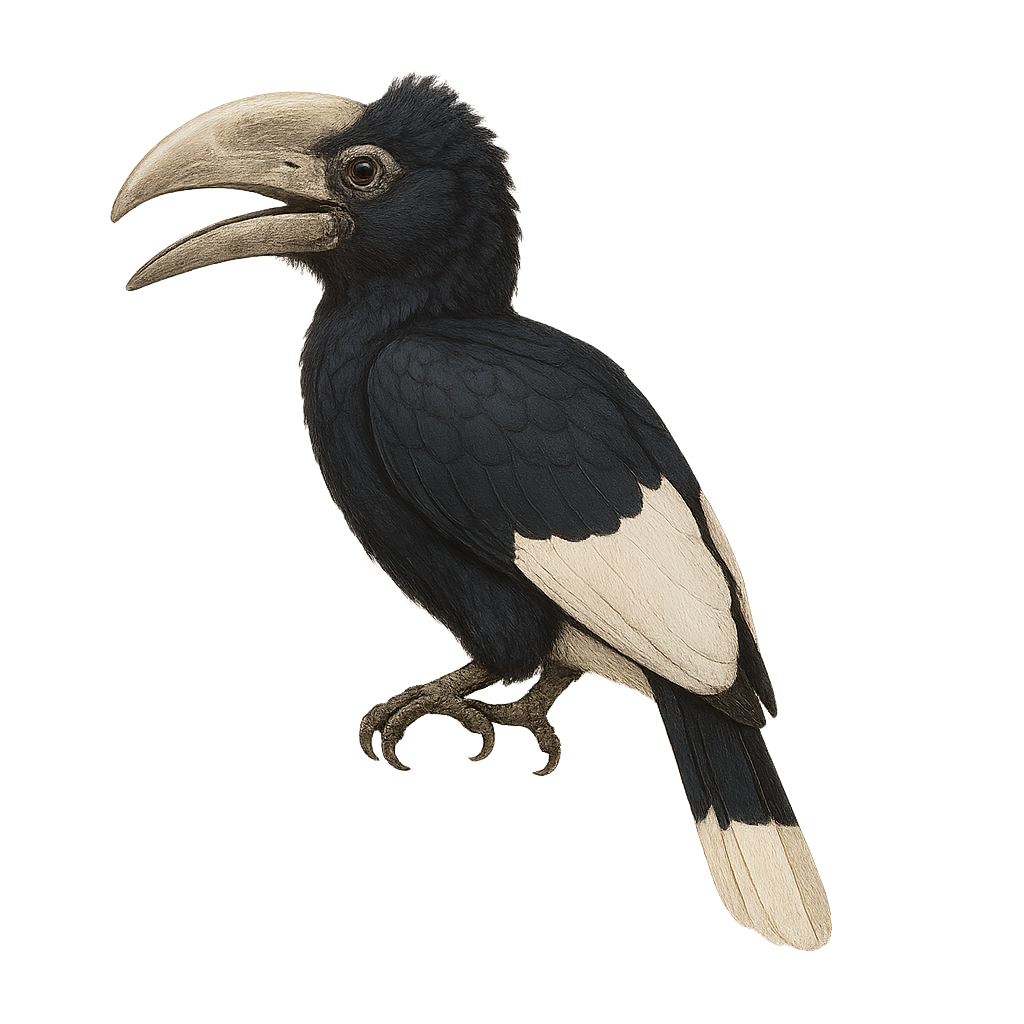
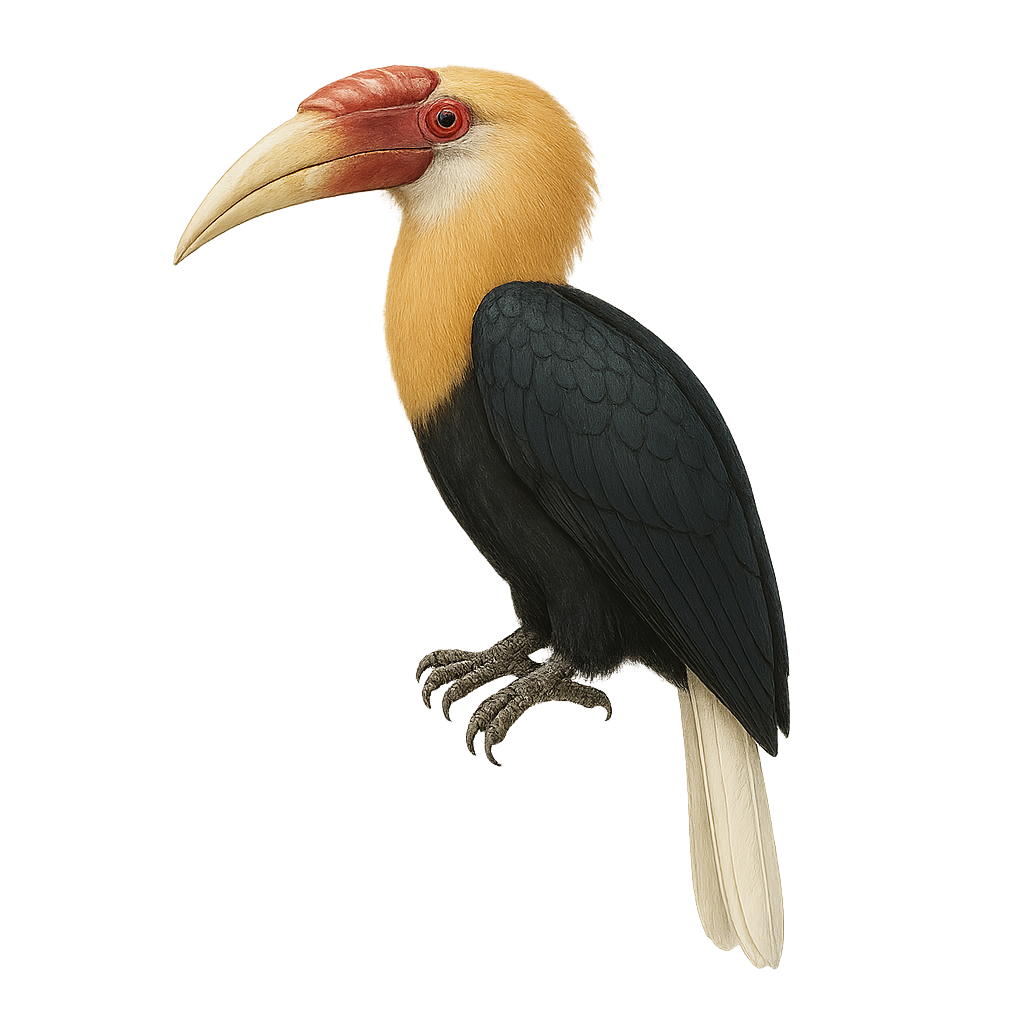
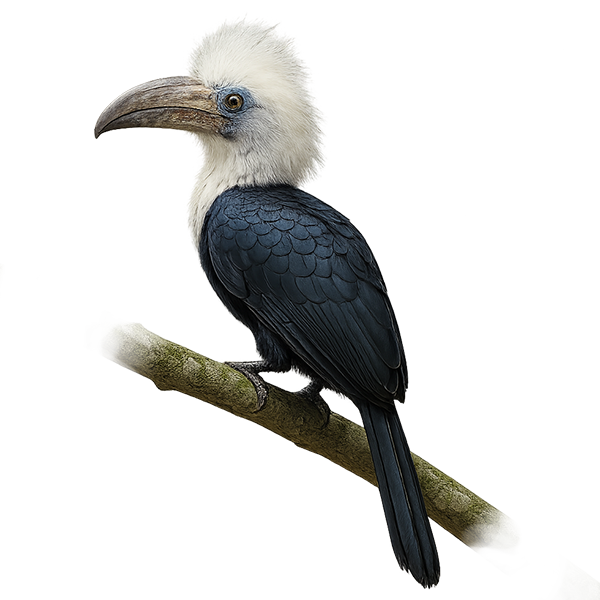
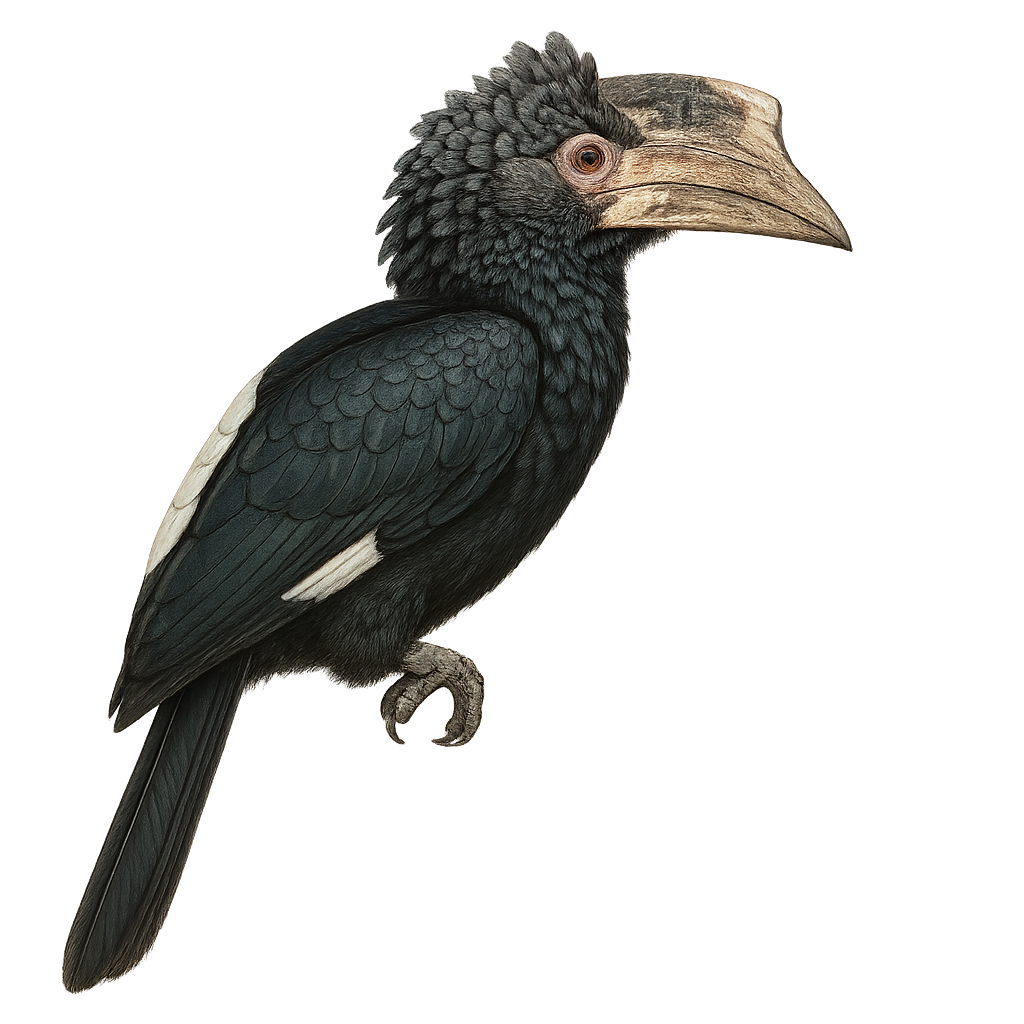
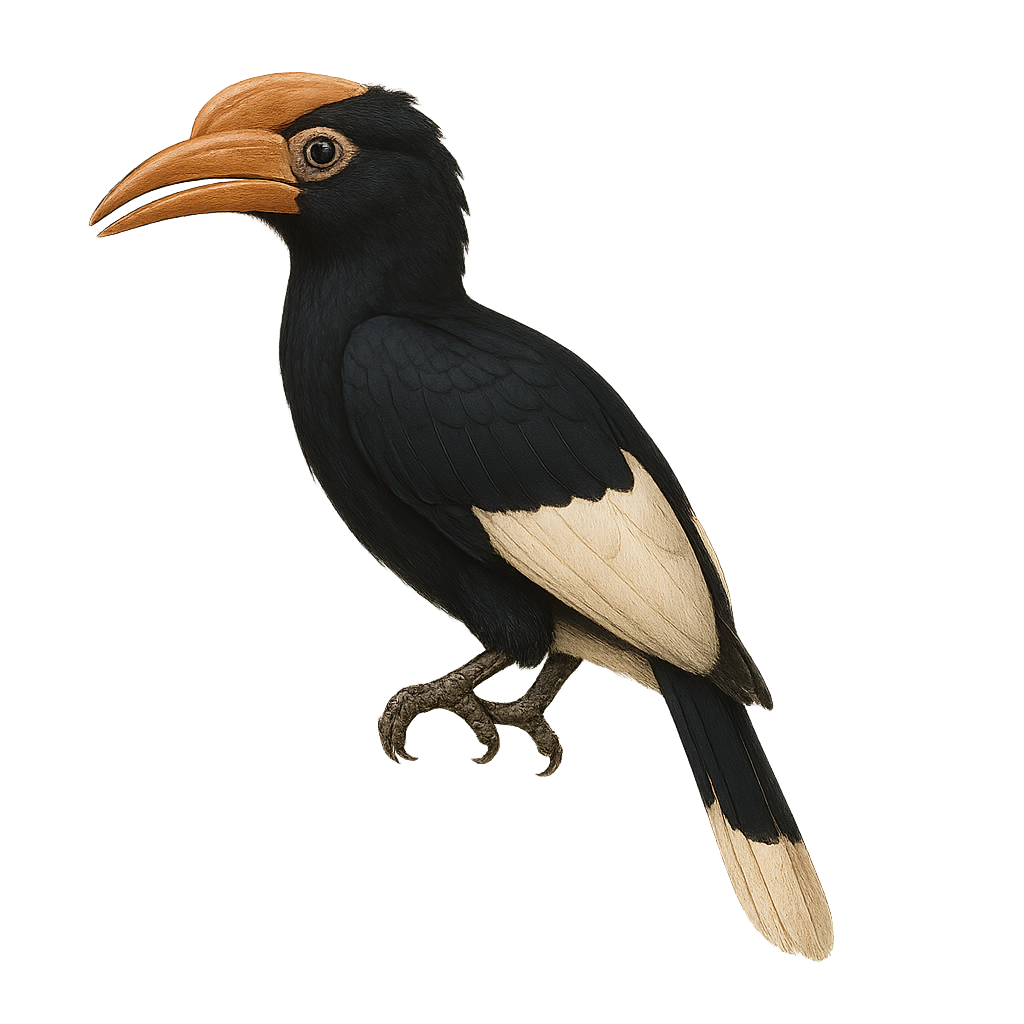
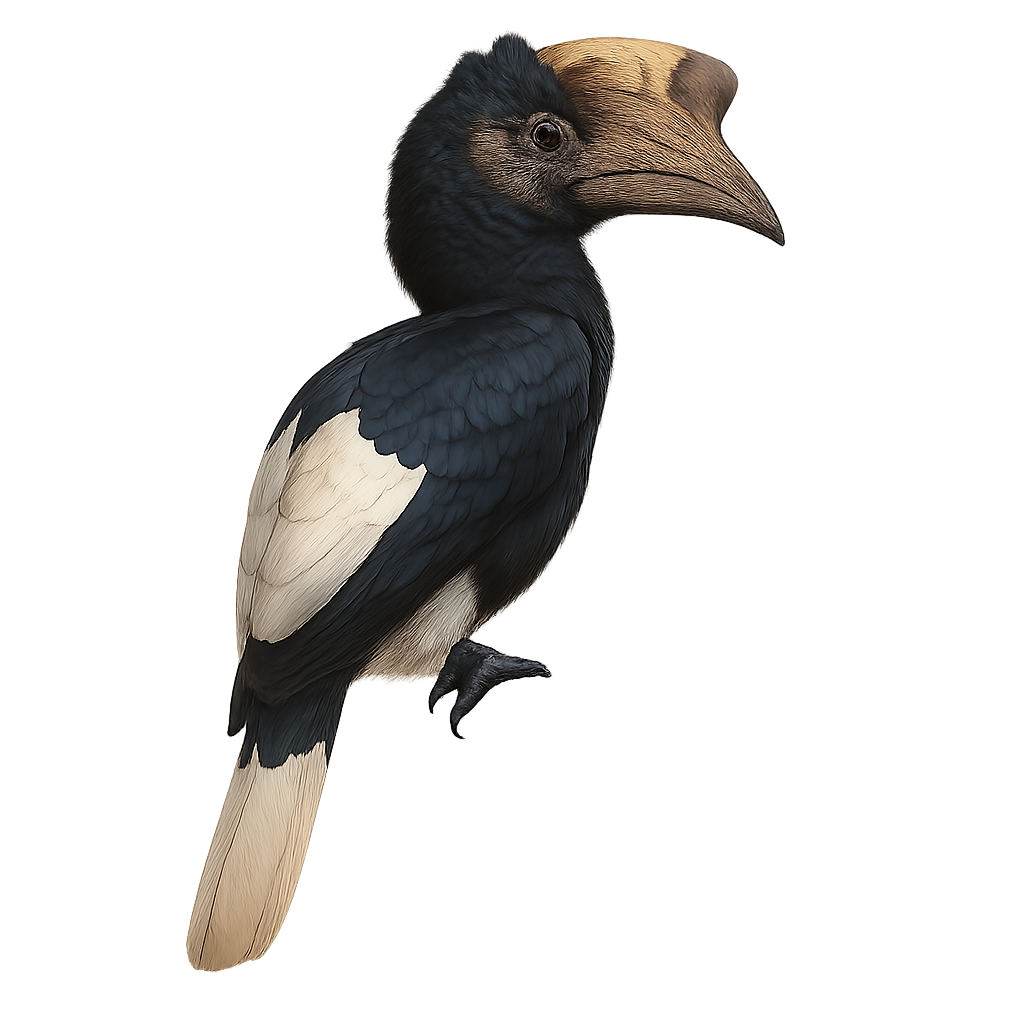
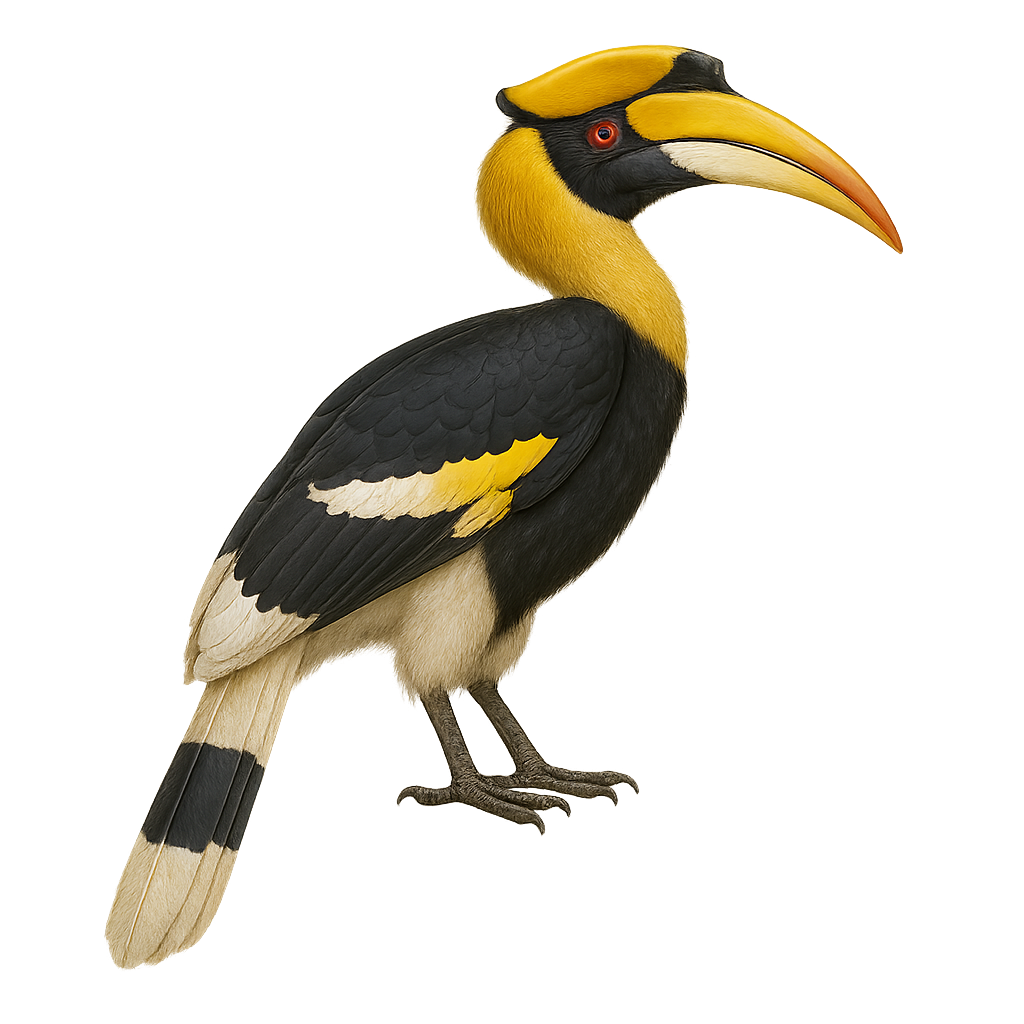
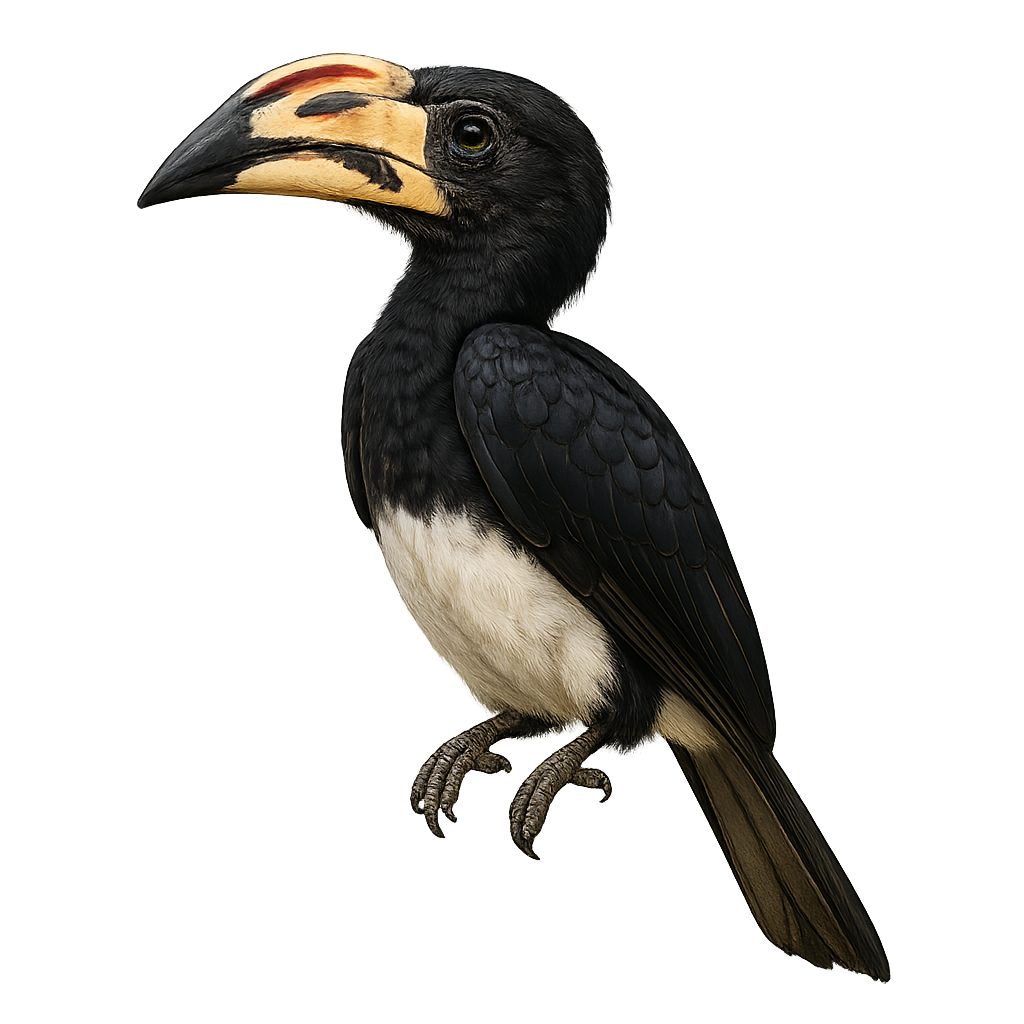
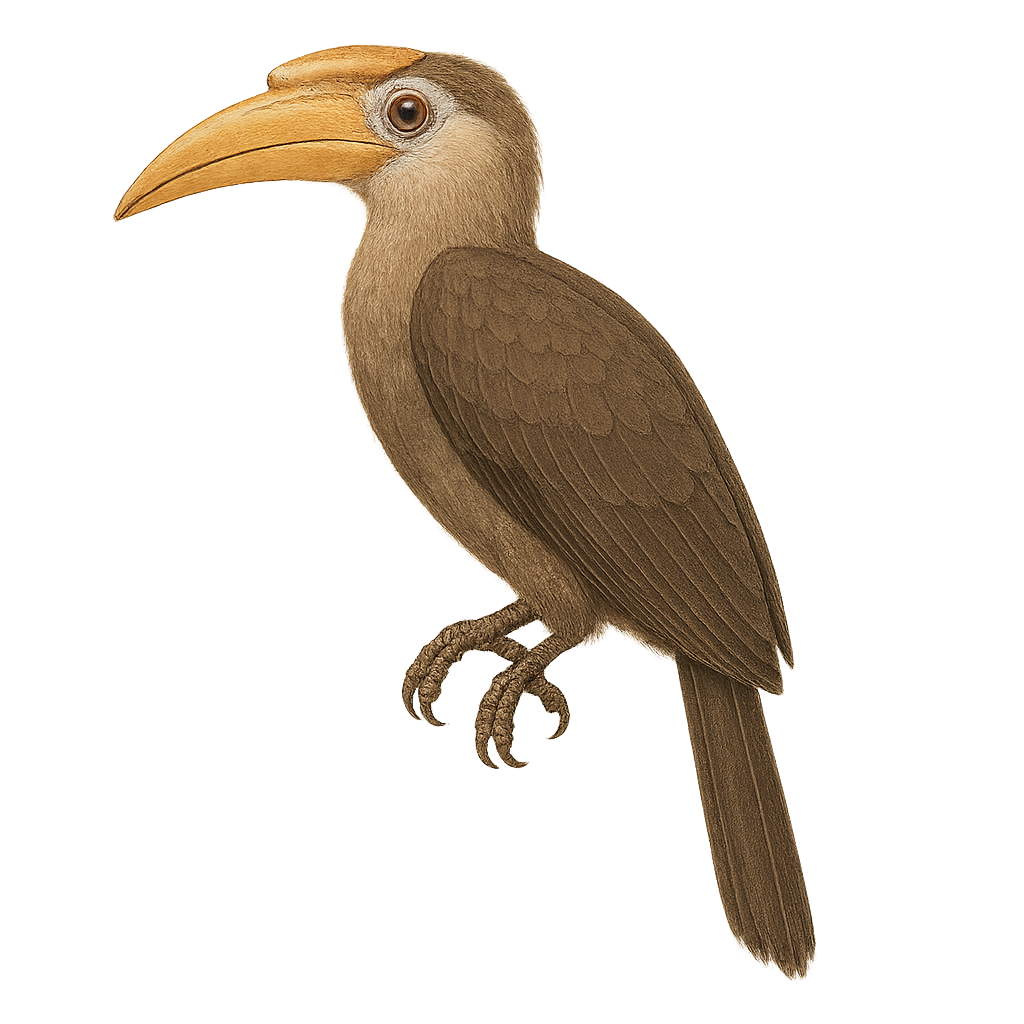
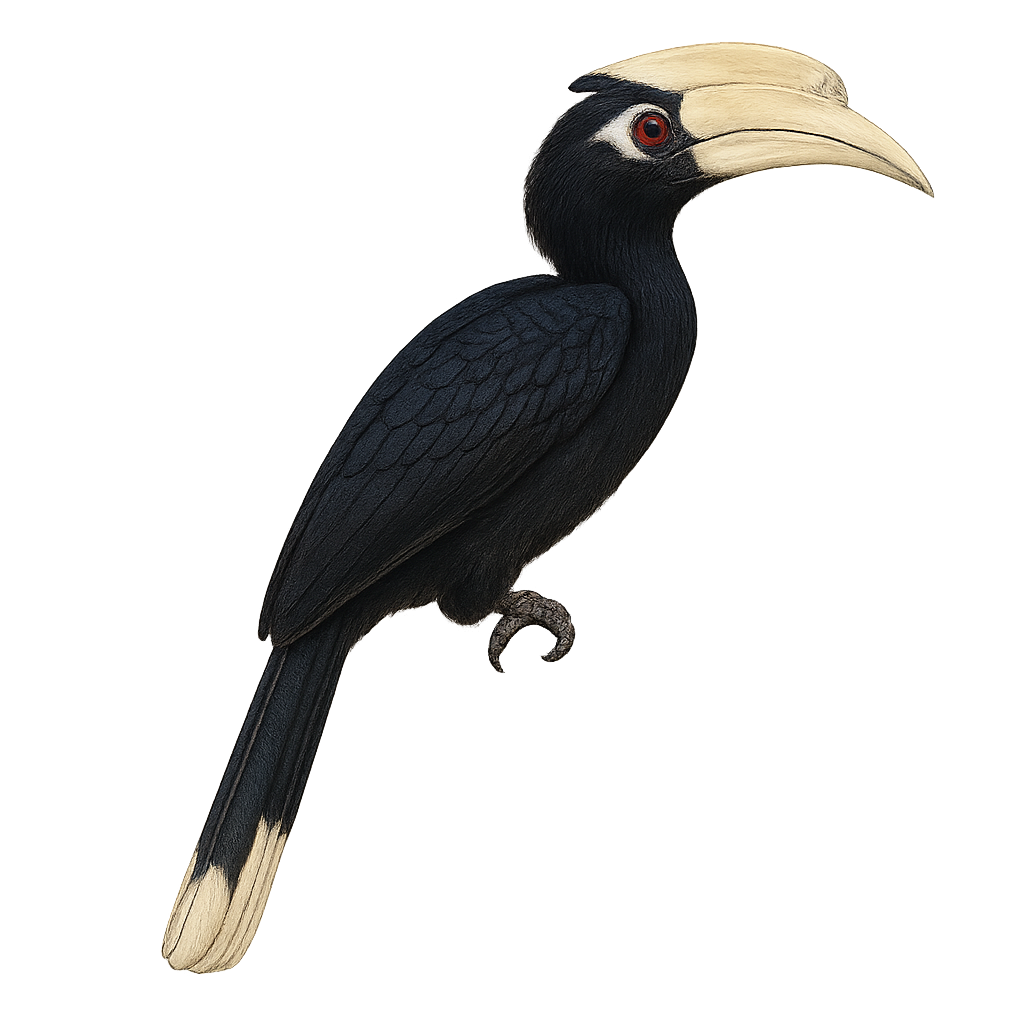
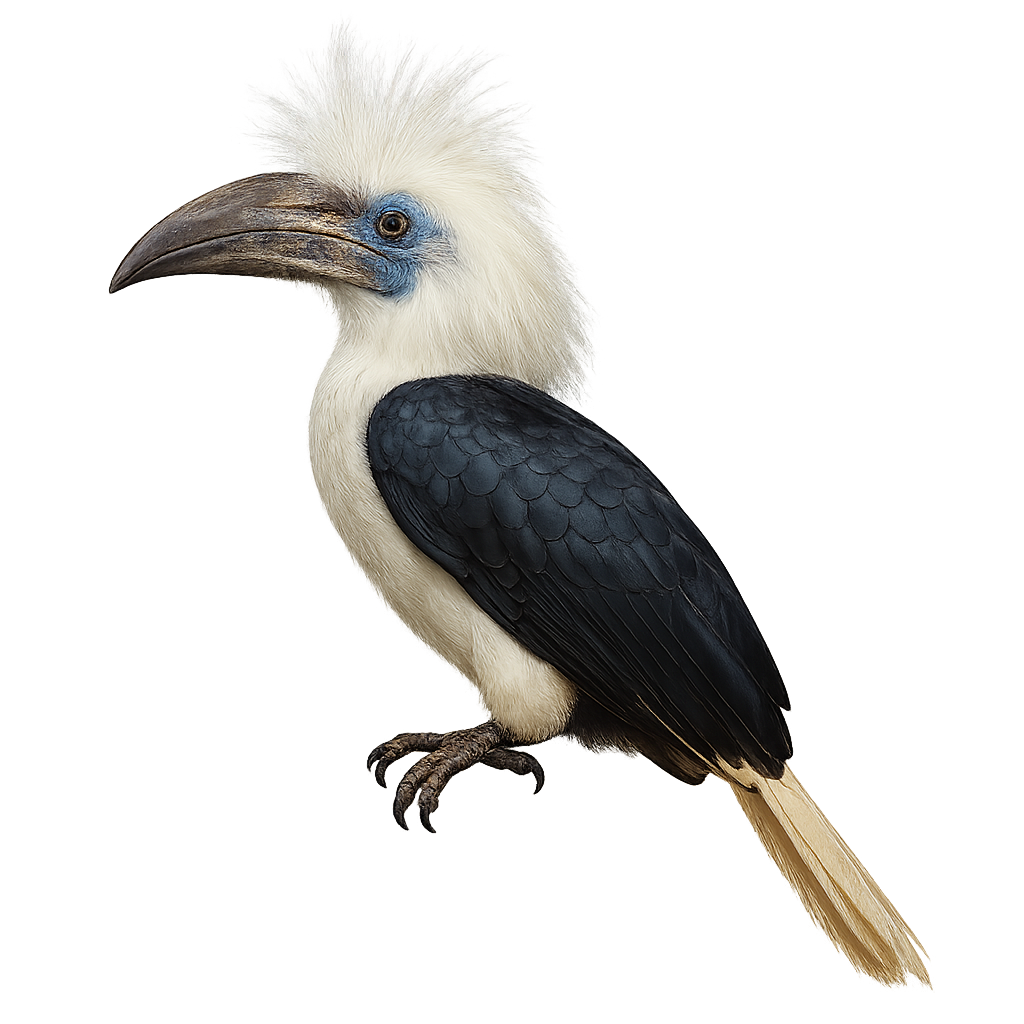
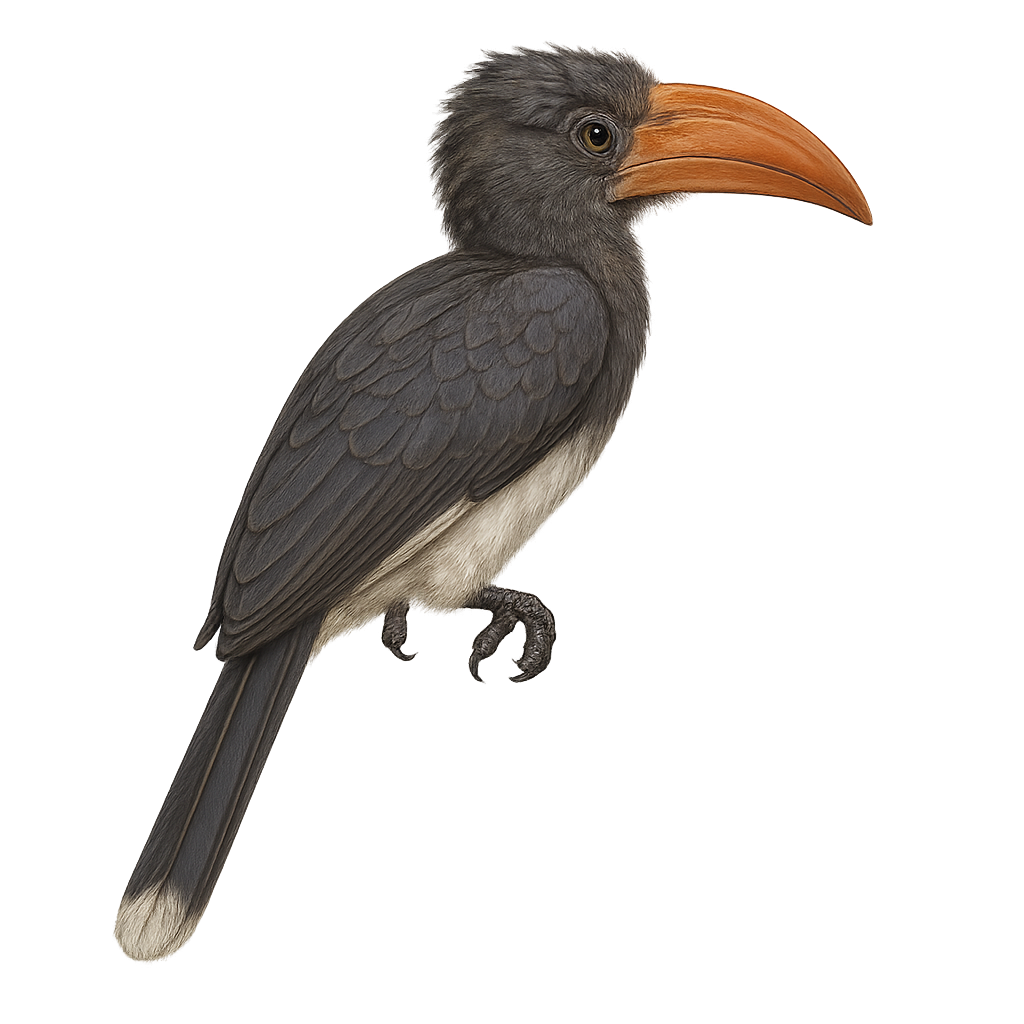
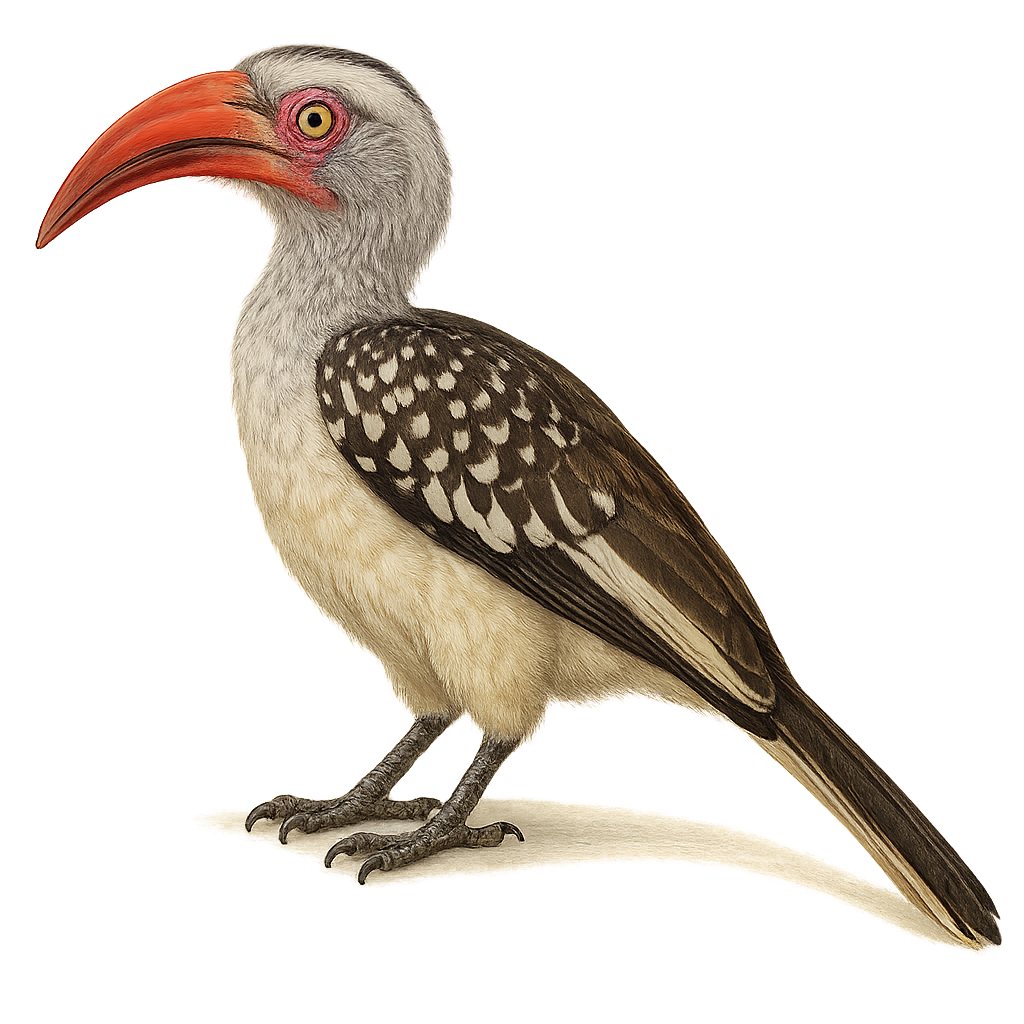
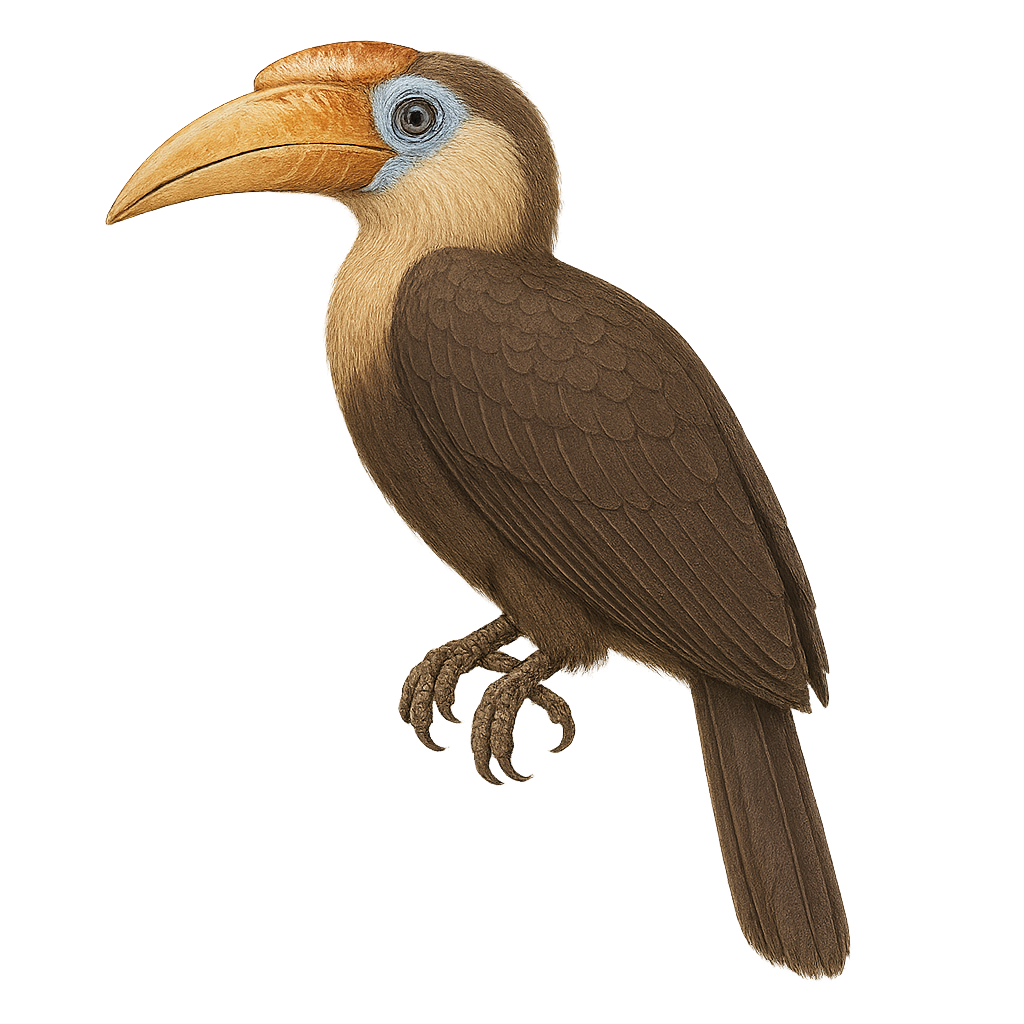
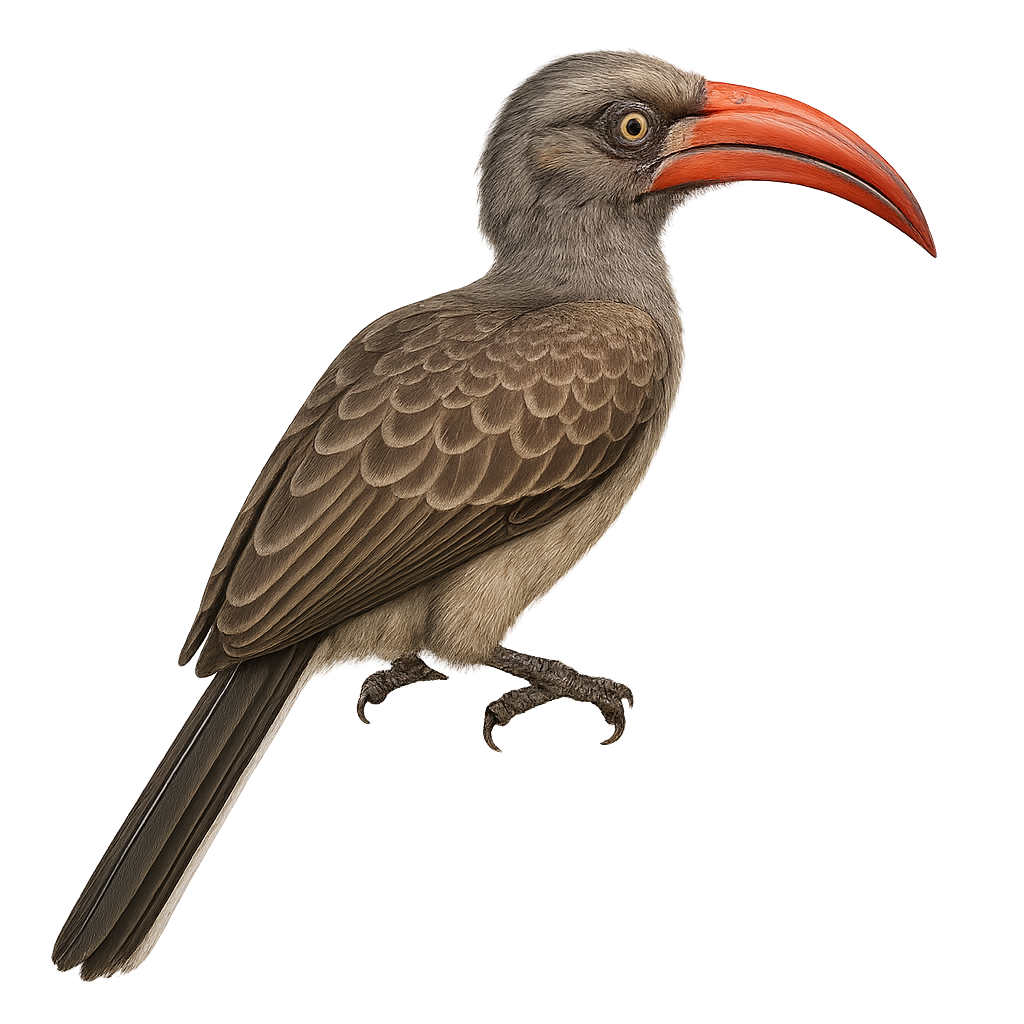
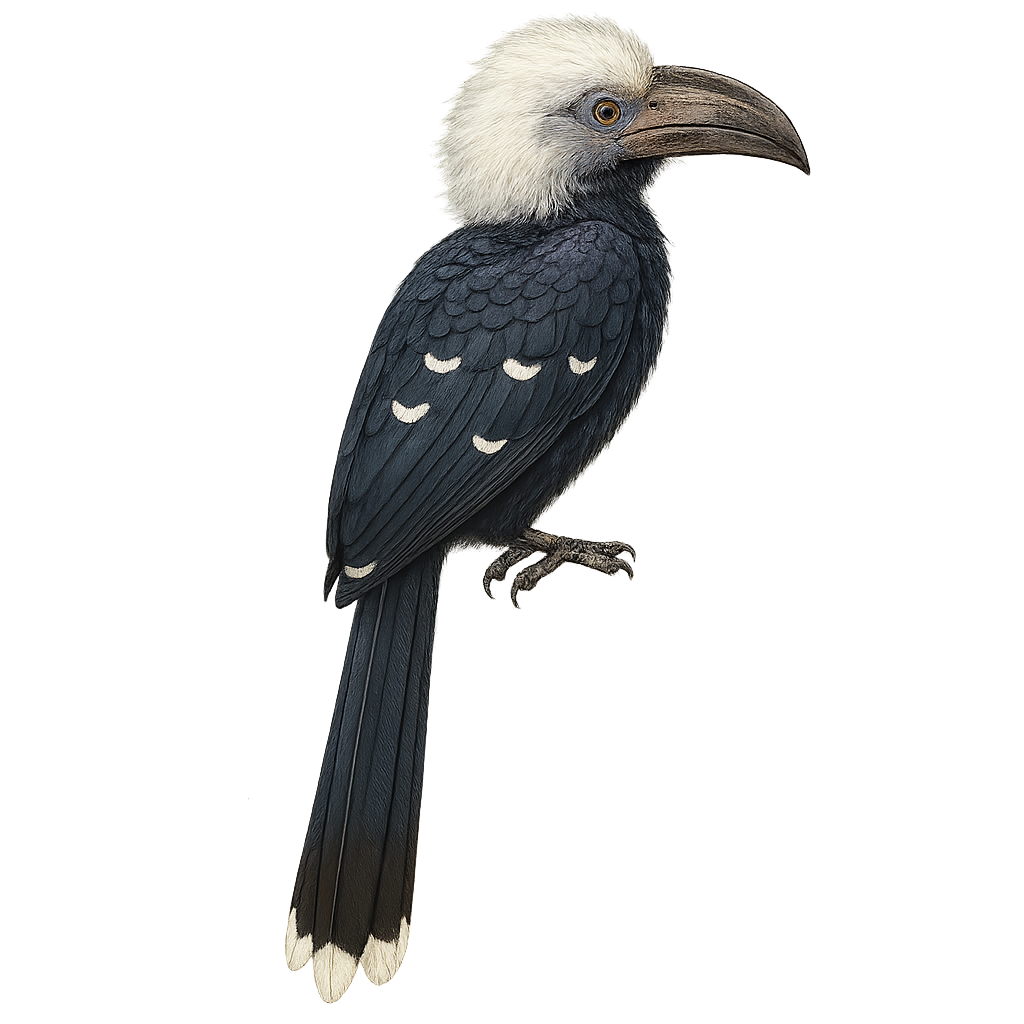
The White-thighed Hornbill, or Bycanistes albotibialis, is a striking bird with distinctive black and white plumage and a large bill. It primarily inhabits the tropical forests of Central and West Africa. This bird mainly feeds on fruits but can also consume insects and small animals. Hornbills are known for their social behavior, often seen in small groups. They nest in tree cavities, where the female is sealed in during the incubation period. The White-thighed Hornbill plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, contributing to forest regeneration. Although their population is stable, deforestation poses a potential threat to their natural habitat.
