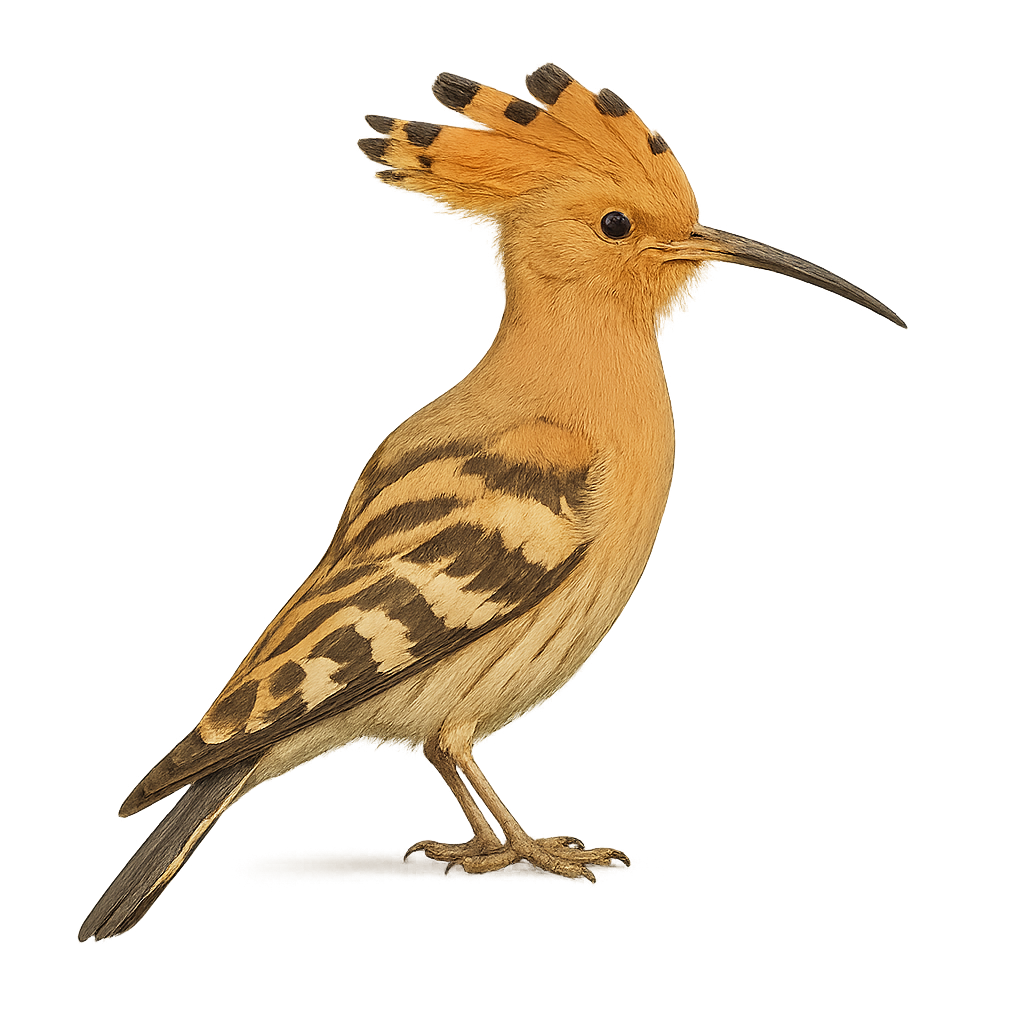
The Eurasian Hoopoe is a bird with a spectacular plumage, easily recognizable by its colorful crest of feathers that it raises in the shape of a tuft on its head. It measures about 25 to 29 cm in length, with a wingspan of 44 to 48 cm, and weighs between 40 and 70 g. Its plumage is primarily light beige, with black and white stripes on the back and wings, and its beak is long, thin, and slightly curved, ideal for probing the ground in search of insects and other small prey. The Eurasian Hoopoe primarily inhabits open areas, such as grasslands, orchards, forest edges, and cultivated areas across Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It mainly feeds on insects, such as ants, termites, and larvae, which it catches by probing the ground. This bird is an excellent flier, capable of flying long distances with powerful wingbeats. Although the species is not endangered, it is vulnerable to habitat loss and the intensification of agriculture.
The Hadada Ibis, or Bostrychia hagedash, is a medium-sized bird known for its metallic brown-green plumage and distinctive call, often heard at dusk. Native to sub-Saharan Africa, it inhabits wetlands, grasslands, and open forests. This gregarious bird primarily feeds on insects, worms, and small invertebrates, which it probes from the ground with its long, curved bill. It is often seen in groups, especially during breeding seasons. Although generally tolerant of human presence, it can become wary if disturbed. The Hadada Ibis plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by controlling insect populations and aiding in seed dispersal.
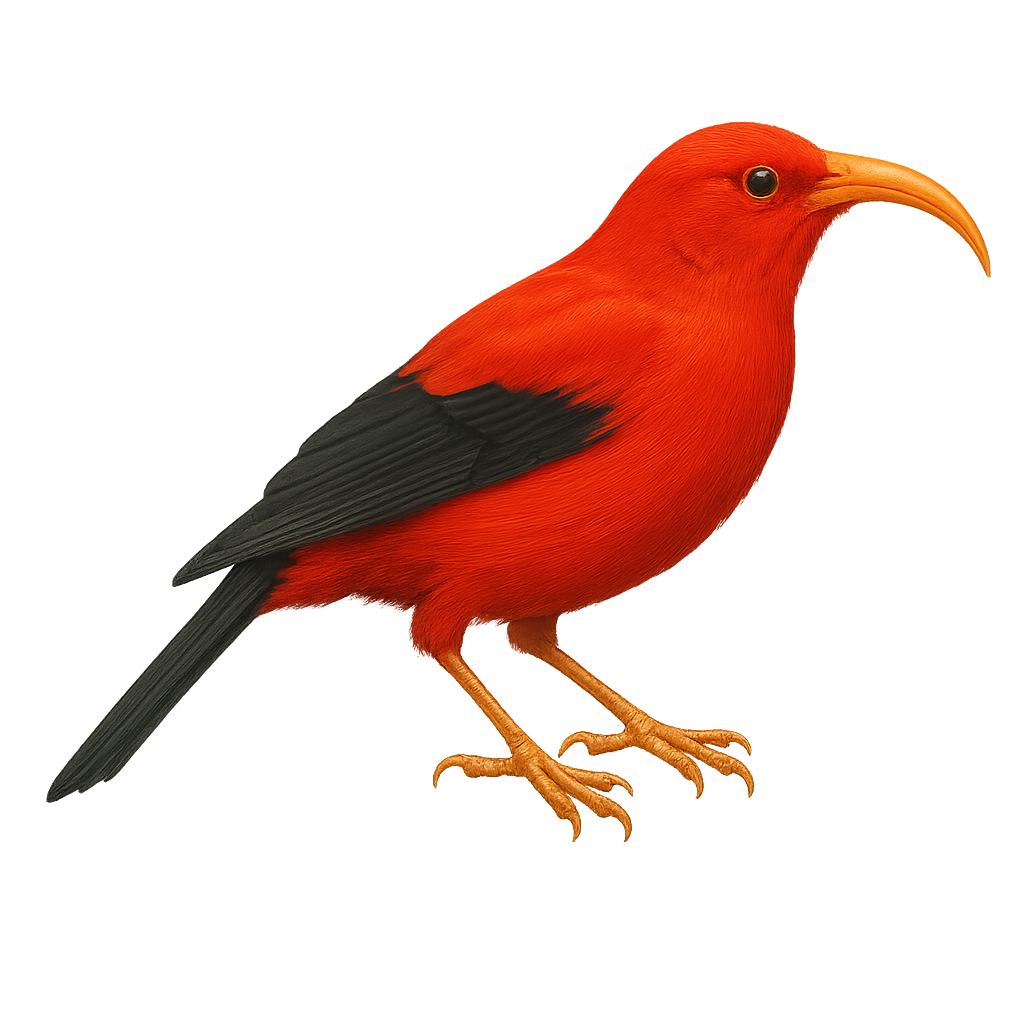
The iiwi, or Drepanis coccinea, is an iconic bird of the Hawaiian forests. With its bright red plumage and black wings, it is easily recognizable. This bird measures about 15 cm in length and has a curved beak, adapted for collecting nectar, its primary food source. The iiwi plays a crucial role in pollinating native plants. Unfortunately, it is threatened by habitat loss, avian diseases, and introduced predators. Conservation efforts aim to protect its natural habitats and control invasive species. The iiwi is often observed in wet forests at various altitudes, where it moves agilely in search of flowers.
