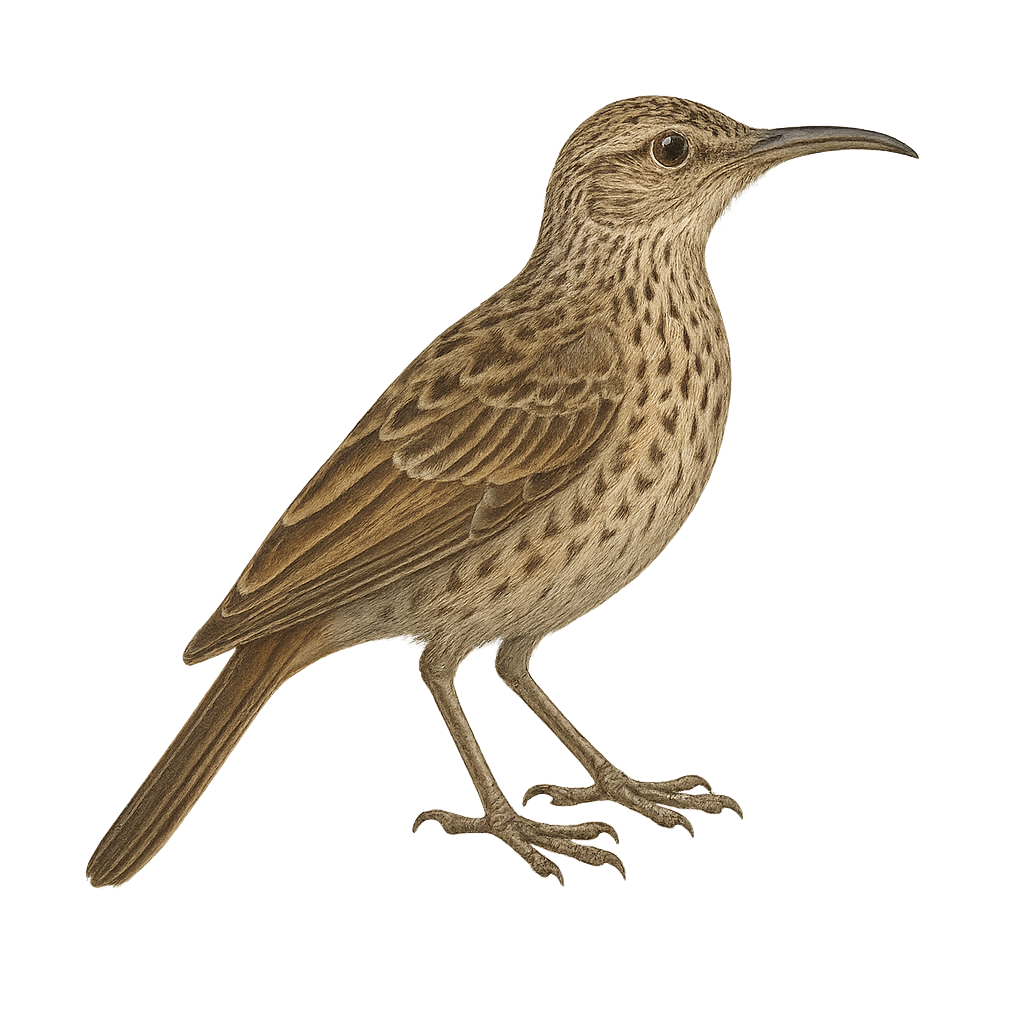
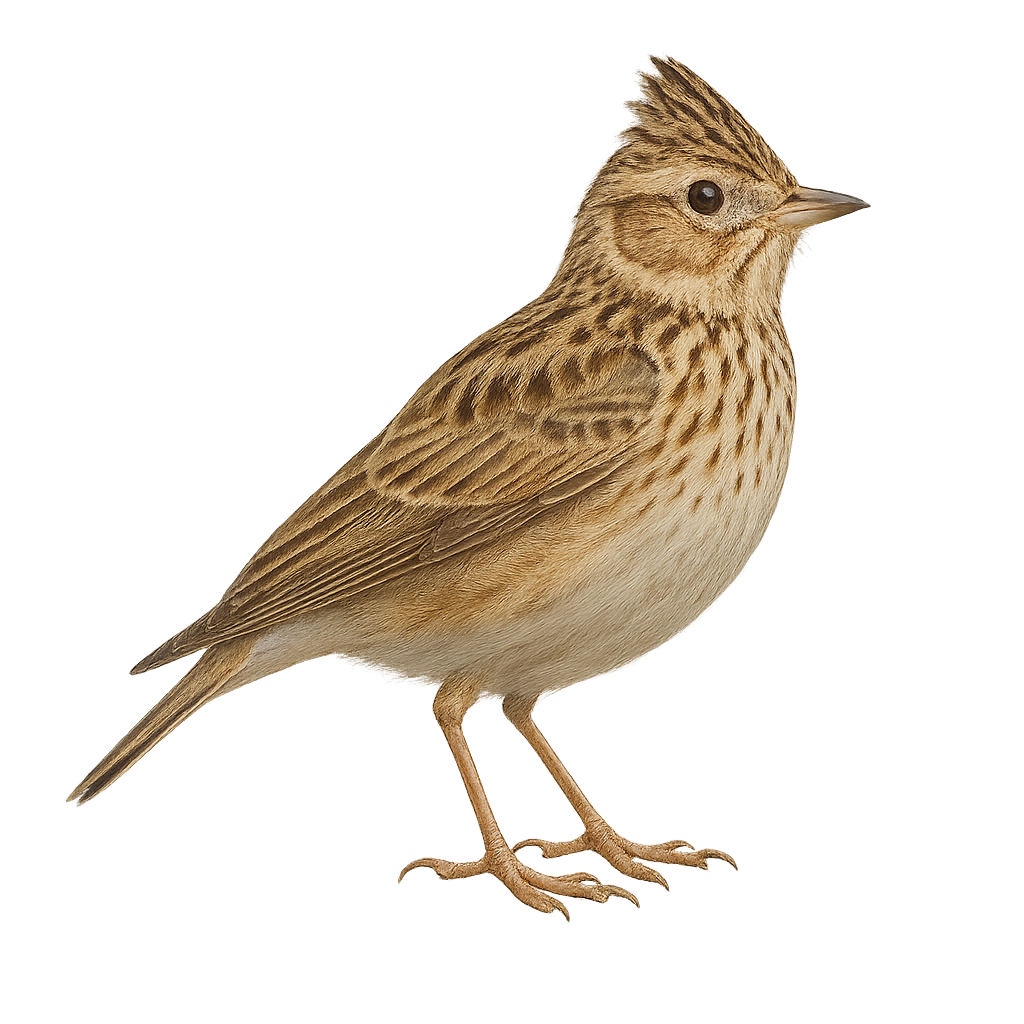
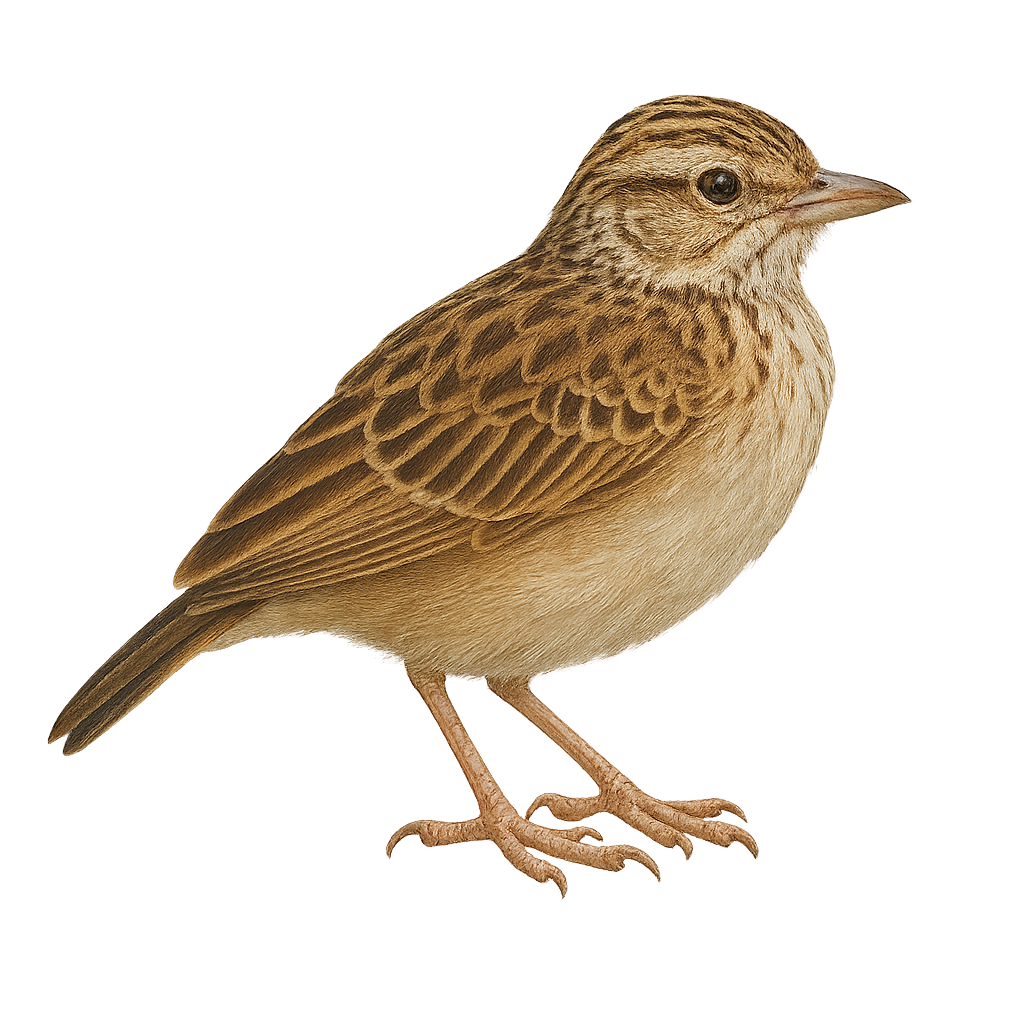
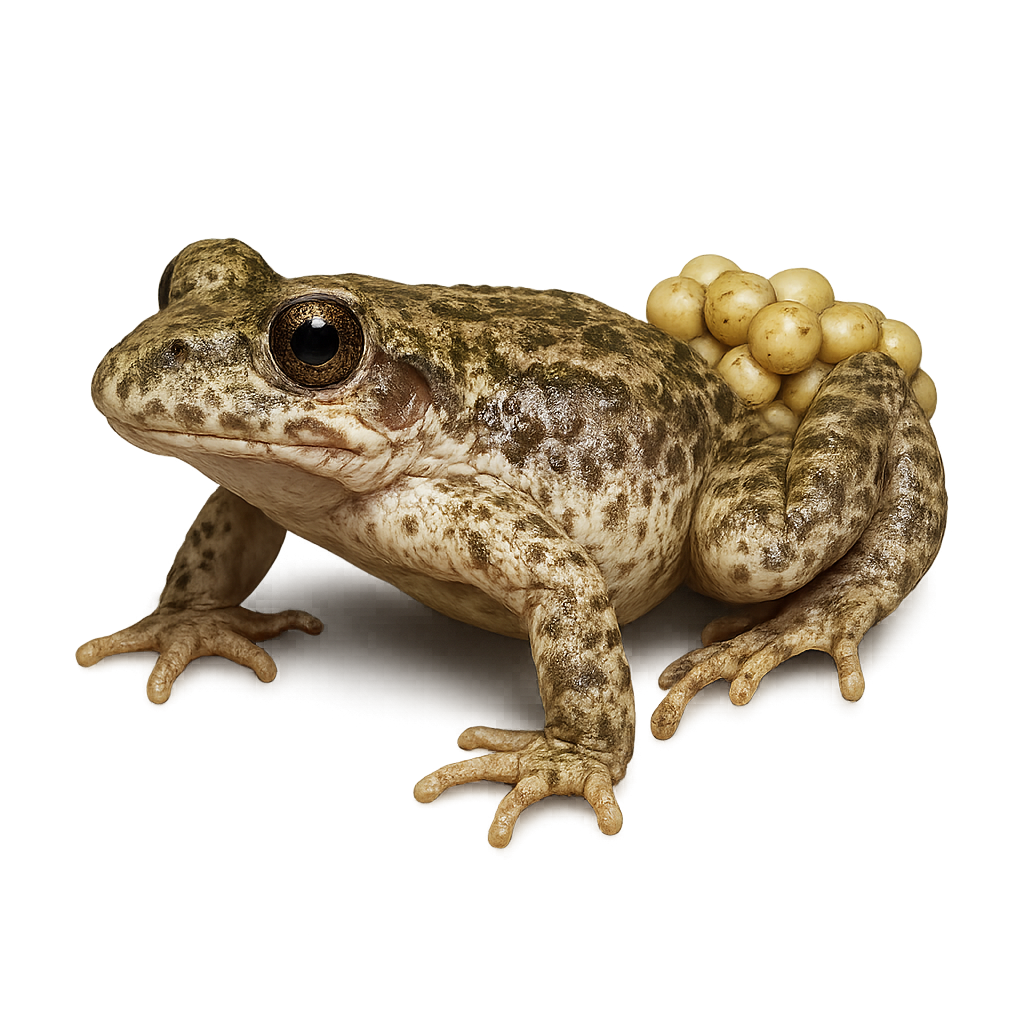
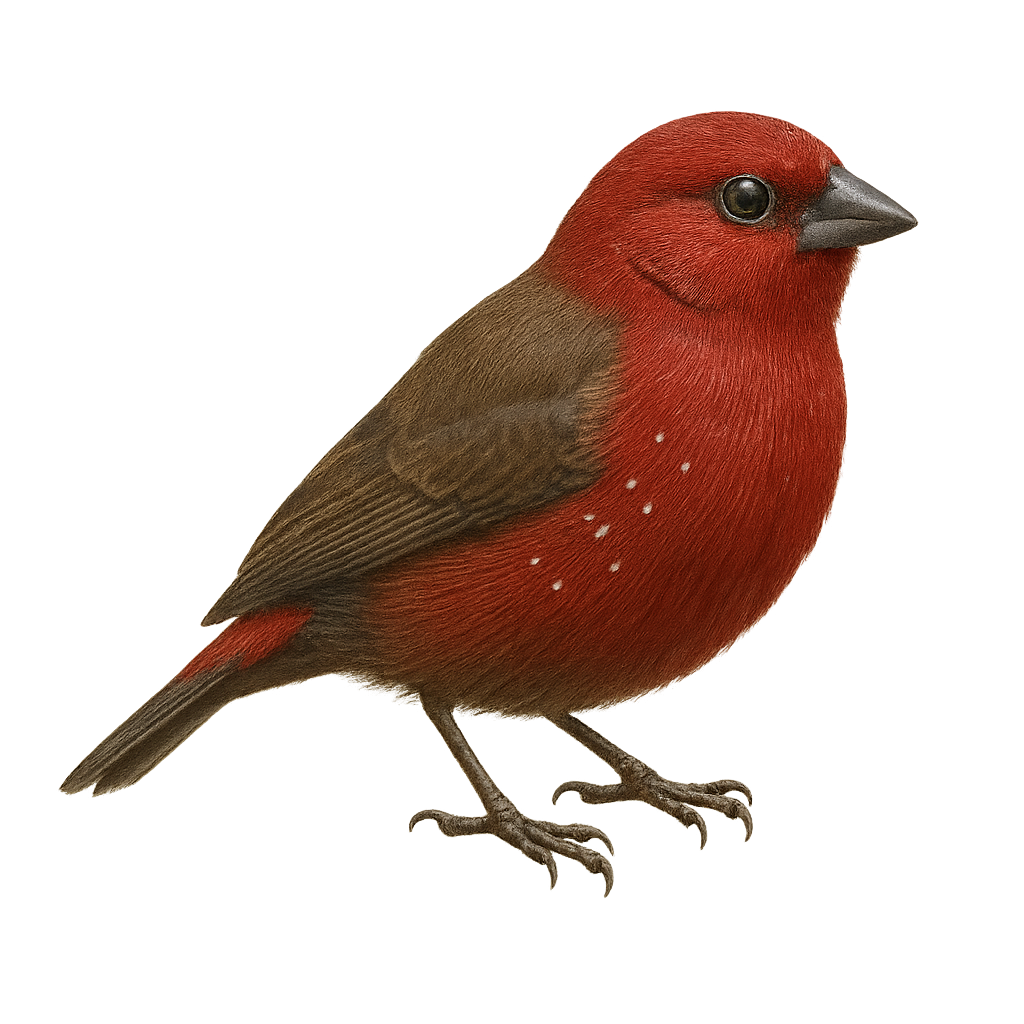
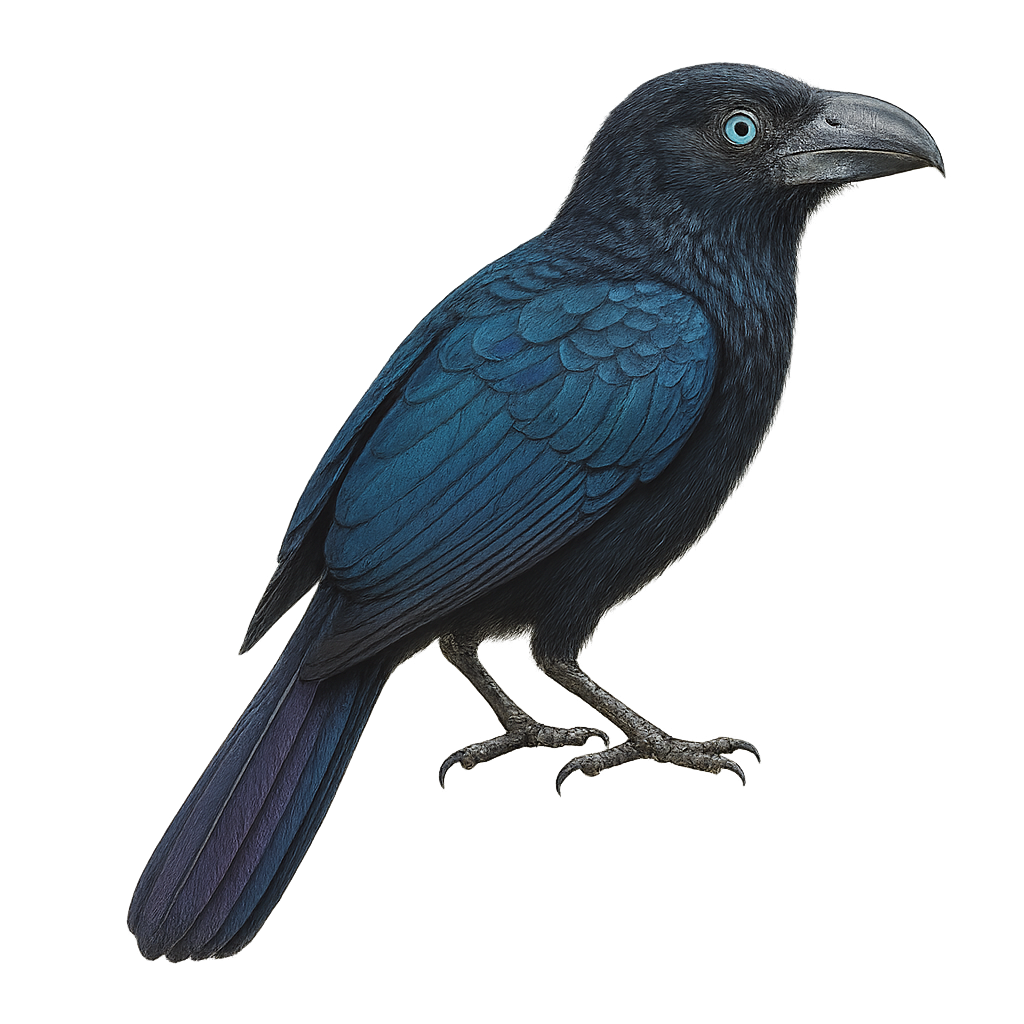
The Cape Long-billed Lark is a bird endemic to South Africa, well adapted to arid and semi-arid environments. It is characterized by its long, curved bill, which it uses to probe the ground for insects and seeds. Its plumage is generally brown with lighter shades on the belly, providing excellent camouflage in its natural habitat. Often seen alone or in small groups, it moves quickly on the ground. Although discreet, it is known for its melodious song, often delivered from a high perch. Its adaptability to harsh conditions makes it a resilient species, although its habitat is threatened by agricultural expansion.
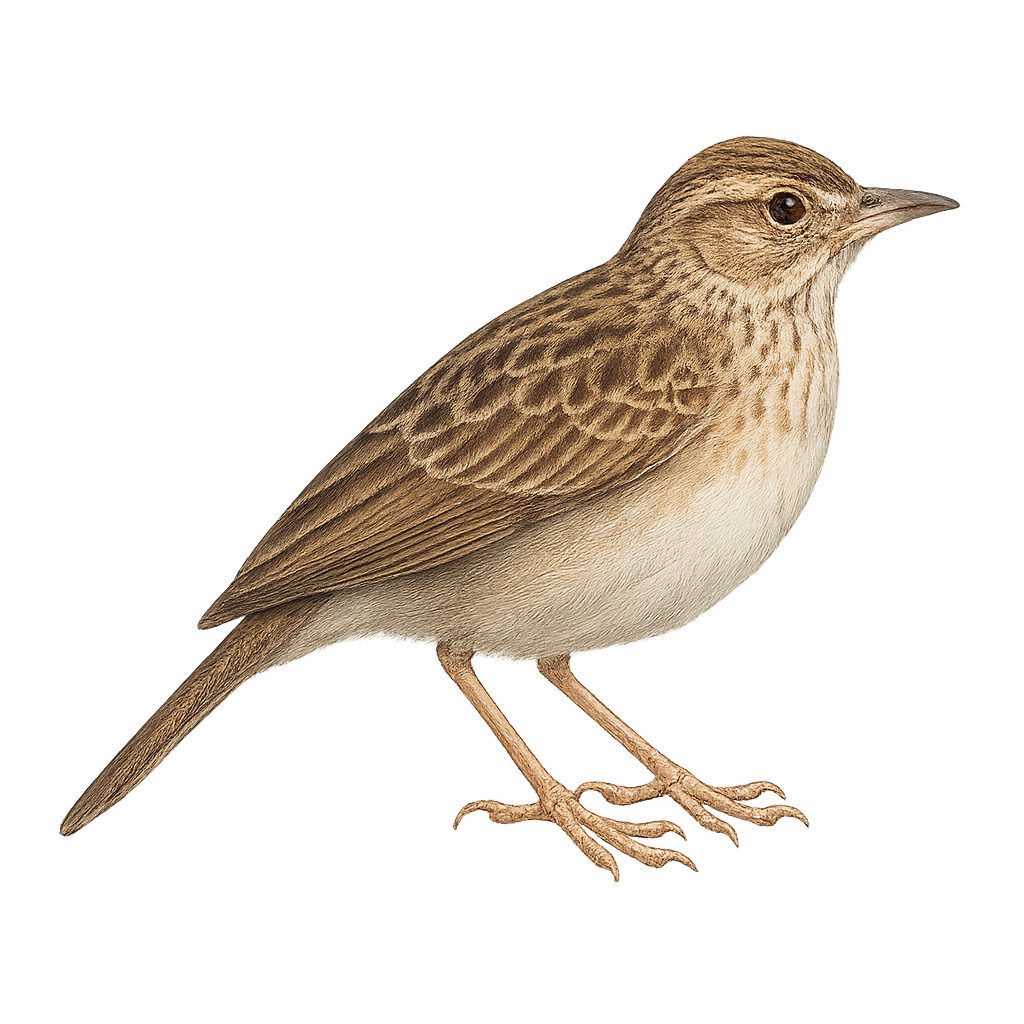
The lesser short-toed lark is a small passerine, 12–14 cm long, with streaked brown-grey plumage, a darker crown, and pale throat. It inhabits dry grasslands, steppes, and cereal fields across Europe, Asia, and North Africa, feeding mainly on insects and seeds on the ground. During breeding (April to July), the male performs song flights and ground displays to attract the female.
The Gillett's Lark (Calendulauda gilletti) is a discreet and little-known bird belonging to the Alaudidae family. It is mainly found in the arid and semi-arid regions of East Africa, particularly in Ethiopia and Somalia. This medium-sized bird has a sandy-brown plumage, perfect for blending into its desert environment. Its melodious and varied song is often heard at dawn and dusk, when it is most active. The Gillett's Lark primarily feeds on seeds and insects, which it finds by foraging on the ground. It builds its nest directly on the ground, hidden among dry grasses and shrubs.
The Alauda razae, commonly known as the Razo Skylark, is a bird species endemic to the island of Razo in the Cape Verde archipelago. This medium-sized bird, with its light brown plumage streaked with black, is perfectly adapted to its insular environment. It is known for its melodious and complex song, often performed in flight. The Razo Skylark is a terrestrial bird that prefers the open and arid areas of the island, where it primarily feeds on seeds and insects. Unfortunately, this species is critically endangered due to habitat loss and predation by introduced species. Conservation efforts are underway to protect this unique bird and its fragile habitat.
