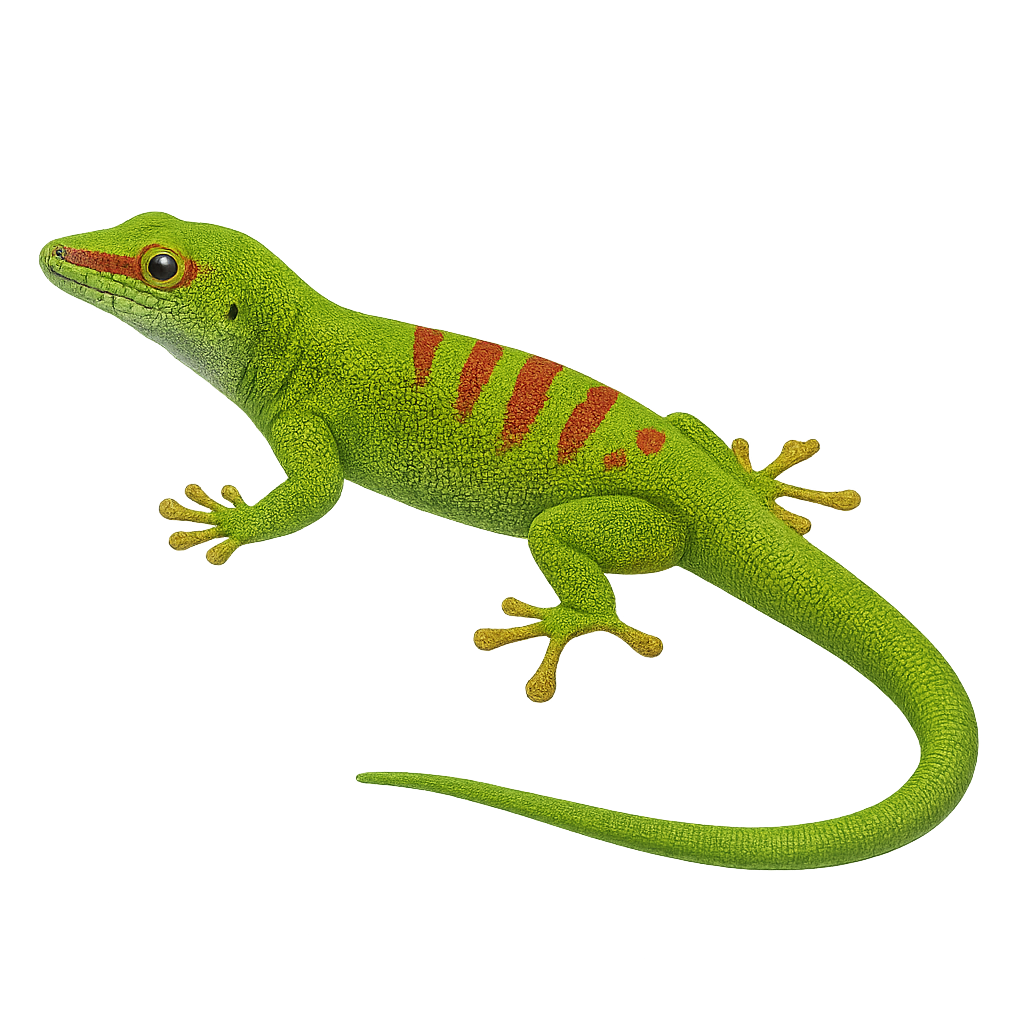
The Phelsuma grandis, or Madagascar giant day gecko, is a fascinating lizard native to Madagascar, known for its vibrant colors and impressive size, reaching up to 30 cm in length. Its skin is typically green with red and blue spots, allowing it to blend effectively into its natural habitat. This gecko is diurnal, meaning it is active during the day. It primarily feeds on insects, fruits, and nectar. In captivity, it is appreciated for its beauty and relatively docile behavior, although it requires a carefully controlled environment to thrive.
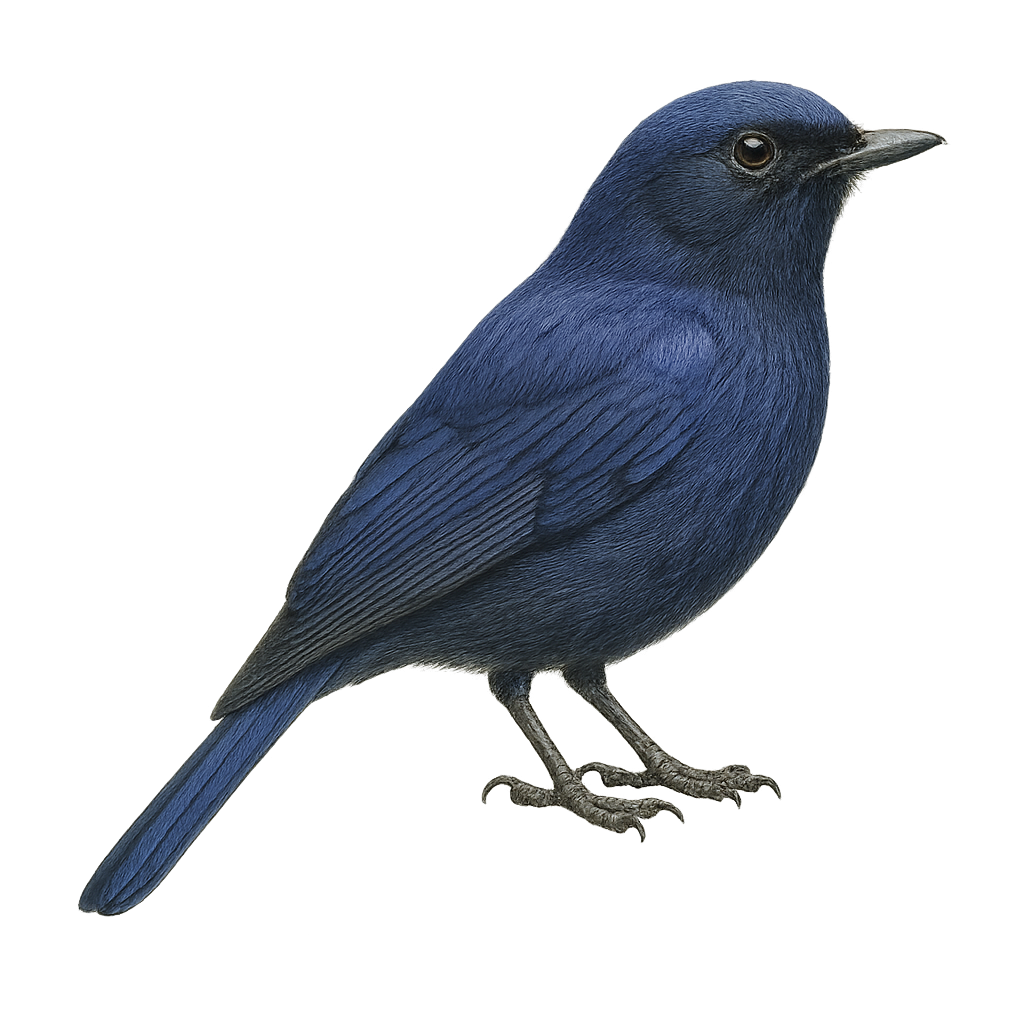
The Large Niltava is a bird from the Muscicapidae family, known for its vibrant plumage and melodious songs. This bird is primarily found in the humid forests of the Himalayas and Southeast Asia. The male sports bright blue plumage with black accents, while the female has more subdued shades of brown and orange. The Large Niltava is a territorial bird that feeds mainly on insects and small fruits. It is often seen alone or in pairs, moving nimbly among dense branches. Although its habitat is threatened by deforestation, it remains relatively common in protected areas.
