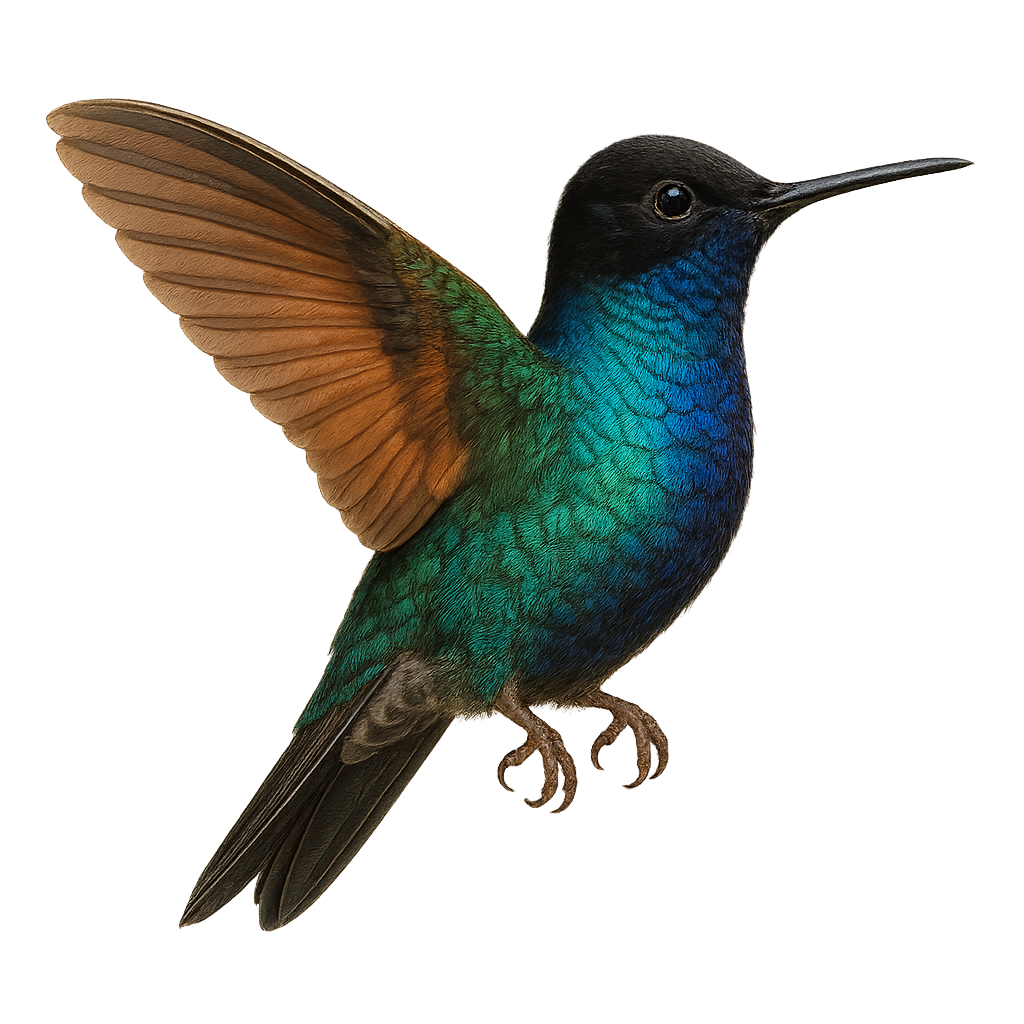
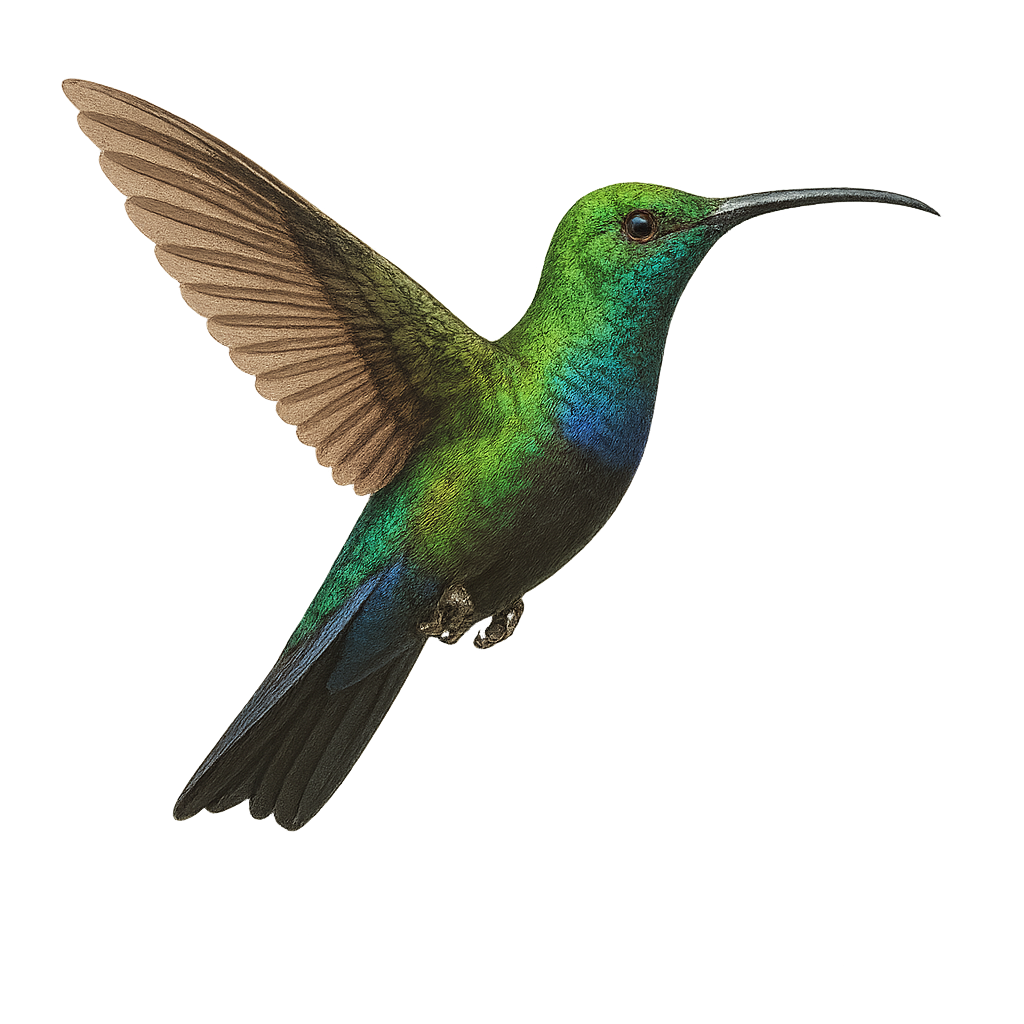
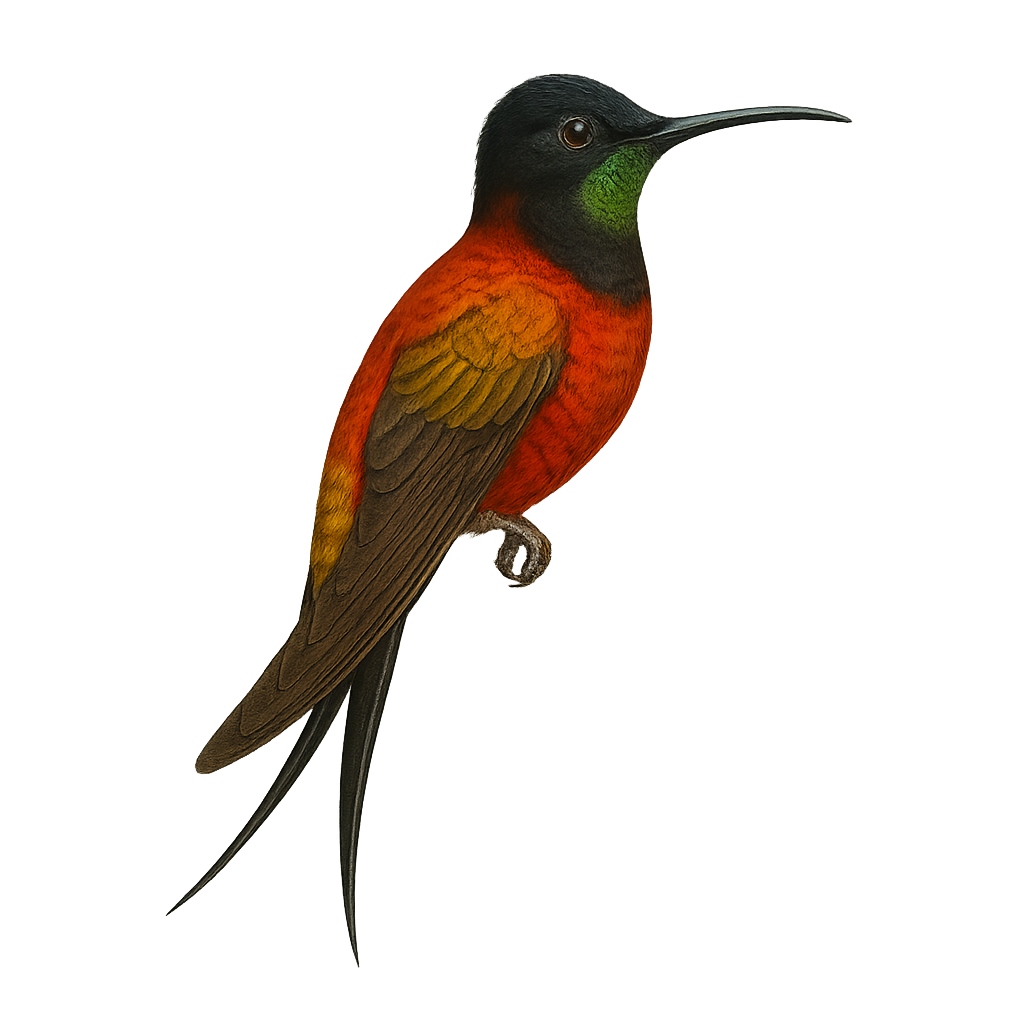
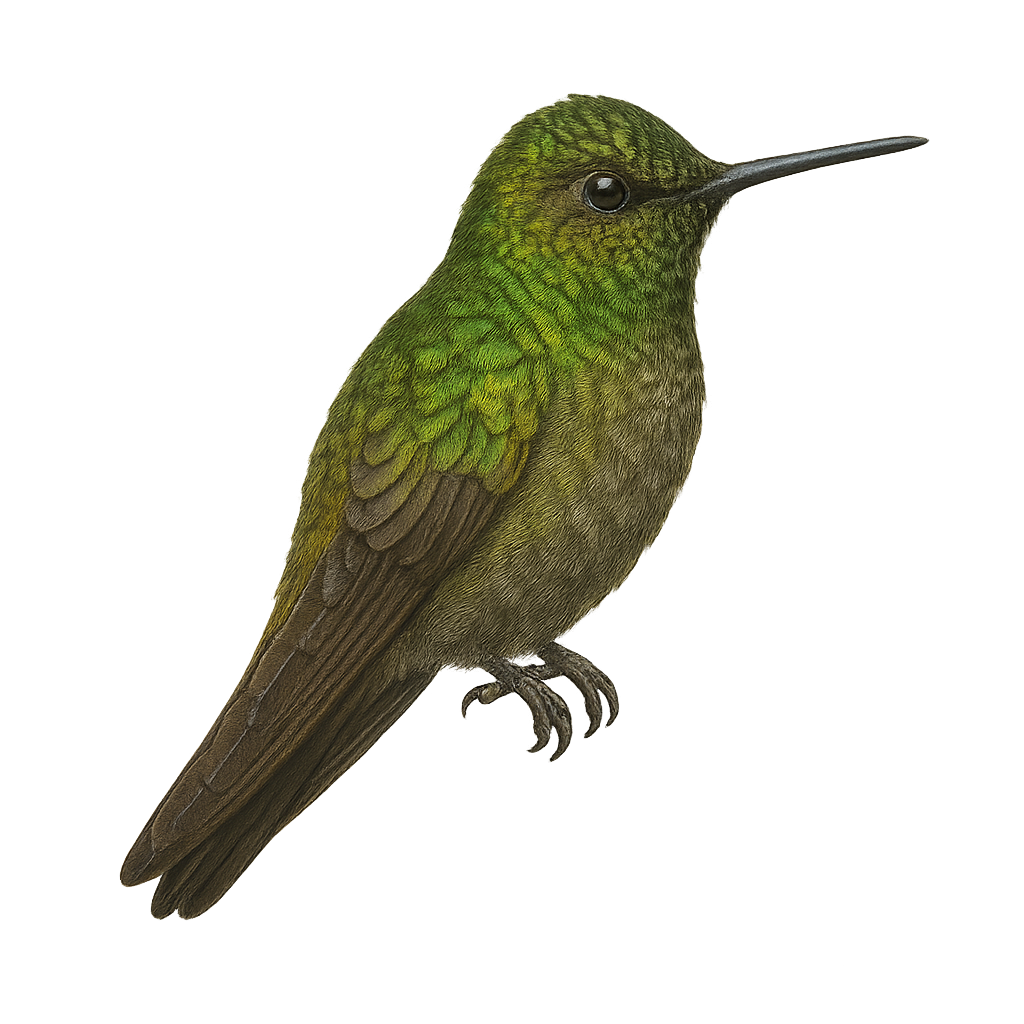
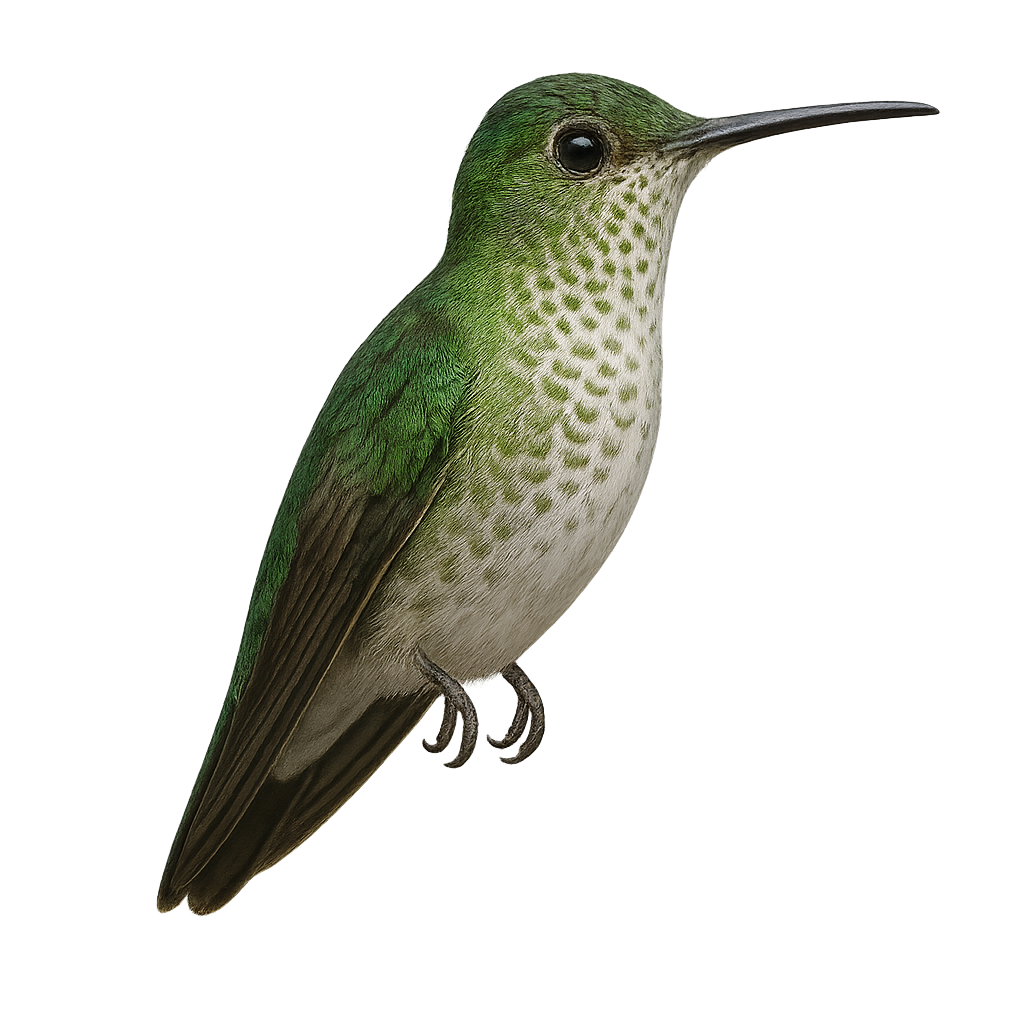
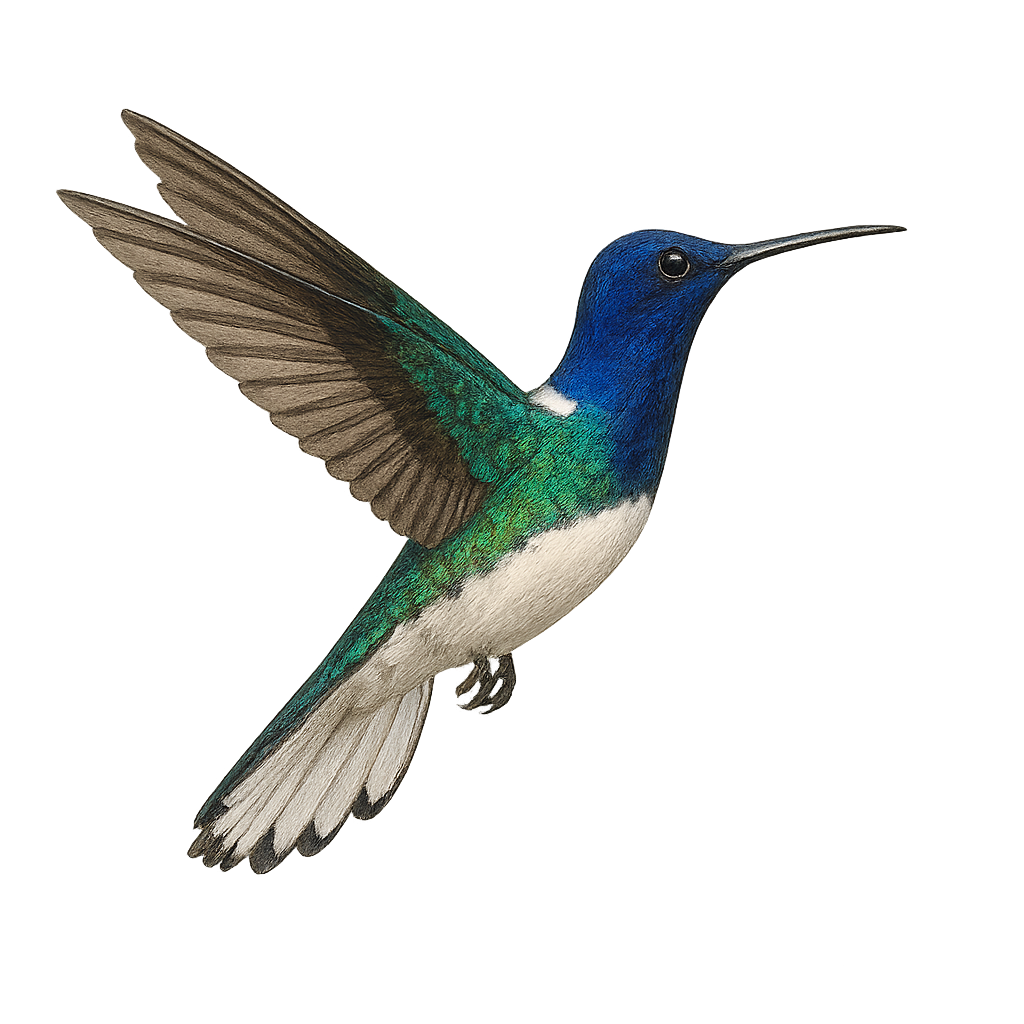
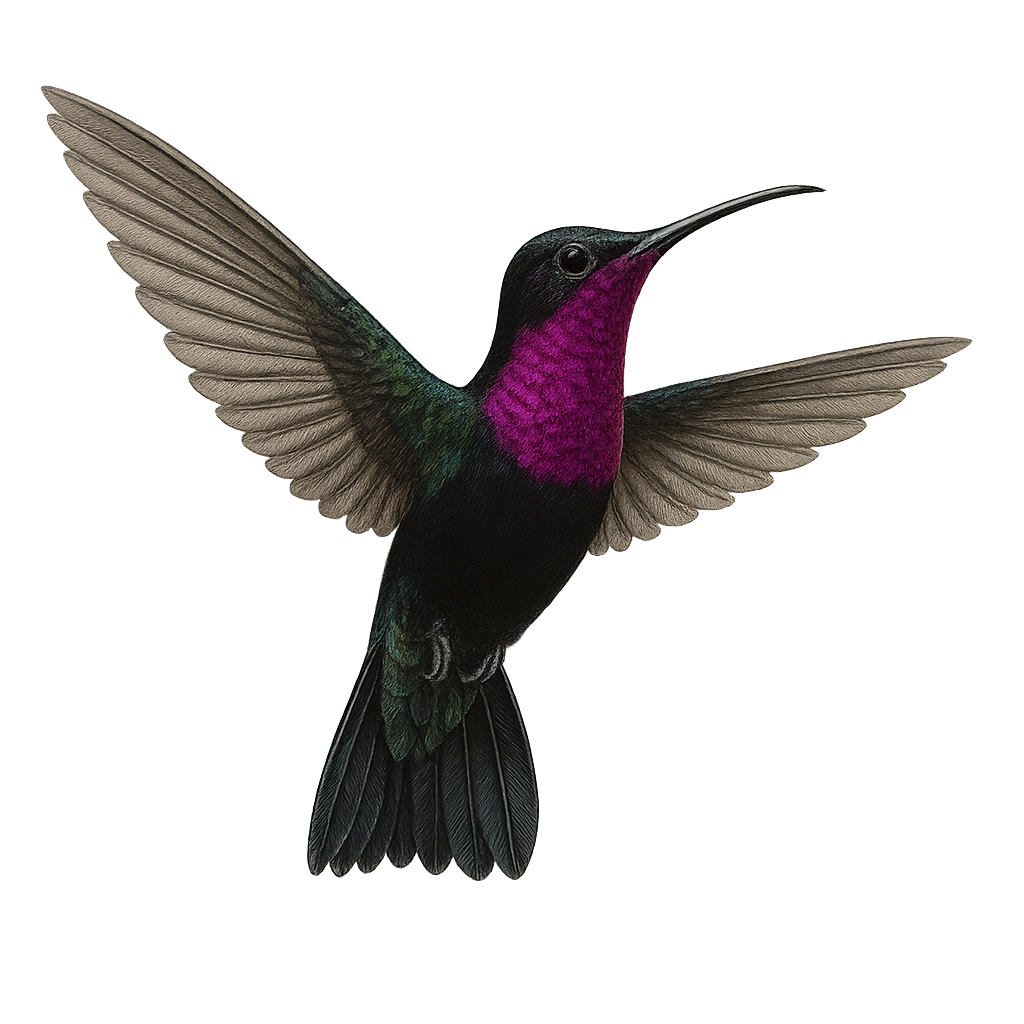
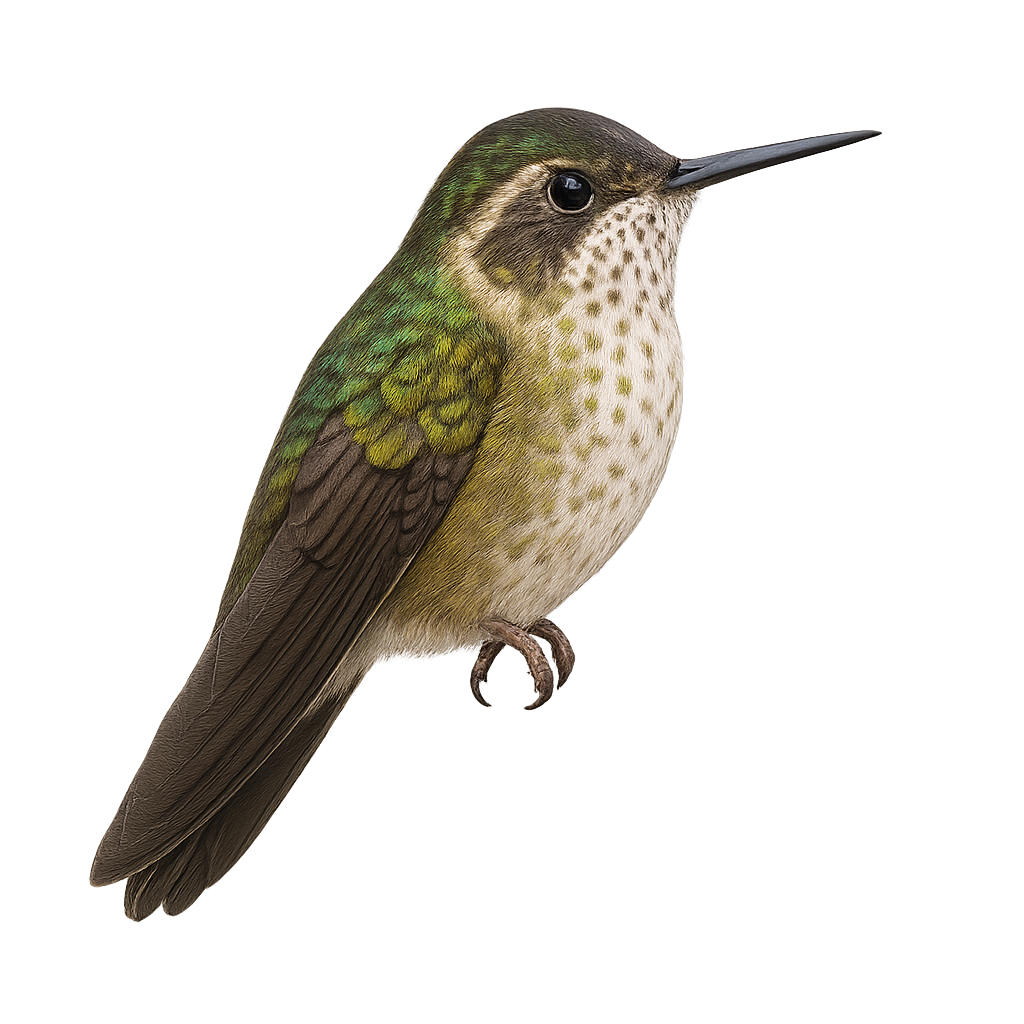
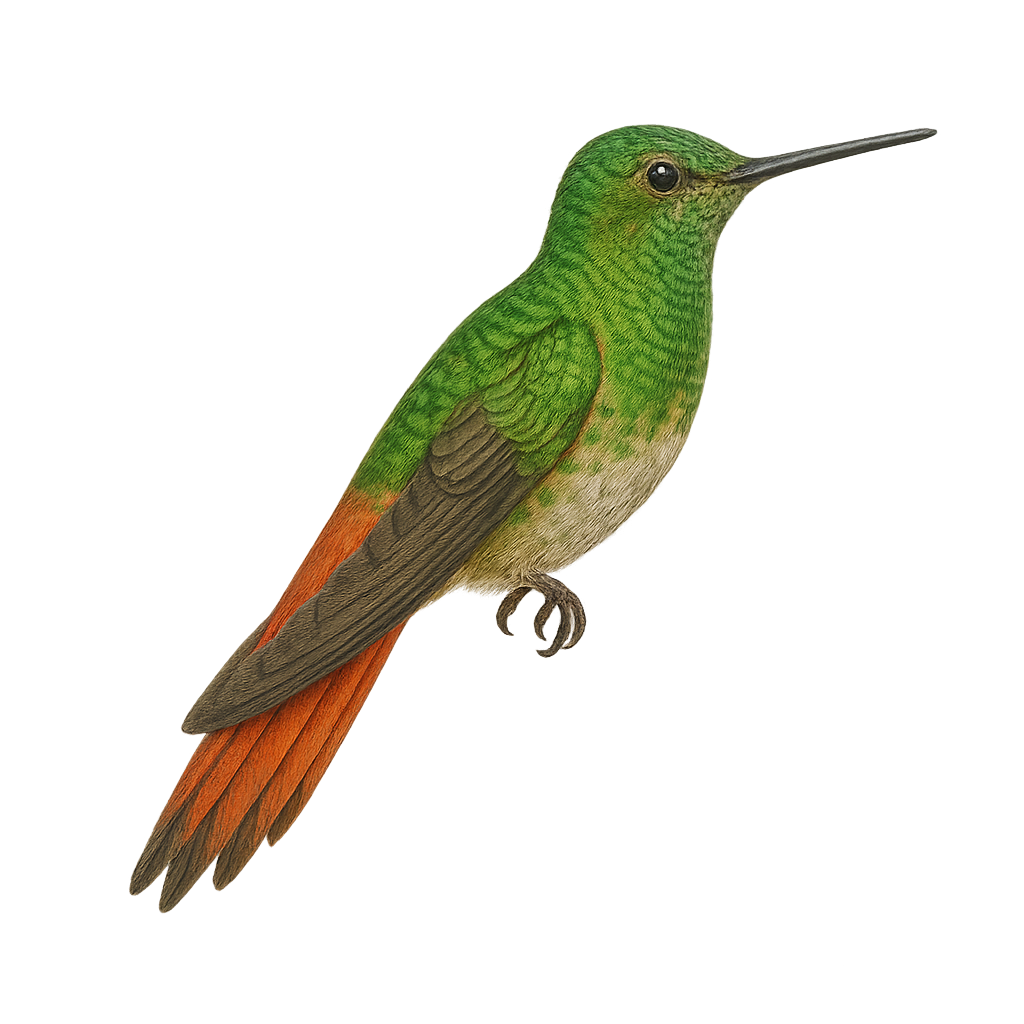
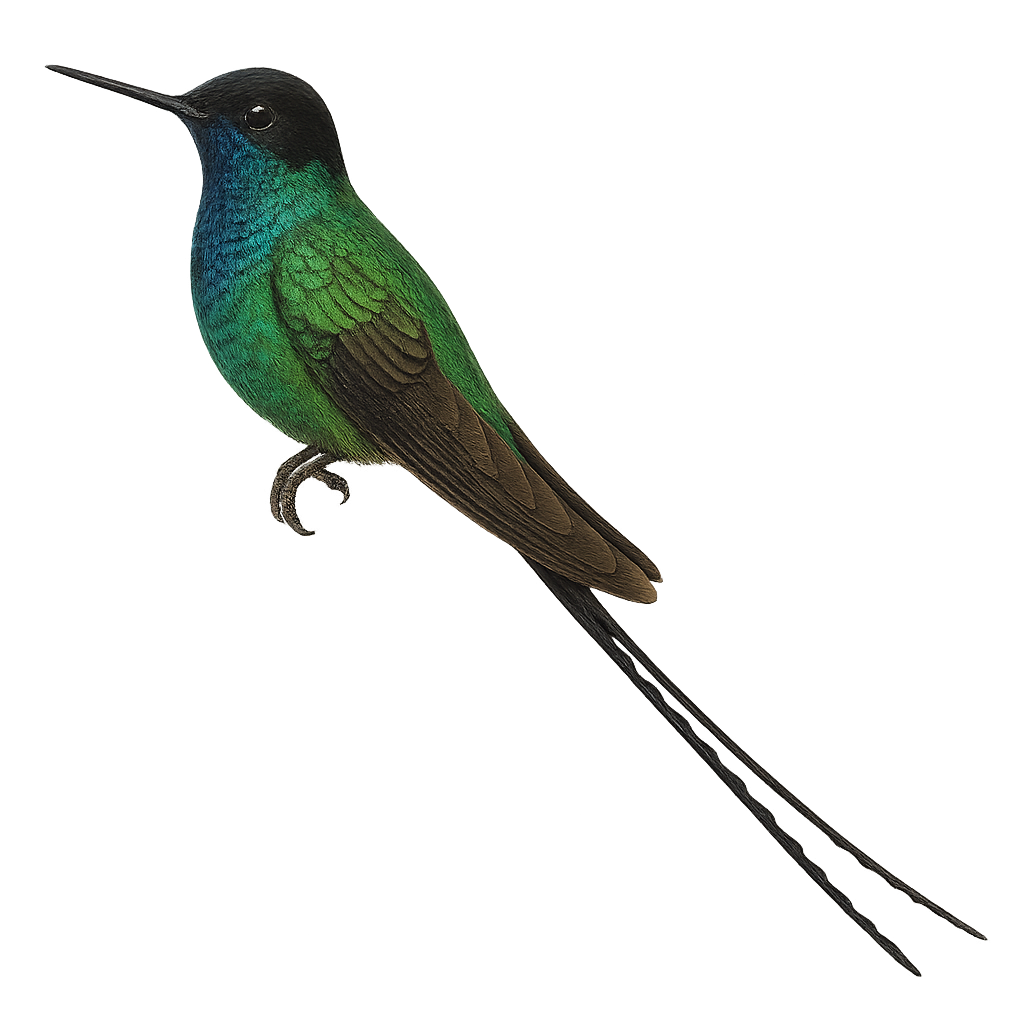
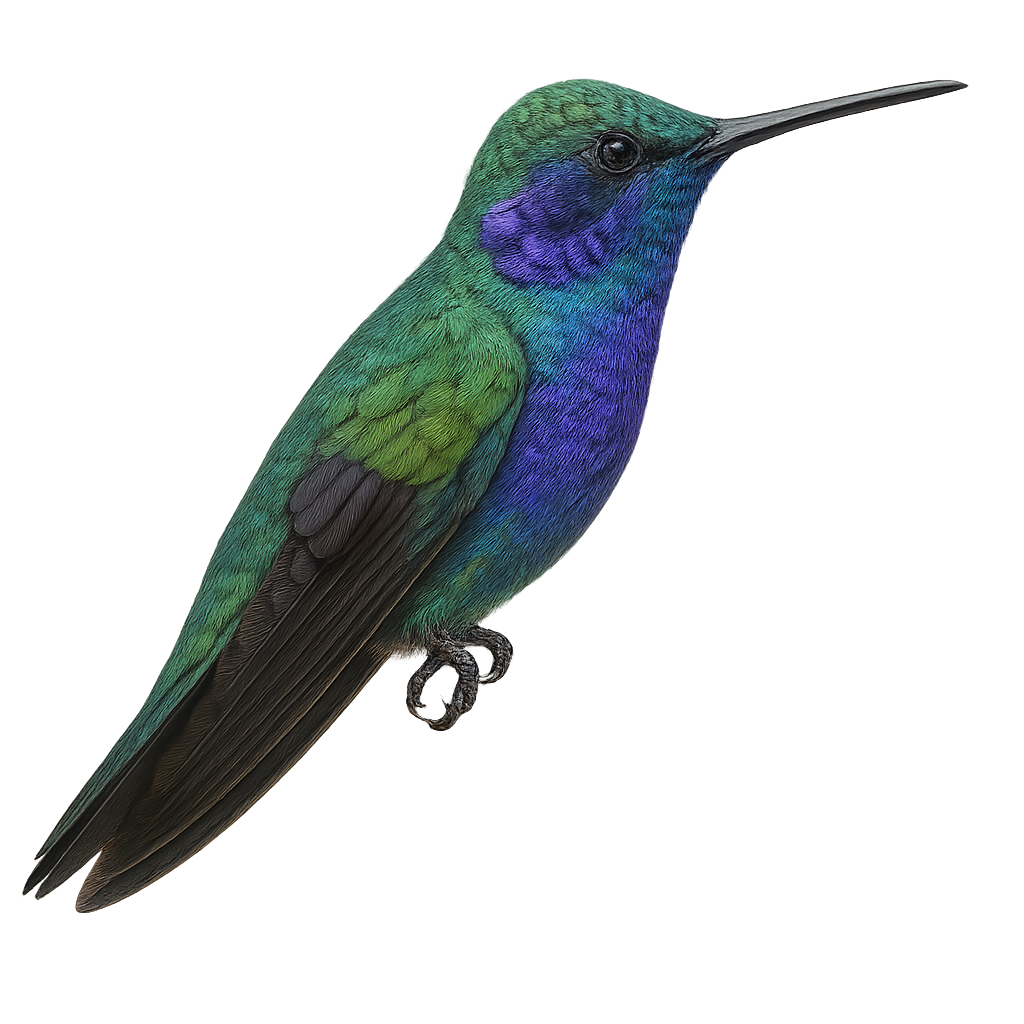
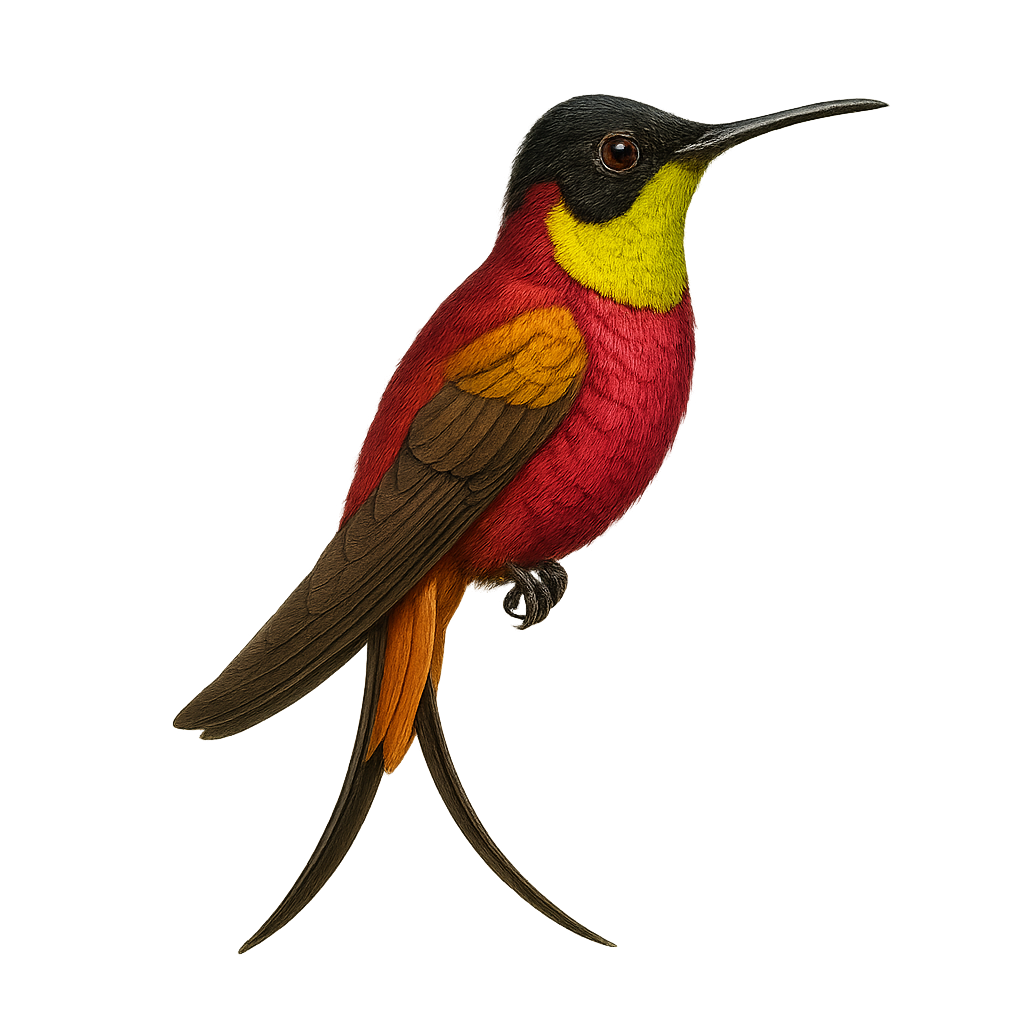