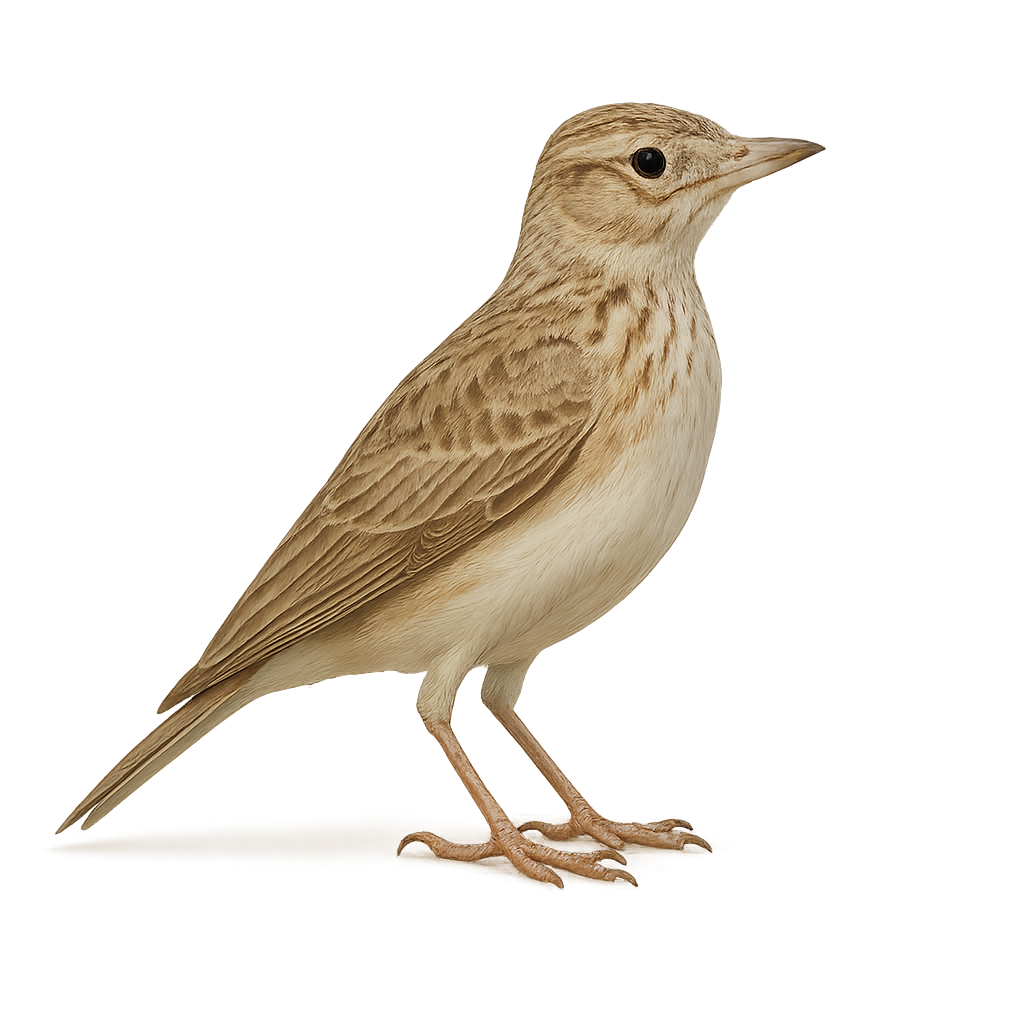
The Eurasian skylark is a small passerine of 15–17 cm with streaked brown plumage and pale underparts. It inhabits grasslands, cultivated fields and fallow land, feeding on seeds and insects on the ground or in flight. During the breeding season, males perform hovering song flights to attract females and defend territory.
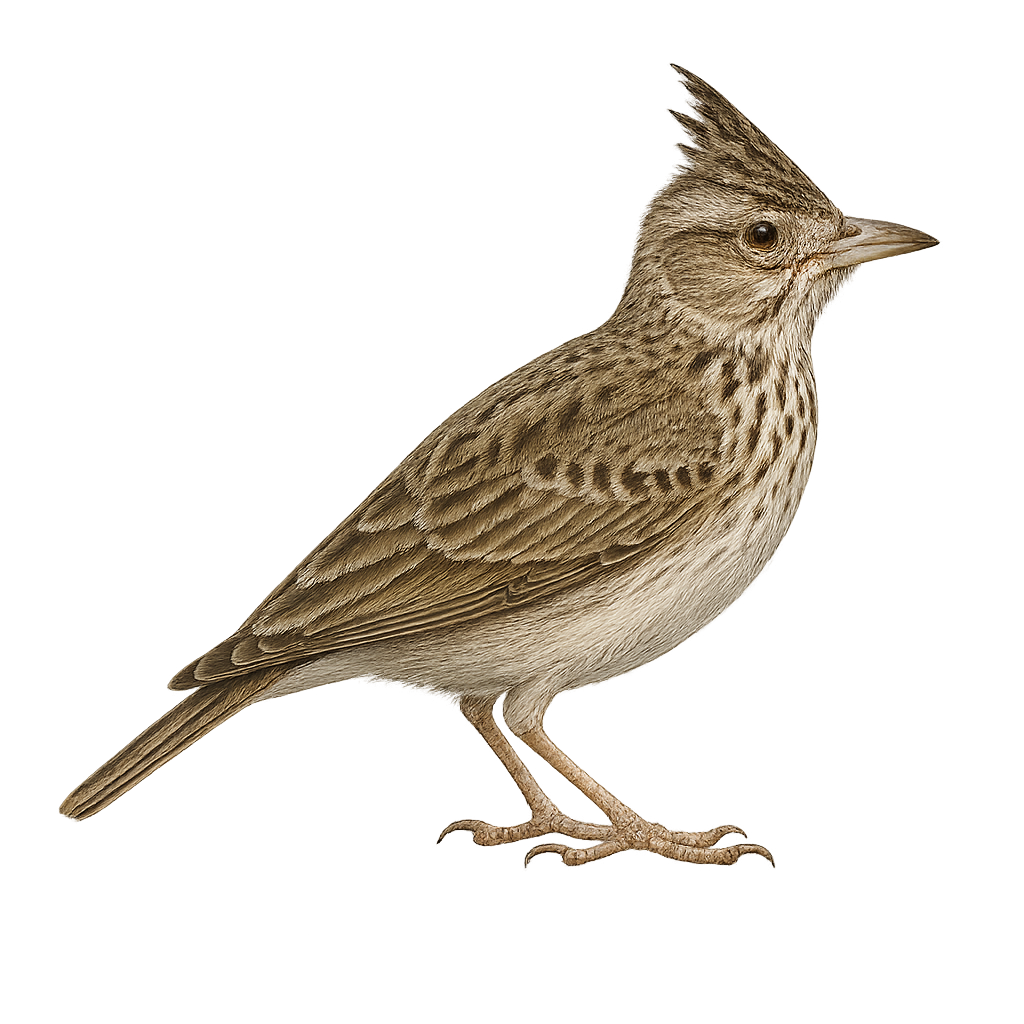
The Lulu's lark is a small lark found primarily in meadows, heathlands, and open fields across Europe and Asia. It is distinguished by its streaked brown plumage, light belly, and its discreet ground movements. This small bird is particularly known for its powerful song, which it performs in flight during its courtship displays. The Lulu’s lark primarily feeds on insects and seeds, which it searches for in low vegetation or on the ground.
The Sabota Lark is a small ground-dwelling bird found mainly in the semi-arid regions and savannas of southern Africa. It is recognizable by its sandy-brown plumage, speckled with darker patterns that allow it to blend seamlessly into its environment. Its melodious song, often delivered in flight, is a distinctive feature of this species. It primarily feeds on seeds and insects, which it finds by foraging on the ground. The Sabota Lark is a sedentary bird, well adapted to arid conditions, and is often observed in small groups or pairs. Although its habitat is sometimes threatened by agricultural expansion, it is currently classified as of least concern by the IUCN.
The common midwife toad is a stocky amphibian of 5–6 cm, with smooth olive-grey dorsal skin and a spotted throat. A terrestrial species of temperate Europe, it inhabits forest edges, meadows and urban areas near water bodies, where females lay eggs that males carry in strands until hatching.
The African Firefinch, or Lagonosticta rubricata, is a small African bird with bright red and brown plumage, often adorned with white spots on its belly. It is primarily found in savannas, open forests, and shrublands. This bird measures about 10 to 11 cm in length and weighs between 8 and 12 grams. Males and females exhibit sexual dimorphism, with males displaying brighter colors. They mainly feed on seeds but also consume insects. The African Firefinch is known for its melodious song and social behavior, often living in small groups. Its geographical range extends from West Africa to East Africa, and it is generally sedentary, although some local movements may occur depending on climatic conditions and resource availability.
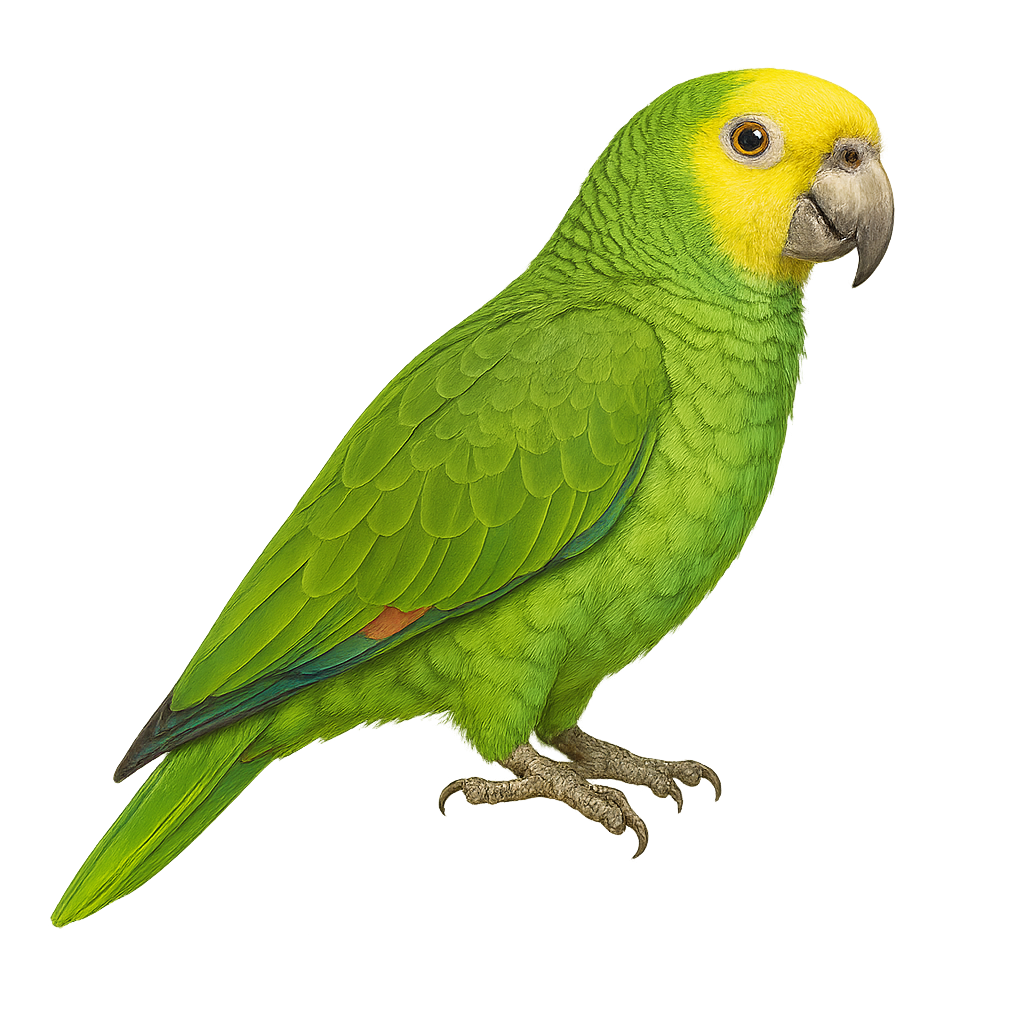
The Yellow-shouldered Amazon is a medium-sized parrot, measuring about 33 cm in length. Its plumage is primarily green, with yellow hues on the shoulders and head. This species is endemic to the islands of Barbados and some coastal regions of Venezuela. It mainly inhabits dry forests and mangroves. The Yellow-shouldered Amazon is known for its ability to mimic sounds and its sociability. Unfortunately, it is threatened by habitat loss and illegal trade. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure its survival.