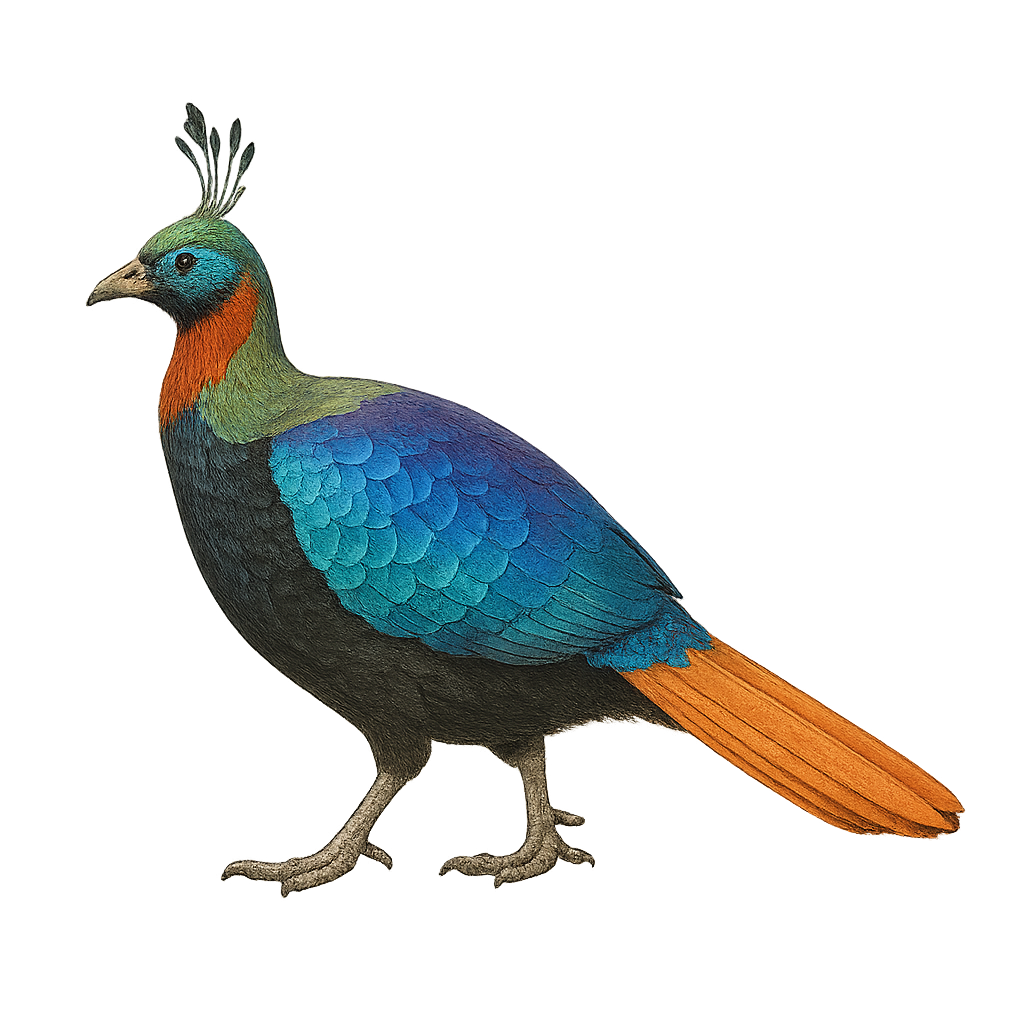
The Himalayan Monal, or Lophophorus impejanus, is a striking bird native to the mountainous regions of the Himalayas. Known for its iridescent plumage, the male displays a dazzling array of metallic blues, greens, and purples, while the female is more subdued with mottled brown feathers for camouflage. These birds inhabit coniferous forests and alpine meadows, feeding on roots, tubers, and insects. Although capable of flight, they prefer to walk or run on the ground. Their call is a sharp, resonant cry that echoes through the mountain valleys.
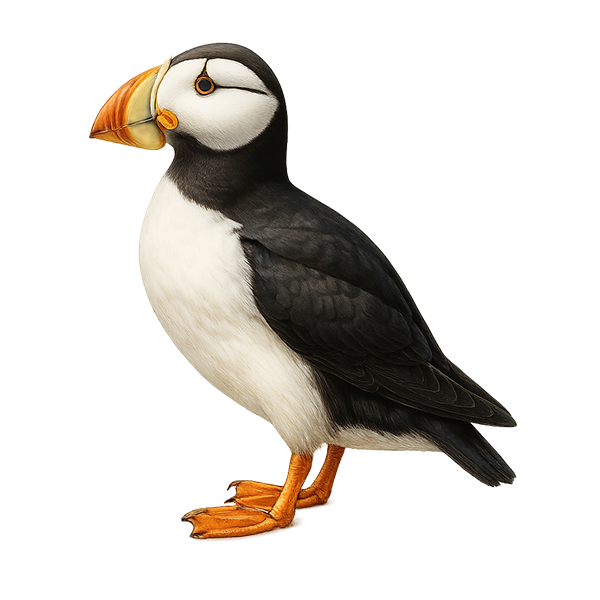
The Horned Puffin, Fratercula corniculata, is a striking seabird known for its colorful bill and distinctive black feather "horns" above its eyes. It primarily inhabits the northern Pacific coasts, especially in Alaska and eastern Russia. This bird is well adapted to marine life, spending most of its time at sea, feeding on fish and small invertebrates. During the breeding season, it nests in rocky crevices on steep cliffs. The Horned Puffin is an excellent diver, capable of descending several tens of meters underwater to catch its prey. Although its populations are currently stable, it is sensitive to climate change and marine pollution.
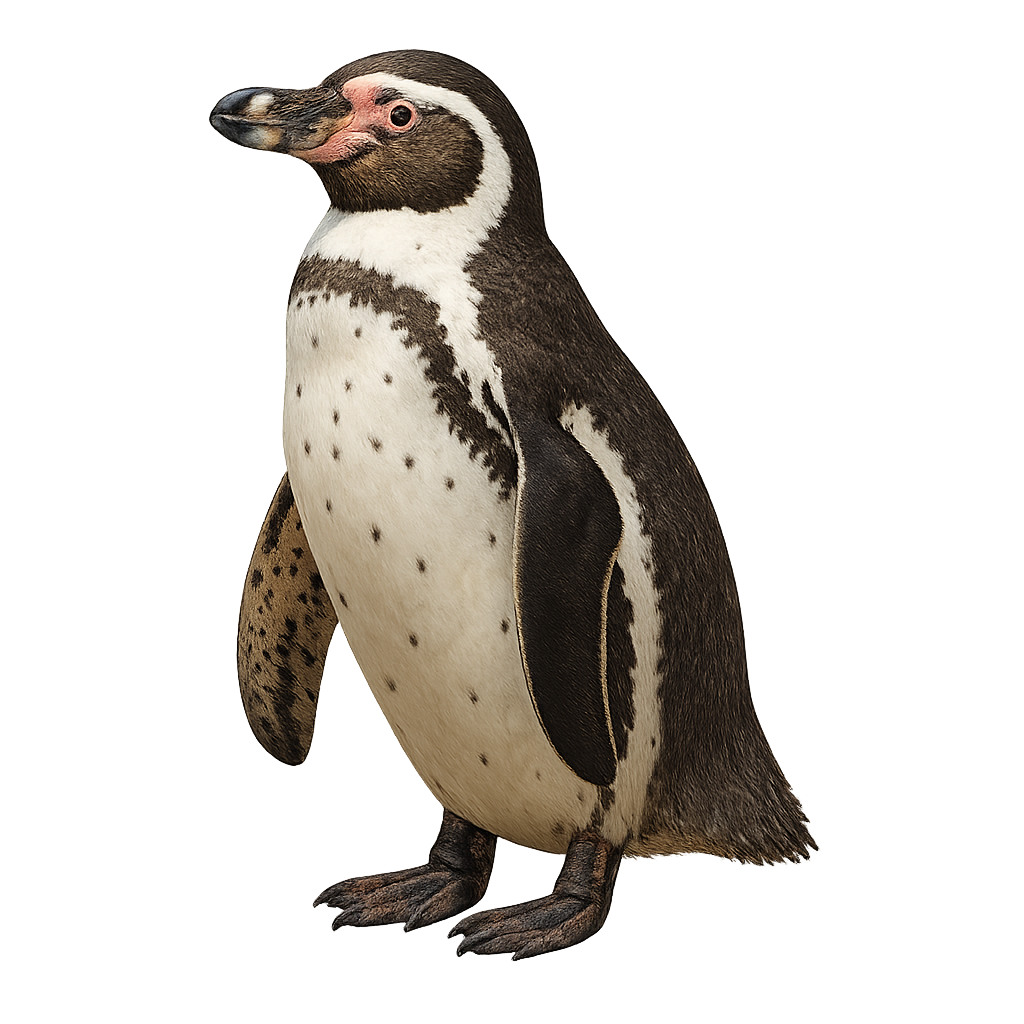
The Humboldt penguin is a medium-sized penguin (56–70 cm, 2.9–6 kg) with dark grey upperparts, a white belly, and a black head bordered by a white band around the eye. It is endemic to the Pacific coast of South America (Peru and Chile), nesting in guano burrows, rocky crevices, and coastal caves. Social, it forms small colonies on islands and coastal cliffs.