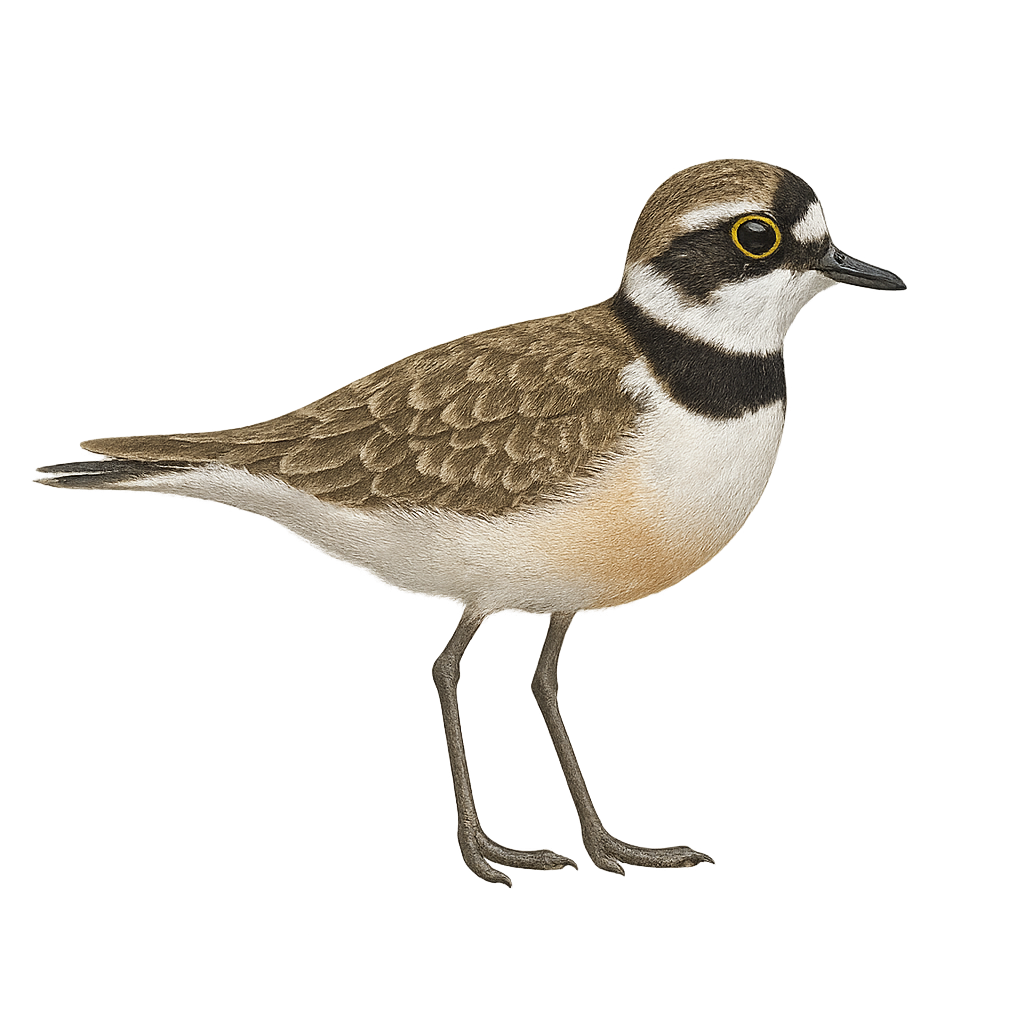
The Ringed Plover is a small coastal bird, easily recognizable by its compact size and distinctive plumage. It measures about 20 to 23 cm in length, with a wingspan of 40 to 45 cm, and weighs between 40 and 60 g. Its plumage is mainly beige and white, with black markings on its head and chest, and a distinctive black band around its eyes. The Ringed Plover is a migratory bird, primarily found on beaches, shorelines, and mudflats, where it feeds on small invertebrates, such as worms, crustaceans, and insects. It is often seen running quickly on the sand, searching for food, then stopping abruptly to catch it. The Ringed Plover lives in colonies during the breeding season, but generally prefers to remain alone or in small groups. Although it is not currently endangered, the Ringed Plover is vulnerable to human disturbances, such as the loss of its coastal habitat and the impact of pollution.
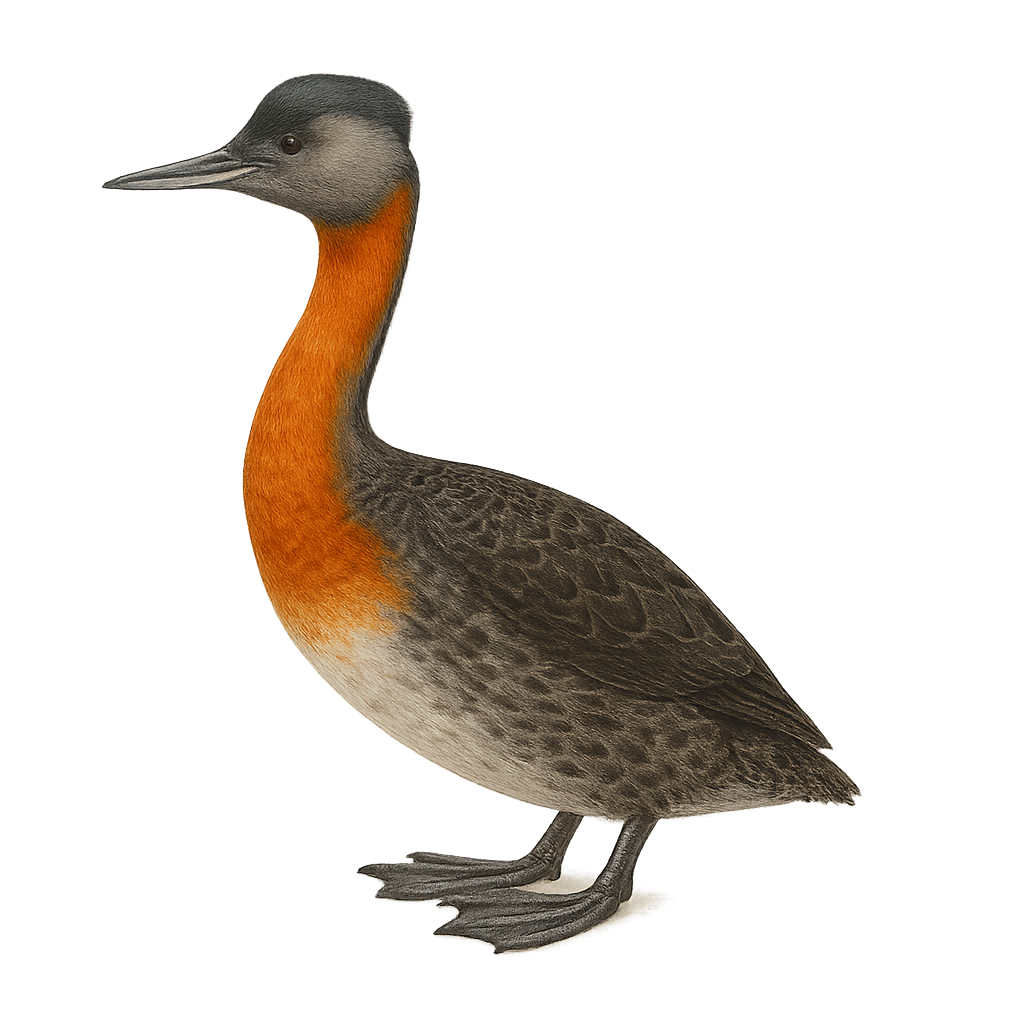
The Great Grebe, or Podiceps major, is a large aquatic bird primarily found in South America. It is characterized by its reddish-brown neck and chest, contrasting with a darker back. Its long, pointed bill is perfect for catching fish, its main food source. This bird prefers large freshwater bodies but can also be found in estuaries and coastal lagoons. It is an excellent diver, capable of staying underwater for several minutes to hunt. During the breeding season, the Great Grebe builds a floating nest from aquatic vegetation. Although its conservation status is currently "least concern," habitat degradation could pose long-term threats.
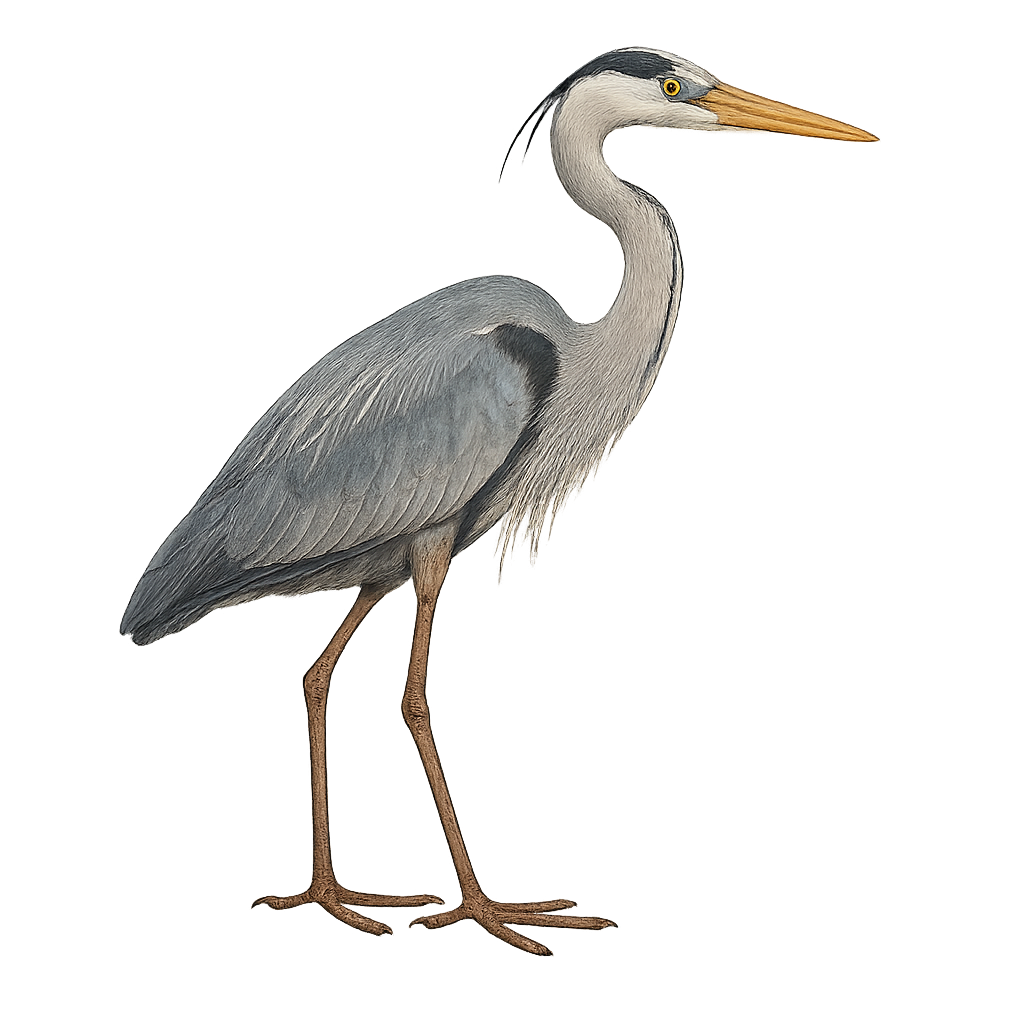
The Great Blue Heron, Ardea herodias, is a majestic bird native to North America's wetlands. With an impressive wingspan of up to 2 meters, it is easily recognized by its blue-gray plumage, white head with a black stripe, and long yellow bill. It inhabits marshes, rivers, and lakes, feeding mainly on fish, but also on small mammals and insects. Its flight is slow and powerful, with deep wing beats. The Great Blue Heron is a solitary bird, although it may gather in colonies for nesting. It builds its nest in trees or shrubs, often high up to avoid predators.