The Plain-pouched Hornbill, or Rhyticeros subruficollis, is a large and rare hornbill found in the tropical forests of Southeast Asia, mainly in southern Myanmar and the Malay Peninsula. It is recognized by its black body, pale orange-beige throat and chest, and large ivory bill topped with a rounded black casque. Males show a more intensely colored throat than females. This species inhabits lowland rainforests, especially near river valleys, and feeds on fruits, insects, and small vertebrates. Due to habitat destruction, the Plain-pouched Hornbill is classified as Endangered.
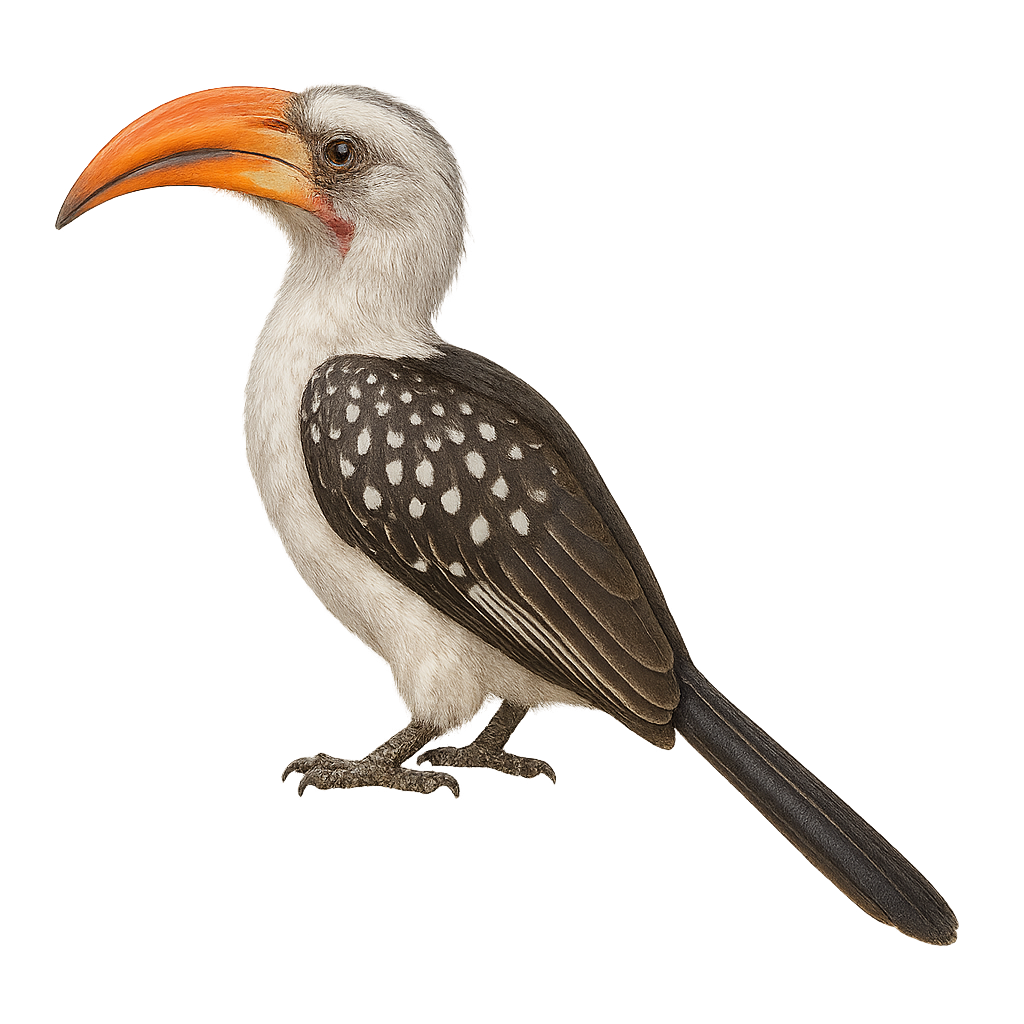
The White-crested Hornbill, or Horizocerus albocristatus, is a fascinating bird found in the tropical forests of West and Central Africa. Its most distinctive feature is its striking white crest, contrasting with its black and brown plumage. It measures about 50 cm in length and has the curved beak typical of hornbills. This bird is often seen in small groups, feeding