The Hispaniolan Mango, or Anthracothorax dominicus, is a captivating bird primarily found on the island of Hispaniola, shared by Haiti and the Dominican Republic. This hummingbird is recognizable by its vibrant plumage, featuring metallic green and blue hues. Males often display an iridescent throat, while females are slightly duller. They primarily feed on nectar but also consume small insects to supplement their diet. These birds are often seen in gardens, tropical forests, and wooded areas, where they play a crucial role in plant pollination. Their fast and agile flight is a spectacle to behold, especially when they defend their territory against other hummingbirds.
The Melidora macrorrhina, commonly known as the Hook-billed Kingfisher, is a fascinating bird native to the tropical forests of New Guinea. This kingfisher is distinguished by its unique, wide, and flattened bill, which allows it to effectively capture aquatic prey. It sports a vibrant plumage with shades of blue, green, and white, giving it an elegant appearance. This bird prefers dense, humid habitats where it can hide among the foliage while watching for prey. Although primarily solitary, it is sometimes observed in small family groups. Its discreet presence and suspicious behavior make it difficult to spot, but it is a true gem for birdwatchers and passionate photographers.
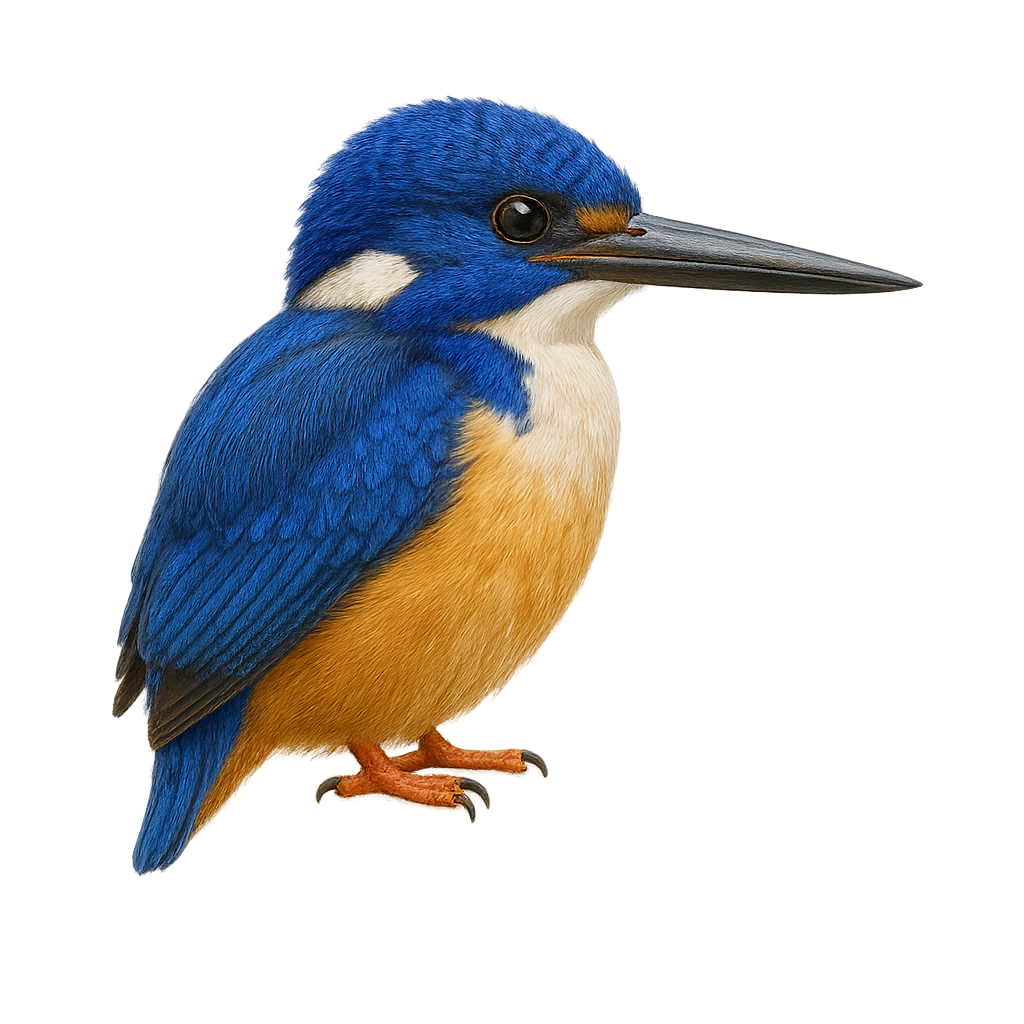
The Half-collared Kingfisher, Alcedo semitorquata, is a captivating bird found in the tropical regions of sub-Saharan Africa. It is notable for its vibrant blue plumage on the back and wings, contrasting with a white belly and a blue chest band. Its head features a dark blue crown, and its long black bill is perfect for catching fish, its primary food source. This kingfisher inhabits rivers, lakes, and wetlands, where it can be seen perched on branches overhanging the water, ready to dive for its prey. Though discreet, it is often detected by its sharp, piercing call.
The Lophotriccus galeatus, or Helmeted Pygmy-Tyrant, is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is recognizable by its distinctive crest, often raised, giving it a unique appearance. Its plumage is primarily olive green with yellowish tones on the belly. This bird mainly inhabits the humid tropical forests of South America, especially in Brazil, Colombia, and Venezuela. It is often observed in dense undergrowth where it feeds on insects. Despite its small size, it is very active and agile, moving quickly through the foliage. Its song is a high-pitched trill that resonates in the canopy.