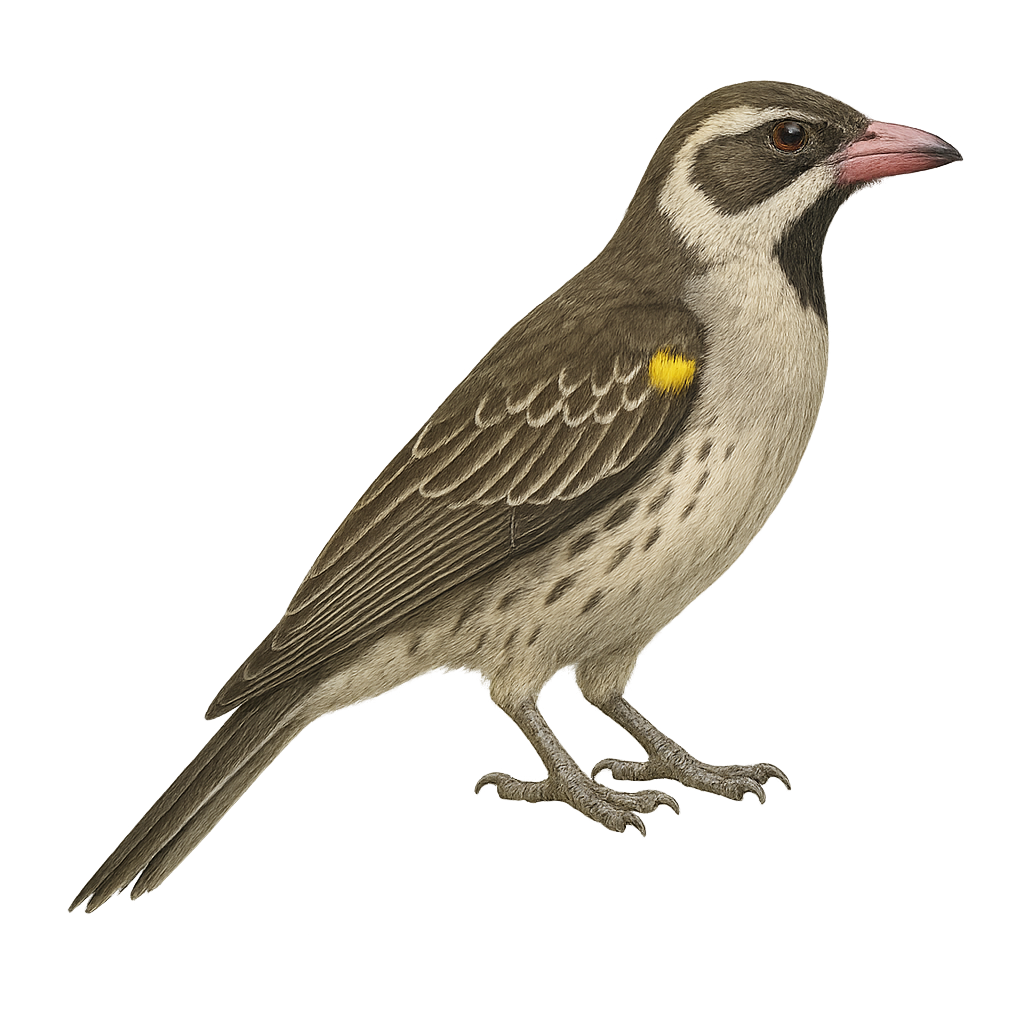
The Greater Honeyguide is a fascinating bird known for its symbiotic relationship with humans and some mammals. It guides them to wild bee hives, hoping they will open them to access the larvae and wax. This medium-sized bird, with brown and white plumage, is mainly found in sub-Saharan Africa. It has a sturdy beak and a relatively long tail. Its song is a mix of whistles and trills. Although often seen following humans, it remains wary and prefers to keep its distance. The Greater Honeyguide is a diurnal bird, active mainly in the morning and late afternoon.
The Great Jacamar, or Jacamerops aureus, is a captivating bird found in the tropical forests of South America. Averaging around 25 cm in length, its dazzling plumage with golden hues makes it a visual spectacle. It primarily feeds on insects, which it catches in flight with its long, slender bill. This bird is often seen perched on low branches, scanning its surroundings for prey. Although its song is subtle, it plays a crucial role in communication among individuals. The Great Jacamar is a solitary bird, but it can occasionally be seen in small family groups.
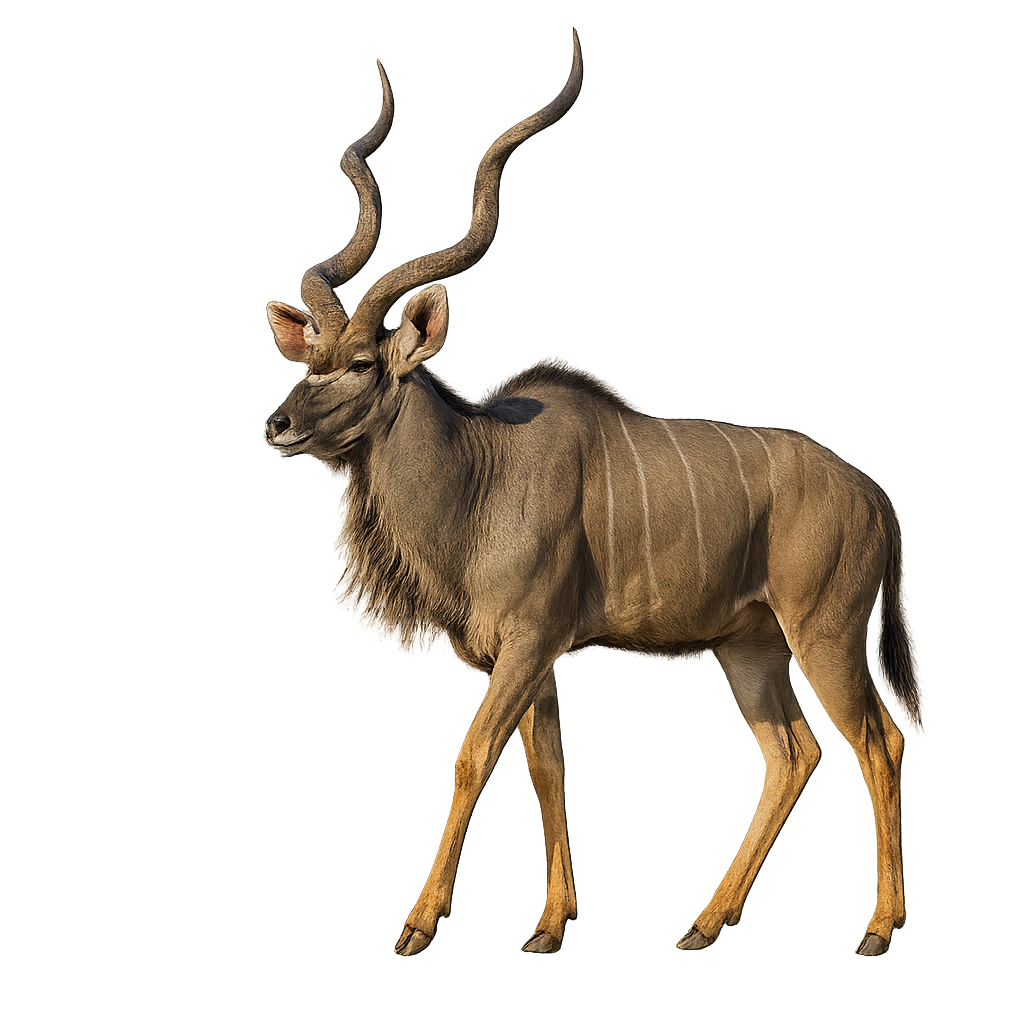
The Greater Kudu is an elegant, large antelope, easily recognized by its long, slender legs, streamlined body, and impressive spiral-shaped horns. It stands between 1.3 and 1.6 meters at the withers, with males weighing between 190 and 270 kg, and females weighing between 120 and 180 kg. Its coat is light gray to brown, with vertical white stripes on the body, which help it blend into forests and savannas. Males have long, spiral-shaped horns that can reach up to 1.5 meters in length, while females lack horns. The Greater Kudu primarily inhabits open forests, wooded areas, and savannas of sub-Saharan Africa, notably in East and Southern Africa. Herbivorous, it feeds mainly on leaves, bark, and fruits. This antelope is rather discreet and shy, typically living alone or in small family groups. While it is not currently in immediate danger, the Greater Kudu is threatened by habitat loss and hunting.