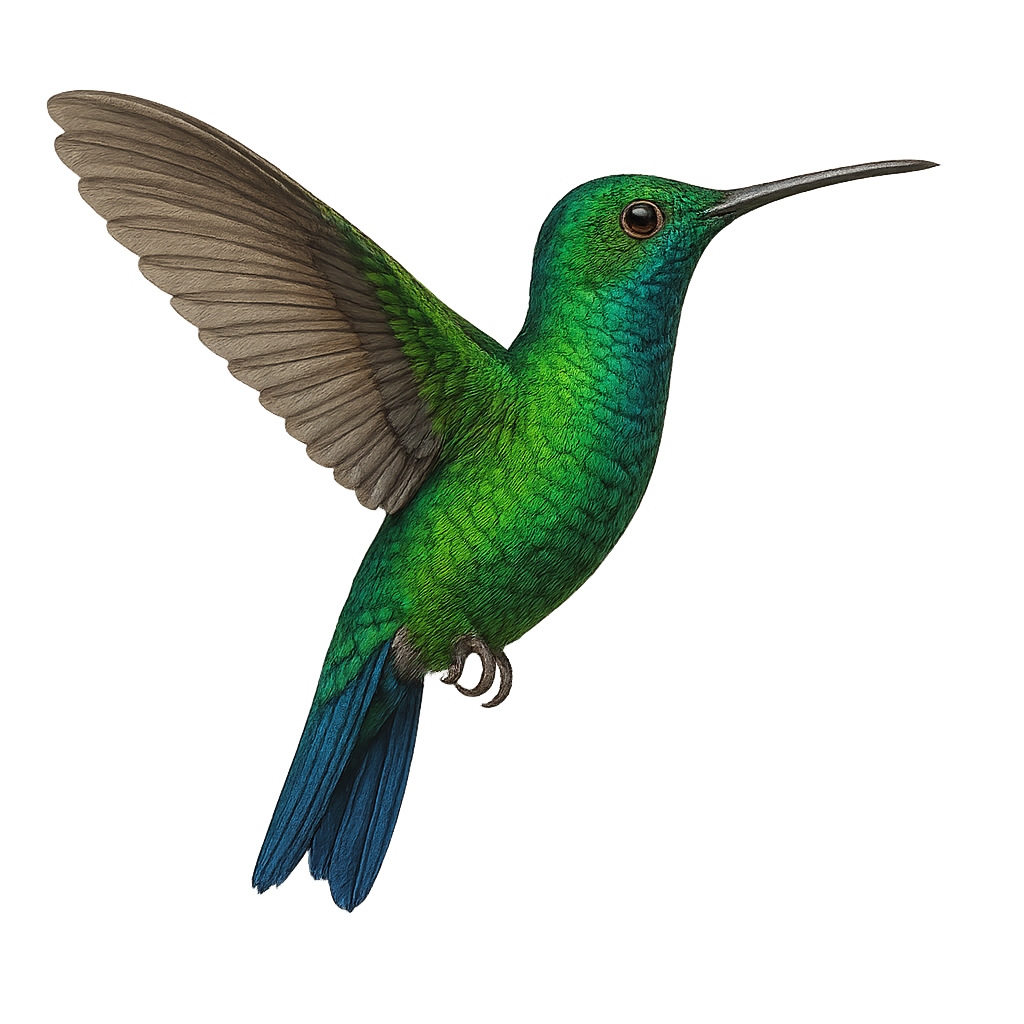
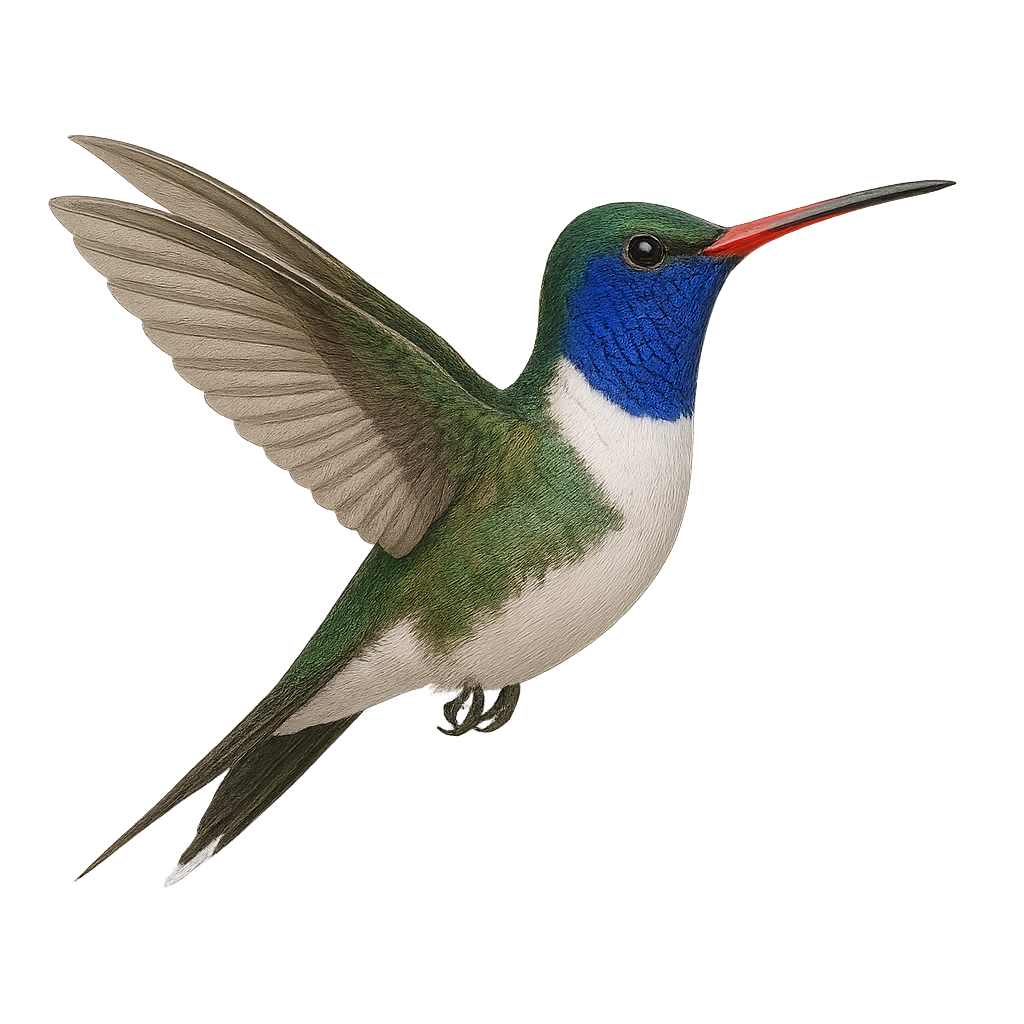
The White-tufted Sunbeam, or Aglaeactis castelnaudii, is a fascinating bird from the Trochilidae family. This hummingbird is distinguished by its brilliant plumage, with metallic green hues and a characteristic white patch on its chest. It is mainly observed in the Peruvian Andes, where it frequents humid forests and shrublands at high altitudes. This hummingbird is an essential pollinator, feeding