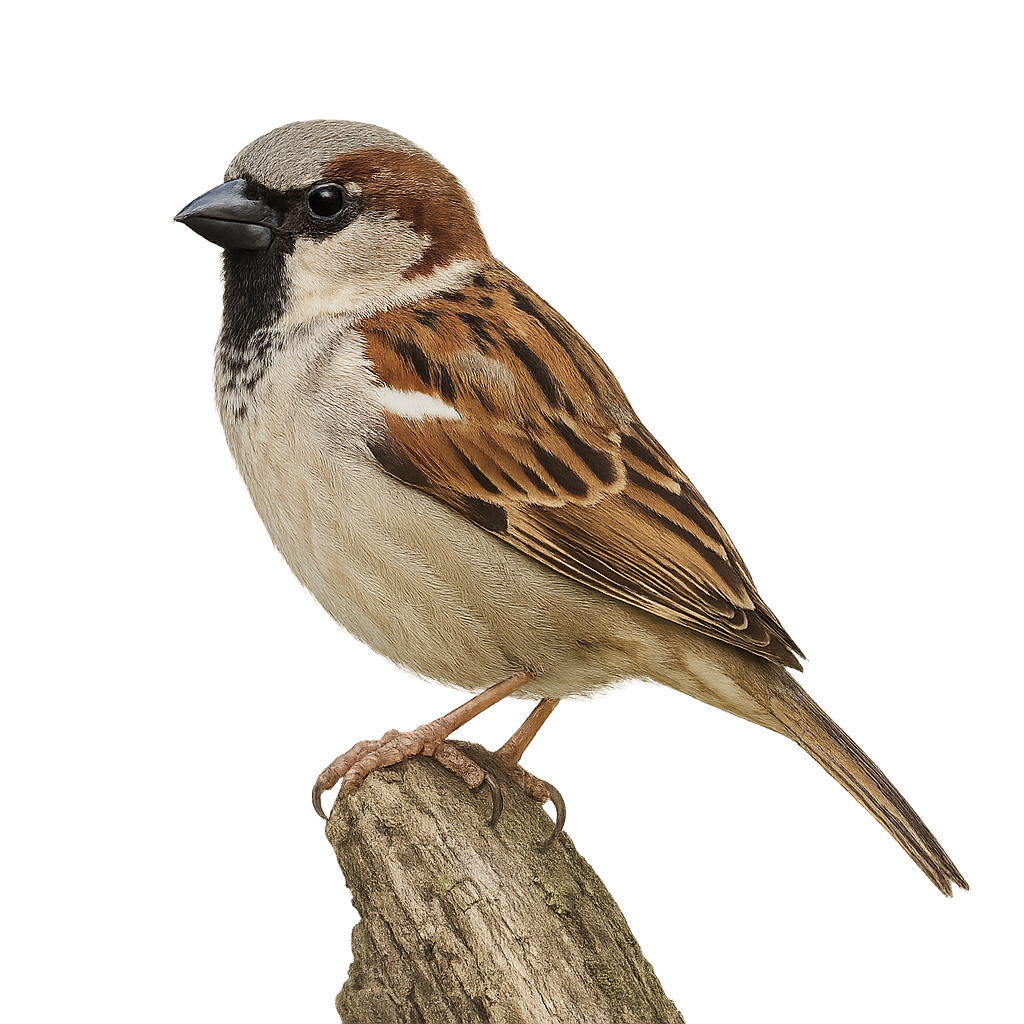
The house sparrow is a very common small bird, found primarily in urban environments, gardens, fields, and parks. It is easily recognized by its brown plumage, grey head, and black markings on its back and chest. This passerine bird is omnivorous, feeding on seeds, insects, and food scraps. Although highly social and often seen in large numbers, the house sparrow is in decline in some regions due to habitat loss and climate change.
The Hammond's Flycatcher, or Empidonax hammondii, is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in the coniferous forests of North America, especially in mountainous regions. This flycatcher is characterized by its gray-olive plumage, lighter belly, and wings marked with two white wing bars. Its beak is relatively short and dark, suitable for its insectivorous diet. During the breeding season, it builds its nest in trees, often at considerable heights. Its song is a key element for identification, consisting of a series of high-pitched, repetitive notes. Although discreet, it is often detected by its distinctive song.
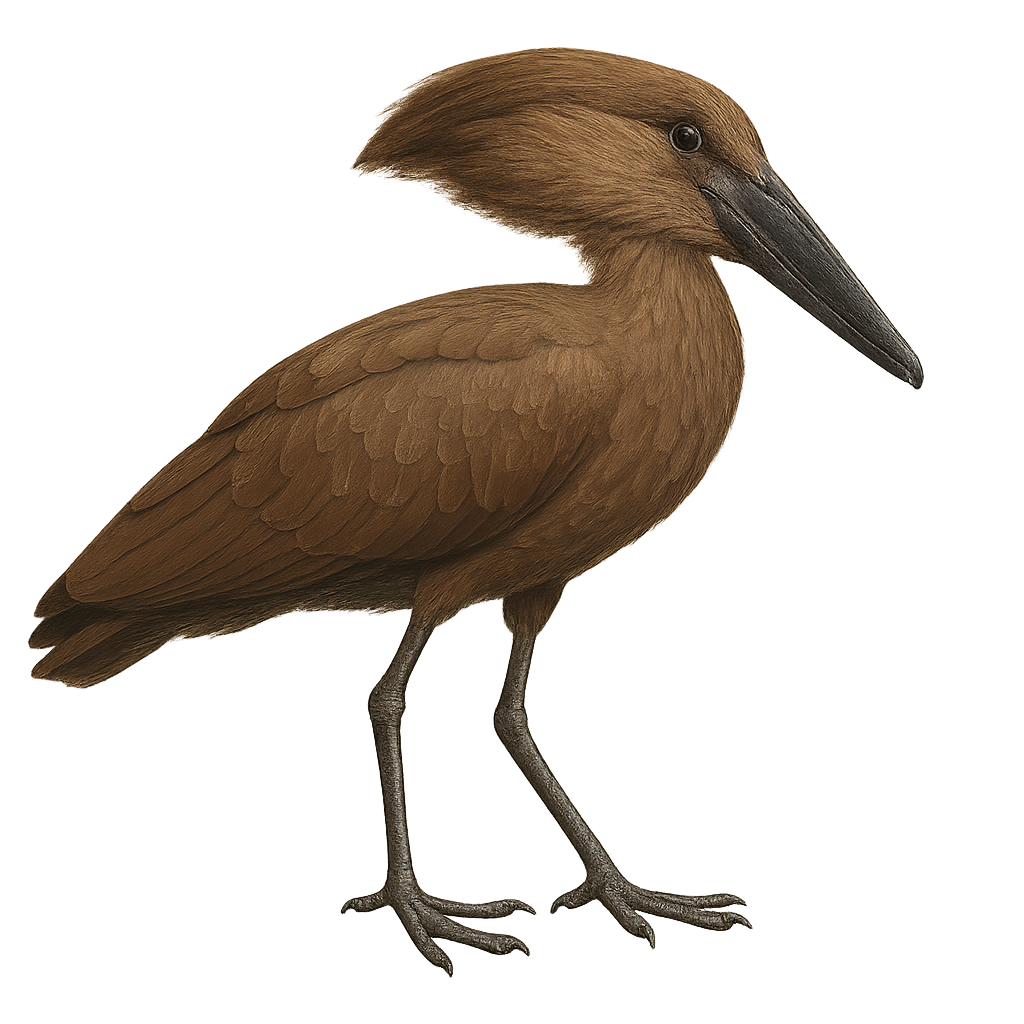
The Hamerkop, or Scopus umbretta, is a unique and fascinating bird, recognizable by its distinctive hammer-shaped head. It measures about 50 cm in length and has a uniform brown plumage. This bird is often seen near water bodies in sub-Saharan Africa, where it builds massive nests weighing up to 50 kg. The Hamerkop is a gregarious bird, often seen in small groups, and feeds primarily on fish, amphibians, and aquatic insects. It is known for its elaborate courtship behavior, which includes dances and twig offerings. Although its conservation status is currently "least concern," habitat degradation could pose future threats.
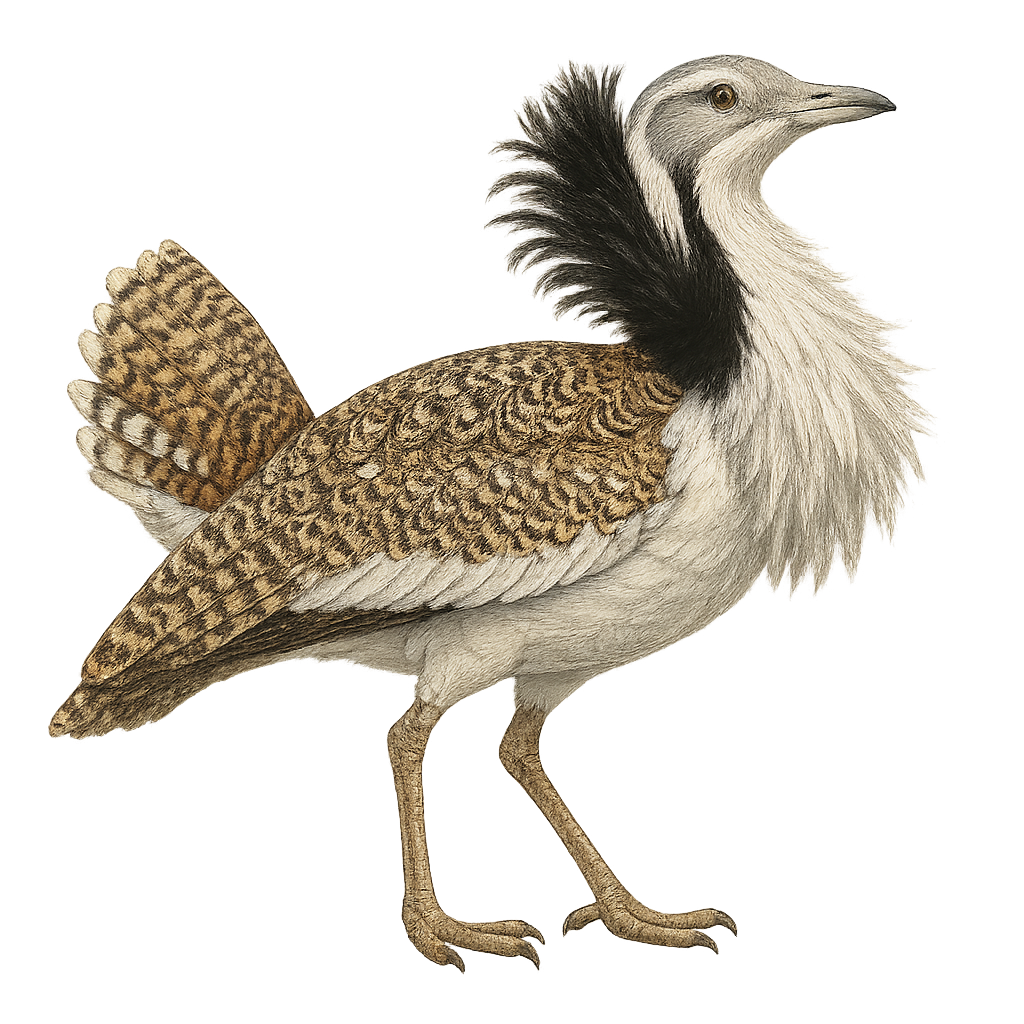
The Houbara bustard, Chlamydotis undulata, is a medium-sized bird known for its sandy-brown plumage, which provides excellent camouflage in desert landscapes. It features a distinctive crest of black and white feathers on its head and neck. This primarily terrestrial bird prefers running to flying when escaping predators. Its diet consists mainly of plants, insects, and small reptiles. The Houbara bustard is famous for its spectacular courtship displays, where the male fans out his feathers to attract a mate. It inhabits the arid and semi-arid regions of North Africa, the Middle East, and Central Asia. Unfortunately, this species is threatened by excessive hunting and habitat loss.