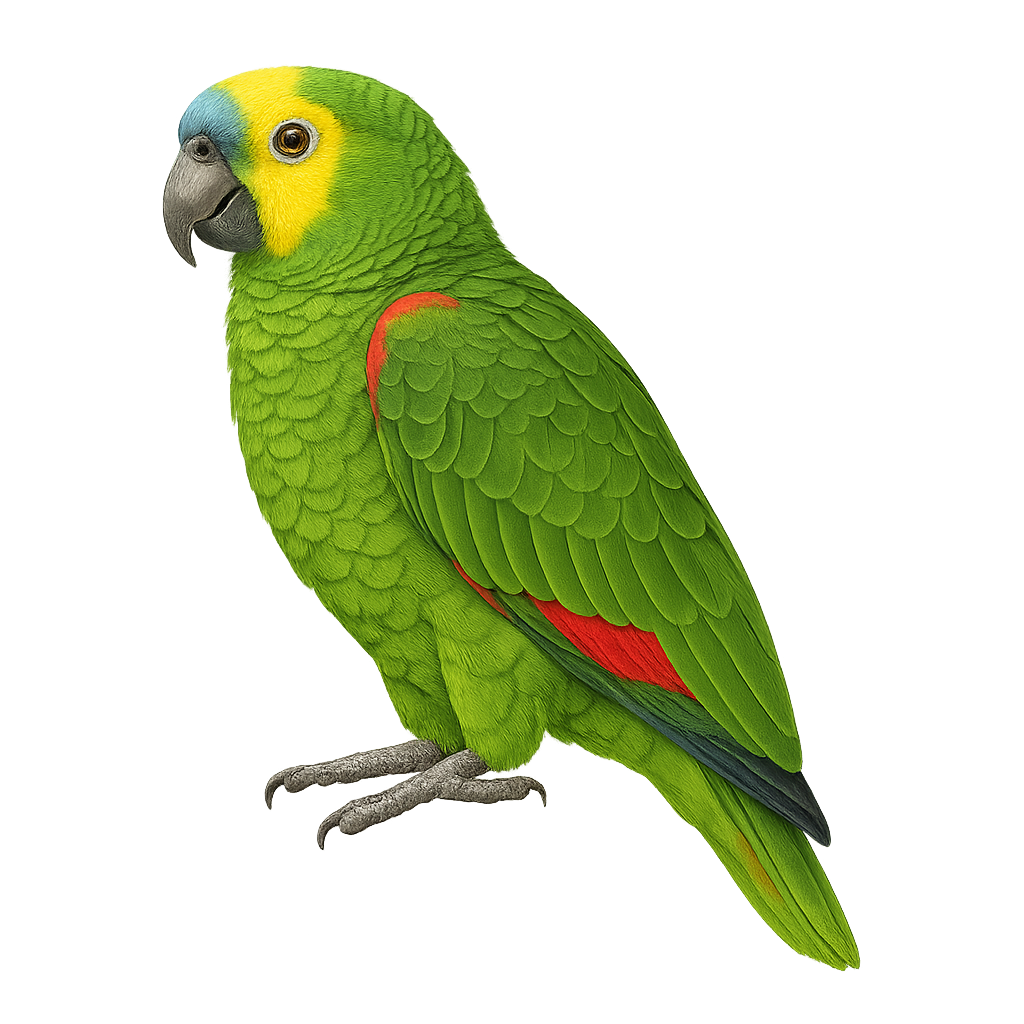
The Blue-fronted Amazon is a medium-sized parrot, measuring about 38 to 40 cm in length. Its plumage is primarily green, with shades of blue on the forehead and yellow patches around the eyes and cheeks. The wings feature red and blue feathers, adding a vibrant touch. Native to South America, it is mainly found in Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay, and Argentina. It inhabits various environments, from tropical forests to open savannas. Sociable and intelligent, this parrot is known for its ability to mimic human speech. Unfortunately, it is threatened by habitat loss and illegal trade.
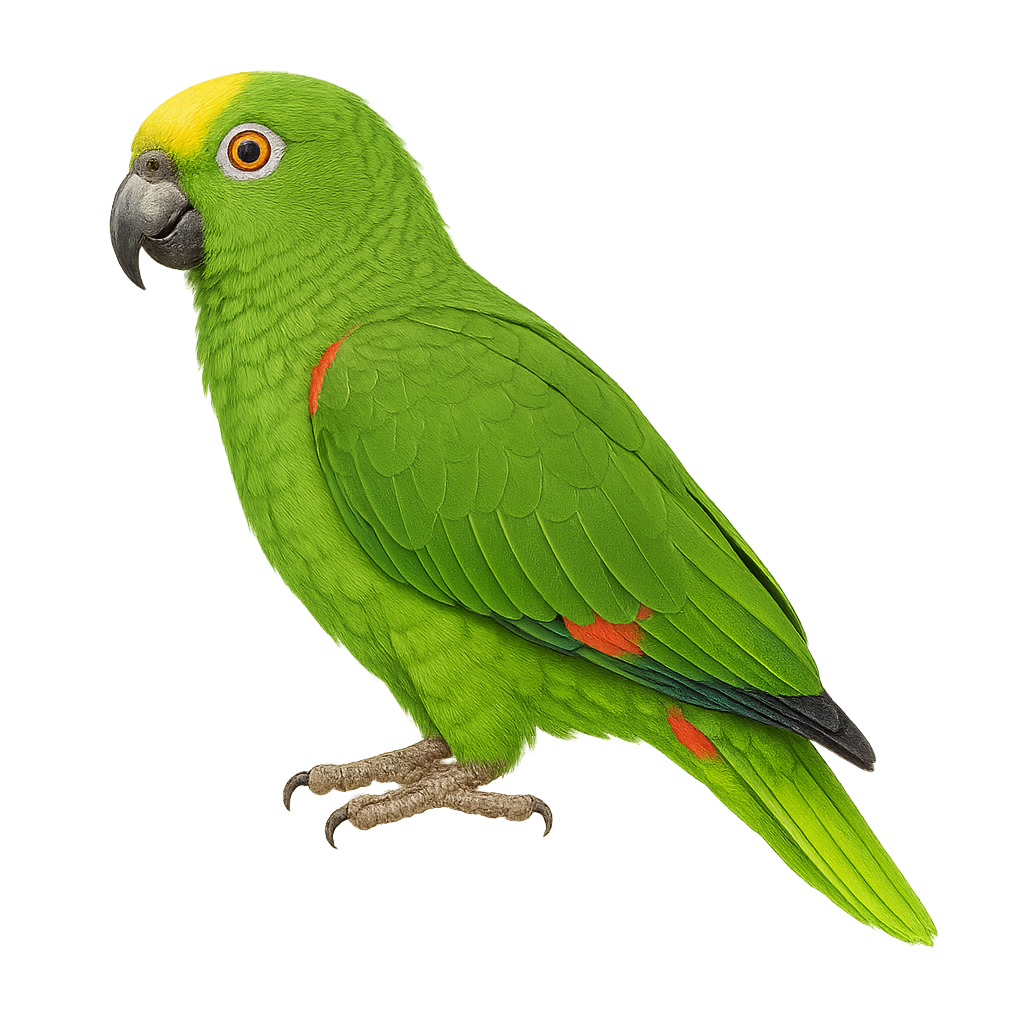
The Yellow-headed Amazon is a medium-sized parrot known for its bright yellow head contrasting with its green body. Native to the tropical and subtropical forests of Central and South America, it is often found in woodlands and mangroves. With remarkable intelligence, this species is famous for its ability to mimic sounds and human speech, making it a popular pet. However, its wild population is declining due to deforestation and illegal trade. It typically lives in groups and feeds on fruits, seeds, and nuts. In captivity, it can live up to 50 years.
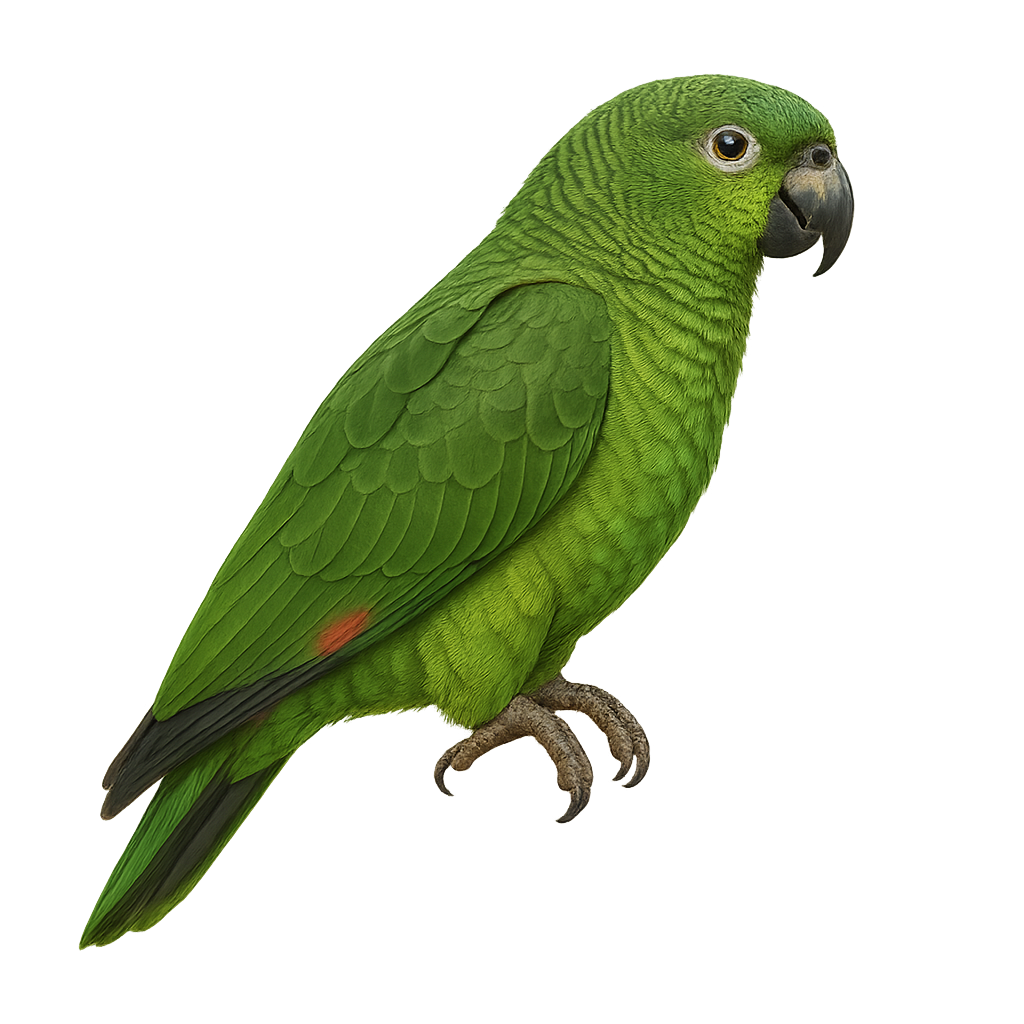
The Scaly-naped Amazon is a medium-sized parrot, measuring about 35 cm in length. Its plumage is primarily green, with blue hues on the head and red feathers on the wings. It is native to the humid forests of the Andes, living at altitudes between 1000 and 3000 m. This parrot is known for its ability to mimic sounds and its sociability. It primarily feeds on fruits, seeds, and flowers. Although its conservation status is concerning, it is still relatively common in some areas. The Scaly-naped Amazon is an intelligent and curious bird, often seen in small groups or pairs.
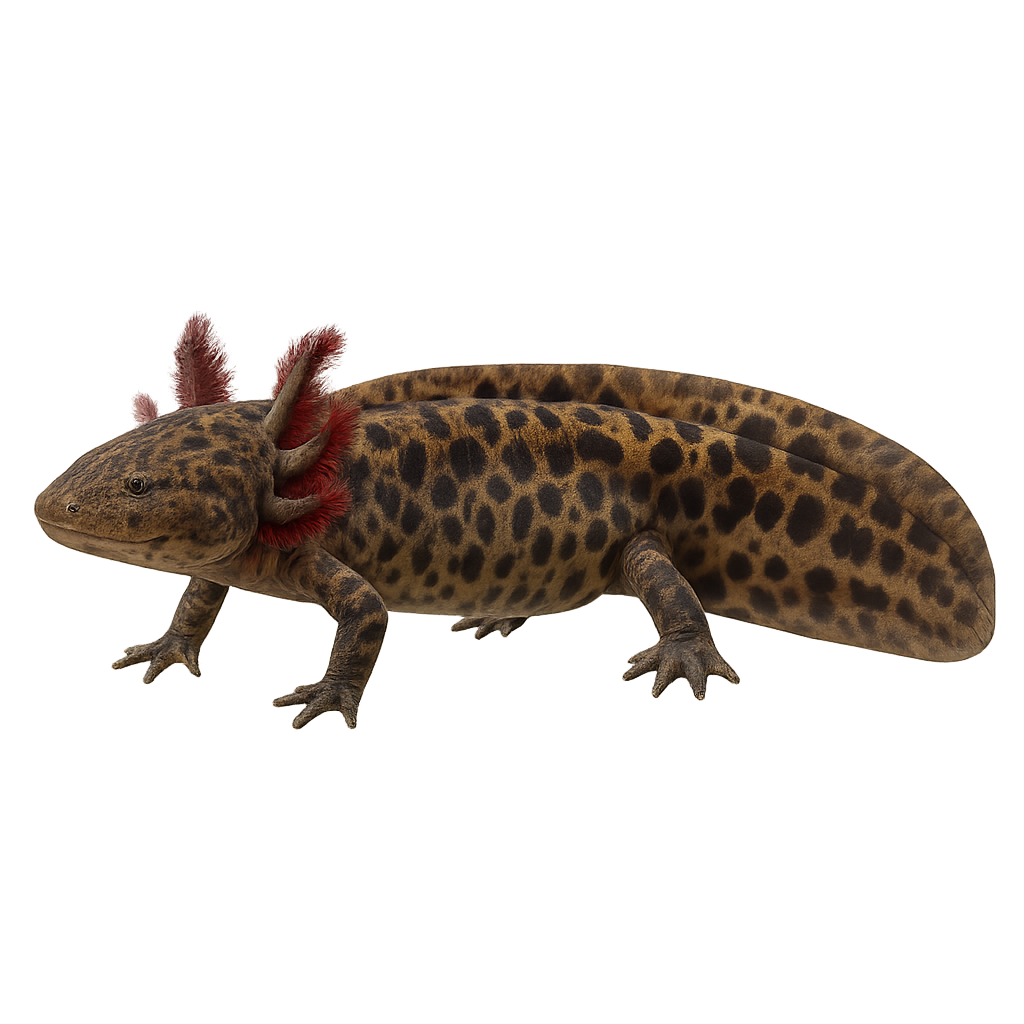
The Fisher’s salamander is an urodele amphibian endemic to the Lake Pátzcuaro basin (Michoacán, Mexico). It inhabits hot springs, marshes and wet meadows at 2030–2120 m elevation. Strictly nocturnal, it feeds on aquatic insects and small crustaceans. During the breeding season (July to September), males become territorial and perform body-undulation displays before egg‐laying.