on flower nectar with its long adapted beak. Its small size and rapid flight make it difficult to observe, but its ecological role is crucial for the pollination of Andean plants. Although its conservation status is concerning, efforts are underway to protect its natural habitat.
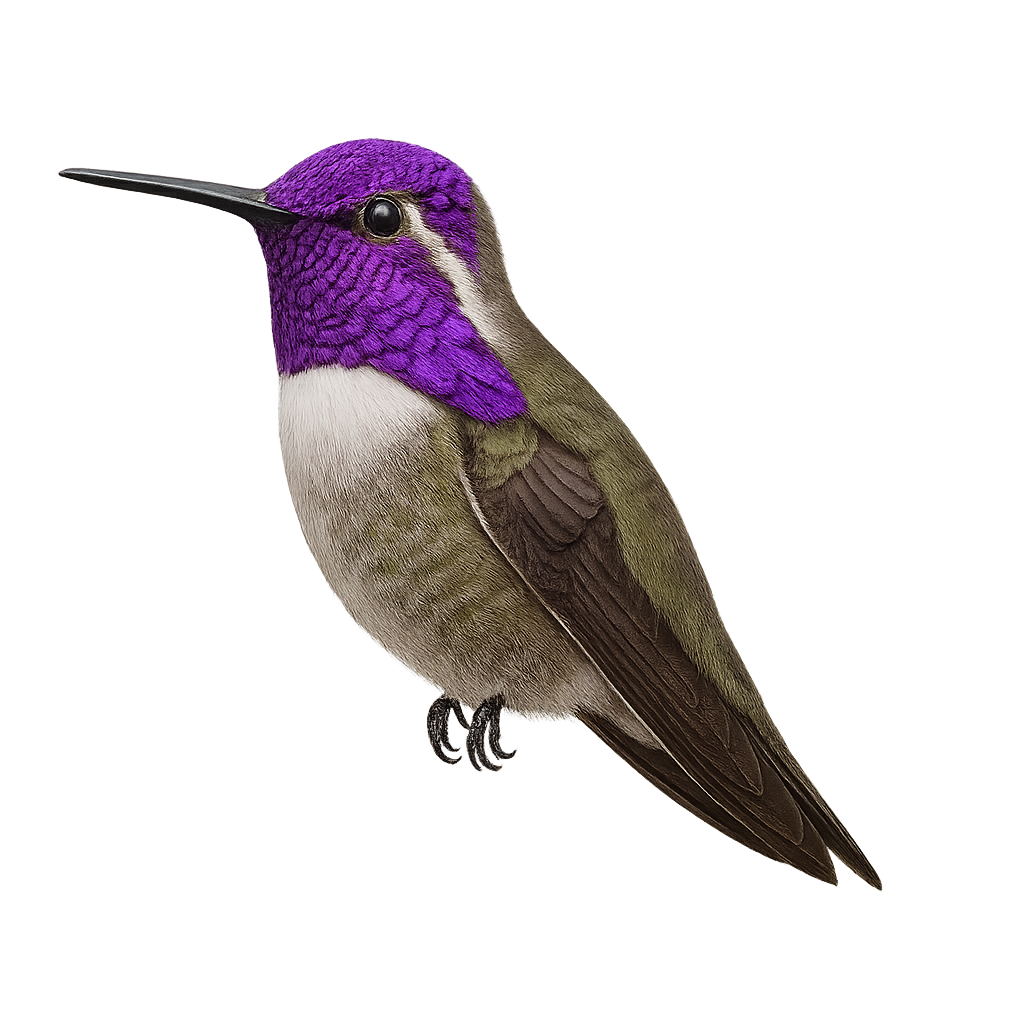
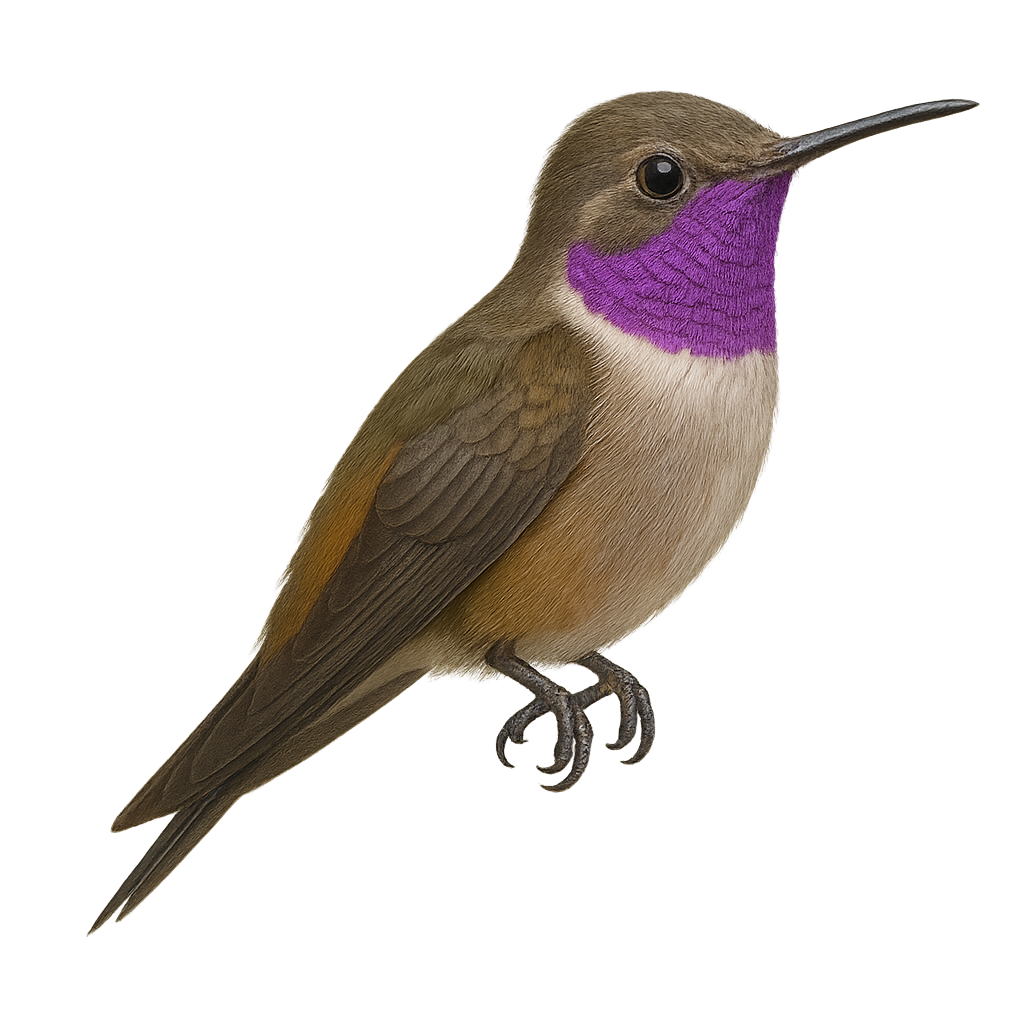
The Costa's Hummingbird, or Calypte costae, is a small, captivating bird known for its vibrant plumage and ability to fly backward. This hummingbird measures about 8 to 9 cm in length and weighs between 2 and 3 grams. Males display a striking violet head and throat, contrasting with their metallic green body. Females are more subdued with shades of green and gray. It is primarily found in the arid and semi-arid regions of the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. It feeds mainly on nectar but also consumes small insects. Its rapid and agile flight allows it to move easily between flowers.