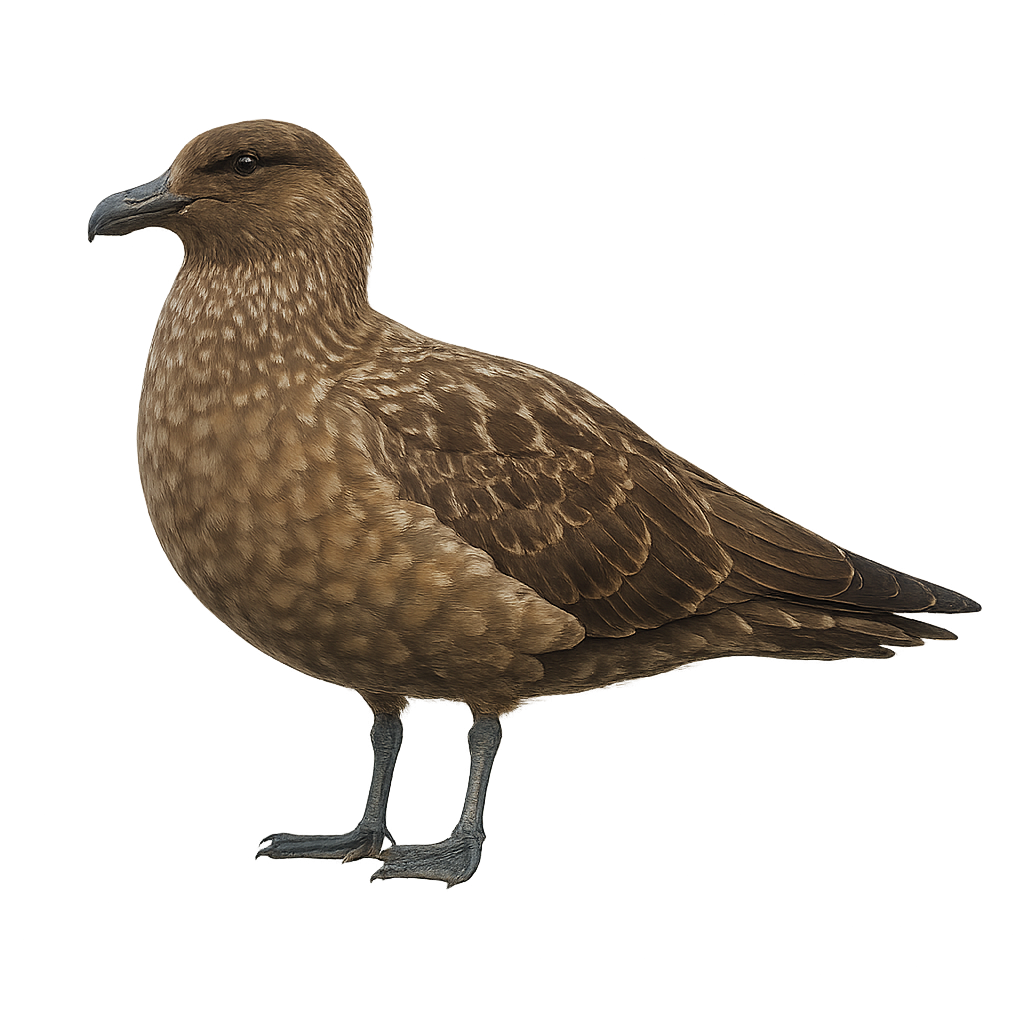
The Great Skua is a large, powerful seabird, belonging to the Stercorariidae family. It measures about 50 to 60 cm in length, with a wingspan of 120 to 130 cm, and weighs between 500 and 1,000 g. Its plumage is primarily brown and gray, with white markings on the wings and a generally dark head. The Great Skua is a migratory bird, found mainly in the coastal regions of the North Atlantic, particularly in Northern Europe, Iceland, Greenland, and parts of Canada. It is especially known for its piratical behavior, stealing food from other seabirds, such as gulls or fishing birds, by chasing them and forcing them to abandon their catch. While territorial, it is also an excellent swimmer and diver, feeding mainly on fish and crustaceans. The Great Skua is vulnerable to the loss of its coastal habitat and human disturbances, including pollution and disruptions caused by tourism.
The Cape Sparrow, or Passer motitensis, is a small, robust bird primarily found in southern Africa. It is characterized by its brown and grey plumage, with a black cap on males and a grey cap on females. These birds are often seen in groups, feeding on seeds, insects, and small fruits. They adapt well to urban and rural environments, nesting in cavities or artificial structures. Their song is a simple yet melodious chirp. Although their population is stable, they are sometimes threatened by habitat loss and competition with other sparrow species.
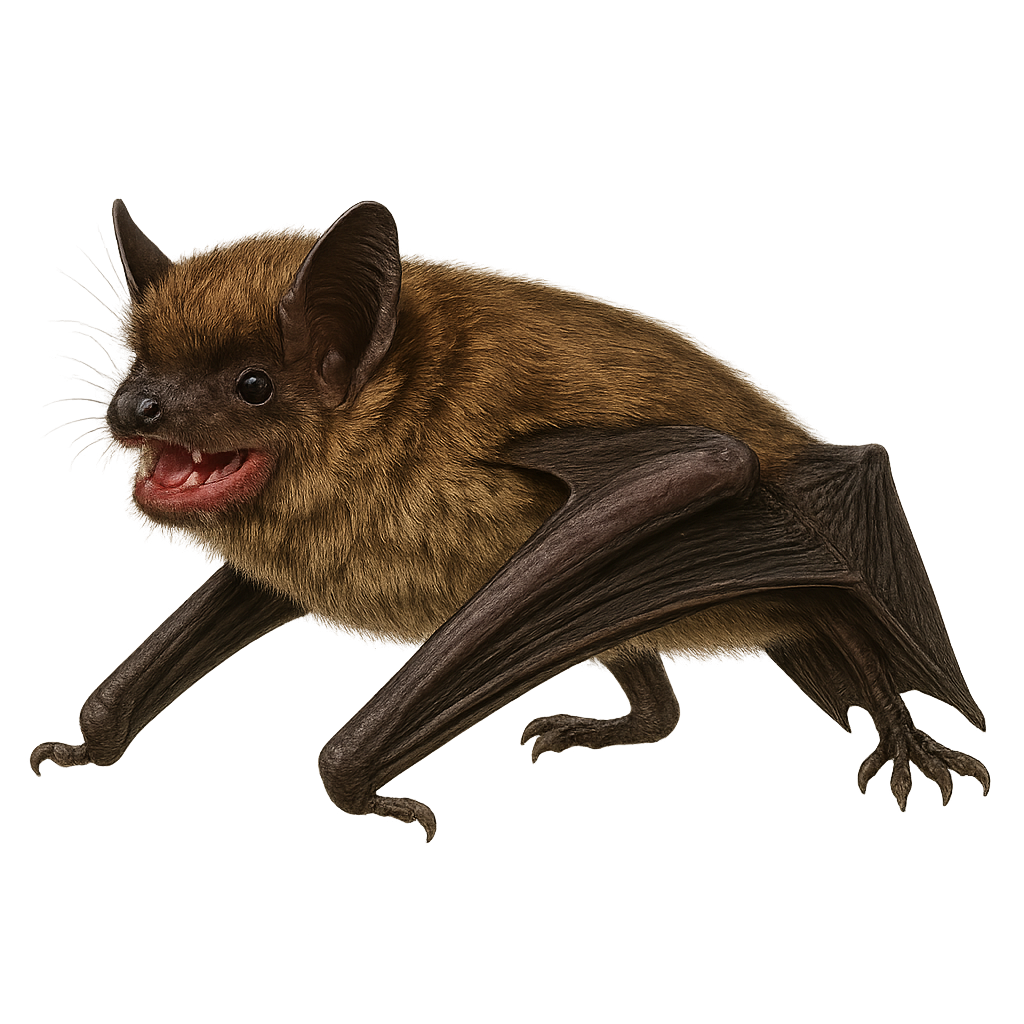
The greater mouse-eared bat is a medium-sized bat, 7–9 cm in body length, with a 35–43 cm wingspan and weighing 20–40 g. Uniform grey-brown fur, long rounded ears. A cave-dwelling species, forages on the ground and in low flight for beetles and other invertebrates.