mainly on fruits, insects, and small animals. Its call is a mix of whistles and croaks, often heard in the dense canopy. Although relatively common in its habitat, deforestation poses a threat to its populations.
The Silvery-cheeked Hornbill, Bycanistes brevis, is a striking bird known for its large size and distinctive appearance. It features silvery cheeks and a massive bill topped with a casque. This hornbill is primarily black with white feathers on its wings and tail. It inhabits the tropical forests of East Africa, from southern Ethiopia to northern South Africa. Its diet mainly consists of fruits, but it also eats insects and small animals. The Silvery-cheeked Hornbill is a social bird, often seen in small groups. It plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding forest regeneration. Although its conservation status is currently "Least Concern," deforestation poses a threat to its natural habitat.
The Brown-cheeked Hornbill, or Bycanistes cylindricus, is a large hornbill of the humid forests of West Africa, recognizable by its black-and-white plumage, brownish cheeks, and large ivory bill with a prominent casque. It inhabits lowland tropical forests, forest edges, and transitional zones, mainly in Guinea, Sierra Leone, Ivory Coast, and Ghana. Often seen in pairs or small groups, it flies noisily through the canopy. It feeds on fruits—especially figs—as well as insects and small animals. Classified as Near Threatened, the Brown-cheeked Hornbill is particularly vulnerable to increasing deforestation.
The Black-and-white-casqued Hornbill, or Bycanistes subcylindricus, is a striking bird known for its distinctive appearance and behaviors. This large hornbill features contrasting black and white plumage and a prominent casque, which helps amplify its calls. It primarily inhabits the tropical rainforests of Central and West Africa, playing a crucial role in seed dispersal due to its mainly frugivorous diet. Social by nature, it often lives in small family groups and shows some tolerance to human presence. However, deforestation and hunting threaten its natural habitat, making its conservation vital.
The great hornbill (Buceros bicornis) is a large forest bird (95–120 cm long, weighing 2–3.4 kg) known for its massive yellow bill topped by a hollow casque. It inhabits humid tropical and gallery forests from India to Vietnam, at elevations from sea level to 1500 m. Primarily frugivorous, it feeds on figs and various fruits, supplementing its diet with small vertebrates and insects. Monogamous and territorial, pairs remain together year-round. During the breeding season (01.01–31.05), the male and female engage in loud duets and casque-butting displays. After pairing, the female seals herself within a tree cavity and incubates 1–2 eggs for 38–40 days, receiving food through a narrow slit provided by the male.
The West African Pied Hornbill, or Lophoceros semifasciatus, is a small forest hornbill from equatorial Africa, easily identified by its bright white belly contrasting with its black head, wings, and tail. It has a pale yellow bill with a dark tip and lacks a prominent casque. It inhabits the canopy of tropical forests and is often seen crossing clearings or flying over roads in small groups. It feeds on fruits, insects, and occasionally small vertebrates. Its call is a series of sharp whistles. Although discreet, the West African Pied Hornbill remains relatively common in undisturbed forest areas.