The Ameerega ignipedis, commonly known as the Fire-legged Poison Frog, is a brightly colored frog species native to the humid tropical forests of South America. It is particularly recognizable by its vivid red legs, which contrast with its black or dark brown body. This diurnal frog is often observed on the forest floor, where it primarily feeds on small insects. Although its bright coloration serves as a warning to potential predators, indicating its toxicity, it is nonetheless vulnerable to habitat loss due to deforestation. Its reproduction typically occurs during the rainy season when conditions are ideal for tadpole development.
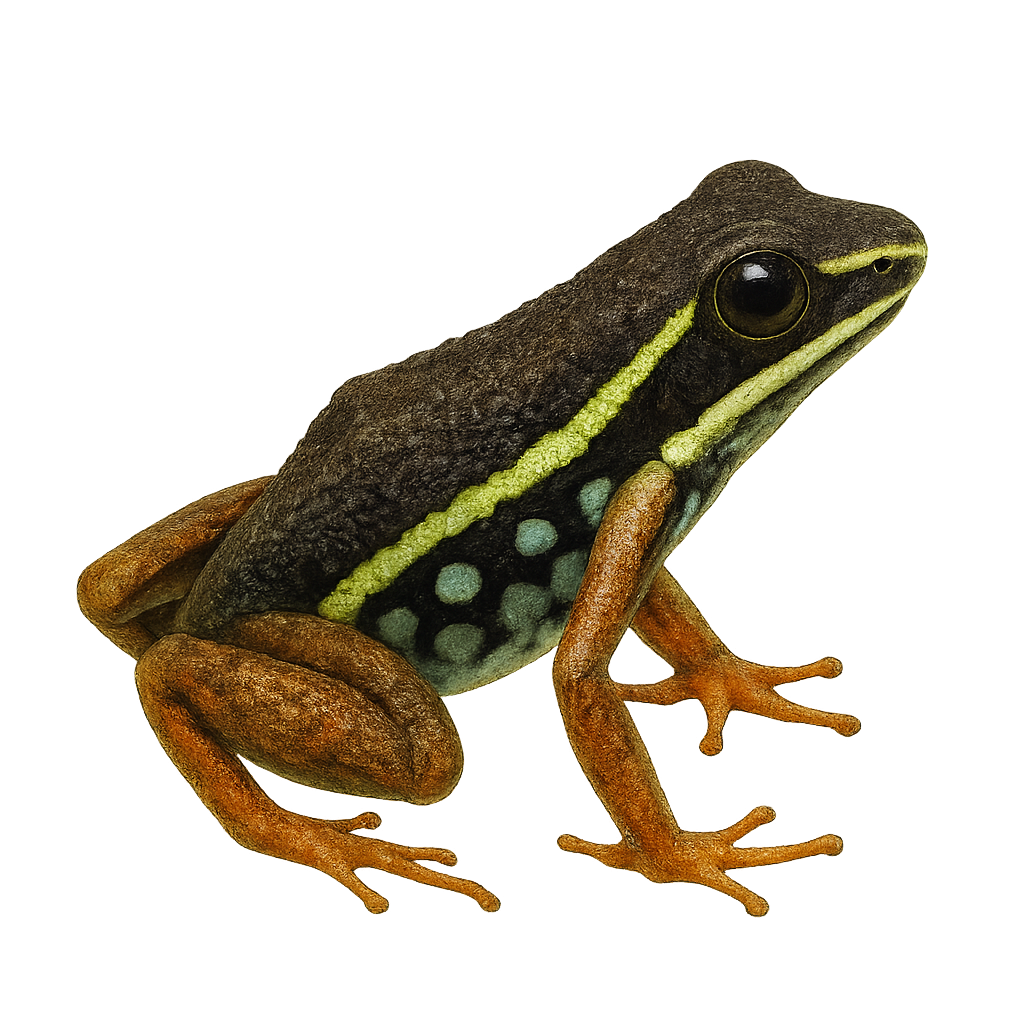
The Ameerega braccata is a captivating species belonging to the Dendrobatidae family. Native to the tropical rainforests of South America, it is renowned for its vibrant colors and intriguing behavior. This diurnal species thrives in humid environments, such as undergrowth and areas near water bodies, and primarily feeds on small insects and invertebrates. Although its conservation status is not currently alarming, deforestation and habitat loss pose potential threats. Reproduction typically occurs during the rainy season when conditions are optimal for tadpole development.
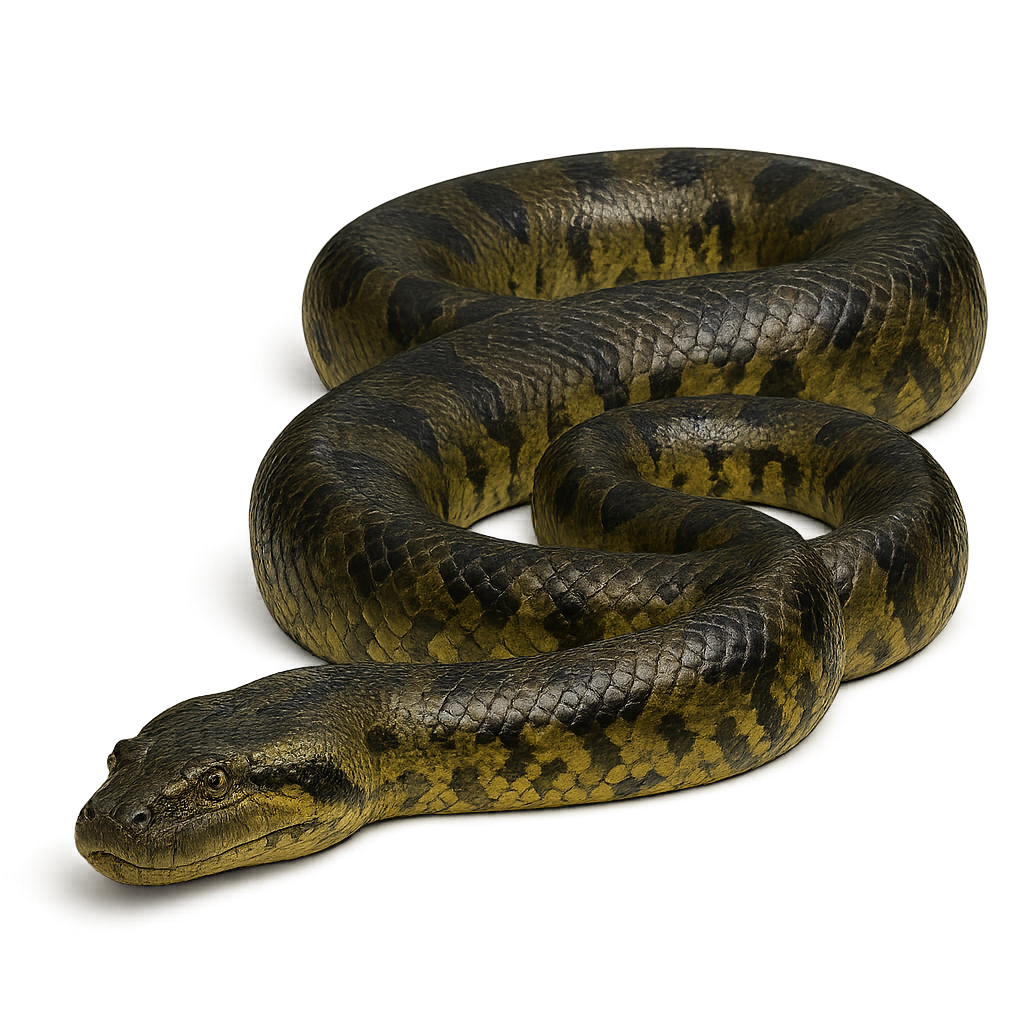
The Green Anaconda is one of the largest and most powerful snakes in the world, known for its impressive size, which can exceed 8 meters in length. This semi-aquatic snake lives in the rivers and swamps of the tropical forests of South America, where it preys on animals as large as caimans, deer, and fish. With its muscular body and constriction technique, the Anaconda can immobilize and swallow prey much larger than itself. It spends most of its time in the water, where it moves with remarkable agility.
Although often feared, the Green Anaconda is a discreet predator, preferring to camouflage itself in dense vegetation while waiting for prey.
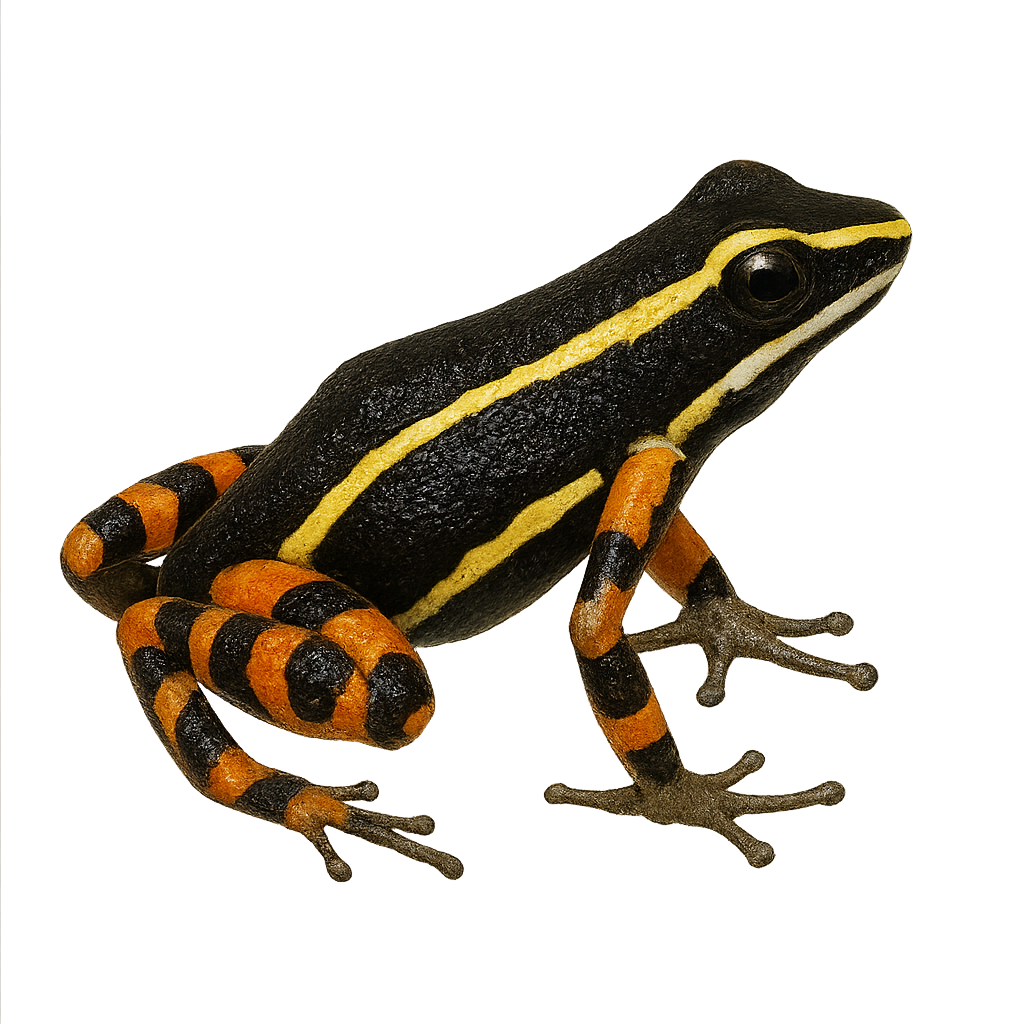
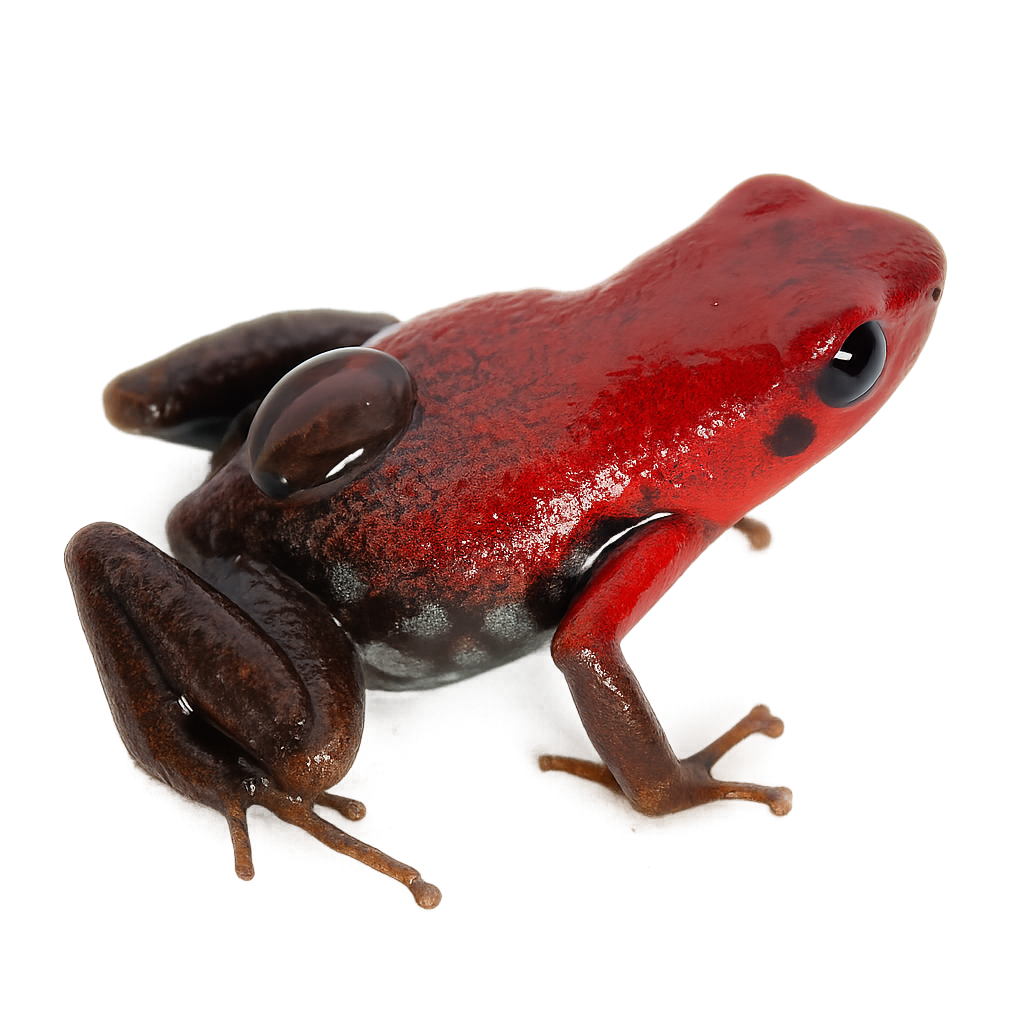
The Andean poison frog is a small, brightly colored frog, predominantly black with red or yellow spots, inhabiting the humid tropical forests of Colombia. Measuring about 2 to 3 cm, this species is known for its toxic skin, a natural defense against predators. It primarily feeds on small insects and arthropods. Males are territorial and use vocalizations to attract females and ward off rivals. Their reproduction involves parental care, with the male carrying tadpoles on his back to suitable water points. This species is threatened by deforestation and habitat loss, leading to its classification as vulnerable by the IUCN.