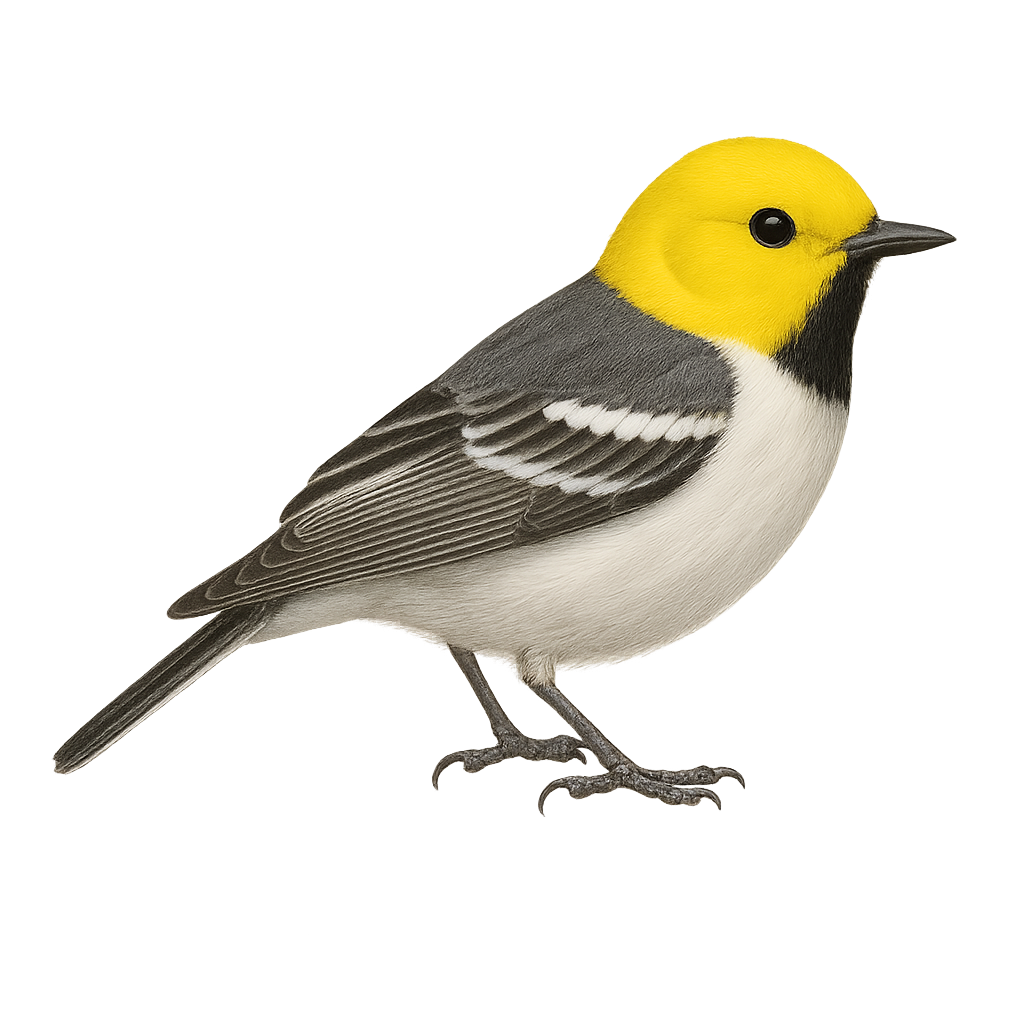
The Hermit Warbler is a small songbird in the Parulidae family, easily identified by its distinctive plumage. It has a black back, wings striped with white, and a black throat contrasting with its white belly. Males display a yellow spot on the cheek, while females have a duller hue. It primarily inhabits coniferous and mixed forests in western North America. A migratory bird, it winters in the southwestern United States and Mexico. Its song is a soft, melodious trill, often heard in spring. It feeds mainly on insects, which it catches by flitting agilely among branches.
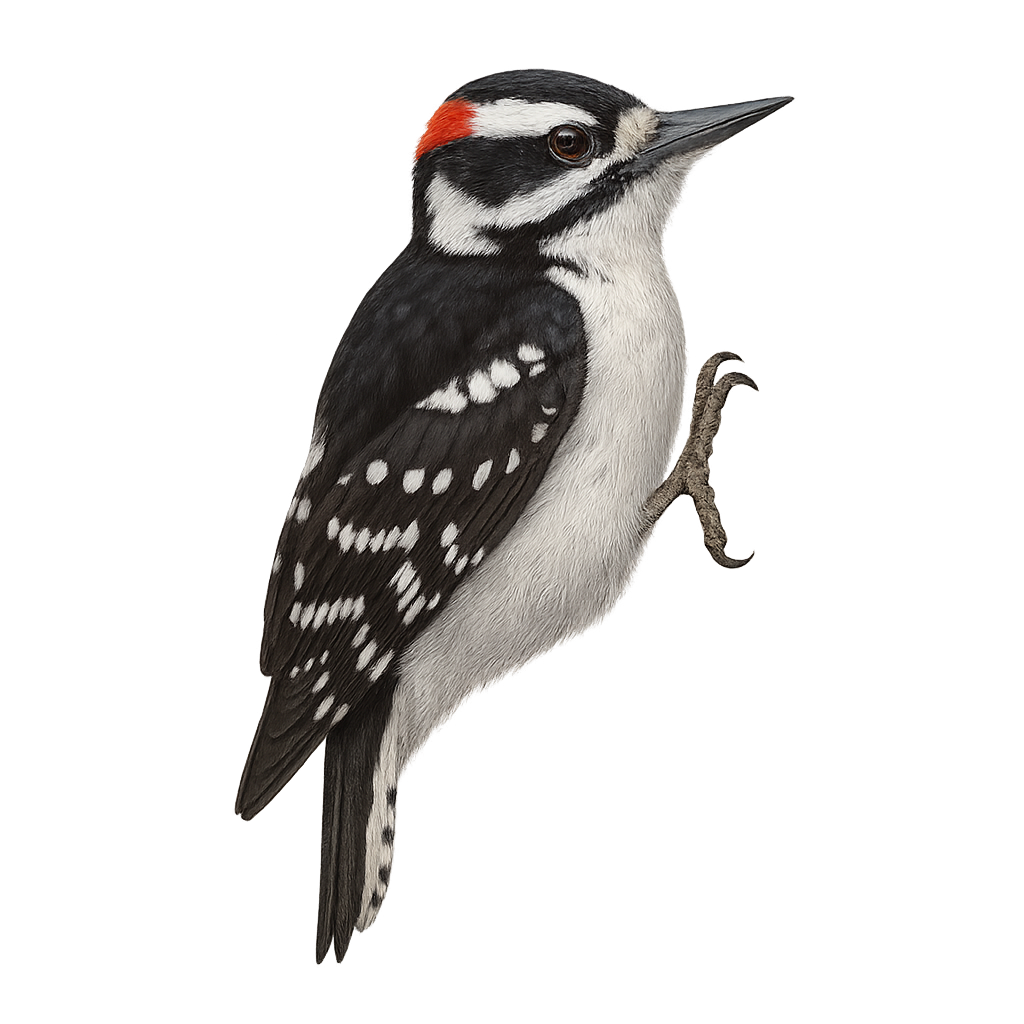
The Hairy Woodpecker, or Picoides villosus, is a medium-sized bird easily recognized by its distinctive black and white plumage. It features a white stripe down its back and wings speckled with white. Males have a small red patch on the back of their heads. This bird is widespread across North America, primarily inhabiting deciduous and coniferous forests. It feeds mainly on insects, which it dislodges by hammering tree trunks with its powerful beak. The Hairy Woodpecker is often mistaken for the Downy Woodpecker but is generally larger with a longer bill. It plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by controlling pest insect populations.