The Velvet-purple Coronet, or Boissonneaua jardini, is a captivating hummingbird known for its striking plumage and agile movements. This hummingbird features a velvety purple plumage on its back and wings, contrasting with a metallic green belly. Males and females are similar, though females are slightly smaller. They inhabit the humid forests of the Andes, mainly in Colombia and Ecuador, where they feed on nectar and insects. Their rapid and precise flight allows them to navigate easily between flowers. The Velvet-purple Coronet plays a crucial role in pollinating local plants. Although generally solitary, these birds can be seen in groups around abundant food sources.
The Velvet-purple Coronet is a fascinating hummingbird, primarily found in the humid forests of the Andes. This small bird boasts a striking plumage with shades of purple and blue that captivate the eye. Known for its rapid flight and agile movements, it primarily feeds on nectar, which it extracts with precision using its long, slender beak. Males and females display similar colors, although males often have more vibrant hues. This hummingbird plays a crucial role in pollinating local plants, thus contributing to the biodiversity of its habitat. Despite its beauty, it can be challenging to observe due to its wary nature and dense habitat.
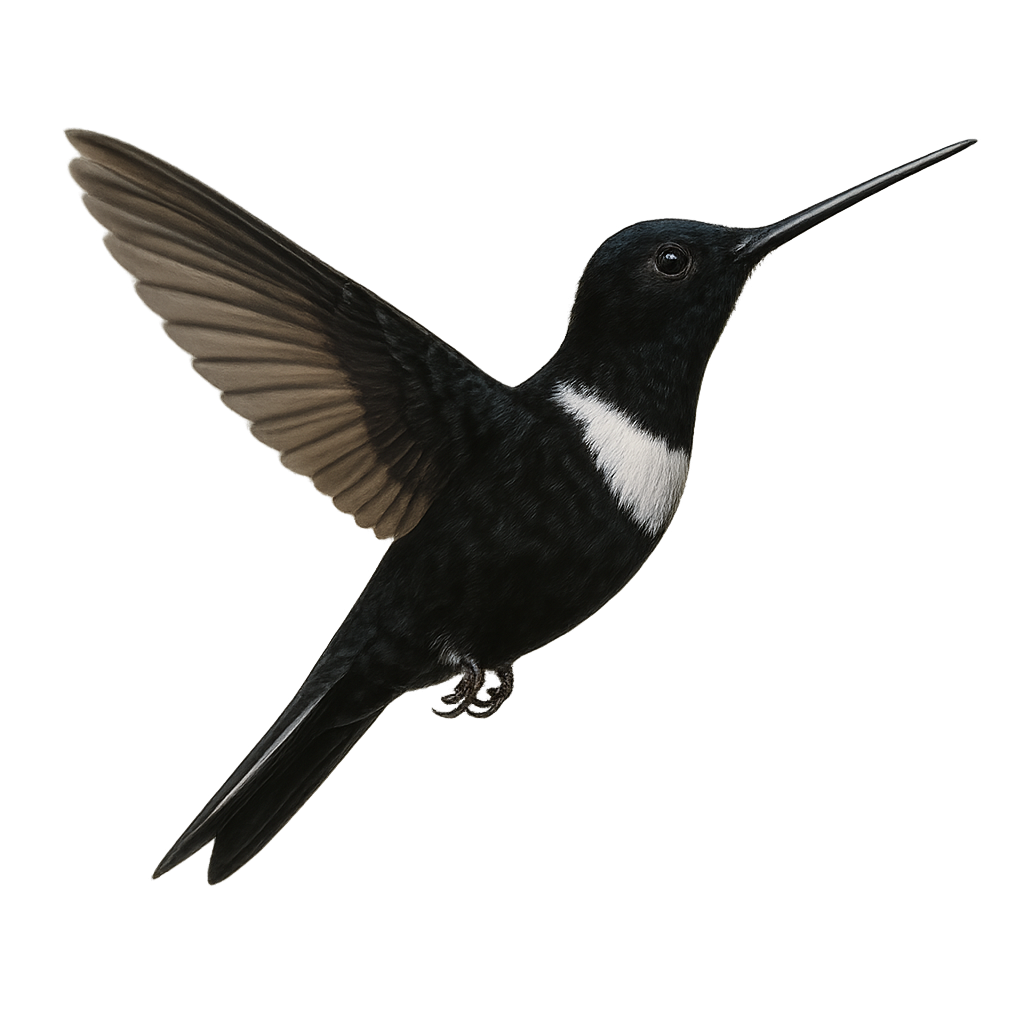
The Black Inca, or Coeligena prunellei, is a hummingbird species endemic to the high-altitude humid forests of Colombia. It is characterized by its glossy black plumage with metallic sheen and a distinctive white patch on its chest. This hummingbird primarily feeds on nectar, using its long slender bill to hover from flower to flower, playing a vital role in plant pollination. Unfortunately, deforestation threatens its natural habitat, leading to a decline in its population. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure its long-term survival.
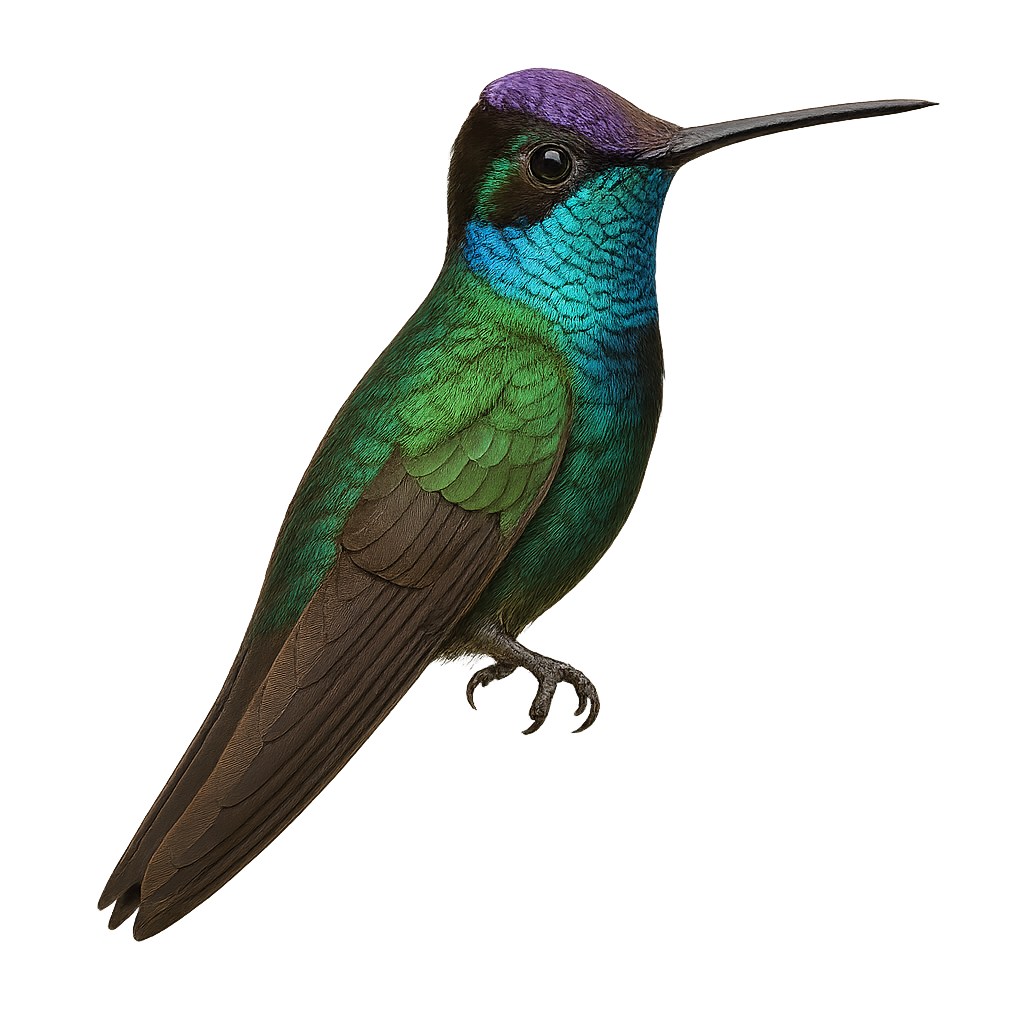
The Magnificent Hummingbird, scientifically known as Eugenes fulgens, is a medium-sized bird, measuring about 13 cm in length. It is renowned for its striking plumage, featuring metallic green hues and an iridescent throat that can appear violet or blue depending on the light. Males boast a brilliant green crown, while females are duller, with grayish tones. This hummingbird primarily inhabits mountain forests and woodland edges, where it feeds on nectar and insects. Its fast and agile flight allows it to maneuver easily between flowers. Although often solitary, it can be seen in small groups during the breeding season.
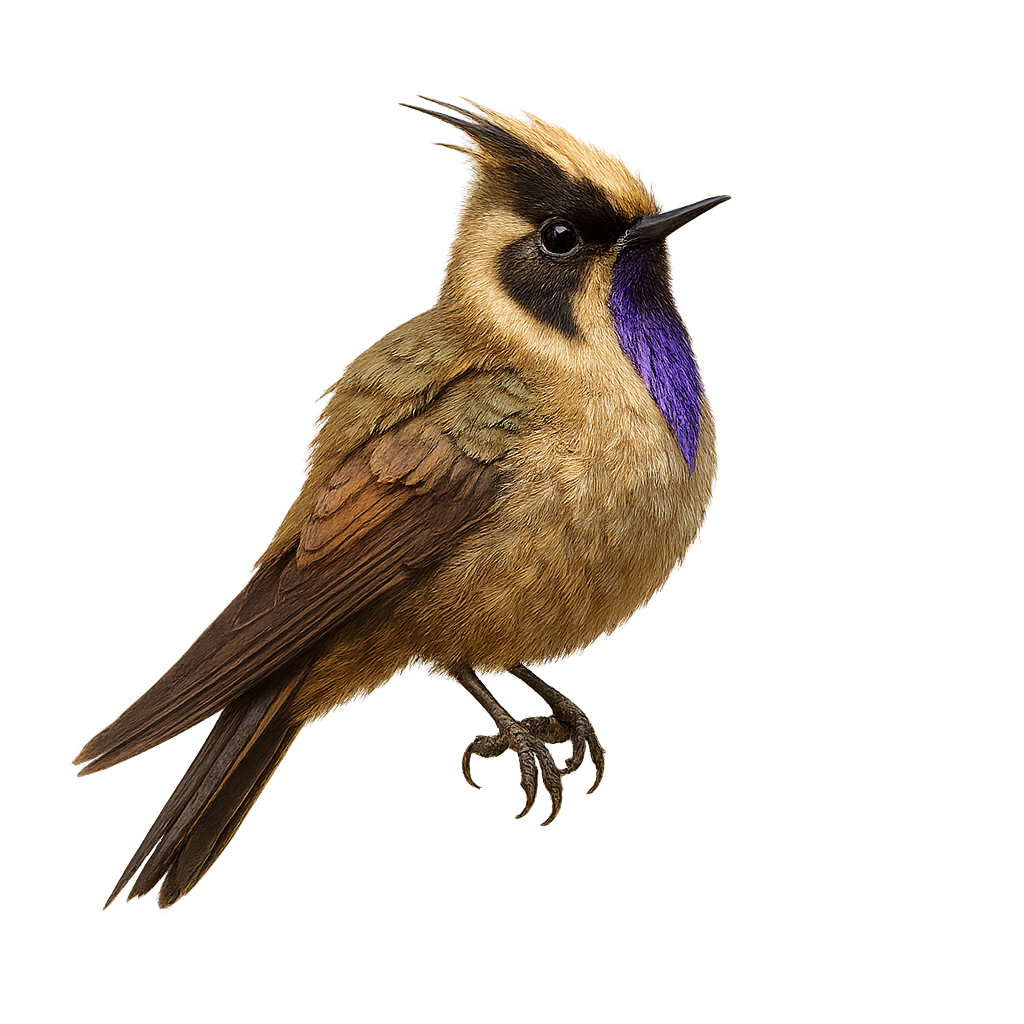
The Stübel's Hummingbird, or Oxypogon stuebelii, is a hummingbird species endemic to the Colombian Andes. This small bird is notable for its striking crest and white facial feathers that form a beard-like appearance. Its plumage is primarily metallic green, with iridescent highlights that catch the sunlight. It inhabits the páramos, high-altitude ecosystems characterized by cool temperatures and strong winds. The Stübel's Hummingbird feeds mainly on nectar, which it gathers by hovering from flower to flower, but it also supplements its diet with small insects. Although its habitat is relatively restricted, it is well adapted to the harsh mountain conditions.
The Bahama Woodstar, scientifically known as Nesophlox evelynae, is a small bird endemic to the Bahamas. This hummingbird is notable for its diminutive size and vibrant plumage, featuring shades of green and pink. Males display an iridescent throat that shimmers in the sunlight, while females have more subdued hues. They primarily feed on nectar but also catch small insects to supplement their diet. These birds are often seen in gardens, forests, and mangroves, where they play a crucial role in pollinating local plants. Their fast and agile flight allows them to easily evade predators.