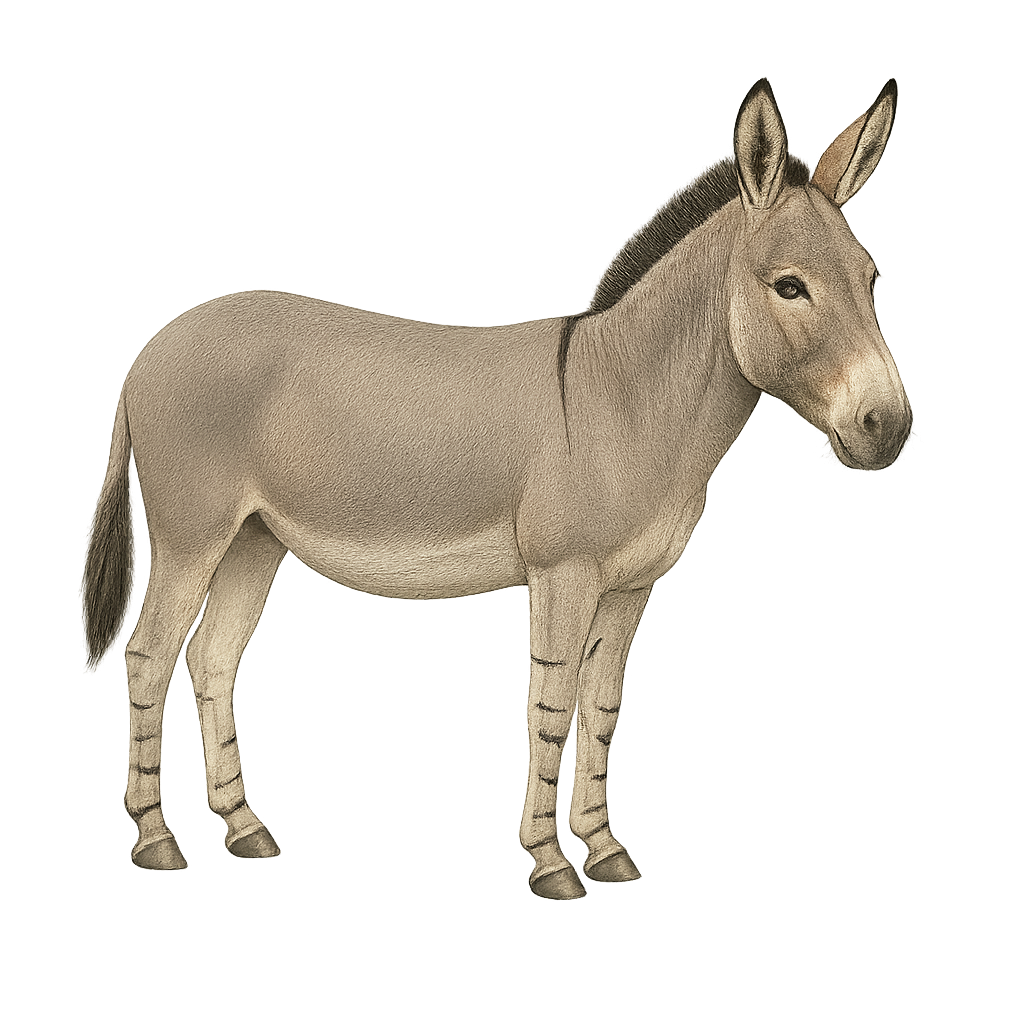
The African Wild Ass, or Equus africanus, is a species of equid native to the arid and semi-arid regions of East and Northeast Africa. It is the wild ancestor of the domestic donkey. This mammal is well adapted to its harsh environment, capable of surviving with minimal water and food. It has a light grey coat with black stripes on its legs, reminiscent of a zebra. Its long, mobile ears allow it to detect predators from a distance. The African Wild Ass lives in small family groups and primarily feeds on grasses and shrubs. Unfortunately, it is critically endangered due to hunting and habitat loss.
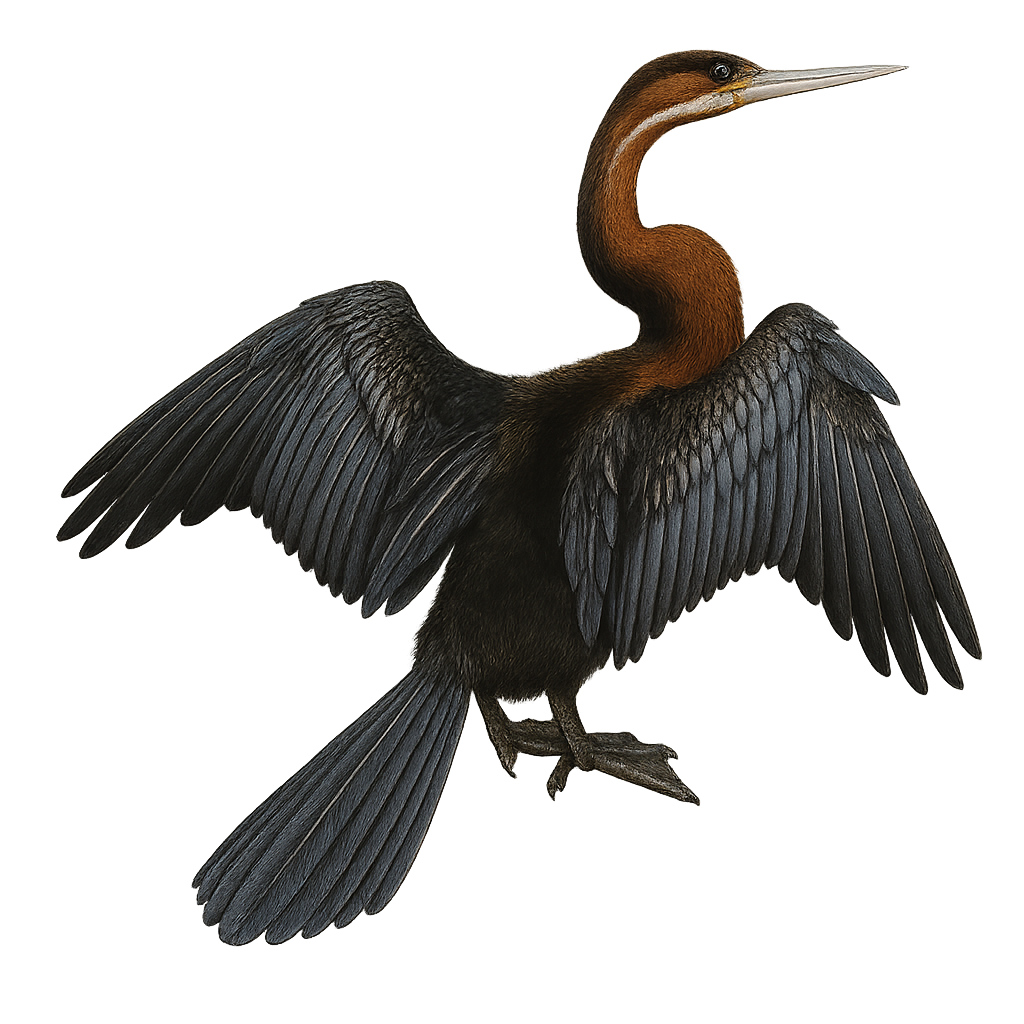
The African Darter, or Anhinga rufa, is a slender waterbird known for its long, snake-like neck and dark plumage. It primarily inhabits lakes, rivers, and marshes in sub-Saharan Africa. This bird is often seen swimming with only its neck and head above water, resembling a snake. The African Darter feeds mainly on fish, which it catches with its sharp, pointed bill. After fishing, it often perches on a branch to dry its wings, as its feathers are not waterproof. This behavior is crucial for maintaining its flight capability.
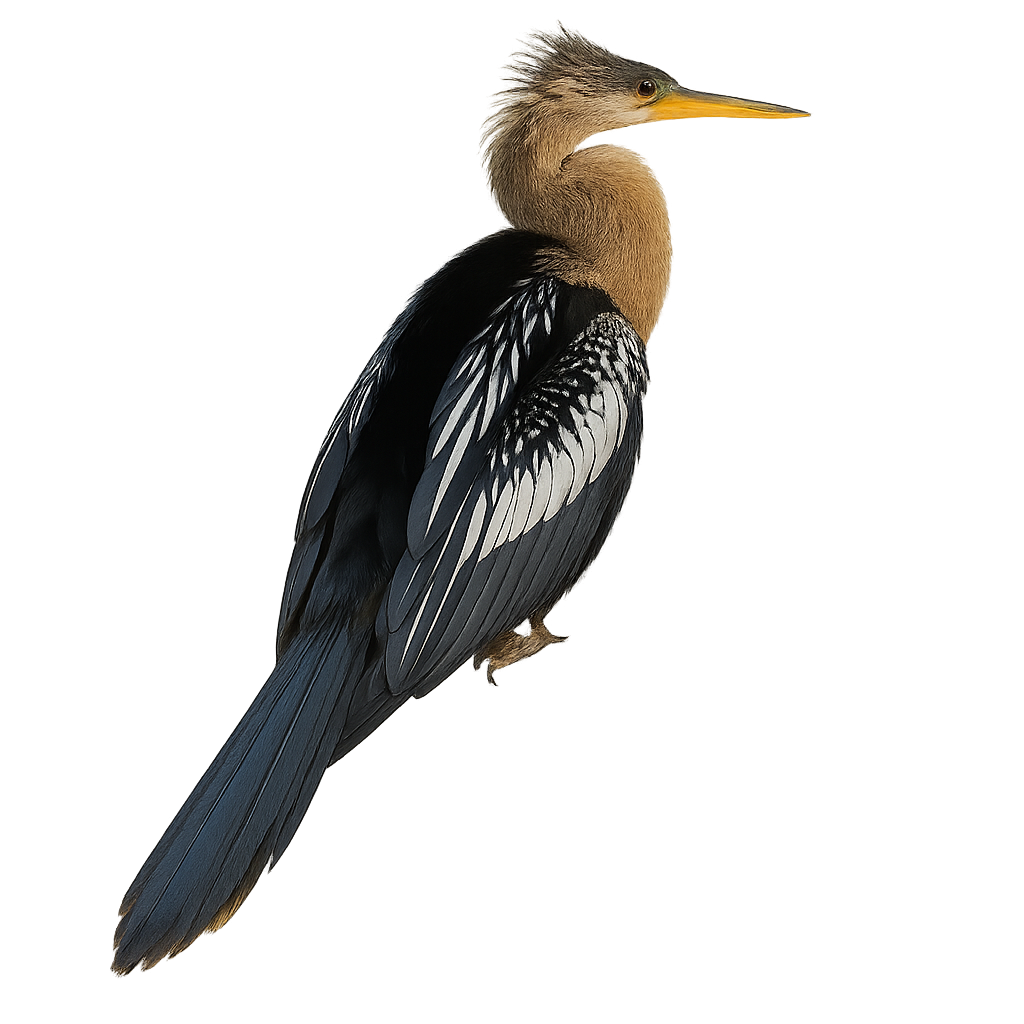
The Anhinga, also known as the "snakebird," is a captivating aquatic bird. It is characterized by its long, sinuous neck and sharp beak, ideal for catching fish. Its plumage is predominantly black with metallic sheens, and its wings feature distinctive silver patterns. Unlike other water birds, the Anhinga lacks oil glands to waterproof its feathers, making it more adept at diving deep to hunt. After fishing, it must dry its wings by spreading them in the sun. It is primarily found in swamps, lakes, and rivers of Central and South America.