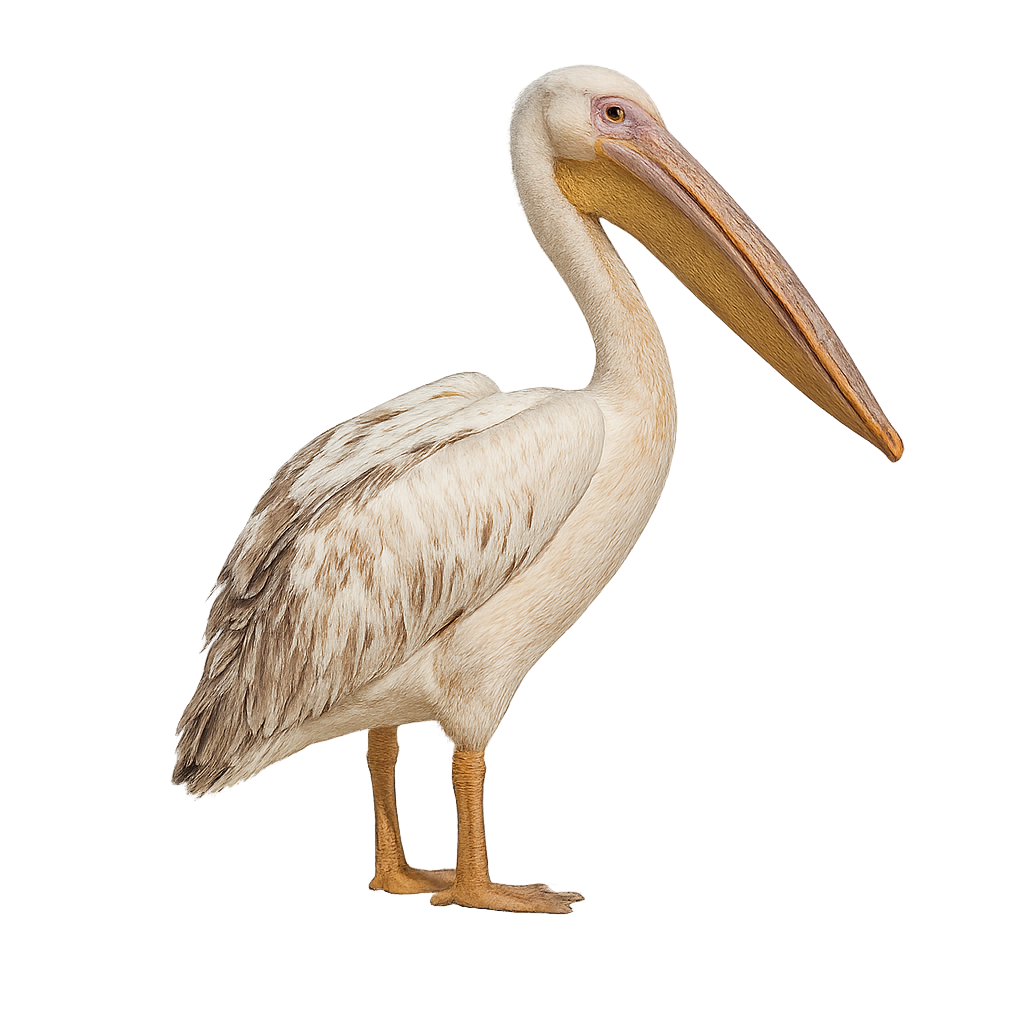
The Great White Pelican, or Pelecanus onocrotalus, is a large aquatic bird easily recognizable by its bright white plumage and long, voluminous bill with an expandable pouch. It primarily inhabits freshwater lakes and marshes, but can also be found in estuaries and coastal lagoons. This gregarious bird is often seen in large groups, flying in formation or resting on shores. It feeds mainly on fish, which it catches by dipping its bill into the water. Its collective fishing technique is fascinating, as several individuals form a circle to trap fish. The Great White Pelican is a symbol of cooperation and harmony in nature.
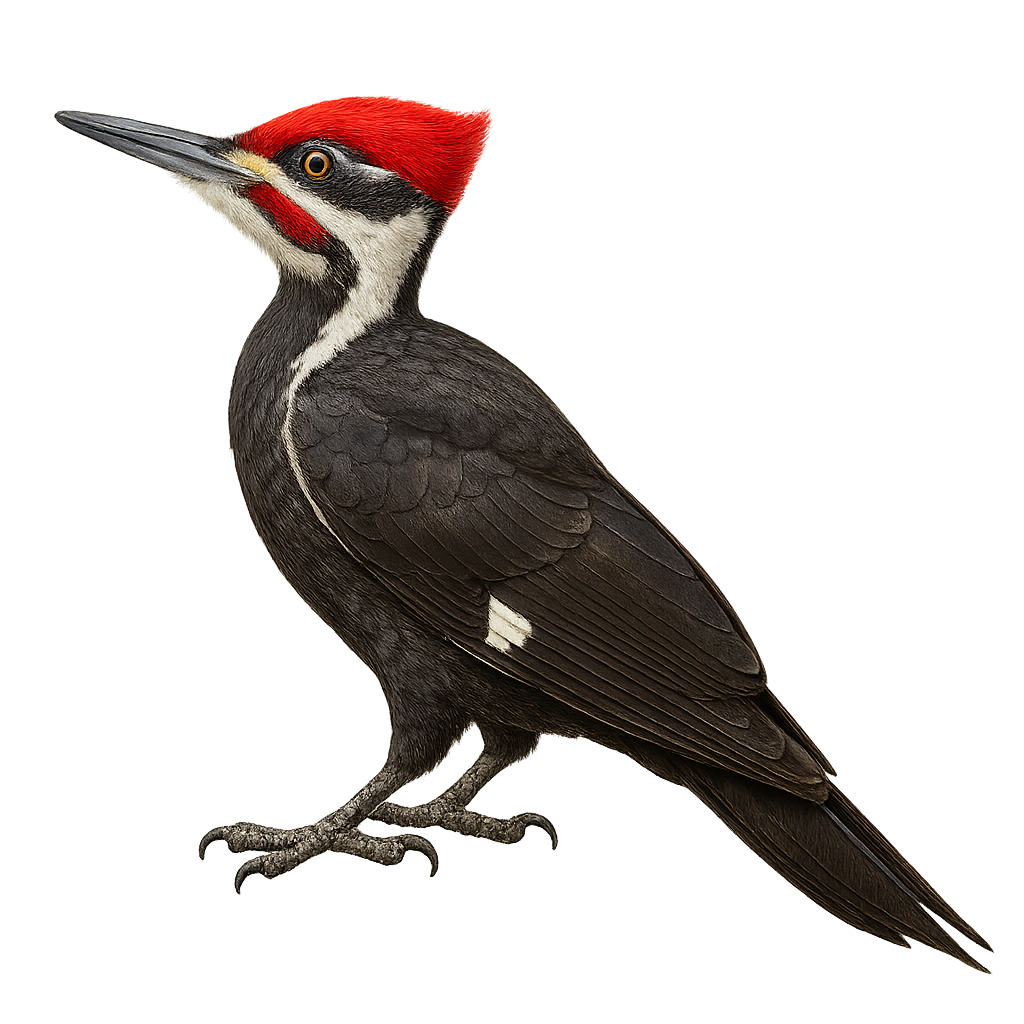
The Pileated Woodpecker is a striking bird, notable for its size and distinctive plumage. It is one of the largest woodpeckers in North America, measuring between 40 and 49 cm in length with a wingspan of up to 75 cm. Its plumage is predominantly black with a bright red crest on its head, more pronounced in males. The wings have white patches visible in flight. This forest bird is often found in coniferous and deciduous forests. Known for its powerful drumming on tree trunks, it uses this to communicate and mark its territory. It primarily feeds on ants and insect larvae, which it extracts from dead wood with its long bill.
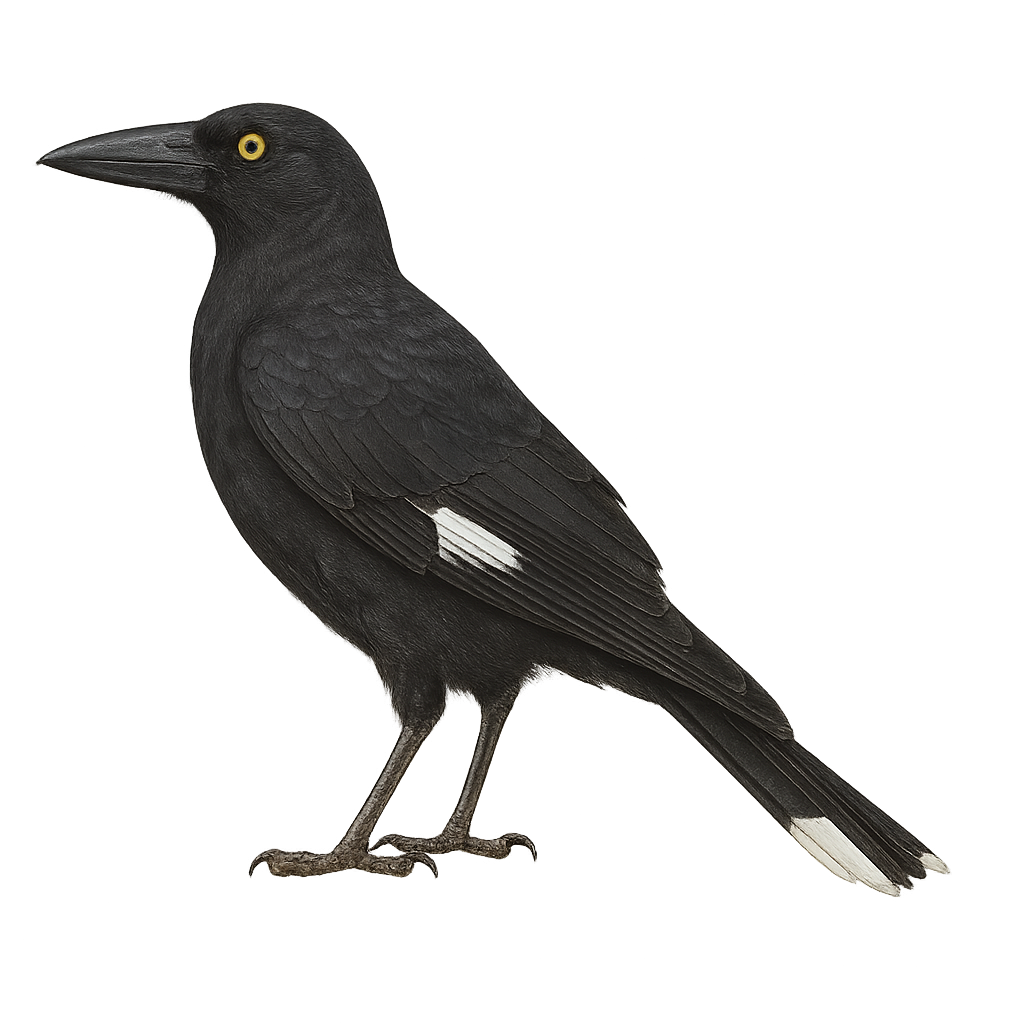
The Pied Currawong, scientifically known as Strepera graculina, is a bird native to Australia, easily identified by its glossy black plumage and striking yellow eyes. It measures about 48 to 50 cm in length and has a strong, slightly hooked beak. This bird is often found in rainforests, open woodlands, and occasionally in urban parks. It is renowned for its melodious and varied song, which can include whistles, calls, and mimicry of other birds. As an opportunistic feeder, it primarily consumes fruits, insects, and small animals. The Pied Currawong is a social bird, often seen in small groups or pairs, especially during the breeding season.