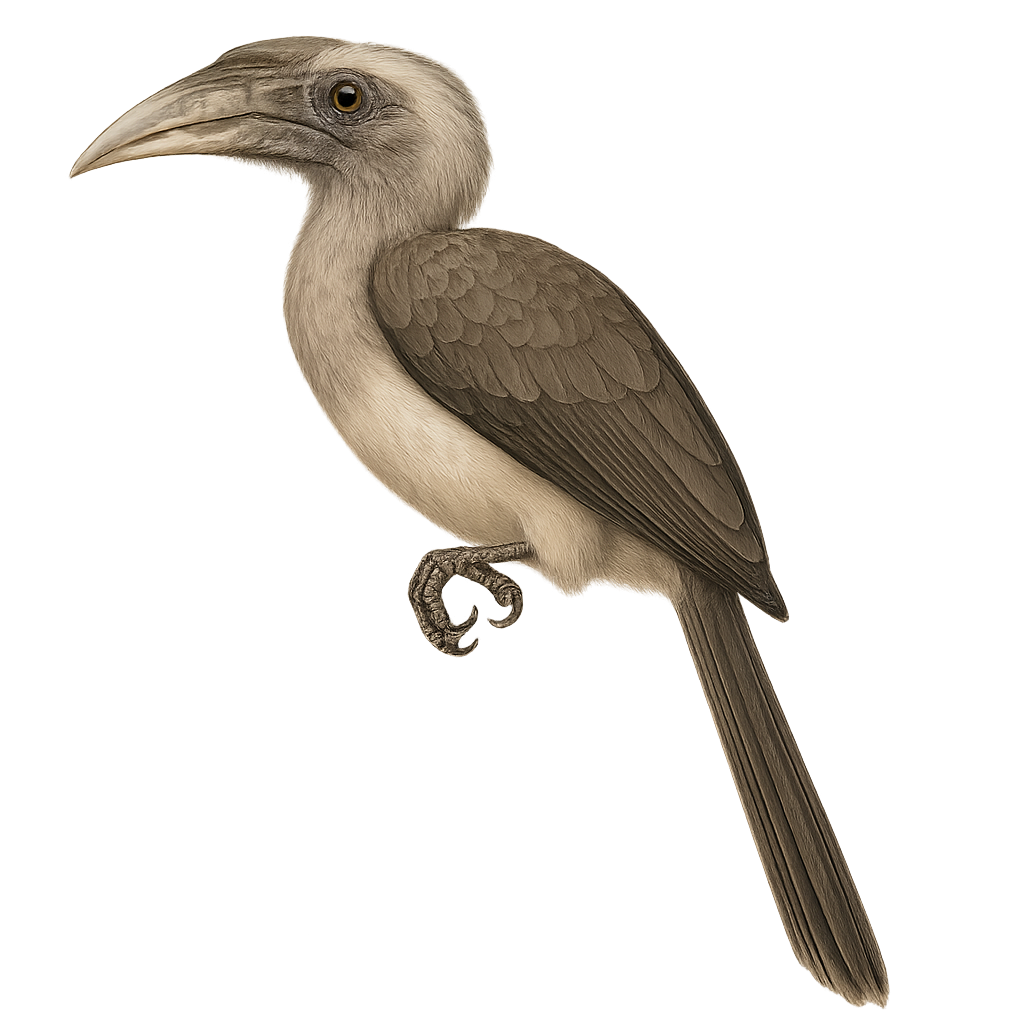
The Austen's Brown Hornbill, or Anorrhinus tickelli, is a medium-sized hornbill found in dry forests and wooded hills of Southeast Asia, especially in Myanmar, Thailand, and western Laos. It is identified by its uniformly dark brown plumage, contrasting black-and-white tail, and dark bill without a prominent casque. Highly social, it moves in family groups and is often noisy, producing harsh calls and barking sounds. It feeds on fruits, insects, and occasionally small vertebrates. Although somewhat tolerant of disturbed areas, this hornbill is vulnerable to deforestation.
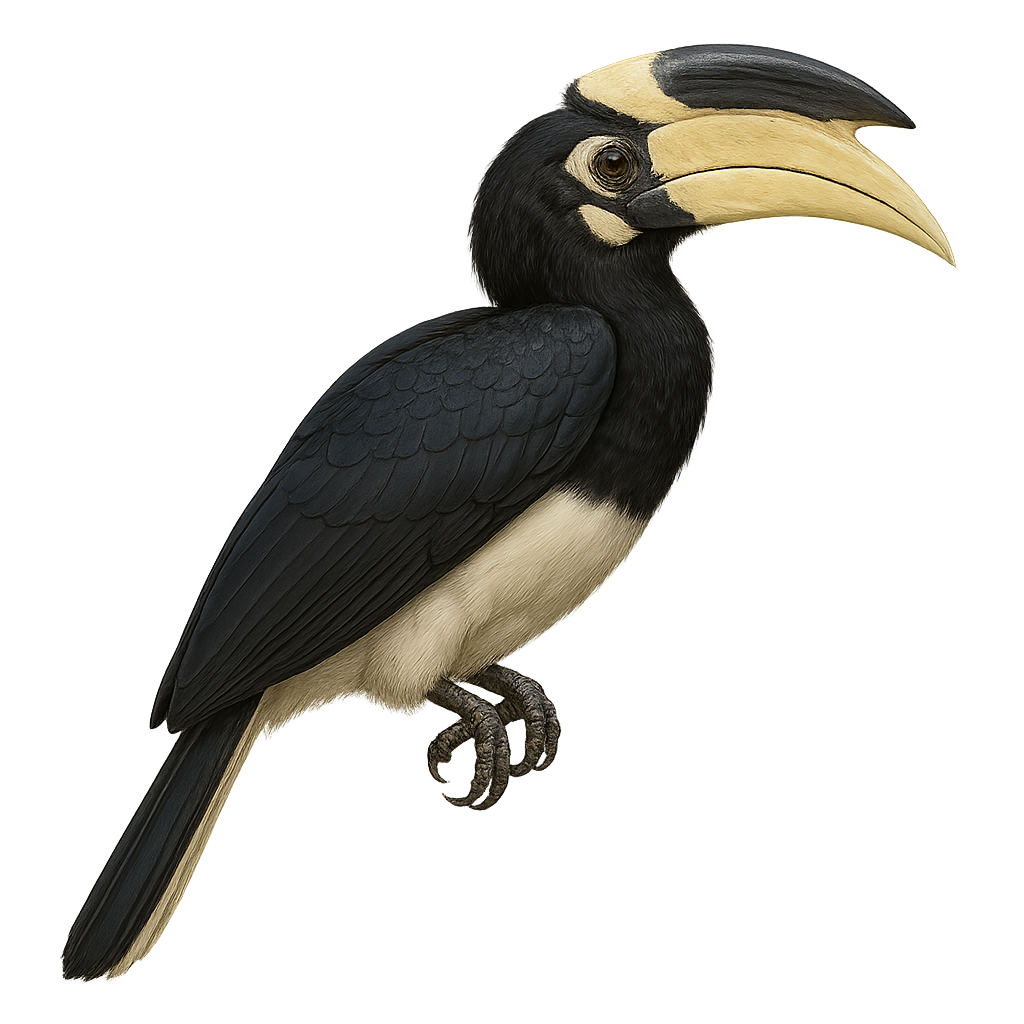
The Black Hornbill, or Anthracoceros malayanus, is a medium-sized hornbill native to the tropical forests of Southeast Asia, especially in Malaysia, Borneo, and Sumatra. It is recognized by its glossy black plumage, white belly, and large ivory bill topped with a flattened black casque. This hornbill inhabits lowland primary forests and is usually seen in pairs or small groups. Its diet consists mainly of fruits—especially figs—but also includes insects, lizards, and occasionally small birds. Though often quiet and elusive, the Black Hornbill is threatened by deforestation and is currently listed as Vulnerable.
The White-crowned Hornbill, or Berenicornis comatus, is a fascinating bird from the Bucerotidae family, recognizable by its distinctive white crest adorning its head. This large bird, measuring about 80 to 90 cm in length, sports predominantly black plumage with white shades on the head and neck. Its long, curved bill is typical of hornbills, and it has bare skin around the eyes, often blue in color. The White-crowned Hornbill primarily inhabits the tropical forests of Southeast Asia, notably in Malaysia, Thailand, and Indonesia. Known for its social behavior, it often lives in small family groups. Its powerful call resonates through the canopy, adding a sonic dimension to its lush environment.
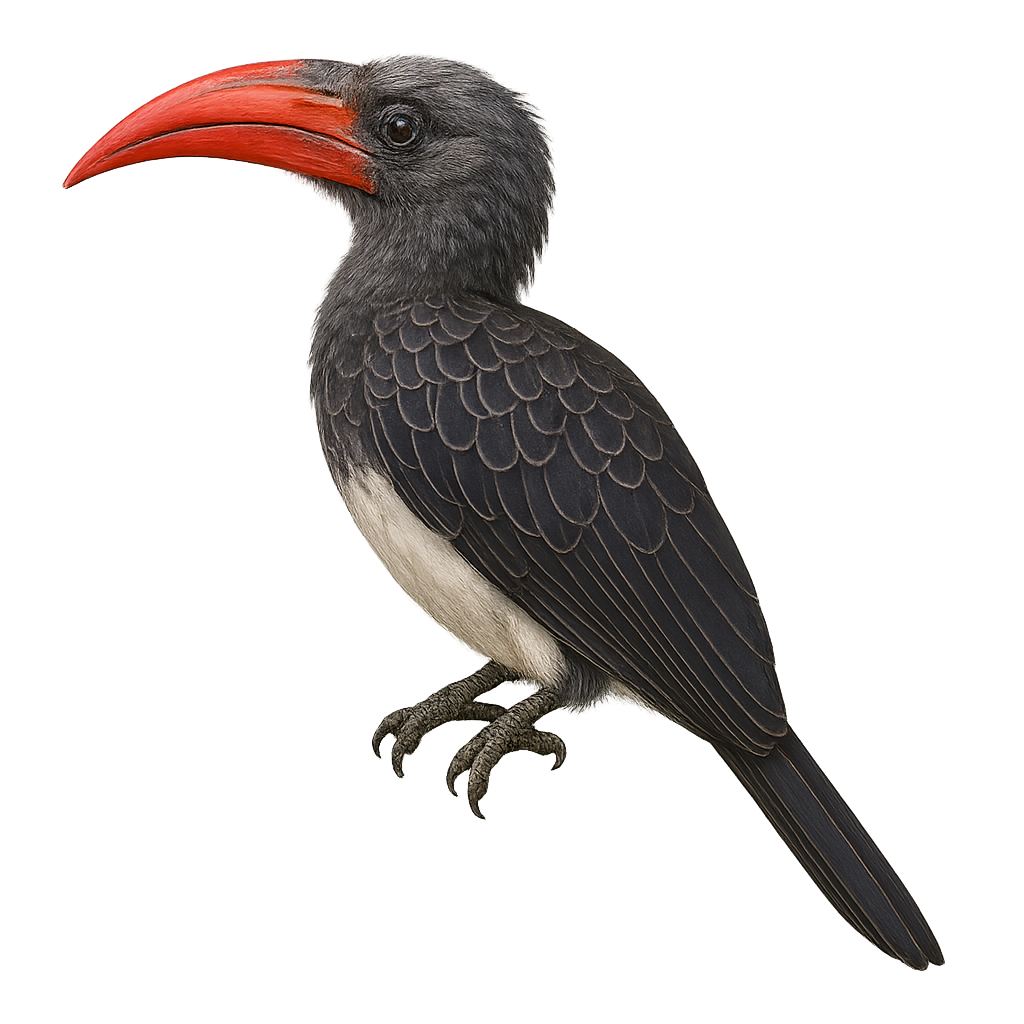
The Crowned Hornbill, or Lophoceros alboterminatus, is a medium-sized hornbill from sub-Saharan Africa, easily recognized by its reddish-orange bill topped with a small casque, its white chest, and white wingtips that are noticeable in flight. It inhabits coastal forests, woodlands, and forest edges from Kenya to northeastern South Africa. Omnivorous, it feeds on fruits, insects, and occasionally small animals. It is often seen in pairs or small, noisy groups. Although relatively common and adaptable to secondary forests, the Crowned Hornbill is still affected by habitat loss.