The Groove-billed Ani is a medium-sized bird, easily identified by its glossy black plumage and distinctive grooved bill. It is primarily found in tropical and subtropical regions of Central and South America. This sociable bird lives in family groups and feeds mainly on insects, fruits, and small vertebrates. It is often seen in open areas, grasslands, and forest edges. Its call is a mix of whistles and chirps. Although generally not very shy, it can be suspicious in the presence of potential threats.
The Greater Ani, scientifically known as Crotophaga major, is a bird belonging to the Cuculidae family, predominantly found in South America. It is recognized by its glossy black plumage and thick, curved bill. This bird measures about 48 cm in length and is often seen in noisy groups. It inhabits wetlands, swamps, and flooded forests. The Greater Ani is a social bird that builds communal nests where multiple females lay their eggs. Its diet mainly consists of insects, small vertebrates, and fruits. Although relatively common within its range, it is sometimes threatened by the destruction of its natural habitat.
The Blue Anole is a small arboreal lizard, measuring approximately 13 to 15 cm in total length. It is notable for its uniform bright blue coloration, unique among reptiles. Males have a pure white dewlap. This species is endemic to Gorgona Island, off the coast of Colombia, where it inhabits the canopy of humid tropical forests. It is diurnal and primarily insectivorous. Reproduction is oviparous, with eggs laid on vegetation surfaces. Classified as Near Threatened by the IUCN, the species is vulnerable due to its limited distribution and deforestation.
The Knight Anole, or Anolis equestris, is a large lizard native to Cuba, although it has been introduced to parts of Florida. It can grow up to 50 cm in length, including the tail, and is known for its bright green color, which can vary depending on its mood or environment. This arboreal lizard prefers humid tropical forests where it primarily feeds on insects, small birds, and fruits. It has a broad head and mobile eyes, allowing for effective peripheral vision. Males have a prominent dewlap used to impress females or intimidate rivals.
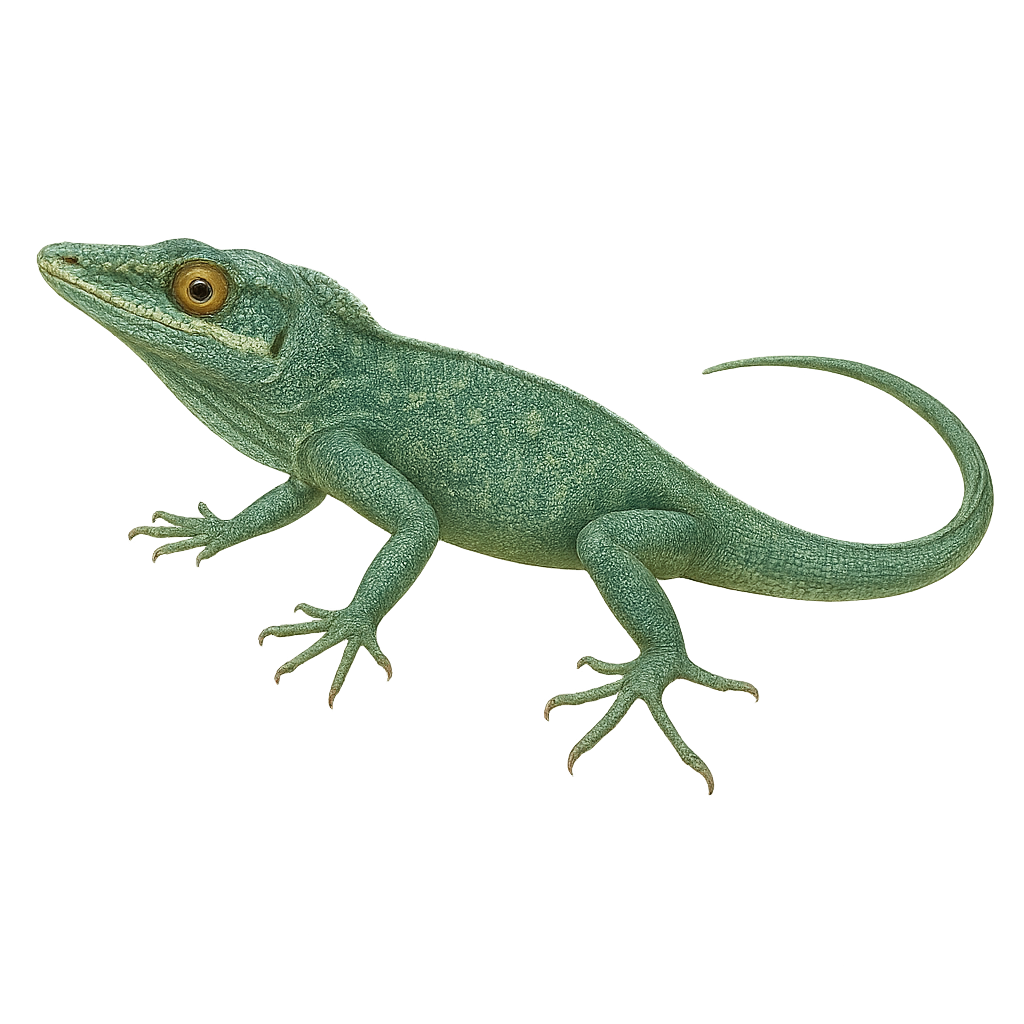
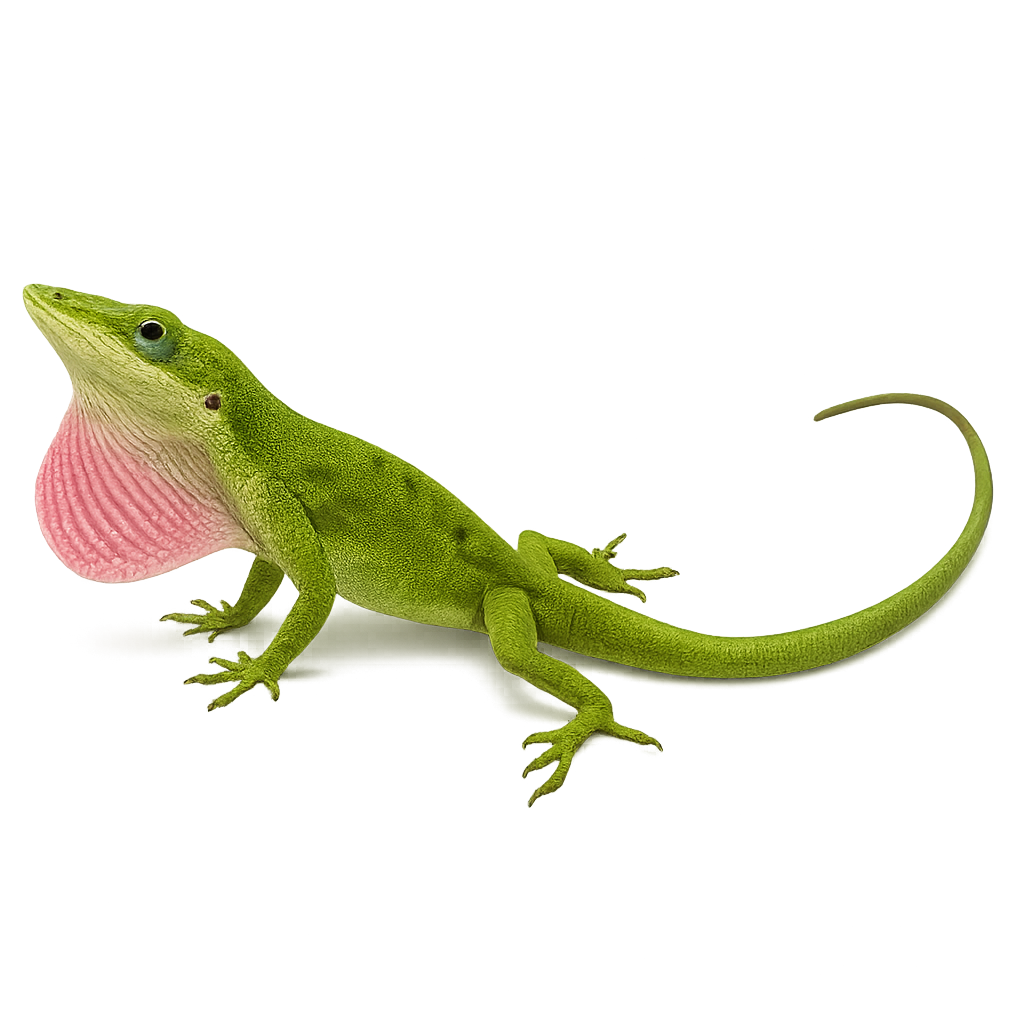
The Anolis carolinensis, commonly known as the green anole, is a small arboreal lizard native to the southeastern United States. It is easily recognizable by its bright green color, although it can change to brown depending on its mood or environment. Typically measuring between 12 and 20 cm, this anole has a long tail and adhesive toes that allow it to climb easily. It primarily feeds on insects and plays an important role in controlling pest insect populations. The green anole is often seen in gardens, forests, and urban areas, where it adapts well to human presence.
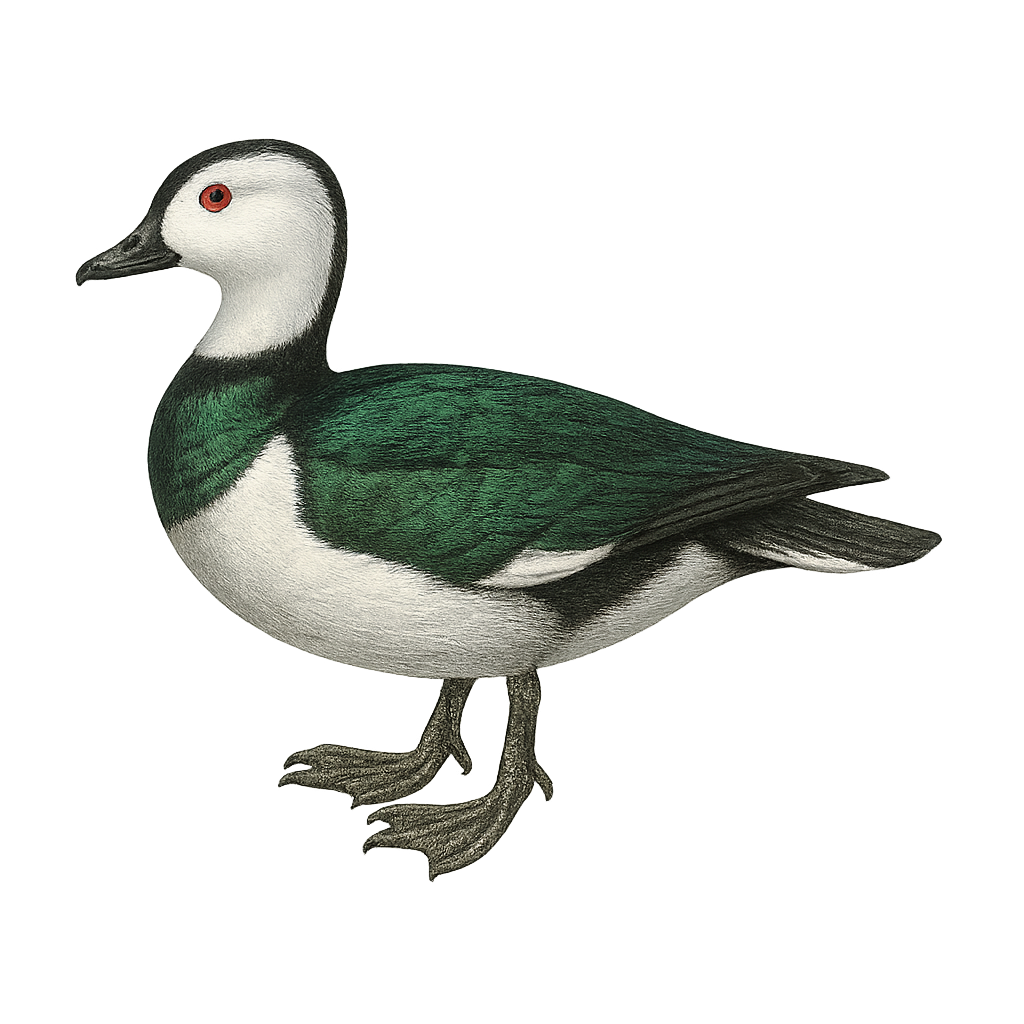
The Cotton Pygmy Goose is a small, tree-dwelling duck often mistaken for a goose due to its English name. It is identifiable by the male's striking black and white plumage, while the female displays more subdued shades of brown and grey. It primarily inhabits the wetlands of South and Southeast Asia, feeding on aquatic plants and small invertebrates. Its small size allows it to navigate dense vegetation with ease. Although its flight is swift and direct, it spends much time swimming on the water's surface. The species is generally discreet but can be seen in small groups.