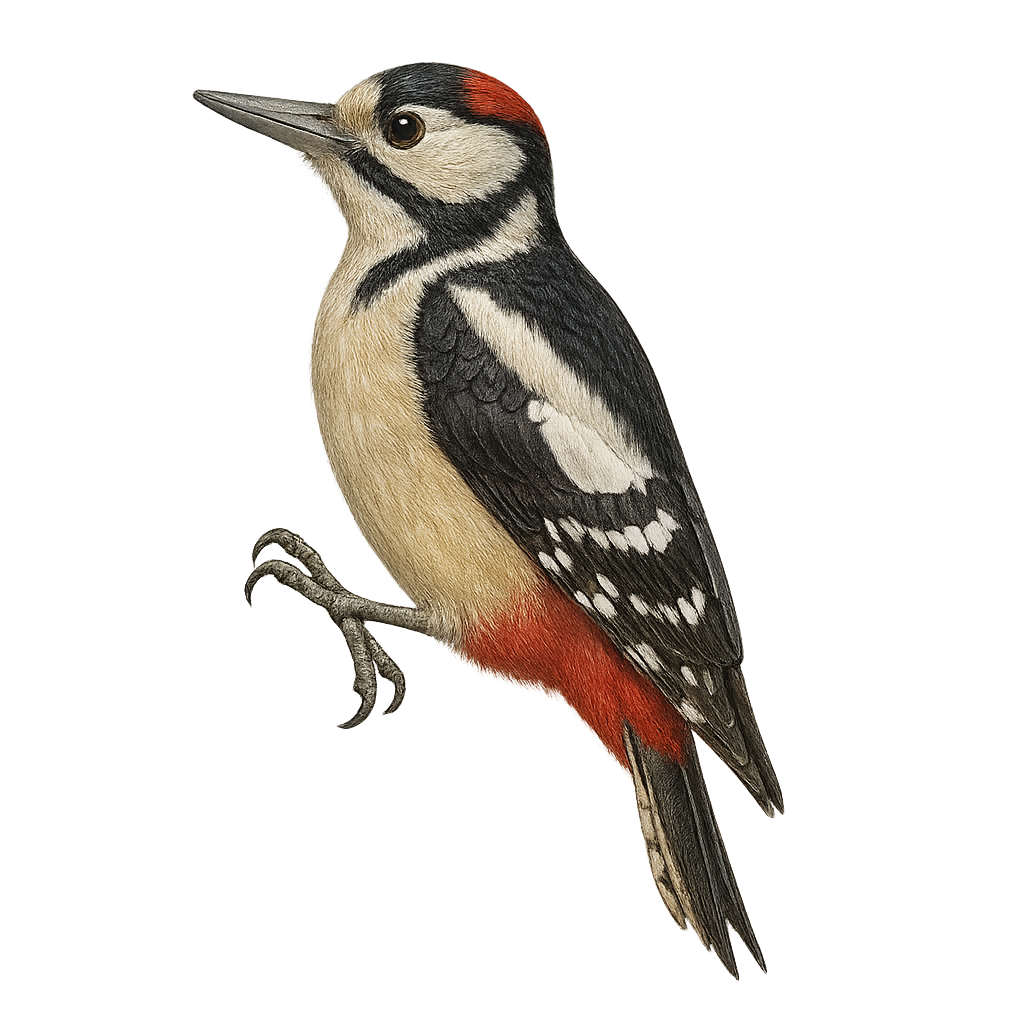
The Himalayan Woodpecker, Dendrocopos himalayensis, is a captivating bird primarily inhabiting the coniferous and mixed forests of the Himalayan mountain regions. This medium-sized bird, measuring about 25 cm in length, is distinguished by its striking black and white plumage, with a red crown in males. It is often seen drumming on tree trunks in search of insects, its main food source. Although primarily insectivorous, it may also consume seeds and berries. The Himalayan Woodpecker is a diurnal bird, active mainly during the day, and is known for its territorial behavior, vigorously defending its territory against intruders.
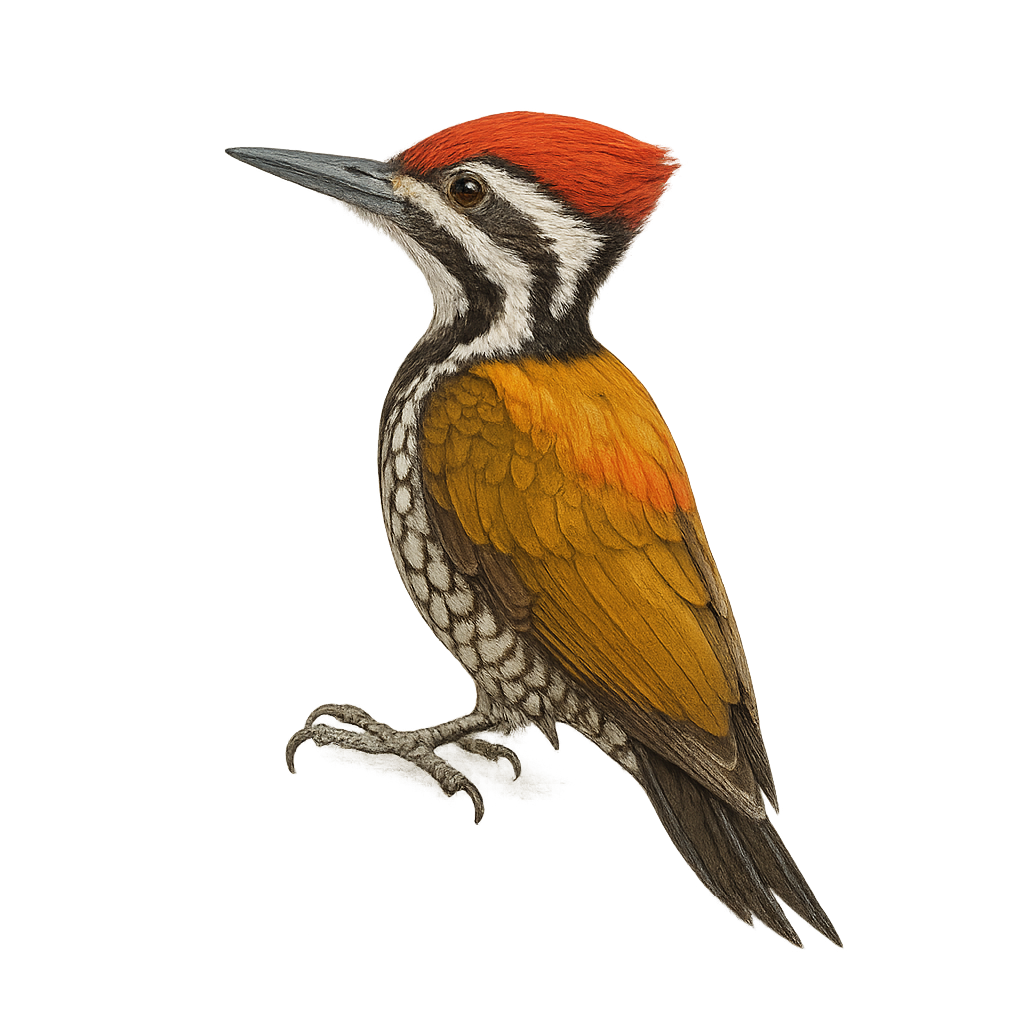
The Himalayan Flameback, or Dinopium shorii, is a captivating bird from the Picidae family, known for its striking plumage and distinctive patterns. It features a brilliant golden back, contrasting with a bright red head in males, while females have a black cap. This bird is primarily found in the subtropical and tropical moist forests of the Indian subcontinent, where it feeds on insects dislodged from tree bark with its strong beak. The Himalayan Flameback is a diurnal bird, active mainly during the day. Although generally suspicious, it can sometimes be spotted at altitudes ranging from 200 m to 1500 m. Its population is currently stable, and it is classified as "least concern" by the IUCN.