The Giant Anteater, also known as the Myrmecophaga tridactyla, is a large insectivorous mammal primarily found in the tropical forests and savannas of South America, notably in Brazil, Guyana, Argentina, and Venezuela. It measures between 1.7 and 2.2 meters in length, with a tail of 60 to 90 cm, and weighs between 25 and 40 kg. Its fur is generally light gray or brown, and it has a long cylindrical snout, as well as an extremely long tongue that can reach up to 60 cm in length, which it uses to catch ants and termites. The Giant Anteater is a nocturnal animal, primarily feeding on ants, termites, and other insects found in nests. While it is an excellent digger and climber, it is threatened by habitat loss and illegal hunting.
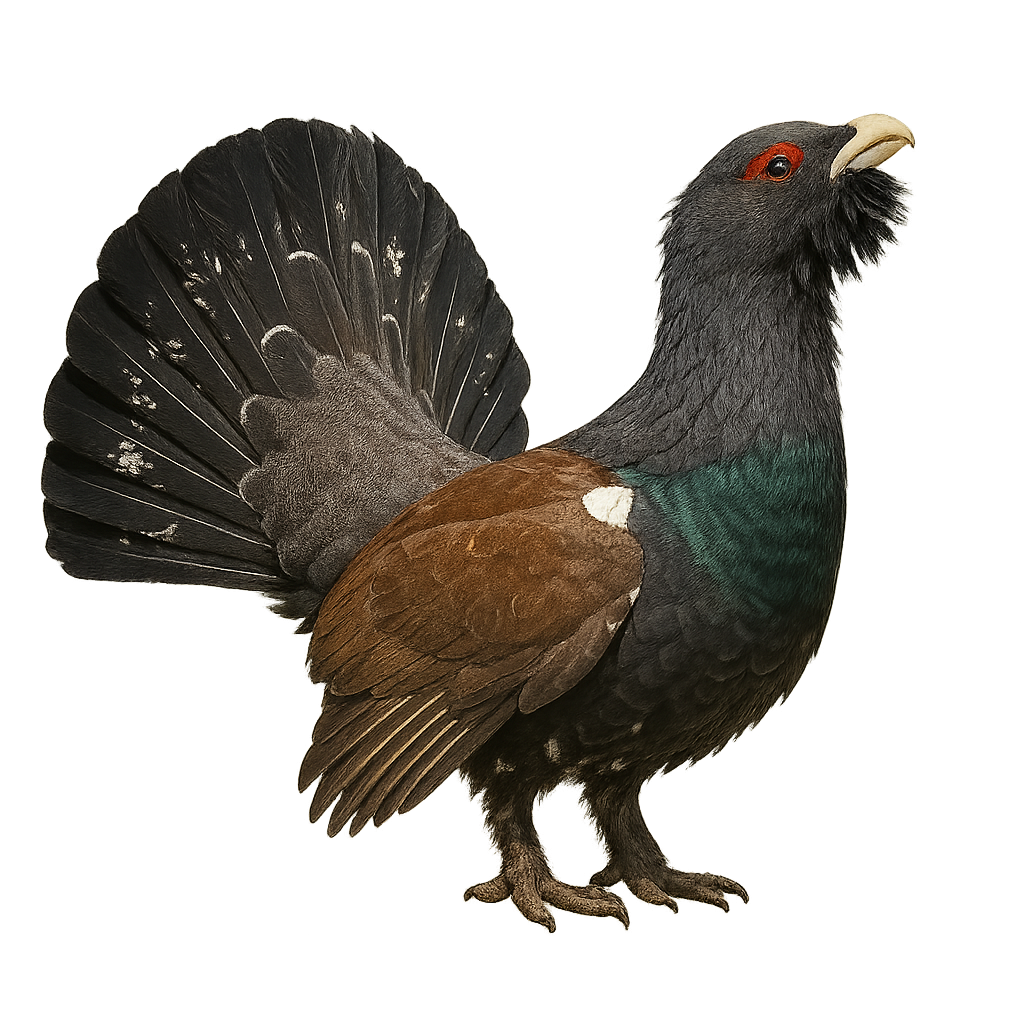

The Capercaillie is a large bird of the pheasant family, easily recognizable by its imposing size and distinctive plumage. It measures about 80 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.2 meters and a weight ranging from 3 to 6 kg for males and 2 to 3 kg for females. The male's plumage is dark, with a reddish chest, a crest of feathers on the head, and a large V-shaped tail. The female, on the other hand, is more discreet, with a brown mottled plumage that allows her to better blend into the environment. The Capercaillie primarily inhabits coniferous and deciduous forests, particularly in the mountains and wooded areas of Europe, notably in France, Switzerland, Germany, and other mountainous regions. It feeds mainly on young shoots, seeds, fruits, and insects. This bird is also known for its spectacular mating displays, during which the male puffs up his chest, spreads his tail, and makes powerful calls to attract females. Although the species is not immediately endangered, the Capercaillie faces threats from deforestation, human disturbance, and habitat loss.
The Great Horned Owl is a large nocturnal raptor, one of the most imposing owls on the American continent. It measures between 50 and 70 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.2 to 1.5 meters, and weighs between 1.5 and 2.5 kg. Its plumage is mainly brown, speckled with black, with lighter markings on its belly and wings. It has large tufts of feathers on its head that resemble ears, and piercing yellow eyes. This owl inhabits a variety of habitats, including forests, wooded areas, and open landscapes across North America, notably in the United States, Canada, and Central America. It is primarily nocturnal and carnivorous, feeding on small mammals, birds, and occasionally reptiles. It is also known for its impressive hunting abilities, flying silently to surprise its prey. Although the Great Horned Owl is not currently threatened, it may be affected by habitat loss and human disturbance.