The Tockus rufirostris, or Southern Red-billed Hornbill, is a fascinating bird from the Bucerotidae family. It is easily recognizable by its bright red bill and predominantly grey and white plumage. This bird is often observed in the savannas and open woodlands of southern Africa. Known for its social behavior and distinctive calls, the Southern Red-billed Hornbill primarily feeds on insects, fruits, and occasionally small reptiles. It plays an important role in the ecosystem by aiding in seed dispersal. During the breeding season, the female seals herself inside a tree cavity with mud to lay her eggs, leaving only a small opening for the male to feed her.
The Austen's Brown Hornbill, Anorrhinus austeni, is a captivating bird belonging to the Bucerotidae family. This medium-sized hornbill is notable for its brown plumage and distinctive white tail band. Males and females exhibit sexual dimorphism, with males having larger, more curved bills. These birds primarily inhabit the tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia, feeding on fruits, insects, and small vertebrates. Known for their social behavior, they often live in family groups. Nesting occurs in tree cavities, where the female is sealed in during incubation. Although their population is stable, deforestation poses a threat to their natural habitat.
The Bradfield's Hornbill, or Lophoceros bradfieldi, is a striking bird known for its large bill and slender silhouette. It features predominantly grey plumage with shades of white and black, and its bill is often adorned with red. This bird is primarily found in the arid and semi-arid regions of southwestern Africa, notably in Namibia, Botswana, and Angola. It prefers dry savannas, open woodlands, and bushy areas. The Bradfield's Hornbill is a diurnal bird, often seen in small groups or pairs. It feeds mainly on insects, small reptiles, and fruits. Although its conservation status is currently "least concern," monitoring its habitat is crucial for its continued survival.
The Cassin's Hornbill is a fascinating bird belonging to the Bucerotidae family. It is distinguished by its black and white plumage, large bill, and distinctive crest. This bird is primarily arboreal, living in the humid tropical forests of Central Africa. It mainly feeds on fruits, but also insects and small animals. Known for its loud vocalizations and social behavior, it is often observed in small groups. Although relatively common in its natural habitat, deforestation poses a threat to its population. Its ability to adapt to different forest environments allows it to survive despite environmental pressures.
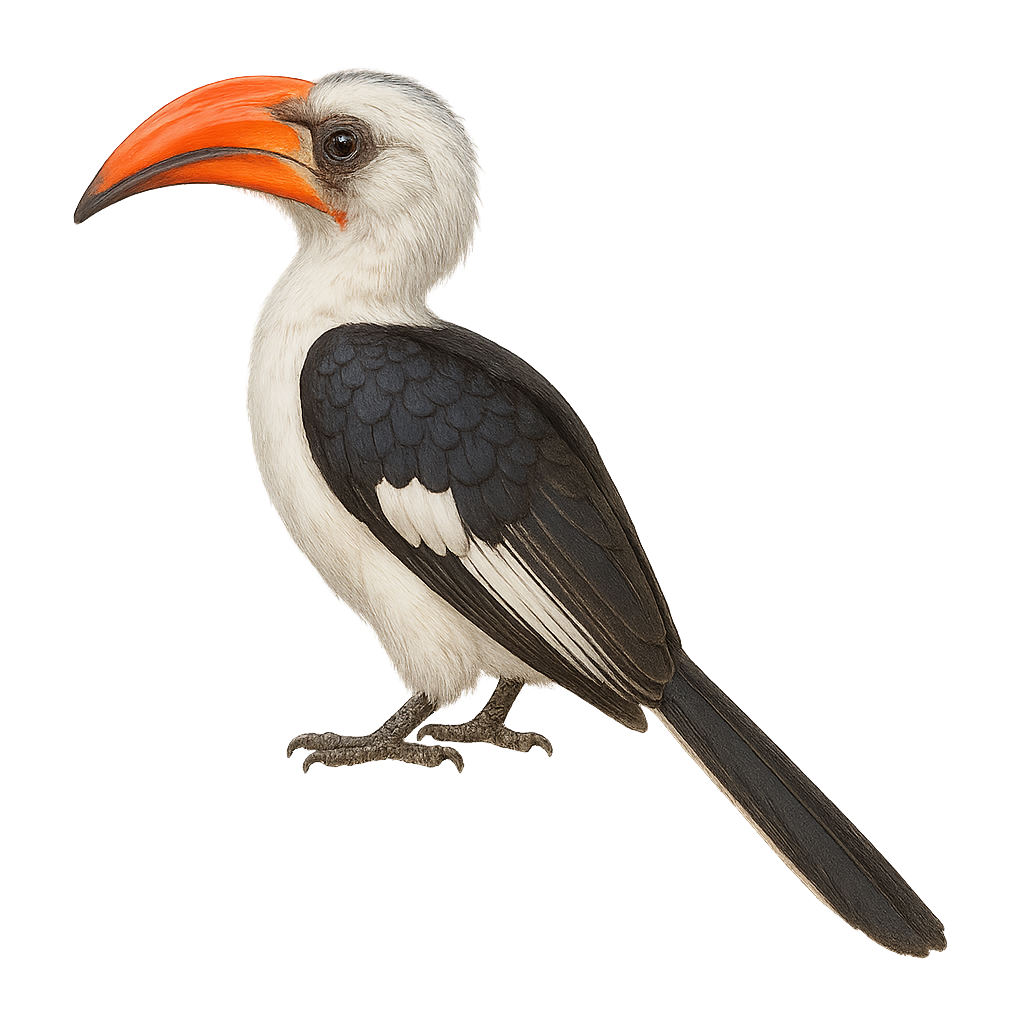
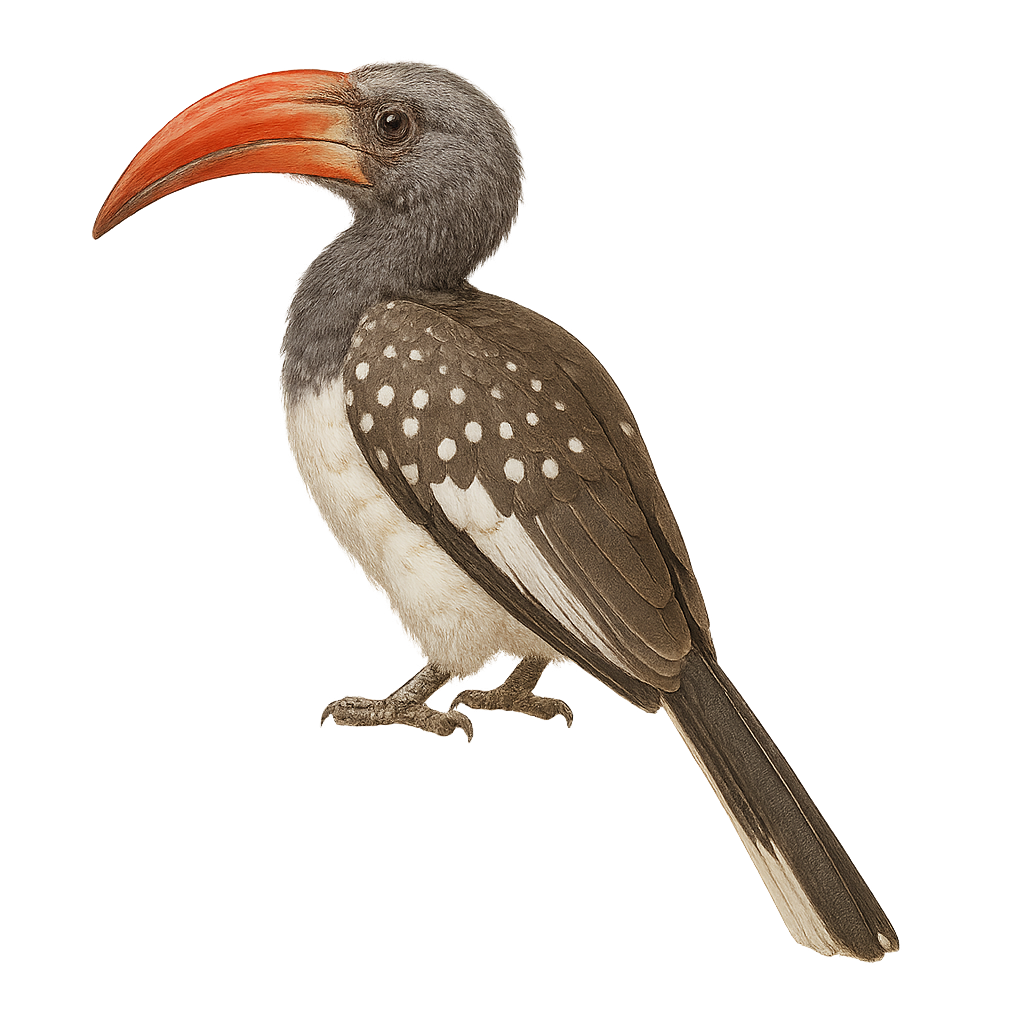
The Von der Decken's Hornbill, scientifically known as Tockus deckeni, is a captivating bird native to East Africa, particularly Tanzania and Kenya. This hornbill is characterized by its striking black and white plumage and a large, often reddish bill in males. It primarily inhabits dry savannas, open woodlands, and bushy areas. These birds are known for their social behavior and tendency to live in small groups. They primarily feed on insects, fruits, and small reptiles. Their calls are often heard at dawn and dusk, marking their territory. The Von der Decken's Hornbill plays a crucial role in its ecosystem by aiding in seed dispersal.