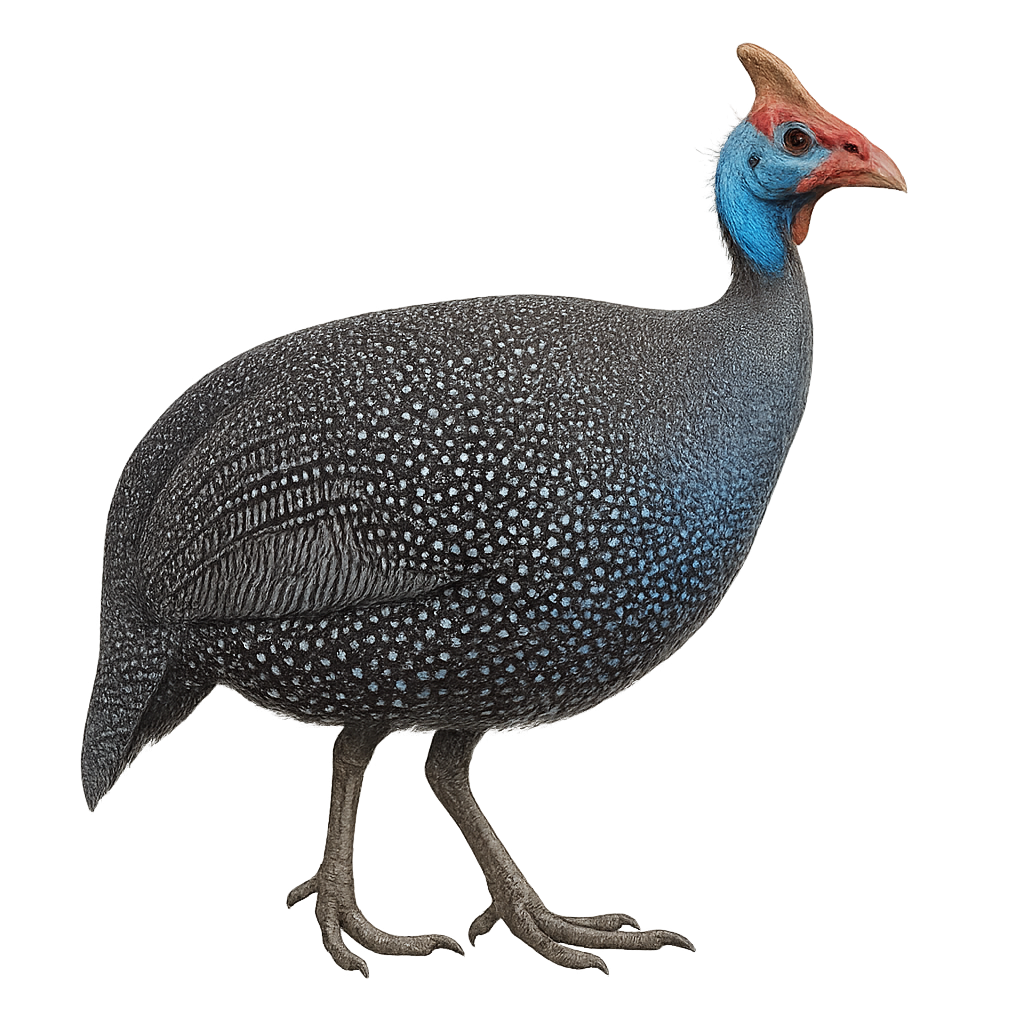
The helmeted guineafowl, Numida meleagris, is a terrestrial bird native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is easily identified by its black plumage speckled with white and its bare head topped with a bony casque. This social bird lives in groups and feeds mainly on seeds, insects, and small invertebrates. Known for its adaptability, it thrives in various habitats, from savannas to open forests. It plays a crucial role in controlling pest insect populations. Although often domesticated for its meat and eggs, it remains suspicious in the wild.
The Hepatic Tanager, or Piranga flava, is a colorful bird primarily found in the forests and woodlands of Central and South America. This bird is easily recognizable by its bright red plumage in males, while females display more yellowish and greenish hues. It primarily feeds on insects and fruits, playing a crucial role in seed dispersal. The Hepatic Tanager is a sociable bird, often seen in small groups or pairs. It is also known for its melodious and varied song that echoes through the forests. Although it is quite tolerant of human presence, it prefers natural habitats away from disturbances.
The Hooded Plover, or Thinornis cucullatus, is a coastal bird endemic to Australia, easily identifiable by its distinctive plumage. It features a black head contrasting with its white and grey body, and a black band around its neck, giving it its name. This small bird, measuring about 20 cm in length, is often seen on sandy beaches and dunes, where it primarily feeds on marine invertebrates. Unfortunately, its habitat is threatened by human activity, leading to a decline in its population. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure its survival.
The Hooded Plover, or Thinornis melanops, is a coastal bird endemic to Australia, easily recognizable by its distinctive plumage. It features a black hood contrasting with its white belly and grey back. This bird prefers sandy beaches and dunes for nesting, making it vulnerable to human disturbances and introduced predators. Its modest size, about 20 cm long, and discreet behavior make it difficult to spot. The Hooded Plover is a threatened species, mainly due to habitat loss and human activities. Conservation efforts focus on protecting its nesting sites and raising public awareness of its precarious status.
The Hartert's Leaf Warbler, or Phylloscopus soror, is a small passerine bird belonging to the Phylloscopidae family. It is primarily found in the temperate and subtropical forests of East Asia, particularly in China and Vietnam. This warbler is characterized by its olive-green upperparts and lighter underparts, with pale eyebrows and a subtle wing bar. It is often mistaken for other warbler species due to its similar size and inconspicuous plumage. Its song is a rapid and melodious trill, often heard before the bird is visually spotted. It primarily feeds on insects, which it catches in dense foliage.
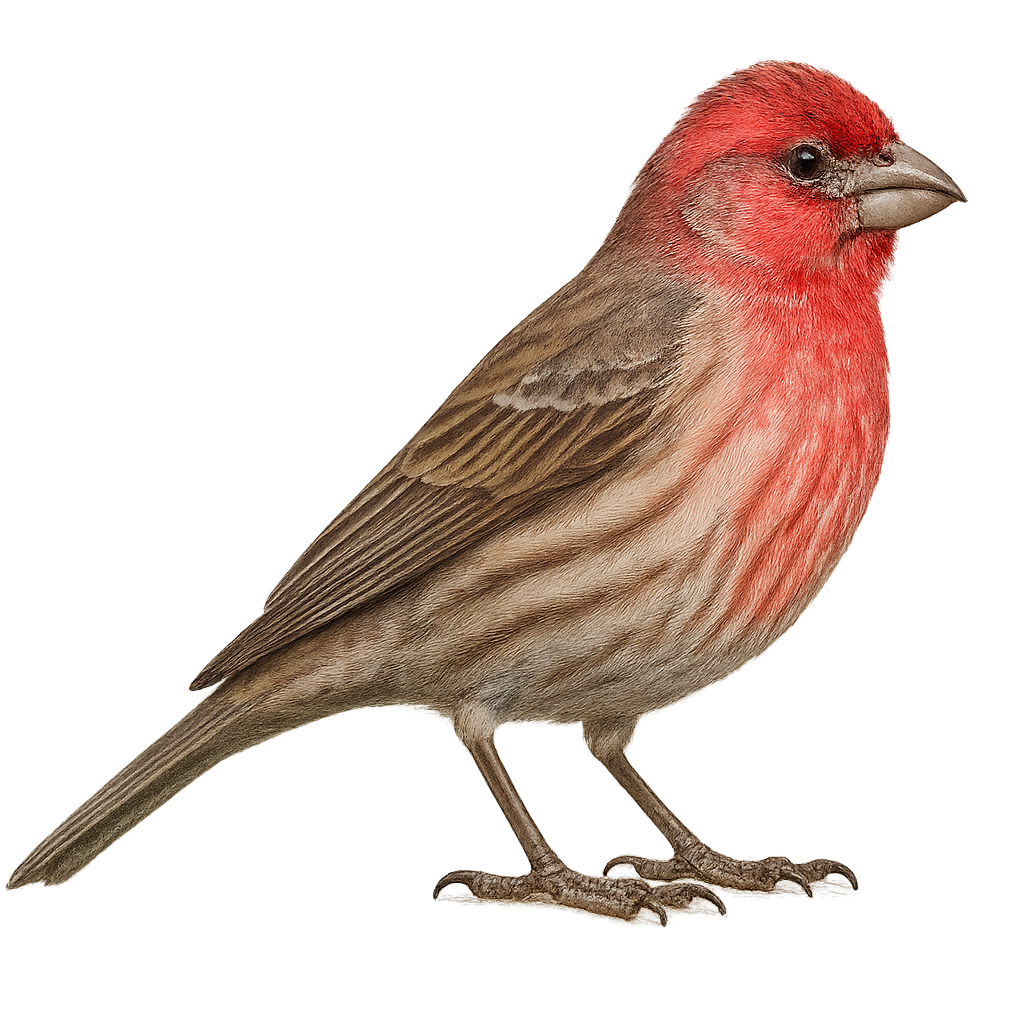
The House Finch, or Haemorhous mexicanus, is a small songbird native to North America. It is easily recognizable by its bright red plumage on the head, chest, and rump in males, while females display more subdued shades of brown and gray. These birds measure about 12 to 15 cm in length and have a wingspan of 20 to 25 cm. They are often seen in flocks, feeding on seeds, fruits, and occasionally insects. The House Finch is highly adaptable and can be found in various habitats, including urban areas, gardens, and open forests. It is known for its melodious song and ability to thrive in human-altered environments.