The Green Pygmy Goose, or Nettapus pulchellus, is a tiny, vibrantly colored duck found in northern Australia and New Guinea. Its plumage features metallic green, white, and dark brown tones, with a compact body and short bill. It inhabits lagoons, swamps, and flooded woodland areas. Omnivorous, it feeds on seeds, aquatic plants, and small invertebrates. Usually shy and solitary, it can also be seen in small groups. Its population is considered stable, although it relies heavily on healthy wetland ecosystems.
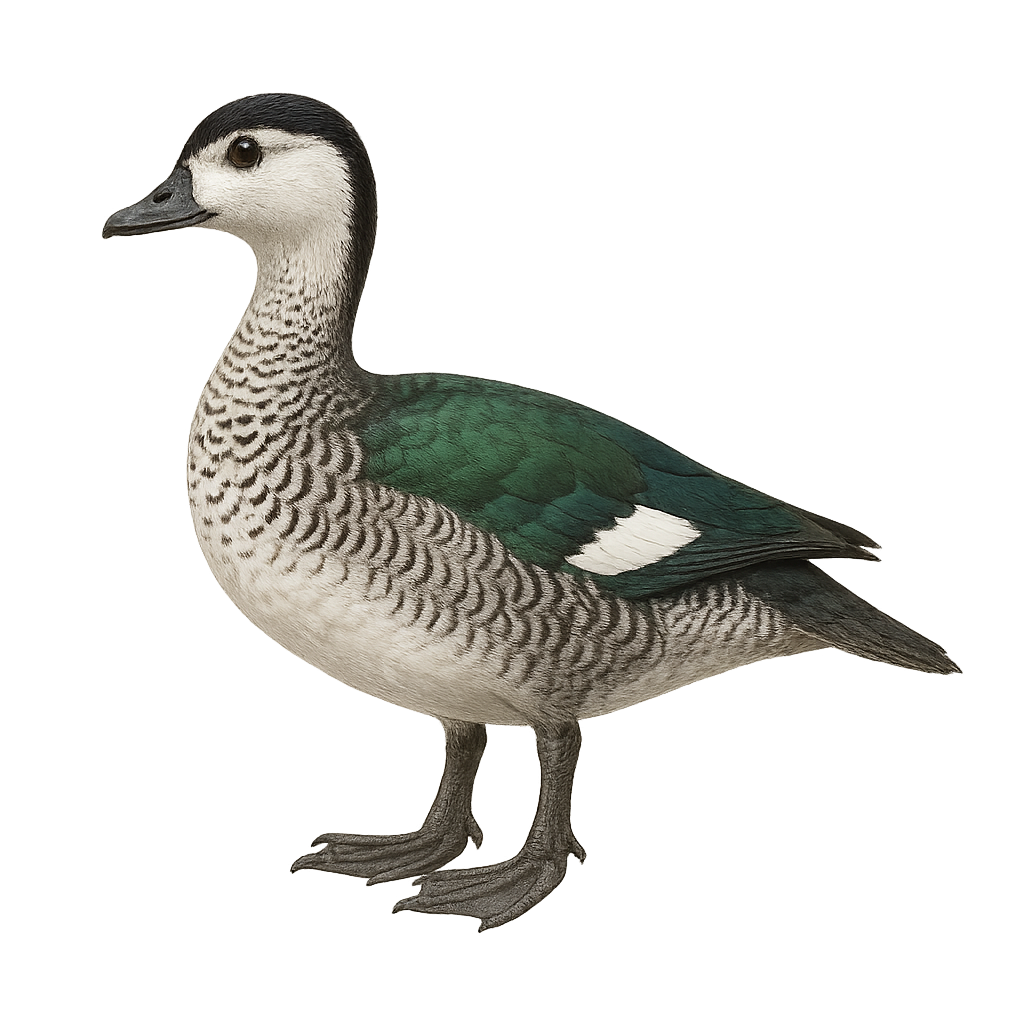
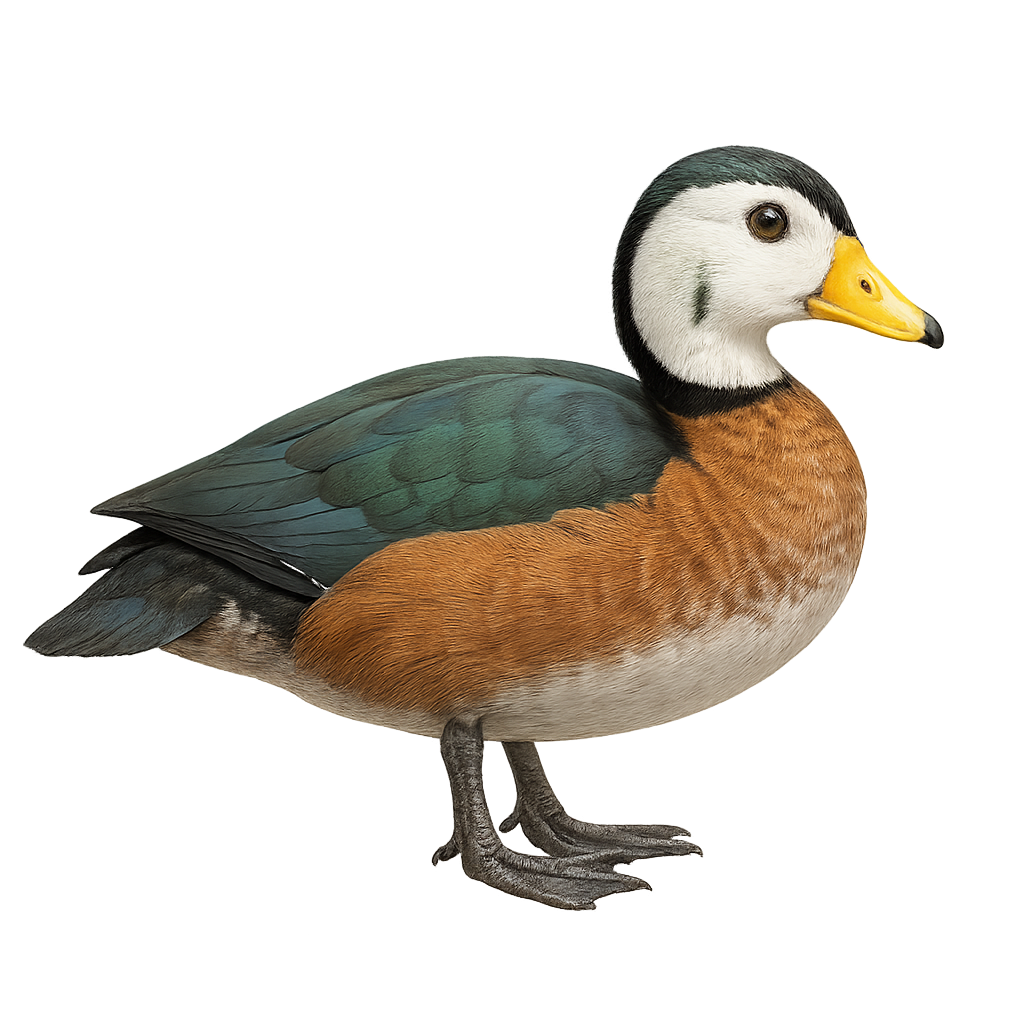
The Nettapus auritus, or African Pygmy Goose, is a small African duck with distinctive plumage. Males have a white head with metallic green patches, while females display more subdued tones. Their body is mainly brown with greenish reflections on the wings. These aquatic birds prefer wetlands such as marshes and shallow lakes where they feed on seeds and aquatic plants. They are often seen in small groups and are known for their fast, direct flight. Their behavior is generally suspicious, making them difficult to approach.
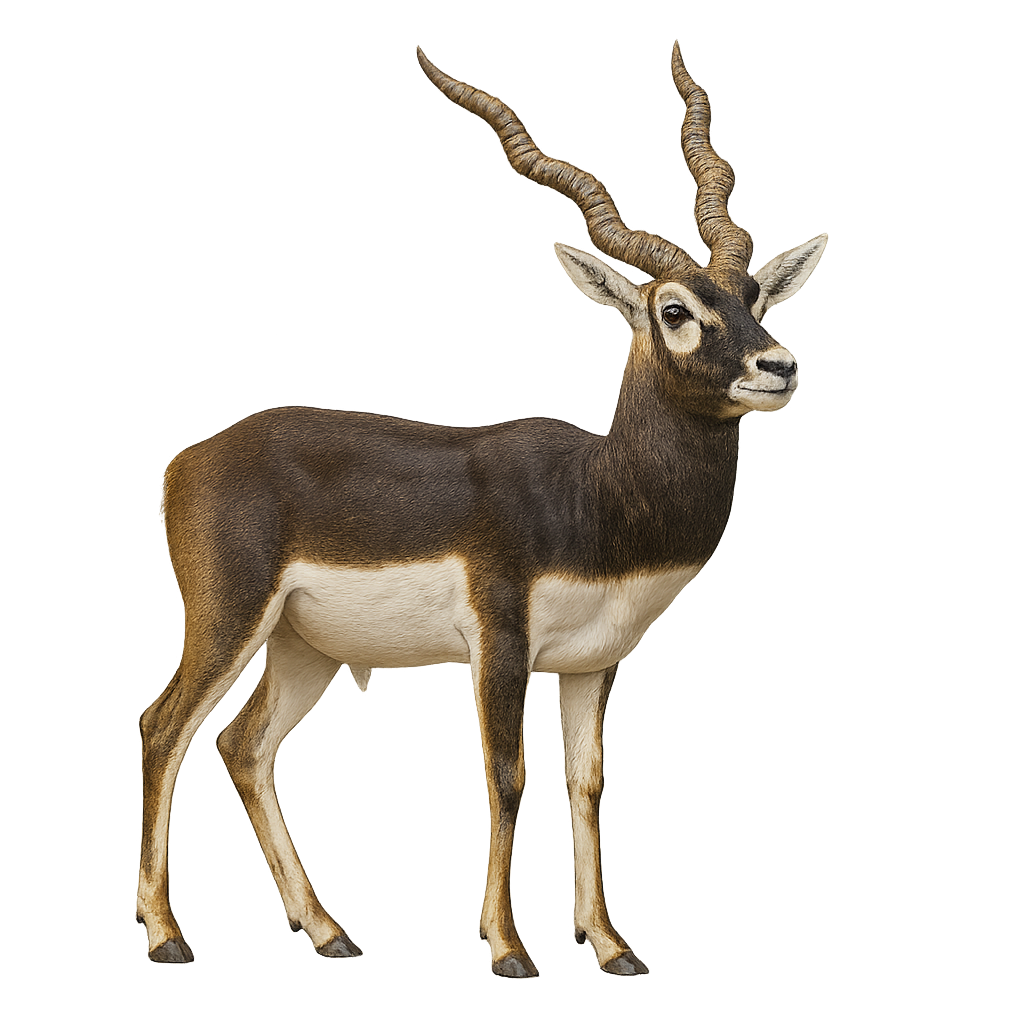
The Blackbuck, or Antilope cervicapra, is a species of antelope native to the Indian subcontinent. It is easily identifiable by its spiral horns and contrasting coat: males have a striking black and white coloration, while females and juveniles are fawn-colored. These antelopes primarily inhabit grassy plains and open savannas, moving in herds. They are diurnal, spending most of the day grazing. Their diet mainly consists of grasses, but they also eat leaves and fruits. Blackbucks are known for their speed and agility, which help them evade predators.