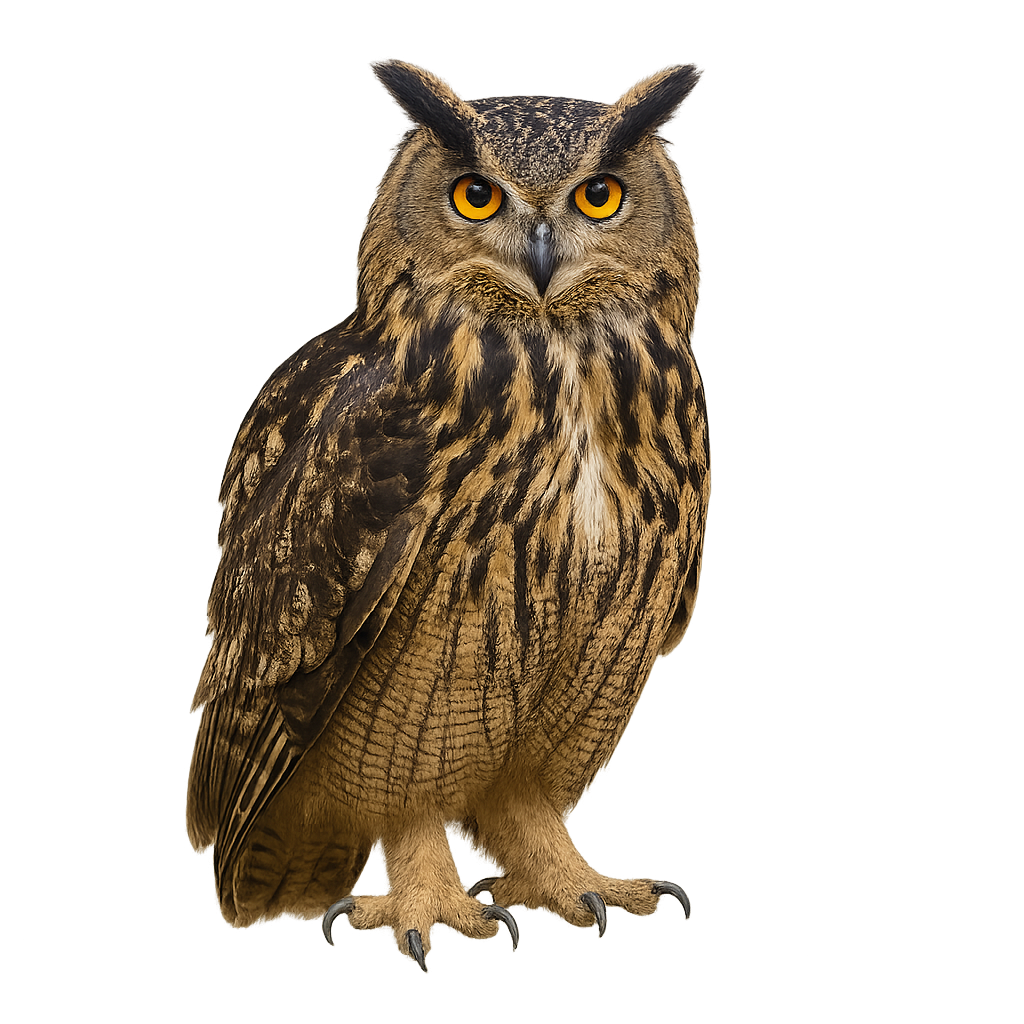
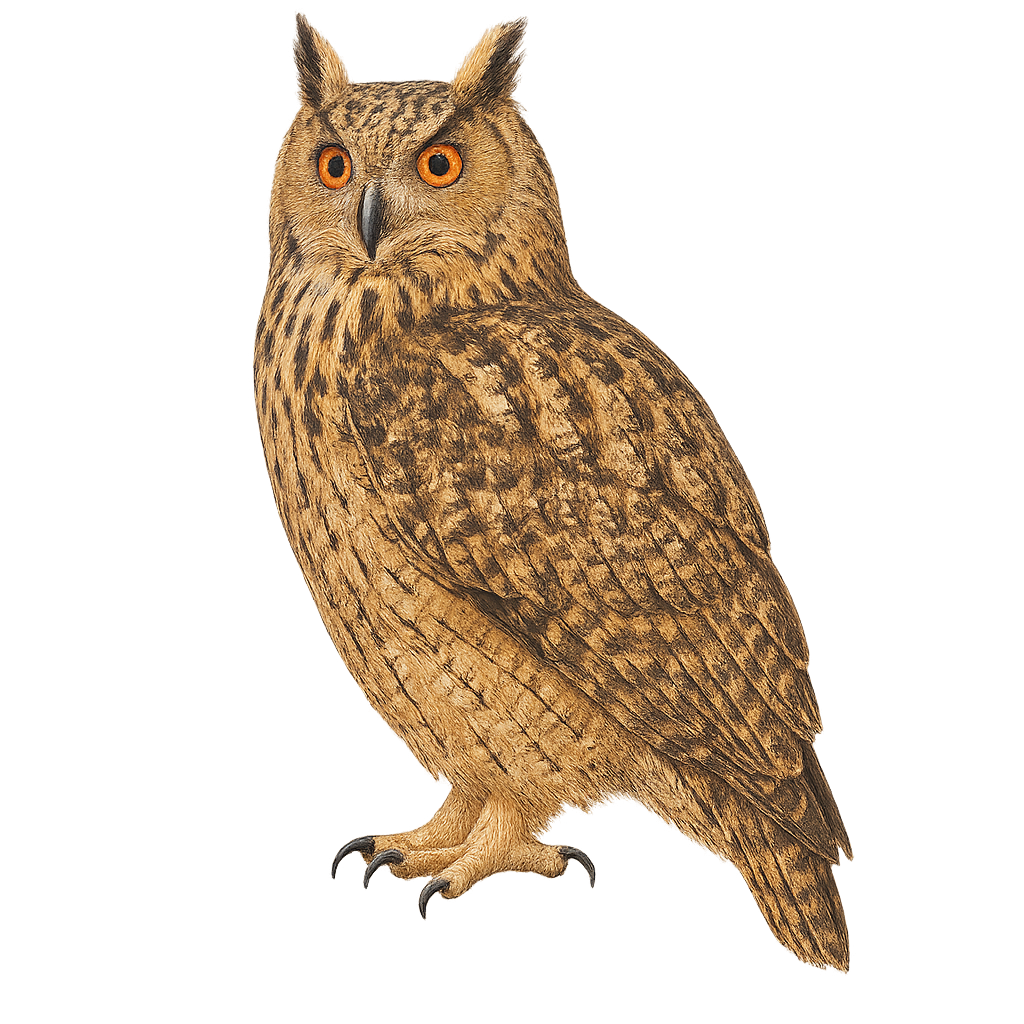
The Eurasian Eagle-Owl is a large nocturnal raptor, one of the most imposing owls in the world. It measures between 60 and 70 cm in length, with a wingspan of 1.6 to 1.8 meters, and weighs between 1.5 and 4.5 kg. Its plumage is primarily brown, with white and black mottled patterns, and its eyes are bright orange, giving the bird a piercing gaze. It also has tufts of feathers on its head that resemble ears, which give it a distinctive appearance. The Eurasian Eagle-Owl primarily inhabits forests, mountains, and rocky areas in Europe, Western Asia, and the Middle East. It is an opportunistic hunter, feeding mainly on small mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles or amphibians. The Eurasian Eagle-Owl is a solitary and territorial bird, known for its powerful and deep calls, often heard at night. While the species is not endangered, it may be affected by the destruction of its natural habitat and human disturbances.
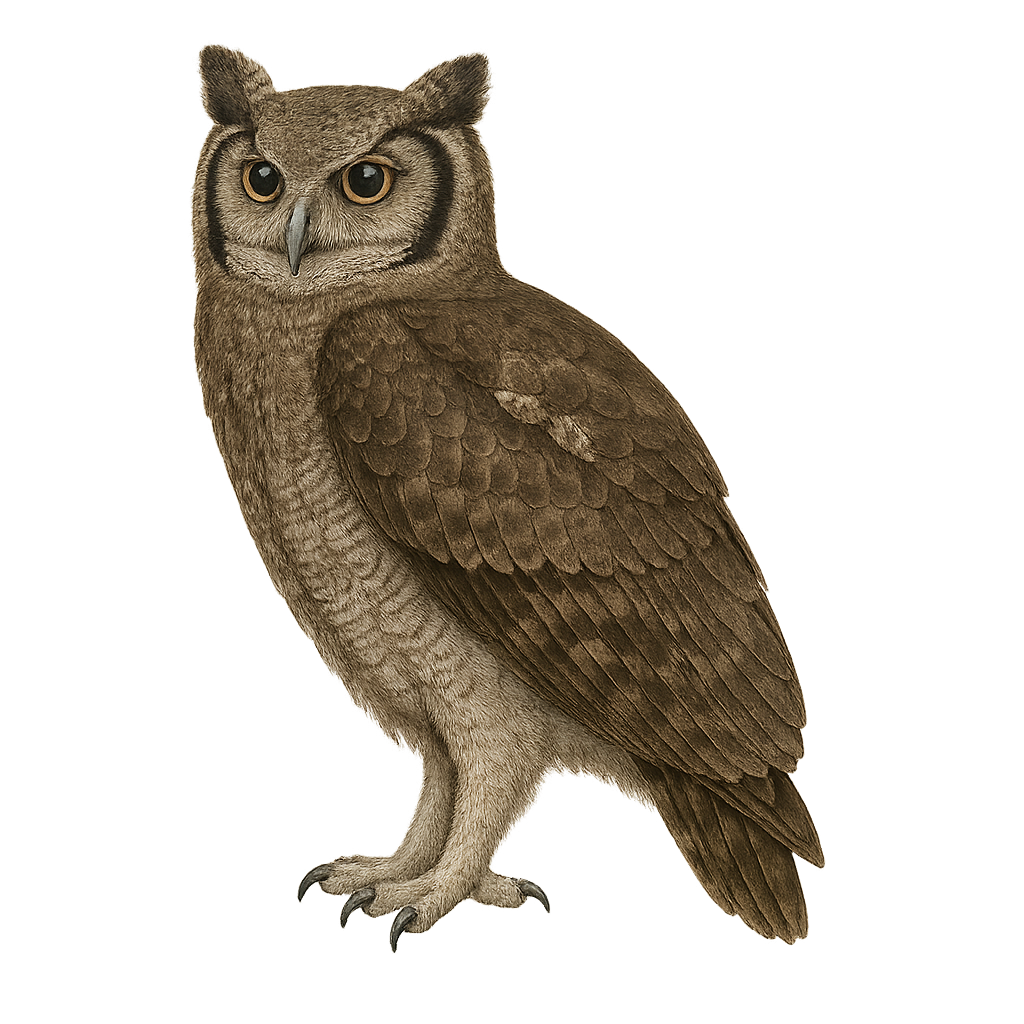
The Verreaux's Eagle-Owl, or Bubo lacteus, is an impressive nocturnal raptor, recognizable by its dark eyes and prominent ear tufts. It is the largest owl in Africa, measuring up to 66 cm in length with a wingspan reaching 1.5 meters. Its plumage is primarily gray with lighter shades on the belly. This skilled predator feeds mainly on small mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles. It is often found in savannas, open forests, and wooded areas near watercourses. Although its conservation status is currently "Least Concern," habitat destruction could threaten its populations in the future.