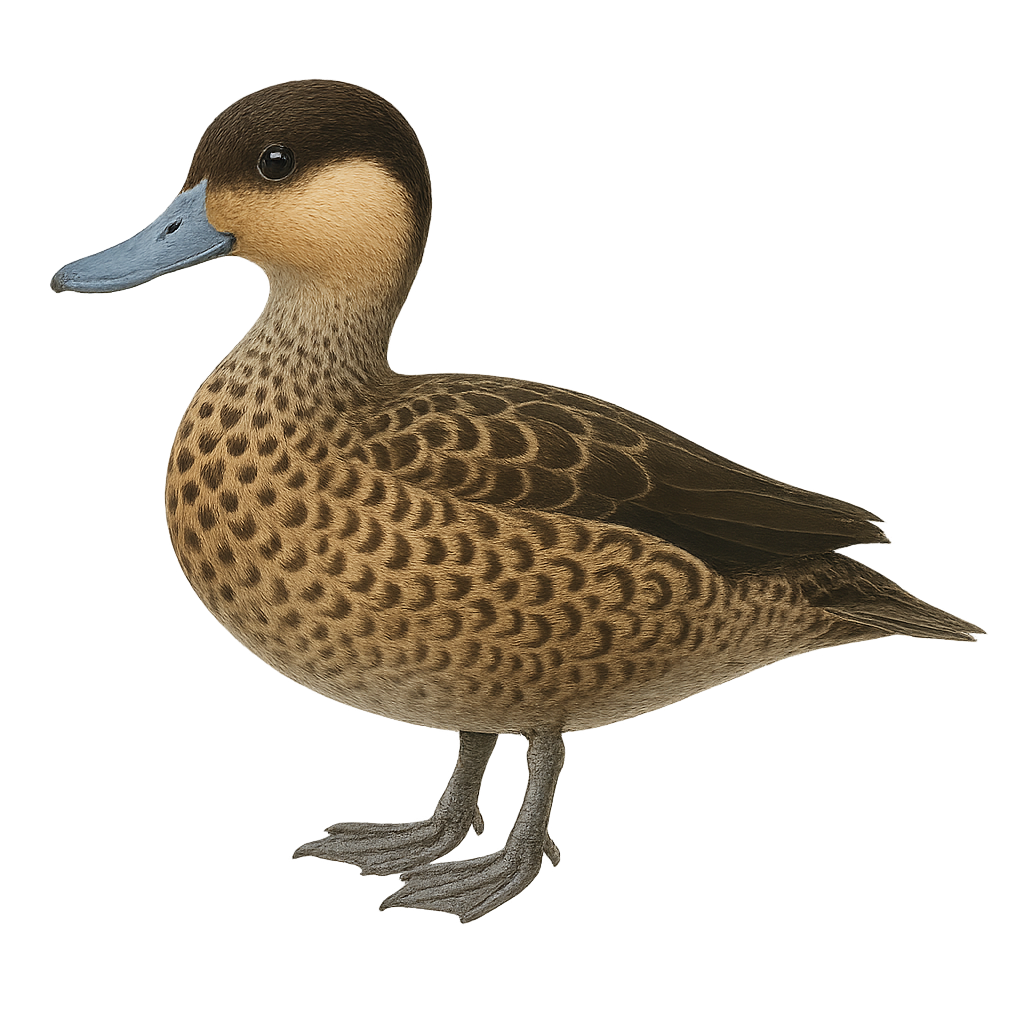
The Hottentot Teal, or Spatula hottentota, is a small dabbling duck found mainly in sub-Saharan Africa. It is characterized by its light brown plumage, wings with greenish sheen, and blue-grey bill. Males and females are similar, although males often have slightly brighter colors. This duck prefers wetlands, such as marshes, lakes, and rivers with dense vegetation. It is primarily herbivorous, feeding on seeds, aquatic plants, and insects. Although generally discreet, it can be seen in small groups, especially during the breeding season. Its call is a soft whistle, often heard at dusk.
The Highland Tinamou, or Nothocercus bonapartei, is a medium-sized ground bird belonging to the Tinamidae family. It is primarily found in the humid forests of the Andes, ranging from Venezuela to Bolivia. This elusive bird is more often heard than seen, due to its cryptic plumage that blends seamlessly into the dense undergrowth. It feeds mainly on fallen fruits, seeds, and insects. The Highland Tinamou is a solitary bird, although it can sometimes be observed in small groups. Its ability to run swiftly and fly short distances allows it to escape predators. Despite its elusive nature, it plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, aiding forest regeneration.
The Hooded Mountain Toucan, or Andigena cucullata, is a captivating bird of the Andes, known for its colorful plumage and distinctive bill. It features a mix of blue, green, and yellow, with a characteristic black hood on its head. This bird favors humid high-altitude forests, where it primarily feeds on fruits, but also insects and small vertebrates. Its social behavior is notable, often seen in small groups. Although its habitat is relatively limited, it plays a crucial role in seed dispersal, contributing to the health of its ecosystem. Unfortunately, deforestation threatens its habitat, making its conservation essential.
The Hartlaub's Turaco is a fascinating bird endemic to the montane forests of East Africa, particularly in Kenya and Tanzania. It is easily recognizable by its bright green plumage, distinctive crest, and vivid red wings visible in flight. This bird measures about 40 cm in length and primarily feeds on fruits, but also flowers and insects. It is often seen in pairs or small groups, moving agilely through the canopy. Its call is a mix of harsh cries and melodious notes. Although relatively common in its natural habitat, deforestation poses a threat to its population.
The Priotelus roseigaster, commonly known as the Hispaniolan Trogon, is an endemic bird of the island of Hispaniola, which includes Haiti and the Dominican Republic. This bird is easily recognizable by its striking plumage, with a green head and back, bright red belly, and a tail marked with black and white bands. It primarily inhabits tropical rainforests and mountainous areas, where it feeds on fruits, insects, and small vertebrates. The Hispaniolan Trogon is a symbol of the island's unique biodiversity, but it is threatened by deforestation and habitat loss. Despite these challenges, it remains a fascinating sight for birdwatchers and nature lovers.
The Hellmayr's Tyrannulet is a small passerine bird belonging to the Tyrannidae family. It is primarily found in humid montane forests, often at altitudes between 1500 and 3000 meters. This bird features a subtle plumage, mainly olive green with lighter shades on the belly. Known for its distinctive voice, it emits a melodious song that echoes through the dense canopy. Although relatively tolerant, it remains cautious of intruders. Its diet mainly consists of insects, which it captures in flight or by foraging through foliage. The Hellmayr's Tyrannulet plays an important role in the ecosystem by controlling insect populations and aiding in seed dispersal.