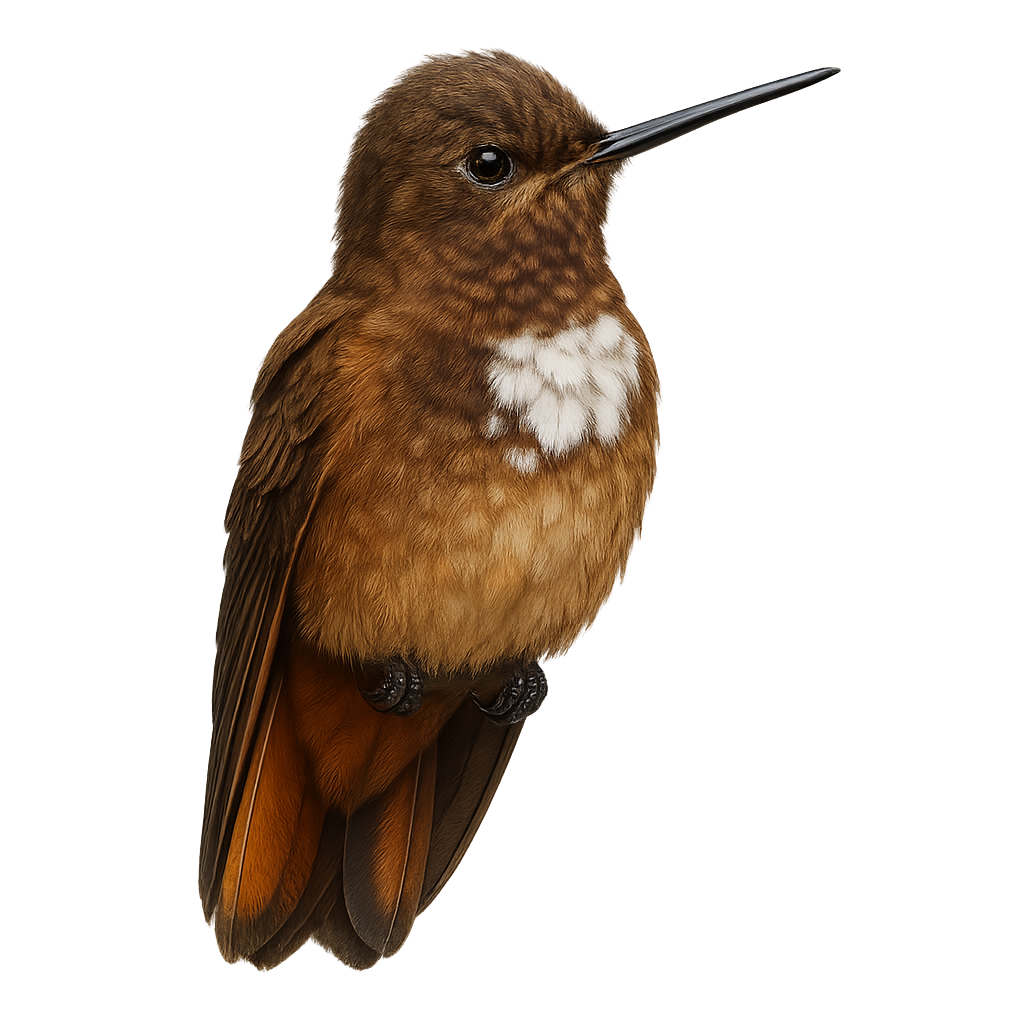
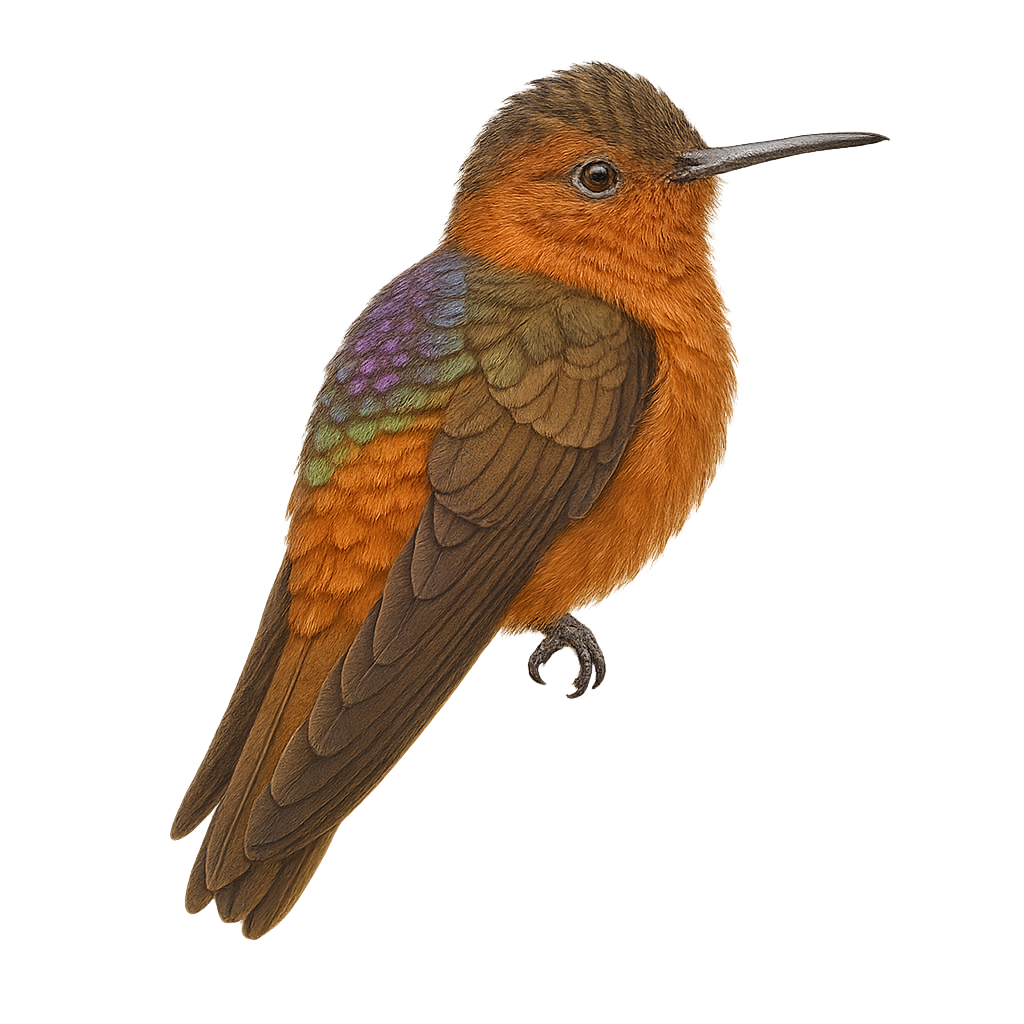
The Shining Sunbeam, Aglaeactis cupripennis, is a captivating bird from the Trochilidae family. It is primarily found in the Andes, inhabiting humid forests and shrublands at altitudes ranging from 1800 to 3200 meters. This hummingbird is notable for its coppery-winged sheen and brownish plumage, which help it blend into its surroundings. It primarily feeds on nectar, using its long, slender bill, but also consumes small insects to supplement its diet. Although generally suspicious in behavior, it can occasionally be tolerant of discreet observers.
The Green-throated Carib, Eulampis holosericeus, is a captivating bird native to the Caribbean, known for its vibrant and iridescent plumage. This medium-sized hummingbird features a shimmering green throat and a body with metallic hues. It is commonly found in tropical forests, gardens, and coastal areas, where it primarily feeds on nectar, supplemented by insects. The Green-throated Carib is an essential pollinator, playing a crucial role in the reproduction of flowering plants. Its rapid and agile flight allows it to maneuver easily among flowers, while its territorial behavior drives it to vigorously defend its food sources.
The Crimson Topaz, or Topaza pyra, is a captivating bird found in the tropical forests of South America, particularly in Guyana, Brazil, and Venezuela. This hummingbird is known for its striking plumage, featuring shades of red, orange, and metallic green. Males have long, forked tails that enhance their elegance during courtship displays. They primarily feed on nectar but also consume small insects to supplement their diet. Their rapid and agile flight allows them to move easily between flowers. Although their habitat is relatively stable, deforestation poses a potential threat to their survival.
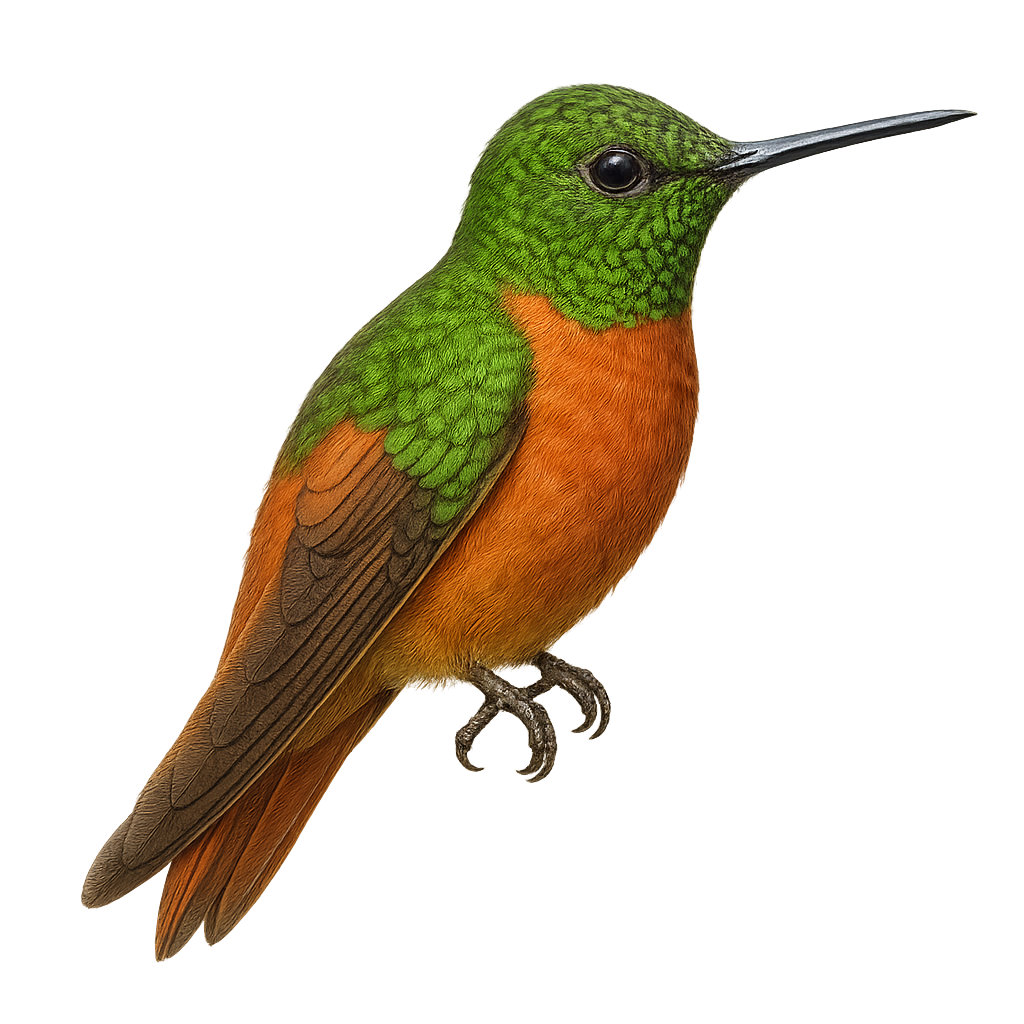
The Buff-tailed Coronet is a medium-sized hummingbird found primarily in the humid forests of the Andes, between 1500 and 2800 meters in altitude. Its plumage is mainly green with a distinctive yellow belly, making it easily identifiable. Known for its speed and agility in flight, it feeds mainly on nectar, which it collects with its long, slender beak. This hummingbird plays a crucial role in the pollination of Andean plants. It is often observed alone or in small groups, and although territorial, it can share its space with other hummingbird species.
The White-bellied Hummingbird, or Taphrospilus hypost, is a small, fascinating bird from the Trochilidae family. This hummingbird is primarily found in the humid forests and wooded areas of the Andes, where it feeds on flower nectar with its long, slender beak. Its plumage is mainly emerald green with a distinctive white belly, making it easily identifiable. Males and females share similar characteristics, although males may have slightly brighter colors. This hummingbird is known for its fast and agile flight, often accompanied by characteristic buzzing sounds. It plays a crucial role in the pollination of local plants.
The White-necked Jacobin, or Florisuga mellivora, is a bird from the Trochilidae family, easily recognizable by its striking plumage. The male boasts a bright blue head and neck, contrasting with a white chest and metallic green back. The female, on the other hand, has a duller plumage with shades of green and blue. This hummingbird is mainly found in the humid tropical forests of Central and South America, where it feeds on nectar and insects. Its fast and agile flight allows it to move easily between flowers. The White-necked Jacobin plays a crucial role in plant pollination, thus contributing to the biodiversity of its habitat.
The Purple-throated Carib, or Eulampis jugularis, is a captivating bird native to the Caribbean, especially found on the islands of Dominica and Martinique. This hummingbird is noted for its striking plumage, with an iridescent purple throat that gives it its name. Males are generally larger than females and display more vibrant colors. They primarily feed on nectar but also consume small insects to supplement their diet. The Purple-throated Carib is a vital pollinator, playing a crucial role in the ecosystem by aiding the reproduction of many plants. It is often seen in tropical rainforests, gardens, and wooded areas, where it flies with agility and speed.
The Speckled Hummingbird, or Adelomyia melanogenys, is a small, captivating bird belonging to the Trochilidae family. It is primarily found in the mountainous regions of South America, particularly in the Andes. This hummingbird is distinguished by its green and brown plumage with speckled patterns, giving it a unique appearance. Its modest size, typically around 8 to 9 cm, makes it agile and swift in flight. It primarily feeds on nectar but also consumes small insects to supplement its diet. The Speckled Hummingbird is often seen in humid forests and wooded areas, where it plays a crucial role in pollinating local plants.