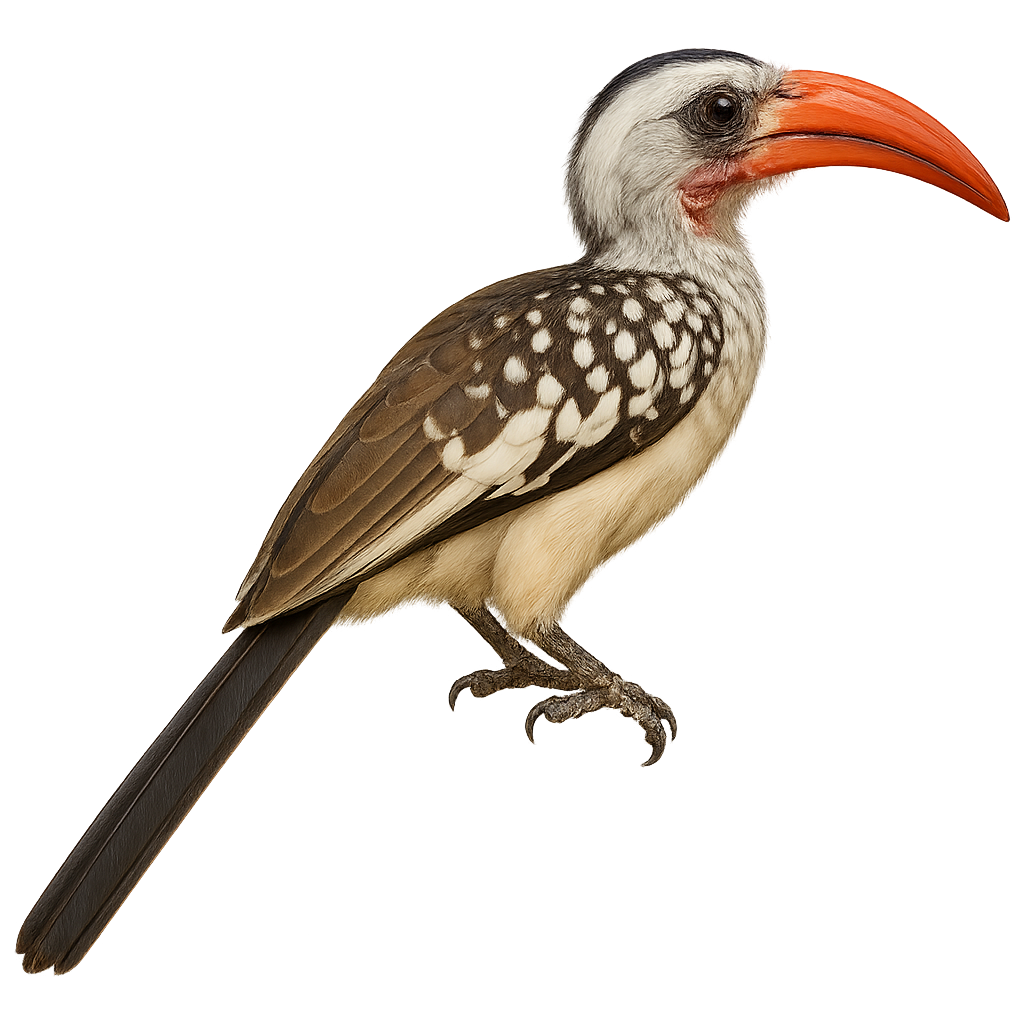
The Indian Grey Hornbill, or Ocyceros birostris, is a small grey hornbill native to wooded and semi-open areas of the Indian subcontinent. It is identified by its uniform grey plumage, black tail with white edges, and a curved two-toned bill—orange at the base and black at the tip. Found in dry forests, farmlands with trees, and even urban areas in India and Sri Lanka, it is usually seen in pairs or family groups, calling with sharp, screeching sounds. Its diet includes fruits, insects, and occasionally small vertebrates. The Indian Grey Hornbill is common and adapts well to human-altered landscapes.
The Western Long-tailed Hornbill, or Horizocerus granti, is a captivating bird belonging to the Bucerotidae family. It is recognized by its striking black and white plumage and long tail. This bird is primarily found in the tropical forests of West Africa, where it feeds on fruits, insects, and small animals. The Western Long-tailed Hornbill is a social bird, often seen in small groups. Its distinctive call echoes through the canopy, adding an auditory layer to its lush habitat. Although its conservation status is currently concerning, it plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, contributing to the health of its ecosystem.
The Hartlaub's Duck is a fascinating bird belonging to the Bucerotidae family. It is recognizable by its glossy black plumage and distinctive bill, often adorned with white markings. This hornbill primarily inhabits the humid tropical forests of West Africa, where it feeds on fruits, insects, and small animals. Its social behavior is interesting, as it often lives in small family groups. The calls of the Hartlaub's Duck are powerful and resonant, playing a crucial role in communication among group members. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, this bird is currently classified as of least concern by the IUCN.
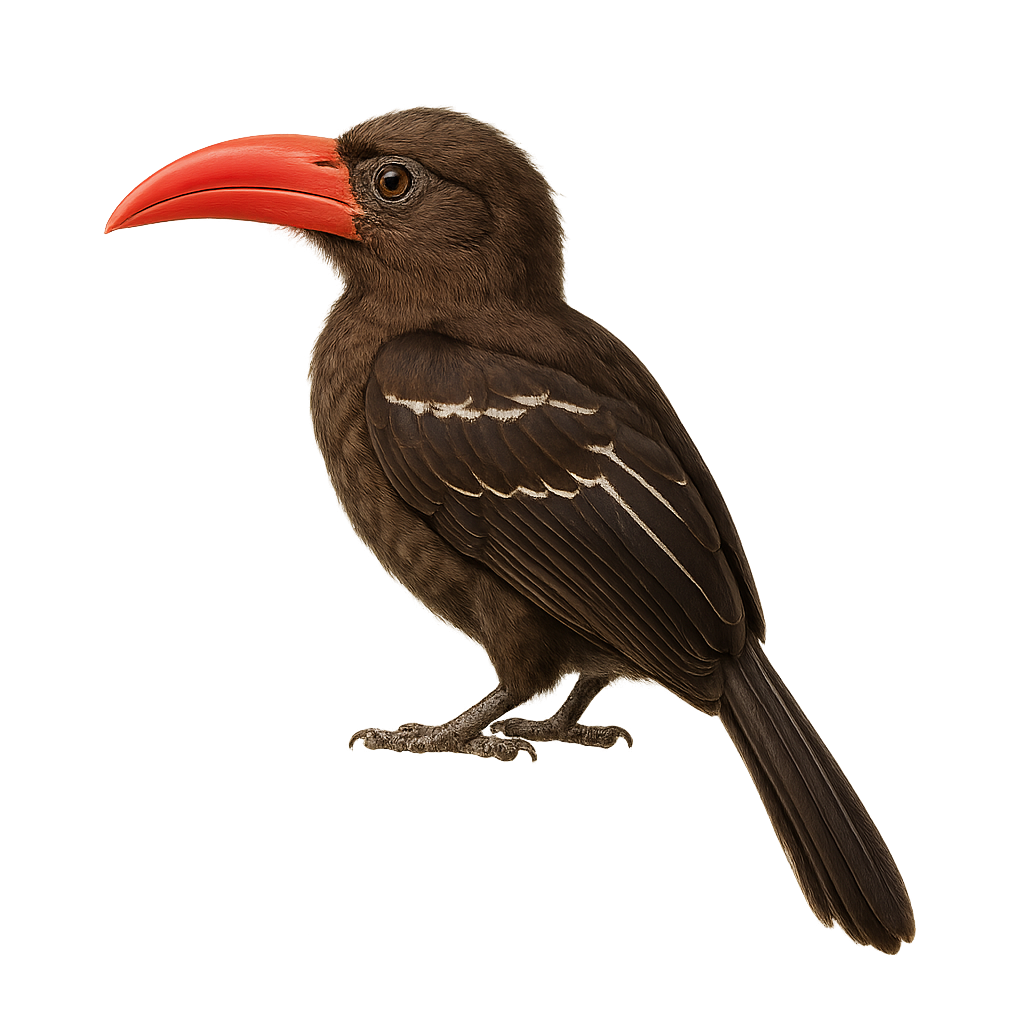
The Hemprich's Hornbill is a fascinating bird, recognizable by its large bill and slender silhouette. It has predominantly black plumage with metallic sheen, contrasting with its white and red bill. This hornbill is often seen in pairs or small groups, moving nimbly through trees. It primarily inhabits the arid and semi-arid regions of East Africa, notably in Ethiopia, Somalia, and Kenya. Its diet is varied, consisting of fruits, insects, and small vertebrates. The Hemprich's Hornbill plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, thus contributing to forest regeneration.
The Jackson's Hornbill is a fascinating bird, endemic to certain regions of East Africa. It is distinguished by its large bill and vibrant coloration, with shades of black, white, and red. This hornbill prefers wooded habitats and savannas, where it primarily feeds on insects, fruits, and small vertebrates. Known for its social behavior, it often lives in small family groups. The breeding period is marked by a unique nesting ritual, where the female is sealed inside a tree cavity by the male, who feeds her throughout the incubation period. This species is currently considered vulnerable due to habitat loss and hunting.
The Kemp's Hornbill, or Tockus kempi, is a fascinating bird belonging to the Bucerotidae family. This medium-sized hornbill is primarily found in West Africa, particularly in dry forests and wooded savannas. It is distinguished by its contrasting black and white plumage and its impressive bill, often adorned with a characteristic casque. The Kemp's Hornbill is a diurnal bird, active mainly in the morning and late afternoon. It primarily feeds on fruits, insects, and occasionally small vertebrates. Its social behavior is interesting, as it often lives in small family groups. The breeding season varies by region but is generally influenced by the rainy season.
The Malabar Pied Hornbill, or Anthracoceros coronatus, is a captivating bird found in the humid tropical forests of the Indian subcontinent. Recognizable by its large bill adorned with a wavy casque, it sports a distinctive black and white plumage. This sociable bird often lives in small groups and primarily feeds on fruits, but also consumes insects and small vertebrates. It plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding forest regeneration. Malabar Pied Hornbills are monogamous and nest in tree cavities, where the female is sealed in during the nesting period, leaving only a small opening for the male to feed her. Although their population is stable, deforestation poses a threat to their natural habitat.
The Monteiro's Hornbill is a captivating bird, endemic to the arid regions of southwestern Africa, mainly in Namibia and Angola. It is distinguished by its long, curved, bright red bill and contrasting black and white plumage. This bird measures about 54 cm in length and weighs between 200 and 300 grams. It is often seen in pairs or small groups, feeding primarily on insects, fruits, and small reptiles. The Monteiro's Hornbill is known for its complex social behaviors, especially during the breeding season when the male feeds the female while she incubates the eggs in a sealed nest. Although its habitat is limited, it is not currently considered threatened.
The Damara Red-billed Hornbill is a fascinating bird, easily recognizable by its large bill and contrasting coloration. It sports primarily black and white plumage, with shades of gray on the wings. This bird is endemic to the arid regions of southwestern Africa, particularly in Namibia and Angola. It is often seen in small groups, exploring savannas and wooded areas in search of food. Its diet is varied, including insects, fruits, and occasionally small vertebrates. The Damara Red-billed Hornbill is also known for its complex social behaviors, especially during the breeding season when pairs are particularly attentive to each other.
The Ruaha Hornbill, Tockus ruahae, is a captivating bird native to the semi-arid regions of East Africa, particularly in Tanzania. This hornbill is notable for its large bill and vibrant coloration, featuring shades of black, white, and red. It is often seen in small groups or pairs, exploring savannas and dry forests in search of food. Its diet is varied, including fruits, insects, and occasionally small vertebrates. The Ruaha Hornbill plays a crucial role in its ecosystem, particularly in seed dispersal from the fruits it consumes. Although its conservation status is not currently concerning, deforestation and habitat loss could pose future threats to its populations.
The Sulawesi Hornbill, or Rhabdotorrhinus exarhatus, is a medium-sized hornbill endemic to Sulawesi Island in Indonesia. It is recognized by its black-and-white plumage, ivory bill with a red casque, and the vivid coloration of its throat: orange in males and pale blue in females. This hornbill inhabits lowland and mid-elevation rainforests and is usually seen in pairs or small groups. It feeds mainly on fruits, but also consumes insects and small animals. The Sulawesi Hornbill is impacted by habitat loss but remains locally common in some protected areas.
The Wreathed Hornbill, Rhyticeros undulatus, is a striking bird known for its large size and distinctive appearance. It features a prominent casque on its large bill, often colorful, which is used to amplify calls. Males and females exhibit marked sexual dimorphism, with males having a bright yellow throat and females a blue one. This bird primarily inhabits the tropical forests of Southeast Asia, playing a crucial role in seed dispersal due to its frugivorous diet. The Wreathed Hornbill is a social bird, often seen in small groups. However, it is threatened by deforestation and hunting, leading to population declines in some areas.
The Malabar Grey Hornbill, or Ocyceros griseus, is a captivating bird native to the lush forests of India. It is characterized by its ash-grey plumage and prominent, slightly curved bill, giving it a majestic appearance. This bird measures about 45 to 58 cm in length and weighs between 200 and 400 grams. Primarily frugivorous, it feeds on various fruits but can also consume insects and small vertebrates. The Malabar Grey Hornbill is often seen in pairs or small family groups, moving agilely through the canopy. Although relatively common in its natural habitat, it is threatened by deforestation and habitat loss.