The Bubo ascalaphus, or Desert Owl, is an impressive nocturnal bird of prey, primarily found in the arid regions of North Africa and the Middle East. This owl is distinguished by its sandy plumage, which allows it to blend seamlessly into its desert environment. It has large yellow eyes and prominent ear tufts. An efficient predator, it primarily feeds on small mammals, birds, and insects. Its call is a deep, resonant hoot, often heard at dusk. The Desert Owl is a solitary bird, except during the breeding season when it forms monogamous pairs. Its ability to survive in extreme conditions makes it a fascinating example of animal adaptation.
The Great Egret is a large wading bird, easily recognizable by its entirely white plumage, long legs, and long, sinuous neck. It stands about 85 to 105 cm tall, with a wingspan of 1.3 to 1.7 meters, and weighs between 800 and 1,500 g. The Great Egret has a long, slender yellow beak and bright green eyes. It primarily inhabits wetlands, marshes, estuaries, and lake shores in Europe, Africa, Asia, and the Americas. This bird is an excellent fisherman, feeding mainly on fish, crustaceans, and aquatic insects, which it captures by diving or slowly probing the water with its beak. During the breeding season, the Great Egret is known for its elegant courtship dances and its plumage adorned with long, delicate feathers, giving it a majestic appearance. While the species is not endangered, it is sometimes threatened by habitat loss and water pollution.
The Eptesicus fuscus, commonly known as the big brown bat, is a widespread species in North America. It is notable for its relatively large size for a North American bat, with a wingspan reaching up to 33 cm. Its fur is dark brown, contrasting with its lighter belly. It inhabits various environments, from forests to urban areas, and primarily feeds on flying insects, which it captures in flight using its efficient echolocation. This species is known for its ability to hibernate in sheltered places during winter, such as caves or abandoned buildings.
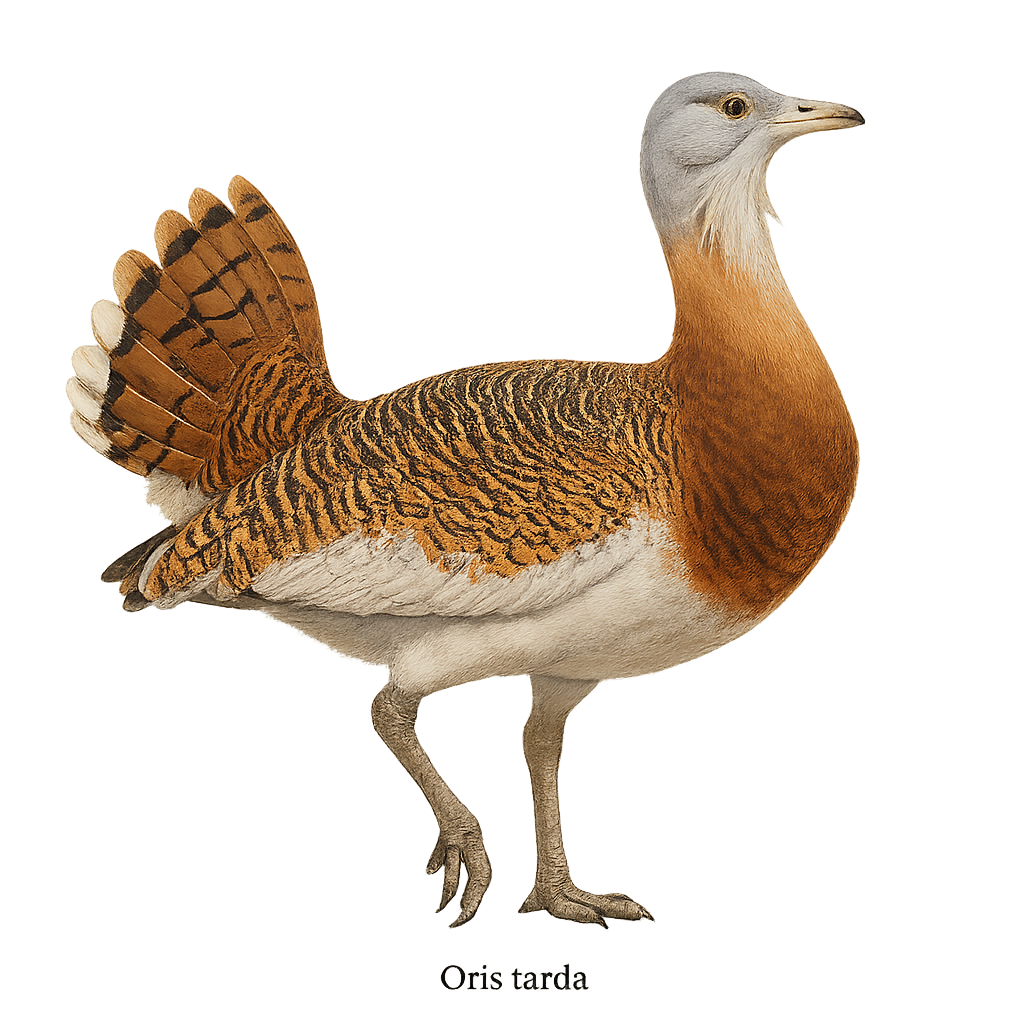
The great bustard, Otis tarda, is one of the heaviest flying birds. It is recognizable by its brown and white plumage, with distinctive patterns on the wings. Males, larger than females, sport a white feather mustache during the breeding season. This bird prefers vast open plains and steppes, where it feeds on plants, insects, and small vertebrates. The great bustard is a symbol of bird conservation in Europe, as it is threatened by habitat loss and hunting. It is known for its spectacular courtship displays, where males puff up their feathers to impress females.
The Wrybill, or Anarhynchus thoracicus, is an endemic bird of New Zealand, known for its uniquely right-curved bill. This small wader measures about 20 cm in length and weighs between 40 and 60 grams. Its plumage is mainly grey with a white belly and a distinctive black band across the chest. It frequents rivers and estuaries, feeding primarily on insects and small invertebrates. Its ability to move quickly over pebbles and use its bill to probe under stones is remarkable. Unfortunately, this species is threatened by habitat loss and predation by introduced species.
The Ringed Plover is a small coastal bird primarily found along beaches, estuaries, and sandy areas in Europe, North Africa, and Asia. It measures about 18 to 20 cm in length, with a wingspan of 40 to 45 cm, and weighs between 30 and 60 g. Its plumage is generally light beige with white underparts and an interrupted black ring around the neck and chest. This collar is more pronounced in males, while females have a less distinct collar. The Ringed Plover primarily feeds on small marine invertebrates and insects found in the sand or along the shore. It is often seen running along the waves, searching for food. While its population remains relatively stable, this species can be threatened by habitat loss, pollution, and human disturbances at its breeding sites.
The Double-banded Plover, Anarhynchus bicinctus, is a medium-sized bird known for its distinctive two black bands on the chest, contrasting with its grey-brown back and white belly. It is primarily found in New Zealand, frequenting sandy beaches, estuaries, and coastal wetlands. This bird is known for its ground-nesting behavior, often in open areas where it can easily watch for predators. Although generally discreet, it can become territorial during the breeding season. Its diet mainly consists of insects, small crustaceans, and worms, which it captures by quickly pecking at the ground.
The Forbes's Plover, scientifically known as Charadrius forbesi, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Charadriidae family. It is characterized by its light brown plumage on the back and white on the belly, with a distinctive black band across the chest. Adults have a dark brown cap and a black bill. This plover is primarily found in the savannas and wet grasslands of West Africa, where it feeds on insects, worms, and small crustaceans. It is often seen in small groups, moving quickly on the ground in search of food. Although its conservation status is currently considered "least concern," habitat degradation could pose a future threat.
The Subantarctic dotterel, or Zonibyx modestus, is a small coastal shorebird with subtle plumage, typically found along sandy shores and lagoons of southern South America. Its pale gray-brown back, white belly, and faint light eyebrow provide excellent camouflage in open habitats. It nests on the ground near water and feeds on aquatic invertebrates, insects, and small crustaceans. A discreet species, it is vulnerable to human disturbance on beaches. Its population is generally considered stable but may be locally threatened.
The Forbes's Plover, or Charadrius forbesi, is a medium-sized bird belonging to the Charadriidae family. It is primarily found in West Africa, particularly in Nigeria, Ghana, and Ivory Coast. This bird prefers open habitats such as grassy plains and wetlands. It is characterized by its brown-grey plumage with a black breast band and white belly. The beak is black, and the legs are yellowish. The Forbes's Plover is a diurnal bird, often seen foraging for food, mainly insects and small invertebrates, on the ground. Although its conservation status is currently considered of least concern, habitat degradation could pose future threats.
The Mountain Plover, Anarhynchus alticola, is a bird species primarily inhabiting mountainous regions. This plover is recognizable by its discreet plumage, usually gray-brown, which allows it to blend into its rocky environment. It is often observed in small groups, feeding on insects and small invertebrates. Its ability to survive at high altitudes demonstrates its remarkable adaptation to harsh conditions. Although its habitat is relatively isolated, it is vulnerable to human disturbances and climate change, which threaten its breeding and feeding areas. Conservation of this bird requires special attention to preserve its natural habitats.