The Rufous hummingbird is a fascinating species of hummingbird, recognized for its small size and brilliant feathers in shades of copper and red. Native to North America, it migrates each year between the United States and Mexico. This hummingbird primarily feeds on nectar, which it collects using its long bill and extendable tongue. It is often seen hovering in place, a feat made possible by its extremely agile wings. The Rufous hummingbird is also known for its territorial behavior, especially when defending its favorite flowers.
The Red-tailed Comet, or Sappho sparganurus, is a fascinating hummingbird known for its spectacular tail and vibrant colors. Native to the Andes, it is distinguished by its iridescent plumage, with shades of green and red. Males boast a long, forked, reddish tail, while females have a shorter, less colorful tail. This hummingbird is often seen in flower gardens and open forests, where it primarily feeds on nectar, playing a crucial role in pollination. Its fast and agile flight allows it to escape predators and vigorously defend its territory. Although its habitat is relatively stable, it remains vulnerable to environmental changes.
The Scintillant Hummingbird is one of the smallest birds in the world, measuring about 6.5 cm in length. The male has bronze-green upperparts, a bright reddish-orange throat, and a rufous tail with black bars. The female is more subdued, with a buffy throat spotted with green and rufous flanks. This species is endemic to Costa Rica and western Panama, inhabiting forest edges, coffee plantations, and gardens between 900 and 2500 meters elevation. It feeds primarily on nectar from small flowers, such as sages, and supplements its diet with small insects for protein. Although listed as Least Concern, deforestation could threaten its habitats.
The Scitulus Hummingbird is a fascinating bird known for its small size and vibrant colors. It primarily inhabits tropical and subtropical forests, playing a crucial role in plant pollination. Its iridescent plumage, ranging from emerald green to deep blue, makes it easily recognizable. This hummingbird is particularly agile in flight, capable of rapid and precise movements to access flower nectar. It primarily feeds on nectar but also consumes small insects to supplement its diet. The Scitulus Hummingbird is a solitary bird, except during the breeding season when it becomes more territorial.
The Mexican Violetear is a small, brightly colored bird, primarily emerald green with metallic sheens. It is recognizable by its violet patches on the sides of its head and slightly forked tail. This hummingbird frequents humid forests and forest edges, often at high altitudes. It feeds mainly on nectar but supplements its diet with small insects. Its flight is fast and agile, allowing it to maneuver easily between flowers. The Mexican Violetear is a solitary bird, except during the breeding season. It is known for its spectacular courtship displays, where the male showcases his colorful feathers to attract the female.
The Crimson Topaz, or Topaza pella, is a fascinating bird found in the tropical forests of South America, particularly in Guyana, Brazil, and Venezuela. This hummingbird is notable for its striking plumage, with red and golden hues that catch the light spectacularly. Males have a long forked tail, enhancing their elegance in flight. They primarily feed on nectar but also consume small insects to supplement their diet. Crimson Topazes are often observed in dense undergrowth and near watercourses, where they find an abundance of flowers. Their fast and agile flight allows them to move easily between flowers, playing a crucial role in pollination.
The Blue-tailed Emerald, or Chlorostilbon mellisugus, is a small bird with vibrant, metallic green plumage and a distinctive bluish tail. It has a slender, slightly curved bill, perfect for feeding on flower nectar. This hummingbird is widespread in South America, inhabiting various environments from tropical forests to urban gardens. Known for its rapid and agile flight, it often produces characteristic buzzing sounds. Males are particularly territorial, vigorously defending their feeding areas. The breeding season varies by region, but nests are typically constructed with plant materials and spider webs.
The Sparkling-tailed Hummingbird, or Tilmatura dupontii, is a captivating bird belonging to the Trochilidae family. This small hummingbird is notable for its sparkling tail and vibrant colors, ranging from emerald green to deep blue. It is primarily found in the tropical and subtropical forests of Mexico and Central America. This hummingbird is an essential pollinator, feeding mainly on flower nectar, but it also consumes small insects to supplement its diet. Its fast and agile flight allows it to maneuver easily between flowers and escape predators. Although its conservation status is not of concern, deforestation and habitat loss pose potential threats to its population.
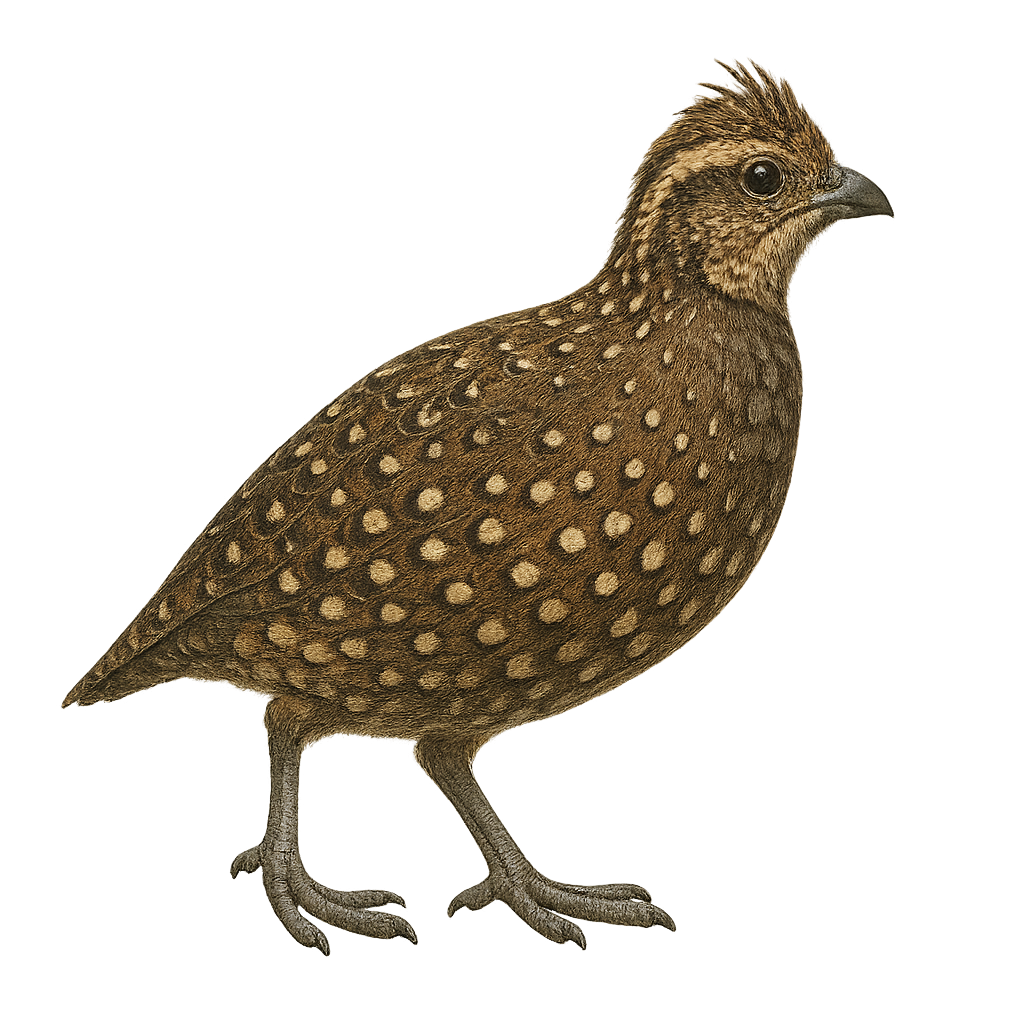
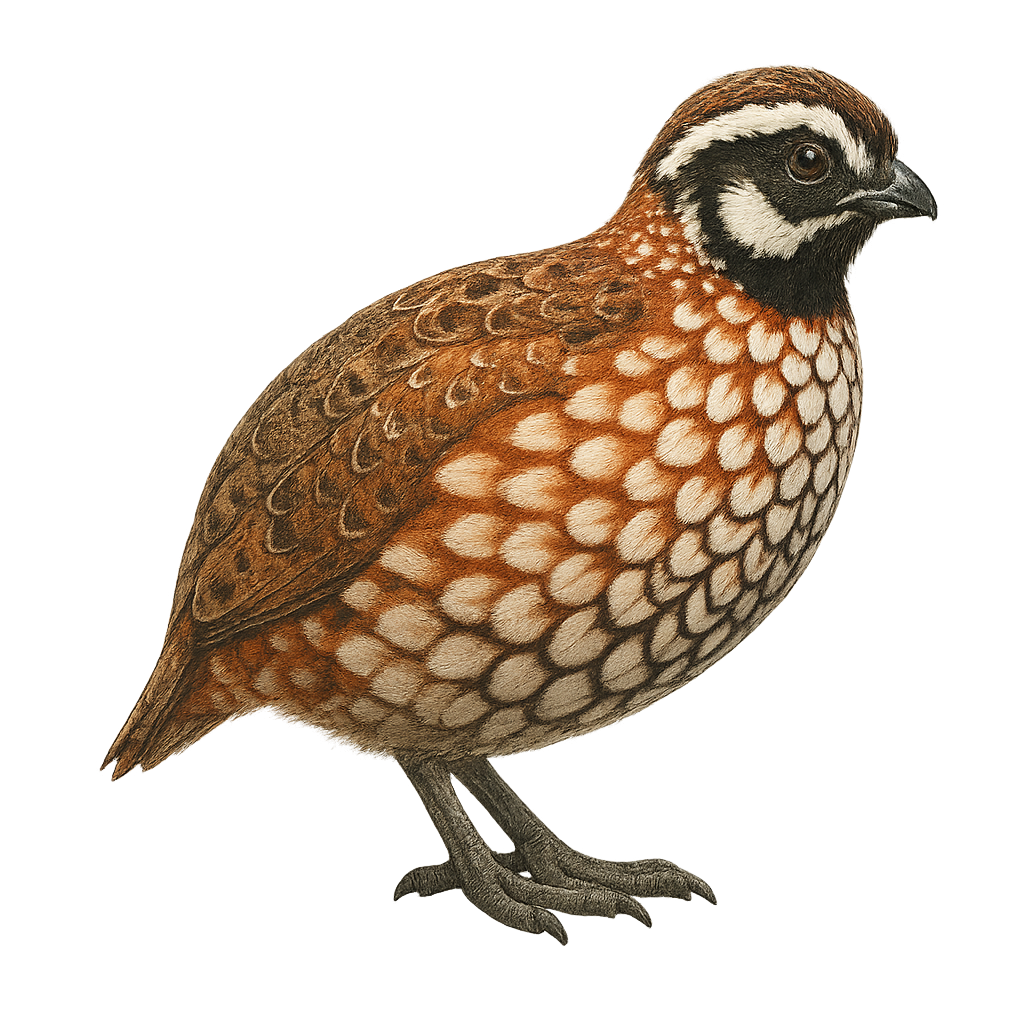
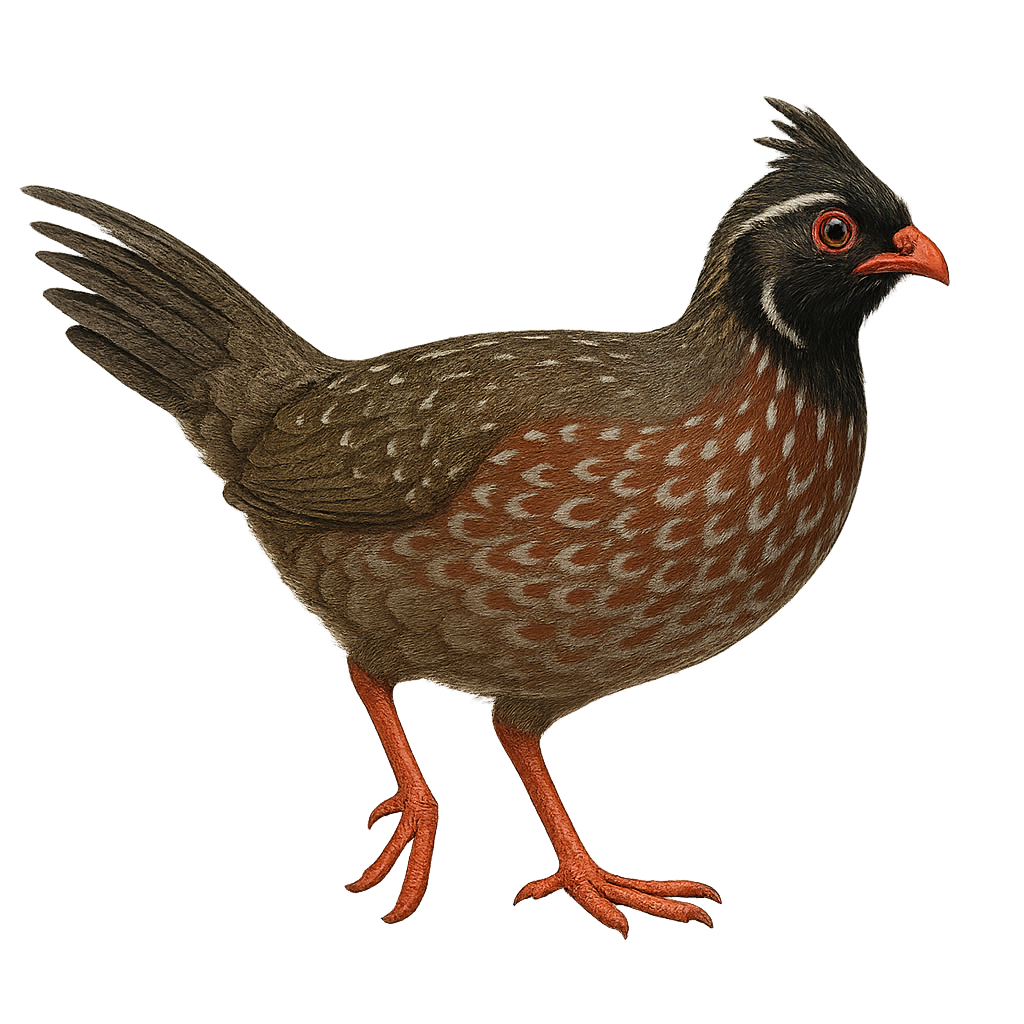
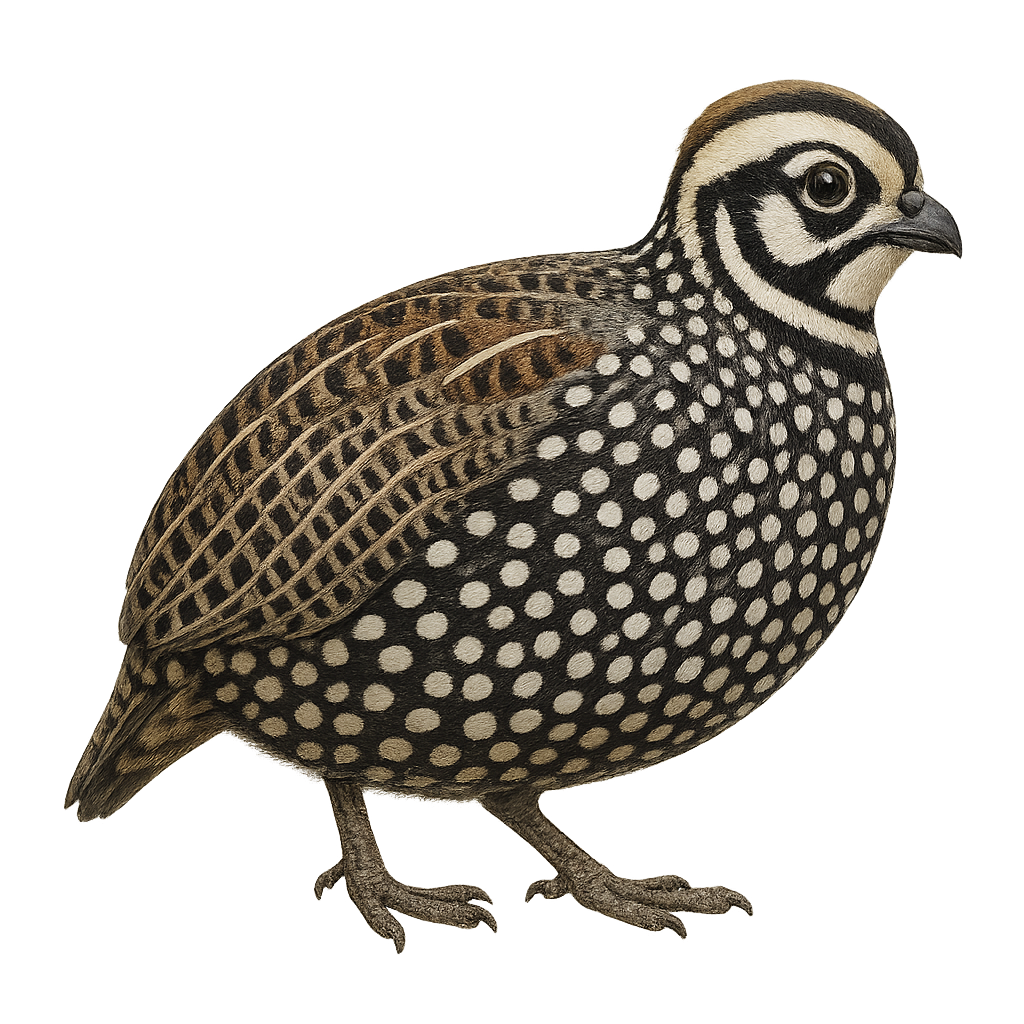
The White-throated Quail-Dove, Colinus leucopogon, is a bird from the Odontophoridae family. It is mainly found in mountainous regions of Mexico and Central America. This bird is characterized by its white throat contrasting with its dark brown plumage. It prefers dense forests and wooded areas where it can easily hide from predators. The White-throated Quail-Dove is a terrestrial bird that feeds mainly on seeds, fruits, and insects. It is often seen in small groups or pairs. Although relatively discreet, its melodious song can be heard throughout the forest. Its population is stable, but deforestation poses a potential threat to its natural habitat.
The Black-throated Bobwhite is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Odontophoridae family. It is primarily found in the Yucatán region of Mexico, as well as in Belize and Guatemala. This bird is distinguished by its characteristic black throat, contrasting with its brown and white plumage. Males and females exhibit sexual dimorphism, with males having a more pronounced black throat. They typically live in groups and prefer open habitats such as grasslands and savannas. Their diet mainly consists of seeds, insects, and small fruits. Although relatively discreet, they can be heard thanks to their distinctive call, especially during the breeding season.
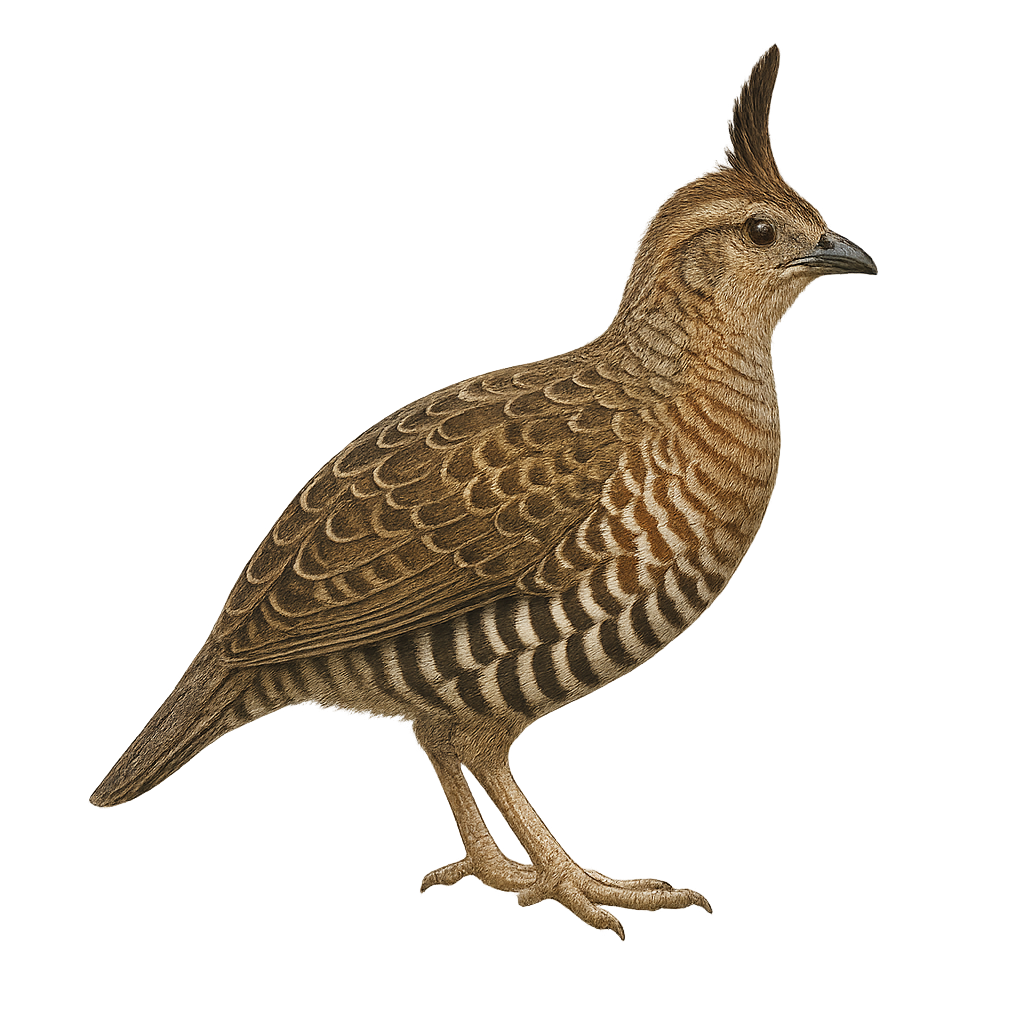
The Long-tailed Wood-Partridge, or Dendrortyx macroura, is a medium-sized terrestrial bird endemic to the mountainous forests of Mexico. It is characterized by its long tail, reddish-brown plumage, and distinctive facial patterns. Preferring oak and pine forests, it primarily feeds on seeds, fruits, and insects. Although discreet, it is often detected by its melodious song. Populations are stable, but deforestation poses a potential threat. The Long-tailed Wood-Partridge is a social bird, living in small family groups. Its ability to blend into its environment makes it difficult to observe, but it is prized by birdwatchers for its distinctive song and interesting behavior.
The Montezuma Quail is a medium-sized ground bird, known for its distinctive and colorful plumage. Males feature a striking black and white head with mask-like patterns, while females have a more subdued brown and speckled appearance. These birds are primarily found in the mountainous regions of the southwestern United States and Mexico, inhabiting grasslands and wooded areas. They feed mainly on seeds, insects, and bulbs, which they dig up with their strong legs. The Montezuma Quail is a discreet bird, often difficult to spot due to its shy behavior and ability to blend into its surroundings.
The Philortyx fasciatus, commonly known as the banded quail, is a bird species belonging to the Odontophoridae family. It is primarily found in the dry and semi-arid regions of Mexico, inhabiting oak forests, scrublands, and open grasslands. This medium-sized bird, measuring approximately 22 to 25 cm in length, is distinguished by its brown plumage with white and black bands on its belly, providing excellent camouflage in its natural habitat. The banded quail is a social bird, often seen in small groups. It primarily feeds on seeds, insects, and small invertebrates. Although it is relatively common within its range, habitat degradation poses a potential threat to its population.
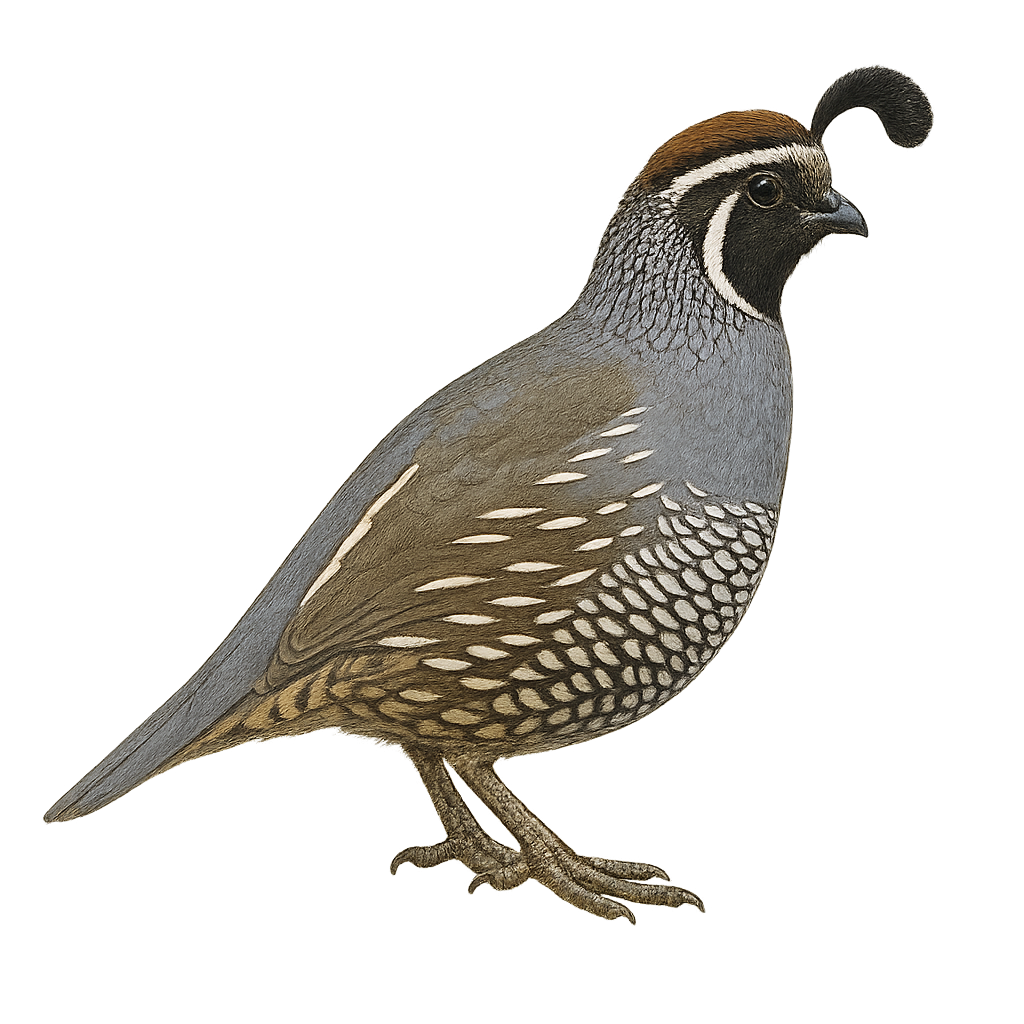
The California Quail, Callipepla californica, is a charming and distinctive bird, easily recognized by its teardrop-shaped plume adorning its head. This bird is primarily found in the western United States, particularly in California, where it inhabits scrublands, open forests, and grasslands. The quail's plumage is a blend of gray, brown, and white, with scaled patterns on the belly. Males are generally more colorful than females. Sociable by nature, it often lives in groups called "coveys," especially outside the breeding season. The California Quail feeds mainly on seeds, leaves, and insects. It is known for its distinctive and melodious calls, often heard at dusk.